DPC Shoppers on Sixth Avenue, New York City 1903



Bubbles are so prevalent people tend not to see them anymore.
• Bubbles Spread Like a Zombie Virus (BBG)
The leading academic theory of asset bubbles is that they don’t really exist. When asset prices skyrocket, say mainstream theorists, it might mean that some piece of news makes rational investors realize that fundamental values like corporate earnings are going to be a lot higher than anyone had expected. Or perhaps some condition in the economy might make investors suddenly become much more tolerant of risk. But according to mainstream theory, bubbles are not driven by speculative mania, greed, stupidity, herd behavior or any other sort of psychological or irrational phenomenon. Inflating asset values are the normal, healthy functioning of an efficient market. Naturally, this view has convinced many people in finance that mainstream theorists are quite out of their minds. The problem is, mainstream theory has proven devilishly hard to disprove.
We can’t really observe how investors in the financial markets form their beliefs. So we can’t tell if their views are right or wrong, or whether they’re investing based on expectations or because of changing risk tolerance. Basically, because we can usually only look at the overall market, we can’t get into the nuts and bolts of how people decide what prices to pay. But what about the housing market? Housing is different from stocks and bonds in at least two big ways. First, because house purchases are not anonymous, we can observe who buys what. Second, housing markets are local, so we can see what is happening around them, and thus have some sort of idea what information they are receiving. These unique features allow us to know much more about the decision-making process of each buyer than we know about investors in the anonymous national financial markets.
In a new paper, economists Patrick Bayer, Kyle Mangum and James Roberts make great use of these features to study the mid-2000s U.S. housing boom. Their landmark results ought to have a major effect on the debate over asset bubbles. Bayer et al. find that as the market overheated, the frenzy spread like a virus from block to block. They look at the greater Los Angeles area – a hotbed of bubble activity – from 1989 through 2012. Since they want to focus on people buying houses as investments (rather than to live in), the authors looked only at people who bought multiple properties, and they tried to exclude primary residences from the sample. They found, unsurprisingly, that the peak years of 2004-2006 saw a huge spike in the number of new investors entering the market. Here is the graph from their paper:
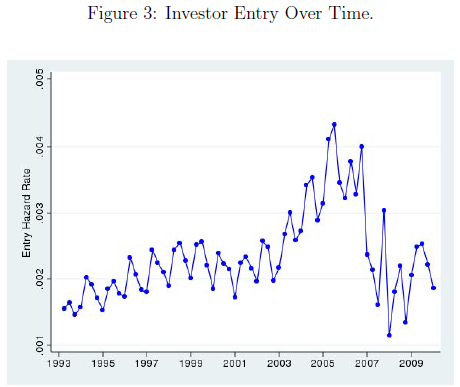

It’s like when you start with a basket with a few bad apples: in the end, everything turns to junk.
• Junk Territory: US Corporate Debt Ratings Near 15-Year Low (CNN)
Red flags are rising on Corporate America’s debt. The average rating on U.S. corporate debt has hit nearly a 15-year low, according to a new report by Standard & Poor’s. “We believe corporate default rates could increase over the next few years,” according to S&P credit analysts Jacob Crooks and David Tesher. The average rating on companies that issue debt has fallen to ‘BB,’ or junk status. That is even below the average S&P rating for U.S. corporate debt during and in the aftermath of the financial crisis in 2008 and 2009. There are already concerns about energy companies defaulting on loans due to low oil prices. But new tech firms like Solera and media companies like iHeart too have had their credit rating downgraded this year, according to S&P. Since 2012, there’s been a surge in low-rated companies seeking cash.
In the past four years, S&P has assigned a single-B rating to 75% of companies accessing the debt markets for the first time. That rating is just one notch up from triple-C, a rating given to companies with a high probability of default. Companies with a single-B rating include PF Chang’s, Toys R US and Men’s Wearhouse (MW). That doesn’t mean they’re going to default: They’re just dangerously close to the territory where companies tend to default. The “rapid rise” in companies with low credit ratings accessing the bond markets can be traced to the easy availability of cash in recent years. How did this happen?
Here are a few key dominoes.
1. The Fed created a super low interest rate environment when it put rates next to zero in 2008.
2. Investors looking for more yield move away from safe assets like U.S. Treasury bonds and into higher-risk assets like bonds issued by lower-rated companies.
3. That makes it easier for low-rated companies to get cash at low rates from the capital markets.
Now, however, the tables are turning. The Fed is slowly starting to increase rates and investors’ appetite – and the cash available – for low-rated companies is on the decline. Add to that the gloomy outlook for the global economy and low commodity prices, and some companies may struggle to pay back what they borrowed.

History rhymes.
• Earnings Growth Based On Debt And Buybacks? Totally Unsustainable (SA)
My grandfather was never rich. He did have some money in the 1920s, but he lost most of it at the tail end of the decade. Some of it disappeared in the stock market crash in October of 1929. The rest of his deposits fell victim to the collapse of New York’s Bank of the United States in December of 1931. I wish I could say that my grandfather recovered from the wrath of the stock market disaster and subsequent bank failures. For the most part, however, living above the poverty line was about the best that he could do financially, as he buckled down to raise two children in Queens. There was one financial feature of my grandfather’s life that provided him with greater self-worth. Specifically, he refused to take on significant debt because he remained skeptical of credit. And with good reason.
The siren’s song of “you-can-pay-me-Tuesday-for-a-hamburger-today” only created an illusion of wealth in the Roaring Twenties; in fact, unchecked access to favorable borrowing terms as well as speculative excess in the use of debt contributed mightily to the country’s eventual descent into the Great Depression. G-Pops wanted no part of the next debt-fueled crisis. Here’s something few people know about the past: Consumer debt more than doubled during the ten year-period of the Roaring 1920s (1/1/1920-12/31/1929). And while you may often hear the debt apologist explain how the only thing that matters about debt is the ability to service it, the reckless dismissal ignores the reality of virtually all financial catastrophes.
During the Asian Currency Crisis and the bailout of Long-Term Capital Management (1997-1998), fast-growing emerging economies (e.g., South Korea, Malaysia, Thailand, etc.) experienced extraordinary capital inflows. Most of the inflows? Speculative borrowed dollars. When those economies showed signs of strain, “hot money” quickly shifted to outflows, depreciating local currencies and leaving over-leveraged hedge funds on the wrong side of currency trades. The Fed-orchestrated bailout of Long-Term Capital coupled with rate cutting activity prevented the 19% S&P 500 declines and 35% NASDAQ depreciation from charting a full-fledged stock bear. Did we see similar debt-fueled excess leading into the 2000-2002 S&P 500 bear (50%-plus)? Absolutely. How long could margin debt extremes prosper in the so-called New-Economy?
How many dot-com day-traders would find themselves destitute toward the end of the tech bubble? Bring it forward to 2007-2009 when housing prices began to plummet in earnest. How many “no-doc” loans and “negative am” mortgages came with a promise of real estate riches? Instead, subprime credit abuse brought down the households that lied to get their loans, destroyed the financial institutions that had these “toxic assets” on their books, and overwhelmed the government’s ability to manage the inevitable reversal of fortune in stocks and the overall economy. Just like 1929-1932. Just like 1997-1998. Just like 2000-2002.

Housing, stocks and now credit.
• Everyone Is Worried That A Third China Bubble Is About To Pop (BI)
First, China’s property bubble popped. Then, China’s stock market bubble burst over the summer, and investors lost a ton of money before the government took control of the system. Now the concern floating around the world of markets is that the third in China’s “triple bubble” is about to burst. That bubble is credit, especially corporate bonds, which have absolutely exploded over the past year as refugees from the other bubble bursts searched for yield. This one is going to be for a very straightforward reason, too — supply. Simply put, there are about to be too many bonds in China, and that could ultimately harm the weakest part of the Chinese economy, the debt-loaded zombie companies that helped form the property bubble and are now unable to turn a healthy profit.
Here’s how all of this happened. When the Chinese stock market went careening downward last summer, a ton of the money that was invested in the market ran into the credit market, specifically corporate bonds. “In our view, China is in the midst of a triple bubble, with the third-biggest credit bubble of all time, the largest investment bubble (proxied by the investment share of GDP) and the second-biggest real-estate bubble,” Credit Suisse analyst Andrew Garthwaite wrote in a note back in July. This was great for China’s debt-laden corporates. They could keep running on easy credit because demand was so high. Corporate-bond issuance increased 21% from 2014 to 2015, and by the end of last year their total stock made up 21.6% of GDP, as opposed 18.4% the year before, according to Societe Generale.
Chinese Treasury-bond supply is set to increase too, from 936 billion yuan in 2015 to 1.4 trillion yuan in 2016. At the same time, the government has been getting a move on an important project it has been working on for some time — turning local-government debt from the country’s infrastructure boom into a real municipal-bond market. We’re talking a lot of money here. In March alone the government allowed 1 trillion yuan ($160 billion) of local-government debt to be converted into local-government bonds (LGB). In 2016 analysts expect the government to issue another 6 trillion yuan in LGBs. That’s a lot of bonds.
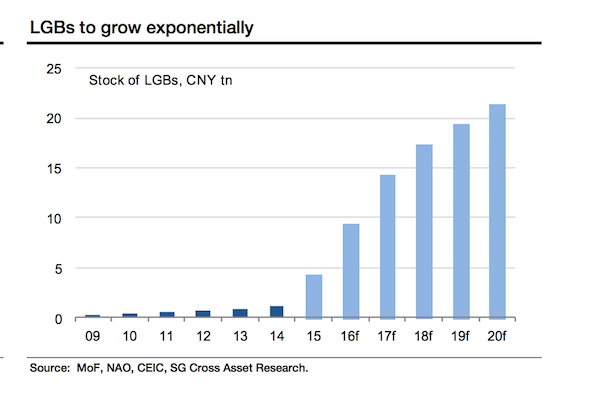

Denial continues.
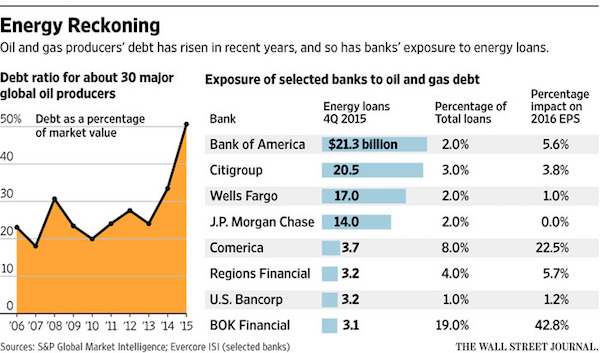
• Coming to the Oil Patch: Bad Loans to Outnumber the Good (WSJ)
Bad loans are likely to outnumber good ones soon in the U.S. oil patch, an indication of the pressure on energy companies and their lenders from the crash in prices. The number of energy loans labeled as “classified,” or in danger of default, is on course to extend above 50% this year at several major banks, including Wells Fargo and Comerica, according to bankers and others in the industry. In response, several major banks are reducing their exposure to the energy sector by attempting to sell off souring loans, declining to renew them or clamping down on the ability of oil and gas companies to tap credit lines for cash, according to more than a dozen bankers, lawyers and others familiar with the plans.
The pullback is curtailing the flow of money to companies struggling to survive a prolonged stretch of low prices, likely quickening the path to bankruptcy for some firms. 51 North American oil-and-gas producers have already filed for bankruptcy since the start of 2015, cases totaling $17.4 billion in cumulative debt, according to law firm Haynes and Boone. That trails the number from September 2008 to December 2009 during the global financial crisis, when there were 62 filings, but is expected to grow: About 175 companies are at high risk of not being able to meet loan covenants, according to Deloitte. “This has the makings of a gigantic funding crisis” for energy companies, said William Snyder, head of Deloitte’s U.S. restructuring unit. If oil prices, which closed at $39.79 a barrel Wednesday, remain at around $40 a barrel this year, “that’s fairly catastrophic.”

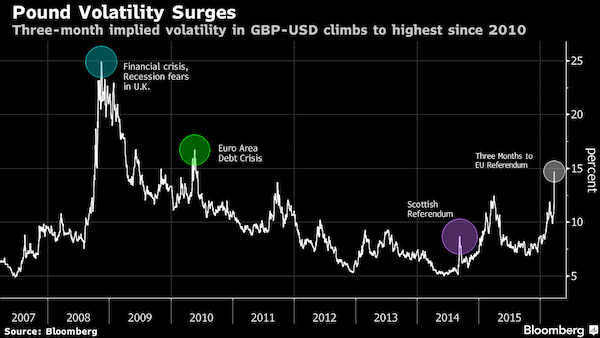
Against the USD is a safe bet if the term is long enough.
• Traders Are Betting Heavily That The Pound Will Drop To 1980s Lows (BBG)
As Britain ponders its future in the EU, investors are betting an amount almost the size of Iceland’s economy on the pound falling to levels last seen in the 1980s. At least 11 billion pounds ($16 billion) has been wagered this year on options that would profit if sterling fell to or below $1.3502, a 4.5% drop from current levels, after the June 23 referendum. More than half of the positions were placed since the date of the vote was set on Feb. 20. The figures give an indication of what’s at stake as investors weigh the possibility of the U.K. quitting the world’s largest single market, which accounts for about half its imports and exports. Even with opinion polls showing no clear lead for either side, the prospect of a “Brexit” has seen the pound fall more than any other major currency versus the dollar this year.
“There is a risk premium in sterling, both in terms of the spot rate and in terms of the volatility market, but this is one of those events where you have no way of calibrating how big it should be,” said Paul Meggyesi at JPMorgan Chase in London. “Few investors believe that sterling has fallen to levels where the risk-reward favors buying.” While tumbling to $1.3502 would barely exceed the pound’s decline so far this year, it would take the U.K. currency to the lowest level since 1985. Traders assign 54% odds to sterling reaching that level by the day of the referendum, according to Bloomberg’s options calculator. Meggyesi sees the pound falling to $1.38 by mid-year, from $1.4145 as of 4:45 p.m. London time on Thursday. Even forecasts of a drop to these levels may be optimistic if the U.K. actually ends up leaving the EU.

In the shadows, China keeps devaluing.
• Yuan Weakens For 6th Straight Day – Longest Losing Streak In 2 Years (ZH)
PBOC fixed the Yuan at its weakest in 3 weeks, pushing the devaluation streak to its longest since early January. However, Offshore Yuan has now dropped over 1.1% against the USD, extending losses for the 6th straight day to 3-week lows. This is the longest streak of weakness in the offshore Yuan since April 2014.

It appears EUR and JPY took enough pain so the basket is reverting to the USD again…

What’s the opposite of passive-aggressive as a clear message is being sent to The Fed – tighten and we unleash the Yuan-weakness-driven turmoil…

Now that’s a housing bubble.
• Sweden Cuts Maximum Mortgage Term To 105 Years -The Average Is 140 (Tel.)
Think there’s a housing affordability crisis in Britain, with low mortgage rates likely to drive house prices even higher? Take a look at Sweden where lending policies have been more generous, and where house price inflation has been (at least recently) more extreme. A number of banks and analysts have warned that Sweden’s housing market is overheating, with HSBC in January saying: “The pace of acceleration in the housing market points to a bubble.” House prices across the country were up 18pc last year. This compares to Britain’s house price rises in 2015 of between 5pc and 10pc, depending on which index is used. Now Sweden is dealing with its overheated housing market by reining in mortgage availability.
Regulators introduced restrictions which will mean mortgage terms – the time homebuyers have to clear the debt – will be drastically reduced to just… 105 years. The move comes because historically there has been no time limit on mortgage duration. So as prices rose and affordability became tougher, Swedish banks’ response was to extend terms, as had been the case in other high-cost property markets including Japan in the Eighties. The average term is reported to be 140 years. This meant many people who inherited property but who could not afford to take on the mortgage debt had to sell up. Swedish banks were quoted in the local press as opposing the move.
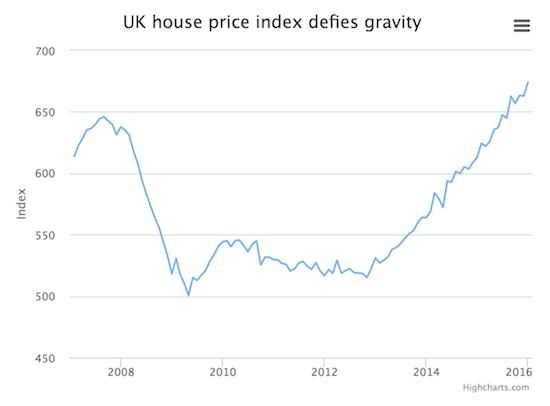
“It isn’t good for the finances of households as it will make mortgages more expensive and the terms not as good. And it isn’t good for financial stability,” the head of Swedish Bankers’ Association was reported to say. In Britain, there has been a move by some lenders to increase mortgage terms but only for younger borrowers. Even then, the maximum term tends to be 35 years, although some lenders – including Halifax and Nationwide – go up to 40, brokers say. The Mortgage Market Review introduced by British regulators in 2013 made it difficult for lenders to arrange loans which went into borrowers’ likely retirement.

And here’s another one. How desperate must Xi be to let this happen?!
• Shenzhen is Home To The Planet’s Fastest Rising House Prices (Guardian)
House prices in Shenzhen, the city which is a hub for technology hardware and known as China’s Silicon Valley, soared by almost 50% last year – the fastest growth in residential property prices worldwide. A new survey puts two Chinese cities – Shenzhen and Shanghai – in the top five fastest-growing property markets despite the Chinese stock market tumbling in 2015. The research, by the estate agents Knight Frank (pdf), also shows the impact of last year’s debt crisis in Greece. House prices in the two biggest Greek cities – Thessaloniki and Athens – were both ranked among the worst six in the survey of 165 cities, falling 5.9% and 4.8% respectively. There were also significant drops in some Italian cities, including Rome, Trieste and Genoa. Nicosia and Larnaca in Cyprus were also among the worst performers.
The Global Residential Cities Index showed that house prices in cities worldwide went up 4.4%. Behind Shenzhen, Auckland was the second fastest growing market with rises of 25.4%, followed by Istanbul (25%) and Sydney (19.9%). Shenzhen has become a hub for the production of hardware used in electronics and has a permanent population of 10 million, rising to 15 million in the summer – autumn electronics season. Their average age is 30. The city bordering Hong Kong did not exist 30 years ago, sporting just a few fishing villages. In 1979, it was declared China’s first special economic zone and surrounded by an 85-mile long, barbed wire fence. Investment and migrant workers flooded the area and factories and housing were built from scratch. By the mid-90s, the population had climbed to 3 million.
In 2004, the first metro station opened and a decade later the network had grown to 131 stations. Two Turkish cities featured in the top 10 – Istanbul and Izmir – while Budapest recorded the biggest rise among European Union cities, with prices up 16.3%. Budapest is also the strongest performing capital city in the index, with demand fuelled by an investment immigration bond for Chinese nationals. Cities traditionally associated with high prices failed to feature prominently. London was ranked at 16 (11.4% growth) with New York at 89th (3.3%). The fast rising prices of Sydney, the fourth fastest rising market, has resulted in high rents and the same sort of concerns about the effects on the young population in the city as in London. In the US, Portland in Oregon and San Francisco were the highest risers, both with increases over the year of 10%. The fastest growing North American city was Vancouver, with prices up nearly 12% on an annual basis.

Greece is ruled by the global finance squid.
• Hedge Funds Control Greek NPLs Anyway (Kath.)
Despite all the government talk about the nonperforming loans secured by borrowers’ homes being protected from falling into the hands of hedge funds, the latest recapitalization process has resulted in the entire credit sector now being controlled by foreign investors – hedge funds no less. Those foreign firms, the majority of which control high-risk portfolios, hold stakes of more than 50% in all of Greece’s systemic lenders, and in some cases far above that. Therefore, by extension, they control a loan portfolio which exceeds 200 billion euros and includes performing loans amounting to some 100 billion and bad loans that also add up to around 100 billion, and there is currently a negotiations battle under way for them not to be sold on to others.
It makes no difference to borrowers who owns their loans; it is the general legal framework and the legal moves they can make in case they are unable to fulfill their obligations that matter. The banks’ planning does not provide for the sale of bad loans, and there are strong indications that the existing stock of NPLs includes many strategic defaulters who have taken advantage of the crisis to avoid fulfilling their obligations. The Bank of Greece estimates that they account for 20% of all bad loans.

“..an economic version of the Hunger Games.”
• Who Will Speak For The American White Working Class? (Guardian)
The National Review, a conservative magazine for the Republican elite, recently unleashed an attack on the “white working class”, who they see as the core of Trump’s support. The first essay, Father Führer, was written by the National Review’s Kevin Williamson, who used his past reporting from places such as Appalachia and the Rust Belt to dissect what he calls “downscale communities”. He describes them as filled with welfare dependency, drug and alcohol addiction, and family anarchy – and then proclaims: “Nothing happened to them. There wasn’t some awful disaster, There wasn’t a war or a famine or a plague or a foreign occupation. … The truth about these dysfunctional, downscale communities is that they deserve to die. Economically, they are negative assets. Morally, they are indefensible. The white American underclass is in thrall to a vicious, selfish culture whose main products are misery and used heroin needles.”
A few days later, another columnist, David French, added: “Simply put, [white working class] Americans are killing themselves and destroying their families at an alarming rate. No one is making them do it. The economy isn’t putting a bottle in their hand. Immigrants aren’t making them cheat on their wives or snort OxyContin.” Both suggested the answer to their problems is they need to move. “They need real opportunity, which means that they need real change, which means that they need U-Haul.” Downscale communities are everywhere in America, not just limited to Appalachia and the Rust Belt – it’s where I have spent much of the past five years documenting poverty and addiction. To say that “nothing happened to them” is stunningly wrong. Over the past 35 years the working class has been devalued, the result of an economic version of the Hunger Games.
It has pitted everyone against each other, regardless of where they started. Some contestants, such as business owners, were equipped with the fanciest weapons. The working class only had their hands. They lost and have been left to deal on their own. The consequences can be seen in nearly every town and rural county and aren’t confined to the industrial north or the hills of Kentucky either. My home town in Florida, a small town built around two orange juice factories, lost its first factory in 1985 and its last in 2005. [..] Over the past 35 years, except for the very wealthy, incomes have stagnated, with more people looking for fewer jobs. Jobs for those who work with their hands, manufacturing employment, has been the hardest hit, falling from 18m in the late 1980s to 12m now.
The economic devaluation has been made more painful by the fraying of the social safety net, and more visceral by the vast increase at the top. It is one thing to be spinning your wheels stuck in the mud, but it is even more demeaning to watch as others zoom by on well-paved roads, none offering help. It is not just about economic issues and jobs. Culturally, we are witnessing a tale of two Americas that are growing more distinct by the day.

Crackdowns deflate economic confidence.
• China ‘Detains 20 Over Xi Resignation Letter’ (BBC)
A total of 20 people have been detained in China following the publication of a letter calling on President Xi Jinping to resign, the BBC has learned. The letter was posted earlier this month on a state-backed website Wujie News. Although quickly deleted by the authorities, a cached version can still be found online. In most countries the contents of the letter would be run-of-the-mill political polemic. “Dear Comrade Xi Jinping, we are loyal Communist Party members,” it begins, and then cuts to the chase. “We write this letter asking you to resign from all party and state leadership positions.” But in China, of course, and in particular on a website with official links, this kind of thing is unheard of and there have already been signs of a stern response by the authorities. The detention of a prominent columnist, Jia Jia, was widely reported to be in connection with the letter.
Friends say he simply called the editor of Wujie to enquire about it after seeing it on line. But now the BBC has spoken to a staff member at Wujie who has asked to remain anonymous and who has told us that in addition to Jia Jia another 16 people have been “taken away”. The source said they included six colleagues who work directly for the website, including a senior manager and a senior editor, and another 10 people who work for a related technology company. And a well-know Chinese dissident living in the US said three members of his family, living in China’s Guangdong Province, had also been detained in connection with the letter. Wen Yunchao said he believed his parents and his brother had been detained because authorities were trying to pressure him to reveal information. But he told the BBC that he knew nothing about the letter.
The letter focuses its anger on what it says is President Xi’s “gathering of all power” in his own hands, and it accuses him of major economic and diplomatic miscalculations, as well as “stunning the country” by placing further restrictions on freedom of speech. The latter is a reference to Mr Xi’s high profile visit last month to state-run TV and newspaper offices, where he told journalists that their primary duty was to obey the Communist Party. The letter first appeared on an overseas-based Chinese language website, well outside the realm of Communist Party censors, but the big question is how it then made its way onto Wujie. The idea that any Chinese editor of sane mind would knowingly publish such a document seems so unlikely that there has been speculation amongst some Chinese journalists, in private, that Wujie was either hacked, or had perhaps been using some kind of automatic trawling and publishing software.

The backdrop of the refugee deal. Yes, we have no decency.
• Facing Life Sentence, Turkish Journalist Vows To Expose State Crimes (Reuters)
One of two prominent Turkish journalists facing life in prison on charges of espionage vowed to make the trial, which begins on Friday, a prosecution of official wrongdoing. Can Dundar, editor-in-chief of Cumhuriyet, told Reuters he would use his trial, which has drawn international condemnation, to refocus attention on the story that landed him in the dock. Dundar, 54, and Erdem Gul, 49, Cumhuriyet’s Ankara bureau chief, stand accused of trying to topple the government over the publication last May of video purporting to show Turkey’s state intelligence agency helping to truck weapons to Syria in 2014. “We are not defendants, we are witnesses,” Dundar said in an interview at his office, promising to show the footage in court despite a ban and at the risk that judges may order the hearings to be held behind closed doors.
“We will lay out all of the illegalities and make this a political prosecution … The state was caught in a criminal act, and it is doing all that it can to cover it up.” Dundar and Gul spent 92 days in jail, almost half of it in solitary confinement, before the constitutional court ruled last month that pre-trial detention was unfounded because the charges stemmed from their journalism. Both were subsequently released pending trial, although President Tayyip Erdogan said he did not respect the ruling. Erdogan has acknowledged that the trucks, which were stopped by gendarmerie and police officers en route to the Syrian border, belonged to the MIT intelligence agency and said they were carrying aid to Turkmens in Syria. Turkmen fighters are battling both President Bashar al-Assad’s forces and Islamic State.
Erdogan has said prosecutors had no authority to order the trucks be searched and that they acted as part of a plot to discredit the government, allegations the prosecutors denied. Erdogan has cast the newspaper’s coverage as part of an attempt to undermine Turkey’s global standing and has vowed Dundar would “pay a heavy price.” The trial comes as Turkey deflects criticism from the European Union and rights groups that it is bridling a once vibrant press. “We were arrested for two reasons: to punish us and to frighten others. And we see the intimidation has been effective. Fear dominates,” Dundar said.

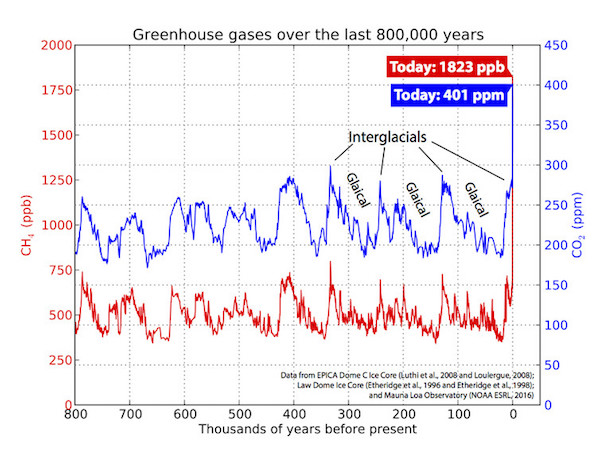
800,000 years and counting.
• Mass Extinctions and Climate Change (C.)
We now know that greenhouse gases are rising faster than at any time since the demise of dinosaurs, and possibly even earlier. According to research published in Nature Geoscience this week, carbon dioxide (CO2 ) is being added to the atmosphere at least ten times faster than during a major warming event about 50 million years ago. We have emitted almost 600 billion tonnes of carbon since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, and atmospheric COC concentrations are now increasing at a rate of 3 parts per million (ppm) per year. With increasing CO2 levels, temperatures and ocean acidification also rise, and it is an open question how ecosystems are going to cope under such rapid change. Coral reefs, our canary in the coal mine, suggest that the present rate of climate change is too fast for many species to adapt: the next widespread extinction event might have already started.
In the past, rapid increases in greenhouse gases have been associated with mass extinctions. It is therefore important to understand how unusual the current rate of atmospheric CO2 increase is with respect to past climate variability. There is no doubt that atmospheric COC concentrations and global temperatures have changed in the past. Ice sheets, for example, are reliable book-keepers of ancient climate and can give us an insight into climate conditions long before the thermometer was invented. By drilling holes into ice sheets we can retrieve ice cores and analyse the accumulation of ancient snow, layer upon layer. These ice cores not only record atmospheric temperatures through time, they also contain frozen bubbles that provide us with small samples of ancient air. Our longest ice core extends more than 800,000 years into the past.
During this time, the Earth oscillated between cold ice ages and warm interglacials . To move from an ice age to an interglacial, you need to increase COC by roughly 100 ppm. This increase repeatedly melted several kilometre-thick ice sheets that covered the locations of modern cities like Toronto, Boston, Chicago or Montreal. With increasing COC levels at the end of the last ice age, temperatures increased too. Some ecosystems could not keep up with the rate of change, resulting in several megafaunal extinctions, although human impacts were almost certainly part of the story. Nevertheless, the rate of change in COC over the past million years was tame when compared to today. The highest recorded rate of change before the Industrial Revolution is less than 0.15 ppm per year, just one-twentieth of what we are experiencing today.

“All hell will break loose in the North Atlantic and neighbouring lands..”
• Has James Hansen Foretold The ‘Loss Of All Coastal Cities’? (G.)
James Hansen’s name looms large over any history that will likely be written about climate change. Whether you look at the hard science, the perils of political interference or modern day activism, Dr Hansen is there as a central character. In a 1988 US Senate hearing, Hansen famously declared that the “greenhouse effect has been detected and is changing our climate now”. Towards the end of his time as the director of NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies, Hansen described how government officials had on other occasions changed his testimony, filtered scientific findings and controlled what scientists could and couldn’t say to the media – all to underplay the impact of fossil fuel emissions on the climate. In recent years, the so-called “grandfather of climate science” has added to his CV the roles of author and twice-arrested climate activist and anti-coal campaigner. He still holds a position at Columbia University.
So when Hansen’s latest piece of blockbuster climate research was finalized and released earlier this week, there was understandable global interest, not least because it mapped a potential path to the “loss of all coastal cities” from rising sea levels and the onset of “super storms” previously unseen in the modern era. So what is Hansen claiming? Well, the first thing to understand is that Hansen’s paper, written with 18 other co-authors, many of them highly-reputable names in climate science in their own right, is far from conventional. Most scientific papers only take up four or five pages in a journal. Hansen’s paper – in the journal Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics – grabs 52 pages (although it’s hard to quibble over space when you’re laying out a possible path to widespread global disruption and the complete reshaping of coastlines).
Nor was the paper published in a conventional way. If you’re getting a faint sense of déjà vu about Hansen’s findings, then that could be down to how a draft version of the study was published and widely covered in July last year. The journal runs an unconventional interactive system of peer review where comments and criticisms from other scientists are published for everyone to see, as are the responses from Hansen and his colleagues. This is arguably a more transparent way of conducting the scientific process of peer review – something usually carried out privately and anonymously. None of this should really detract from Hansen and his co-author’s central claims. Firstly, Hansen says they may have uncovered a mechanism in the Earth’s climate system not previously understood that could point to a much more rapid rise in sea levels. When the Earth’s ice sheets melt, they place a freshwater lens over neighboring oceans.
This lens, argues Hansen, causes the ocean to retain extra heat, which then goes to melting the underside of large ice sheets that fringe the ocean, causing them to add more freshwater to the lens (this is what’s known as a “positive feedback” and is not to be confused with the sort of positive feedback you may have got at school for that cracking fifth grade science assignment). Secondly, according to the paper, all this added water could first slow and then shut down two key ocean currents – and Hansen points to two unusually cold blobs of ocean water off Greenland and off Antarctica as evidence that this process may already be starting. If these ocean conveyors were to be impacted, this could create much greater temperature differences between the tropics and the north Atlantic, driving “super storms stronger than any in modern times”, he argues. “All hell will break loose in the North Atlantic and neighbouring lands,” he says in a video summary.

Europe is waiting for unrest in Greece to break out. Then it can send in it own police and military forces. or so it thinks.
• Greece Pledges To Provide Shelters For 50,000 Refugees Within 20 Days (Kath.)
The government said Thursday it will fast-track procedures to create new centers to accommodate 30,000 people within the next 20 days as it finds itself in a race against time to meet an obligation to provide shelter to more than 50,000 asylum seekers stranded in the country, and to prevent an imminent humanitarian disaster. The current capacity of shelters is 38,000. The decision came after a meeting of the government’s council of ministers, chaired by Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras, amid a growing sense of urgency surrounding camps around the country and the increasing realization that the existing infrastructure simply cannot cope with the huge refugee numbers. It also follows the worsening toll on migrants’ health after the withdrawal on Wednesday of aid agencies from camps in Greece to protest the recent EU-Turkey deal – which was activated last Sunday – to stem refugee inflows to Europe, which, they say, contravenes international law.
At the same time, the spokesman of the coordinating committee for refugees, Giorgos Kyritsis, said legislation facilitating the implementation of the EU deal will be tabled in Parliament on Wednesday. The government also said it will further empower the Immigration Policy Ministry to deal with increased obligations implicit in the deal, while temporary staff will also be enlisted. Kyritsis also announced the creation of a monitoring mechanism under the general secretary of the Defense Ministry, Yiannis Tafyllis. The government’s immediate priority, Kyritsis said, will be to provide relief to the sprawling and overcrowded border camp of Idomeni in northern Greece. He added that transport means will be made available over the next few days to transfer refugees to other centers affording more humane conditions.
The mayor of the nearby town of Paionia, Christos Goudenoudis, is calling for the camp’s immediate evacuation as the local community, he said, is feeling increasingly insecure as crime in the area has proliferated. Meanwhile the latest figures suggest a marked decrease in refugee flows into the country over the last few days, while none arrived Thursday – for the first time since the deal between the European Union and Turkey was struck. Authorities, however, have attributed this mostly to bad weather. On Tuesday, inflows were limited to 260 – a significant decrease from the several thousand a couple of weeks ago.