Fred Stein Chinatown 1944

And here we are: The WaPo, left with almost zero credibility after so many anti-Trump and anti-Russia opinions more often than not disguised as factual reports, can only find a willing ear anymore inside its echo chamber. As usual, the WaPo article is based on anonymous sources. America is trapped inside it own narrative.
• White House: Report Trump Shared Classified Info With Russians is ‘False’ (RT)
Multiple White House officials, including National Security Advisor H.R. McMaster, are refuting a Washington Post story claiming that President Donald Trump revealed highly classified information to Russian officials in the Oval Office last week. But some believe McMaster’s statement contained holes. On Monday evening, National Security Advisor McMaster called a report published earlier in the day by the Washington Post “false.” The report that went viral cited unverifiable sources, unnamed current and former US officials, who claimed that Trump disclosed to Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov and Ambassador to the US Sergey Kislyak “code-word information” relating to Islamic State during a May 10 meeting in the Oval Office at the White House.
The intelligence was reportedly from “a US partner through an intelligence-sharing arrangement” and not authorized to be shared with Russia, US allies or even within much of the US government. “I was in the room. It didn’t happen,” McMaster told reporters outside the White House. Deputy National Security Adviser Dina Powell also called the story “false” Monday. “The president only discussed the common threats that both countries faced,” Powell said. Secretary of State Rex Tillerson, who was also at the meeting, denied the allegation. McMaster told reporters that Trump did discuss civil aviation threats with Lavrov and Kislyak. [..] The Russian Embassy in DC had no comment on the media claim, according to a representative.

Besides, the WaPo article doesn’t describe anything illegal. But it’ll take a while before that sinks in, if ever.
• Trump’s Classified Disclosure Is Shocking But Legal (BBG)
Oh for the days when Donald Trump wasn’t taking the presidential daily brief – and didn’t know highly classified information that he could give to the Russians. But a bit bizarrely, Trump’s reported disclosure of Islamic State plans to two Russian officials during an Oval Office visit last week wasn’t illegal. If anyone else in the government, except possibly the vice president, had revealed such classified information that person would be going to prison. The president, however, has inherent constitutional authority to declassify information at will. And that means the federal laws that criminalize the disclosure of classified secrets don’t apply to him. If this doesn’t make much sense to you, I feel your pain.
To understand the legal structure of classification and declassification requires a brief journey into the constitutional law of separation of powers. That’s not always especially fun. But at this juncture in U.S. history, it’s essential. Not since Richard Nixon’s administration has separation of powers been so central to the fate of the republic. The authority to label facts or documents as classified rests with the president in his capacity as a commander in chief. Or at least that’s what the U.S. Supreme Court said in a 1988 case, Department of the Navy v. Egan. Justice Harry Blackmun, who wrote the opinion, said that the executive’s “authority to classify and control access to information bearing on national security … flows primarily from this constitutional investment of power in the President and exists quite apart from any explicit congressional grant.”
Blackmun’s idea that the president has an inherent right to decide who gets access to classified information seems to imply the converse: that the president has the inherent authority to declassify information, too. Although there’s no case on this point, scholars took that view during the years of the George W. Bush administration, when the president was thought to have declassified some information that was leaked to the news media by White House aide I. Lewis “Scooter” Libby. It makes sense. If it is up to the president to decide what can’t be disclosed, it should be up to him to decide what can be.
[..] If you’re following closely, you’ll have noticed an anomaly: The president can classify and declassify. But the president can’t send people to prison for disobeying his order. That requires a federal law passed by Congress, and a conviction before a judge. Thus, under the separation of powers, the president has inherent authority to fire his own employees for disclosing classified information, but lacks the power to punish them criminally without Congress and the courts. That law exists: 18 U.S. Code Section 798, if you care to look it up. It makes it a federal crime to communicate “classified information” to an “unauthorized person.” The catch is that the law defines classified information as information determined classified by a U.S. government agency, and similarly defines an unauthorized person as someone not determined authorized by the executive branch. That puts Trump in the clear insofar as he has an inherent authority to declare information unclassified.

And Robert Parry can tell you why things like that WaPo ‘report’ get so blown up.
• The ‘Soft Coup’ of Russia-Gate (Robert Parry)
I realize that many Democrats, liberals and progressives hate Donald Trump so much that they believe that any pretext is justified in taking him down, even if that plays into the hands of the neoconservatives and other warmongers. Many people who detest Trump view Russia-gate as the most likely path to achieve Trump’s impeachment, so this desirable end justifies whatever means. Some people have told me that they even believe that it is the responsibility of the major news media, the law enforcement and intelligence communities, and members of Congress to engage in a “soft coup” against Trump – also known as a “constitutional coup” or “deep state coup” – for the “good of the country.”
The argument is that it sometimes falls to these Establishment institutions to “correct” a mistake made by the American voters, in this case, the election of a largely unqualified individual as U.S. president. It is even viewed by some anti-Trump activists as a responsibility of “responsible” journalists, government officials and others to play this “guardian” role, to not simply “resist” Trump but to remove him. There are obvious counter-arguments to this view, particularly that it makes something of a sham of American democracy. It also imposes on journalists a need to violate the ethical responsibility to provide objective reporting, not taking sides in political disputes. But The New York Times and The Washington Post, in particular, have made it clear that they view Trump as a clear and present danger to the American system and thus have cast aside any pretense of neutrality.
The Times justifies its open hostility to the President as part of its duty to protect “the truth”; the Post has adopted a slogan aimed at Trump, “Democracy Dies in Darkness.” In other words, America’s two most influential political newspapers are effectively pushing for a “soft coup” under the guise of defending “democracy” and “truth.” But the obvious problem with a “soft coup” is that America’s democratic process, as imperfect as it has been and still is, has held this diverse country together since 1788 with the notable exception of the Civil War. If Americans believe that the Washington elites are removing an elected president – even one as buffoonish as Donald Trump – it could tear apart the fabric of national unity, which is already under extraordinary stress from intense partisanship.
That means that the “soft coup” would have to be carried out under the guise of a serious investigation into something grave enough to justify the President’s removal, a removal that could be accomplished by congressional impeachment, his forced resignation, or the application of Twenty-fifth Amendment, which allows the Vice President and a majority of the Cabinet to judge a President incapable of continuing in office. That is where Russia-gate comes in. The gauzy allegation that Trump and/or his advisers somehow colluded with Russian intelligence officials to rig the 2016 election would probably clear the threshold for an extreme action like removing a President. And, given the determination of many key figures in the Establishment to get rid of Trump, it should come as no surprise that no one seems to care that no actual government-verified evidence has been revealed publicly to support any of the Russia-gate allegations.

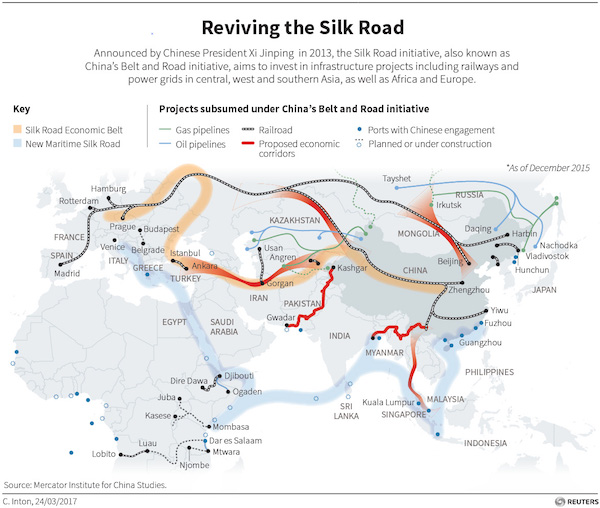
China wants to own the new Silk Road, and to be the leader. The original one knew neither ownership nor leadership.
• China’s Silk Road Vision: Cheap Funds, Heavy Debt, Growing Risk (R.)
Behind China’s trillion-dollar effort to build a modern Silk Road is a lending program of unprecedented breadth, one that will help build ports, roads and rail links, but could also leave some banks and many countries with quite a hangover. At the heart of that splurge are China’s two policy lenders, China Development Bank (CDB) and Export-Import Bank of China (EXIM), which have between them already provided $200 billion in loans throughout Asia, the Middle East and even Africa. They are due to extend at least $55 billion more, according to announcements made during a lavish two-day Belt and Road summit in Beijing, which ends on Monday. Thanks to cheaper funding, CDB and EXIM have helped to unblock what Chinese president Xi Jinping on Sunday called a ‘prominent challenge’ to the Silk Road: the funding bottleneck.
But as the Belt and Road project grows, so do the risks to policy banks, commercial lenders and borrowers, all of whom are tangled in projects with questionable business logic, bankers and analysts say. EXIM, seeking to contain risk, says it has imposed a debt ceiling for each country. CDB says it has applied strict limits on sovereign borrowers’ credit lines and controls the concentration of loans. “For some countries, if we give them too many loans, too much debt, then the sustainability of its debt is questionable,” Sun Ping, vice governor of EXIM, told reporters last week. For now, funds are cheap and plentiful, thanks to Beijing. Belt and Road infrastructure loans so far have been primarily negotiated government to government, with interest rates below those offered by commercial banks and extended repayment schedules, bankers and analysts said.
[..] 47 of China’s 102 central-government-owned conglomerates participated in 1,676 Belt and Road projects, according to government statistics. China Communications Construction alone has notched up $40 billion of contracts and built 10,320 kilometres of road, 95 deepwater ports, 10 airports, 152 bridges and 2,080 railways in Belt and Road countries. China’s central bank governor Zhou Xiaochuan is among those to warn that this reliance on cheap loans raises “risks and problems”, starting with moral hazard and unsustainability. China has been caught out before; it is owed $65 billion by Venezuela, now torn by crisis. “The jurisdictions where many of these loans are going are places that would have difficulty getting loans from Western commercial banks – their credit ratings are not very good, or the projects in question often are not commercially viable,” said Jack Yuan at Fitch in Shanghai. “The broader concern is that capital continues to be mis-allocated by Chinese banks.”

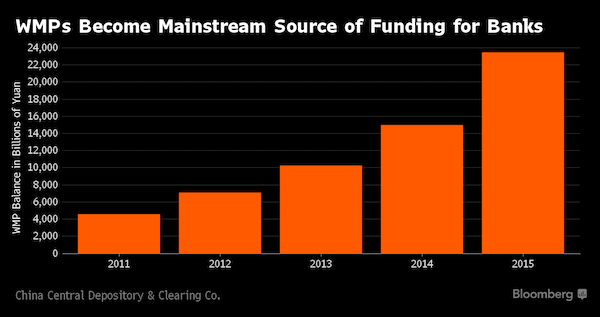
We’ll believe it when the bankruptcies start accumulating.
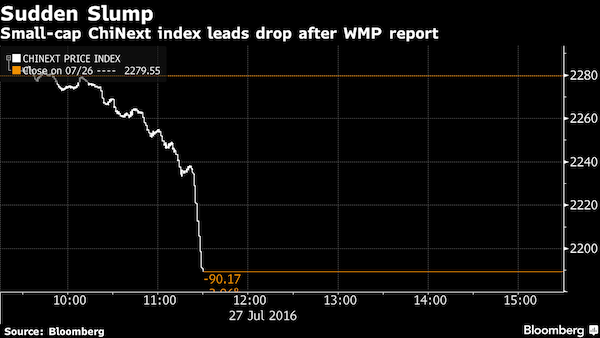
• China Banking Regulator Tightens Rules On WMPs, Flags More Curbs (R.)
China’s banking regulator is tightening disclosure rules on lenders’ wealth management products (WMP) as it tries to track risky lending practices in the shadow banking sector, the latest in a series of steps by Beijing aimed at defusing financial risks. The China Banking Regulatory Commission (CBRC) said in a notice late on Monday it plans to launch 46 new or revised rules this year, part of which targets risks related to shadowbanking activities. Authorities are trying to better regulate 30 trillion yuan ($4.35 trillion) of WMPs, much of it sitting off-balance sheet in the shadowbanking sector. The WMPS have been used to channel deposits into risky investments, often via many layers of asset management schemes to skirt lending and capital rules.
The CBRC will now require that banks report the underlying assets and liabilities of their WMPs, as well as all layers of investment schemes, on a weekly basis. Previously, banks were required to hand in less detailed information, and on a monthly basis. The new rules – published by a WMP management platform under CBRC – reflect regulators’ desire to have a full picture of banks’ activities, and could slow the growth of WMPs. In March, China’s newly appointment banking regulator Guo Shuqing, vowed to strengthen supervision of the lending sector, underscoring Beijing’s determination to fend off financial risks and push reforms this year. Separately, CBRC unveiled a long list of rules it aims to publish this year, many of these related to risk-management. The rules are to “ensure that (risk) does not become systemic,” CBRC said.

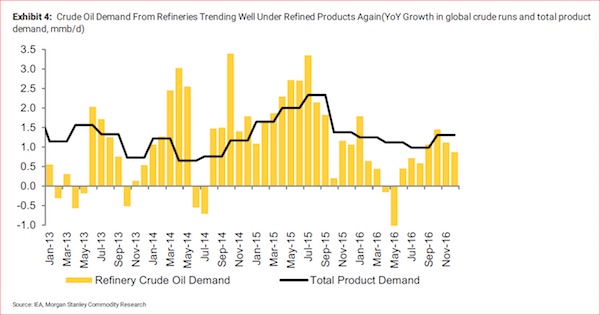
Useless numbers from Goldman Sachs.
• New Zealand Housing Market Most at Risk of Bust – Goldman (BBG)
New Zealand’s housing market is the most over-valued among the so-called G-10 economies and the most at risk of a correction, according to Goldman Sachs. In research published this week, the investment bank said there is about a 40% chance of a housing “bust” in New Zealand over the next two years, which it defines as house prices falling 5% or more after adjustment for inflation. The report looks at housing markets in the G-10 countries – those with the 10 most-traded currencies in the world – and finds they are most elevated in small, open economies such as New Zealand, where house prices have rocketed in recent years. In Auckland, the nation’s largest city, the average price has surged 91% since 2007 to more than NZ$1 million ($688,000).
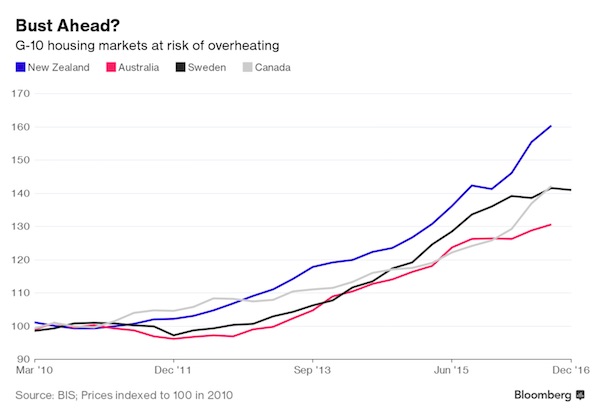
Goldman compares house-price levels across economies using three standard metrics: the ratio of house prices to rent, the ratio of house prices to household income and house prices adjusted for inflation. “Using an average of these measures, house prices in New Zealand appear the most over-valued, followed by Canada, Sweden, Australia and Norway,” it said. “According to the model, the probability of a housing bust over the next five to eight quarters is the highest in Sweden and New Zealand at 35 to 40%.” A graph in the report shows that New Zealand’s probability of a housing bust is just above 40%, while Sweden’s is just above 35%. The risk of a bust in Australia is about 25%.

Chelsea Manning is free as of tomorrow.
• Snowden & Chomsky Lead Calls To Drop DOJ Case Against WikiLeaks (RT)
Former intelligence officers, journalists and artists are among more than 100 signatories of an open letter calling on President Trump to close the Grand Jury investigation into WikiLeaks and drop any planned charges against the whistleblower group.
The letter released Monday by the Courage Foundation includes NSA whistleblower Edward Snowden and renowned scholar and activist Noah Chomsky among the original signatories. A significant number of former personnel from US intelligence agencies are backing the letter. Among them are former senior NSA officials Thomas Drake, William Binney and Kirk Wiebe. Daniel Ellsberg, the former State and Defense Department official who released top secret Pentagon Papers in 1971 and retired FBI Special Agent and former Minneapolis Division Legal Counsel Coleen Rowley also signed the letter.The plea to President Trump is in response to comments made by US Attorney General Jeff Sessions last month, in which he confirmed that the arrest of WikiLeaks founder Julian Assange was a “priority” for the US government. Fears are growing that charges including conspiracy, theft of government property and violating the Espionage Act are being considered against members of WikiLeaks. Several artists are also pushing the call for Trump to drop any proposed charges against the whistleblower organization. Among the big names are Oliver Stone, Ken Loach, Pamela Anderson, Patti Smith, PJ Harvey and Vivienne Westwood.
The letter acknowledges that the Obama administration prosecuted more whistleblowers than all previous presidents combined and opened a Grand Jury investigation into WikiLeaks that had no precedent. “It now appears the US is preparing to take the next step — prosecuting publishers who provide the “currency” of free speech, to paraphrase Thomas Jefferson,” the document states. “A threat to WikiLeaks’ work — which is publishing information protected under the First Amendment — is a threat to all free journalism. If the DOJ is able to convict a publisher for its journalistic work, all free journalism can be criminalized.”

They know something you don’t.
• Large Hedge Funds Moved Out Of Financial Stocks In First Quarter (R.)
Several big-name hedge fund investors trimmed their stakes in financial companies in the first quarter as hopes for immediate tax cuts and loosening of regulations after President Donald Trump’s victory in November began to fade. Adage Capital Management cut its position in Wells Fargo, which has come under fire for its sales practices, by 3.9 million shares, according to regulatory filings, while John Burbank’s Passport Capital cut its stake in the company by 947,000 shares. Third Point cut its stake in JPMorgan Chase by 28%, to 3.75 million shares, while Suvretta Capital Management sold all of its shares of Morgan Stanley, JPMorgan and Citigroup. Overall, financial companies in the S&P 500 were up 2.1% in the first quarter, compared with 5.5% for the index as a whole.
Financials significantly outperformed the broad market following Trump’s Nov. 8 election. Trump had pledged to do a “big number” on the landmark Dodd-Frank financial reform law, which raised banks’ capital requirements and restricted their ability to make speculative bets with customers’ money. The Treasury Department is still filling vacancies and will not be able to complete a review of the law by Trump’s June deadline, sources told Reuters. Quarterly disclosures of hedge fund managers’ stock holdings, in what are known as 13F filings with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, are one of the few public ways of tracking what the managers are selling and buying. But relying on the filings to develop an investment strategy comes with some risk because the disclosures come out 45 days after the end of each quarter and may not reflect current positions.

Lean and efficient, and losing sales.
• Ford To Cut North America, Asia Salaried Workers By 10% (R.)
Ford plans to shrink its salaried workforce in North America and Asia by about 10% as it works to boost profits and its sliding stock price, a source familiar with the plan told Reuters on Monday. A person briefed on the plan said Ford plans to offer generous early retirement incentives to reduce its salaried headcount by Oct. 1, but does not plan cuts to its hourly workforce or its production. The move could put the U.S. automaker on a collision course with President Donald Trump, who has made boosting auto employment a top priority. Ford has about 30,000 salaried workers in the United States.
The cuts are part of a previously announced plan to slash costs by $3 billion, the person said, as U.S. new vehicles auto sales have shown signs of decline after seven years of consecutive growth since the end of the Great Recession. The Wall Street Journal reported Monday evening that Ford plans to cut 10% of its 200,000-person global workforce, but the person briefed on the plan disputed that figure. The source requested anonymity in order to be able to discuss the matter freely. Ford declined to comment on any job cuts but said it remains focused on its core strategies to “drive profitable growth”. “Reducing costs and becoming as lean and efficient as possible also remain part of that work,” it said in a statement. “We have not announced any new people efficiency actions, nor do we comment on speculation.”

FEMA rules!
• How High Should Congress Let Flood Insurance Rates Rise? (USAT)
Congress is considering dramatic changes to the National Flood Insurance Program, which has a $25 billion debt that its director says cannot be repaid. But as a Sept. 30 deadline looms for the program to be renewed, disagreements remain over how much homeowners should be forced to pay for flood insurance to make the program more solvent. If Congress can’t reach an agreement, a lapse in the Federal Emergency Management Agency’s legal authority to write new policies could disrupt real estate sales in flood-prone areas around the country.
Republican Sen. Bill Cassidy of Louisiana and Democratic Sen. Kirsten Gillibrand of New York are circulating draft legislation to renew the program, but it contains provisions – such as vouchers to help low-income homeowners keep the cost of premiums and fees from getting too high — that are not in a draft that Republicans on the House Financial Services Committee plan to release this week. Disputes also remain over how to address wrongdoing by insurance companies and affiliated contractors in the wake of Superstorm Sandy and last year’s floods in Louisiana, and whether older properties that flood repeatedly should still receive discounts. Many in Congress also want to encourage more private insurers to enter the market, but some warn the government could be left with only the riskiest properties.

Macron has to focus on France. and will do so until well after Merkel is re-elected. Still, these new views could have prevented Brexit.
• Macron Wins Merkel Backing For Bid To Shake Up Europe (AFP)
France’s new President Emmanuel Macron secured backing Monday from key ally Chancellor Angela Merkel for his bid to shake up Europe, despite scepticism in Berlin over his proposed reforms. Travelling to the German capital to meet the veteran leader in his first official trip abroad, Macron used the opportunity to call for a “historic reconstruction” of Europe. During his campaign, Macron had thrown up ideas on reforming the eurozone, noting that the currency bloc cannot go on as it is if it wanted to avoid falling prey to protest and populism. Among reforms he wants to see are setting up a separate budget for the 28-member group, as well as giving it its own parliament and finance minister. But the proposals have sent alarm bells ringing in Berlin, and initial relief about his victory against far-right leader Marine Le Pen had quickly given way to fears about his reform plans.
Finance Minister Wolfgang Schaeuble warned that such deep-reaching reforms would require treaty changes, which were “not realistic” at a time when Europe is hit by a surge of anti-euro populism. Saturday’s edition of weekly news magazine Der Spiegel featured a cover picture of Macron with the headline “expensive friend”. But at a joint press conference following their talks, Merkel adopted a conciliatory tone and offered what appeared to be a key concession. “From the German point of view, it’s possible to change the treaty if it makes sense,” she said. “If we can say why, what for, what the point is, then Germany will be ready.” Merkel’s approach underlined her view that it was crucial not only for France, but for Germany, to help Macron succeed – a point that she has repeatedly stressed.
Yet it remains to be seen if her approach would go down well in Germany, which is deeply adverse to shouldering burdens of eurozone laggards. Macron sought to bat away German fears on debt, saying he was opposed to mutualising “old debt” between eurozone countries. However, he signalled readiness to look at sharing future burdens. “I am not a promoter of the mutualisation of old debt” within the eurozone, said Macron after meeting Merkel, adding however that the joint financing of future projects should be considered. Underlining the concerns over Macron’s proposals, Germany’s biggest selling daily Bild warned ahead of the French leader’s meeting with Merkel that before seeking deeper EU integration, “France must once again be at the same level as Germany politically and economically”. “Only then can the EU be reformed or develop deeper integration,” it said.

Ye olde ‘there is stil time’ delusion: there is still time to make Germany change its stance on the EU, in the same way that there is still time to save the planet. No, there isn’t, if you include the time it will take to turn around what has been the ‘normal’. You need a revolution, not a change.
• Germany Must Decide: Budget Rigour Or Europe’s Future (R.)
After Emmanuel Macron’s victory in France’s presidential election, Germany must decide whether it wants to continue its single-minded focus on budget rigour or work with him to ensure the future of the European project, a German diplomat said. In an interview with Reuters hours before the new French president travels to Berlin to meet Chancellor Angela Merkel, Wolfgang Ischinger, chairman of the Munich Security Conference, pushed back against German politicians who have picked holes in Macron’s ideas for Europe since his election win. Among those are Finance Minister Wolfgang Schaeuble, who has come to personify Berlin’s focus on the “Schwarze Null”, or balanced budget. He has suggested Macron’s plans to create a budget and finance minister for the euro zone are unrealistic.
“My wish is that this issue is not used in the (German) election campaign, but that we have a serious discussion over the question: ‘What is more important to us? The Schwarze Null as a categoric imperative or the future of Europe?'” Ischinger said. “If compromises are necessary and make sense, then I would support compromise rather than categorical imperatives.” Mainstream parties in Germany applauded Macron’s victory over far-right leader Marine Le Pen earlier this month. But since then, conservative politicians and media have criticized his plans, suggesting they would lead to a “transfer union” in which German money would be used to pay for uncompetitive member states that are reluctant to reform. Schaeuble has suggested some of Macron’s more ambitious plans would require politically thorny changes to the EU treaty. But Ischinger, a former German ambassador to Britain and the United States, said much could be done on an intergovernmental basis.

The illusion that the ECB can manage the EU economy.
• The Euro Area – A Simple Model Of Savings, Debt & Private Spending (Terzi)
In 2010, with the first casualty (Greece) in the emergency room and the first economic adjustment programme (with financial package) approved, the Eurosystem eventually became an occasional buyer of government debt. Two years later, with three more casualties (Ireland, Portugal, and Spain) and a systemic collapse in sight, the ECB added the newly crafted Outright Monetary Transactions (OMT) to its toolbox. This meant that the ECB had formally become ready to be an unlimited, albeit conditional, outright buyer in the secondary market for Eurozone government debts. The introduction of OMTs was the way to restore systemic liquidity buffers in a monetary system that had become unsustainable, while remaining consistent with the monetary financing prohibition laid down in the Treaty.
As events during the crisis unfolded, and depending on the narrative about its causes, several different meanings have been attached to the notion of the Eurozone crisis. This has been seen, alternatively, as the unwinding of intra-euro lending and borrowing, the consequence of private credit bubbles, the product of unsustainable public debt, the failure of inadequately supervised banking and financial institutions, and, most notably, as a double-dip recession followed by an unusually weak expansion combined with a visibly inadequate policy (and political) response. Today, six years after the crisis erupted, and notwithstanding the modified ECB practice that saved the day, the Eurozone is still visibly failing to enact sustainable policies that can effectively restore economic prosperity.
Accordingly, there have been two distinct phases in the Eurozone crisis. Between 2010 and 2012 the monetary union was in jeopardy of undergoing an operational breakdown up until the change in the operational practice in the market for public sector securities, complemented by the banking union reform. Since 2012, the problems have been the continuing sluggishness of the real economy, the acute lack of demand, vulnerability to internal and external shocks, and, ultimately, the risk of a political implosion. While the ECB has successfully reclaimed one indispensable tool to operationally manage the euro, the deflationary bias of the euro area has not gone away. Effectively, Europe’s economic performance has been vastly disappointing ever since the launch of the euro.

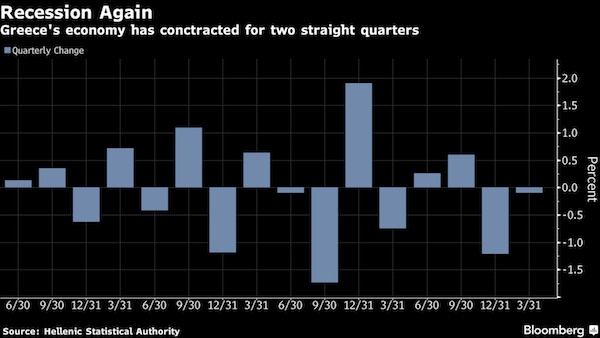
Greece has no way to escape recession, drawn out talks have nothing to do with it.
• Greek Economy Pays for Drawn-Out Talks With Return to Recession (BBG)
Greece’s economy returned to recession in the first quarter as delays in concluding talks between the government and its creditors raised the specter of another debt drama. GDP contracted 0.1% in the first three months of the year after shrinking 1.2% in the previous quarter, the Hellenic Statistical Authority said in a statement on Monday. The seasonally adjusted contraction was 0.5% from a year earlier. Talks between creditors on easing the country’s debt load are accelerating after Greece and officials from the IMF and euro-area institutions ended a months-long impasse over the austerity measures the government needs to take. While that’s prompted a rally in Greek stocks and bonds this month, the delay has taken a toll on the economy. That cost led the government to cut its GDP growth forecast for this year to 1.8% from 2.7% on Saturday. The European Commission reduced its estimate to 2.1% last week.