Dorothea Lange Gravestone St. George, Utah 1953
There are numerous ways to define the Precautionary Principle. It’s something we can all intuitively understand, but which many parties seek ways to confuse since it has the potential to stand in the way of profits. Still, in the end it should all be about proof, not profits. That is exactly what the Principle addresses. Because if you first need to deliver scientific proof that some action or product can be harmful to mankind and/or the natural world, you run the risk of inflicting irreversible damage before that proof can be delivered.
In one of many definitions, the 1998 Wingspread Statement on the Precautionary Principle says: “When an activity raises threats of harm to human health or the environment, precautionary measures should be taken even if some cause and effect relationships are not fully established scientifically.”
Needless to say, that doesn’t easily fly in our age of science and money. Cigarette makers, car manufacturers and oil companies, just to name a few among a huge number of industries, are all literally making a killing while the Precautionary Principle is being ignored. Even as it is being cited in many international treaties. Lip service “R” us. Are these industries to blame when they sell us our products, or are we for buying them? That’s where governments must come in to educate us about risks. Which they obviously do not.
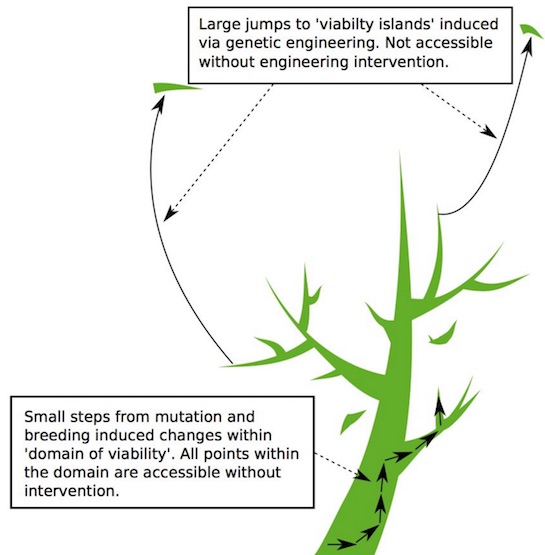
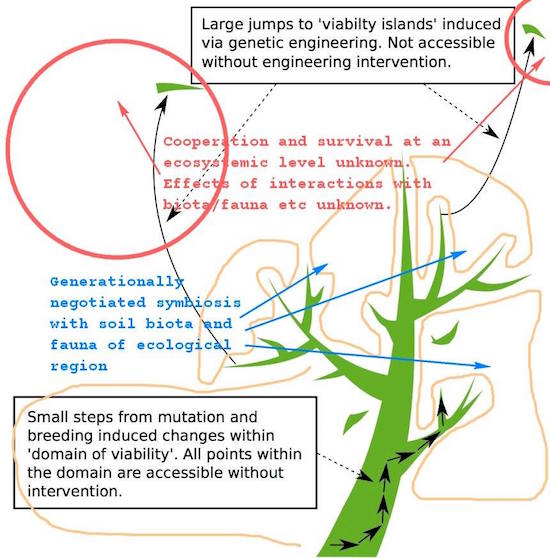
Nassim Nicholas Taleb -of Black Swan and Antifragile fame- has made the case, in his usual strong fashion, for applying the Precautionary Principle when it comes to GMOs. His argument is that allowing genetically modified organisms in our eco- and foodsystems carries unknown risks that we have no way of overseeing, and that these risks may cause irreversible damage to the very systems mankind relies on for survival.
Taleb is not popular among GMO producers. Who all insist there is no evidence that their products cause harm. But that is not the point. The Precautionary Principle, if it is to be applied, must turn the burden of proof on its head. The absence of evidence is not evidence of absence. Monsanto et al must prove that their products do no harm. They can not. Which is why they have, and need, huge lobbying, PR and legal departments.
But I didn’t want to talk about GMOs today, and not about Precautionary Principle alone. I wanted to talk about this: Paragraph 2 of article 191 of the European Union’s Lisbon Treaty (2009) states that:
“Union policy on the environment shall aim at a high level of protection taking into account the diversity of situations in the various regions of the Union. It shall be based on the precautionary principle and on the principles that preventive action should be taken, that environmental damage should as a priority be rectified at source and that the polluter should pay.”
In other words, the EU has committed itself to the Precautionary Principle. Well, on paper, that is. However, then we get to a whole series of reports on wildlife in Europe, and they indicate all sorts of things, but not that Brussels cares even one bit about adhering to the Precautionary Principle, either for its people or its living environment. One voice below calls it a “state of denial”, but I would use some other choice words. Let’s start with the Guardian this morning, because they have an interesting perspective:
Most Britons remain blithely unaware that since the Beatles broke up, we have wiped out half our wildlife…
…since the fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989, the number of flying insects on nature reserves in Germany had dropped by at least 76% – more than three-quarters…
Things like ‘since you were born’, ‘since man landed on the moon’, ‘since the wall came down’ or ‘since 9/11’ may be a bit clearer than 100 years, or 25 years. Moreover, I read somewhere that since Columbus landed in 1492, America has lost on third of all its biodiversity, but that doesn’t yet explain the rate of acceleration that is taking place.
In October last year, the Guardian had this:
Three-Quarters Of Flying Insects In Germany Have Vanished In 25 Years
The abundance of flying insects has plunged by three-quarters over the past 25 years , according to a new study that has shocked scientists. Insects are an integral part of life on Earth as both pollinators and prey for other wildlife and it was known that some species such as butterflies were declining. But the newly revealed scale of the losses to all insects has prompted warnings that the world is “on course for ecological Armageddon”, with profound impacts on human society.
The new data was gathered in nature reserves across Germany but has implications for all landscapes dominated by agriculture, the researchers said. The cause of the huge decline is as yet unclear, although the destruction of wild areas and widespread use of pesticides are the most likely factors and climate change may play a role. The scientists were able to rule out weather and changes to landscape in the reserves as causes, but data on pesticide levels has not been collected.
“The fact that the number of flying insects is decreasing at such a high rate in such a large area is an alarming discovery,” said Hans de Kroon, at Radboud University in the Netherlands and who led the new research. “Insects make up about two-thirds of all life on Earth [but] there has been some kind of horrific decline,” said Prof Dave Goulson of Sussex University, UK, and part of the team behind the new study. “We appear to be making vast tracts of land inhospitable to most forms of life , and are currently on course for ecological Armageddon. If we lose the insects then everything is going to collapse.”
[..] When the total weight of the insects in each sample was measured a startling decline was revealed. The annual average fell by 76% over the 27 year period, but the fall was even higher – 82% – in summer, when insect numbers reach their peak. Previous reports of insect declines have been limited to particular insects, such European grassland butterflies, which have fallen by 50% in recent decades. But the new research captured all flying insects, including wasps and flies which are rarely studied, making it a much stronger indicator of decline.
Then last week from AFP:
France’s Bird Population Collapses As Pesticides Kill Off Insects
Bird populations across the French countryside have fallen by a third over the last decade and a half, researchers have said. Dozens of species have seen their numbers decline, in some cases by two-thirds, the scientists said in a pair of studies – one national in scope and the other covering a large agricultural region in central France. “The situation is catastrophic,” said Benoit Fontaine, a conservation biologist at France’s National Museum of Natural History and co-author of one of the studies. “Our countryside is in the process of becoming a veritable desert,” he said in a communique released by the National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS), which also contributed to the findings.
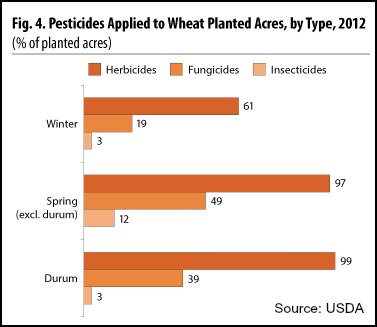
The common white throat, the ortolan bunting, the Eurasian skylark and other once-ubiquitous species have all fallen off by at least a third, according a detailed, annual census initiated at the start of the century. A migratory song bird, the meadow pipit, has declined by nearly 70%. The museum described the pace and extent of the wipe-out as “a level approaching an ecological catastrophe”. The primary culprit, researchers speculate, is the intensive use of pesticides on vast tracts of monoculture crops, especially wheat and corn. The problem is not that birds are being poisoned, but that the insects on which they depend for food have disappeared.
“There are hardly any insects left, that’s the number one problem,” said Vincent Bretagnolle, a CNRS ecologist at the Centre for Biological Studies in Chize. Recent research, he noted, has uncovered similar trends across Europe, estimating that flying insects have declined by 80%, and bird populations has dropped by more than 400m in 30 years. Despite a government plan to cut pesticide use in half by 2020, sales in France have climbed steadily, reaching more than 75,000 tonnes of active ingredient in 2014, according to EU figures. “What is really alarming, is that all the birds in an agricultural setting are declining at the same speed, even ’generalist’ birds,” which also thrive in other settings such as wooded areas, said Bretagnolle.
Not that it’s just Europe, mind you. Still ‘ove’ this one from Gretchen Vogel in ScienceMag, about a year ago, on a phenomenon most of you stateside will have noticed too:
Where Have All The Insects Gone?
Entomologists call it the windshield phenomenon. “If you talk to people, they have a gut feeling. They remember how insects used to smash on your windscreen,” says Wolfgang Wägele, director of the Leibniz Institute for Animal Biodiversity in Bonn, Germany. Today, drivers spend less time scraping and scrubbing. “I’m a very data-driven person,” says Scott Black, executive director of the Xerces Society for Invertebrate Conservation in Portland, Oregon. “But it is a visceral reaction when you realize you don’t see that mess anymore.”
Some people argue that cars today are more aerodynamic and therefore less deadly to insects. But Black says his pride and joy as a teenager in Nebraska was his 1969 Ford Mustang Mach 1—with some pretty sleek lines. “I used to have to wash my car all the time. It was always covered with insects.” Lately, Martin Sorg, an entomologist here, has seen the opposite: “I drive a Land Rover, with the aerodynamics of a refrigerator, and these days it stays clean.”
Though observations about splattered bugs aren’t scientific, few reliable data exist on the fate of important insect species. Scientists have tracked alarming declines in domesticated honey bees, monarch butterflies, and lightning bugs. But few have paid attention to the moths, hover flies, beetles, and countless other insects that buzz and flitter through the warm months. “We have a pretty good track record of ignoring most noncharismatic species,” which most insects are, says Joe Nocera, an ecologist at the University of New Brunswick in Canada.
After all those numbers, and before they get worse -which they will, it’s already baked in the cake-, you would expect the EU to remember the Precautionary Principle all its member nations signed on to for the Lisbon Treaty. You would expect wrong. Instead Brussels vows to continue with the exact same policies that have led to its mind-boggling biodiversity losses.
EU In ‘State Of Denial’ Over Destructive Impact Of Farming On Wildlife
Europe’s crisis of collapsing bird and insect numbers will worsen further over the next decade because the EU is in a “state of denial” over destructive farming practices, environmental groups are warning. European agriculture ministers are pushing for a new common agriculture policy (CAP) from 2021 to 2028 which maintains generous subsidies for big farmers and ineffectual or even “fake” environmental or “greening” measures, they say. In a week when two new studies revealed drastic declines in French farmland birds – a pattern repeated across Europe – the EU presidency claimed that the CAP continued to provide safe food while defending farmers and “protecting the environment”.
“The whole system is in a state of denial,” said Ariel Brunner, head of policy at Birdlife Europe. “Most agriculture ministers across Europe are just pushing for business as usual. The message is, keep the subsidies flowing.” Farm subsidies devour 38% of the EU budget and 80% of the subsidies go to just 20% of farmers , via “basic payments” which hand European landowners £39bn each year.
Because these payments are simply related to land area, big farmers receive more, can invest in more efficient food production – removing hedgerows to enlarge fields for instance – and put smaller, less intensive farmers out of business. France lost a quarter of its farm labourers in the first decade of the 21st century, while its average farm size continues to rise.
A smaller portion – £14.22bn annually – of EU farm subsidies support “greening” measures but basic payment rules work against wildlife-friendly farming: in Britain, farmers can’t receive basic payments for land featuring ponds, wide hedges, salt marsh or regenerating woodland. Signals from within the EU suggest that the next decade’s CAP [..] will continue to pay farmers a no-strings subsidy, while cash for “greening”, or wildlife-friendly farming, may even be cut. Birdlife Europe said the “greening” was mostly “fake environmental spending” and wildlife-friendly measures had been “shredded” by “loophole upon loophole” introduced by member states.
[..] This week studies revealed that the abundance of farmland birds in France had fallen by a third in 15 years – with population falls intensifying in the last two years. It’s a pattern repeated across Europe: farmland bird abundance in 28 European countries has fallen by 55% over three decades, according to the European Bird Census Council. Conservationists say it’s indicative of a wider crisis – particularly the decimation of insect life linked to neonicotinoid pesticides.
20% of farmers work 80% of the land in Europe. That is used as an argument to single them out to pay them billions in subsidies. But it simply means these 20% use the most detrimental farming methods, most pesticides, most chemicals. The subsidies policy guarantees further deterioration of an already disastrous situation. The polluter doesn’t pay, as the Lisbon Treaty demands, but the polluter gets paid.
And even that is apparently still not enough for the fast growing bureaucracy. In a move perhaps more characteristic of the EU than anything else, it approved something last week that a million people had vehemently protested: the Bayer-Monsanto merger. The European parliament may have thrown out all Monsanto lobbyists recently, and voted to ban Roundup, but the die has been cast.
A million citizens can protest in writing, many millions in France and Germany and elsewhere may do the same on the street, none of it matters. The people who brought you WWII nerve gases and Agent Orange can now come together to take over your food supply.
EU Approves Buyout Of Monsanto By German Chemical Firm Bayer
German conglomerate Bayer won EU antitrust approval on Wednesday for its $62.5bn (£44.5bn) buy of US peer Monsanto, the latest in a trio of mega mergers that will reshape the agrochemicals industry. The tie-up is set to create a company with control of more than a quarter of the world’s seed and pesticides market. Driven by shifting weather patterns, competition in grain exports and a faltering global farm economy, Dow and Dupont, and ChemChina and Syngenta had earlier led a wave of consolidation in the sector. Both deals secured EU approval only after the companies offered substantial asset sales to boost rivals.
Environmental and farming groups have opposed all three deals, worried about their power and their advantage in digital farming data, which can tell farmers how and when to till, sow, spray, fertilise and pick crops based on algorithms. The European Commission said Bayer addressed its concerns with its offer to sell a swathe of assets to boost rival BASF [..] “Our decision ensures that there will be effective competition and innovation in seeds, pesticides and digital agriculture markets also after this merger,” European Competition Commissioner Margrethe Vestager said in a statement. “In particular, we have made sure that the number of global players actively competing in these markets stays the same.”
[..] Vestager said the Commission, which received more than a million petitions concerning the deal, had been thorough by examining more than 2,000 different product markets and 2.7 million internal documents to produce a 1,285-page ruling. [..] Online campaigns group Avaaz criticised the EU approval. “This is a marriage made in hell. The Commission ignored a million people who called on them to block this deal, and caved in to lobbying to create a mega-corporation which will dominate our food supply,” Avaaz legal director Nick Flynn said.
Dow-Dupont, ChemChina and Bayer Monsanto have a lot more political influence than a million Europeans, or ten million Americans. They have even convinced numerous, if not most, people that without their products the world would starve. That their chemicals are needed to feed a growing human population. Farming based on algorythms.
They are not ‘seed companies’. They are ‘seeds-that-need-our-chemicals-to-grow’ companies. And they are out to conquer the entire world. A 100-times worse version of Facebook. And our governments subsidize the use of their products. As we not-so-slowly see our living world be massacred by those products.
We don’t know how bad GMOs will turn out to be. Which is in itself a very good reason to ban them. Since once they spread, they can’t be stopped anymore. Then the chemical boys will own all of our food. But we do know how bad the pesticides and other chemicals they produce are. And we’re not even banning those. We just eat all that sh*t and shut up.
It’s a failure to understand what science is: that you must proof harm first before banning stuff. The only real science is the one that has adopted the Precautionary Principle. Because science is supposed to be smart, and there’s nothing smart about destroying your own world. Because science should never be used to hurt people or nature. Science can only be good if it benefits us. Not our wallets, but our heads and hearts and forests, and our children. Do no harm.
Yeah, I know, who am I fooling, right?