
Vincent van Gogh Vineyards with a View of Auvers 1890

What Yellen says is not so interesting. What lies beyond those carefully crafted speeches is.
BTW, no Trump today, but maybe we can start a separate gossip page.
“The Fed says it’s going to hike again this year, markets says 50-50. The Fed says three, four times next year, the market says it’s not going to happen at all..”
• ‘Investors Underestimate How Low The Bar Is For The Fed’ (CNBC)
Patrick Armstrong, the CIO at Plurimi Investment Managers, believes that very high valuations, an expected tightening in monetary policy and too much optimism over tax cuts and new fiscal spending should leave investors cautious on the United States. “Valuation doesn’t matter in the short term but at current CAPE (cyclically adjusted price to earnings, which gives a more clear indication of a stock price in comparison to average earnings over the last 10 years) of 29 times, U.S. equities have historically delivered negative real returns over periods of two to five years,” he said in an investment outlook published earlier this month. The U.S. Federal Reserve has begun normalizing its policy in the wake of improved economic growth and low unemployment levels.
According to Armstrong, the easy monetary policy of the past had boosted equities but this might change with the Fed’s plans to hike rates and reduce its balance sheet. “I think there was a clear warning in the last (meeting) minutes talking about risk premium, price earnings and investors haven’t acknowledged it, but when the Fed starts worrying about equity markets, as an equity investor they’ve given you that warning,” he told CNBC on Tuesday. The third reason to be “short” – where a trader takes a bet that prices will fall – on U.S. equities is the government’s plans on fiscal policy. President Donald Trump promised tax cuts and big infrastructure spending, which made U.S. equities rally since he took office last November. However, such policies are yet to reach the consultation stage and doubts have emerged over the president’s ability to deliver.
[..] Speaking to CNBC Tuesday, Armstrong suggested that investors aren’t listening to the U.S. Federal Reserve. “What investors are completely underestimating is how low the bar is for the United States Federal Reserve. They have told us what they intend to do, the markets don’t believe any of it,” Armstrong said. “The Fed says it’s going to hike again this year, markets says 50-50. The Fed says three, four times next year, the market says it’s not going to happen at all,” he added.

Central banks are trying to get out before the blast. But in doing so they bring it forward. Were given far too much power.
• Unwinding QE will be “More Disruptive than People Think” (WS)
“We’ve never had QE like this before, and we’ve never had unwinding like this before,” said JPMorgan CEO Jamie Dimon at the Europlace finance conference in Paris. “Obviously that should say something to you about the risk that might mean, because we’ve never lived with it before.” He was referring to the Fed’s plan to unwind QE, shedding Treasury securities and mortgage-backed securities on its balance sheet. The Fed will likely announce the kick-off this year, possibly at its September meeting. According to its plan, there will be a phase-in period. It will unload $10 billion the first month and raise that to $50 billion over the next 12 months. Then it will continue at that pace to achieve its “balance sheet normalization.” Just like the Fed “created” this money during QE to buy these assets, it will “destroy” this money at a rate of $50 billion a month, or $600 billion a year.
It’s the reverse of QE, with reverse effects. Other central banks are in a similar boat. The Fed, the Bank of Japan, and the ECB together have loaded up their balance sheets with $14 trillion in assets. Unwinding this is going to have some impact – likely reversing some of the asset price inflation in stocks, bonds, real estate, and other markets that these gigantic bouts of asset buying have caused. The Bank of Japan has been quietly tapering its asset purchases for a while to where it buys only enough to keep the 10-year yield barely above zero. And the ECB has tapered its monthly purchases by €20 billion earlier this year and is preparing the markets for more tapering. Once central banks stop buying assets, the phase starts when central banks try to unload some of those assets. The Fed is at the threshold of this phase.
Dimon was less concerned about the Fed’s rate hikes. People are too focused on rate hikes, he said, according to a Bloomberg recording of the conference. If the economy is strong, economic growth itself overcomes the issues posed by higher rates, he said. The economy has been through rate hikes many times before. They’re a known quantity. But “when selling securities in the market place starts,” that’s when it gets serious. “When that happens of size or substance, it could be a little more disruptive than people think,” he said. Whatever it will do, no one knows what it will do – because “it never happened before.”

Don’t woryy, they serve the same lords.
• I Wouldn’t Rule Out Another Financial Crisis – IMF’s Lagarde (CNBC)
The IMF’s Managing Director, Christine Lagarde, has said that she would not rule out another financial crisis in her lifetime, indicating that comments made recently by Federal Reserve Chair Janet Yellen may have been premature. “There may, one day, be another crisis,” Lagarde told CNBC Tuesday on the sidelines of a joint conference with the IMF and the Croatian National Bank in Dubrovnik. Lagarde’s comments responded to a statement made by Yellen a fortnight earlier in which she said she does not expect to see another financial crisis in her lifetime. “I plan on having a long life and I hope she (Yellen) does, too, so I wouldn’t absolutely bet on that because there are cycles that we have seen over the past decade and I wouldn’t exclude that,” Lagarde said.
She, however, noted the unpredictability of financial crises and said that finance ministers and policymakers should act with caution to prepare for such eventualities. “Where it will come from, what form it takes, how international and broad-based it will be is to be seen, and typically the crisis never comes from where we expect it,” she added. “Our duty, and certainly the message that we give to the finance ministers, to the policymakers, is ‘be prepared’. Make sure that your financial sector is under good supervision, that it’s well regulated, that the institutions are rock-solid, and anticipate at home with enough buffers so that you can resist the potential crisis.”

And we will see undershoot on the way down. The Fed killing off price discovery will be a scourge on society.
• The US Stock Market Is 66% Higher Than It Should Be (Kee jr)
I have, in previous articles here on MarketWatch, pointed out the fundamental risks in the U.S. stock market. I have identified the liquidity risks created by the ECB and the Federal Reserve in the tightening of monetary policy, in the reduction of the Fed’s balance sheet, and the likelihood that these risks will prick the asset bubble that the market is in today. Most people I speak and email with agree. The risks are high, as the price-to-earnings multiple of the S&P 500 (about 25, depending on the indicator) is far greater than its historical norm (14.5). The truth, however, is that no one knows for sure. But, still, people are apathetic. In fact, my experience over the past 20 years and through each of the past two major asset bubbles (the internet bubble in 2000 and the credit crisis in 2008-2009), is that the unanimous identification of an asset bubble did not take place until after the asset bubble had burst.
By that time, all of the major indices — the Dow Jones Industrial Average S&P 500, Nasdaq 100 and Russell 2000 — had already fallen. The result largely handcuffed investors to investments that were severely underwater. As luck would have it, though, after the credit crisis, the Fed’s policy-making body printed $2 trillion and, with that money, bought assets to prop up the economy and save investors from destruction. Largely, this perceived savior is probably why investors are so lethargic when it comes to the asset bubble that we are probably in right now. This bubble even seems to include real estate and bonds in addition to stocks, and it has been driven by fabricated central bank liquidity.
Admittedly, I cannot be sure what will happen. I do not know if this bubble will burst, and I do not know if central banks will come running to the rescue again, as they did after the credit crisis. Unfortunately, I do know a great deal of people who believe that the central banks of the world will simply print more money if the going gets tough again, but that is a seriously risky bet. With major indices coming off all-time highs and technical trading patterns (dojis) surfacing in long-term chart patterns last week, potential reversal signals are coming on a technical basis. As much as it is appealing to opt for relaxation and vacationing during the summer months, some time must be spent evaluating the conditions the market is facing right now.
In previous articles, I have offered alternatives to the traditional buy-and-hold methodology, and I think everyone should consider heading that way because strategies like “lock and walk” can work no matter what happens. The risks in the market today are extremely high for buy-and-hold investors because the liquidity picture is changing for the worse, and that is fundamental in nature. But longer-term technical observations point toward serious risks as well. My longer-term macroeconomic analysis, The Investment Rate, is offering warnings that this market is 66% higher than it should be. Given the changes in liquidity and technical observations happening now, those risk warnings should be heard with an acute ear.

A whole bunch of Lance graphs again. Hard to choose. But pretty as the graphs are, they do not paint a pretty picture. They say BUBBLE.
• Valuation Measures & Forward Returns (Lance Roberts)
[..] if the market can reverse the current course of weakness and rally above recent highs, it will confirm the bull market is alive and well, and we will continue to look for a push to our next target of 2500. With portfolios currently fully allocated, we are simply monitoring risk and looking for opportunities to invest “new capital” into markets with a measured risk/reward ratio. However, this is a very short-term outlook which is why “price is the only thing that matters.” “Price measures the current “psychology” of the “herd” and is the clearest representation of the behavioral dynamics of the living organism we call “the market.” But in the long-term, fundamentals are the only thing that matters. I have shown you the following chart many times before. Which is simply a comparison of 20-year forward total real returns from every previous P/E ratio.
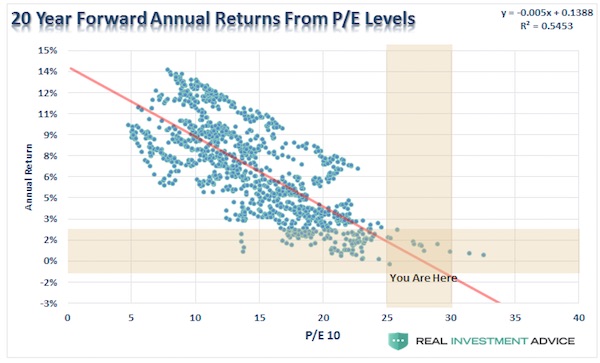
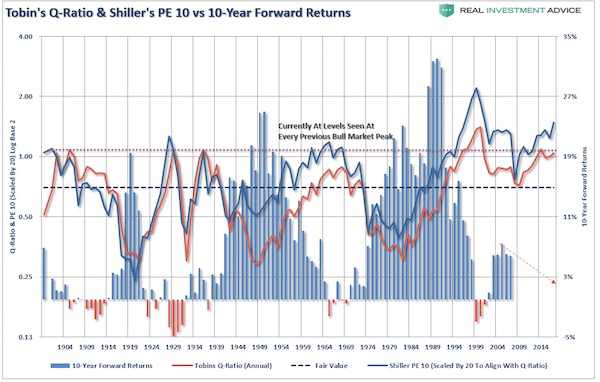
I know, I know. “P/E’s don’t matter anymore because of Central Bank interventions, accounting gimmicks, share buybacks, etc.” Okay, let’s play. In the following series of charts, I am using forward 10-year returns just for consistency as some of the data sets utilized don’t yet have enough history to show 20-years of forward returns. The purpose here is simple. Based on a variety of measures, is the valuation/return ratio still valid, OR, is this time really different? Let’s see. Tobin’s Q-ratio measures the market value of a company’s assets divided by its replacement costs. The higher the ratio, the higher the cost resulting in lower returns going forward. Just as a comparison, I have added Shiller’s CAPE-10. Not surprisingly the two measures not only have an extremely high correlation, but the return outcome remains the same.
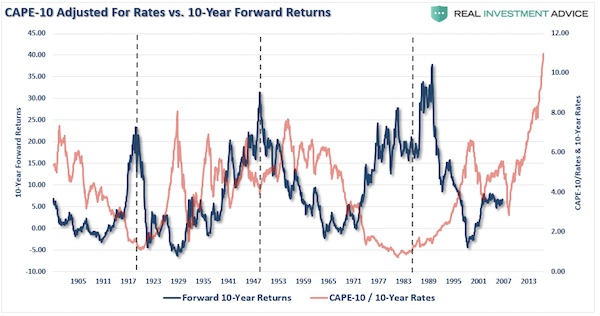
One of the arguments has been that higher valuations are okay because interest rates are so low. Okay, let’s take the smoothed P/E ratio (CAPE-10 above) and compare it to the 10-year average of interest rates going back to 1900. The analysis that low rates justify higher valuations clearly does not withstand the test of history.

Substitute nonprime for subprime and you open a whole new can of suckers again. “No, these are fine and upstanding citizens. They just don’t have access to normal bank loans.” Gee, why is that?
• Nonprime Mortgages Prove Leery Investors Are Finally Hungry Again (CNBC)
The appetite for riskier mortgages is rising, and a small cadre of investment firms is ready to feed it. Angel Oak Capital Advisors just announced its second rated securitization of nonprime residential mortgages this year, a deal worth just more than $210 million and its largest ever. Its first deal was slightly less, but demand from borrowers and investors alike is growing, and the securitizations are growing with it. Angel Oak is one of very few firms offering these private-label mortgage-backed securities — the ones that were so very popular during the last housing boom and which were later blamed for the financial crisis. Today’s nonprime loans, however, are nothing like the ones of the past. The government cracked down on faulty loan products, those with low teaser rates, negative amortization and no documentation.
Still, for the past decade investors wouldn’t touch anything that wasn’t government-backed. Only now are they seeing value and dipping their toes in again. The number of nonprime mortgage-backed securities “skyrocketed” in the second quarter of this year, according to Inside Mortgage Finance — a total of $1.08 billion of MBS backed by nonprime home loans. That was the strongest quarter for the sector since the financial crisis. It is still, however, nothing compared with the volume that caused the housing crash. “At one point during the housing boom, we had a third of all mortgage originations that were nonprime [subprime or Alt-A, the latter having low or no documentation]. We’re not going to be even 5% of the market if we have a record year this year. It still has a long, long way to go,” said Guy Cecala, CEO of Inside Mortgage Finance.
That is because while investors are hungry for yield, they are still very skeptical. The ratings agencies are as well. That makes it difficult for companies like Angel Oak, and its competitors — Lone Star and Deephaven Mortgage — to issue large quantities of nonprime MBS. Nonprime securitizations today are far less risky, consisting of loans that were underwritten far more stringently. Angel Oaks’ securitization does consist of both fixed- and floating-rate loans. “In addition to borrowers that had prior credit events, our loans are also for borrowers who are self-employed,” said Lauren Hedvat, capital markets director at Angel Oak. “They are of high credit quality, but they are not able to access mortgage products by the more traditional bank routes.”

Start paying cash everywhere.
• VISA takes its War on Cash to US Retailers (WS)
“We’re focused on putting cash out of business,” Visa’s new CEO Al Kelly said on June 22 at Visa Investor Day. Pushing consumers into digital and electronic payments is the company’s “number-one growth lever.” Visa has been dogged by the stubborn survival of cash and checks, despite widespread government and corporate efforts to kill them off. Globally, check and cash transactions totaled $17 trillion in 2016, Visa President Ryan McInerney said. Confusingly, that’s up 2% from a year earlier. So today, Visa rolled out a new initiative on its war on cash. It’s designed “for small business restaurants, cafés, or food truck owners,” and the like. In this trial, it will award up to $10,000 each to 50 eligible businesses (online businesses are excluded) when they commit to refusing cash payments.
Going “100% cashless,” as Visa calls it, means that consumers can only pay with debit or credit cards or with their smartphones. That’ll be the day. You go to your favorite taco truck, and when it comes time to pay, you pull out a wad of legal tender, only to be treated to an embarrassed nod toward a sign that says, “No Cash.” I’d walk. But Visa hopes that other folks will pull out their Visa-branded card or a smartphone with a payment app that uses the Visa system. This would help Visa extract its fees from the transaction. “We have an incredible opportunity to educate merchants and consumers alike on the effectiveness of going cashless,” Jack Forestell, Visa’s head of global merchant solutions, said in the press release, which touted a “study” that Visa recently “conducted” that “found that if businesses in 100 cities transitioned from cash to digital, their cities stand to experience net benefits of $312 billion per year.”
However dubious these “net benefits” may be, one thing is not dubious: Visa gets a cut from every transaction made via Visa-branded cards or digital payment systems that use Visa. The merchant pays the cut and then tries to pass it on to customers via higher prices. The total card fees normally range between 1% and 3%. Among the entities that get to divvy this moolah up are the bank that issued the visa card and the credit card network – such as Visa, MasterCard, and the like. Visa gets just a small piece of the pie, but if it is on every transaction, it adds up. And payments by cash and check seriously get in the way of a lot of money. In 2016, Visa extracted $15 billion from processing transactions globally without even carrying any credit risk (the banks have to deal with that).

Purely symbolic. Everyone loves to present a meme of recovery, but it’s not there. Ironically, the move from deficit to -forced- surplus guarantees it. Greece should run a deficit now to boost its economy.
• Greece To Exit EU’s Excessive Deficit Procedure (K.)
After eight years, Greece emerged on Wednesday from the European Commission’s process for countries with excessive deficit. The Commission proposed Greece’s exit from the process as its general government debt has dropped below the threshold of 3% of GDP. This is a largely symbolic move, but it does have some significance given that the government is planning to return to the bond markets for the first time since 2014. Economic Affairs Commissioner Pierre Moscovici gave a wink to the markets on Wednesday, saying that the disbursement of the tranche of 7.7 billion euros on Monday and the decision on the deficit is “good news that the markets ought to read,” even though he explained that what the investors do is not up to him.
Commission Vice President Valdis Dombrovskis called on Greece to capitalize on its achievements and continue to strengthen confidence in its economy, which is crucial as the country prepares its return to the credit markets. The Commission’s proposal for Greece’s emergence from the deficit procedure has to be ratified by the EU’s finance ministers, but has little practical use. Ultimately, Greece’s fiscal targets are dictated by the bailout agreement and not by the rules that apply to other eurozone members. As one European official told Kathimerini, “nothing changes essentially, the fiscal targets Greece must hit remain high and [yesterday’s] decision is only of a symbolic dimension.”

Greece can only get worse, for many years into the future.
• Brain Drain Gathers Pace as One in Three Greeks Looks for a Job Abroad
A new study highlights the problem in the Greek labor market as more than 30% of Greek unemployed say that they are actively seeking a job abroad. According to the annual survey by the firm Adecco titled “Employability in Greece,” the brain drain phenomenon has been increasing over the last three years. In 2015 only about 11% of unemployed respondents said that they were actively looking for a job abroad. This figure increased to 28% in 2016 and reached 33% this year. The responses show that the unemployed have different reasons to seek work abroad. Whereas in 2005, the main reason was the prospect of a better wage, in 2016 and 2017 the main reason given were better career opportunities.
The study conducted for the third year running, in collaboration with polling company LMG, was based on a sample of 903 people from the age of 18 to 67. According to other findings, 37% of respondents say that they have been out of the labor market for at least 12 months. Despite the slight improvement in official unemployment rates, the Adecco survey finds that there is an increasing number of people who state that they have been at least once without a job – 58% this year compared to 54% in 2016. According to the data, more than 1 out of 4 (28%) are out of the labor market, a higher rate compared with the previous two years.

Money that could have helped Greece escape the claws of Schäuble et al. The pattern is not coincidental.
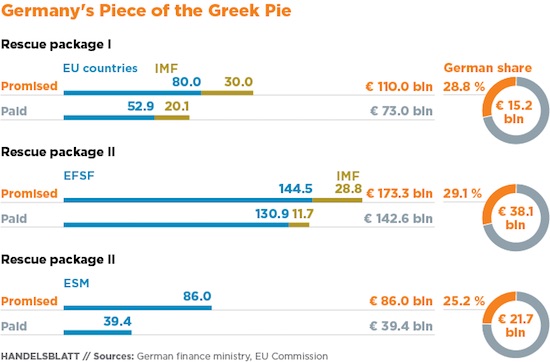
• Germany Profits From Greek Debt Crisis (HB)
The German government has long been accused by critics of profiting from Greece’s debt crisis. Now there are some new numbers to back it up: Loans and bonds purchased in support of Greece over nearly a decade have resulted in profits of €1.34 billion for Germany’s finance ministry, which confirmed the number in response to a parliamentary query from the Green Party, according to a report by German daily Süddeutsche Zeitung. The profits come from a range of programs, running into the hundreds of billions, that Germany and other euro-zone countries have backed to keep Greece’s government and economy afloat since its massive debt crisis emerged in 2009. It includes, for example, a €393-million profit generated from a 2010 loan by the development bank KfW, which is owned by the German government.
The report also shows that Germany’s central bank, the Bundesbank, has received profits from the Securities Market Program (SMP), a now-defunct government bond-buying plan initiated by the ECB and run from 2010 to 2012. The ECB collected more than €1.1 billion in 2016 in interest payments on the nearly €20 billion-worth of Greek bonds it bought through the SMP, according to the report. This year, the figure will be €901 million, which will again be redistributed to the euro zone’s 19 member states. Since 2015, Germany has collected a total of €952 million in SMP profits. The new revelations drew strong criticism from the Greens Party, in opposition. “The profits from collecting interest must be paid out to Greece. [Finance Minister] Wolfgang Schäuble cannot use the Greek profits to clean up Germany’s federal budget,” Manuel Sarrazin, EU expert for the Green Party in the parliament, told the Süddeutsche newspaper.
Mr. Schäuble, a member of Chancellor Angela Merkel’s conservative Christian Democrats, has been cannily keeping Germany’s federal budget balanced over the past four years, taking on no new debt. Berlin’s surplus amounted to €6.2 billion in 2016 alone. Critics complain that Greece’s crisis has helped it achieve that goal. “It might be legal for Germany to profit from the crisis in Greece, but from a moral and solidarity perspective, it is not right,” Sven-Christian Kindler, budget policy spokesperson for the Green Party, also told the paper. Mr. Schäuble has said he is open to reducing Greece’s interest burden but has resisted calls to end them completely. His finance ministry has argued that, with inflation, deferring interest payments would eventually end up costing Greece’s creditors.

There are many parties not too keen on such an investigation, and Varoufakis is not one of them.
• Defiant Varoufakis Ready to Face ‘Even Martial Court’ Over Plan B (GR)
Undeterred over the controversy surrounding the new disclosures over the system of a parallel currency that was apparently considered by the government of Alexis Tsipras in 2015, Yanis Varoufakis said that he is ready to face any court to respond to the charges. Speaking in a radio show, Varoufakis, the finance minister at the time and the instigator of the parallel payments system or Plan B, said that Tsipras had a copy of the proposals from as early as 2012 when he was still in opposition. “I have handed the plan to Tsipras in 2012,” so it could become the government’s plan B if negotiations with Greece’s creditors collapsed.
Mr. Varoufakis said he was willing to accept any kind of judicial investigation into Plan B and his role in drafting it. “Let’s have a special court of inquiry, or even a martial court, or any other court, so all the facts can be revealed,” he said responding to calls from the opposition for a judicial inquiry. He also attacked the SYRIZA-led government for refusing to proceed with an investigation. The Varoufakis Plan B for the Greek economy in the event that the country clashed with creditors and went bankrupt was to partially pay civil servants with coupons. Parts of the plan were revealed last week by his financial advisor Glenn Kim.








