Marc Riboud Street seen from inside antique dealer’s shop, Beijing 1965

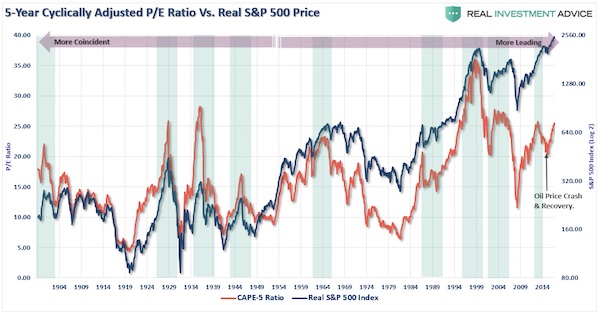
John Hussman correcting Buffett.
• US Equities “At Most Offensive Level Of Overvaluation In History” (BI)
Billionaire investor Warren Buffett made a lot of people feel better about historically stretched stock prices earlier this month. Speaking in an interview with CNBC on October 3, the chairman and CEO of Berkshire Hathaway said, “Valuations make sense with interest rates where they are.” The investment community breathed a sigh of relief. After all, Buffett is arguably the most successful stock investor in world history. An all-clear from him surely gives a green light for adding more equity exposure, right? Wrong, says John Hussman, the president of the Hussman Investment Trust and a former economics professor. In his mind, Buffett only gets half of the equation right. While Hussman acknowledges that low lending rates do, by nature, improve future cash flows, he argues that they must also be accompanied by strong growth — something that he notes the US is not currently enjoying.
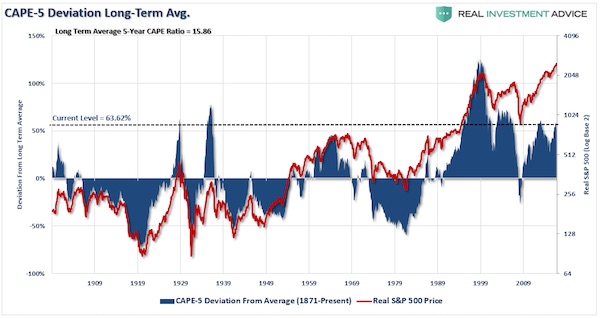
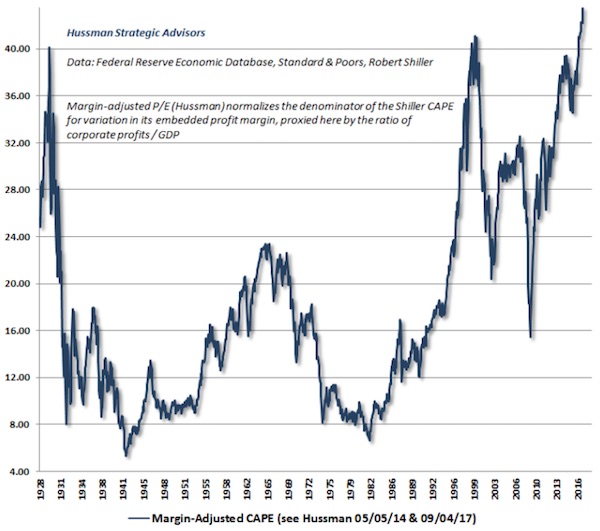
To Hussman, the simple idea that “lower interest rates justify higher valuations” is one that gives people false confidence. “It’s an incomplete sentence ,” Hussman wrote in a recent blog post. “Unfortunately, the convenience of investing-by-slogan, rather than carefully thinking about finance and examining evidence, is currently leading investors into what is likely to be one of the worst disasters in the history of the U.S. stock market.” Hussman calculates that stock valuations are stretched 175% above their historic norms, and predicts the S&P 500 will see negative total returns over the next 10 to 12 years. Along the way, the benchmark index will experience an interim loss of more than 60%, he estimates. As touched on above, at the core of Hussman’s bearish argument is a lack of economic growth. He specifically points to slowing expansion in the US labor force, as shown by this chart:
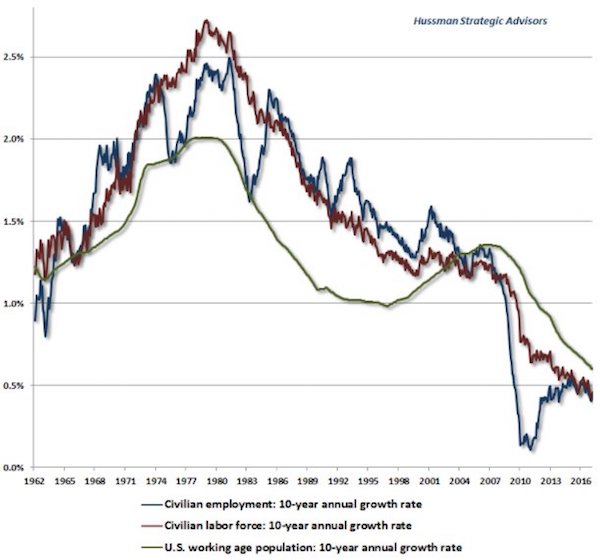
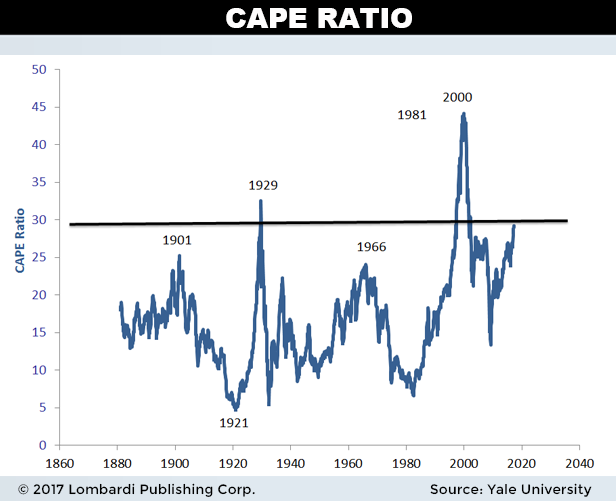
“Put simply, if interest rates are low because growth rates are also low, no valuation premium is ‘justified,'” Hussman wrote. “The long-term rate of return on the security will be low anyway without any valuation premium at all. This observation has enormous implications for current U.S. stock market prospects.” So where does that leave the market at this very moment? In the very near term, Hussman’s neutral, citing the continued speculative impulses of investors. Still, he stresses that traders should be hedging and using other safety nets to protect against potential downside, which he says could materialize quickly. To say he’s less than warm and fuzzy about the stock market is an understatement. And when discussing price levels, he doesn’t exactly pull any punches, saying US equities are now “at the most offensive level of overvaluation in history” — even worse than in 1929 and 2000.
Read more …

People like Yellen focus on one activity: explain away the consequences of their blindly taken actions. They grope in the dark.
• Yellen Doubles Down: “Valuations Are At High Levels Historically” (ZH)
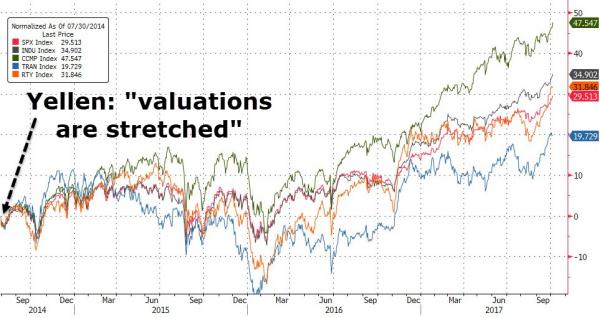
On the heels of San Franciso Fed Governor John Williams’ warning that The Fed “doesn’t want there to be excesses in financial markets… ” Janet Yellen has reiterated her concerns that markets are a bit toppy… Market valuations “are at high level in historical terms” when assessed on metrics akin to price-earnings ratios, warned Fed Chair Janet Yellen in response to a question on an IMF panel in Washington, but was careful to add that “overall financial stability risks in the U.S. remain moderate.” “Prospects for U.S. fiscal stimulus have buoyed sentiment but not yet had much impact on spending or investment,” she said. “Broader financial stability risks depend on more than just asset prices and it may also be important just why asset valuations are high. So one factor that clearly comes into play is an environment of low interest rates and central bankers like many market participants have been adjusting our notions of what” interest rates are likely to be in the longer term.
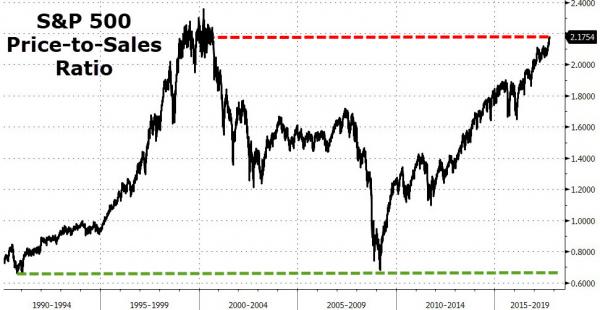
So – to sum up – The Fed doesn’t want excesses… Yellen thinks stock valuations are stretched… but don’t worry coz rates are low (although we are dedicated to raising them) and financial stability (despite record high corporate leverage and record low spreads) is not a problem. Well… The market has almost never been this expensive… As Peter Boockvar warns: “Almost there. S&P 500 price to sales ratio is just 4% from March 2000 peak.”
Additionally, Draghi and Kuroda were also said they saw little evidence of frothiness in markets. Others in Washington were less sanguine… The market “feels as benign in 2017 as it felt in 2006,” said Jes Staley, the chief executive of Barclays Plc, referencing the eve of the crisis. Yellen also added in a subtle jab at Trump that while prospects for U.S. fiscal stimulus have buoyed sentiment but not yet had much impact on spending or investment… “It is a source of uncertainty,” Yellen says of fiscal policy changes, “we’ve taken,” as many households have, “a kind of wait-and-see attitude.” Of course, The Fed head being worried about stock valuations is a nothing-burger for the mainstream. Since Janet Yellen’s first warning in July 2014: “Equity market valuations appear stretched”
Read more …

So there.
• Goldman Sachs: 88% Chance We’re Heading Into A Bear Market (BI)
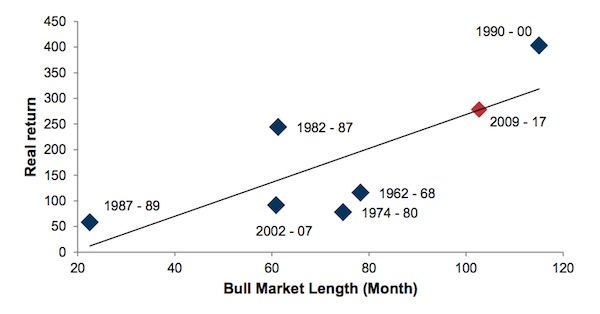
Goldman Sachs has circulated a fascinating but scary research note to clients suggesting that the probability of stocks entering a bear market in the next 24 months currently stands at about 88%, based on the history of previous bear markets. The note is titled “Bear Necessities. Should we worry now?” It is an exhaustive, 87-page dive through macroeconomic data and stock market activity going all the way back to the early 20th Century. It was written in September by London-based Chief Global Equity Strategist Peter Oppenheimer, and European strategists Sharon Bell and Lilia Iehle Peytavin. Most of their data focus on the US S&P 500 index of stocks – the largest and most-followed of the share indices globally. The S&P is currently the second largest and longest bull run in history.
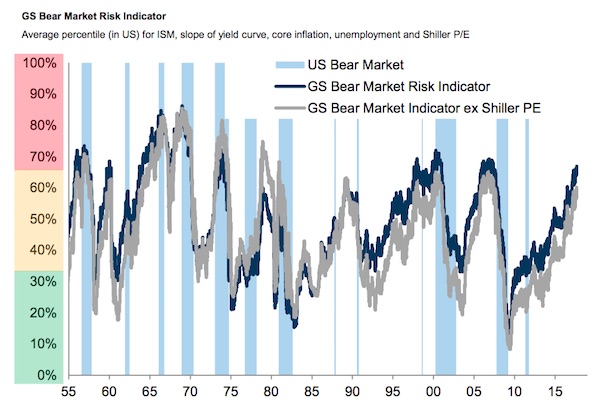
The index is also relatively expensive, the Goldman trio says. The aggregate valuation of the S&P 500 is now in its 88th percentile, as measured since 1976, according to Goldman’s calculations. The median stock is in the 99th percentile. The trio calculated a risk index based on the Shiller price-earnings ratio (the price of S&P 500 stocks divided by the average of 10 years of earnings, adjusted for inflation), the US ISM manufacturing index, unemployment (very low), the bond yield curve, and core inflation. The resultant “GS Bear Market Indicator” is currently flashing at 67%. The indicator typically hits highs right before a bear market in US stocks appears:
 Historically, when the indicator is at 67%, there is an 88% chance of stocks falling into a bear market in two years’ time, the Goldman analysts say:
Historically, when the indicator is at 67%, there is an 88% chance of stocks falling into a bear market in two years’ time, the Goldman analysts say:
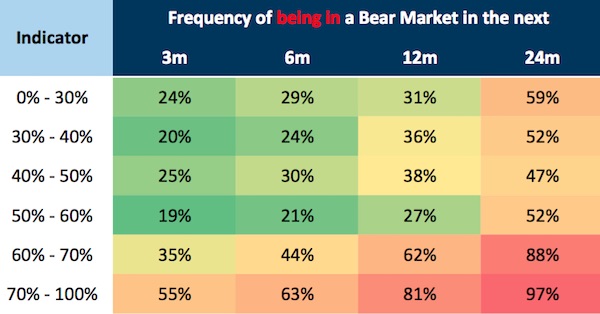
However, the chance of a bear growling into view in the near-term remains low — just 35%. Bear markets are triggered in three different ways, Oppenheimer et al argue: “Cyclical” bear markets are trigged by rising interest rates and recessions; “Event-driven” bears come from negative economic shocks like war or emerging market crises; “Structural” bears come from financial bubbles. Depending on your point of view, all three of those triggers are hovering on the horizon: The Fed and the Bank of England are both signalling interest rates will rise; US President Trump is threatening military action in North Korea; and plenty of people think the low-interest rate environment of the last 10 years has inflated asset bubbles in stocks, real estate and property in Europe, and private equity tech startup valuations.
Read more …

Those for whom this is a mystery are not fit for their jobs. If you export millions of jobs to Asia, take workers’ negotiating powers away and push them into crappy jobs with no benefits, only one outcome is possible.
• The Mystery Of Weak Wage Growth (BI)
Many economists say they can’t figure out why US wage growth remains so meager nine years into the economic expansion, especially given a decline in the unemployment rate to a historically low 4.4%. A new study from the IMF might help them out. It finds that shifts in the labor market toward less stable, temporary or contract jobs, including odd hours and often no health insurance, likely play a substantial role in preventing wages from rising. That’s because job uncertainty makes it harder for workers to bargain for higher wages, giving employers a strong upper hand in any salary negotiation. The trend is happening not just in the United States but also in other rich economies, the Fund says. “Labor market developments in advanced economies point to a possible disconnect between unemployment and wages,” IMF staffers write in their latest World Economic Outlook report.
“Subdued nominal wage growth has occurred in a context of a higher rate of involuntary part-time employment, an increased share of temporary employment contracts, and a reduction in hours per worker,” the report adds. That’s not the only factor. The Great Recession of 2007 to 2009, which was a global phenomenon, set labor markets back years, and suppressed wages sharply as unemployment surged, peaking at 10% in the United States. The IMF suggests the policy reaction to that global downturn was underwhelming, particularly when it came to fiscal policies, which were restrictive both in the United States and Europe.
“Whereas in many economies headline unemployment is approaching ratios seen before the Great Recession, or has even dipped below those levels, nominal wage growth rates continue to grow at a distinctly slower pace,” the Fund said. “For some economies, this may reflect policy measures to slow wage growth and improve competitiveness in the aftermath of the global financial crisis and euro area sovereign debt crisis.” [..] “To the extent that declining unemployment rates partly reflect workers forced into part-time jobs, increases in such types of employment may overstate the tightening of the labor market,” the IMF said.
Read more …

It’s all for the Party Congress: close industries so air is cleaner, and let scarcity push producer prices higher. But wait till consumers feel those higher prices. It’s just, that is AFTER the Congress.
• China Factory Prices Jump As Government Reduces Capacity (BBG)
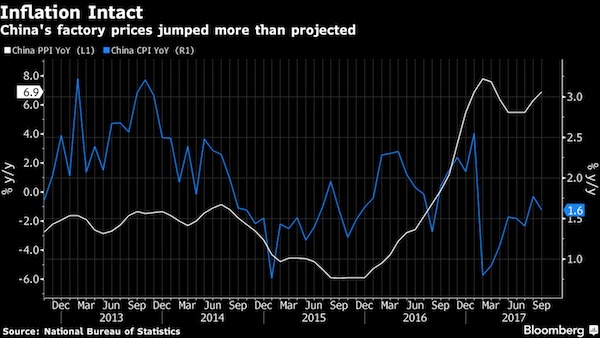
China’s factory prices jumped more than estimated, as domestic demand remained resilient and the government continued to reduce excess industrial capacity. Consumer price gains matched projections. • The producer price index rose 6.9% in September from a year earlier. • The manufacturing PPI sub-index climbed 7.3%, the most in nine years • The consumer price index climbed 1.6%, versus a prior reading of 1.8%, the statistics bureau said Monday. Aggressive cuts to capacity in industries like steel and cement, coupled with resilient demand, have contributed to factory inflation that’s lasted longer than economists expected. The drive to cut pollution and boost firms’ efficiency will probably continue as the Communist Party begins its 19th Congress this week.
“The economy has pretty strong momentum now, monetary policy remained loose ahead of the 19th Party Congress, and the environmental cleanup has cut the supply of commodities,” said Shen Jianguang, chief Asia economist at Mizuho in Hong Kong and the lone forecaster in Bloomberg’s survey to correctly predict the PPI reading. “But this is not sustainable. Deleveraging will be moving up on the agenda after the congress.” “Strong PPI shows that economic momentum is pretty robust in the second half,” said Liu Xuezhi, an analyst at Bank of Communications in Shanghai. “It was widely expected that factory-gate inflation could slow in the second half, but apparently it’s still quite resilient, which may lead to a more positive outlook.”
“China’s manufacturing industry, upstream in particular, continues to see decent demand,” said Raymond Yeung, chief Greater China economist at Australia & New Zealand Banking in Hong Kong. “This PPI figure foretells a decent growth number to be out later this week. We see GDP of 6.8% at the moment but should be prepared for an upside risk.”
Read more …

I don’t normally post 3-week-old articles, but this one (h/t Tyler) is just too good. The Chinese never borrowed much, but now they borrow more than anyone. Scary: “..a person without a flat has no future in Shenzhen.” It’ll keep the economy going until it doesn’t.
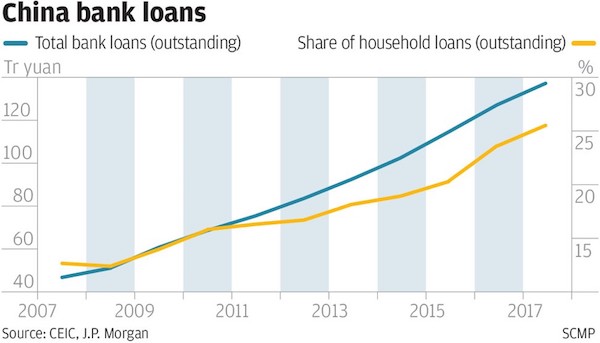
• China’s Mortgage Debt Bubble Raises Spectre Of 2007 US Crisis (SCMP)
Young Chinese like Eli Mai, a sales manager in Guangzhou, and Wendy Wang, an executive in Shenzhen, are borrowing as much money as possible to buy boomtown flats even though they cannot afford the repayments. Behind the dream of property ownership they share with many like-minded friends lies an uninterrupted housing price rally in major Chinese cities that dates back to former premier Zhu Rongji’s privatisation of urban housing in the late 1990s. Rapid urbanisation, combined with unprecedented monetary easing in the past decade, has resulted in runaway property inflation in cities like Shenzhen, where home prices in many projects have doubled or even tripled in the past two years. City residents in their 20s and 30s view property as a one-way bet because they’ve never known prices to drop.
At the same time, property inflation has seen the real purchasing power of their money rapidly diminish. “Almost all my friends born since the 1980s and 1990s are racing to buy homes, while those who already have one are planning to buy a second,” Mai, 33, said. “Very few can be at ease when seeing rents and home prices rise so strongly, and they will continue to rise in a scary way.” The rush of millions young middle-class Chinese like Mai into the property market has created a hysteria that eerily resembles the housing crisis that struck the United States a decade ago. Thanks to the easy credit that has spurred the housing boom, many young Chinese have abandoned the frugal traditions of earlier generations and now lead a lifestyle beyond their financial means.
The build-up of household and other debt in China has also sparked widespread concern about the health of the world’s second largest economy. The Chinese leadership headed by President Xi Jinping has taken a note of the problem and launched an unprecedented campaign in the second half of last year to curb home price rises in major cities by raising down payment requirements, disqualifying some buyers and squeezing the bank credit available for home buyers. The campaign is still deepening, with five more cities introducing rules last weekend that will freeze some property deals.
[..] Government policies are also protecting the interests of homeowners. City governments have squeezed land supply to keep land prices high and made secondary market trading less attractive, with new home buyers left to compete for a few new developments. Meanwhile, there is no property tax, which encourages homeowners to hold on to appreciating property assets. The result has been skyrocketing housing prices in Shenzhen, Beijing and Shanghai, where property prices can match those in Hong Kong or London. The lesson was that “if you don’t buy a flat today, you will never be able to afford it”, Wang, 29, said. [..] “The debts are huge to me,” Wang said. “But a person without a flat has no future in Shenzhen.”
Read more …

Half of one banker’s loan books are interest-only. Most are 40%. That is an insane amount of principal that is not being paid off.
• Interest-only Loans Are A Huge Problem For The Australian Economy (Holden)
I’m not normally a fan of parliament hauling private sector executives before them and asking thorny questions. But when the Australian House of Representatives did so this week with the big banks it was both useful and instructive. And, to be perfectly frank, terrifying. Let’s start with Westpac CEO Brian Hartzer. First, he confirmed the little-known but startling fact that half of his A$400 billion home loan book consists of interest-only mortgages. Yep, half. Of A$400 billion. At one bank. Oh, and ANZ, CBA and NAB are all nearly at 40% interest-only. Hartzer went on to make the banal statement: “we don’t lend to people who can’t pay it back. It doesn’t make sense for us to do so.” So did it make sense for all those American mortgage lenders to lend to people on adjustable rates, teaser rates, low-doc loans, no-doc loans etc. before the global financial crisis?
Of course not. The point is that banks are not some benevolent, unitary actor taking care of their own money. There are top managers like Harzter acting on behalf of shareholders. Those top managers delegate authority to lower-level managers, who are given incentives to write lots of mortgages. And, as we know, the incentives of those who make the loans are not necessarily aligned with those of the shareholders. Those folks may well want to make loans to people who can’t pay them back as long as they get a big payday in the short term. ANZ CEO Shayne Elliot repeated Hartzer’s mantra, saying: “It’s not in our interest to lend money to people who can’t afford to repay.” Recall, this is the man who on ABC’s Four Corners said that home loans weren’t risky because they were all uncorrelated risks (the chances that one loan defaults does not affect the chances of others defaulting).
That is a comment that is either staggeringly stupid or completely disingenuous. Messers Harzter and Elliot must take us all for suckers. They have made a huge amount of interest-only loans, at historically low interest rates, to buyers in a frothy housing market, who spend a large chunk of their income on interest payments. This certainly looks troubling. It may not be US sub-prime, but it could be ugly. Very ugly. To put it in context, there appears to be in the neighbourhood of A$1 trillion of interest-only loans on the books of Australian banks. I say “appears to be” because reporting requirements are so lax it’s hard to know for sure, except when CEOs cough up the ball, like this week. The big lesson of the US mortgage meltdown is that the risks on these mortgages are all correlated. If a few people aren’t paying back an interest-only loan, that is a fair predictor that others won’t pay back their loans either.
Read more …

From a “gated” Ambrose Evans-Pritchard article. Troubles grow fast.
• Revised Figures Reveal UK Is £490 Billion Poorer Than Previously Thought (FL)
“Global banks and international bond strategists have been left stunned by revised ONS figures showing that Britain is £490bn poorer than had been assumed and no longer has any reserve of net foreign assets, depriving the country of its safety margin as Brexit talks reach a crucial juncture. A massive write-down in the UK balance of payments data shows that Britain’s stock of wealth – the net international investment position – has collapsed from a surplus of £469bn to a net deficit of £22bn. This transforms the outlook for sterling and the gilts markets. “Half a trillion pounds has gone missing. This is equivalent to 25pc of GDP,” said Mark Capleton, UK rates strategist at Bank of America. Making matters worse, foreign direct investment (FDI) by companies is plummeting. It fell from a £120bn surplus in the first half 2016 to a £25bn deficit over the same period of this year.”
The news comes on top of the OBR confessing to a miscalculation of their own last week in UK productivity potential. Not good news for the UK or pound so let’s see if it plays out as the session progresses.
Read more …

Too late? Won’t happen under Tories.
• How To Weather Brexit: Focus Less On Trade, More On Investment (Pettifor)
“Strong and stable” seems of a world so far, far away. Yesterday’s Daily Mail headline “PM slaps treacherous Chancellor down” portrays a government in political chaos. Thanks to open, unresolved intra-Brexiteer warfare, ministers are unable to agree the basics of how to exit the European Union. This state of uncertainty intensifies just as the risks to British jobs and living standards are becoming starker and more potent. Ironically, just as we teeter towards the cliff, ONS data reveals that exports of goods to the EU grew over the last three months, while those to the rest of world fell back, a fact not devoid of dark humour. Yet while ministers appear obsessed by trade, net trade comprises only a small part of UK GDP. Surely, through the coming period of Brexit chaos, government priority must be to “take back control” and maintain and support the domestic economy.
This means a commitment to support not only investment technically defined as “capital” but also public investment in the health, education, and training of the British people. In that way, Britain will have some chance of weathering the storm. George Magnus highlighted the OBR’s acceptance that UK productivity growth is likely to stay much lower than previously assumed. This leads to the inevitable conclusion that—on present course—the ever-weaker economy will lead this government to continue to slash public revenues. Yet even this gloomy OBR data underestimates the dangers. For the OBR has not yet factored in the far greater damage that will flow from a chaotic, unplanned Brexit in less than 18 months.
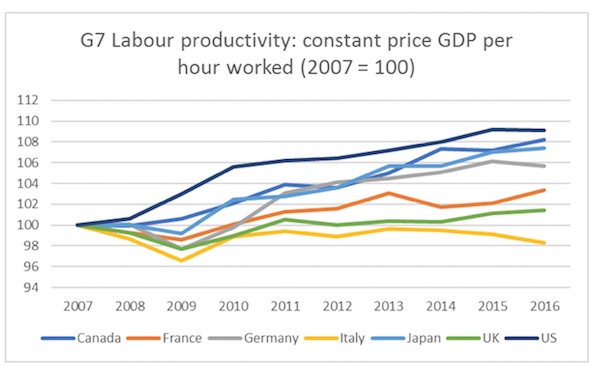
[..] Investment in the UK has since 2007 been in the 14 – 18% range as a share of GDP. In 2016, the figure was 17%. France, by contrast, has annual investment of between 22 – 24% of GDP, and Germany around 19 – 21%. The UK in 2016 slumped to 116th place out of 141 countries in terms of capital investment as a percentage of GDP. In the EU, only Greece, Portugal, Lithuania and Cyprus were below us. Low levels of investment by the “timid mouse” that is the private sector is directly a function of low levels of aggregate demand. Firms can’t see future customers coming through the door, and are made timid by volatile financial conditions and political uncertainty. Weak demand and financial instability are exacerbated by low levels of public investment.
Read more …

More UK misery: “We should not think this is reckless borrowing, this is directed at essential living costs.”
• UK Financial Regulator Warns Of Growing Debt Among Young People (BBC)
The chief executive of the Financial Conduct Authority has warned of a “pronounced” build up of debt among young people. In an interview with the BBC, Andrew Bailey said the young were having to borrow for basic living costs. The regulator also said he “did not like” some high cost lending schemes. He said consumers, and institutions that lend to them, should be aware that interest rates may rise in the future and that credit should be “affordable”. Action was being taken to curb long term credit card debt and high cost pay-day loans, Mr Bailey said. The regulator is also looking and charges in the rent-to-own sector which can leave people paying high levels of interest for buying white goods such as washing machines, he added.
“There is a pronounced build up of indebtedness amongst the younger age group,” Mr Bailey said. “We should not think this is reckless borrowing, this is directed at essential living costs. It is not credit in the classic sense, it is [about] the affordability of basic living in many cases.” [..] “There are particular concentrations [of debt] in society, and those concentrations are particularly exposed to some of the forms and practices of high cost debt which we are currently looking at very closely because there are things in there that we don’t like,” Mr Bailey said. “There has been a clear shift in the generational pattern of wealth and income, and that translates into a greater indebtedness at a younger age. “That reflects lower levels of real income, lower levels of asset ownership. There are quite different generational experiences,” he said.
Read more …

Haven’t seen anything from Ellen in a while. This makes a ton of sense. But Puerto Rico’s not the only place that needs it.
• How to Wipe Out Puerto Rico’s Debt Without Hurting Bondholders (Ellen Brown)
DWiping out Puerto Rico’s debt, they warned, could undermine confidence in the municipal bond market, causing bond interest rates to rise, imposing an additional burden on already-struggling states and municipalities across the country. True, but the president was just pointing out the obvious. As economist Michael Hudson says, “Debts that can’t be paid won’t be paid.” Puerto Rico is bankrupt, its economy destroyed. In fact it is currently in bankruptcy proceedings with its creditors. Which suggests its time for some more out-of-the-box thinking . . . . In July 2016, a solution to this conundrum was suggested by the notorious Goldman Sachs itself, when mom and pop investors holding the bonds of bankrupt Italian banks were in jeopardy. Imposing losses on retail bondholders had proven to be politically toxic, after one man committed suicide.
Some other solution had to be found. Italy’s non-performing loans (NPLs) then stood at 210bn, at a time when the ECB was buying 120bn per year of outstanding Italian government bonds as part of its QE program. The July 2016 Financial Times quoted Goldman’s Francesco Garzarelli, who said, “by the time QE is over – not sooner than end 2017, on our baseline scenario – around a fifth of Italy’s public debt will be sitting on the Bank of Italy’s balance sheet.” His solution: rather than buying Italian government bonds in its quantitative easing program, the ECB could simply buy the insolvent banks’ NPLs. Bringing the entire net stock of bad loans onto the government’s balance sheet, he said, would be equivalent to just nine months’ worth of Italian government bond purchases by the ECB.
Puerto Rico’s debt is only $73 billion, one third the Italian debt. The Fed has stopped its quantitative easing program, but in its last round (called “QE3”), it was buying $85 billion per month in securities. At that rate, it would have to fire up the digital printing presses for only one additional month to rescue the suffering Puerto Ricans without hurting bondholders at all. It could then just leave the bonds on its books, declaring a moratorium at least until Puerto Rico got back on its feet, and better yet, indefinitely. Shifting the debt burden of bankrupt institutions onto the books of the central bank is not a new or radical idea. UK Prof. Richard Werner, who invented the term “quantitative easing” when he was advising the Japanese in the 1990s, says there is ample precedent for it. In 2012, he proposed a similar solution to the European banking crisis, citing three successful historical examples.
One was in Britain in 1914, when the British banking sector collapsed after the government declared war on Germany. This was not a good time for a banking crisis, so the Bank of England simply bought the banks’ NPLs. “There was no credit crunch,” wrote Werner, “and no recession. The problem was solved at zero cost to the tax payer.” For a second example, he cited the Japanese banking crisis of 1945. The banks had totally collapsed, with NPLs that amounted to virtually 100% of their assets: But in 1945 the Bank of Japan had no interest in creating a banking crisis and a credit crunch recession. Instead it wanted to ensure that bank credit would flow again, delivering economic growth. So the Bank of Japan bought the non-performing assets from the banks – not at market value (close to zero), but significantly above market value.
Read more …

Set for confrontation. Combine with Brexit and Austria’s push to the right, and you get an EU with crumbling foundations.
• Catalan Leader Fails To Spell Out Independence Stance, Calls For Talks (R.)
Catalan leader Carles Puigdemont failed to clarify on Monday whether he had declared Catalonia’s independence from Spain last week, paving the way for the central government to take control of the region and rule it directly. The wealthy region’s threatened to break away following a referendum in Oct. 1 that Spain’s Constitutional Court said was illegal. That plunged the country into its worst political crisis since an attempted military coup in 1981. Puigdemont made a symbolic declaration of independence on Tuesday, but suspended it seconds later and called for negotiations with Madrid on the region’s future. Spain’s Prime Minister Mariano Rajoy gave him until Monday 10:00 a.m. (0800 GMT) to clarify his position, and until Thursday to change his mind if he insisted on a split – and said Madrid would suspend Catalonia’s autonomy if he chose independence.
Rajoy had said Puigdemont should answer the formal requirement with a simple “Yes” or “No” and that any ambiguous response would be considered a confirmation that a declaration of independence had been made. Puigdemont did not directly answer the question in his letter to Rajoy, made public by local Catalan media. The Catalan leader said instead that the two should meet as soon as possible to open a dialogue over the next two months. “Our offer for dialogue is sincere and honest. During the next two months, our main objective is to have this dialogue and that all international, Spanish and Catalan institutions and personalities that have expressed the willingness to open a way for dialogue can explore it,” Puigdemont said in the letter.
Read more …

And this will go up as the blockchain grows.
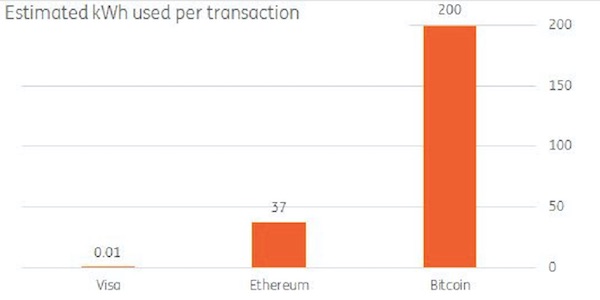
• Electricity Required For Single Bitcoin Trade Could Power Home For A Month (BI)
Bitcoin transactions use so much energy that the electricity used for a single trade could power a home for almost a whole month, according to a paper from Dutch bank ING. Bitcoin trades use a lot of electricity as a means to make verifying trades expensive, therefore making fraudulent transactions costly and deterring those who would seek to misuse the currency. “By making sure that verifying transactions is a costly business, the integrity of the network can be preserved as long as benevolent nodes control a majority of computing power,” wrote ING senior economist Teunis Brosens. “Together, they will dominate the verification (mining) process. To make the verification (mining) costly, the verification algorithm requires a lot of processing power and thus electricity.”
Comparing the amount of energy used for a bitcoin transaction to running his home in the Netherlands, Brosens says: “This number needs some context. 200kWh is enough to run over 200 washing cycles. In fact, it’s enough to run my entire home over four weeks, which consumes about 45 kWh per week costing €39 of electricity (at current Dutch consumer prices).” Not only does Bitcoin use a vast amount of electricity to complete transactions, it uses an almost exponentially larger amount than more traditional forms of electronic payment. “Bitcoin’s energy costs stand in stark contrast to payment systems that have the luxury of working with trusted counterparties. E.g. Visa takes about 0.01kWh (10Wh) per transaction which is 20000 times less energy,” Brosens notes, pointing to the chart below:
Read more …

3-dimensional quantum clocks. Much of our electronic infrastructure already relies on atomic clocks.
• New Quantum Atomic Clock May Finally Reveal Nature of Dark Matter (USci)
Physicists have created a quantum atomic clock that uses a new design to achieve unprecedented levels of accuracy and stability. Its broad range of potential applications could even stretch to research into dark matter. Scientists at the University of Colorado Boulder’s JILA (formerly the Joint Institute for Laboratory Astrophysics) have developed an incredibly precise quantum atomic clock based on a new three-dimensional design. The project has set a new record for quality factor, a metric used to gauge the precision of measurements. The clock packs atoms of strontium into a cube, achieving 1,000 times the density of prior one-dimensional clocks. The design marks the first time that scientists have been able to successfully utilize a so-called “quantum gas” for this purpose.
Previously, each atom in an atomic clock was treated as a separate particle, and so interactions between atoms could cause inaccuracies in the measurements taken. The “quantum many-body system” used in this project instead organizes atoms in a pattern, which forces them to avoid one another, no matter how many are introduced to the apparatus. A state of matter known as a degenerate Fermi gas — which refers to a gas comprised of Fermi particles — allows for all of the atoms to be quantized. [..] It’s been suggested that monitoring minor inconsistencies in the ticking of an atomic clock might offer insight into the presence of pockets of dark matter. Previous research has shown that a network of atomic clocks, or even a single highly-sensitive system, might register a change in the frequency of vibrating atoms or laser light in the clock if it passed through a dark matter field.
Read more …

Ai himself grew up in miserable conditions due to Mao.
• Ai Weiwei On Art, Exile And Refugee Film ‘Human Flow’ (AFP)
In the most tender moments of “Human Flow,” Ai Weiwei’s epic documentary on the worldwide migrant crisis, he is seen hugging, cooking with and cutting the hair of refugees. An ordinary filmmaker might be accused of getting too close to his subject but, as far as the Chinese dissident and internationally renowned artist is concerned, he is the subject. “When I look at people being pushed away from their home because of war, because of all kinds of problems, because of environmental problems, famine, I don’t just have sympathy for them,” he tells AFP. “I do feel that they are part of me and I am part of them, even with very different social status.”
[..] “Human Flow,” his powerful expression of solidarity with refugees around the world, demonstrates the staggering scale of the refugee crisis and its profoundly personal human impact. Captured over a year in 23 countries, it follows a chain of human stories that stretches from Bangladesh and Afghanistan to Europe, Kenya and the US-Mexico border. Ai travels from teeming refugee camps to barbed-wire borders, witnessing refugees’ desperation and disillusionment as well as hope and courage. “I’m so far away from their culture, their religion or whatever the background. But with a human being, you look at him, you know what kind of person he is,” says Ai.
“I have this natural understanding about human beings. So I try to grab them with this kind of approach, a very intimate approach. They can touch me, cut my hair. I can cut their hair. I can cook in their camp.” “Human Flow” is far from Ai’s first work on the refugee crisis. Just last week he scattered over 300 outdoor works across New York as part of a new illustration of his empathy for refugees worldwide. Ai dismisses a common criticism that his work has little artistic merit and that he is more of a campaigner, telling AFP “a good artist should be an activist and a good activist should have the quality of an artist.”
Read more …