NPC “Georgetown-Marines game” 1923

It’s nice to be able to agree with Ambrose once in a while.
• Dollar Hegemony Endures As Share Of Global Transactions Keeps Rising (AEP)
The US dollar is tightening its grip on the global financial system at the expense of the euro, entrenching American hegemony and rendering the US Federal Reserve more powerful than at any time in history. Newly-released data from the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) show that the dollar’s share of the $5.1 trillion in foreign exchange trades each day has continued rising to 87.6pc of all transactions. It is the latest evidence confirming the extraordinary resilience of the dollar-based international order, confounding expectations of US financial decline a decade ago. Roughly 60pc of the global economy is either in the dollar zone or closely tied to it through currency pegs or ‘dirty floats’, and the level of debt issued in dollars outside US jurisdiction has soared to $9 trillion.
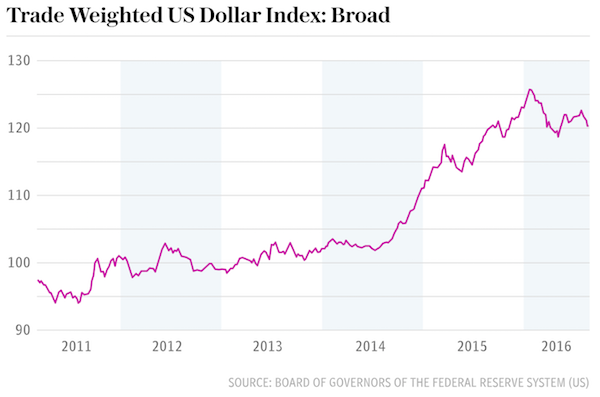
This has profound implications for monetary policy. The Fed has become the world’s central bank whether it likes it or not, setting borrowing costs for much of the global system. The BIS data shows that the volume of transactions in which the euro was on one side of the trade has slipped to 31.3pc from 37pc in 2007. The dollar share has ratcheted up to 87.6pc over the same period. It is much the same picture for the foreign exchange reserves of central banks, a good barometer of global trust. The dollar share has recovered to 63.6pc, roughly where it was a decade ago. The euro share has tumbled over the last eight years from 28pc to 20.4pc, and is barely above Deutsche Mark share in the early 1990s.
“There are no foreseeable rivals to the dollar as a viable reserve currency,” said Eswar Prasad from Cornell University, author of “The Dollar Trap: How the US Dollar Tightened Its Grip on Global Finance”. “The US is hard to beat. The US has deep financial markets, a powerful central bank and legal framework the rest of the world has a great deal of trust in,” he said. The eurozone is crippled by the lack of a unified EU treasury, joint bond issuance, and a genuine banking union to back up the currency. It would require a change in the German constitution to open the way for fiscal union, an unthinkable prospect in the current political climate.

Many years ago I dubbed it the ‘Bulgaria Model’.
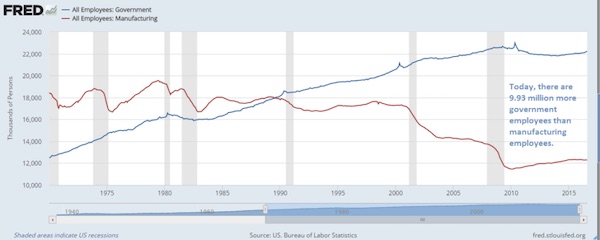
• US Has 9.93 Million More Government Workers Than Manufacturing Workers (CI)
The August jobs report was filled with some interest factoids, like there are now 9.93 million government workers than there are manufacturing workers. That is a ratio of 1.81 government workers for every manufacturing worker. Such was not always the case. But a variety of factors such as labor cost differentials, EPA regulations and taxes had led to manufacturing jobs to be sent overseas. Now a 1.81 government to manufacturing employment ratio is called OVERHEAD. And you wonder why high paying manufacturing jobs are fleeing to other countries?

“German saving and Greek suffering are two sides of the same coin..”
• German Budget Surpluses Are Bad For The Global Economy (Economist)
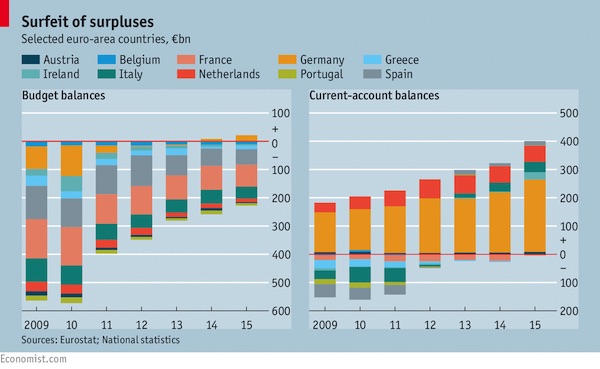
On August 24th Germans received news to warm any Teutonic heart. Figures revealed a larger-than-expected budget surplus in the first half of 2016, and put Germany on track for its third year in a row in the black. To many such excess seems harmless enough—admirable even. Were Greece half as fiscally responsible as Germany, it might not be facing its eighth year of economic contraction in a decade. Yet German saving and Greek suffering are two sides of the same coin. Seemingly prudent budgeting in economies like Germany’s produce dangerous strains globally. The pressure may yet be the undoing of the euro area. German frugality and economic woes elsewhere are linked through global trade and capital flows.
In recent years, as Germany’s budget balance flipped from red to black, its current-account surplus—which reflects net cross-border flows of goods, services and investment—has soared, to nearly 9% of German GDP this year. The connection between budgets and current accounts might not be immediately obvious. But in a series of papers published in 2011 IMF economists found evidence that cutting budget deficits is associated with reduced investment, greater saving and a shift in the current account from deficit toward surplus. Two IMF economists, John Bluedorn and Daniel Leigh, reckoned that a fiscal consolidation of one percentage point of GDP led to an improvement in the ratio of the current-account balance to GDP of 0.6 percentage points.
On that reckoning, the German government’s thriftiness accounts for a small but meaningful share of its growing current-account surplus; perhaps as much as three percentage points of GDP over the past five years.
That has helped to resurrect an old problem. Global imbalances were a scourge of the world economy before the financial crisis of 2007-08. Back then, China and oil-exporting economies accounted for the surplus side of the world’s trade ledger, which reached nearly 3% of the world’s GDP on the eve of the crisis. Other countries, notably America, ran correspondingly large current-account deficits, financed in part by flows of investment from surplus countries that flooded into the country’s overheating housing market. A similar dynamic played out in miniature within the euro area, as core economies like Germany ran current-account surpluses and peripheral countries like Spain ran deficits.

Taking away their powers is the only solution. But … that’s not going to happen.
• ECB’s Mersch: Central Banking Based On “Mathematical Models”, Not Reality (ZH)
At first (literally the day the Fed announced QE1) it was just “tinfoil fringe blogs” who predicted the failure of the central bank’s attempt to boost the economy by printing money, instead warning that all the Fed would do is unleash an unprecedented income and wealth divide that may culminate in civil war and hyperinflation. Then, gradually, analysts, pundits and even the mainstream press admitted the truth, i.e., that tin-foilers were right all along, until recently even the Fed’s own mouthpiece, Jon Hilsenrath, one day before the Jackson Hole meeting wrote that “Years of Fed Missteps Fueled Disillusion With the Economy and Washington”, an article which set the stage for the pivot to the US issuance of much more debt, because apparently $9 trillion in new debt under Obama is not considered enough “fiscal stimulus.”
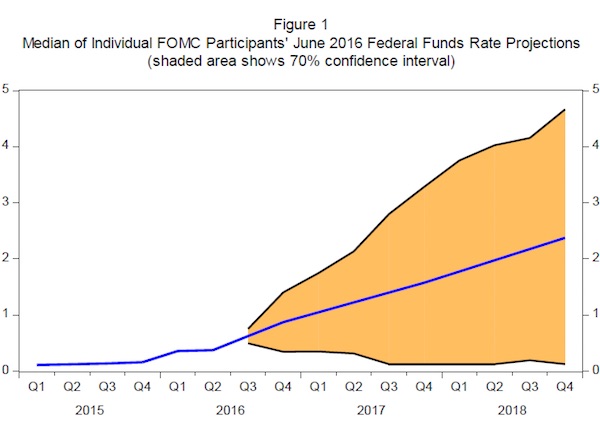
However, with virtually everyone else now slamming central banks for fooling the world for the past 7 years that they knew what they were doing, now that even Yellen admitted she has no idea what will happen in just the next 3 years projecting a 70% confidence interval of the Fed Funds rate of between 0% and 5% by the end of 2018 (we wonder what a 100% confidence would look like)…
.. overnight central bankers themselves attacked central bank policies, when ECB board member Yves Mersch warned on Saturday against using “extreme [policy] measures [with] unacceptable side effects” to shore up the eurozone’s weak economy, which he said could undermine trust in the single currency, a warning aimed squarely at Mario Draghi. Mersch’s comments come amid a growing debate over whether central banks in Europe and Japan should bolster economic growth by turning to even more tools such as “helicopter money.” Even more ludicrous, as we reported yesterday, Reuters already lobbed a tentative trial balloon, hinting that the ECB may be “forced” to buy ETFs and equities having virtually run out of bonds to monetize. Still, despite all ongoing ECB deflationary counter-measures, eurozone inflation was just 0.2% in August, far below the ECB’s near-2% target. Investors are increasingly concerned that the central bank is running out of tools.
Surprisingly, at this point Mersch joined the Weidmann bandwagon, and cautioned against “academic proposals [that] seem to prefer sophisticated models to social psychology.” Or in other words, for the first time, a central banker has suggested that broken (which is a far more accurate definition that sophisticated) financial models should be ignored when dealing with reality. “We cannot fulfill our mandate with mathematical equations, but only with instruments that maintain trust in the currency,” Mersch said at an annual economic forum on the shores of Lake Como, Italy. Expanding his tongue in cheek criticism of Mario Draghi’s relentless crusade to hurt the euro and reflate asset prices at all costs, Mersch then said that “extreme measures or legal violations of our mandate aren’t among those instruments.”

Restructure. Only way. And again, not going to happen.
• Europe’s Broken Banks Need the Urge to Merge (BBG)
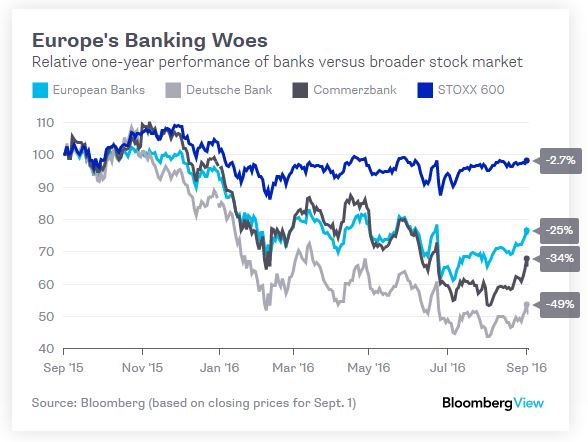
The recent flurry of excitement at the idea that Germany’s Deutsche Bank and Commerzbank contemplated a merger reinforces the view that the European finance industry is ripe for consolidation. Banking leaders themselves talk about the need for mergers in an overbanked market, but no one among the bigger banks seems to want to go first. If something doesn’t change soon, Europe won’t have a banking industry worthy of the name. The relentless collapse in bank share prices this year may speak to difficult market conditions, but they also suggest that Europe’s banking model is broken, amid a deadly combination of negative interest rates, anemic economic growth and a lack of clarity about the future regulatory outlook (albeit in large part because European banks have fought every line of every proposed rule change).
The region’s banks have lost almost a quarter of their value this year, according to the Stoxx 600 Banks index. As Germany has by far the least consolidated banking sector in the euro zone, it’s no surprise that both Commerzbank and Deutsche Bank have done even worse. Merger talk sparked a bit of a rally in the two German banks in recent days, even though the discussions, reported to have taken place over two weeks this summer, have been abandoned. With both banks embarking on major cost-cutting and restructuring projects, it may have been too early to talk of a merger.

It’s all in the choice of terminology: populism, protectionism, they sound very negative, so they are what you read. But it makes no difference: without growth, centralization withers away all by itself.
• Economic Czars Warn G-20 of Risk From Populist Backlash on Trade (BBG)
The heads of three world economic bodies warned of the risk to trade from the protectionist headwinds sweeping many developed nations as global leaders met in Hangzhou, China. In a panel session Saturday ahead of the Group of 20 summit, Christine Lagarde, Managing Director of the IMF, urged business chiefs to lobby governments to help keep trade flows up as she issued a warning about the outlook for growth into 2017. Her views were echoed by Roberto Azevedo, Director-General of the WTO. “Trade is way too low and has been way too low for a long time,” Lagarde said. “There is at the moment an undercurrent of anti-trade movement. It’s at the political level. It’s at the public opinion level” and also being reflected in policy, she added.
“If there is no international trade, if there is no cross-border investment, if services, capital, people and goods do not cross borders, then it’s less activity for you, it’s less jobs in whichever country you are headquartered,” she said. Lagarde’s comments come as momentum for ratifying the U.S.-led Trans-Pacific Partnership, which would link 12 nations making up about 40% of the world economy, falters in the final months of U.S. President Barack Obama’s term. Both presidential candidates have spoken against the deal, which does not include China, while progress on a U.S.-EU trade and investment deal, known as TTIP, has also stalled.
France’s trade minister Matthias Fekl said late last month that the U.S. hasn’t offered anything substantial in negotiations with the EU on the free-trade deal and that talks should come to an end. His comments followed those of German Economy Minister Sigmar Gabriel, who said discussions on the TTIP “have de-facto broken down, even if no one wants to say so.” Many Western nations are grappling with a mood of protectionism that is leading to calls for caution on free trade, and on foreign investment in things like property and utilities. Chinese companies recently were dealt a blow on prospective projects in both the U.K. and Australia.

Let’s see: more debt AND more cars. It’s a win-win! Happy days!
• Chinese Consumers Take Credit For Boom In Car Loans (R.)
Chinese households, traditional savers with an aversion to debt, are rapidly warming to the idea of borrowing to buy a car, as automakers push financing deals to boost sales and margins in an increasingly competitive market. Nearly 30% of Chinese car buyers bought on credit last year, up from 18% in 2013, according to analysts from Sanford C. Bernstein and Deloitte, helping a rebound in the car market after a sticky 2015. That is welcome news to China’s government, which wants consumers to borrow and spend more to shift its slowing economy away from heavy industry and investment-led growth. Beijing resident Wang Danian said he planned to buy his first car on credit, saying it was the smart move.
“I can use my cash to do other things,” the 28-year-old said. “If I use all my savings at once to buy a car, and then something happens, I can’t manage the risk.” Six consumers interviewed by Reuters said they would all consider loans, lured by low-fee and interest-free deals, with half saying they’d prefer to buy on credit and save cash for other items. “I’d estimate after the manufacturer came out with the low-interest deal that about 30% of potential cash buyers switched to buying on credit,” said a salesman at a Volkswagen dealership in eastern China’s Jiangsu province who gave his name as Mr. Zhao. That is still a far cry from the more than 80% of cars bought on loans in the United States, but Deloitte predicts China will reach 50% by 2020.
[..] China’s auto market struggled last year thanks to the slowest economic growth in 25 years and a stock market rout, but rebounded in October when the government cut sales tax on smaller cars. By July, vehicle sales were rising at their fastest monthly rate in three and a half years. “While the government’s tax reduction was the most obvious explanation for the rebound in Chinese car sales at the end of 2015, soaring auto financing penetration represented another, lesser noticed, driver of the boom,” Bernstein said in April.

Excellent thread from The Property Pin. A lot more under the link.
• 6 Steps To Avoiding All EU (Incl. Irish) And US Taxes Via Ireland (PP)
1. Making the Intellectual Property (IP). Let’s say that Apple US spent $200m (validly) developing iOS (it’s iPhone operating system). What Apple does next is to “sell” a non-US version of iOS to an Apple Ireland entity (generic name), for c $500m. Apple US will then pay full US taxes on this gain of $300m. Easy so far. The US IRS is already starting to probe these “internal” sales.
2. Stepping up the IP value (when the “magic” happens). Specialist IP corporate finances (why Dublin accountancy firms have big corporate finance practices) make two discoveries. First, if the Apple device has no iOS software, it can’t function. iOS is the “secret sauce” (like a drug patent). They then show Apple Ireland that it has done an amazing deal at the expense of its parent, Apple US. They show that if the non-US version of iOS is converted in to 200 different languages (and local network formats), then Apple Ireland can sell devices all over the world (fancy that). The global commercial value is over €50bn (why many MNC jobs in Ireland are “localisation”, or language translation, jobs). Apple has the tax equivalent of “Alchemy”.
3. Avoiding tax on the IP step-up. A €50bn gain in Apple Ireland is going to incur tax (both Irish and US), and would distort Ireland’s National Accounts (our 2014 GDP was only €200bn). Apple, and the Irish State, worked a scheme to have Apple Ireland both resident in Ireland (essential so Apple Ireland can avail of EU TP (Transfer Pricing) rules; you can’t do EU TP from Cayman, or worse, “Stateless” locations), and non-resident in Ireland (to avoid Irish tax). The EU’s Apple report, proves the recent 26% increase in Irish GDP (“leprechaun economics”) was all Apple, forced to unwind it’s “dual” status (as EU report drew near). Apple paid a once-off tax on the transfer (€500m vs. €50bn gain), which increased our EU GDP levies by 380m. Per Annum.
4. Executing the TP of this IP into Europe. Before step 3., if Apple Ireland sold an iPhone in Germany for €500, Apple Germany would offset valid incurred cash costs (Apple China/Foxconn manufacturing costs of about €150, and Apple Germany marketing costs of about €50) giving a German profit of €300 on that iPhone. German Revenue would take €100 of this in German taxes, and €200 can go back to Ireland. EU TP rules allow EU resident companies, like Apple Ireland, to charge Apple Germany a share of their €50bn IP value, expressed as a royalty charge. Charging this royalty to Apple Germany wipes out all Apple’s German profits. Apple Germany pays no German taxes, and the full €300 goes back to Apple Ireland tax-free.
5. The Cherry on Top. EU challenged step 4. in 2011 (we will get to CCCTB), but the UK Veto stopped it (Osborne was turning Britain into an even bigger EU tax-haven than Ireland). Despite Ireland having the “golden ticket” of being INSIDE the EU’s TP system (why Apple Ireland had to be legally resident in Ireland), AND having the lowest EU corporate tax rate, that was not enough. In 2010, Apple Ireland’s tax rate collapsed from a tiny 0.5% to effectively 0%. Apple Ireland’s profits quadrupled (and doubled every year after). The Irish State had perfected a “straw” for Apple, stuck into the EU, allowing Apple to suck all its EU profits (Germany, France, Italy etc.), via Ireland, to offshore locations, free of EU, Irish and US taxes.
6. Locking it in. US tax law requires US MNCs to remit non-US profits back to the US for final taxing. US tax rate is high at 35% (even by EU standards). The Double Tax Treaty system allows the MNCs to get a credit for taxes paid in the countries in which the profits were made. If Apple pays 35% on German profits, no further US taxes apply. The US IRS allows MNCs to leave non-US profits outside of the US if these non-US profits are going to be re-invested in the non-US location. Apple claimed this right in their US 10K Returns (Margrethe showed how Apple violate this). That is how Apple built the largest offshore cash hoard of modern economic history. Profits from the EU, on which they have never paid EU, Irish or US taxes. Period.

In France, as in UK and US and many other places, voters vote against someone, not for.
• Rural France Pledges To Vote For Marine Le Pen As Next President (G.)
In the picturesque hamlet of Brachay, in scorching late summer heat, Marine Le Pen was preaching to the politically converted. “Marine, président”, they chanted. “On va gagner” (we’re going to win). A banner stretching the length of one of the stone buildings overlooking the village square read: “Marine: Save France.” Le Pen’s stump speech was the most closely watched and significant campaign launch of la rentrée, the national return to work after the long summer holidays, and the leader of France’s far-right Front National was welcomed like a conquering hero. Le Pen has been largely absent from the political scene for several weeks and has refrained from adding her 10 cents’ worth to the raging polemic over the burkini and rows about security following deadly attacks by Islamic fundamentalists, both fertile ground for her party.
In the meantime, the country’s governing Socialists and centre-right opposition Les Républicains have engaged in what one FN heavyweight described with schadenfreude as a “bloodbath, left and right”. The Parti Socialiste is bitterly split and in turmoil over whether François Hollande, with his calamitous popularity ratings will, or indeed should, stand for a second term. The alternative, to stand down, would be unprecedented for a serving leader. Emmanuel Macron, the finance minister who resigned last week, might be the rabbit that the party pulls out of the hat, but he is disliked by the PS’s leftwing, which is fielding its own candidates. In any case, Macron has not said whether he will even throw his hat into the presidential ring.
On the right, things are scarcely more harmonious. The deadline for Les Républicains candidates is Friday, and already former president Nicolas Sarkozy, mayor of Bordeaux Alain Juppé and former prime minister François Fillon have either announced they are standing or are expected to do so. Amid this political free-for-all, Le Pen is trying to throw off the party’s divisive reputation and market herself as a politician above and beyond the fray of the same-old-same-old French elite: a new, unifying, patriotic force who will break the shackles of Europe, end “mass immigration” and give France back to the French. Her slogan is La France apaisée – a soothed France.

So if people have to spend more to buy the same stuff, that’s good for the economy, right?
• Shops Set For Christmas Price Hikes As Millions Of Shipments Stranded (Ind.)
Summer is not yet over but Christmas could be about to get more expensive as millions of gifts including TVs and electrical gadgets could be stranded at sea for months. Retailers have been thrown into turmoil after one of the world’s largest shipping companies collapsed into bankruptcy. South Korean company Hanjin’s vessels have been seized at Chinese ports, while others have been banned from docking until unpaid fees are received. As a result, the cost of transporting goods from Asia to the US and Europe has jumped by more than half, threatening margins as retailers begin stocking up for Christmas. September marks the start of the busiest period of the year for transporting goods.
The US National Retail Federation, the world’s largest retail trade association, wrote to Penny Pritzker, secretary of commerce, on Thursday, urging them to work with the South Korean government, ports and others to prevent disruptions. The bankruptcy is having “a ripple effect throughout the global supply chain” that could cause significant harm to both consumers and the economy, the association wrote. “Retailers’ main concern is that there (are) millions of dollars’ worth of merchandise that needs to be on store shelves that could be impacted by this,” said Jonathan Gold, the group’s vice president for supply chain and customs policy.
“Some of it is sitting in Asia waiting to be loaded on ships, some is already aboard ships out on the ocean and some is sitting on US docks waiting to be picked up. It is understandable that port terminal operators, railroads, trucking companies and others don’t want to do work for Hanjin if they are concerned they won’t get paid.” With an estimated half a million 40-foot containers full of goods stuck at sea or in ports there appears to be little hope of a quick resolution to the issue. September marks the start of the busiest time of the year for transporting goods, but a Korean court on Thursday set a deadline of 25 November to submit a plan to resolve the dispute.

Hilarious!
• Row On Tarmac An Awkward G20 Start For US, China (R.)
A Chinese official confronted U.S. President Barack Obama’s national security adviser on the tarmac on Saturday prompting the Secret Service to intervene, an unusual altercation as China implements strict controls ahead of a big summit. The stakes are high for China to pull off a trouble-free G20 summit of the world’s top economies, its highest profile event of the year, as it looks to cement its global standing and avoid acrimony over a long list of tensions with Washington. Shortly after Obama’s plane landed in the eastern city of Hangzhou, a Chinese official attempted to prevent his national security adviser Susan Rice from walking to the motorcade as she crossed a media rope line, speaking angrily to her before a Secret Service agent stepped between the two.
Rice responded but her comments were inaudible to reporters standing underneath the wing of Air Force One. It was unclear if the official, whose name was not immediately clear, knew that Rice was a senior official and not a reporter. The same official shouted at a White House press aide who was instructing foreign reporters on where to stand as they recorded Obama disembarking from the plane. “This is our country. This is our airport,” the official said in English, pointing and speaking angrily with the aide. The U.S. aide insisted that the journalists be allowed to stand behind a rope line, and they were able to record the interaction and Obama’s arrival uninterrupted, typical practice for U.S. press traveling with the president.

“.. the leader of the world’s largest economy, who is on his final tour of Asia, was forced to disembark from Air Force One through a little-used exit in the plane’s belly..”
• Barack Obama ‘Deliberately Snubbed’ By Chinese In Chaotic Arrival At G20 (G.)
China’s leaders have been accused of delivering a calculated diplomatic snub to Barack Obama after the US president was not provided with a staircase to leave his plane during his chaotic arrival in Hangzhou ahead of the start of the G20. Chinese authorities have rolled out the red carpet for leaders including India’s prime pinister Narendra Modi, Russian president Vladimir Putin, South Korean president Park Geun-hye, Brazil’s president Michel Temer and British prime minister Theresa May, who touched down on Sunday morning. But the leader of the world’s largest economy, who is on his final tour of Asia, was forced to disembark from Air Force One through a little-used exit in the plane’s belly after no rolling staircase was provided when he landed in the eastern Chinese city on Saturday afternoon.
When Obama did find his way onto a red carpet on the tarmac below there were heated altercations between US and Chinese officials, with one Chinese official caught on video shouting: “This is our country! This is our airport!” “The reception that President Obama and his staff got when they arrived here Saturday afternoon was bruising, even by Chinese standards,” the New York Times reported. Jorge Guajardo, Mexico’s former ambassador to China, said he was convinced Obama’s treatment was part of a calculated snub. “These things do not happen by mistake. Not with the Chinese,” Guajardo, who hosted presidents Enrique Peña Nieto and Felipe Calderón during his time in Beijing, told the Guardian.
“I’ve dealt with the Chinese for six years. I’ve done these visits. I took Xi Jinping to Mexico. I received two Mexican presidents in China. I know exactly how these things get worked out. It’s down to the last detail in everything. It’s not a mistake. It’s not.” Guajardo added: “It’s a snub. It’s a way of saying: ‘You know, you’re not that special to us.’ It’s part of the new Chinese arrogance. It’s part of stirring up Chinese nationalism. It’s part of saying: ‘China stands up to the superpower.’ It’s part of saying: ‘And by the way, you’re just someone else to us.’ It works very well with the local audience. “Why [did it happen]?” the former diplomat, who was ambassador from 2007 until 2013, added. “I guess it is part of Xi Jinping playing the nationalist card. That’s my guess.”

I am not optimistic.
• Half The Forms Of Life On Earth Will Be Gone By 2050 (ZH)
Humanity should start saving nature and switch to 80% renewables by 2030, otherwise the Earth will keep losing species, and within 33 years around 800,000 forms of life will be gone, conservation biologist Reese Halter told RT’s News with Ed. Humans have changed the Earth so much that some scientists think we have entered a new geological age. According to a report in the Science Magazine, the Earth is now in the anthropocene epoch. Millions of years from now our impact on Earth will be found in rocks just like we see fossils of plants and animals which lived years ago – except this time scientists of the future will find radioactive elements from nuclear bombs and fossilized plastic.
RT: Tell us about this new age.
Reese Halter: Yes. There are three things that come to mind. First of all, imagine you’re back on the football field. Each year in America – America alone – we throw away the equivalent of one football field, a 100 miles deep. That is the first thing. The second thing, we’ve entered the age of climate instability. That means from burning subsidized climate altering fossil fuels our food security is in jeopardy. The third thing that is striking is we’re losing species a thousand times faster than in the last 65 million years. At this rate within 33 years, by midcentury – that means 800,000 forms of life, or half of everything we know will be gone. The only way we can reverse this is to two things: save nature now, our life support system, and we do this by switching to 80% renewables by 2030. It is a WWIII mentality. In America we have the technology; we have the blueprint. We lack the political will just right now. But in the next short while we will, because it is a matter of survival.RT: We’ve just gone through the hottest month on record. There is plenty of data out there to suggest that we truly are entering something our world has never seen in our lifetime. To brand it as a new geological age, what impact is that going to have? RH: It’s got the impact that humans are here. As I said earlier, we’re talking a 160% more than mother Earth can sustain 7.4 billion people. The way to do it is to pull it back to 90%. If we were a big bathtub the ring will read: toxicity, toxicity, toxicity. We’ve got to peal that back, because what we do to the Earth, we do to ourselves.