DPC Oyster luggers along Mississippi, New Orleans 1906

Absolutely brilliant by Chris Hamilton. Many more graphs in the article. h/t Tyler
• Euro Saves Germany, Slaughters the PIGS, & Feeds the BLICS (Hamilton)
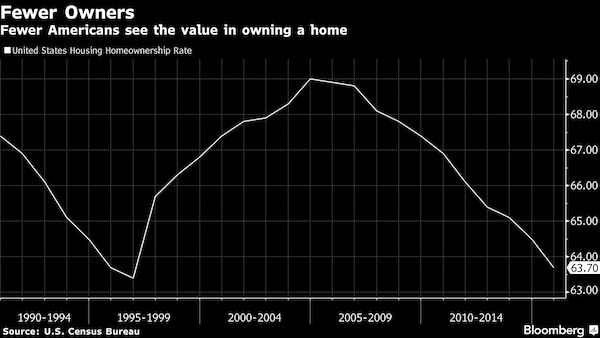
Germany was well aware of it’s post WWII collapsing birth rate and the impact of this on economic growth as this shrinking population of young made it’s way into the Core. Consider Germany’s Core population peaked in 1995 and it’s domestic consumer base has been shrinking since, now down over 3.3 million potential consumers (about a 9% Core decline…remember a depression is a 10% decline in economic activity, which a 9% and growing decline in German consumers would have almost surely induced).
GERMANY
The chart below shows Germany’s Core population from 1950–>2040…but understand this is no guestimate through 2040. This is simply taking the existing 0-24yr/old population (plus anticipated immigration) and sliding them into the Core through 2040. Germany’s Core population is set to fall by over 30% or 10+ million by 2040 (far more than the 7 million Germans of all ages who died in WWII).
But Germany had a plan. With the advent of the EU and Euro just as Germany’s Core began shrinking, Germany was able to avoid the pitfalls of a shrinking domestic consumer base, circumvent the strong German currency, and effectively quadruple it’s effective export market across Europe. German exports, as a % of GDP, have essentially doubled since the advent of the Euro (22% in ’95 to almost 50% in ’16). The chart below highlights Germany’s shrinking Core vs. rising GDP (primarily via exports) since 1995.
[..] the German motivation for the EU and Euro are fairly plain as are the resultant economic transfusion from South to North. But for Germany to be a winner, there had to be a loser in this shrinking pie game. Hello PIGS (Portugal, Italy, Greece, Spain), you lost. As the old poker adage goes, when you don’t know who the sucker at the table is…it’s you. Particularly when you “win big” at first and it all seems so easy…but then it all turns.
PIGS
The chart below shows the PIGS Core population peaking about 15 years later than in Germany but likewise clearly rolling over. By 2040, the PIGS Core population will be back at it’s 1960 levels…down from the 2010 peak by 17 million or about a 30% decline.
But if we look at the PIGS combined GDP and Core population…we see a very different picture than in Germany. The chart below shows the PIGS GDP turned down ahead of the Core population peak. The rise in GDP in these nations was a credit bubble premised on cheap EU wide interest rates more appropriate for Germany. Exports as a % of GDP (which were higher than Germany’s in ’95) have risen less than half of Germany’s increase (rising as a % primarily due to declining PIGS GDP). Low German wage increases and high quality German goods helped displace PIGS domestic manufacturing base.

The logical consequence of the article above. Economic warfare. Tsipras complains about the Troika “moving the goalposts”, but that’s exactly the game, Alexis.
• Greece Wants Eurozone Summit If Deal On Bailout Doesn’t Happen Soon (AP)
Top Greek and European officials indicated Wednesday that it’s possible to reach a breakthrough in the country’s difficult bailout talks over the next two days. Greece’s prime minister said that if a deal on paying Athens the next bailout installment fails to materialize, the eurozone should hold a special summit. Alexis Tsipras said negotiators are “just a breath away” from an agreement at Friday’s scheduled meeting in Malta of the so-called eurogroup, the gather of finance ministers from countries that use the euro. But Tsipras blamed unnamed negotiators among Greece’s European creditors and the IMF for “moving the goalposts” each time Greece was getting close to meeting approval conditions for the bailout. “We are not playing games here … that must stop,” he said, after talks in Athens with EU Council President Donald Tusk.
Greece has to agree on budget measures to get access to its loans. But the talks have dragged on for months, freezing the latest loan payout and hurting chances of a Greek economic recovery after years of recession and turmoil. Without the bailout payment, Greece would struggle to make a debt payment in July, raising anew the prospect of default. Tsipras’ left-led government is pushing for a comprehensive deal that would cover more than just spending cuts and harsh reforms by Greece, but also alleviate the country’s debt burden and ease its access later this year to international bond markets. “If the eurogroup is not in a position to (reach an agreement) on Friday, I have asked President Tusk to convene a eurozone summit to achieve an immediate agreement,” Tsipras said. “I don’t think that will be needed, because there will be a result on Friday, but these delays cannot continue.”

Is it just me, or do we see similar surveys once a week these days? How can anyone maintain that the US economy is doing fine?
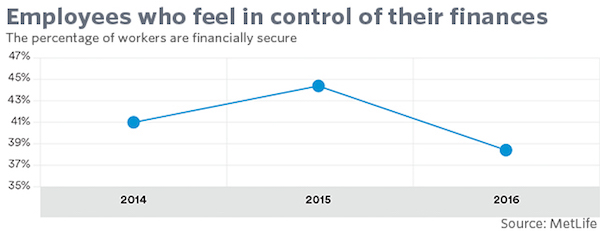
• Half Of American Working Families Are Living Paycheck To Paycheck (MW)
More than seven years after the Great Recession officially ended, there is yet more depressing research that at least half of Americans are vulnerable to financial disaster. Some 50% of people is woefully unprepared for a financial emergency, new research finds. Nearly 1 in 5 (19%) Americans have nothing set aside to cover an unexpected emergency, while nearly 1 in 3 (31%) Americans don’t have at least $500 set aside to cover an unexpected emergency expense, according to a survey released Tuesday by HomeServe USA, a home repair service. A separate survey released Monday by insurance company MetLife found that 49% of employees are “concerned, anxious or fearful about their current financial well-being.”
One explanation: Americans are crippled under the same amount of debt as they had during the recession. The New York Federal Reserve on Monday predicted that total household debt will reach its previous peak of $12.68 trillion in 2017. The last time it reached that level was in the third quarter of 2008, during the depths of the Great Recession. Indeed, it’s already close: Total household debt in the fourth quarter of 2016 was $12.58 trillion. Fewer borrowers have housing-related debt in 2017 and, instead, have taken on auto and student loans.
One illness can push people to the brink of financial ruin. Wanda Battle, a registered nurse for four decades, was recently hit with a $100,000 medical bill. She has visited her local emergency room on more than one occasion due to severe migraines and mini-strokes. Battle, who is based near Nashville, Tenn., managed to reduce her latest hospital bill to $32,000 based on her relatively low income, but still faces $650 monthly payments for a previous $22,000 medical bill. “There were times I couldn’t work,” she told MarketWatch. “I have not held a job that is continuous.”

Glass Steagall. Interesting.
• Trump Top Economic Adviser Cohn Backs Split Of Lending, Investment Banks (BBG)
In a private meeting with lawmakers, White House economic adviser Gary Cohn said he supports a policy that could radically reshape Wall Street’s biggest firms by separating their consumer-lending businesses from their investment banks, said people with direct knowledge of the matter. Cohn, the ex-Goldman Sachs executive who is now advising President Donald Trump, said he generally favors banking going back to how it was when firms like Goldman focused on trading and underwriting securities, and companies such as Citigroup primarily issued loans, according to the people, who heard his comments. The remarks surprised some senators and congressional aides who attended the Wednesday meeting, as they didn’t expect a former top Wall Street executive to speak favorably of proposals that would force banks to dramatically rethink how they do business.
Yet Cohn’s comments echo what Trump and Republican lawmakers have previously said about wanting to bring back the Glass-Steagall Act, the Depression-era law that kept bricks-and-mortar lending separate from investment banking for more than six decades. In the years after the law’s 1999 repeal, banks such as Citigroup, Bank of America and JPMorgan Chase gobbled up rivals and pushed into all sorts of new businesses, becoming one-stop-shopping financial behemoths. Many banking executives believed that the inclusion of former finance executives like Cohn in Trump’s White House would temper major changes such as a Glass-Steagall return. But his Wednesday remarks suggest he could be a wildcard should Congress get serious about reinstating the law. White House officials haven’t said what an updated version of Glass-Steagall might look like.

They actually wrote a manual.
• IMF Explains How To Subvert Resistance Against Elimination Of Cash (Häring)
The IMF has published a Working Paper on “de-cashing”. It gives advice to governments who want to abolish cash against the will of their citizenry. Move slowly, start with harmless seeming measures, is part of that advice. In “The Macroeconomics of De-Cashing”, IMF-Analyst Alexei Kireyev recommends in his conclusions:
“Although some countries most likely will de-cash in a few years, going completely cashless should be phased in steps. The de-cashing process could build on the initial and largely uncontested steps, such as the phasing out of large denomination bills, the placement of ceilings on cash transactions, and the reporting of cash moves across the borders. Further steps could include creating economic incentives to reduce the use of cash in transactions, simplifying the opening and use of transferrable deposits, and further computerizing the financial system. The private sector led de-cashing seems preferable to the public sector led decashing. The former seems almost entirely benign (e.g., more use of mobile phones to pay for coffee), but still needs policy adaptation.
The latter seems more questionable, and people may have valid objections to it. De-cashing of either kind leaves both individuals and states more vulnerable to disruptions, ranging from power outages to hacks to cyberwarfare. In any case, the tempting attempts to impose de-cashing by a decree should be avoided, given the popular personal attachment to cash. A targeted outreach program is needed to alleviate suspicions related to de-cashing; in particular, that by de-cashing the authorities are trying to control all aspects of peoples’ lives, including their use of money, or push personal savings into banks. The de-cashing process would acquire more traction if it were based on individual consumer choice and cost-benefits considerations.”
Note, that the author is not talking about unreasonable objections and imagined disadvantages: He does count it among the advantages of de-cashing in the very next paragraph that personal savings are pushed into banks and he also does count total control of all aspects of financial life under the pros, as in the last sentence of the last quote below.
“As de-cashing gives incentives to economies’ agents to convert their currency in bank deposits, the deposit base of the banking system will increase, which can help reduce the lending rates and expand credit.”
And finally the advice to do it together:
“Coordinated efforts on de-cashing could help enhance its positive effects and reduce potential costs. At least at the level of major countries and their currencies, the authorities could coordinate their de-cashing efforts. Such coordinated efforts are, in particular, important in the decisions to phase out large denomination bills for all major currencies, to use ceilings and other restrictions on cash transactions, and to introduce the reporting requirements for cash transactions or their taxation. For currency areas, a single decashing policy would be clearly preferable to a national one. Finally, consensus between the public and the private sector and outreach on the advantages and modalities of gradual decashing should be viewed as key preconditions for its success.”

They’re all over the place.
• Precursors to the ’08 Crisis are Repeating Now (Nomi Prins)
The biggest banks are still as dangerous as they were before the last crisis, even as they push for less regulation. The big six banks U.S. banks are JP Morgan Chase, Bank of America, Wells Fargo, Citigroup, Goldman Sachs, and Morgan Stanley. Despite their belly-aching about heinous Dodd-Frank Act regulations cramping their betting style, they have all done damn good recently. Since Trump was elected and started talking about deregulation, the big six bank stock values have collectively skyrocketed 33.5% (as of March 10th). Bank of America tops that rise with an eye-popping increase of 48.8% in three months. Goldman Sachs and Morgan Stanley shares shot up 36.6%. Of course, most stocks have been moving up since the election. But keep in mind that the S&P 500 rose just 10.9% during that same period.
Beyond a few extra capital requirements (mostly in the form of a set of rules called Basel III coming from Europe), the need to establish a “living will” in case of another financial emergency, and some limitations on risky trading, not much has changed for these banks. Since the 2008 financial crisis, the big six banks’ total assets have increased by 21%. The big four by 25%. Yet, of the total Global Derivatives Notional amount of $544 trillion, the big six U.S. banks carry $168 trillion of it. Comparing that figure to their total assets, we get a leverage amount of 24 times. To put that in perspective, that’s only slightly less than the leverage their derivatives positions before the 2008 crisis. The biggest banks are still the ones most at risk, and most threatening to anyone with money in the stock market. Cracks have started popping up that make it clear to us that the next financial crisis is just around the corner.
[..] The Fed’s data shows bank lending to businesses has been strong, perhaps too strong. That’s why it’s just now starting to trail off. We’ve had an epic credit expansionary cycle on the back of cheap, central bank fabricated money and ultra-loose monetary policy — what I call “artisanal” money. But defaults and distressed credit activity is rising. Last year, corporates posted their fifth-highest yearly default volume. According to Forbes, “62 companies defaulted on $59.3 billion in debt — 57% higher than the $37.7 billion of defaults in 2015.” That’s an ominous trajectory.
Bank of America just revealed that its 30-90 day consumer credit delinquencies are rising significantly again. So are delinquencies at Wells Fargo. The bank card default rate is at a 42 month high. U.S. subprime auto loan losses are at their highest level since the ’08 crisis. Banks that had been offering more commercial real estate loans now say they will tighten standards. Fears are rising that a greater%age will become delinquent just as they did in the lead up to the last financial crises. A downturn is inevitable. It’s a matter of when, not if.

Of course it shouldn’t.
• Former Fed Advisor Says Central Bank Shouldn’t Comment On Equities (CNBC)
Federal Reserve officials commented on the stock market in March, as minutes from the Federal Open Market Committee meeting revealed the central bank is working to reduce its $4.5 trillion in bonds on its balance sheet this year. Danielle DiMartino Booth, a former Dallas Fed advisor and president of Money Strong, said on CNBC’s Power Lunch on Monday, “It always makes me uncomfortable,” when the central bank comments on U.S. equities. In the summary of the March meeting, Fed members “commented that the recent increase in equity prices might in part reflect investors’ anticipation of a boost to earnings from a cut in corporate taxes or more expansionary fiscal policy, which might not materialize.
They also expressed concern that the low level of implied volatility in equity markets appeared inconsistent with the considerable uncertainty attending the outlook for such policy initiatives.” “I don’t think it’s necessarily the purview of central bankers to comment on this,” DiMartino Booth said. She said the Fed’s comments on the market shows “they are also verbally concerned about financial instability,” and may consider it when the Fed makes fiscal policy decisions, in addition to labor and inflation mandates. David Nelson, chief strategist at Belpointe Asset Management, agreed, “I don’t think the Fed should be commenting on stock prices.”

“..getting from Point A ($4.5 trillion) to Point B ($2 trillion based on balance sheet contracting just over a tenth the size of the country’s GDP) will take at least five years.”
• Is the Fed’s Balance Sheet Headed for the Crapper? (DiMartino Booth)
The good news, for those fearing having to enter monetary rehab, is that it’s going to take a mighty long time to shrink the balance sheet. The fine folks over at Goldman Sachs figure that getting from Point A ($4.5 trillion) to Point B ($2 trillion based on balance sheet contracting just over a tenth the size of the country’s GDP) will take at least five years. (An aside for you insomniacs out there: Have a look back at Mind the Cap, penned back on December 16, 2015, released hours before the Fed hiked rates for the first time in order to raise the cap on the Reverse Repo Facility (RRP) to $2 trillion. (Mind The Cap via DiMartinobooth.com) Come what may, you can consider Goldman’s estimate of the terminal value of a $2 trillion balance sheet and the size of the RRP to be anything but coincidental.)
In any event, things change. As per Goldman, by 2022, “…changes in Fed leadership, regulation, Treasury issuance policy, or macroeconomic conditions could alter both the near-term path and the intended terminal size of the balance sheet.” Indeed. It is entertaining to watch market pundits shift in their skivvies trying to assure the masses that a shrinking balance sheet will be welcomed by risky assets. It was downright comical to read that the Fed’s strategically allowing only long-dated Treasuries to expire and not be replaced would prevent the yield curve from inverting, thus staving off recession. Pardon the interruption, but domestic non-financial sector debt stood at about 140% of GDP in 1980. Today, it’s crested 250% of GDP and keeps rising.
Interest rate sensitivity, especially in commercial real estate, household finance and junk bonds is particularly acute. Oh, and by the way, monetary policy is a global phenomenon. At last check, the European periphery and emerging market corporate bond market were not in the best position to weather a rising rate environment. The best performance, though, was delivered by Chair Janet Yellen herself. In the spirit of giving credit its due, Business Insider’s Pedro da Costa highlighted this delightful nugget from testimony Yellen presented to Congress in February: “Waiting too long to remove accommodation would be unwise, potentially requiring the FOMC to eventually raise rates rapidly, which could risk disrupting the financial markets and pushing the economy into recession.” Isn’t the rapidly flattening yield curve communicating that ‘removing accommodation’ today is one and the same with ‘pushing the economy into recession’?

Better do something, Justin. This is going to blow up in YOUR face.
• Toronto House Price Bubble Goes Nuts (WS)
Residential property sales in Greater Toronto soared 17.7% year-over-year to 12,077 homes, according to the Toronto Real Estate Board (TREB). New listings jumped 15.2% to 17,052. Prices for all types of homes, based on the MLS Home Price Index Composite “Benchmark,” soared 28.6%. The “average” selling price soared 33.2%! That average selling price of C$916,567 is up from C$688,011 a year ago. Over the past five years, it has doubled! The heavenly manna was spread across the spectrum. For condos, the average price in Greater Toronto soared 33.1% to C$518,879; for townhouses it soared 32.9% to C$705,078; for semi-detached houses, 34.4% to C$858,202; and for detached houses, 33.4% to C$1,214,422. Even the house price bubble in Beijing cannot compete with this sort of miracle; new house prices there increased only 22% year-over-year in February.
And Sydney’s fabulous house price bubble just flat out pales compared to the spectacle transpiring in Toronto, with prices up only 19% in March. Vancouver has its own housing bubble to deal with. But there, the government of British Columbia has tried to tamp down on wild speculation with various measures, including a transfer tax aimed squarely at foreign non-resident investors, with “mixed” success. Now the great fear in Toronto’s real estate circles is that the government of Ontario might impose similarly cruel and unusual punishment on the participants in this spectacle. Some measures are on the table, with folks wondering how to stop the bubble from inflating further and causing even greater harm to the real economy when it deflates, as all bubbles eventually do.
They’re reluctant. It seems they want to see how BC’s measures are washing out in Vancouver. The central government too is trying to fine-tune some macroprudential measures, but they’ve had absolutely no effect on Toronto’s housing bubble. And the Bank of Canada, which has been fretting about the housing bubble for a while – always couched in its very careful terms – refuses to raise rates. Everyone is talking. No one dares to do anything real about Toronto’s house price bubble. In Toronto, according the real estate folks, it’s all based on fundamentals. It’s based on supply and demand and very rational calculated thinking, and there is no bubble in sight, lenders are just fine, and if Canadians are locked out of the housing market, so be it, it’s just a shortage of housing, really.

We’re supposed to believe Australia never got the memo? Get real.
• Interest-Only Loans ‘To End In Tears’ (Aus.)
Former National Australia Bank boss Don Argus has added to warnings about the overreliance of interest-only loans, declaring it is going to “lead to tears” as interest rates eventually move higher. After a widely expected decision by the Reserve Bank to leave its official cash rate unchanged at a record low 1.5% at its monthly board meeting yesterday, Mr Argus declared that borrowers had “forgotten” the cyclical nature of interest rates. “You can only hope that some of these dizzy values that you see people paying for houses now, you hope that they stand up on any correction, any economic correction”, Mr Argus told The Australian. Backing a tightening of so-called macroprudential controls on home lending announced by the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority last week, Mr Argus, a former BHP Billiton chairman, said the capacity of borrowers to repay loans “was always a primary concern in housing loans of yesteryear”.
“If you progressed to just an interest-only environment, that’s only going to lead to tears.” However, in a speech given in Melbourne last night, RBA governor Philip Lowe took aim at banks and other lenders for making overly generous serviceability assessments. “Despite the focus on this area over recent times, too many loans are still made where the borrower has the skinniest of income buffers after interest payments”, Dr Lowe said. “In some cases, lenders are assuming that people can live more frugally than in practice they can, leaving little buffer if things go wrong. So APRA quite rightly has said lenders can expect a strong supervisory focus on loans with a very low net income surplus.” Dr Lowe also noted that the prevalence of interest-only lending was “unusual” globally.
“A reduced reliance on interest-only loans in Australia would be a positive development and would help improve our resilience. With interest rates so low, now is a good time for us to move in this direction,” he said. Almost 40% of residential mortgage lending in Australia is interest-only, where the borrower pays off the interest rather than the principal.

“It is about regime survival for a Chinese Communist Party that faces existential risk if they stumble.”
• China Is More Fragile than You Realize (DR)
China’s economy is not just about providing jobs, goods and services. It is about regime survival for a Chinese Communist Party that faces existential risk if they stumble. Given the systemic problems inherent in trying to run an economy in the absence of the accurate price signals only free markets provide (a problem for both Chinese socialism and the West’s corrupt crony markets), their challenges are worsening every day. Malinvestments the size of ghost cities are not lost on the world’s central bankers who fear a systemic collapse of China’s economy, nor on the brilliant investors who are betting on China’s collapse like they bet against the corrupt banking products in the U.S. housing bubble. Before the 2008 financial crisis, the Chinese debt-to-GDP ratio was 147%; now, it is at about 250%.
Quietly, the Chinese leadership has begun to lower growth expectations but even those numbers should be taken with skepticism. The methodology used to calculate their GDP figures is not publicly known but uses economic data that can be manipulated for sake of appearances. Declining growth impacts China’s financial market as well. Local banks are struggling with non-performing debt rapidly increasing. Non-bank financial institutions referred to as the “shadow banking system” are spreading, with little regulation or recognition of the risks. The government’s attempts to better regulate the system is stymied by local corruption where exaggerated assets and little documentation mask a wave of malinvestments. Like the appearance of no-doc “liar” loans in the U.S. in 2004-2006, the entire shadow banking system is signalling risk of systemic collapse.
Another source of malinvestment is the real estate market. Commercial real estate bubbles are breathtaking and residential real estate values have begun to fall. This seriously threatens social unrest as many Chinese families have put their life savings into real estate believing well intended but nonsensical government assurances of support to an ever increasing housing market. As is typical with most countries, the Chinese government tries to mask the ravages of inflation by adjusting their public measurement downwards. Doing so conceals the impact it has on households. But when values collapse wiping out the entire family savings for their old age, there will be a terrifying political backlash.
Yet another concern is that the 2008 Lehman bankruptcy marked a plateau in world trade. This has been particularly difficult for China as exports accounted for more than 40% of their GDP. With reduced global trade, China began to lose competitiveness in the market place. Inflation of the money supply in the Chinese economy required higher wages to offset rising prices. In turn, China tried to move into higher value exports by manufacturing more technologically advanced and complicated products. Unfortunately, in the transition, quality suffered and foreign markets began to look for alternatives to Chinese components.

Good to see I’m not the only one who questions the narrative (see Any of this Sound Familiar?).
• Syria Gas Attack: Assad’s Doing…Or False Flag? (Ron Paul)
Just days after the US Administration changed course on Syrian President Assad, saying he could stay, an alleged chemical weapon attack that killed dozens of civilians has been blamed on the Syrian government. Did Assad sign his own death warrant with such an attack…or does some other entity benefit?

“Sort of like in a divorce case where lawyers are hired, investigators are hired just to find out what the other person is doing from morning until night and then you try to piece it together later on.”
• Reports In Unmasking Controversy Were Detailed (Fox)
The intelligence reports at the center of the Susan Rice unmasking controversy were detailed, and almost resembled a private investigator’s file, according to a Republican congressman familiar with the documents. “This is information about their everyday lives,” Rep. Peter King of New York, a member of the House Intelligence committee said. “Sort of like in a divorce case where lawyers are hired, investigators are hired just to find out what the other person is doing from morning until night and then you try to piece it together later on.” On the House Intelligence Committee, only the Republican chairman, Devin Nunes of California, and the ranking Democrat Adam Schiff, also of California, have personally reviewed the intelligence reports. Some members were given broad outlines.
Nunes has consistently stated that the files caused him deep concern because the unmasking went beyond the former national security adviser Mike Flynn, and the information was not related to Moscow. Schiff said in a statement, “I cannot comment on the content of these materials or any other classified documents, and nothing should be inferred from the fact that I am treating classified materials the way they should be treated – by refusing to comment on them. Only the Administration has the power to declassify the information and make it available to the public.” Former National Security Adviser Rice is under scrutiny after allegations she sought to unmask the identities of Trump associates caught up in surveillance – such as phone calls between foreign intelligence targets. Rice denies ever having sought such information for political purposes and has defended her requests as routine.
[..] During his March 20 testimony before the House Intelligence Committee, NSA director Admiral Mike Rogers said only 20 individuals within the agency are authorized to approve those requests. “They receive specific training, there are specific controls put in place in terms of our ability to disseminate information out of the databases associated with U.S. persons,” Rogers said at the time. What it appears to suggest is that the NSA itself agreed that the instances in which Rice requested unmasking warranted that action. FBI Director James Comey was less direct. “I don’t know for sure. As I sit here, surely more, given the nature of the FBI’s work,” he testified.

What’s a 100 million more or less?
• We Are Heading For The Warmest Climate In Half A Billion Years (Conv.)
Carbon dioxide concentrations are heading towards values not seen in the past 200m years. The sun has also been gradually getting stronger over time. Put together, these facts mean the climate may be heading towards warmth not seen in the past half a billion years. A lot has happened on Earth since 500,000,000 BC – continents, oceans and mountain ranges have come and gone, and complex life has evolved and moved from the oceans onto the land and into the air. Most of these changes occur on very long timescales of millions of years or more. However, over the past 150 years global temperatures have increased by about 1ºC, ice caps and glaciers have retreated, polar sea-ice has melted, and sea levels have risen.Some will point out that Earth’s climate has undergone similar changes before. So what’s the big deal?
Scientists can seek to understand past climates by looking at the evidence locked away in rocks, sediments and fossils. What this tells us is that yes, the climate has changed in the past, but the current speed of change is highly unusual. For instance, carbon dioxide hasn’t been added to the atmosphere as rapidly as today for at least the past 66m years. In terms of geological time, 1ºC of global warming isn’t particularly unusual. For much of its history the planet was significantly warmer than today, and in fact more often than not Earth was in what is termed a “greenhouse” climate state. During the last greenhouse state 50m years ago, global average temperatures were 10-15ºC warmer than today, the polar regions were ice-free, palm trees grew on the coast of Antarctica, and alligators and turtles wallowed in swamp-forests in what is now the frozen Canadian Arctic.