
Lewis Wickes Hine Workshop of Sanitary Ice Cream Cone Co., OK City 1917

Did Carney really not see this coming? That would be stunning indeed. Not hard at all to find out.
• Bank Of England Suffers Stunning Failure On Second Day Of QE (ZH)
It started off well enough. On the first day of the Bank of England’s resumption of Gilt QE after the central bank had put its monetization of bonds on hiatus in 2012, bondholders were perfectly happy to offload to Mark Carney bonds that matured in 3 to 7 years. In fact, in the first “POMO” in four years, there were 3.63 offers for every bid of the £1.17 billion in bonds the BOE wanted to buy. However, earlier today, when the BOE tried to purchase another £1.17 billion in bonds, this time with a maturity monger than 15 years, something stunning happened: it suffered an unexpected failure which has rarely if ever happened in central bank history: only £1.118 billion worth of sellers showed up, meaning that the BOE’s second open market operation was uncovered by a ratio of 0.96.
Simply stated, the Bank of England encountered an offerless market. What makes this particular failure especially notable – and troubling – is that while technically uncovered sales of government securities happen frequently, and Germany is quite prominent in that regard as numerous Bund auctions have failed to find enough demand in the open market in recent years forcing the “retention” of the offered surplus, when it comes to a central bank’s buying of securities, there should be, at least in practice, full coverage of the operation as the central bank is willing and able to pay any price to sellers to satisfy its quota. For example, in today’s operation, the scarcity led to the BOE accepting all submissions, even as some investors offered prices above the prevailing market.
The highest accepted price for the 4% bond due in 2060, for example, was 194.00, compared with a weighted average of 192.152, which means that the happy seller obtained a yield well in excess of that implied by the market. And yet, despite having a completely price indiscriminate buyer, some £52 million worth of bond sellers simply refused to sell to the BOE at any price! The QE failure quickly raised alarm signals among the bond buying community. In a Bloomberg TV interview, Luke Hickmore at Aberdeen Asset Management said that “lots of people are bidding us for bonds – Mark Carney is now bidding me for bonds and he still can’t have them. The problem is he was trying to buy 15-year plus bonds today in the gilt market. That’s a really difficult area.”

“One might as well try to improve one’s health by playing a few rounds of Russian roulette every morning before breakfast.”
• Bank of England QE and the Imaginary “Brexit Shock” (AM)
For reasons we cannot even begin to fathom, Mark Carney is considered a “superstar” among central bankers. Presumably this was one of the reasons why the British government helped him to execute a well-timed exit from the Bank of Canada by hiring him to head the Bank of England (well-timed because he disappeared from Canada with its bubble economy seemingly still intact, leaving his successor to take the blame). The adulation he receives is really a major head-scratcher. What has he ever done aside from operating the “Ctrl. Prnt.” buttons? As far as we are aware, nothing. As we have discussed previously, his main legacy is that he has left Canada with one of the greatest and scariest real estate and consumer credit bubbles extant in the world today. Some accomplishment!
With respect to his economic analysis, it seems not the least bit different from the neo-Keynesian/ semi-monetarist mumbo jumbo we get to hear from central bankers everywhere. This is by the way no surprise: they’re an incestuous bunch and have largely received their education at the same institutions. Most of them seem genuinely convinced that central planning not only works, but is necessary to improve on the alleged drawbacks of an “unfettered market” (i.e., the mythical unhampered free market economy no-one alive today has ever experienced). If one looks closely at what they are actually doing, it soon becomes clear that it is in principle not much different from what John Law did in France in the early 18th century (the difference is one of degree only).
The much-dreaded “Brexit” has now given Mr. Carney the opportunity to do what he does best, namely open the monetary spigots wide. One might as well try to improve one’s health by playing a few rounds of Russian roulette every morning before breakfast.

NIRP scares the sh*t out of people. And rightly so.
• Negative-Yield Debt Is Doing The Opposite Of What It Was Supposed To Do (CNBC)
Paying someone to borrow your money sounds like a questionable idea on paper, and seems not to be working out so well in practice. Yet that’s exactly what people who buy negative-yielding bonds do: Instead of collecting payments in the form of yields, investors have to pay someone to take their cash. Investors ostensibly hope they can sell the debt elsewhere and make a profit, as prices go up when yields fall. It’s a strange arrangement that nonetheless has become policy in Japan and parts of Europe. The goal that sovereign debt issuers and central banks hope to achieve is a world where money is pushed toward risk and all that no-yielding debt causes inflation that leads to growth.
However, as the arrangement spreads around the world to the point where more than $11 trillion of global debt holds negative yields, questions are growing quickly about its efficacy. “It’s the definition of insanity: Keep doing the same thing over and again and expect a different result. That’s my assessment of central banks in a nutshell,” said Kim Rupert, managing director of global fixed income analysis at Action Economics. “I never thought I’d say that. I had a lot of respect for central bankers. But they’re getting way overindulgent with very little success as far as I can tell.”

“..urged local officials to “chant bright songs about the China economy loudly” to boost confidence..”
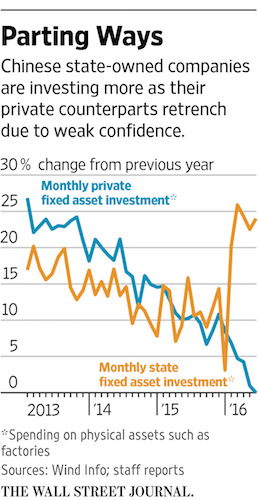
• The Private Pain of China’s Economy (WSJ)
Private investment is withering in China. Companies are shying away from risking their capital, discouraged by a cloudy global outlook and four years of slowing Chinese growth, intermittent deflation and conflicting policy messages. The development risks setting back Beijing’s aim to shift the economy from low-end manufacturing to the kind of high-tech industries and services that dynamic private companies tend to provide. Private investment on capital goods like factories and trucks grew by just 2.8% in the year’s first half following nearly 30% annual average growth over the past decade. In June, it fell for the first time since China started tracking the data in 2004. The July figure, to be released Aug. 12, is expected to show further weakness.
In a bid to reverse the trend, Beijing has stepped up efforts to slash red tape and reduce barriers for entrepreneurs and urged local officials to “chant bright songs about the China economy loudly” to boost confidence, according to one circular. Beijing also has tried to flood the economy with credit to compensate for the decline in private investment. It boosted total social financing, a broad measure of credit that includes both bank loans and nonbank lending, to a first-quarter record. But state banks, China’s main lenders, aren’t always cooperating. In the second quarter, state banks charged private companies interest rates that were 6 percentage points higher than for their public-sector counterparts, according to investment bank CICC. Officials at two state banks said they are careful when lending to smaller private borrowers given concerns over risk and lack of sufficient collateral.
Private companies also report more difficulty in raising informal loans from nonbank lenders, friends and relatives as bad loans increase and lenders grow more cautious. China’s leaders also have pressured state-owned firms to invest more. They responded with a 23% first-half jump in investment that helped prop up economic growth. But the strategy sidelines private companies that account for three-fifths of China’s economy and four-fifths of its workforce. “The government plans a lot of large-scale investments but rarely thinks about private investors getting squeezed out,” said Jon Chan Kung, founder of research group Beijing Anbound Information Co. “Companies are facing a lot of confusion and questions about China’s future.”

It’s all about hoping prices will rise. If they don’t, and soon, these guys are toast.
• Oil Companies Face $110 Billion Debt Wall Over Next 5 Years (BBG)
The worst may be yet to come for some strained oil services companies as $110 billion in debt, most of it junk rated, creeps closer to maturity. More than $21 billion of debt from oilfield services and drilling companies is estimated to be maturing in 2018, almost three times the total burden in 2017, according to a report from Moody’s Investors Service on Aug. 9. More than 70% of those high-yield bonds and term loans are rated Caa1 or lower, and more than 90% are rated below B1. Speculative-grade debt is becoming increasingly risky, as the default rate is expected to reach 5.1% in November, according to a separate Moody’s report.
The 12-month global default rate rose to 4.7% in July, up from its long-term average of 4.2%, Moody’s wrote. Of the 102 defaults this year, 49 have come from the oil and gas sector, Moody’s noted. “While some companies will be able to delay refinancing until business conditions improve, for the lowest-rated entities, onerous interest payments and required capital expenditure will consume cash balances and challenge their ability to wait it out,” Morris Borenstein, an assistant vice president at Moody’s, said in the report.

The problem is the silly assumptions it was built on.
• The Problem With Europe Is The Euro (Stiglitz)
Advocates of the euro rightly argue that it was not just an economic project that sought to improve standards of living by increasing the efficiency of resource allocations, pursuing the principles of comparative advantage, enhancing competition, taking advantage of economies of scale and strengthening economic stability. More importantly, it was a political project; it was supposed to enhance the political integration of Europe, bringing the people and countries closer together and ensuring peaceful coexistence. The euro has failed to achieve either of its two principal goals of prosperity and political integration: these goals are now more distant than they were before the creation of the eurozone. Instead of peace and harmony, European countries now view each other with distrust and anger.
Old stereotypes are being revived as northern Europe decries the south as lazy and unreliable, and memories of Germany’s behaviour in the world wars are invoked. The eurozone was flawed at birth. The structure of the eurozone – the rules, regulations and institutions that govern it – is to blame for the poor performance of the region, including its multiple crises. The diversity of Europe had been its strength. But for a single currency to work over a region with enormous economic and political diversity is not easy. A single currency entails a fixed exchange rate among the countries, and a single interest rate. Even if these are set to reflect the circumstances in the majority of member countries, given the economic diversity, there needs to be an array of institutions that can help those nations for which the policies are not well suited.
Europe failed to create these institutions. Worse still, the structure of the eurozone built in certain ideas about what was required for economic success – for instance, that the central bank should focus on inflation, as opposed to the mandate of the Federal Reserve in the US, which incorporates unemployment, growth and stability. It was not simply that the eurozone was not structured to accommodate Europe’s economic diversity; it was that the structure of the eurozone, its rules and regulations, were not designed to promote growth, employment and stability. Why would well-intentioned statesmen and women, attempting to forge a stronger, more united Europe, create something that has had the opposite effect? The founders of the euro were guided by a set of ideas and notions about how economies function that were fashionable at the time, but that were simply wrong.

Strong by Kevin Dowd: “..what is the point of her insisting that the UK maintain completely open borders with the EU when nearly a dozen continental EU members no longer do so?”
• The EU Enters Its Endgame (Dowd)
The list of countries with strong sentiment for their own Exit votes is a long one: according to a recent opinion poll, over half of the French and Italian electorates want their own exit referenda, and around 40% of the Swedish, Belgian, German, Hungarian, Polish and Spanish electorates want them. There is also strong support in Austria, Denmark, Finland, the Netherlands, Portugal, Slovakia and Sweden. Other opinion polls suggest even stronger support, but by my count, there is strong support for exit referenda in at least 16 of the 28 member countries of the EU—and then there is Greece, which has its own bone or two to pick with the EU.
Further afield, there were calls for secessionist votes in the United States and the Canadian Prime Minister was soon fending off calls for a Quexit vote. The cat is well and truly out of Pandora’s bag. The issues now are not whether there will be a similar referendum in another country but rather which country will be next and then how many will follow after that. Brexit was merely the first domino. The EU will not survive the process—and by that I do not mean that it will not survive in its current form, which is obvious—I mean that it will not survive at all. The EU “project”—the attempt to establish a federalist European superstate against the wishes of many of its subjects—has failed and the EU itself is unraveling. The only question now is how unpleasant the endgame will be.
[..] A week or so ago, I saw the German Chancellor on the news again repeat her mantra that the UK will only have access to the Single Market if it complies with her demand that it maintain free movement of peoples across what is still now the EU. I found myself scratching my head. Memo to Planet Merkel: does she not see that free movement no longer exists? Schengen has largely broken down: border controls within the EU are already a reality and the Nordics are preparing or already have plans to impose further controls to prevent their welfare states being overwhelmed by migrants. So would someone please explain to me: what is the point of her insisting that the UK maintain completely open borders with the EU when nearly a dozen continental EU members no longer do so?

“Anybody in the world can make it eventually, at much lower cost and probably much more efficiently..”
• Marc Faber: Tesla Shares Are Going To $0 (CNBC)
Marc Faber, editor of the Gloom, Boom & Doom Report, is well-known his perennially bearish take on the overall market. But there are also some specific stocks of which the investor known as “Dr. Doom” takes a particularly dim view – and right now, prime among those is Tesla. “What they produce can be produced by Mercedes, BMW, Toyota, Nissan. Anybody in the world can make it eventually, at much lower cost and probably much more efficiently,” Faber said Monday on CNBC’s “Trading Nation.”
“The market for Toyota and these large automobile companies is simply not big enough, but the moment it becomes bigger, they’ll move into the field and then Tesla will have a lot of competition.” Faber sees this increased competition causing more than a small dent in the company’s business and stock performance. “I think Tesla is a company that is likely to go to zero eventually,” Faber said.

“Others have suggested that returns should be closer to risk-free rates which would imply an even more draconian $8.4 trillion underfunding.”
• The US Public Pensions Ponzi (ZH)
Defined Benefit Pension Plans are, in many cases, a ponzi scheme. Current assets are used to pay current claims in full in spite of insufficient funding to pay future liabilities… classic Ponzi. But unlike wall street and corporate ponzi schemes no one goes to jail here because the establishment is complicit. Everyone from government officials to union bosses are incentivized to maintain the status quo…public employees get to sleep better at night thinking they have a “retirement plan,” public legislators get to be re-elected by union membership while pretending their states are solvent and union bosses get to keep their jobs while hiding the truth from employees.
We even published a note several days ago entitled “Establishment Tries To Suppress “Dissident Actuaries” Explosive Report On Public Pensions,” which pointed out that the American Academy of Actuaries and the Society of Actuaries killed a report that would have warned about the implications of lowering long-term expected returns on pension assets. Apparently the truth was just too scary. Bill Gross has been warning of the unintended consequences of low interest rates for years, and reiterated his concerns to Bloomberg recently: “Fund managers that have been counting on returns of 7% to 8% may need to adjust that to around 4%, Gross, who runs the $1.5 billion Janus Global Unconstrained Bond Fund, said. Public pensions, including the California Public Employees’ Retirement System, the largest in the U.S., are reporting gains of less than 1% for the fiscal year ended June 30.”
To our great surprise, certain pension funds are finally taking notice. Richard Ingram of Illinois’s largest pension fund recently announced that he would be taking another look at long-term return expectations noting that “anybody that doesn’t consider revisiting what their assumed rate of return is would be ignoring reality.” Ingram’s Illinois Teachers’ Retirement System is only 41.5% funded and currently assumes annual returns of 7.5%, down from 8% in 2014. We decided to take a look at what would happen if all federal, state and local pension plans decided to heed the advice of Mr. Gross. As one might suspect, the results are not pleasant.
We conservatively assume that public pensions are currently $2.0 trillion underfunded ($4.5 trillion of assets for $6.5 trillion of liabilities) even though we’ve seen estimates that suggest $3.5 trillion or more might be more appropriate. We then adjusted the return on asset assumption down from the 7.5% used by most pensions to the 4.0% suggested by Mr. Gross and found that true public pension underfunding could be closer to $5.5 trillion, or over 2.5x more than current estimates. Others have suggested that returns should be closer to risk-free rates which would imply an even more draconian $8.4 trillion underfunding.

There’s lots of this in Europe.
• Housing ‘Shell Shock’ Faces Danes Who Think Market Can Only Rise (BBG)
Denmark’s biggest mortgage bank is urging homeowners to remember that a seemingly unstoppable series of price gains can end, and even go into reverse. At Nykredit, chief analyst Mira Lie Nielsen says Danes need to start putting the possibility of housing price declines “on their radars” or risk going into “shell shock when it happens.” “Our expectation isn’t that home prices will fall in the near future, but it’s important to say, again and again, that especially apartment prices can also fall,” Nielsen said in an e-mail. After almost half a decade of negative interest rates, many homeowners in Denmark are being paid to borrow, excluding bank fees.
Most analysts estimate Danish rates won’t go positive until 2018 at the earliest, threatening to create an atmosphere of complacency as borrowers take on bigger mortgages based on assumptions that low rates are here to stay. Home prices rose an annual 4.5% across Denmark in July, according to Boligsiden.dk, a web portal that tracks the property market. Copenhagen apartment prices soared 9.4%, underpinning the “continued need to be particularly aware” of the potential risks, Nielsen said. “Prices for city dwellings are at a markedly higher level today and are in a range where few people who aren’t already benefiting from the price gains can join in,” Nielsen said.
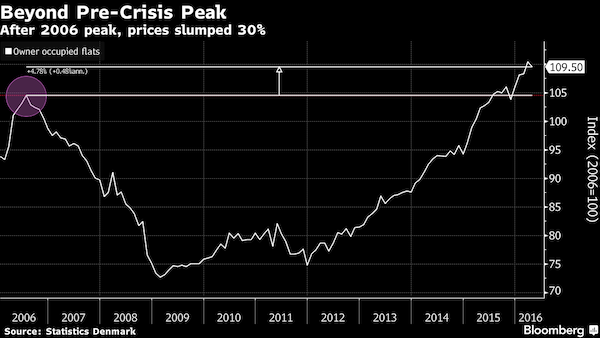
“So the price level is playing its own damping role on the market, because incomes haven’t quite been able to keep up. This is already visible in Copenhagen.” Apartment prices in Denmark are about 5% above their 2006 peak, according to the latest data from Statistics Denmark. Back then, the country’s bubble burst and apartment prices slumped about 30% through 2009. But there’s also a flip side to record-low interest rates. Banks have suffered fewer writedowns as borrowers find it easier to repay cheaper loans. The number of homeowners unable to honor their mortgage commitments is falling, with just 0.19% failing to meet payment deadlines in the first quarter, according to industry data published on Tuesday.

“..the romance of decentralization..”
• Call Blockchain Developers What They Are: Fiduciaries (Walch)
The recent hack of the DAO (short for Decentralized Autonomous Organization) and the subsequent reversal of funds on Ethereum’s blockchain should finally put an end to a decentralization charade. People are, in fact, governing public blockchains, and we need to be able to trust them. From the beginning, the core developers (who write, evaluate and modify the software code) and the powerful miners (holders of significant chunks of computing power within the network) have been the governing bodies of these so-called decentralized systems. Yet the romance of decentralization – with the seductive idea that we don’t have to trust anyone because no human is doing anything – has allowed many to overlook this important truth.
In the techno-utopian world of blockchain technology, it has become fashionable to proclaim that software code and its operation can replace the need for human governance. Hence, the push toward “decentralized autonomous organizations,” which are essentially corporations run through code rather than by people. The first of these, the DAO, began operating in May 2016, raising $150 million from investors to operate as a venture fund for blockchain technology. The DAO is just software, coded by an ambitious group at the company Slock.It. It was embarrassingly compromised through a computer hack for $60 million within a month of its inception.
The theft’s fallout has been dramatic. Since the DAO was built on the Ethereum blockchain, everyone involved with the technology was affected: DAO investors, owners of ether (the cryptocurrency of Ethereum) and anyone building anything on Ethereum, which has sought to be a platform for so-called smart contracts. This raised serious questions like: Should folks try to get the stolen ether back? Should they leave it be, as the hack was simply an exploitation of a bug in the purportedly unstoppable code?

“The rivers are the arteries of the Earth. When we block them up, the earth becomes unhealthy.”
• Construction Of Giant Dam In Canada Prompts Human Rights Outcry (G.)
Human rights campaigners are calling on Canadian authorities to halt construction of a huge hydroelectric dam in western Canada over concerns that the mega-project tramples on the rights of indigenous peoples in the area. A global campaign launched by Amnesty International on Tuesday called on the federal government and the provincial government of British Columbia to withdraw all permits and approvals for the Site C hydroelectric dam, a C$9bn project that will see more than 5,000 hectares (12,350 acres) of land – roughly equivalent to about 5,000 rugby fields – flooded in north-east British Columbia. The land is part of the traditional territories of indigenous peoples in the region, said Craig Benjamin of Amnesty International Canada.
“It’s an area that people have used for thousands upon thousands of years. Their ancestors are buried in the land; there are hundreds of unique sites of cultural importance; there is cultural knowledge of how to live on land that is associated with this specific spot.” Many continue to rely on the land to hunt, fish, plant medicines, gather berries and conduct ceremonies. “There are really few other places where they can go to practice their culture and to exercise their rights because this is a region that has been so heavily impacted by large-scale resource development.” Amid protests by several First Nations groups, the project was approved by provincial and federal authorities in 2014, allowing preparatory work to begin last summer.
Earlier this year, as clear-cutting began in the area, part of the construction was held up by a protest camp set up by indigenous activists. “This is home,” said Helen Knott, one of the half a dozen protesters who occupied the site. “The rivers are the arteries of the Earth. When we block them up, the earth becomes unhealthy. It’s about being able to protect something to pass on to our children.” After two months in the snow and braving temperatures that dropped as low as -20C, a provincial court ordered them to dismantle the camp.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle August 10 2016