�DPC St. Catherine Street, Montréal, Québec 1916



This is what we’ve come to, and it’s hardly surprising. Where are the raised voices, though?
• Most US Cities Unaffordable For Average Americans To Live In (MarketWatch)
Most big American cities are no longer affordable for the average worker. Home buyers earning a median income can only afford a median-priced home in 10 of the 25 largest metropolitan areas in the U.S., according to a survey by personal finance site Interest.com. That’s still a slight improvement on last year when only 8 of those metropolitan areas were affordable, but still lower than 2012 when 14 of those 25 areas were affordable for people on a median income in those regions. Being priced out of buying a home in the country’s major cities means more multi-family buildings in big cities and more people moving into second-tier cities and rural areas, says Stuart Gabriel, director of UCLA’s Richard S. Ziman Center for Real Estate.
“The consequences are large,” he says, “and they’re not just about affordability. It affects economic growth and economic viability of our major metropolitan areas.” While some people will find ways to work from home, for instance, spiraling housing costs also hurt people who need to work in cities. “Teachers, firefighters and police, these are people who are absolutely essential to the functioning of our urban areas, are priced out of those areas and have to commute long distances to get to work,” Gabriel says. “It’s certainly true here in L.A.” Sacramento had the biggest drop in home affordability over the past 12 months, falling to No. 18 this year from No. 12 in 2013. But it’s still more affordable than the other three California metro areas on the list: Los Angeles (No. 22), San Diego (No. 24) and San Francisco (No. 25) where the median income is 46% less than what is required to buy a median-priced home here. New York is No. 23 on the list.
The cheapest areas are Minneapolis, Atlanta, St. Louis and Detroit. “Low mortgage rates are helping home affordability to some extent, but the key ingredient — which has been missing to this point — is substantial income growth,” says Mike Sante, managing editor of Interest.com. “Millennials, in particular, are struggling to overcome their student loans and save enough money for a down payment.” The Interest.com survey reflects a broader trend: 52% of Americans have made at least one major sacrifice to cover their rent or mortgage over the last three years, according to research commissioned by the nonprofit John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation released earlier this year. These sacrifices include getting a second job, deferring saving for retirement and cutting back on health care.
Read more …

Here’s why Americans can’t afford their own cities anymore.
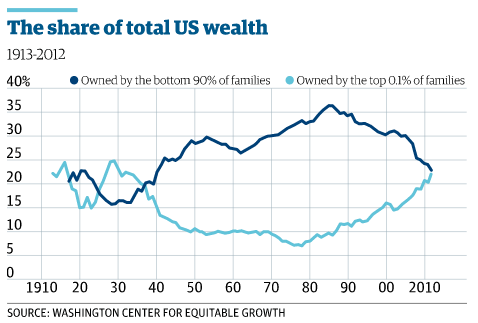
• US Wealth Inequality: Top 0.1% Worth As Much As The Bottom 90% (Guardian)
Wealth inequality in the US is at near record levels according to a new study by academics. Over the past three decades, the share of household wealth owned by the top 0.1% has increased from 7% to 22%. For the bottom 90% of families, a combination of rising debt, the collapse of the value of their assets during the financial crisis, and stagnant real wages have led to the erosion of wealth. The research by Emmanuel Saez and Gabriel Zucman [pdf] illustrates the evolution of wealth inequality over the last century. The chart shows how the top 0.1% of families now own roughly the same share of wealth as the bottom 90%. The picture actually improved in the aftermath of the 1930s Great Depression, with wealth inequality falling through to the late 1970s. It then started to rise again, with the share of total household wealth owned by the top 0.1% rising to 22% in 2012 from 7% in the late 1970s. The top 0.1% includes 160,000 families with total net assets of more than $20m (£13m) in 2012.
In contrast, the share of total US wealth owned by the bottom 90% of families fell from a peak of 36% in the mid-1980s, to 23% in 2012 – just one percentage point above the top 0.1%. The growing indebtedness of most Americans is the main reason behind the erosion of the wealth share of the bottom 90%, according to the report’s authors. Many middle-class families own their homes and have pensions, but too many have higher mortgage repayments, higher credit card bills, and higher student loans to service. The average wealth of bottom 90% jumped during the stock market boom of the late 1990s and the housing bubble of the early 2000s. But it then collapsed during and after the most recent financial crisis. Since then, there has been no recovery in the wealth of the middle class and the poor, the authors say. The average wealth of the bottom 90% of families is equal to $80,000 in 2012— the same level as in 1986. In contrast, the average wealth for the top 1% more than tripled between 1980 and 2012.
Read more …

No surprise here either.
• US Foreclosure Filings Climb 15% In October (MarketWatch)
The pace of new foreclosures picked up last month as more troubled properties were pushed through the system, according to data released Thursday. In October, there were default notices and other foreclosure filings reported on more than 123,000 U.S. homes, up 15% from September — the largest monthly growth since foreclosure activity peaked in early 2010, online foreclosure marketplace RealtyTrac reported. Last month’s pop was driven by seasonal factors — banks were trying to “get ahead of the usual holiday foreclosure moratoriums,” said Daren Blomquist, vice president at RealtyTrac.
October’s spike narrowed the year-over-year contraction in foreclosure filings to 8%, the slowest annual drop since May 2012. “Distressed properties that have been in a holding pattern for years are finally being cleared for landing at the foreclosure auction,” Blomquist said. Despite October’s increase in filings, the pace of the foreclosure-related notices is trending closer to levels seen before the U.S. housing bubble burst. In 2006, as home prices were near their peak, there were average monthly foreclosure filings on 105,000 properties. October’s 123,000 foreclosure filings were down about 66% from a peak of 367,000 hit in 2010.
Read more …

Not going to boost holiday sales.
• Sub-$2-a-Gallon Gasoline Futures Hand US Motorists Gift (Bloomberg)
U.S. drivers will have some extra money in their pockets this holiday season as gasoline futures tumbling below $2 a gallon mean lower prices at the pump. “The drop in futures is eventually going to translate into further declines at the pump,” Tim Evans, an energy analyst at Citi Futures Perspective in New York, said by phone yesterday. “There will be a little extra discretionary spending that consumers can use somewhere else this holiday season.” The nation’s largest motoring club says retail prices “have a very good chance” of being the lowest for the Nov. 28 Thanksgiving holiday in five years. Motorists are already paying the least since 2010 after crude oil tumbled more than 20% in the past four months. Gasoline futures added 0.7 cent, or 0.3%, to $2.0085 a gallon in electronic trading at 12:12 p.m. Singapore time.
Yesterday the contract closed at the lowest since September 2010. The average retail price for regular gasoline fell 0.6 cent to $2.917 a gallon on Nov. 12, the least since December 2010, according to Heathrow, Florida-based AAA. Based on the drop in the futures market, pump prices could fall to $2.70 or thereabouts, Michael Green, a Washington-based spokesman for AAA, said by telephone yesterday. “At this point, the market refuses to stabilize, the price of crude oil continues to fall and refiners are making more gasoline. There’s no end in sight.” Almost one-fourth of filling stations in the U.S. are selling gasoline for less than $2.75 a gallon, Green said. Less than 1% are under $2.50, he said. “We’re still a long way from getting down to $2,” Green said. “But I didn’t think it was going below $3, and here we are.”
Read more …

Edwards is one scary guy. Because he’s mostly right.
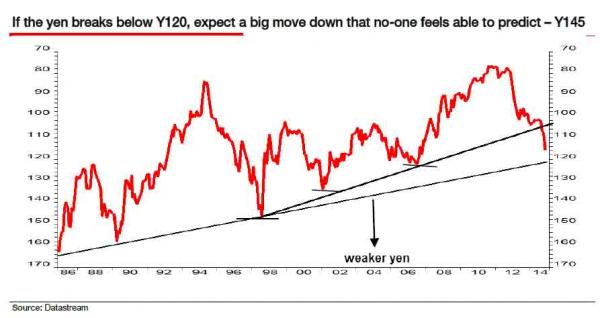
• Albert Edwards: USDJPY 145, “Tidal Wave Of Deflation Westward” (Zero Hedge)
Less than two months ago, Albert Edwards presented “The Most Important Chart For Investors” in which he predicted, correctly, that the real action will come not in the Euro but the Japanese Yen, and at a time when the USDJPY was trading around 108, Edwards forecast a sharp move to 120. A month later, Abe’s just as shocking “all in” bet on boosting QE to a level where it matches the Fed’s peak monthly POMO despite an economy that is a third the size of the US, proved Edwards correct and has since sent the USDJPY some 800 pips higher and just 400 pips shy of Edwards’ 120 forecast. At this rate, the 120 target may be taken out within weeks not months. So what happens next? Here, straight from the horse’s mouth that got the first part of the rapid Yen devaluation so right, is the answer.
As Edwards updates with a note from this morning, “the yen is set to follow the US dollar DXY trade-weighted index by crashing through multi-decade resistance – around ¥120. It seems entirely plausible to me that once we break ¥120, we could see a very quick ¥25 move to ¥145, forcing commensurate devaluations across the whole Asian region and sending a tidal wave of deflation westwards.” Edwards, never one to beat around the bush, slams strategists who are at best willing to get the direction of a given move, if not the magnitude. So he will be the outlier:
… in the foreign exchange (FX) world, extreme volatility is often readily apparent but seldom ever predicted. We explained recently that investors were overly focusing on the euro/US$ when a further round of Japanese QE would make the yen the dominant currency story. I expect the key ¥120/$ support level to be broken soon and the lows of June 2007 (¥124) and Feb 2002 (¥135) to be rapidly taken out. If you want a target to reflect historic volatility, think about the Y145 low of August 1998 (see chart). That is my Q1 forecast.
Read more …

I see little value in predicting anything 10 years out today. The US dollar looks strongest, stocks definitely do not, they’re way too overvalued. in 2024, who says there’ll be much of any financial markets remaining? But hey, someone has to lose all that money going forward. Might as well this guy.
• Oil, Other Commodities Will Be In The Dumps For Another Decade (MarketWatch)
Remember the commodities supercycle, that seemingly endless 2000s commodities boom? It drove oil, gold, copper and other commodities to record levels. The supercycle was driven by exploding demand from China and other emerging countries, supply bottlenecks caused by years of not developing wells and mines, and rock-bottom interest rates that inflated demand for hard assets all around the world. But now gold, oil and other commodities are well off their peaks, so far off, in fact, and for so long that they can only be described as in a supercycle in reverse, or a secular bear market. If that’s true – and I’m pretty sure it is – investors who piled in to commodities are in for a bruising decade ahead unless they take profits or cut their losses.
Meanwhile, stocks, which run counter to commodities, may well go much higher, along with the U.S. dollar. “We believe that we are in the initial years of a secular down cycle in commodities,” wrote Shawn Driscoll, manager of the natural resource-focused T. Rowe Price New Era Fund in the fund’s most recent semiannual report. “Commodity cycles are very long on the way up and the way down,” he told me in a phone interview. They last around 13 to 15 years, because it takes that long for fundamentals of supply and demand to go to extremes. When the most recent supercycle began in 1998, Driscoll said, commodities prices had plummeted, so producers shuttered old mines and wells and hadn’t opened new ones in a while. But when demand revived, it took years for producers to catch up. Ultimately, companies built too much capacity just in time for the next peak.
Read more …

“With this key level out of the way a move towards $75 now looks likely as the hunt for a real floor in oil prices goes on.” WTI at $74 this morning, Brent at $78.
• Oil Price Rout To Deepen Amid Supply Glut, Warns IEA (Telegraph)
The rout which has sent oil prices to a four-year low is expected to deepen, the International Energy Agency warned in its latest monthly market report. The Paris-based watchdog said Friday: “While there has been some speculation that the high cost of unconventional oil production might set a new equilibrium for Brent prices in the $80 to $90 range, supply/demand balances suggest that the price rout has yet to run its course.” Against a backdrop of weakening demand, oil supply in October increased adding further downward pressure on prices, the IEA said in its monthly market report. According to the watchdog, global oil supply inched up by 350,000 barrels per day (bpd) in October to 94.2m bpd.
However, in London Brent crude bounced at the open up almost 1pc at around $78 per barrel after heavy losses overnight in the US saw West Texas Intermediate blend crude fall to $74 per barrel. “Crude prices are enduring another hefty move lower, with Brent shifting below $80 for the first time since late 2010,” said Chris Beauchamp, Market Analyst, IG. “With this key level out of the way a move towards $75 now looks likely as the hunt for a real floor in oil prices goes on.” The supply glut will add to pressure on the Organisation of Petroleum Exporting Countries to sharply cut back on production at their meeting on November 27. However, the group’s major producers may be reluctant to do so due to the risk of losing more market share to shale oil drillers in the US.
The IEA’s warning on prices follows the US Energy Department, which this week pared back its forecasts for prices in 2015. The US Energy Information Administration (EIA) – part of the Department of Energy – has slashed its price forecasts for 2015. The EIA now expects US crude blends to average $77.75 per barrel next year, down from a previous forecast of $97.72, and Brent to average $83.42 in 2015, down from its old estimate of $101.67. The EIA has also revised down its global demand forecast by 200,000 barrels per day (bpd) to average 92.5m bpd in 2015, based on weaker global economic growth prospects for next year.
Read more …

The US doesn’t produce enough domestically yet, or so I guess.
• Keystone Left Behind as Canadian Oil Pours Into US (Bloomberg)
Delays of the Keystone XL pipeline are providing little obstacle to Western Canadian oil producers getting their crude to the U.S. Gulf Coast, with shipments set to more than double next year. The volume of Canadian crude processed at Gulf Coast refineries could climb to more than 400,000 barrels a day in 2015 from 208,000 in August, according to Jackie Forrest, vice president of Calgary-based ARC Financial. The increase comes as Enbridge’s Flanagan South and an expanded Seaway pipeline raise their capacity to ship oil by as much as 450,000 barrels a day. Canadian exports to the Gulf rose 83% in the past four years.
The expansion shows Canadians are finding alternative entry points into the U.S. while the Keystone saga drags on. In the latest chapter, a Democratic senator and a Republican representative are seeking votes in their chambers to set the project in motion. The two are squaring off in a runoff election for a Senate seat from Louisiana, a state where support for the project is strong. “Keystone is kind of old news,” Sandy Fielden, director of energy analytics at Austin, Texas-based consulting company RBN Energy, said Nov. 12 in an e-mail. “Producers have moved on and are looking for new capacity from other pipelines.” TransCanada’s Keystone XL, which would transport Alberta’s heavy oil sands crude to refineries on the Gulf, has been held up for six years, awaiting Obama administration approval.
Read more …

Over the top headline and commentary. Russia buys gold because sanctions make access to dollar markets harder.
• Putin Stockpiles Gold As Russia Prepares For Economic War (Telegraph)
Russia has taken advantage of lower gold prices to pack the vaults of its central bank with bullion as it prepares for the possibility of a long, drawn-out economic war with the West. The latest research from the World Gold Council reveals that the Kremlin snapped up 55 tonnes of the precious metal – far more than any other nation – in the three months to the end of September as prices began to weaken. Vladimir Putin’s government is understood to be hoarding vast quantities of gold, having tripled stocks to around 1,150 tonnes in the last decade. These reserves could provide the Kremlin with vital firepower to try and offset the sharp declines in the rouble. Russia’s currency has come under intense pressure since US and European sanctions and falling oil prices started to hurt the economy.
Revenues from the sale of oil and gas account for about 45pc of the Russian government’s budget receipts. The biggest buyers of gold after Russia are other countries from the Commonwealth of Independent States, led by Kazakhstan and Azerbaijan. In total, central banks around the world bought 93 tonnes of the precious metal in the third quarter, marking it the 15th consecutive quarter of net purchases. In its report, the World Gold Council said this was down to a combination of geopolitical tensions and attempts by countries to diversify their reserves away from the US dollar. By the end of the year, central banks will have acquired up to 500 tonnes of gold during the latest buying spell, according to Alistair Hewitt, head of market intelligence at the World Gold Council.
“Central banks have been consistently adding to their gold holdings since 2009,” Mr Hewitt told the Telegraph. In the case of Russia, Mr Hewitt said that the recent increases in its gold holdings could be a sign of greater geopolitical risk that has arisen since it seized Crimea sparking a dispute with Ukraine and the West. Overall, the World Gold Council said that global demand for gold was down 2pc year-on-year to 929 tonnes in the third quarter amid signs that buying in China, one of the main markets, had tailed off. Jewellery demand in the quarter ending in September was down 39pc to 147 tonnes, signalling weaker consumer sentiment in the world’s second-largest economy.
Read more …

After 2.5 years, and countless comments at TAE about Abe’s inevitable failure, mainstream America is catching on. Even a jibe at Krugman here.
• It May Be Too Late for Japan PM to Fix World’s Third Largest Economy (TIME)
Tokyo is abuzz with speculation that Prime Minister Shinzo Abe is about to dissolve the Diet, as the country’s legislature is known, and call a snap election. He by no means has to take such action. It has only been two years since his Liberal Democratic Party, or LDP, swept to power in a massive landslide, and the opposition is in such disarray that there is little doubt Abe would be returned to office in a new election. Nevertheless, Abe apparently feels the need for another vote of confidence from the public, likely in part to bolster support for his radical program to revive Japan’s economy, nicknamed Abenomics. The problem is that it could already be too late. Abenomics is a failure, and Abe isn’t likely to fix it, no matter how many seats his party holds in parliament.
When Abe first introduced Abenomics, many economists – most notably, Nobel laureate Paul Krugman – believed the unconventional program would finally end the economy’s two-decade slump. The plan: the Bank of Japan (BOJ), the country’s central bank, would churn out yen on a biblical scale to smash through the economy’s endemic and destructive cycle of deflation, while Abe’s government would pump up fiscal spending and implement long-overdue reforms to the structure of the economy. Advocates argued that Abenomics was just the sort of bold action to jump-start growth and fix a broken Japan, and we all had reason to hope that it would work. Japan is still the world’s third largest economy, and a revival there would add another much-needed pillar to hold up sagging global economic growth.
However, I had my concerns from the very beginning. In my view, Japan’s economy doesn’t grow because there is a lack of demand. Pumping more cash into the economy, therefore, will not restart growth. Only deep reform to raise the potential of the economy can do that — by improving productivity and unleashing new economic energies. Unless Abe changed the way Japan’s economy works — and I doubted he would — all of the largesse from the BOJ would at best come to nothing. In a worst-case scenario, Abe’s program could turn Japan into an even bigger economic mess than it already is.
Read more …

The G20 is the most useless gathering on the planet. They see one thing only, growth, whether it’s there or not.
• Europe’s Debt Fight May Undermine Push for Growth Deal (Bloomberg)
Europe’s infighting over debt rules may be the biggest challenge to its ambitions for a new commitment to growth at the Group of 20 summit in Australia. World leaders have already expressed their frustration with the European Union’s German-mandated obsession with budget deficits. When they sit down in Brisbane this weekend to consider the 28-nation bloc’s call for a “comprehensive” growth strategy that seeks to boost private investment and rein in fiscal excess, the G-20 group will include France and Italy, the euro nations that have most publicly fought the EU view. Germany and its allies say the debt rules are essential for the EU’s credibility yet the euro area’s six-year slump has already weakened the bloc’s reputation for economic management, regardless of whether the 18 euro members can eventually wrestle their budget deficits under control.
As global growth wanes, the rest of the world’s capacity to keep indulging Europe’s budget focus is narrowing too. “Europe has, from a global perspective, been too tight for years,” said Jacob Funk Kirkegaard, senior fellow at the Peterson Institute for International Economics in Washington. Even if the euro area relaxes its stance somewhat, “the global economy is growing slower now, so any undershoot matters more.” Behind the united facade European leaders will present in Brisbane, France and Italy are straining at the budget limits they’ve been set, spurred on by calls from European Central Bank President Mario Draghi for nations to supplement his “whatever it takes” monetary policy stance.
Read more …

A big relief, was the announcement. So why are EU stocks falling?
• Cold Comfort As France, Germany Eke Out Tiny Q3 Growth (Reuters)
European stocks were flat on Friday after gross domestic product numbers showed both France and Germany grew marginally in the third quarter, while the dollar rose further against the yen on expectations of a snap election in Japan. The European data confirmed that the outlook for much of the world economy still looks much shakier than for the United States, although France beat expectations. Asian stocks fell following the latest signs that growth in China is slowing. Energy stocks were depressed as crude oil hovered near a four-year low in an oversupplied market and the Russian ruble, hammered in recent weeks as world oil prices fell, was again testing record lows around 48 rubles per dollar. Germany’s economy eked out growth of 0.1% on the quarter, while France – generally seen as in deeper trouble than its neighbor – grew by 0.3%. Overall euro zone data was due later. “The German number is slightly positive in line with expectations but it’s still soft,” said Patrick Jacq, a rate strategist at BNP Paribas in Paris.
“The (French) growth in Q3 is only driven by inventories. It’s just a one-off positive figure in a very weak environment and therefore this is not something which could lead the market to think that the economic situation is improving in France.” A Reuters poll showed Japanese companies overwhelmingly want Prime Minister Shinzo Abe to delay or scrap a planned tax increase, a move expected to come along with a decision, expected by many, to call a new election. The yen, down more than 3% against a stronger dollar this month, fell another half% to a seven-year low of 116.385 yen per dollar. “The argument is that delaying the sales tax hike means the impulse to CPI inflation will start to drop,” said Alvin Tan, a currency strategist at French bank Societe Generale in London. “If there’s no additional sales tax hike, the impulse to higher inflation starts to fade away quite rapidly. So in order to push inflation higher, which is what everybody wants, you need the currency to weaken a lot more.”
Read more …

All those years lost for growth that will never come. Renzi is not a smart guy.
• Italy’s Slump Enters Fourth Year, Complicating Renzi’s Plans (Bloomberg)
Italy’s economy shrank in the third quarter pushing the nation into a fourth year of a slump that has complicated Prime Minister Matteo Renzi’s efforts to revive growth and keep public finances in check. Gross domestic product fell 0.1% from the previous three months, when it declined 0.2%, the national statistics institute Istat said in a preliminary report in Rome today. That matched the median forecast in a Bloomberg survey of 22 economists. Output was down by 0.4% from a year earlier. GDP in the euro region’s third-biggest economy has fallen in all but two of the last 13 quarters as the jobless rate rose to the highest on record.
Renzi is relying on estimated 0.6-percent growth next year to rein in a public debt of more than €2 trillion ($2.50 trillion) and preserve a tax rebate to low-paid employees aimed at reviving consumer demand. The Bank of Italy said yesterday in a report that the country needs to avoid a “recessionary demand spiral” due to the “persistence of economic difficulties, which have been exceptional in terms of duration and depth.” Italians rallied in Rome last month to protest an overhaul of labor market rules tha Renzi proposed to make it easier for businesses to hire and fire workers. The premier has repeatedly said the plan is a way to attract investments and that its framework will get parliamentary approval by year’s end before being fully implemented in 2015.
Read more …

Finally a Bloomberg poll that gets something right?
• World Outlook Darkening as 89% in Poll See Europe Deflation Risk (Bloomberg)
The world economy is in its worst shape in two years, with the euro area and emerging markets deteriorating and the danger of deflation rising, according to a Bloomberg Global Poll of international investors. A plurality of 38% of those surveyed this week described the global economy as worsening, more than double the number who said that in the last poll in July and the most since September 2012, when Europe was mired in a recession. Much of the concern is again focused on the euro area: Almost two-thirds of those polled said its economy was weakening while 89% saw disinflation or deflation as a greater threat there than inflation over the next year. Respondents said the European Central Bank and the region’s governments are making the situation worse by pursuing too-tight policies, and fewer expressed confidence in ECB President Mario Draghi and German Chancellor Angela Merkel.
“The euro-zone economy has deteriorated and will get worse if there are no fiscal policy actions from core European countries, mainly Germany,” poll participant Sanwook Lee, a senior portfolio manager at Shinhan Bank in Seoul, said in an e-mail. Europe isn’t the only source of concern in the global economy, according to the quarterly poll of 510 investors, traders and analysts who are Bloomberg subscribers. More than half of those contacted said conditions in the BRIC economies – Brazil, Russia, India and China – are getting worse, compared with 36% who said so in July.
Read more …

China is filled to its credit boom with this kind of shady deals.
• China Busts Underground Banks Linked to $23 Billion Transactions (Bloomberg)
Beijing police raided and shut down more than 10 underground banks that were involved in 140 billion yuan ($23 billion) of transactions over the past few years. The banks were raided on Sept. 18, with 59 people arrested and 264 bank accounts frozen, Beijing Municipal Public Security Bureau said in a statement today. The investigation started in February when Beijing police found that a man with surname Yao had transferred more than $5 million abroad in a year, according to the statement. Yao, who had a number of bank accounts, frequently bought $50,000 of foreign exchange, the police said. That’s the most overseas currency that a Chinese citizen can buy annually. The underground banks, most of which are family-run and operating out of homes, use online and mobile payment devices to buy or sell foreign exchange and illegally transfer funds abroad, according to the statement. Beijing police said they would continue to crackdown on crimes that threaten China’s economic and financial security.
Read more …

Investors are clueless and befuddled. Ideal patsies.
• Stock Market Fear, Stress And Tensions Climbing (MarketWatch)
What happens if we get another melt-up, maybe to 18,000 on the Dow Jones Industrial Average before we see 17,000 again? I’m in a less aggressive mode for now, but feet to fire, if this bubble-blowing bull market is to keep on blowing, why not a total melt-up into and above 18,000 before year-end? Stranger things have happened. I often ask, who’s more scared right now, the bulls or the bears because when there’s an overwhelming consensus in the answer to that question, it’s often time for the markets to put on a big contrarian move opposite that sentiment. Are you a bull or one of the few bears remaining? Are you scared right now? Do you think most bulls are scared right now?
Fear, stress and tensions have been climbing along with the markets, which isn’t what you’d expect, is it? I’ve noticed throughout this week that tensions have been very high on Latest Scuttles and that’s a reflection of the stress felt by most traders and investors right now. There’s likely a lot of money managers who missed this last leg higher from the Ebola lows and now find themselves drastically behind their market benchmarks with just 45 days to go into year-end. That kind of technical setup into year-end could be a catalyst for the winners to keep their momentum heading higher. I personally am not trying and wouldn’t suggest trying to game the next market move, but it’s something to think about.
And what if you’ve missed this bull run over the last five years and still aren’t in the markets or even if you just find yourself like the aforementioned money managers and feel underinvested here? Like I said, I don’t think the continuing bubble-blowing bull market that I’ve predicted would play out like this is over yet. I wouldn’t be aggressive, but if you don’t think you own enough stocks (or any for that matter) then I do suggest scaling into some of the best stocks you can find, including some of the very best, most revolutionary growth stocks you can find.
Read more …

The take-away: Apple is an 800-pound bubble.
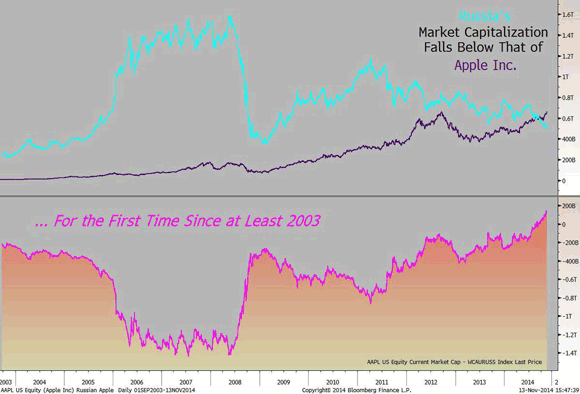
• Apple Could Swallow Whole Russian Stock Market (Bloomberg)
If you owned Apple Inc., and sold it, you could purchase the entire stock market of Russia, and still have enough change to buy every Russian an iPhone 6 Plus. The CHART OF THE DAY shows the total market capitalization of all public companies in the world’s largest country slipped below that of the world’s most-valued company for the first time on record. The gap, at $121 billion on Nov. 12, is about the price of 143 million contract-free 64-gigabyte iPhones, based on Apple Store prices. The value of Russian equities has slumped $234 billion to $531 billion this year, while Apple gained $147 billion to $652 billion, according to data compiled by Bloomberg.
The technology company’s innovation and brand value attract investors, while Russia’s political conflicts, sanctions and the threat of economic stagnation next year make them nervous, according to Vadim Bit-Avragim, a portfolio manager who helps oversee about $4 billion at Kapital Asset Management LLC in Moscow. “Apple works with shareholders to maximize returns and is based where property is protected by law,” Bit-Avragim said. “In Russia, the legislative protection for property is not as good, most state-run companies have poor corporate governance, resources are concentrated in state hands and borrowing costs are shooting up. After all this, when you get involved in conflicts with your neighbors, it becomes very hard to persuade investors from all over the world to invest here.”
Read more …

Destruction is our middle name.
• Fracking Boom Spurs Demand for Sand and Clouds of Dust (Bloomberg)
A little sand mine down the road didn’t seem like a big deal 17 years ago, when Alphonse Dotson picked the site for a vineyard in the Texas Hill Country. Today he’s surrounded by four mines blasting sand from the earth, filling the air with a fine dust that drifts across acres of sensitive grape vines. A fifth will open soon, and he says he’s worried. “I don’t want us to be smothered to death,” he said. Add sand mining to the list of industries transformed by the U.S. oil boom. The tiny grains of silica are what keep frackers fracking, propping open cracks punched into rock so oil and natural gas can flow. As drilling surged, so has demand for sand. Sand production has more than doubled in the U.S. over the past seven years. By the end of 2016, oil companies in North America will be pumping 145 billion pounds (66 billion kilograms) of it down wells annually. That’s enough to fill railcars stretching from San Francisco to New York – and back.
That’s triggering complaints from local communities, according to a Grant Smith, senior energy policy adviser at the Civil Society Institute. Dust from sand can penetrate deep into lungs and the bloodstream; mines consume massive amounts of water; sand-laden trucks are damaging roads; and property values can be affected. The surge in mining is a “little-understood danger of the fracking boom,” Smith said in a September call with reporters. Energy companies are paying 6% more for sand this year at a time when oil prices are plunging. While low prices may slow down drilling, that won’t make up for a supply bottleneck, said Samir Nangia, a principal at the Houston-based research company PacWest Consulting Partners. Fracking companies are struggling to get enough sand because there aren’t enough trucks and railcars to deliver it. Higher transportation costs are eating into profits at oil-services companies like Schlumberger, Halliburton and Baker Hughes.
Read more …

A company that had revenues of $17 billion in 2013 just topples over, and no-one pays attention, because it happened to be in Denmark and SIngapore.
• Massive OW Bunker Bankruptcy: Questions Of Governance And Oversight (SeaTrade)
The rapid collapse into bankruptcy of OW Bunker just 48 hours after it revealed a $125m fraud at Singapore subsidiary Dynamic Oil Trading, as well as $150m in risk management losses announced at the same time, leaves an awful lot of unanswered questions. OW Bunker was not a two-bit marine fuel supplier, it had revenues of $17bn in 2013 and claimed a 7% share of the global marine fuel supply market. In March this year its IPO on Copenhagen’s NASDAQ exchange valued the company at DKK5.33bn ($900m), making it one of Denmark’s largest IPOs in recent years. In May this year OW Bunker made Forbes list of top 2,000 list of the world’s biggest public companies. As it stands just seven months on the from the IPO some 20,000 investors will have lost everything they put into the company, based on the statement when it filed for in-court restructuring of its main operating subsidiaries that it “must be assumed that the group’s equity is lost”.
Suppliers and sub-contractors will find themselves with large unpaid bills, something which P&I insurers Skuld have warned shipowners about. And more than 600 employees of the group worldwide face a very uncertain future. Trading is a risky business, and anyone investing in it needs to understand this, but this is also why corporate governance and oversight are so important. It is worth noting that according to reports in the Danish media the company did not actually uncover the fraud at Dynamic itself; one of its senior executives flew to Denmark and tearfully confessed to it. How long it would have gone on if this had not happened we can only speculate. Two employees have since been reported to the Danish police as OW Bunker filed for bankruptcy. What fraud was actually committed we do not know, although we do know it was over a six month period, so its open to question whether it was actual embezzlement or the hiding of losses as the market turned against the executives involved.
Certainly the recent sharp falls in the oil and bunker price point to the latter as a possibility. The case bears certain parallels to then Singapore-based, British national, rogue trader Nick Leeson who caused the collapse of Barings Bank in 1995 having run up losses on speculative trades that eventually totaled in the region of $1.4bn. Indeed the BBC is reporting the fraud at Dynamic could be one of Singapore’s largest financial scandals in the last 10 years, joining what is already a huge scandal in Denmark. The fraud revelations came on top of the $150m in risk management losses that resulted in the firing of OW Bunker head of risk management and evp Jane Dahl Christensen. The full extent of the fallout of OW Bunker’s sudden bankruptcy will most likely take years to unravel. However, lessons do need to be learned on corporate governance and oversight for the benefit of all going forward.
Read more …

That Tony Abbott is one dumb f*ck: “Sydney before British settlement was “nothing but bush.”
• Aboriginals Decry G-20 Host Australia as Leaders Gather (Bloomberg)
Across the Brisbane River from where some of the world’s biggest leaders will soon gather, a group of 200 indigenous Australians is seeking to present another side to the country’s image as host and regional power. “We want to talk to the people of the world,” said twenty-seven-year-old Meriki Onus, who joined the Aboriginal people protesting in a city park after a two-day, 1,100-mile bus ride to the Queensland state capital. “The police system here is racist, the government systems here are racist and we’ve used the G-20 as an opportunity to tell the world that it’s not OK.” Australia’s first inhabitants – who lived on the continent at least 40,000 years prior to British settlement in 1788 and now make up about 3% of the population – are among groups using the draw of leaders like U.S. President Barack Obama at the Group of 20 meetings to highlight their causes.
The indigenous people gathered in the subtropical city, where police outnumber the 7,000 delegates and media, say the system of government has entrenched poverty. “This country is occupied by force, like what happened in Poland and France during War War II, but for us this has been going on for more than two centuries,” Wayne Wharton, spokesman for the Brisbane Aboriginal Sovereign Embassy, said today at the park protest. “Our people want our rightful place in the world, and that means economic benefits, social benefits, responsibility and services.” Speaking at a business breakfast today in Sydney with U.K. Prime Minister David Cameron, Australia’s leader Tony Abbott, a self-declared prime minister for Aborigines and host of this weekend’s G-20 summit, said Sydney before British settlement was “nothing but bush.”
“As we look around this glorious city, as we see the extraordinary development, it’s hard to think that back in 1788 it was nothing but bush and that the marines and the convicts and the sailors that straggled off those 12 ships just a few hundred yards from where we are now must have thought they’d come almost to the moon,” Abbott said. Daubed with “mourning paint” across his face and torso to highlight indigenous deaths in police custody, Wharton said the G-20 won’t help his people or other Aboriginal races throughout the world because it’s designed to make rich nations wealthier at the expense of the poor. “It all comes back to having the ability to accumulate and then distribute wealth – my people have never had that,” he said.
Read more …