DPC Masonic Temple, New Orleans 1910

A theoretical approach to austerity as a creator of poverty.
• Greece: The Economic Consequences of Depression Economics (Prime)
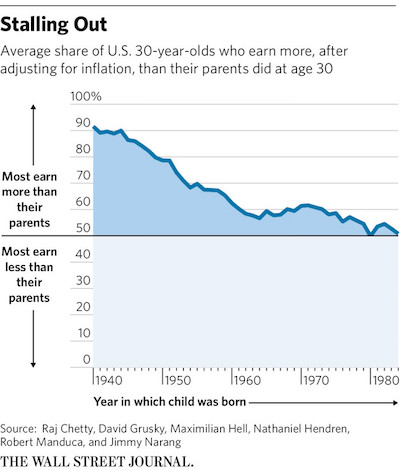
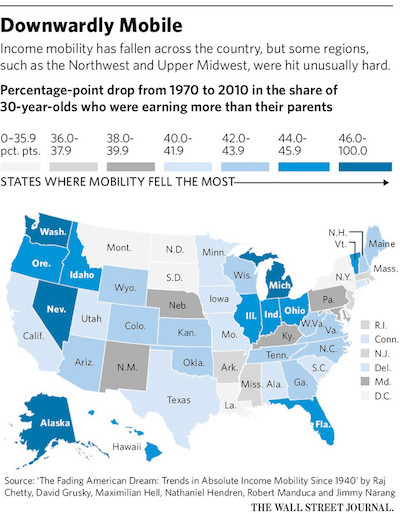
The policy debate in Greece and the EU is burdened with hysteria over the issue of budget deficit and public debt. The proposition is that the less the governments borrow the better and, therefore, the main policy has been to put pressure on the State to curtail as far as possible all capital expenditure, without concern on how productive and desirable that is in itself. The idea is that cuts in government expenditures are not to be used by the government to tax the general population less but to borrow less on the assumption that if the government borrows less the private sector necessarily borrows more, though taxing less the highest rungs of the income distribution might be desirable as it is considered as an incentive to investment.
Second, led by the belief that the main thrust of policy should be internal devaluation, a program of cutbacks in expenditures, decrease in deficits and debts and wage and income restraint is pursued even in a time of recession. The idea is that if producers have reduced costs of production they will produce more and the prices of the produced goods will fall as much as wages. However, as Keynes pointed out that there is no reason to expect that any reduction of purchasing power will be offset by increases in other directions. Certainly, this reduction of purchasing power may cause a reduction of domestic expenditures on imports, which may improve the trade balance. It may also reduce savings, as public employees and others whose salaries are cut and those who lost their jobs may save less or draw on their passed savings to maintain their habitual standard of life.
However, producers will find that the expenditures of consumers (public employees, pensioners, unemployed) are reduced. Consequently, they can only match this reduction of revenue by either cutting down their own expenditure or making redundant some of their employees or both. As a necessary consequence of reduced incomes and profits there should be an increase in unemployment and a decrease in government tax revenues. Importantly, as Keynes noticed, deflation of wages, incomes and prices transfers wealth from the rest of the public to the rentiers and to those who hold titles to money. In effect, internal devaluation redistributes wealth as it transfers money from borrowers to lenders. The real assets in the country constitute the wealth of its citizens. Such real assets are buildings, stocks of commodities, goods in the process of production and the like. As is the usual practice, owners of these assets frequently purchase them by borrowing money.

Don’t forget, it’s not Greece that’s being bailed out.
• After Seven Years Of Bailouts, Greeks Sink Yet Deeper In Poverty (R.)
Greek pensioner Dimitra says she never imagined a life reduced to food handouts: some rice, two bags of pasta, a packet of chickpeas, some dates and a tin of milk for the month. At 73, Dimitra – who herself once helped the hard-up as a Red Cross food server – is among a growing number of Greeks barely getting by. After seven years of bailouts that poured billions of euros into their country, poverty isn’t getting any better; it’s getting worse like nowhere else in the EU. “It had never even crossed my mind,” she said, declining to give her last name because of the stigma still attached to accepting handouts in Greece. “I lived frugally. I’ve never even been on holiday. Nothing, nothing, nothing.” Now more than half of her €332 ($350) monthly income goes to renting a tiny Athens apartment. The rest: bills.
The global financial crisis and its fallout forced four euro zone countries to turn to international lenders. Ireland, Portugal and Cyprus all went through rescues and are back out, their economies growing again. But Greece, the first into a bailout in 2010, has needed three. Rescue funds from the EU and IMF saved Greece from bankruptcy, but the austerity and reform policies the lenders attached as conditions have helped to turn recession into a depression. Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras, whose leftist-led government is lagging in opinion polls, has tried to make the plight of Greeks a rallying cry in the latest round of drawn-out negotiations with the lenders blocking the release of more aid. “We must all be careful towards a country that has been pillaged and people who have made, and are continuing to make, so many sacrifices in the name of Europe,” he said this month.
Much of the vast sums in aid money has simply been in the form of new debt used to repay old borrowings. But regardless of who is to blame for the collapse in living standards, poverty figures from the EU statistics agency are startling. Greece isn’t the poorest member of the EU; poverty rates are higher in Bulgaria and Romania. But Greece isn’t far behind in third place, with Eurostat data showing 22.2% of the population were “severely materially deprived” in 2015. And whereas the figures have dropped sharply in the post-communist Balkan states – by almost a third in Romania’s case – the Greek rate has almost doubled since 2008, the year the global crisis erupted. Overall, the EU level fell from 8.5% to 8.1% over the period. The reality of such statistics becomes clear at places like the food bank run by the Athens municipality where Dimitra collects her monthly handouts.
Here, dozens more Greeks waited solemnly with a ticket in hand to get their share. All are registered as living below the poverty line of about €370 a month. “The needs are huge,” said Eleni Katsouli, a municipal official in charge of the center. Figures for the food bank, which serves central Athens, show a similar trend on a local scale to the wider Eurostat data. About 11,000 families – or 26,000 people – are registered there, up from just 2,500 in 2012 and 6,000 in 2014, Katsouli said. About 5,000 are children.

Delusional theoretics: “..a greater emphasis on growth..”
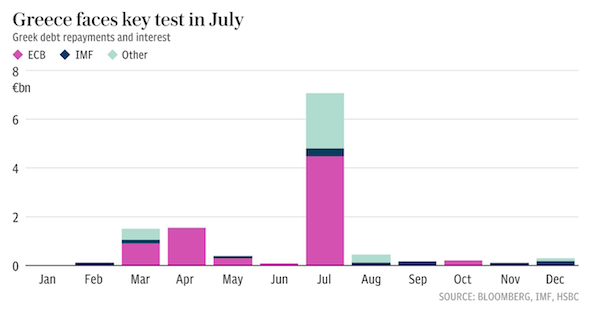
• Greece’s Creditors Dash Hopes For Quick Deal (Tel.)
Greece’s creditors have dashed hopes of a quick resolution to the country’s looming cash crunch, even as talks paved the way for debt inspectors to return to Athens. Jeroen Dijsselbloem, the head of the Eurogroup, told reporters that there had been a “clear shift” in creditor demands following a meeting of finance ministers in Brussels on Monday. Yields on Greek government bonds fell sharply after he announced that representatives from the European Commission and IMF would return to Athens to thrash out an “additional package of structural reforms” to support long term growth and debt sustainability. Greece needs around €7bn in fresh rescue funds before July in order to cover substantial debt repayments to the ECB and private creditors. The Dutch finance minister said new measures would be “designed and agreed on the ground” in Athens, with a greater emphasis on growth.
“At face value, that means less tax rises and spending cuts and deep reforms to the country’s tax system, pensions and labour laws,” Mr Dijsselbloem told reporters. However, he played down reaching a solution before Dutch elections next month or even the French presidential election in May and said creditors were “looking towards the summer” for an agreement. “There is still a lot of work to do, a lot of issues to discuss and calibrate so I want to temper expectations,” he said. “There is no need for a disbursement in March, April or May.” Mr Dijsselbloem also signalled that differences remained between Greece, Brussels and the IMF over the reforms needed to unlock the next loan tranche and secure the institution’s participation in Greece’s third, €86bn rescue package.
Speaking after the meeting, a Greek government official said Athens was prepared to implement reforms beyond 2019. The official added: “The agreement includes the inviolable condition that was set by the Greek side for not even one euro more of austerity.” However, Pierre Moscovici, European Commissioner for economic and financial affairs, signalled that structural reforms, including pension cuts as well as tax and labour reforms would be required before pro-growth measures could be sanctioned. “I think that one word was forgotten [in the Greek official’s statement]. That was ‘net’,” he said.

This one may be hard for Tsipras to explain. What’s the use of red lines if they mean nothing?
• Greek Government In Damage Control Mode After Giving In To Troika, Again (K.)
After the government backed down on its vow not to take new measures at Monday’s Eurogroup, its number one priority now is damage control. In the runup to Monday’s meeting of eurozone finance ministers, Athens had insisted it had drawn its “red lines,” but it left Brussels having promised its EU partners that it will legislate measures after the current bailout program expires in 2018, in exchange for the return of technical experts to Athens in the bid to conclude the second review of the country’s third bailout. Faced with the challenge of explaining its turnaround and agreement to take new measures to an increasingly disillusioned electorate and lawmakers of ruling SYRIZA and Independent Greeks (ANEL), the government is using the term “neutral fiscal balance” in an attempt to sweeten the pill.
According to government sources, the term essentially means that for every euro saved from the new measures, there will be equivalent reductions in value-added, corporate or property taxes. In other words, the government’s narrative is that even though new measures will be implemented, these will be neutral as their burden will be canceled out by tax relief. Senior government officials were also busy laying the groundwork last week, saying that the government may have to accept new measures “for the good of the country” as the protracted negotiations to conclude the review were having a negative impact on the prospects of the country’s economic recovery.

Nice legal twist.
• Mr Draghi, What Are You Afraid Of? Release #TheGreekFiles! (DiEM25)
Deep in a vault in the headquarters of the European Central Bank (ECB) lie #TheGreekFiles, a legal opinion about the ECB’s actions towards Greece in 2015 that could send shockwaves across Europe. As a European taxpayer, you paid for these documents. But the ECB’s boss, ex-Goldman Sachs head Mario Draghi, says you can’t see them. So former Greek Finance Minister Yanis Varoufakis and MEP Fabio de Masi, together with a broad alliance of politicians and academics (below), have announced they will file a mass freedom of information request to the ECB to uncover #TheGreekFiles once and for all. If Mario says no, they’ll take the campaign to the next level, and consider all options – including legal action – to make this vital information public. Support their request to release critical documents you paid for by signing this petition now!
What are #TheGreekFiles? In June 2015, the newly-elected Greek government was locked in tense negotiations with its creditors (the ‘Troika’ – the ECB, EC and IMF), doing what it had been voted in to do: renegotiate the country’s public debt, fiscal policy and reform agenda, and save its people from the hardship of the most crushing austerity programme in modern history. The Troika knew they needed to make a drastic move to force the Greek government to capitulate. And that’s just what they did: through the ECB, they took action to force Greece’s banks to close, ultimately driving the Greek government – against its democratic mandate – to accept the country’s third ‘bailout’, together with new austerity measures and new reductions in national sovereignty.
But in their haste, their zeal to crush the Greek government’s resistance, the ECB feared their actions might be legally dubious. So they commissioned a private law firm to examine whether those decisions were legal. The legal opinion of this law firm is contained in #TheGreekFiles. In July 2015, the German MEP Fabio De Masi asked Mario Draghi to release the legal opinion. Mario refused, hiding behind ‘attorney-client privilege’. Clearly #TheGreekFiles contain something he doesn’t want you to see. One of the foremost experts on European Law, Professor Andreas Fischer-Lescano, examined whether the ECB was right to refuse to release #TheGreekFiles. His detailed conclusion leaves no room for doubt: the ECB has no case for withholding from MEPs and the citizens of Europe the legal opinion the ECB secured (and paid for using your money) regarding its own conduct.

“..lost in a hall of mirrors with the lights off..” Building infrastructure for a world that’s gone, strip malls etc.
• Fumbling Towards Collapse (Jim Kunstler)
[..] the real issue hidden in plain sight is how America — indeed all the so-called “developed” nations — are going to navigate to a stepped-down mode of living, without slip-sliding all the way into a dark age, or something worse. By the way, the Ole Maestro, Alan Greenspan, also chimed in on the “productivity” question last week to equally specious effect in this Business Insider article. None of these celebrated Grand Viziers knows what the fuck he’s talking about, and a nation depending on their guidance will find itself lost in a hall of mirrors with the lights off. So, on one side you have Trump and his trumpets and trumpistas heralding the return of “greatness” (i.e. a booming industrial economy of happy men with lunchboxes) which is not going to happen; and on the other side you have a claque of clueless technocrats who actually believe they can “solve” the productivity problem with measures that really only boil down to different kinds of accounting fraud.
You also have an American public, and a mass media, who do not question the premise of a massive “infrastructure” spending project to re-boot the foundering economy. If you ask what they mean by that, you will learn that they uniformly see rebuilding our highways, bridges, tunnels, and airports. Some rightly suspect that the money for that is not there – or can only be summoned with more accounting fraud (borrowing from our future). But on the whole, most adults of all political stripes in this country think we can and should do this, that it would be a good thing. And what is this infrastructure re-boot in the service of? A living arrangement with no future. A matrix of extreme car dependency that has zero chance of continuing another decade. More WalMarts, Target stores, Taco Bells, muffler shops, McHousing subdivisions, and other accoutrement of our fast-zombifying mode of existence? Isn’t it obvious, even if you never heard of, or don’t understand, the oil quandary, that we have shot our wad with all this? That we have to start down a different path if we intend to remain human?
It’s not hard to describe that waiting world, which I’ve done in a bunch of recent books. We’re going there whether we like it or not. But we can make the journey to it easier or harsher depending on how much we drag our heels getting on with the job. History is pretty unforgiving. Right now, the dynamic I describe is propelling us toward a difficult reckoning, which is very likely to manifest this spring as the political ineptitude of Trump, and the antipathy of his enemies, leaves us in a constitutional maelstrom at the very moment when the financial system comes unglued. Look for the debt ceiling debate and another Federal Reserve interest rate hike to set off the latter. There may be yet another converging layer of tribulation when we start blaming all our problems on Russia, China, Mexico, or some other patsy nation. It’s already obvious that we can depend on the Deep State to rev that up.

US manufacturing is inferior.
• Why Trumponomics Will Fail Spectacularly (Robert Reich)
When Donald Trump gave a speech last Friday at Boeing’s factory in North Charleston, South Carolina – unveiling Boeing’s new 787 “Dreamliner” – he congratulated Boeing for building the plane “right here” in South Carolina. It’s pure fantasy. I’ll let you know why in a moment. Trump also used the occasion to tout his “America First” economics, stating “our goal as a nation must be to rely less on imports and more on products made here in the U.S.A.” and “we want products made by our workers in our factories stamped by those four magnificent words, ‘Made in the U.S.A.’” To achieve this goal Trump would impose “a very substantial penalty” on companies that fired their workers and moved to another country to make a product, and then tried to sell it back to America. The carrot would be lower taxes and fewer regulations “that send our jobs to those other countries.” Trump seems utterly ignorant about global competition – and about what’s really holding back American workers.
Start with Boeing’s Dreamliner itself. It’s not “made in the U.S.A..” It’s assembled in the United States. But most of it parts come from overseas. Those foreign parts total almost a third of the cost of the entire plane. For example: The Italian firm Alenia Aeronautica makes the center fuselage and horizontal stabilizers. The French firm Messier-Dowty makes the aircraft’s landing gears and doors. The German firm Diehl Luftfahrt Elektronik supplies the main cabin lighting. The Swedish firm Saab Aerostructures makes the cargo access doors. The Japanese company Jamco makes parts for the lavatories, flight deck interiors and galleys. The French firm Thales makes its electrical power conversion system. Thales selected GS Yuasa, a Japanese firm, in 2005 to supply it with the system’s lithium-ion batteries. The British company Rolls Royce makes many of the engines. A Canadian firm makes the moveable trailing edge of the wings.
Notably, these companies don’t pay their workers low wages. In fact, when you add in the value of health and pension benefits – either directly from these companies to their workers, or in the form of public benefits to which the companies contribute – most of these foreign workers get a better deal than do Boeing’s workers. (The average wage for Boeing production and maintenance workers in South Carolina is $20.59 per hour, or $42,827 a year.) They also get more paid vacation days. These nations also provide most young people with excellent educations and technical training. They continuously upgrade the skills of their workers. And they offer universally-available health care. To pay for all this, these countries also impose higher tax rates on their corporations and wealthy individuals than does the United States. And their health, safety, environmental, and labor regulations are stricter.
Not incidentally, they have stronger unions. So why is so much of Boeing’s Dreamliner coming from these high-wage, high-tax, high-cost places?

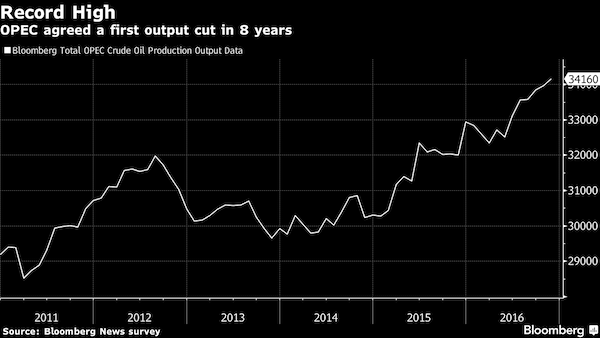
Yeah, big cuts, remember?
• Saudi Arabia Breaks Records on Oil Exports and Output for (BBG)
Saudi Arabia boosted oil exports and production last year to the highest monthly averages on record as the global crude market endured oversupply. Exports climbed to 7.65 million barrels a day on average last year, from 7.39 million barrels a day a year earlier, according to Joint Organisations Data Initiative monthly data compiled by Bloomberg. Production rose to 10.46 million barrels a day from 10.19 million, on average, over the same period. Saudi Arabia led the push by global producers to end a crude glut by cutting output as of Jan. 1. JODI data indicate that the kingdom’s exports surged to more than 8 million barrels a day in November and December right before the cuts were due to start. Shipments in November were the highest since May 2003, JODI data show.
“Whenever there was no agreement with others, Saudi Arabia was running after expanding its market share,” said Mohamed Ramady, an independent analyst in London. Saudi Arabia pumped 10.2 million barrels to 10.67 million barrels a day in the first 10 months as producers discussed output cuts without making an agreement. It reined in production in January following the deal between the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries and non-OPEC nations to reduce output by 1.8 million barrels a day, according to data compiled by Bloomberg.

This is just a part of the shadow banking sector, the part that’s held by official banks.
• Chinese Banks’ Off-Book Wealth Products Exceed $3.8 Trillion (BBG)
Chinese banks had more than 26 trillion yuan ($3.8 trillion) of wealth-management products held off their balance sheets at the end of December, a 30% increase from a year earlier, according to the central bank. The expansion of this form of shadow banking, with money eventually being diverted to quasi-loans and bonds, outpaced the 10% growth for normal lending during the same period, raising risks for the broader economy and undermining the country’s “deleveraging” efforts, the People’s Bank of China said Friday in its quarterly monetary policy report. The central bank is including off-balance sheet WMPs in its so-called macro prudential assessment framework starting this quarter to better gauge the expansion of credit and potential risks in the financial system.
The move will probably lead to banks reporting higher credit growth and may require them to take steps to maintain sufficient capital reserves to limit risks posed by the investment products. Since late 2014, the China Banking Regulatory Commission has been tightening rules on WMPs, most of which are non-principal guaranteed, meaning they can reside off banks’ balance sheets. The products are a key reason behind the growth of shadow banking in China, and have been used by some financial institutions as a way to extend funds to risky borrowers and evade capital requirements. The investment vehicles are asset-management products by nature and therefore investors should shoulder any risks by themselves, the central bank said in its report. More work is needed to solve problems such as the real amount of capital banks should hold to cover WMPs, risk segmentation, regulatory arbitrage, and the perception of an implicit guarantee of repayment, the PBOC said.

Tax addiction.
• Why Toronto (and Other Cities) Inflate Housing Bubbles to the Bitter End (WS)
“Let’s drop the pretense. The Toronto housing market and the many cities surrounding it are in a housing bubble,” Bank of Montreal (BMO) Chief Economist Doug Porter told clients in a note last week. Many have called it “housing bubble” for a while, but now it’s official, according to BMO. In January, the benchmark price and the average price were both up 22% year-over-year, with the average price of detached homes up 26%, of semi-detached homes 28%, of townhouses 27%, and of condos 15%. Double-digit price increases have become the rule in recent years. But this jump was “the fastest increase since the late 1980s – a period pretty much everyone can agree was a true bubble – and a cool 21 percentage points faster than inflation and/or wage growth,” Porter explained in his note, cited by BNN.
Home prices in Greater Toronto have become “dangerously detached” from economic fundamentals and are soaring simply on the belief that they will continue to soar, he wrote. “The market is far too hot for comfort.” BNN: “The often-cited mantra that Toronto’s real estate market is being driven largely by a lack of supply is wearing thin, he argues. Housing starts in Toronto and Vancouver recently hit an all-time high of 70,000 units per year and overall Canadian starts are above demographic demand at 200,000 units in the past year, according to BMO.” The “massive price gains” are not driven by lack of supply, but “first and foremost by sizzling hot demand, whether from ultra-low interest rates (negative in real terms), robust population growth, or non-resident investor demand.”
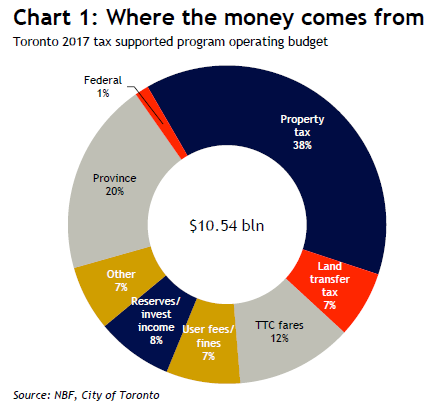
“Toronto and any city that is remotely within commuting distance are overheating, and perhaps dangerously so,” he said. But don’t expect the city of Toronto to do anything other than inflate the bubble further. It has to – unless it wants to fall into a fiscal and financial sinkhole. This became apparent last week, when the city councilors approved Toronto’s operating and capital budgets. What a mess!
The tax-supported operating budget is now expected to grow by 4.4% in 2017, to C$10.5 billion. So more taxes must be extracted from the hapless folks in Toronto. Among sundry fees, taxes, and levies, the councilors approved a 3.29% increase in the residential property tax and raised the municipal land transfer tax. Under the new budget, property taxes would provide 38% of the revenues, and the land transfer tax 7%, for a total of 45% of the C$10.5 billion in taxes, or C$4.7 billion. Just how dependent the funding for Toronto’s ballooning operating budget has become on the house price bubble – and the property-related taxes it generates – is made clear in this chart by Warren Lovely, Head of Public Sector Research & Strategy at National Bank Financial, Toronto:

A most curious difference.
• Refugee Claimants From US Strain Canada’s Border Resources (R.)
Canadian police said on Monday they had bolstered their presence at the Quebec border and that border authorities had created a temporary refugee center to process a growing number of asylum seekers crossing from the United States. The Canada Border Services Agency, or CBSA, said at a news conference that it had converted an unused basement into a refugee claimant processing center. Both the border agency and the Royal Canadian Mounted Police are reassigning staff from other locations in the province, as needed, to accommodate rising demand. The CBSA said the number of people making refugee claims at Quebec-U.S. border crossings more than doubled from 2015 to 2016. Last month, 452 people made claims in Quebec compared with 137 in January 2016, the agency said.
The influx is straining police, federal government and community resources from the western prairie province of Manitoba, where people arrive frostbitten from hours walking in freezing conditions, to Quebec, where cabs drop asylum seekers off meters away from the Quebec-U.S.border, the border agency said. A Reuters reporter on Monday saw RCMP officers take in for questioning a family of four – two men, a woman and a baby in a car seat – who had walked across the snowy gully dividing Roxham Road in Champlain, New York, from Chemin Roxham in Hemmingford, Quebec. “Please explain to her that she’s in Canada,” one Canadian officer told another officer.
Police take people crossing the border in for questioning at the border agency’s office in Lacolle, Quebec, which is the province’s biggest and busiest border crossing. Police identify them and ensure they are not a threat or carrying contraband. They are then transferred to the CBSA for fingerprinting and further questions. If people are deemed a threat or flight risk, they are detained. If not, they can file refugee claims and live in Canada while they wait for a decision “It’s touching, and we are not insensitive to that,” Bryan Byrne, the RCMP’s Champlain Detachment commander, told reporters near the border. “Some of these people had a long journey. Some are not dressed for the climate here.”
Asylum seekers cross illegally because Canada’s policy under the Canada-U.S. Safe Third Country Agreement is to turn back refugees if they make claims at border crossings. But as U.S. President Donald Trump cracks down on illegal immigrants, Amnesty International and refugee advocacy groups are pressuring the Canadian government to abandon the agreement, arguing the United States is no safe haven. On Monday, Montreal, Canada’s second most populous city, voted to declare itself a “sanctuary city,” making it the fourth Canadian city to protect illegal immigrants and to provide services to them.

European governments criticizing Trump’s refugee policies have no credibility. But the people still can.
• ‘Casa Nostra, Casa Vostra’ (K.)
Thousands of people marched through the streets of downtown Barcelona on Saturday shouting the slogan “Casa nostra, casa vostra” (Our home, your home). Barcelona had prepared its plan for welcoming Syrian and Iraqi refugees back in September 2015. It put its municipal services on standby and organized an army of volunteers, whose generosity inspired residents in Madrid and Valencia to open their own cities to refugees. In the meantime, much of the rest of Europe was busy building walls, fencing itself in, warding inflows off, hardening its laws and ignoring not just the plight of the refugees themselves, but also the difficulties faced by Greece and Italy, Lesvos and Lampedusa. This amazing show of solidarity – not rhetorical but actual and tangible – from the Catalans convinced the Spanish government to raise its commitment for taking in refugees trapped in Greece and Italy from the 2,749 it had initially agreed to up to 17,680.
But numbers often suffer the same fate as words, dying out without leaving a single political or moral trace. Up until February 2016, just 18 refugees had been relocated to Spain, a number that makes sense when you consider that of the 160,000 relocations agreed on by the countries of the European Union, just 600 had actually taken place by that time. This failure to live up to commitments prompted Barcelona Mayor Ada Colau at this precise time last year to lash out against the Spanish government and the strategy centers in Brussels, which seem happy to confine their action to the deal made between the European Union and Turkey, even though this has been condemned by every respected humanitarian organization.
Colau’s protests fell on deaf ears, so on August 1, 2016, authorities in Barcelona placed a “counter of shame” on the city’s most popular beach, recording daily how many people are lost at sea in their effort to escape war or extreme poverty. We don’t know whether the counter triggered any feelings of guilt, but it certainly failed to awaken any sense of responsibility. When it was inaugurated, the number of victims stood at 3,034. By the end of the year, and according to official data from Europe, ever the passive observer, this surpassed 5,000. And as far as relocations to Spain go, these barely came to more than 1,000 last year. This, in general terms, is the background of that very encouraging rally we saw in Barcelona on Saturday. Whether the people who took to the streets were motived by their feelings or by their ideological beliefs is a question that only means something to those who think ideology is a fixation and feelings a sign of immaturity.