
Pablo Picasso Self portrait 1938

Macron wants Eurobonds, anathema to Germany et al because they would allegedly “sharply reduce each euro zone government’s motivation to pursue sensible fiscal policies..”.
Many in Brussels want a banking union, anathema to quite a few countries. There is no democratic way that leads to such a union. It’s like handing the EU the keys to your country.
• Macron Is Not The Solution To Europe’s Top Existential Threat (CNBC)
The future of the euro zone is dependent on a common commitment to solid government finances, says Commerzbank’s chief economist, and France’s new president-elect does not bring the bloc any closer to achieving this reality. The pro-EU and centrist candidate, Emmanuel Macron, stormed to victory against his far-right political rival, Marine Le Pen, on Sunday and is now poised to become France’s youngest ever premier. However, the former economy minister is in favor of joint bond issuance which, according to Jörg Krämer, would sharply reduce each euro zone government’s motivation to pursue sensible fiscal policies. “The EU can’t keep feeling its way from one election to the next. At some point an election might go the wrong way – and if that happens in a large country, the survival of the monetary union would be in jeopardy,” Krämer said in a note.
Commerzbank’s chief economist also warned the repeated near misses of anti-EU political leaders in several European elections in recent years would not last forever and suggested the monetary union’s survival now rests on the bloc’s ability to create a genuine banking union. “To lay these existential risks to rest, the euro zone at long last needs a common commitment to solid government finances. The monetary union’s long-term survival depends on it. But new French President Macron won’t bring this any closer to reality,” he added. Meanwhile, just one day after the pro-business and market-friendly candidate Macron secured his country’s presidential election, EC President Juncker publically lambasted high state spending in the euro zone’s second largest economy. “With France, we have a particular problem … The French spend too much money and they spend too much in the wrong places. This will not work over time,” Reuters reported him as saying in Berlin on Monday.

Le Pen would have lost against anyone. But tons of Europeans still don’t like what the EU has become. All it takes is a candidate somewhere who’s not Le Pen or Wilders.
• “Europe’s Not Out Of The Woods With Macron Win” (ZH)
It appears the chairmen of UBS have plenty to say on Europe.Following former UBS chairman Peter Kurer’s comments that “to the elites, the EU is a means to get rich quickly and export their problems,” UBS current chairman Axel Weber has warned bankers that Europe is not “out of the woods” from its political risks even after Emmanuel Macron’s reassuring victory in the French presidential election. Peter Kurer recently remarked on the end of the Euro…
“Following an unfortunate combination of wrong decisions at the top and the uncontrolled flourishing of a self-serving bureaucracy, the union has moved in a direction where it has become a prisoner of its own constructed reality. The EU was a great idea but it has been ridden to death. Back in 1992, almost half of Swiss voted to join the European Economic Area, including the traveller. If there was a vote today on joining the union, the latest polls say just 15% would vote yes. The EU had its chances. It squandered them, and maybe it will come to an end in the foreseeable future under the weight of its burdens: La messa e finita, andate in pace.”
And over the weekend speaking in Tokyo, as the FT reports, UBS Chairman Axel Weber said that political risk in Europe remained “actually quite high” even though “we’ve seen the centre hold in France” with Macron’s victory over far-right candidate Marine Le Pen, and even though all the signs were that the centre will also hold in the upcoming German location elections.
“That doesn’t mean Europe is out of the woods,” he told the International Institute of Finance’s spring meeting. “There is still Italy where it is very unclear that the centre will hold. And there is still Greece.” He continued: “Where you find some bright side….there are (also) some downside risks that are not really priced into the market but could derail (Europe).” “Brexit is a time bomb… and the countdown is on. It will be two years from now,” Mr Weber said. He added that “if the British really do leave the customs union and single market there could be a lot of volatility which could impact on the global economy”.

How long can bubbles hold?
• Commodities Send Ominous Signal On Global Economy (BBG)
By almost any measure last week was a bad one for commodities, as practically every part of the market lost value. West Texas Intermediate crude oil fell under $44 per barrel, Brent crude broke below $50 per barrel and copper tested $5,500 per metric ton. In China, coal and iron ore tumbled. Gold, the supposed ultimate haven, dropped to almost $1,225 per ounce. Last week’s purge capped a steady decline in prices since mid-April and, more broadly, since February based on the Bloomberg Commodities Index. Although much of the blame is being tied to rather high and growing inventory levels, a lack of real demand shouldn’t be discounted. The market is experiencing something greater than a technical correction or speculative positioning. It is signaling something ominous about the state of the global economy.
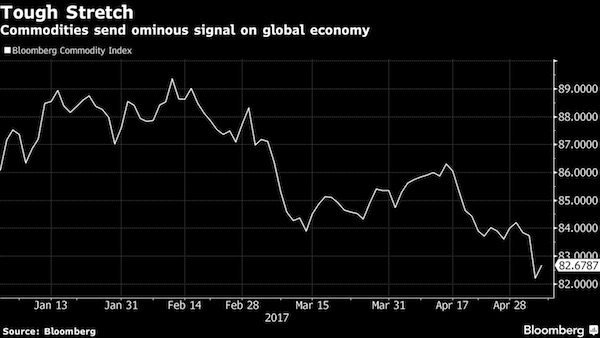
So while Friday saw a small recovery, it appears to be merely a “dead cat bounce” rather than a sign of any market bottom. Traders have reason to question global economic strength. They are concerned about fresh signs of an over-extended Chinese economy and an ongoing slowdown in developed markets faced with aging demographics. In the U.S., they question President Donald Trump’s infrastructure promises along with his administration’s relaxed standards in the mining and drilling sectors, whose commodities we already have too much of. OPEC’s output cuts have failed to do enough to stymie the global oil glut as U.S. drillers add to their rig counts. Such negative sentiment has carried through in the equity markets, particularly among commodity-producing nations such as Australia, Canada and Brazil.

A liquidity problem. And a confidence one.
• Traders Are Fleeing the Options Market (WSJ)
Falling volumes and spiraling costs are pushing trading firms out of U.S. options, raising concerns about fragility in a market that investors rely on to protect portfolios. Trading has dwindled in most areas of the market, and investors and traders are grappling with increasing fragmentation. Liquidity, the crucial ability to do trades without significantly moving prices, has deteriorated, according to interviews with market participants and data reviewed by The Wall Street Journal. Options on key indexes, exchange-traded funds and high-volume stocks dominate trading. Meanwhile, there is less activity in the rest of the listed U.S. options world. The stresses prompted at least six prominent options market makers to exit from the business since 2012. Market makers are firms willing to both buy and sell using automated programs.
Thomas Peterffy, a pioneer of electronic options trading, said in March that his firm, Interactive Brokers, would pull the plug on options market making. KCG Holdings announced its exit from retail options market making last year, while UBS and Credit Suisse have also left automated options market making. JP Morgan and Bank of America made similar decisions in 2014, according to people familiar with the matter. “Most market makers congregate in the highly traded products,” Mr. Peterffy said in an interview. “It’s difficult for a market maker to maintain hundreds of thousands of bids and offers all the time.” It is hard to pinpoint what triggered the trader exodus, but industry experts say as firms leave, liquidity gets further drained, which spurs more market makers to retrench.
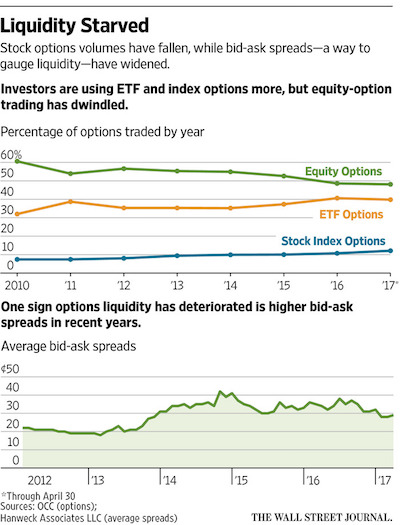
The dangerous feedback loop could sap appetite for options, key derivative securities that investors use to manage risk in their portfolios. “We could ill afford to lose any more market makers at this junction,” said Alan Grigoletto, who previously worked at the Boston Options Exchange, and now runs Grigoletto Consulting while trading options in his retirement account. Data show the liquidity bifurcation. Index and ETF options volume rose in April by 28% and 4%, respectively, data from the Options Clearing Corporation show. Meanwhile, total equity options volume shrank by 10% from the prior year.

The car loans issue keeps growing.
• The Debt-Bubble Landmine Obama Left For Trump (NYP)
President Trump came in for much jeering when he told reporters he had “inherited a mess” from President Barack Obama. On the economy, though, Obama did indeed leave behind a hidden mess: a seemingly healthy jobs market dependent on cheap debt. When this debt bubble bursts, just as the last one did, the manufacturing jobs Trump wants to save will be in even greater peril. [..] who is borrowing for used cars – and at much higher interest rates – is a huge concern. People with not-great credit scores have always made up about a fifth of the auto-loan market. But the percentage of people borrowing even though they have really bad credit scores has surged, reports Bloomberg. It’s now a third of the subprime auto-bond market, up from just 5% seven years ago. A Standard & Poor’s analysis of just one big subprime auto bond tells the story.
Last week, a company called DriveTime, which sells used cars in 26 states to people with bad credit, was in the market to issue $442 million worth of bonds backed by auto loans. The average credit score of borrowers was 538 — indicating a history of serious default. And, as S&P notes, “today’s subprime customer appears to be . . . weaker . . . than that of several years ago,” because people who defaulted right after the housing crash at least had the excuse that they were caught up in a global bubble. These loans are for people who have no choice but to borrow to buy a car, and no bargaining power on the interest rate they pay: close to 20%. Even though the borrowers pay through the nose, they depend on cheap global credit. With interest rates still near record lows, lenders have to take ever more risk in a low-interest-rate environment to make a little money.
As for that risk: Delinquency rates are rising, with 4.32% of subprime borrowers in general at least 60 days late last year, up from 3.52 two years earlier, says S&P. The bigger risk here isn’t the risk to investors, though. The auto-loan market is still much smaller than the housing market, and the investment world hasn’t created trillions of dollars of derivative securities based on this market (at least not that we know of). And unlike with houses, no one ever expects the value of a car to increase with use. No, this bubble presents a much more direct risk to the economy — and manufacturing jobs. If people with terrible credit can’t borrow an average of nearly $18,000 to buy a used car (what the DriveTime customer pays), the market for used cars collapses. That, in turn, affects the market for new cars. Indeed, the US auto industry has seen sales decline this year, after clocking half a decade of record highs.

Canadians do the subprime car thing too.
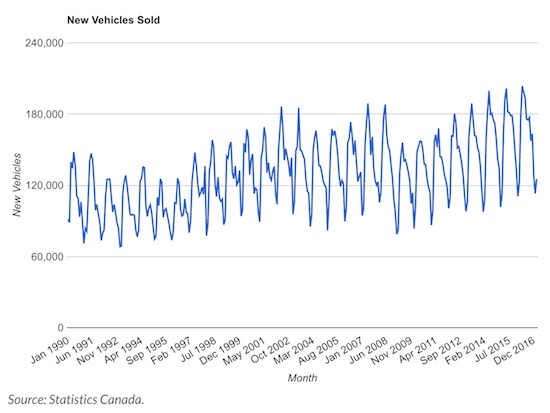
• Canadians Buy Record Number of New Cars With Record Amount of Financing (BD)
Canadians aren’t just buying real estate, they’re also treating themselves to new cars. According to a new release from Statistics Canada, sales of new cars reached a record high for February. Great for automobile manufacturers, but not so great for the economy. Debt-fuelled financing makes this more of a warning sign than a boom-time trend. Sales of new motor vehicles across Canada rose to an all-time record for February. The month saw 125,284 sales – a 2.74% increase from the same time last year. The largest segment of sales were seen in Ontario, where 41% of them occurred. This is up slightly from 2016, where Ontario accounted for 39% of sales. Booming real estate prices, and massive numbers for car sales… Ontario better be facing the greatest economy its ever experienced, or it’s in trouble.
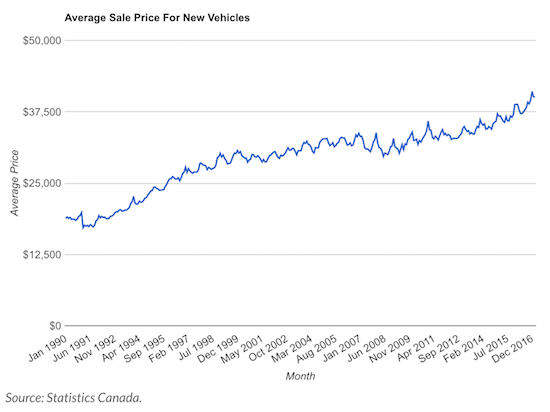
Consumers are purchasing more expensive vehicles too. Over $5 billion was spent on new vehicles for the month, bringing the average to $40,100 – up 3.4% from the same time last year. Ontario was below the average for the country, where the average price was $39,400. While prices are lower in Ontario, they’re not exactly budget vehicles either. The uptick in average sale price is due to longer financing terms for buyers. According to the Financial Consumer Agency of Canada (FCAC), Canadians are “increasingly purchasing more car than they can afford,” due to longer financing becoming fashionable. The agency notes that average leases have crept up 2 months, every year since 2010. According to the Bank of Canada (BoC), the average loan was 74 months as of 2015.

The Canadian debt issue is turning into a total craze.
• Majority of Consumers Now See Canadian Home Prices Rising (BBG)
Expectations for Canada’s housing market are heating up, with more than half of respondents in a weekly telephone survey predicting home prices will rise, the first time the measure has topped 50% in records dating back to 2008. The bullishness comes even as a run on deposits at Toronto-based mortgage lender Home Capital leads to heightened scrutiny of a market which policy makers have said is divorced from economic fundamentals. The broad Bloomberg Nanos Canadian Confidence Index fell to 59 in the week ended March 5. Some 50.1% of respondents said they expect local home prices to rise. The figure has climbed for six straight weeks and is higher than the average for the series of 37.1%. Thepercentage of people surveyed in the week ending May 5 who said local home prices will decline in the next six months slid to 10% from 10.7%.
“Consumer sentiment on real estate has gone from hot to hotter,” said Nanos Research Group Chairman Nik Nanos. Housing has led the world’s 10th largest economy over most of this decade as exporters have struggled. The latest burst of housing momentum has led policy makers to question whether it’s being led by supply and demand or by speculation. The Ontario Securities Commission opened hearings into whether Home Capital failed to properly disclose an internal probe into fraudulent mortgage applications, a shakeup in a nation lauded for having the world’s safest banks. The latest Toronto figures also showed prices up 25% in April from a year earlier, still close to the 30% March pace that Ontario Finance Minister Charles Sousa called unsustainable on April 20 when he imposed a foreign buyers tax. Those events haven’t led to more bets on a price decline either, and housing optimists now outnumber pessimists by a factor of five to one.

So much in debt they can’t pay their bills. Maybe someone should take a look at Canadian inequality, too.
• Over 50% of Canadians $200 or Less Away From Not Being Able To Pay Bills (Gl.)
More than half of Canadians are living within $200 per month of not being able to pay all their bills or meet their debt obligations, according to a recent Ipsos survey conducted on behalf of accounting firm MNP. “With such a small amount of wiggle room, any kind of unanticipated hardship, such as a job loss or even a car repair, could send an already struggling family into financial despair,” said Grant Bazian, president of MNP’s personal insolvency practice, which is one of the largest in Canada. For 10% of Canadians, the margin of error when it comes to household finances is even thinner, at $100 or less. But those with anything at all left at the end of the month were in better shape than many: A whopping 31% of respondents said they already don’t make enough to meet all their financial obligations.
Debt is causing Canadians a fair bit of stress, the polling suggests, but few appear to be on track to buff up their monthly financial cushion. Two-thirds of survey takers said they are “less than very confident” about their ability to create an emergency fund. Another hair-raising finding from the survey: Roughly 60% said they don’t have a firm grasp of how interest rates affect debt repayments. The statistic helps explain why many indebted Canadians end up taking on more debt and high-cost loans, said Bazian. “That’s how so many end up in an endless cycle of debt,” he noted. But the data also raises the question of whether Canadians understand the implications of an interest rate hike by the Bank of Canada (BoC). A decision by the BoC to start lifting its key policy rate from historic lows would raise the cost of carrying debt across the country.
The Bank uses interest rates, among other tools, to influence inflation and economic activity. Many economists believe it could start to raise rates in the first half of 2018, as economic growth picks up pace. Although the BoC will probably lift rates gradually and over time, the impact on Canadian wallets will be substantial. For example, as Global News has reported before, a onepercentage point rise in the BoC’s key interest rate would likely push up variable mortgage rates by a similar amount. A variable mortgage rate that’s currently set at 3%, for example, would go up to 4%, which represents a 33% increase in interest payments for the mortgage holder. That’s an extra $83 a month for every $100,000 in outstanding mortgage debt.

Quebec has strong US trade ties.
• Quebec’s Finance Minister: Don’t Dawdle on NAFTA Overhaul (BBG)
Quebec Finance Minister Carlos Leitao has a message for government officials considering a renegotiation of NAFTA: Time is of the essence. “If we are going to renegotiate Nafta, then let’s do it,” Leitao said in an interview Friday at Bloomberg headquarters in New York. “The worst case scenario would be if we spend years talking about renegotiating, but don’t actually do it and it just keeps hanging around and doesn’t get addressed. The longer it drags on, the bigger the real impact on investment.” Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau is facing a lengthy trade battle with the U.S., which also includes calls for a new softwood lumber pact and Donald Trump’s complaints about Canada’s system of protectionist dairy quotas.
It’s all set to drag on as the president has yet to trigger a 90-day notice period to Congress to renegotiate Nafta. The last softwood lumber dispute lasted five years. “The problem with the uncertainty is we don’t know what kind of process we will have,” Leitao said. “Is this going to be along the same lines as the last Nafta negotiations? That was very systematic. There were panels on various issues. It’s that kind of certainty that we would like. The actual nuts and bolts will take time.” Leitao has good reason to be wary of protracted trade battles, with his most recent budget already predicting Quebec’s economic growth will lag behind the Canadian average. Output in Quebec will grow 1.7% this year before slowing to 1.6% in 2018, budget forecasts show. That’s less than the 2.2% and 2.3% forecast for all of Canada over the same period.

Deleveraging.
• Chinese Stocks Head For Longest Losing Streak In 3 Years (BBG)
Chinese stocks pared declines, with technical indicators signaling that a five-day slide may have been overdone. The Shanghai Composite Index was little changed at 3,077.78 as of 1:07 p.m. local time, after declining as much as 0.7% earlier in the day. Consumer shares were the worst performers on the CSI 300 gauge, while telecom companies led gains. The Hang Seng Index climbed 0.4%. An intensifying campaign to reduce leverage in the financial system pushed the Shanghai benchmark to a 2.4% loss in the five days through Monday. This drove the gauge’s relative strength index to below 30, a level that suggests to some traders that an asset is oversold.
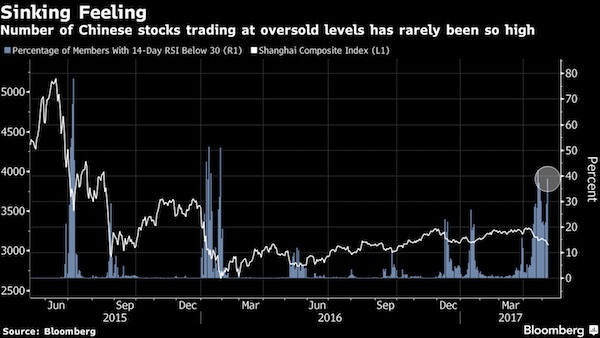
The nation’s banking regulator said Monday that lenders should carry out collateral pressure tests at least once a year, while the Securities Times reported that some rural banks had suspended interbank businesses temporarily while officials conduct spot checks. “Some stocks appeared to be very cheap at current levels, and this triggered some bargain hunting,” said Banny Lam, head of research at CEB in Hong Kong. State-owned enterprises that dominate old growth industries, such as banks and commodity producers, have been among the hardest-hit by the deleveraging drive, while new-economy shares remain in favor among overseas investors. That’s led to a wide gap between the nation’s two main offshore gauges: the Hang Seng China Enterprises Index and the MSCI China Index.
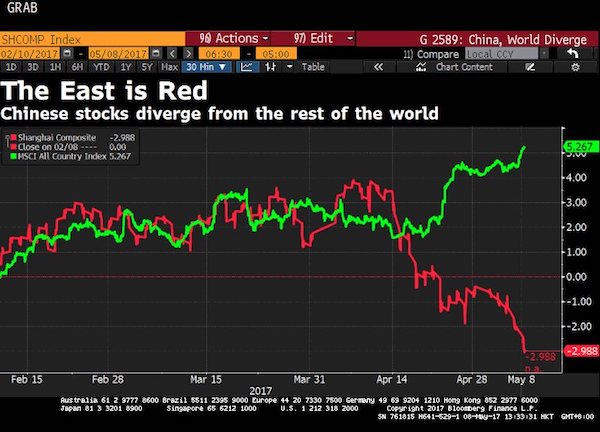

Much collateral doesn’t actually exist. Wealth management products, shadow banks, it’s all not much more than a mirage. It takes faith.
• How China Keeps Its Financial System From Collapsing (ZH)
With “risk” in most of the developed world seemingly a long forgotten four-letter word, as seen by today’s plunge in the VIX to a level not seen in 34 years, traders hoping for some “risk event” have been confined to the recent turmoil in China, where overnight not only did trade data disappoint, with both imports and exports missing, but bond yields jumped to the highest level since 2015, dragging stocks lower even as the local commodity crash slammed iron ore and copper to new YTD lows.
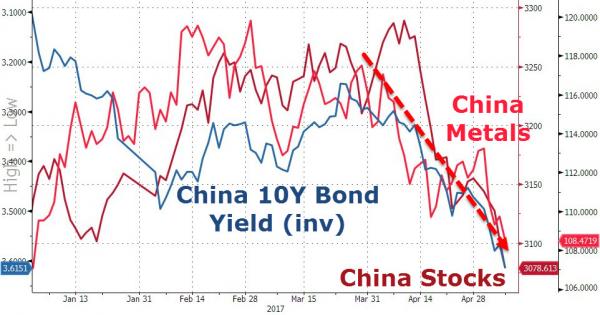
While largely a “controlled” tightening, meant to contain China’s out-of-control shadow banking system, the recent gyrations in Chinese capital markets are starting to have a profound impact on local funding, resulting in a collapse in new bond issuance, and according to FT calculations, in April the number of aborted issues rose to 154, up from 94 in March, 32 in February and 31 in January.
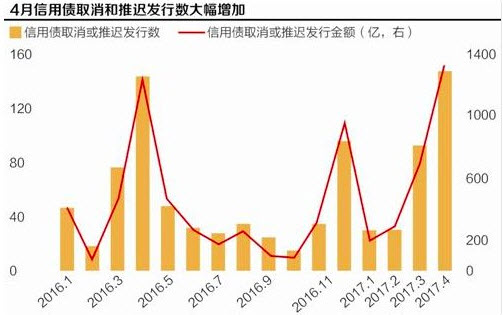
As DB added, “local bond markets are practically shut for corporates. In fact, YTD issuance is down 40%+ yoy and net issuance has been negative in three out of the first four months this year. A number of issuers are being forced to cancel bond issuances (over RMB100 billion YTD) and there were reports (Bloomberg) of even CDB halting issuance (though subsequently denied). Some AA corporates are now issuing at north of 7%.” These signs of mounting stress in China’s $9.3 trillion bond market come less than a month after the country’s banking regulator, Guo Shuqing, was quoted as supporting a campaign to sort out chaotic practices, and threatening to resign if the banking system became “a complete mess”.
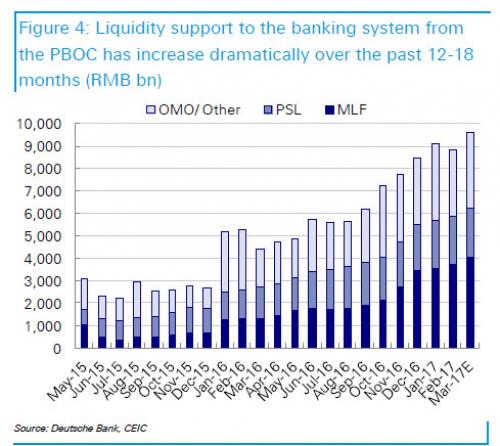
[..] whether or not China keels over and has a hard (or worse) landing, will depend on the PBOC; when (not if) the central bank gets involved, will depend on how soon China’s banks and various CD-funded financial institutions run out of collateral (whether it exists or not) to sell, such as iron ore, copper, precious metals, bonds and even stocks. This will hardly come as a surprise. As we showed last month, the only reason the Chinese banking system hasn’t imploded, is due to nearly CNY 10 trillion in central bank liquidity support for the local banks, just under 100% of China’s GDP.

Europe too.
• Parts of Asia Will Grow Old Before Getting Rich, IMF Warns (BBG)
Asia’s rapidly aging population means the region is shifting from being the biggest contributor to the global workforce to subtracting hundreds of millions of people from it, according to the International Monetary Fund. The reversal of the so-called “demographic dividend” will drag on global growth and also that in Asia, the world’s fastest growing region, the IMF warned in its annual outlook for the area. The population growth rate will fall to zero for Asia by 2050 – it’s already negative in Japan – and the share of the population who are working-age has already hit its peak, the IMF estimates. That means the ratio of the population aged 65 and older will be almost two and a half times the current level by 2050, and even higher in East Asia.
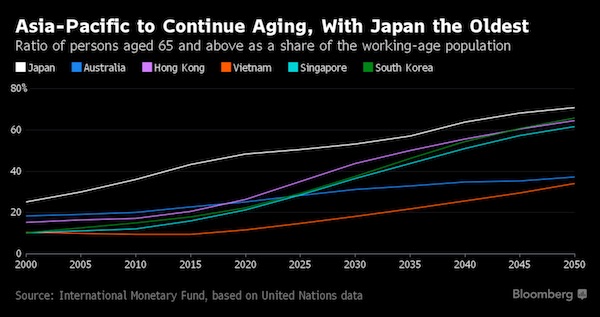
“The speed of aging is especially remarkable compared to the historical experience in Europe and the United States,” the IMF said. Per capita income in Asia relative to the U.S. remains at much lower levels than those achieved by mature advanced economies in the past. “Countries in Asia will have less time to adapt policies to a more aged society than many advanced economies had,” the fund wrote. “As such, parts of Asia risk becoming old before becoming rich.” For economic growth, the aging process could erode up to one percentage point from annual output over the next three decades in Japan, and between 0.5-0.75 percentage point in China, Hong Kong, South Korea and Thailand.
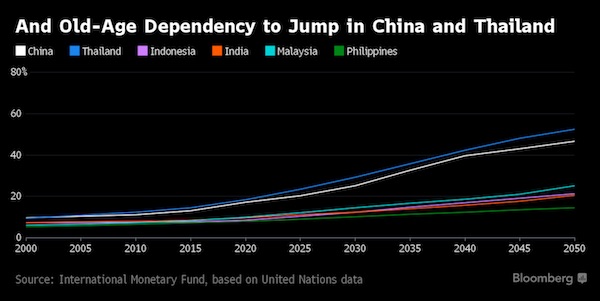
While some bright spots remain, such as India and Indonesia, demographics could subtract 0.1 of a percentage point from annual global growth over the next three decades, the IMF estimates. It also means Asia is at risk of falling into secular stagnation if an older population leads to excessive savings and low investment renders monetary policy ineffective. The demographic shift will also likely keep downward pressure on real interest rates and asset returns for most major countries in Asia, the IMF said. “Adapting to aging could be especially challenging for Asia, as populations living at relatively low per capita income levels in many parts of the region are rapidly becoming old,” the IMF said.

It’s time to come clean on how bad Italy is really doing.
• Italy Adds Bum Note To Macron’s Ode To Euro Zone Joy (R.)
Italy is adding a bum note to Emmanuel Macron’s ode to joy. While it’s encouraging that a Europhile will take the French presidency after Sunday’s vote, attention can now turn to Europe’s other crisis-in-waiting. Elections are coming in Italy, and there are more of the ingredients for a populist shock than in France. The economy has fared much worse since the creation of the euro zone, with growth averaging zero since 2001, according to the IMF. GDP per capita has fallen in that time. The IMF expects the unemployment rate to reach 11.7% this year, 2 percentage points higher than in France. Anti-EU forces are also spread widely across Italy’s messy political landscape. Stagnation has fuelled support for the 5-Star Movement, which could lead Italy out of the euro zone and currently polls just below 30%.
Mainstream parties are shaky. The left fragmented after former prime minister Matteo Renzi lost his referendum on constitutional reform in December. The right is an awkward alliance between ageing former premier Silvio Berlusconi and more radical anti-EU parties, like the Lega Nord. The risk is that 5-Star forms a coalition with the Lega after elections that must take place by May next year. The economy is picking up, but tighter monetary policy, as the European Central Bank reins in bond buying, could strangle the recovery, as could an overly stern fiscal policy. Italy needs to cut spending or increase taxes by 2percentage points to meet European targets through 2019. Job losses from the restructuring of banks and bankrupt national airline Alitalia could become a lightning rod for anti-EU sentiment.
Europe can help. Italy is likely to miss its fiscal targets anyway, but loosening bloc-wide budget rules to encourage investment and spread out cuts over a long period would cement the recovery. A strong France, aided by Macron’s victory, might persuade Germany to spend more, and give other countries freer rein. However, even if a political shock is avoided, the next election may produce a weak government with no mandate for taking tough decisions to boost growth. Italy could be bringing discord to the region for years.

MMT must go mainstream.
• The Rock-Star Appeal of Modern Monetary Theory (Nation)
To a layperson, MMT can seem dizzyingly complex, but at its core is the belief that most of us have the economy backward. Conventional wisdom holds that the government taxes individuals and companies in order to fund its own spending. But the government—which is ultimately the source of all dollars, taxed or untaxed—pays or spends first and taxes later. When it funds programs, it literally spends money into existence, injecting cash into the economy. Taxes exist in order to control inflation by reducing the money supply, and to ensure that dollars, as the only currency accepted for tax payments, remain in demand.
It follows that currency-issuing governments could (and, depending on how you lean politically, should) spend as much as they need to in order to guarantee full employment and other social goods. MMT’s adherents like to point out that the federal government never “runs out” of money to fund the military, but routinely invokes budget constraints to justify defunding social programs. Money, in other words, isn’t a scarce commodity like silver or gold. “To people who’ve worked in financial markets, who work at the Fed, this isn’t controversial at all,” says Galbraith, who, while not an adherent, can certainly be described as “MMT-friendly.”
The decisions about how to issue, lend, and spend money come down to politics, values, and convention, whether the goal is reducing inequality or boosting entrepreneurship. Inflation, MMT’s proponents contend, can be controlled through taxation, and only becomes a problem at full employment—and we’re a long way off from that, particularly if we include people who have given up looking for jobs or aren’t working as much as they’d like to among the officially “unemployed.” The point is that, once you shake off notions of artificial scarcity, MMT’s possibilities are endless. The state can guarantee a job to anyone who wants one, lowering unemployment and competing with the private sector for workers, raising standards and wages across the board.

No matter how deep you dig, you can’t guarantee safety for a million years. That’s what’s halted Yucca Mountain. The Bloomberg editors don’t understand the issue either.
• To Bury Nuclear Waste, Dig Deeper Than Yucca Mountain (BBG)
Energy Secretary Rick Perry is right to say the U.S. needs a long-term solution to its massive nuclear waste problem. It also makes sense for Perry and some members of Congress to see Yucca Mountain as part of that solution – though many Nevadans promise to make sure it won’t be. But even if Yucca can survive the political fight, it can’t be the only option for disposing of America’s spent nuclear fuel. More than 75,000 metric tons of the stuff are cooling in pools and casks at dozens of power-plant sites around the country. That’s already too much to fit in Yucca Mountain, and the total grows by more than 2,000 tons a year. Other strategies are needed, ideally ones that are less politically radioactive. Consider, for instance, the idea of sinking the waste into boreholes that reach three miles below ground – 15 times as deep as the proposed chambers inside Yucca. Such shafts could be drilled in states that, unlike Nevada, benefit from the use of clean, reliable nuclear power.
Boring into the Earth’s deep rock layers could provide the kind of bury-it-and-forget-it underground disposal necessary for material that will remain dangerous for hundreds of millennia. Local opposition can still be expected; in North and South Dakota, residents have shouted down some plans to dig test holes. That’s why a so-called consent-based strategy, identifying locations with both the appropriate geology and an agreeable population, is necessary. If hosting a waste site means more funding for local public works and services, more communities might be willing to accept one. (This proved to be the case in Carlsbad, New Mexico, home to a storage place for low-level waste from nuclear weapons.) A familiarity with nuclear power may also encourage acceptance, perhaps because there is a nuclear plant in the area employing people and providing power.
The same approach could also be used to locate six or seven centers where waste from several nuclear plants could be stored while it awaits burial. Such containment facilities could also include research centers – mini national laboratories where scientists could work out new ways of reprocessing fuel and perhaps conduct demonstration projects for reactors designed to use safer fuels. The one thing the U.S. should not do is continue to neglect the growing quantities of nuclear waste. Over the past few decades, electricity ratepayers have contributed more than $34 billion to a national fund to pay for a geologic disposal site. And because none yet exists, taxpayers are forking over billions more to enable nuclear-plant operators to manage interim storage. The political barriers to solving this problem may be high, but further delay – and an undue fixation on Yucca Mountain – won’t make them any easier to overcome.

Turkey will provoke Greece at some point, and US and Europe had better prevent that from happening.
• Dangerous Times in the Aegean and Cyprus (K.)
The concept of gray zones (the claim that the sovereignty of a number of islands and islets in the Aegean is undetermined) was a novel idea that Turkey came up with 20 years ago. At some point, Ankara reached the point of including the Greek island of Gavdos in its gray zones list. Whenever Athens made an official request regarding the islands or rocky outcrops that Turkey had on its list, the answer was always very vague: “Anything that is not clearly included the bilateral agreements that set out Greece’s borders with other countries.” At first, many people thought this was a bargaining chip that Ankara would trade as part of a grand bargain. They were wrong. The failure to settle differences between Greece and Turkey gave Ankara the opportunity to add more issues to the agenda.
Over time, these have become permanent and ever-expanding. Currently, Turkey considers significant parts of the Aegean to be gray zones. This includes islands that have been inhabited for decades. It is questioning Greek sovereignty through its actions, not just its words, by the frequent presence of naval vessels in Greek waters and overflights by fighter jets. Over the last few months, it has being doing this more systematically and openly. Greece’s approach has also changed. The doctrine that existed in the wake of the Imia crisis in 1996, when the two countries almost went to war, was based around not building up tension following various incidents and maintaining a low profile.
[..] A dangerous situation is also playing out in Cyprus. The Turks are trying to impose the concept of gray zones there as well. July (when a new round of drilling for hydrocarbons is due to begin off Cyprus) promises to be a difficult month. Ankara will attempt before then to intimidate the companies that plan to start drilling or try to obstruct them if they are not scared off by threats.

Prison camps are no solution.
• New Refugee Center Planned On Chios As Tensions Simmer (K.)
The exact site for the creation of a new so-called pre-departure camp for migrants and refugees on the island of Chios will be determined by May 20, authorities said on Monday. The new camp will come as tensions at overcrowded reception centers on the eastern Aegean island continue to simmer, with almost daily clashes between stranded migrants of different ethnicities. “The experience of Lesvos and Kos where such centers have been created is positive,” said Lieutenant General Zacharoula Tsirigoti of the Greek Police in a press briefing Monday on Chios. Pre-departure centers are deemed essential as they house refugees and migrants returning to Turkey. Tsirigoti added that building a new center on the island is a “one-way street” as locals – many of whom have campaigned for the immediate removal of all migrants and refugees from Chios – say the situation has reached breaking point and that the large police force on the island has been unable to cope.

The season is just starting: “..the trend points to around 250,000 people arriving over the course of 2017”. There is no place for these people in Italy and Greece.
• Nearly 200 Missing, 11 Dead As Migrant Boats Sink Off Libya (AFP)
Eleven migrants have died and nearly 200 are missing after two boats sank off the coast of Libya, UN agencies said Monday citing survivors, in the latest such tragedy. The first involved an inflatable craft which left Libya early Friday with 132 people on board, only to start deflating a few hours later, before overturning. Some 50 survivors were picked up by a Danish container ship, the Alexander Maersk, which was alerted to divert by Italian coastguards and dropped them off on Sunday in Pozzallo, southern Sicily. Representatives of the UN High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) and the International Organization for Migration (IOM) were able to meet them on Monday to hear their accounts. Survivors told them that women and children were among those missing.
At the same time, the bodies of 10 women and one child were found Monday on a beach in Zawiya, 50 kilometres (31 miles) west of Tripoli, according to an official for the Libyan Red Crescent. Then on Sunday seven migrants – a woman and six men – were rescued by Libyan fishermen and coastguards off the coast of the Libyan capital. An IOM spokesman who met them said they had set out on a boat with at least 120 people on board, including about 30 women and nine children. In all more than 6,000 migrants were rescued Friday and Saturday in international waters off the coast of Libya and brought to Italy, while several hundred were rescued in Libyan waters and taken back to Libya.
The number of people leaving Libya in the hope of starting a new life in Europe is up nearly 50% this year compared with the opening months of 2016. With most departures coming in the warm summer months, the trend points to around 250,000 people arriving over the course of 2017. Some 500,000 migrants were registered in Italy in the three years spanning 2014-16.

Europe’s reputation is tarnished for decades. But everyone thinks they can deflect responsibility. Time for skin in the game.
• Hundreds Of Migrants Feared Dead In Mediterranean Over Weekend (R.)
More than 200 migrants are feared to have died in the Mediterranean over the weekend, according to testimony from survivors, and several bodies, including that of an infant, have washed up on a Libyan beach. About 7,500 people have been rescued off the coast of Libya since Thursday, the Italian and Libyan coastguards said. Two groups of survivors told the organizations that hundreds drowned when their rubber boats began to deflate before rescuers arrived. More than 60 are feared dead and three bodies were recovered on Saturday, survivors brought to Sicily on Sunday told Italian coastguards. The boat left Libya carrying about 120, they said. There was some discrepancy in the numbers. Based on its interviews with some of the survivors in Pozzallo, Italy, the U.N. refugee agency estimated the number of dead at more than 80.
Separately, Libya’s coastguard picked up seven survivors over the weekend who said they had been on a boat packed with 170 migrants. Aid agency International Medical Corps, which gave medical care to the survivors, also confirmed their account. “We rescued on Sunday seven illegal migrants – six men and a woman,” said Omar Koko, a coastguard commander in the western city of Zawiya. “According to these survivors, there were 170 on board the boat, which sank because of overloading.” Among those missing were more than 30 women and nine children, Koko said. Eleven bodies washed up on the shore west of Zawiya, said Mohanad Krima, a spokesman for the Red Crescent in Zawiya. “All the bodies are of female victims and there is a girl of less than one year old,” he said.









Home › Forums › Debt Rattle May 9 2017