
Russell Lee Dillon, Montana, trading center for a prosperous cattle and sheep country Aug 1942



We already knew.
• Financial ‘Experts’ No Better At Finance Than Normal Humans (HuffPo)
Knowing more about finance does not lead to better financial decisions. In fact, some of the most supposedly financially knowledgeable people – mutual-fund managers – don’t make better financial decisions than other people, according to a new study by Michigan State and Notre Dame researchers, as reported in The Atlantic. It’s the latest evidence that a years-long campaign to help normal Americans achieve “financial literacy” is ineffective at best and misguided at worst. As The Atlantic notes, expert stock-pickers in finance and forecasters in other fields have been derided for decades as no better than dart-throwing monkeys. When it comes to getting ordinary people to know more about finance, however, the consensus has been that this time it’s different. On the surface, it’s a well-intentioned and uncontroversial mission: Helping people help themselves by making better decisions. And there’s plenty of evidence that people have a scary lack of financial knowledge: One study found that just a third of Americans would correctly answer three simple financial questions.
And those questions are models of transparency compared with the opaque language consumers often face when making even the simplest financial decisions. The goal of making people financially literate seems to imply that it’s the individual’s responsibility to safely navigate what is often intentionally inscrutable financial language. The same companies who create the problem of financial products Americans can’t understand push financial literacy as the solution. For instance, Bank of America thinks the key is an online course. The financial industry’s self-regulatory organization has an entire foundation devoted to investor education. But financial literacy in this gauzy, generalized form simply doesn’t work. The Cleveland Fed found no “conclusive support that any benefit at all exists” from financial education as it is currently taught. Shocking no one who has been to high school, one study showed that taking a financial literacy class in high school does nothing to improve financial literacy.
And a study by researchers at the Brookings Institution could not find “strong evidence that financial literacy efforts have had positive and substantial impacts.” In a 2011 presentation titled “The Financial Education Fallacy,” Lauren Willis, a professor at Loyola Law School, shot down the idea that “ordinary consumers would have made better mortgage choices and would have accumulated sufficient precautionary savings to weather the recession” if they’d just been financially educated. Straightforward consumer protections, like putting limits on how many single stocks people can own in retirement accounts, are most effective. Financial education is no substitute for financial regulation, she argues.

This is QE for you. 40.5% child poverty in Greece, 32% in the US.
• Child Poverty Up In More Than Half Of Developed World Since 2008 (Guardian)
Child poverty has increased in 23 countries in the developed world since the start of the global recession in 2008, potentially trapping a generation in a life of material deprivation and reduced prospects. A report by Unicef says the number of children entering poverty during the recession is 2.6 million greater than the number who have been lifted out of it. “The longer these children remain trapped in the cycle of poverty, the harder it will be for them to escape,” it says in Children of Recession: the Impact of the Economic Crisis on Child Wellbeing in Rich Countries. Greece and Iceland have seen the biggest percentage increases in child poverty since 2008, followed by Latvia, Croatia and Ireland. The proportion of children living in poverty in the UK has increased from 24% to 25.6%. Eighteen of the 41 countries in the study have seen falls in child poverty, topped by Chile which has seen a reduction from 31.4% to 22.8%.
Norway has the lowest child poverty rate, at 5.3% (down from 9.6% in 2008), and Greece has the highest, at 40.5% (up from 23% in 2008). Latvia and Spain also have child poverty rates above 36%. In the US, the rate is 32%. “In the past five years, rising numbers of children and their families have experienced difficulty in satisfying their most basic material and educational needs,” says the report. “Unemployment rates not seen since the Great Depression of the 1930s have left many families unable to provide the care, protection and opportunities to which children are entitled. Most importantly, the Great Recession is about to trap a generation of educated and capable youth in a limbo of unmet expectations and lasting vulnerability.” It adds: “The impact of the recession on children, in particular, will be felt long after the recession itself is declared to be over.”
The study’s authors asked people about their experiences and perceptions of deprivation, based on four indicators: not having enough money to buy food for themselves or their family; stress levels; overall life satisfaction; and whether children have the opportunity to learn and grow. In 18 of the 41 countries, scores showed a worsening situation between 2007 and 2013, revealing “rising feelings of insecurity and stress”. The percentage of households with children unable to afford a meal with meat, chicken, fish or a vegetable equivalent every second day more than doubled in four European countries – Estonia (to 10%), Greece (18%), Iceland (6%) and Italy (16%).

It did for broke banks.
This week saw not only the end of QE but an unending parade of told-you-so talking-head willing to proclaim not only QE’s success (unemployment ~6%, stocks at record highs, corporate profits at record highs) but to scoff at the naysayers warnings that post-QE stocks will slide since ‘the whole rally has been driven by central bank liquidity’ because “see, stocks are ripping higher post-FOMC.” Obviously they fail to see the link between extraordinarily low rates (enabling cheap-funded financial engineering), printed money (repressing investors into buying stocks), and the fact that stocks are surged after another central bank – the BoJ – unleashed another round of even bigger insanity.To those that suggest QE was a victory, we have words and pictures… If it was so successful, why did they stop? And does this look like the chart of a successful monetary policy action?
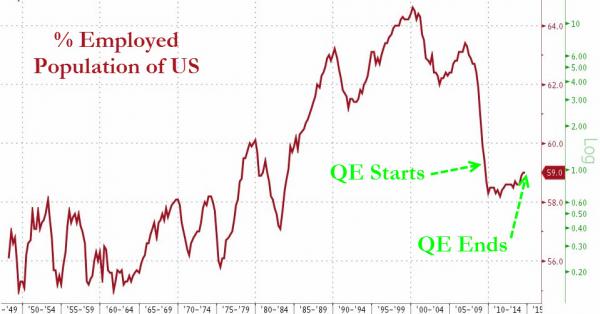

“As UK state spending has surged over recent years, with our national debt doubling to £1,400bn since 2008, we’ve kept our public finances afloat only by effectively selling government debt back to the state …” You mean, the BoE is not ‘inedependent’?
• History Will Surely See QE As A Major Mistake (Telegraph)
“The final word on quantitative easing will have to wait for historians,” wrote Ambrose Evans-Pritchard this week. Now the US Federal Reserve has apparently ended QE, I’d like to take a cue from my esteemed Telegraph colleague by suggesting what future historians might say. On Wednesday, the Fed terminated QE3 – the latest incarnation of its money-creation programme. The American version of this highly unorthodox policy began in late 2008, with the Fed creating virtual balances ex nihilo and purchasing assets such as government debt and mortgage-backed securities, often from bombed-out banks. The US authorities originally billed QE as a $600bn exercise. By unlocking frozen interbank markets, it was supposed to spur growth, breaking the credit crunch. As meaningful recovery remained elusive, though, QE2 was launched in 2010, with its successor two years later. In sum, the world’s most important central bank has fired $3,700bn from its monetary bazooka. America’s QE has been six times bigger than envisaged.
The Fed’s balance sheet has grown more than three-fold in just over half a decade – an unprecedented monetary expansion. And it’s not just America, of course. Launched in March 2009, British QE was presented as a £50bn program. It has since ballooned to £375bn, some 7.5 times the official prediction. The Bank of England’s balance sheet has quadrupled, with our QE focusing on gilt purchases. The Bank now holds over a third of all outstanding sovereign bonds. Ordinarily, governments borrow from pension funds, insurance companies and other long-term investors. As UK state spending has surged over recent years, with our national debt doubling to £1,400bn since 2008, we’ve kept our public finances afloat only by effectively selling government debt back to the state, using newly-created money. If that sounds like dubious circular financing, that’s what it is. Future historians will no doubt discuss this uncomfortable reality more than we do.

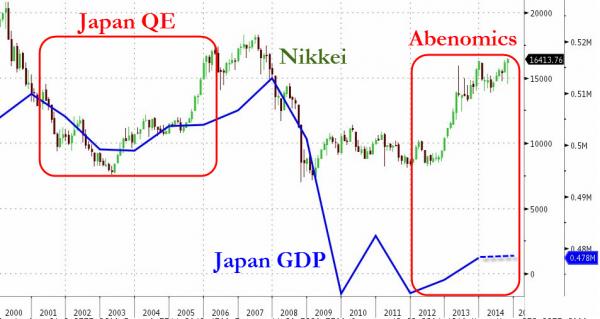
“ … we are in the midst of a big bubble that will – down the line – be referred to as ‘The QE Bubble.”
• Beware The QE Bubble, This Feels A Lot Like 1999 (Zero Hedge)
It appears few remember the epic failure of Japan’s first experiment with quantitative easing from 2001 to 2006 (that even the NY Fed can’t find a silver lining to crow about) and yet, not only is QE heralded as a success (or not) but additional QE seems to be something to celebrate (even when it’s shown to fail to achieve anything economically). How’s QE working out for Japan? [..] As Michael Chadwick notes in an oddly bearish interview on CNBC, where has Japan gone in the last 14 years (since its QE started), “absolutely nowhere,” and yet, he exclaims, “sadly, across the globe all central banks are following the same failed path.” Chadwick reflects on the explosion of central bank balance sheets and asks, rhetorically, “do we really need QE every time the market gets nervous?”
Chadwick, rightly proclaims: “At this point not much matters apart from central banker comments, QE, and political promises… I wanna know about valuations, I worry about the consumer; this feels a lot like 1999 to me.” “We have to wonder, are the central banks working together; our QE ends one day; Japan QE ramps up the next – you gotta wonder?” “Right now the world is a very vulnerable place… we are in the midst of a big bubble that will – down the line – be referred to as ‘The QE Bubble'”

I don’t think -10% is a major sell-off, that’s just a correction.
• ‘Another, Bigger Market Selloff Coming’ (CNBC)
U.S. stocks rallied on Friday, with the Dow industrial average and S&P 500 closing at record highs. While the recent selloff may be in the rearview mirror, there’s a bigger one coming within the next three months, Empire Execution president Peter Costa told CNBC Friday. “The market has been on a tear for over five years. We had a small pullback of 8% I don’t think that’s enough. I think that the market needs to come back a little bit more than that for a longer duration,” Costa said in an interview with “Closing Bell.” In fact, he’s predicting a selloff of “probably” more than 10%.

It’s not elusive, it’s simple gone and it’s not coming back.
• European Growth As Elusive As Quicksilver (Reuters)
Data from both sides of the Atlantic will give clues in the coming week on just how bad the euro zone economy is and just how sustainable is its U.S. counterpart. Europe offers a rate meeting from the European Central Bank and a new slate of economic forecasts; the United States will release its influential monthly jobs data. Purchasing manager indexes for the past month will also show how businesses see things shaping up in the United States and Europe. One for China’s has already come in lower than expected. For many, the ECB meeting on Thursday will be the main money event – despite the fact that it is not likely to be one of action or suspense. As usual, the attention will be on ECB President Mario Draghi’s nuances at the news conference that follows the likely non-move on rates. When it comes to the ECB, the news is often all about the journey rather than the destination. This week’s inflation data let the ECB off the hook on taking any immediate additional action to combat the threat of deflation.
At 0.4% in October, inflation is worryingly slight, but it is higher than it was a month earlier. ECB policymakers are also in no rush to move on to something new when they have not yet seen how their targeted loans and purchases of asset-backed securities are doing. Many in financial markets would like to see the ECB move to a full quantitative easing (QE) asset-buying program like the one the U.S. Federal Reserve has just closed. But as these words from ECB Governing Council member Ewald Nowotny suggest, it is not likely. “I don’t think we should be pushed by the markets to produce a new program at every meeting we have.” The bank will also be looking at the U.S. Federal Reserve’s ending of QE and relatively hawkish tone for some spillover succour. The euro is down more than 1.5% against the dollar since the Fed meeting on Wednesday, and down more than 10% since May. A weaker euro not only boosts euro zone exports, it imports inflation, both of which the ECB wants to see.

‘Germany continues to resist a much-needed stimulus to boost eurozone demand.’ Roubini’s just another geezer proclaiming: ‘if only they picked the right policies, we’d return to growth … ‘ Yawn. It’s boring, it’s stupid, it’s costly, it’s destructive and it’s utterlyuseless. Why can’t anyone think beyond that narrow notion? Where is the power of the human brain? Where did it go? We’re stuck in a broken record rut.
• The World Economy Is Flying With Only One Engine (Roubini)
The global economy is like a jetliner that needs all of its engines operational to take off and steer clear of clouds and storms. Unfortunately, only one of its four engines is functioning properly: the Anglosphere (the United States and its close cousin, the United Kingdom). The second engine – the eurozone – has now stalled after an anaemic post-2008 restart. Indeed, Europe is one shock away from outright deflation and another bout of recession. Likewise, the third engine, Japan, is running out of fuel after a year of fiscal and monetary stimulus. And emerging markets (the fourth engine) are slowing sharply as decade-long global tailwinds – rapid Chinese growth, zero policy rates and quantitative easing by the US Federal Reserve, and a commodity super-cycle – become headwinds. So the question is whether and for how long the global economy can remain aloft on a single engine. Weakness in the rest of the world implies a stronger dollar, which will invariably weaken US growth.
The deeper the slowdown in other countries and the higher the dollar rises, the less the US will be able to decouple from the funk everywhere else, even if domestic demand seems robust. Falling oil prices may provide cheaper energy for manufacturers and households, but they hurt energy exporters and their spending. And, while increased supply – particularly from North American shale resources – has put downward pressure on prices, so has weaker demand in the eurozone, Japan, China, and many emerging markets. Moreover, persistently low oil prices induce a fall in investment in new capacity, further undermining global demand. Meanwhile, market volatility has grown, and a correction is still underway. Bad macro news can be good for markets, because a prompt policy response alone can boost asset prices.
But recent bad macro news has been bad for markets, owing to the perception of policy inertia. Indeed, the European Central Bank is dithering about how much to expand its balance sheet with purchases of sovereign bonds, while the Bank of Japan only now decided to increase its rate of quantitative easing, given evidence that this year’s consumption-tax increase is impeding growth and that next year’s planned tax increase will weaken it further. As for fiscal policy, Germany continues to resist a much-needed stimulus to boost eurozone demand. And Japan seems to be intent on inflicting on itself a second, growth-retarding consumption-tax increase. Furthermore, the Fed has now exited quantitative easing and is showing a willingness to start raising policy rates sooner than markets expected. If the Fed does not postpone rate increases until the global economic weather clears, it risks an aborted takeoff – the fate of many economies in the last few years.

The land of the free and the home of the depraved.
• Warning: Avoid This Corrupt, Third-World Country At All Costs (Simon Black)
John Anderson, an American tourist from San Clemente, California, was driving down a poorly-maintained highway when he saw flashing lights in his rearview mirror. After a brief exchange with the local police officer, Anderson was shocked when the cop started searching his vehicle. Anderson had $25,180 in US dollar cash in the car, which by the way was not a crime according to the local laws. When the cop saw it, he told Anderson that we would take it and threatened him with arrest if he protested. Anderson couldn’t believe it. This is the sort of stuff you always hear about in these third world countries—corrupt cops and state robbery. Ultimately Anderson gave in; the cop let him go and did not charge him with a crime, but took every last penny in the vehicle. And for the last two years, Anderson has been trying to unsuccessfully fight it in the country’s Kangaroo court system.
Clearly we should all avoid going to such dangerously corrupt third world countries. Except in this case, Anderson was in the United States of America. And he is far from being the only victim of this highway robbery known as Civil Asset Forfeiture. Since 9/11, police forces in the Land of the Free made over 62,000 seizures without charging anyone with any crime, stealing $2.5 billion in cash alone. The cost of taking legal action against the government is so high, that only about 17% of the victims actually challenged the seizures. And even then, only 41% of those that challenged have been able to get their money back. This means that the government has a better than 93% success rate in outright theft. This is worse than mafia—it’s blatant theft with impunity from the people that are sworn to protect and serve. It’s the kind of thing that is thought to only occur in heinously corrupt countries.
Here’s the good news: many people are waking up to the reality that they’re not living in a free country. They are starting to understand what I call ‘the criminalization of existence.’ Every last detail of our lives is regulated—what we can/cannot put in our bodies, whether we can collect rainwater or unplug from the grid, how we are allowed to educate our own children, etc. Driving this point home, a Tennessee woman was actually thrown in jail earlier this month for ignoring a city citation to trim some overgrown bushes in her yard. This isn’t freedom. The irony is that, even though many people are starting to realize this, they’re looking to the very institution that has enslaved them to solve the problem.

Try that in Texas.
• UK Courts Islamic Finance Market (Reuters)
The scope of Britain’s Islamic finance market is widening with several initiatives from the government and private sector, although the country is about to lose one of its six full-fledged Islamic banks. In June, Britain became the first Western country to sell sovereign sukuk (Islamic bonds), helping boost its industry credentials as competition intensifies among global financial centres for a slice of Islamic business. Britain has 22 firms that offer sharia-compliant financial products and they held an estimated $19 billion in assets last year, according to a report by lobby group TheCityUK. These include six full-fledged Islamic banks such as Bank of London and the Middle East, European Islamic Investment Bank, Gatehouse Bank and the Islamic Bank of Britain (IBB).
Last week a government official said the central bank would look into developing a liquidity management tool for use by Islamic banks, while Britain’s export credit agency expects to guarantee sukuk for the first time next year, an issue by a customer of European plane maker Airbus. In May, the Bank of England widened the types of sharia-compliant debt instruments that Islamic banks can use in their liquidity buffers, under a policy statement known as PS4/14.

We know.
• China’s Economy Goes From Bad To Worse (Zero Hedge)
Prepare to once again hear the word “decoupling” a whole lot more. The reason is that while the US economy is supposedly on an upward tear after the 3.5% Q3 GDP print (thanks to the war against ISIS sending defense spending soaring and a very contradictory plunge in imports which suggest US tollers are seeing far less end-demand) and despite the immediate cut to Goldman’s Q4 GDP estimate from 3.0% to 2.2% after US consumer spending tumbled in September it is, for now at least – because GDP-crushing snow is just around the corner – doing better than Europe (where Germany just joined the ranks of Spain, Italy and Portgual in the deflation column), Japan, where the BOJ just crashed recovery hopes and unleashed more QE for the official reason that the economy is tanking once more due to the inability to keep inflation steady above 1%, and certainly China, whose economy – driven by the housing market slide now in its 5th month and which has sent Y/Y prices negative for the first time since 2012 – keeps contracting, as confirmed overnight by the latest official PMI data from the National Bureau of Statistics. The Chinese data in a nutshell: overnight the official NBS PMI report indicted the October manufacturing PMI printed at a disappointing 50.8, below the 51.1 in September, and well below the consensus hopes for a rebound and uptick at 51.2.

Elections are not free.
• Ukraine Rebels Hold Russia-Backed Polls Condemned by UN (Bloomberg)
Russian-backed militias in eastern Ukraine are holding elections today in their self-proclaimed people’s republics in defiance of the United Nations and governments from Kiev to Washington. Voters in rebel-held territory in Donetsk and Luhansk will each select a head of government as well as a People’s Council, according to their websites. Voting was underway and was expected to end at 8 p.m. Both regions switched to Moscow time, one hour later than the rest of Ukraine, on Oct. 26. About 5.2 million people live in the conflict zones, according to the United Nations. Some 4.3 million and 2.2 million people, mainly Russian speakers, lived in Donetsk and Luhansk, respectively, before the uprising began. Seven months of fighting has displaced about 1 million people and claimed more than 4,000 lives, the UN says. Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon “deplores” the elections as a “breach of the constitution and national law,” according to the UN’s website. “These ‘elections’ will seriously undermine the Minsk protocol and memorandum, which need to be urgently implemented in full.”

Neither is gas.
• Gazprom To Resume Gas Supply Once Ukraine Pays $2.2 Billion (Reuters)
Russia could resume natural gas deliveries to Ukraine as soon as next week if Kiev pays $2.2 billion in debt and pre-payments, gas exporter Gazprom said on Friday, under a deal that also safeguards winter deliveries to Europe. Moscow, Kiev and the European Union reached an agreement on Thursday over the gas supplies despite tensions over a pro-Russian separatist rebellion in east Ukraine. Gazprom cut off Ukraine in June amid a bitter dispute over unpaid bills and pricing for the former Soviet republic, which is seeking closer ties with the West. Gazprom CEO Alexei Miller said Gazprom would restart the flow of gas within two days of Kiev covering part of its debt and pre-paying for deliveries in November. “Everything depends on when Ukraine makes this payment. We understand this can happen by the end of next week,” Miller told Russian state TV broadcaster Rossiya 24.
The Kremlin on Friday welcomed the deal as “an important step in the context of ensuring further uninterrupted gas transit to Europe”. The EU receives about a third of its gas from Russia and about half of that is piped across Ukraine. Speaking in Kiev, Ukraine Prime Minister Arseny Yatseniuk said he was determined to ensure safe transit to the EU, a crucial partner for Kiev in dealing with Russia over the rebellion in the east and a creditor of Ukraine’s bankrupt economy. “Ukraine will safeguard the transit and … won’t give Russia a chance to blackmail Ukraine and Europe,” Yatseniuk said. Thursday’s agreement covers November through next March and calls for Ukraine to pay $1.45 billion. Miller put the pre-payment portion of that at $760 million. Kiev must also pay off $3.1 billion for past deliveries by the end of the year, or supplies will cease from 2015, according to the protocol from Thursday’s talks in Brussels published by the Ukrainian government on Friday.

It’s the Ukraine that keeps shelling. At least until there’s so much snow and ice no-one can figure out what happened to MH-17. A bitter winter awaits Donetsk and Luhansk.
• Ukraine Fighting Flares After Gas Deal as Winter Nears (Bloomberg)
Fighting flared in Ukraine’s easternmost regions hours after the conclusion of a natural gas deal with Russia, highlighting the challenges in reaching peace as the Red Cross warned about winter’s onset. Ukrainian President Petro Poroshenko called on his parliamentary party yesterday to support Arseniy Yatsenyuk as prime minister, saying the country needs to be united “as never before” following Oct. 26 elections. “Despite the cease-fire in eastern Ukraine, acts of indiscriminate shelling and security incidents continue to put civilians at risk,” the International Committee of the Red Cross said in a statement. “The approaching winter makes the situation of both residents and displaced people even more difficult.” While the pact brokered by the European Union on Oct. 30 is designed to keep homes warm through the winter, rebels still hold large chunks of Ukraine’s east and are planning a controversial election tomorrow. Crimea remains under Russian control and the Kremlin, bristling at an EU accord Ukraine signed, is testing NATO with daily airspace violations.








