
Ansel Adams Church, Taos, Pueblo 1942
The Automatic Earth and its readers have been supporting refugees and homeless in Greece since June 2015. It has been and at times difficult and at all times expensive endeavor. Not at least because the problems do not just not get solved, they actually get worse. Because the people of Greece and the refugees that land on their shores increasingly find themselves pawns in political games.
Therefore, even if the generosity of our readership has been nothing short of miraculous, we must continue to humbly ask you for more support. Because our work is not done. Our latest essay on this is here: The Automatic Earth for Athens Fund – Christmas and 2018 . It contains links to all 14 previous articles on the situation.
Here’s how you can help:

For donations to Konstantinos and O Allos Anthropos, the Automatic Earth has a Paypal widget on our front page, top left hand corner. On our Sales and Donations page, there is an address to send money orders and checks if you don’t like Paypal. Our Bitcoin address is 1HYLLUR2JFs24X1zTS4XbNJidGo2XNHiTT. For other forms of payment, drop us a line at Contact • at • TheAutomaticEarth • com.
To tell donations for Kostantinos apart from those for the Automatic Earth (which badly needs them too!), any amounts that come in ending in either $0.99 or $0.37, will go to O Allos Anthropos.
Please give generously.


All the lovely things that debt buys.
• S&P 500 Hits Most Overbought Level In 22 Years (MW)
Following a year in which the U.S. stock market hit a record number of records and seen basically nothing in the way of pullbacks or volatility, investors have gone all-in on stocks. Exchange-traded funds, perhaps the most popular way to get exposure to broad parts of the market, have seen record-breaking inflows over the year, with both domestic and foreign-based stock funds seeing heavy interest and no major category seeing outflows. Both retail and institutional investors have gotten in on the action and are positioning in a way that suggests both see further gains ahead. The S&P 500 has rallied about 20% over 2017, on track for its best year since 2013.
According to Torsten Sløk, Deutsche Bank’s chief international economist, “U.S. retail investors say that today is the best time ever to invest in the market,” based on data from the University of Michigan consumer sentiment report, which asks about the probability of an increase in stock prices over the coming year. Younger investors in particular are warming up to equities, according to E*Trade. The latest AAII investor sentiment survey indicates that 50.5% of polled investors are bullish on the market, meaning they expect prices will be higher in six months. That’s the highest level in nearly two years, and significantly above the 38.5% historical average. The number of bullish investors has gone up by 5.5 percentage points in the last week alone, while the percentage of bearish investors has dropped to 25.6%, down 2.5 percentage points over the last week.
Optimism has gotten so high that cash balances for Charles Schwab clients reached their lowest level on record in the third quarter, according to Morgan Stanley, which wrote that retail investors “can’t stay away.” The investment bank noted a similar trend in institutional investors, who it wrote were “loading the boat on risk,” with “long/short net and gross leverage as high as we have ever seen it.”
There have been fundamental reasons for this optimism, including a strong labor market and improving economic data. Furthermore, the recently passed tax bill will cut corporate taxes, which should boost corporate profits — which have already been enjoying their fastest year of growth since 2011. However, the incessant buying has pushed valuations to levels that are not only stretched, but stretched to a historic extent. As was recently noted by LPL Financial, the relative strength index, an indicator of technical momentum, is at its highest level since 1995, which indicates the S&P 500 is at its most overbought level in 22 years.
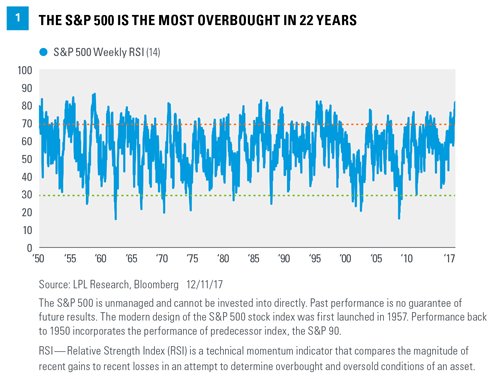

Thank your central banker.
• Peak Good Times? Stock Market Risk Spikes to New High (WS)
Margin debt is the embodiment of stock market risk. As reported by the New York Stock Exchange today, it jumped 3.5%, or $19.5 billion, in November from October, to a new record of $580.9 billion. After having jumped from one record to the next, it is now up 16% from a year ago. Even on an inflation-adjusted basis, the surge in margin debt has been breath-taking: The chart by Advisor Perspectives compares margin debt (red line) and the S&P 500 index (blue line), both adjusted for inflation (in today’s dollars). Note how margin debt spiked into March 2000, the month when the dotcom crash began, how it spiked into July 2007, three months before the Financial-Crisis crash began, and how it bottomed out in February 2009, a month before the great stock market rally began:
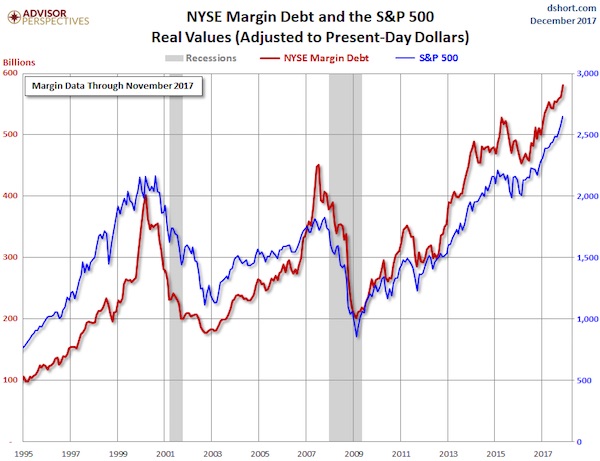
Margin debt, which forms part of overall stock market leverage, is the great accelerator for stocks, on the way up and on the way down. Rising margin debt – when investors borrow against their portfolios – creates liquidity out of nothing, and much of this new liquidity is used to buy more stocks. But falling margin debt returns this liquidity to where it came from. Leverage supplies liquidity. But it isn’t liquidity that moves from one asset to another. It is liquidity that is being created to be plowed into stocks, and that can evaporate just as quickly: When stocks are dumped to pay down margin debt, the money from those stock sales doesn’t go into other stocks or another asset class, doesn’t become cash “sitting on the sidelines,” as the industry likes to say, and isn’t used to buy gold or cryptocurrencies or whatever. It just evaporates without a trace.
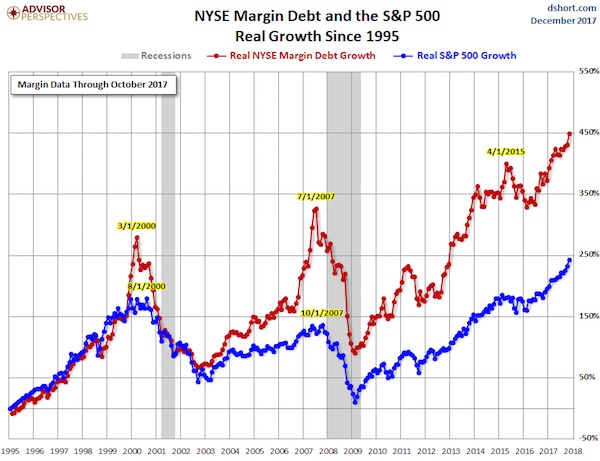
After stirring markets into an eight-year risk-taking frenzy, the Fed is now worried that markets have gone too far. Among the Fed governors fretting out loud over this was Dallas Fed President Robert Kaplan who recently warned about the “record-high levels” of margin debt, along with the US stock market capitalization, which, at 135% of GDP, is “the highest since 1999/2000.” “In the event of a sell-off, high levels of margin debt can encourage additional selling, which could, in turn, lead to a more rapid tightening of financial conditions,” he mused. The growth in margin debt has far outpaced the growth of the S&P 500 index in recent years. The chart below (by Advisor Perspectives) shows the percentage growth of margin debt and the S&P 500 index, both adjusted for inflation:

Will Russia set the model for the rest of the world? Don’t be surprised if others follow.
• Russia’s Finance Minister Confirms Upcoming Bitcoin Regulations (CCN)
The Russian Ministry of Finance has prepared a sweeping regulatory law that will cover many facets of cryptocurrencies like bitcoin in Russia. In an interview with state-owned television broadcaster Rossiya 24 over Christmas, Russia’s finance minister Anton Siluanov confirmed the ministry’s draft law on a regulatory framework for cryptocurrencies. The regulation, as expected, will cover bitcoin mining rules, taxation laws for adopters and guidelines for exchanges selling cryptocurrencies. As reported by Russian news source TASS, Siluanov stated: The Ministry of Finance has prepared a draft law, currently under consideration, which will determine the procedure for issuing, taxing, buying and circulation of cryptocurrency. In conjunction, the Ministry of Finance is also reportedly preparing amendments to Russian legislation toward the broader regulation of new financial technologies and digital payments.
The developments are a remarkable contrast to legislation proposed by Russia’s Finance Ministry as recently as March 2016. At the time, the ministry proposed a 7-year prison sentence for bitcoin adopters and users. Earlier in September, Siluanov called for the Russian government to accept and understand “that cryptocurrencies are real.” “There is no sense in banning them,” Siluanov said at the time, “there is a need to regulate them.” The new laws, in its draft, is expected to be submitted to the State Duma (the lower house of the Russian Parliament) tomorrow before its anticipated adoption sometime in March 2018. The new laws were fast-tracked by authorities following Russian President Vladimir Putin’s mandate to develop regulations for cryptocurrencies, mining and initial coin offerings (ICOs). The amendments to existing Russian laws to recognize cryptocurrencies will also aid in the prepping for the launch of Russia’s own national cryptocurrency – the CryptoRuble.

Korea may be the first to copy Moscow. This is not action, it’s reaction.
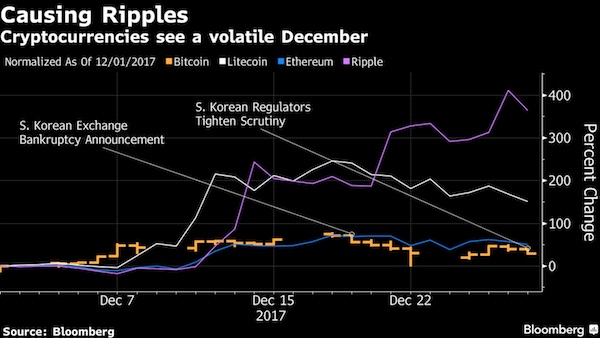
• Bitcoin Tumbles Over Exchange-Closure Fears (BBG)
Bitcoin resumed its tumble on Thursday after South Korea said it was eyeing options including a potential shutdown of at least some cryptocurrency exchanges to stamp out a frenzy of speculation. South Korea has been ground zero for a global surge in interest in bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies as prices surged this year, prompting the nation’s prime minister to worry over the impact on Korean youth. While there’s no immediate indication Asia’s No. 4 economy will shutter exchanges that have accounted by some measures for more than fifth of global trading, the news poses a warning as regulators the world over express concerns about private digital currencies. Bitcoin fell as much as 9% to as low as $13,828 in Asia trading, erasing modest gains after the South Korean release, composite Bloomberg pricing shows.
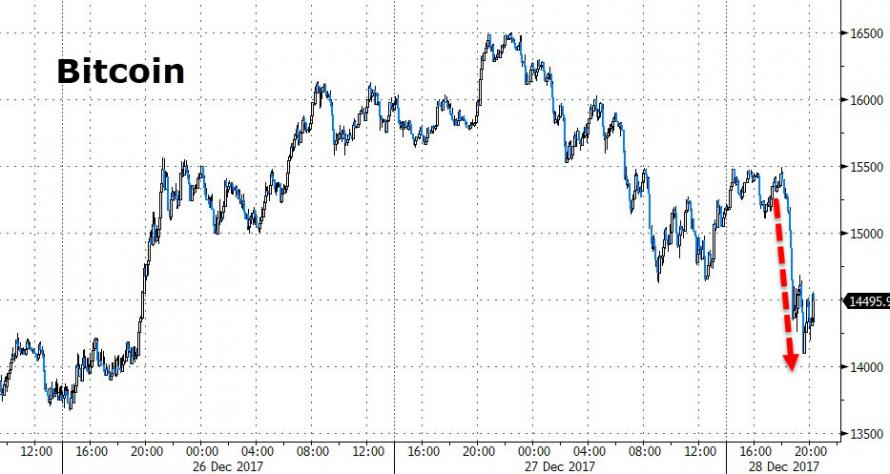
It’s now down about 28% from its record high reached last week. South Korea will require real-name cryptocurrency transactions and impose a ban on the offering of virtual accounts by banks to crypto-exchanges, according to a statement from the Office for Government Policy Coordination. Policy makers will review measures including the closure of crypto-exchanges suggested by the Ministry of Justice and take proper measures swiftly and firmly while monitoring the trend of the speculation. Bitcoin was trading at about a 30% premium over prevailing international rates on Thursday in Seoul – a continuing sign of the country’s obsession, and the difficulty in arbitraging between markets. “Cryptocurrency speculation has been irrationally overheated in Korea,” the government said in the statement, which comes little more than a week after the bankruptcy filing of one South Korean exchange. “The government can’t leave the abnormal situation of speculation any longer.”

The combination of crypto and derivatives sends shivers.
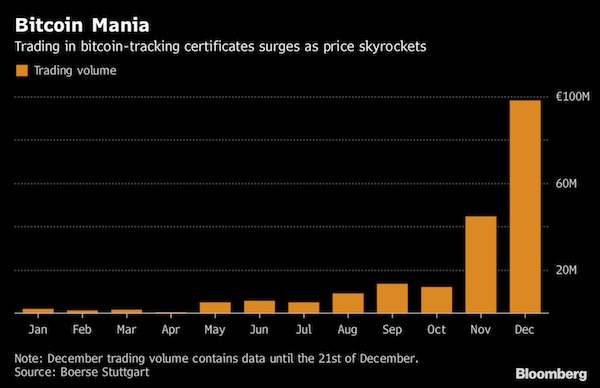
• Bitcoin’s Surging Price Drives Private Investor Demand For Derivatives (BBG)
Bitcoin’s surging price has driven private-investor demand for derivatives tracking the virtual currency. Trading in so-called participation notes has skyrocketed this year on Boerse Stuttgart, Europe’s largest exchange for retail derivatives. The number of executed orders jumped 22-fold from 436 in January to almost 10,000 in December.

Beware when stirring up a complex system.
• Trump Tax Reform Blew Up The Treasury Market (ZH)
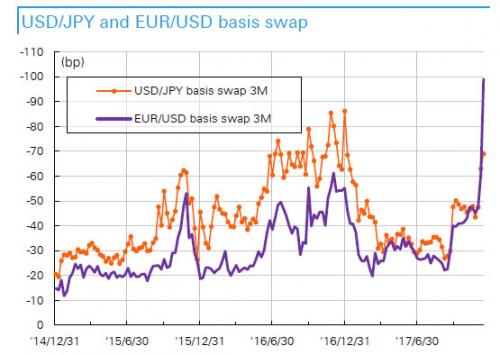
Over the past week we have shown on several occasions that there once again appears to be a sharp, sudden dollar-funding liquidity strain in global markets, manifesting itself in a dramatic widening in FX basis swaps, which – in this particular case – has flowed through in the forward discount for USDJPY spiking from around 0.04 yen to around 0.23 yen overnight. As Bloomberg speculated, this discount for buying yen at future dates widened sharply as non-U.S. banks, which typically buy dollars now with sell-back contracts at a future date, scrambled to procure greenbacks for the year-end. However, as Deutsche Bank’s Masao Muraki explains, this particular dollar funding shortage is more than just the traditional year-end window dressing or some secret bank funding panic.
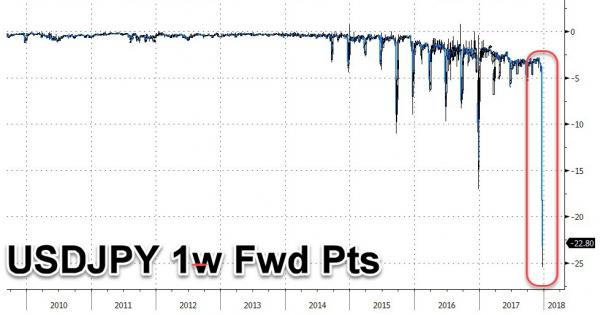
Instead, the DB strategist observes that the USD funding costs for Japanese insurers and banks to invest in US Treasuries – which have surged reaching a post-financial-crisis high of 2.35% on 15 Dec – are determined by three things, namely (1) the difference in US and Japanese risk-free rates (OIS), (2) the difference in US and Japanese interbank risk premiums (Libor-OIS), and (3) basis swaps, which illustrate the imbalance in currency-hedged US and Japanese investments. In this particular case, widening of (1) as a result of Fed rate hikes and tightening of dollar funding conditions inside the US (2) and outside the US (3) have occurred simultaneously. This is shown in the chart below.
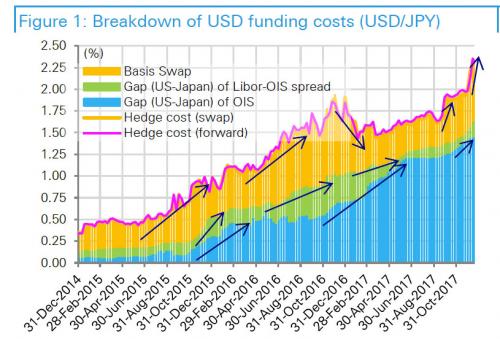
What is causing this? Unlike on previous occasions when dollar funding costs blew out due to concerns over the credit and viability of the Japanese and European banks, this time the Fed’s rate hikes could be spurring outflows from the US, European, and Japanese banks’ deposits inside the US. Absent indicators to the contrary, this appears to be the correct explanation since it’s not just Yen funding costs that are soaring. In fact, at present EUR/USD basis swaps are widening more than USD/JPY basis swaps. [..] According to Deutsche, it is possible that an increase in hedged US investments by Europeans could be indirectly affecting Japan, and that market participants could also be conscious of the risk that the repatriation tax system could spur a massive flow-back into the US, of funds held overseas by US companies In fact, one can draw one particularly troubling conclusion: the sharp basis swap moves appear to have been catalyzed by the recently passed Trump tax reform.

More ‘unintended’ consequences?!
• The Tax Plan Could Change How Wall Street Works (BBG)
Leon Black recently posed a question whose answer will determine how profitable the new U.S. tax regime could make Wall Street firms like his Apollo Global Management. Publicly traded partnerships, including private equity firms Apollo, Blackstone and Carlyle Group, are taxed differently than corporations. So should they take advantage of the overhauled tax rules to pay less in taxes? Or should they use this chance to change to an Inc. from an LLC or LP, which would increase tax bills but allow them to attract investments from mutual funds that have previously been out of reach? “We’re still analyzing,’’ Black told the Goldman Sachs U.S. Financial Services Conference Dec. 6. “It’s an uncertain outcome.’’
Either way, it’s most likely a money-making outcome. The tax changes are a boon for firms such as Apollo, where Black is chief executive officer. The new lower corporate rate has made it possible for bigger publicly traded partnerships to consider the change. As it is, management fees, which typically account for 30 percent or more of their earnings, are already taxed at the corporate rate. That will drop. The legislation scarcely touched the 23.8 percent rate paid on incentive fees, also called carried interest, which incur no additional levy when paid out to shareholders. If the partnerships converted to corporations, the incentive fees would be hit with a second layer of tax when they’re paid out. That would push the combined tax rate on incentive income paid out as dividends to nearly 40 percent, according to Peter Furci, co-chair of Debevoise & Plimpton’s global tax practice.

I’m sure this guy is smart, but he misses the point here by a mile. What has happened is the data have been centralized to the NSA and CIA and their peers. Zuckerberg is just a conduit.
• “We’ve Centralized All Of Our Data To A Guy Called Mark Zuckerberg” (HN)
At its inception, the internet was a beautifully idealistic and equal place. But the world sucks and we’ve continuously made it more and more centralized, taking power away from users and handing it over to big companies. And the worst thing is that we can’t fix it – we can only make it slightly less awful. That was pretty much the core of Pirate Bay’s co-founder, Peter Sunde‘s talk at tech festival Brain Bar Budapest. TNW sat down with the pessimistic activist and controversial figure to discuss how screwed we actually are when it comes to decentralizing the internet. In Sunde’s opinion, people focus too much on what might happen, instead of what is happening. He often gets questions about how a digitally bleak future could look like, but the truth is that we’re living it.
“Everything has gone wrong. That’s the thing, it’s not about what will happen in the future it’s about what’s going on right now. We’ve centralized all of our data to a guy called Mark Zuckerberg, who’s basically the biggest dictator in the world as he wasn’t elected by anyone. Trump is basically in control over this data that Zuckerberg has, so I think we’re already there. Everything that could go wrong has gone wrong and I don’t think there’s a way for us to stop it.” One of the most important things to realize is that the problem isn’t a technological one. “The internet was made to be decentralized,” says Sunde, “but we keep centralizing everything on top of the internet.”
To support this, Sunde points out that in the last 10 years, almost every up-and-coming tech company or website has been bought by the big five: Amazon, Google, Apple, Microsoft and Facebook. The ones that manage to escape the reach of the giants, often end up adding to the centralization. We don’t create things anymore, instead we just have virtual things. Uber, Alibaba and Airbnb, for example, do they have products? No. We went from this product-based model, to virtual product, to virtually no product what so ever. This is the centralization process going on. Although we should be aware that the current effects of centralization, we shouldn’t overlook that it’s only going to get worse. There are a lot of upcoming tech-based services that are at risk of becoming centralized, which could have a huge impact on our daily lives.
[..] Feeling a bit optimistic, I asked Sunde whether we could still fight for decentralization and bring the power back to the people. His answer was simple. “No. We lost this fight a long time ago. The only way we can do any difference is by limiting the powers of these companies – b�y� �g�o�v�e�r�n�m�e�n�t�s� �s�t�e�p�p�i�n�g� �i�n� – but unfortunately the EU or the US don’t seem to have any interest in doing this.”

Right in theory, but…
• The Petro-yuan Bombshell (Escobar)
The website of the China Foreign Exchange Trade System (CFETS) recently announced the establishment of a yuan-ruble payment system, hinting that similar systems regarding other currencies participating in the New Silk Roads, a.k.a. Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) will also be in place in the near future. Crucially, this is not about reducing currency risk; after all Russia and China have increasingly traded bilaterally in their own currencies since the 2014 US-imposed sanctions on Russia. This is about the implementation of a huge, new alternative reserve currency zone, bypassing the US dollar. The decision follows the establishment by Beijing, in October 2015, of the China International Payments System (CIPS). CIPS has a cooperation agreement with the private, Belgium-based SWIFT international bank clearing system, through which virtually every global transaction must transit.
What matters in this case is that Beijing – as well as Moscow – clearly read the writing on the wall when, in 2012, Washington applied pressure on SWIFT; blocked international clearing for every Iranian bank; and froze $100 billion in Iranian assets overseas as well as Tehran’s potential to export oil. In the event Washington might decide to slap sanctions on China, bank clearing though CIPS works as a de facto sanctions-evading mechanism. Last March, Russia’s central bank opened its first office in Beijing. Moscow is launching its first $1 billion yuan-denominated government bond sale. Moscow has made it very clear it is committed to a long term strategy to stop using the US dollar as their primary currency in global trade, moving alongside Beijing towards what could be dubbed a post-Bretton Woods exchange system.
Gold is essential in this strategy. Russia, China, India, Brazil & South Africa are all either large producers or consumers of gold – or both. Following what has been extensively discussed in their summits since the early 2010s, the BRICS are bound to focus on trading physical gold. Markets such as COMEX actually trade derivatives on gold, and are backed by an insignificant amount of physical gold. Major BRICS gold producers – especially the Russia-China partnership – plan to be able to exercise extra influence in setting up global gold prices. [..] The current state of play is still all about the petrodollar system; since last year what used to be a key, “secret” informal deal between the US and the House of Saud is firmly in the public domain.
Even warriors in the Hindu Kush may now be aware of how oil and virtually all commodities must be traded in US dollars, and how these petrodollars are recycled into US Treasuries. Through this mechanism Washington has accumulated an astonishing $20 trillion in debt – and counting. Vast populations all across MENA (Middle East-Northern Africa) also learned what happened when Iraq’s Saddam Hussein decided to sell oil in euros, or when Muammar Gaddafi planned to issue a pan-African gold dinar. But now it’s China who’s entering the fray, following on plans set up way back in 2012. And the name of the game is oil-futures trading priced in yuan, with the yuan fully convertible into gold on the Shanghai and Hong Kong foreign exchange markets.

The UK Labour party need to cash in now on the government’s mishandling of Brexit and the country’s economy, or risk being seen as part of that government. Corbyn et al know thay could jump in the polls by denouncing Brexit itself, but they don’t have the courage to do that. So on the no. 1 problem, they’re the same as the Tories.
• John McDonnell Warns Over ‘Alarming Increase’ In UK Household Debt (G.)
John McDonnell has said the UK is in the grip of a personal debt crisis with levels of unsecured borrowing predicted to hit a record of £19,000 per household by the end of this parliament. The shadow chancellor said the increase in debt, to more than £14,000 per household this year, was alarming. Analysis from Labour shows unsecured debt is on course to exceed £15,000 per household next year and could go on to exceed £19,000 per household by 2022 if it follows the current trajectory. It is understood Labour plans to focus on the issue in the new year, warning that the continuing squeeze on wages and the high level of inflation are contributing to high levels of personal debt.
On Wednesday the Resolution Foundation, a thinktank, predicted that the stagnation in real wages was set to continue throughout 2018 and may only begin to lift towards the end of the year. McDonnell said: “The alarming increase in average household debt already means many families in our country are struggling over the Christmas period. The Tories have no real answers to tackle the debt crisis gripping our country and have no solutions to offer those struggling to get by as prices run ahead of wages. “The next Labour government will introduce a £10 per hour real living wage, scrap student fees, end the public sector pay cap and cap interest on consumer credit to build an economy for the many, not the few.”

Why go this crazy route? Well, money of course.
• Another Fukushima? Tepco Plans To Restart World’s Biggest Nuclear Plant (G.)
If a single structure can define a community, for the 90,000 residents of Kashiwazaki town and the neighbouring village of Kariwa, it is the sprawling nuclear power plant that has dominated the coastal landscape for more than 40 years. When all seven of its reactors are in operation, Kashiwazaki-kariwa generates 8.2m kilowatts of electricity – enough to power 16m households. Occupying 4.2 sq km of land along the Japan Sea coast, it is the biggest nuclear power plant in the world. But today, the reactors at Kashiwazaki-kariwa are idle. The plant in Niigata prefecture, about 140 miles (225km) north-west of the capital, is the nuclear industry’s highest-profile casualty of the nationwide atomic shutdown that followed the March 2011 triple meltdown at Fukushima Daiichi.
The company at the centre of the disaster has encountered anger over its failure to prevent the catastrophe, its treatment of tens of thousands of evacuated residents and its haphazard attempts to clean up its atomic mess. Now, the same utility, Tokyo Electric Power [Tepco], is attempting to banish its Fukushima demons with a push to restart two reactors at Kashiwazaki-kariwa, one of its three nuclear plants. Only then, it says, can it generate the profits it needs to fund the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi and win back the public trust it lost in the wake of the meltdown. This week, Japan’s nuclear regulation authority gave its formal approval for Tepco to restart the Kashiwazaki-kariwa’s No. 6 and 7 reactors – the same type of boiling-water reactors that suffered meltdowns at Fukushima Daiichi.
After a month of public hearings, the nuclear regulation authority concluded that Tepco was fit to run a nuclear power plant and said the two reactors met the stricter safety standards introduced after the 2011 disaster.

What hope is there for us, if there’s none for our children? And yes, all children are our children, not just the ones that live in our homes and communities.
• Children Increasingly Used As Weapons Of War – Unicef (G.)
Children caught in war zones are increasingly being used as weapons of war – recruited to fight, forced to act as suicide bombers, and used as human shields – the United Nations children’s agency has warned. In a statement summarising 2017 as a brutal year for children caught in conflict, Unicef said parties to conflicts were blatantly disregarding international humanitarian law and children were routinely coming under attack. Rape, forced marriage, abduction and enslavement had become standard tactics in conflicts across Iraq, Syria and Yemen, as well as in Nigeria, South Sudan and Myanmar. Some children, abducted by extremist groups, are abused again by security forces when they are released.
Others are indirectly harmed by fighting, through malnutrition and disease, as access to food, water and sanitation are denied or restricted. Some 27 million children in conflict zones have been forced out of school. “Children are being targeted and exposed to attacks and brutal violence in their homes, schools and playgrounds,” said Manuel Fontaine, Unicef’s director of emergency programmes. “As these attacks continue year after year, we cannot become numb. Such brutality cannot be the new normal.” Much of the fighting affecting children occurred in long-running conflicts in Africa.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle December 28 2017