
DPC H.A. Testard Bicycles & Automobiles, New Orleans 1910



Behind the curtain.
• September Liquidity Crisis Forced Fed Into Massive Reverse Repo Operation (IRD)
Something occurred in the banking system in September that required a massive reverse repo operation in order to force the largest ever Treasury collateral injection into the repo market. Ordinarily the Fed might engage in routine reverse repos as a means of managing the Fed funds rate. However, as you can see from the graph below, there have been sudden spikes up in the amount of reverse repos that tend to correspond the some kind of crisis – the obvious one being the de facto collapse of the financial system in 2008. You can also see from this graph that the size of the “spike” occurrences in reverse repo operations has significantly increased since 2014 relative to the spike up in 2008. In fact, the latest two-week spike is by far the largest reverse repo operation on record.
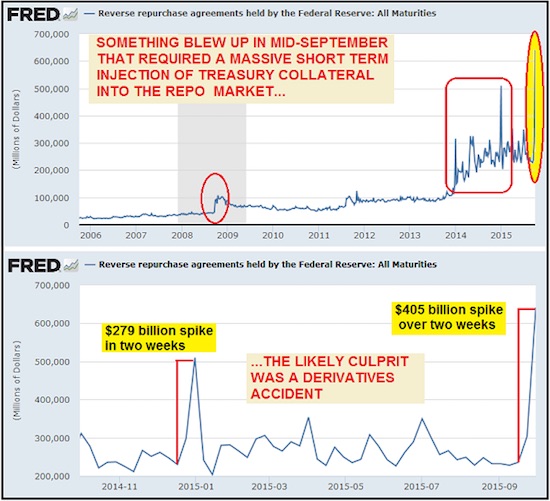
Besides using repos to manage term banking reserves in order to target the Fed funds rate, reverse repos put Treasury collateral on to bank balance sheets. We know that in 2008 there was a derivatives counter-party default melt-down. This required the Fed to “inject” Treasury collateral into the banking system which could be used as margin collateral by banks or hedge funds/financial firms holding losing derivatives positions OR to “patch up” counter-party defaults (see AIG/Goldman).
What’s eerie about the pattern in the graph above is that since 2014, the “spike” occurrences have occurred more frequently and are much larger in size than the one in 2008. This would suggest that whatever is imploding behind the scenes is far worse than what occurred in 2008. What’s even more interesting is that the spike-up in reverse repos occurred at the same time – September 16 – that the stock market embarked on an 8-day cliff dive, with the S&P 500 falling 6% in that time period. You’ll note that this is around the same time that a crash in Glencore stock and bonds began. It has been suggested by analysts that a default on Glencore credit derivatives either by Glencore or by financial entities using derivatives to bet against that event would be analogous to the “Lehman moment” that triggered the 2008 collapse.
The blame on the general stock market plunge was cast on the Fed’s inability to raise interest rates. However that seems to be nothing more than a clever cover story for something much more catastrophic which began to develop out of sight in the general liquidity functions of the global banking system. Without a doubt, the graphs above are telling us that something “broke” in the banking system which necessitated the biggest injection of Treasury collateral in history into the global banking system by the Fed.

BoA says $100 billion exposure to Glencore alone, and Bernstein says 6 UK traders have only $6 billion? Hard to believe.
• Bank Of England Warns Financial Institutions Over Commodities Exposure (Guardian)
The Bank of England has told major banks to check the impact of falling commodity prices on their lending positions. Threadneedle Street has been asking for information from the major players in light of the rout in the shares in Glencore, the commodity trading and mining firm. Glencore’s shares plunged by 29% a week ago on Monday to 68.62p. Although they have subsequently recovered to 120p, the shares are trading far below their 2011 flotation price of 530p. The fall in Glencore stock came amid concerns about its debt position and fears that the Chinese economy was on the cusp of a hard landing that would further reduce already softening global demand for commodities.
The demand for information by the Bank of England has emerged at a time when banking analysts have been questioning the exposure of banks to the the fallout in the commodity sector. In a research note entitled The $100bn Gorilla in the Room, Bank of America analysts said: “The banking industry may have significantly more exposure to Glencore than is generally appreciated in the market.” Analysts at Bernstein, the broking firm, have conducted a wider analysis of UK banks’ exposure to six commodity trading houses, including Glencore, and concluded about $6bn (£3.9bn) worth of loans are outstanding. Standard Chartered, the Asian-focused London-based bank, was given the highest exposure of $1.9bn.
The move by the Bank to ask financial institutions to check their exposure to commodities follows similar health checks during the Greek crisis and amid Chinese stock market volatility in the summer. The requests are made through the Prudential Regulation Authority, the Bank of England’s regulatory arm. The Bank of England is launching stress tests on the major lenders and has said China is among the factors that will be included in the financial health check. The results are expected to be published in December.

Bubble after bubble, until there’s none left.
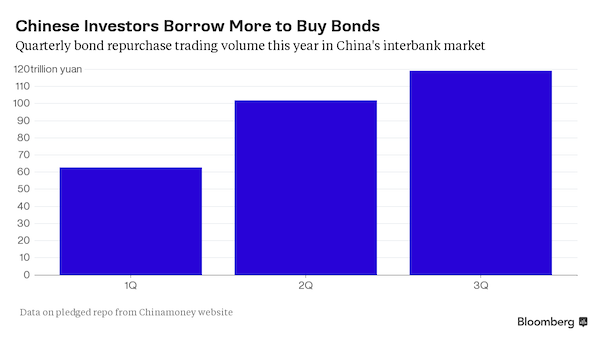
• If You Thought China’s Equity Bubble Was Scary, Check Out Bonds (Bloomberg)
As a rout in Chinese stocks this year erased $5 trillion of value, investors fled for safety in the nation’s red-hot corporate bond market. They may have just moved from one bubble to another. So says Commerzbank, which puts the chance of a crash by year-end at 20%, up from almost zero in June. Industrial Securities and Huachuang Securities are warning of an unsustainable rally after bond prices climbed to six-year highs and issuance jumped to a record. The boom contrasts with caution elsewhere. A selloff in global corporate notes has pushed yields to a 21-month high, and credit-derivatives traders are demanding near the most in two years to insure against losses on Chinese government securities.
While an imminent collapse isn’t yet the base-case scenario for most forecasters, China’s 42.1 trillion yuan ($6.6 trillion) bond market is flashing the same danger signs that triggered a tumble in stocks four months ago: stretched valuations, a surge in investor leverage and shrinking corporate profits. A reversal would add to challenges facing China’s ruling Communist Party, which has struggled to contain volatility in financial markets amid the deepest economic slowdown since 1990. “The Chinese government is caught between a rock and hard place,” said Zhou Hao, a senior economist in Singapore at Commerzbank, Germany’s second-largest lender. “If it doesn’t intervene, the bond market will actually become a bubble. And if it does, the market could crash the way the equity market did due to fast de-leveraging.”

Deutsche equals tens of trillions in derivatives exposure. Why is it getting scared, and why now?
• CEO: Deutsche Isn’t Worth What It Once Was And Can’t Pay What It Used To (BBG)
Deutsche Bank’s new boss delivered a harsh message to shareholders and employees: Europe’s biggest investment bank isn’t worth what it once was and can’t pay them what they’re used to. Co-CEO John Cryan decided to mark down the value of the securities unit because of rules that will force the company to hold more capital, Deutsche Bank said in a statement late Wednesday. Higher equity requirements have hurt profitability. Cryan is preparing to shrink the trading empire built by his predecessor, Anshu Jain, to lower costs, lift capital levels and raise Deutsche Bank from its position as the worst-valued stock among global banks. That could mean giving up the aspiration to remain a top global investment bank and rolling back parts of the expansion it pursued over the last two-and-a-half decades.
“This perhaps is the beginning of the new chief executive taking a close look and saying, ‘actually, are we better off being the German champion bank, or do we want to maintain this ambition of being a global player?”’ Robert Smithson at THS Partners said. Deutsche Bank said it wrote down goodwill, a measure of the value a company expects to extract from acquisitions, to zero at both its investment- and consumer-banking units. The charge at the securities business relates in part to the $9 billion purchase of Bankers Trust in 1998, Cryan said in a memo to staff. That deal was a major step in the company’s transformation into a global investment bank because it expanded access to the U.S., home to the world’s biggest capital markets. Paul Achleitner, Deutsche Bank’s supervisory board chairman, advised the bank on the purchase while at Goldman Sachs.
The writedown at the securities unit, as well as charges at the company’s retail-banking division and legal costs, will probably cause a third-quarter net loss of €6.2 billion, Deutsche Bank said. The bank may cut or eliminate this year’s dividend, and employees, by way of compensation, will have to share the pain with investors, Cryan said. The stock fell 1.8% to €25.03. Cryan isn’t alone in writing down the value of acquisitions that failed to deliver anticipated returns. UniCredit, Italy’s biggest bank, posted a record loss for the fourth-quarter of 2013 after taking more than 9 billion euros of impairments, including those on the goodwill of units in Italy, central and eastern Europe and Austria. Investors were already valuing Deutsche Bank at less than it says its assets are worth. The company trades at about 0.6 times book value, the lowest ratio among its global peers.

Deutsche, Credit Suisse and UniCredit. Dominoes starting to drop.
• Day After Deutsche Says Not All’s Well, Credit Suisse Also Admits Trouble (ZH)
Not everything is “fine” in the land of European banks, in fact quite the opposite. One day after Deutsche Bank warned of a massive $7 billion loss and the potential elimination of the bank’s dividend which had been a German staple since reunification, a move which many said was a “kitchen sinking” of the bank’s problems (but not Goldman, which said it was “not a kitchen sinking, but a sign of the magnitude of the challenge” adding that “this development confirms our view that the task facing new management is very demanding. Litigation issues do not end with this mark down – we expect them to persist for a multi-year period. We do not see this as a “clean up” but rather an indication of what the “fixing” of Deutsche Bank will entail over the 2015-18 period), it was the turn of Switzerland’s second biggest bank after UBS, Credit Suisse, to admit it too needs more cash when moments ago the FT reported that the bank is “preparing to launch a substantial capital raising” when the new CEO Thiam unveils his strategic plan for the bank in two weeks’ time.
FT adds that “while not specifying an amount, they pointed to a poll published last week by analysts at Goldman Sachs concluding that 91% of investors expect the Swiss bank to raise more than SFr5bn in new equity.” The stock price did not like it, although just like with DB, we expect the “story” to quickly become that the Swiss bank is putting all its dirty laundry to rest, so an equity dilution is actually quite positive. Incidentally, with DB stock green on the day following a dividend cut, perhaps it would go limit up if Deutsche Bank had announced a negative dividend? The official narrative is well-known: the bank does not need the funds, it is simply a precaution ahead of new, more stringent capital requirements:
The capital is likely to be used to absorb losses triggered by a faster restructuring of the Swiss group, the people said. But Credit Suisse will also need higher capital ratios to comply with toughening demands from regulators. The Swiss authorities are expected to announce an increase of minimum capital ratios over the coming months, which could prove more challenging for the bank than its better capitalised local rival, UBS. Credit Suisse’s common equity tier one capital ratio of 10.3% compares with UBS’s 13.5%..
The real reason, of course, has nothing to do with this, and everything to do with the collapse of manipulation cartels involving Liebor, FX, commodities, bonds, equities, gold, and so on, because when banks can no longer collude with each other to push markets in any given direction, that’s when they start losing money. That and, of course, the fact that central bank intervention in capital markets has made it virtually impossible to trade any more. Or as they call it, “miss capital ratios.” Expect many more such announcements in the coming weeks.

While Brussels insists there is a cyclical recovery…
• Bruised Germany Is Canary in Coal Mine for Europe Economic Woes (Bloomberg)
The euro area’s pillar of economic strength is starting to show cracks. Germany’s manufacturing industry is taking a hit from cooling demand in emerging markets. Two of its icons – Deutsche Bank and Volkswagen – are in turmoil. And refugees are flooding across its borders at a rate of 10,000 a week. The strains are putting the resilience of Europe’s economic powerhouse to the test after exports in August fell the most since the height of the 2009 recession, and factory orders and industrial output unexpectedly declined. The flood of bad news is all the more troubling as the 19-nation euro area strives to sustain an economic revival that remains fragile. “Germany is the canary in the mine for Europe,” said Pau Morilla-Giner at London & Capital Asset Management in London.
“It is the most exposed country to what happens outside of the continent.” German exports slumped 5.2% in August from the previous month, the Federal Statistics Office in Wiesbaden said on Thursday. That’s the most since the recession of 2009. Imports slid 3.1%, shrinking the trade surplus to €15.3 billion from €25 billion. Weakening trade with China and Russia prompted Hamburger Hafen und Logistik, which handles about three in four containers at the city port, to cut its 2015 earnings forecast on declining container volume. Germany’s gateway to Asia serves as a major transfer hub for containers carried by deep-sea ships from the Pacific region and then reloaded onto smaller feeder vessels destined for Baltic Sea ports, including the Russian harbor of St. Petersburg.
BASF, whose dominance in the global chemical industry makes it a barometer for the German economy, is curbing spending and scrapped its 2020 profit and sales target on Sept. 28 after becoming more pessimistic on economic growth and chemical production. The risks for Germany’s steel producers “have increased significantly, especially in the area of foreign trade, in recent weeks and months,” the Wirtschaftsvereinigung Stahl industry group said on Thursday in a report showing crude steel production fell almost 4% in September. “One of the biggest pressure points for the euro zone’s fragile economic recovery is German export orders,” said Nicholas Spiro, managing director of Spiro Sovereign Strategy in London. “News that they fell sharply throws the China-driven weakness in the global economy into sharp relief.”

Problems mount for the House of Saud. Only option left is to increase pumping.
• Saudi Arabia Orders Deep Spending Curbs Amid Oil Price Slump (Bloomberg)
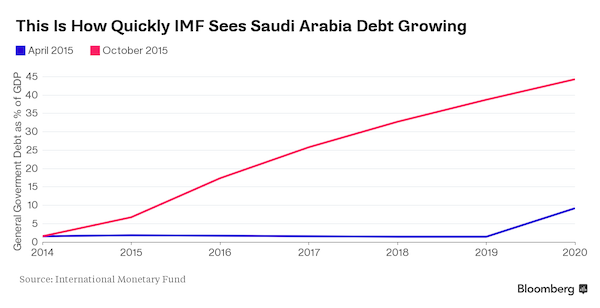
Saudi Arabia is ordering a series of cost-cutting measures as the slide in oil prices weighs on the kingdom’s budget, according to two people with knowledge of the matter. The finance ministry told government departments not to contract any new projects and to freeze appointments and promotions in the fourth quarter, the people said, asking not to be identified because the information isn’t public. It also banned the buying of vehicles or furniture, or agreeing any new property rentals and told officials to speed up the collection of revenue, they said. With oil accounting for about 90% of revenue in the Arab world’s largest economy, a drop of more than 40% in crude prices in the past 12 months has combined with wars in Yemen and Syria to pressure Saudi Arabia’s finances.
While public debt is among the world’s lowest, with a gross debt-to-GDP ratio of less than 2% in 2014, that may rise to 33% in 2020, according to estimates from the IMF. “In order to demonstrate a bit of fiscal discipline the government needed to take some measures in 4Q to moderate spending,” John Sfakianakis, Middle East director at Ashmore Group, said. “Going forward Saudi Arabia will have to implement spending cuts and efficiencies in order to avoid a runaway fiscal deficit in 2016.” To help shore up its finances, authorities plan to raise between 90 billion riyals ($24 billion) and 100 billion riyals in bonds before the end of the year, people with knowledge of the matter said in August. The kingdom’s net foreign assets fell for a seventh month to $654.5 billion in August, the lowest level in more than two years.

Maybe someone should define PQE. Would seem handy for future discussion.
• Former IMF Chief Economist Blanchard Backs ‘People’s QE’ (Reuters)
“People’s QE” could be an option to help economies fight future crises, Olivier Blanchard, who has just stepped down as chief economist of the IMF, said on Wednesday. Quantitative easing, where central banks buy assets such as government bonds from banks in exchange for newly created money, has been used in the euro zone, the United States and Britain to increase financial market liquidity and stimulate growth. But the verdict is still out on whether central banks should be buying assets, as they do now, or instead tie up with governments to spend it on ‘real’ goods, known as “people’s QE”, as a way of stimulating the economy, Blanchard said during a lecture at the Cass Business School.
“There is clearly something else you can do if you get to zero (inflation) and still want to increase spending. You can buy goods.” “Which one should you choose? We haven’t asked the question in the crisis but we should,” he said. Blanchard said that this does not mean central banks would buy goods directly. Rather, governments can increase their fiscal deficits by spending on infrastructure projects. Central banks can then buy this debt with newly created money. He also stressed that these fiscal deficits should be “a certain size and not more”. People’s QE was a prominent part of the leadership election campaign for British Labour Party leader Jeremy Corbyn.
QE has come under popular criticism because banks, which were supposed to lend out the new money into the wider economy to stimulate growth, have not necessarily done so. Blanchard argues that buying goods rather than assets can get the money out into the economy another way. People’s QE has also been criticised because it may compromise central bank independence. Bank of England chief economist Andy Haldane said in September people should be “very cautious” about encroaching on the separation between fiscal and monetary policy.

Any questions?
• Hong Kong High Street Shop Rents Fall Up To 43% From Their Peaks (SCMP)
Hong Kong’s high street shop rents have fallen as much as 43% when compared with the peak levels in the fourth quarter of 2013, according to international property consultant DTZ/Cushman & Wakefield. Plagued by smaller growth in tourist arrivals and a decrease in sales of luxury products, retailers have been facing a challenging business environment and find the rents they are paying in prime street shops as too expensive. Some retailers requested landlords to cut rents while others opted to relocate. As a result, the retail high street rents in Causeway Bay, Tsim Sha Tsui, Central and Mongkok had gone down by 26-43% as of the third quarter from their respective peak levels in the fourth quarter of 2013, or during lease renewal compared to the last rent a few years ago, said Kevin Lam, DTZ/Cushman & Wakefield’s Head of Business Space, Hong Kong.

It was all El-Erian after all.
• Bill Gross Sues Pimco For At Least $200 Million (NY Times)
The man known as the bond king, William H. Gross, is suing the company that he built into one of the largest asset managers in the world, providing his own colorful version of an ugly feud that led to his departure last year. The lawsuit, filed on Thursday, represents a bold effort by Mr. Gross to repair the damage that was done to his reputation in the year before and after he was fired from Pimco. News media reports have portrayed Mr. Gross’s departure as a product of his erratic and domineering behavior at the firm he helped found in 1971. Mr. Gross is seeking “in no event less than $200 million” from Pimco for breach of covenant of good faith and fair dealing, among other causes of action.
But to underscore the degree to which the suit is motivated by Mr. Gross’s desire to correct the public record, he has promised to donate any money he recovers to charity, his lawyer, Patricia L. Glaser, said. The lawsuit presents a picture of Pimco — an asset manager based in California that is responsible for billions of dollars in retirement savings — as a den of intrigue riven by back stabbing and competing egos. The first sentence of the suit says that Mr. Gross was pushed out by a “cabal” of Pimco managing directors who were “driven by a lust for power, greed, and a desire to improve their own financial position.” “Their improper, dishonest, and unethical behavior must now be exposed,” the opening paragraph concludes.
The suit takes aim at the man who was once in line to succeed Mr. Gross, Mohamed El-Erian, and at the man who has succeeded Mr. Gross as Pimco’s group chief investment officer, Daniel J. Ivascyn. Mr. El-Erian is now the chief economic advisor at Allianz, Pimco’s parent company. Both men, the suit says, were eager to take Pimco away from its traditional focus on bond funds and into riskier investment strategies that would earn it higher fees and lead to bigger bonuses for top executives. Mr. Gross, on the other hand, is said in the suit to have consistently advocated for keeping the firm focused on lower-fee investment products.

“If the banks had just Googled this guy, they would have known enough to stay away..”
• Ponzi Suspect’s 17 Accounts Raise Questions Over Bank Safeguards (Bloomberg)
The U.S. requires banks to know their customers. Looks like several big ones, including Citigroup, JPMorgan and Wells Fargo, may have missed getting acquainted with Daniel Fernandes Rojo Filho. Filho, a 48-year-old Brazilian self-proclaimed billionaire living in Orlando, Florida, came under U.S. investigation in 2009 related to an alleged conspiracy involving drug trafficking, money laundering and a Ponzi scheme. Around then, he and others under the federal probe forfeited tens of millions of dollars worth of Lamborghinis, gold bars and other assets, according to court documents. He agreed in 2013 to forfeit another $25 million in accounts registered to his children and businesses. That was all a matter of public record in mid-2014, when Filho started opening new bank accounts.
He set up at least 17 of them in the name of his company – DFRF Enterprises, derived from his initials – and signed his own name. Filho’s banking flurry is detailed in several fresh cases against him, including an August criminal indictment alleging he used some of these accounts in a scheme that promised investors income from nonexistent gold-mining operations. Filho faces similar allegations in separate lawsuits filed this year by the Securities and Exchange Commission and by a group of investors. “If the banks had just Googled this guy, they would have known enough to stay away,” said Evans Carter, a Framingham, Massachusetts-based attorney who brought the investors’ class-action suit early this year. Filho, who was arrested in July, awaits a hearing today in Boston connected to the criminal charges against him.

“Today, there are 46 million Americans in an electronic soup kitchen line..”
• Why This Feels Like A Depression For Most People (Jim Quinn)
Everyone has seen the pictures of the unemployed waiting in soup lines during the Great Depression. When you try to tell a propaganda believing, willfully ignorant, mainstream media watching, math challenged consumer we are in the midst of a Greater Depression, they act as if you’ve lost your mind. They will immediately bluster about the 5.1% unemployment rate, record corporate profits, and stock market near all-time highs. The cognitive dissonance of these people is only exceeded by their inability to understand basic mathematical concepts. The reason you don’t see huge lines of people waiting in soup lines during this Greater Depression is because the government has figured out how to disguise suffering through modern technology. During the height of the Great Depression in 1933, there were 12.8 million Americans unemployed.
These were the men pictured in the soup lines. Today, there are 46 million Americans in an electronic soup kitchen line, as their food is distributed through EBT cards (with that angel of mercy JP Morgan reaping billions in profits by processing the transactions). These 46 million people represent 14% of the U.S. population. There are 23 million households on food stamps in a nation of 123 million households. Therefore, 19% of all households in the U.S. are so poor, they require food assistance to survive. In 1933 there were approximately 126 million Americans living in 30 million households. The government didn’t keep official unemployment records until 1940, but the Department of Labor estimated 12.8 million people were unemployed during the worst year of the Great Depression or 24.9% of the labor force.
By 1937 it had fallen to 14.3% or approximately 8 million people. The number of people unemployed during the 1930’s is an excellent representation of the number of households on government assistance during the Great Depression because 79% of all households were occupied by married couples with 4 people per household versus 48% married couple households today with 2.5 people per household. The unemployment rate averaged 19% during the heart of the Great Depression. Therefore, approximately 19% of all the households in the U.S. needed government assistance to feed themselves. That happens to be the exact %age of households currently needing food stamps to feed themselves.

Do they really think this’ll fly? “..it sure does cause you to scratch your head that we have this software that just happens to be in 11 million cars and no one in the whole company noticed it.”
• VW Exec Blames ‘A Couple Of’ Rogue Engineers For Emissions Scandal (LA Times)
A top Volkswagen executive on Thursday blamed a handful of rogue software engineers for the company’s emissions-test cheating scandal and told outraged lawmakers that it would take years to fix most of the nearly half million vehicles affected in the U.S. “This was a couple of software engineers who put this in for whatever reason,” Michael Horn, VW’s U.S. chief executive, told a House subcommittee hearing. “To my understanding, this was not a corporate decision. This was something individuals did.” Horn, chief executive of Volkswagen Group of America, revealed that three VW employees had been suspended in connection with software that detects and fools emissions testing equipment in the company’s diesel vehicles. The automaker said that the so-called defeat device is loaded onto as many as 11 million vehicles worldwide.
Horn’s testimony before the House Energy and Commerce Committee’s oversight and investigations panel coincided with a raid Thursday by German investigators at Volkswagen’s Wolfsburg headquarters. The exact number of engineers the company blames remained unclear. Horn said both “couple” and three, then said under questioning that he did not yet know the exact number. Regardless, the claim that such a small number of people could have pulled off such a massive fraud brought immediate skepticism from lawmakers and industry experts. “I cannot accept VW’s portrayal of this as something by a couple of rogue software engineers,” said Rep. Chris Collins (R-N.Y.). “Suspending three folks — it goes way, way higher than that.”
Auto industry veterans agreed. “There are not rogue engineers who unilaterally decide to initiate the greatest vehicle emission fraud in history. They don’t act unilaterally,” said Joan Claybrook, former administrator of the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. “They have teams that put these vehicles together. They have a review process for the design, testing and development of the vehicles.” James Womack, an expert on the international auto industry, also expressed doubts. “It might not be reviewed and discussed leaving an email or voicemail trail,” Womack said, “but it sure does cause you to scratch your head that we have this software that just happens to be in 11 million cars and no one in the whole company noticed it.”

The bosses knew. But will that come out?
• VW Facilities, Worker Homes Raided in Diesel Investigation (Bloomberg)
Police and prosecutors swooped in on Volkswagen facilities and private homes on Thursday in a dawn raid to gather evidence about who was behind the carmaker’s decision to cheat on diesel emissions tests. Three prosecutors and some 50 state criminal investigators searched the carmaker’s factories and employees’ homes starting in the early morning and continuing through the afternoon in Wolfsburg, its headquarters city, and elsewhere, said Birgit Seel, a senior prosecutor in the German state of Lower Saxony. Investigators took documents and electronic media, and it may take several weeks to review the material, Seel said. She didn’t identify employees whose homes were searched.
“We will fully support the prosecutor’s office with its investigation into the facts of the case and into the people responsible to swiftly and completely get to the bottom of the matter,” Volkswagen said in an e-mailed statement. The company filed its own criminal complaint on Sept. 23. The raids come as pressure on Volkswagen intensifies. The company’s U.S. chief, Michael Horn, will face U.S. lawmakers Thursday in the first public hearing on the scandal. In Europe alone, Volkswagen will probably need to exchange or rebuild parts for about 3.6 million engines equipped with illegal software that turned on full pollution controls only during tests, German Transport Minister Alexander Dobrindt said. Volkswagen told German regulators the parts for 1.6-liter engines that need the fix won’t be available until September 2016, Dobrindt said.

“.. I think the American people ought to ask that we fire you and hire West Virginia University to do our work.”
• US House Slams Regulators For Not Catching VW For Years (Reuters)
Volkswagen US chief executive blamed “individuals” for using software to cheat on diesel emissions at a House hearing on Thursday as lawmakers attacked federal environmental regulators for failing to catch the fraud for years. Michael Horn, head of Volkswagen Americas, testified before a House of Representatives oversight and investigations panel about the emissions scandal that has chopped more than a third of the company’s market value and sent tremors through the global auto industry. Volkswagen’s use of defeat devices, software that evaded U.S. tests for emissions harmful to human health, was not a corporate decision, but something a few employees engineered, Horn said under oath. “This was a couple of software engineers who put this in for whatever reason,” Horn said about the software code inserted into diesel cars since 2009.
Volkswagen used different defeat devices in Europe and the United States, Horn said, as emissions standards are different in the two regions. “Some people have made the wrong decisions in order to get away with something,” Horn said when asked by lawmakers if Volkswagen cheated with defeat devices because it was cheaper than using special injection systems to cut emissions. Lawmakers slammed an Environmental Protection Agency official who testified after Horn for not catching Volkswagen. Representative Michael Burgess, a Texas Republican, questioned the size of EPA’s annual budget, noting that the cheating was uncovered by a West Virginia University study that had a budget of less than $70,000.
“I’m not going to blame our budget for the fact that we missed this cheating,” replied the EPA’s Christopher Grundler, who said his transportation and air quality office has an annual budget of roughly $100 million. “I do think we do a very good job of setting priorities.” Burgess replied: “With all due respect, just looking at the situation, I think the American people ought to ask that we fire you and hire West Virginia University to do our work.”

“What we are seeing here is a dieselgate that covers many brands and many different car models..”
• Four More Carmakers Join ‘Dieselgate’ Emissions Row (Guardian)
Mercedes-Benz, Honda, Mazda and Mitsubishi have joined the growing list of manufacturers whose diesel cars are known to emit significantly more pollution on the road than in regulatory tests, according to data obtained by the Guardian. In more realistic on-road tests, some Honda models emitted six times the regulatory limit of NOx pollution while some unnamed 4×4 models had 20 times the NOx limit coming out of their exhaust pipes. “The issue is a systemic one” across the industry, said Nick Molden, whose company Emissions Analytics tested the cars. The Guardian revealed last week that diesel cars from Renault, Nissan, Hyundai, Citroen, Fiat, Volvo and Jeep all pumped out significantly more NOx in more realistic driving conditions.
NOx pollution is at illegal levels in many parts of the UK and is believed to have caused many thousands of premature deaths and billions of pounds in health costs. All the diesel cars passed the EU’s official lab-based regulatory test (called NEDC), but the test has failed to cut air pollution as governments intended because carmakers designed vehicles that perform better in the lab than on the road. There is no evidence of illegal activity, such as the “defeat devices” used by Volkswagen. The new data is from Emissions Analytics’ on-the-road testing programme, which is carefully controlled and closely matches the real-world test the European commission wants to introduce. The company tested both Euro 6 models, the newest and strictest standard, and earlier Euro 5 models.
[..] “These new test results [from Emissions Analytics] prove that the Volkswagen scandal is just the tip of the iceberg. What we are seeing here is a dieselgate that covers many brands and many different car models,” said Greg Archer, an emissions expert at Transport & Environment. “The only solution is a strict new test that takes place on the road and verified by an authority not paid by the car industry.”

“The eastern Europeans — and I’m counting myself as an eastern European — we have experienced that isolation doesn’t help..”
• Merkel Slams Eastern Europeans On Migration (Politico)
German Chancellor Angela Merkel harshly criticized eastern European governments for not having learned from their own history in their responses to the migration crisis. “The eastern Europeans — and I’m counting myself as an eastern European — we have experienced that isolation doesn’t help,” she told members of the center-right European People’s Party Wednesday in a closed-door meeting, according to a recording of the session obtained by POLITICO. “It makes me a bit sad that precisely those who can consider themselves lucky that they have lived to see the end of the Cold War, now think that one can completely stay out of certain developments of globalization,” Merkel said, referring to the reluctance of some EU countries to accept refugees.
“It just strikes me as somehow very weird. And that’s why we have to keep talking about that, as friends,” Merkel said, speaking German, as she responded to a question from a Czech MEP on the refugee crisis. “A rejection [of taking refugees in] as a matter of principle, that is — excuse me for being that blunt — that’s a danger for Europe,” Merkel said.

This just keeps going on as the EU discusses ‘fighting’ the smugglers.
• 542 People Rescued In 24 Hours Off Greece (AP)
The latest developments as hundreds of thousands of people seeking safety make an epic trek through Europe. All times local.
9:40 a.m. – Greece’s coast guard says it has rescued 542 people in 12 search and rescue incidents from Thursday morning to Friday morning. The rescues occurred off the coasts of the eastern Aegean islands of Lesbos, Chios, Samos, Agathonissi and Farmakonissi, the coast guard said. Hundreds of thousands of people fleeing war and poverty in their homelands have reached Greece so far this year, the vast majority on rickety boats or cheap inflatable dinghies from the nearby Turkish coast. Although a short sea journey, it can be fatal as the unseaworthy and overloaded boats sometimes sink.
9:30 a.m. – Greece’s coast guard says a wooden boat carrying a large number of refugees or other migrants has run aground on the small eastern Aegean island of Leros, while an infant died after the inflatable dinghy he was in partially sank off the coast of Lesbos island. The wooden boat, carrying about 100 people, ran aground Friday on the northeast coast of Leros, the coast guard said. Those on board were being taken to shore by coast guard and private vessels that arrived to help. In the Lesbos incident, the coast guard rescued 56 people from the sea Thursday night after the rear part of their dinghy burst, partially sinking the boat. A 1-year-old boy was recovered unconscious and transported to a hospital, but rescuers were unable to revive him.

And so does this. No humanity, no shame, no decency.
• Baby Dies After Migrant Boat Breaks Down Off Greek Island Lesbos (Reuters)
A baby died after the rubber boat carrying him and another 56 migrants broke down and was left adrift off the Greek island of Lesbos, the Greek coastguard said on Friday. The 1-year-old boy, whose nationality was not made known, was found unconscious on a rubber dinghy which had broken down and went adrift late on Thursday. The boy was taken to a hospital where he was pronounced dead. The coastguard rescued the rest of the migrants, some of whom were in the sea. The baby was one of thousands of refugees – mostly fleeing war-torn Syria, Afghanistan and Iraq – who attempt the short but perilous crossing from the Turkish coast to Greek islands by boat, often in rough seas.
Almost 400,000 people have arrived in Greece this year, the U.N. refugee agency UNHCR has said, overwhelming the crisis-stricken government’s ability to cope. Most have rapidly headed north towards Germany. The coastguard has rescued a total of 542 migrants and refugees off the Aegean islands of Lesbos, Chios, Samos, Farmakonisi and Agathonisi since early on Thursday. Europe’s migration commissioner, Dimitris Avramopoulos, and Luxembourg Foreign Affairs Minister Jean Asselborn are expected in Athens on Friday and will give a joint news conference on the refugee crisis on Saturday.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle October 9 2015