Gottscho-Schleisner L Motors at 175th Street and Broadway, NYC Mar 24 1948



This contradicts a whole lot of western ‘experts’.
• Oil Prices Won’t Recover Above $100 – Russian Finance Ministry (RT)
Decreasing oil prices are “inevitable” and the chance they will exceed $100 per barrel is “unlikely” the Russia’s Finance Ministry said. However, the Russian budget can withstand lower prices. “The market is biased in favor of excess supplies. That is why price reduction is inevitable; it will have a structural character. We are unlikely to see prices higher than $100 per barrel in the near future,” Maksim Oreshkin, the head of the Russian Finance Ministry’s strategic planning department told RBC TV in an interview. “In general, the current downward price movement is structural. Investments in oil production have increased dramatically in the past ten years,” Oreshkin said. Russian officials have stressed there will be no sharp rise in Russia’s budget deficit, but the country’s largest bank, Sberbank, says an oil price of $104 is required to balance the 2015 budget. A drop of prices to $80 per barrel could cost Russia 2% of GDP.
The weak ruble will be a buffer to lower oil prices, since costs are in rubles, but revenue in dollars. “The ruble is down which allows Russia to maneuver a bit by making some extra cash from oil sales, since those are done in dollars,” RT correspondent Egor Piskunov reported from Moscow. The Russian state budget is based on oil prices of $96 per barrel, which both Brent and WTI crude fell below in previous days. Last week prices hit a 4-year low, with Brent futures reaching a critical point of $84 per barrel. Just months ago, at the height of the Iraq turmoil, Brent was trading at $116 per barrel. WTI crude, the main North American blend, hit a four-year low dropping below $80 Thursday. Both blends have been falling for the last four months.
Read more …

Glad someone brings it up …
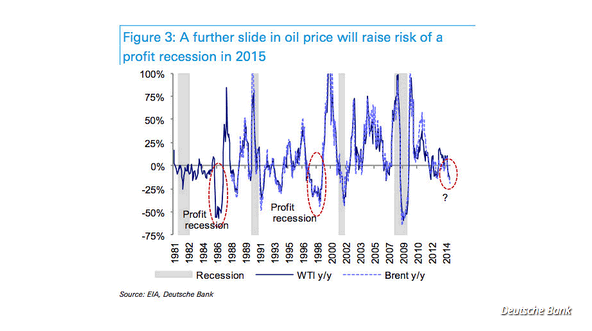
• Oil Collapse Raises Risk Of ‘Profit Recession’ (MarketWatch)
American drivers are almost giddy over gasoline prices that are now below $3 a gallon in some areas. Investors, however, might want to check themselves, says David Bianco, Deutsche Bank’s top equity strategist. Light, sweet crude traded on the New York Mercantile Exchange has plunged from around $107 a barrel in June to test two-year lows near $80 a barrel. The collapse has prompted Bianco and his team to cut their forecast for S&P 500 fourth-quarter earnings per share by 50 cents to $30.50 and to drop their forecast for full-year 2015 earnings by $3 to $123 a share. That still points to 2015 earnings per share growth of around 4% on expectations global growth will remain underpinned by U.S. growth, which will be enhanced, in part, by stronger consumption aided by cheaper oil. But lower oil prices (Deutsche Bank is now penciling in a 2015 average price of $85 a barrel), will weigh heavily on the energy sector, Bianco said in a note.
Deutsche Bank slashed its forecast for fourth quarter energy earnings by nearly 10% — accounting for almost all of the cut in the bank’s estimate of fourth quarter S&P 500 EPS. Deutsche now sees energy earnings falling 10% in 2015 as well, versus an earlier forecast for a fall of 2%. While it’s no surprise that the energy sector will bear the brunt, plunging oil is also bad news for the industrials and materials sectors. They’ll suffer as energy firms reduce capital spending in the U.S. and worldwide, Bianco says, noting that a third of S&P 500 capital spending comes from the energy sector. Meanwhile, the boost to consumer sector earnings from the lower oil price is small, Bianco says. So is the S&P 500 in danger of suffering a “profit recession?” Probably not, but much depends on the oil price, Bianco writes. He notes that since 1960 there have been only 10 instances when there was a fall in trailing fourth-quarter earnings per share.
Read more …

They add flights when oil is cheaper …
• How Cheap Oil Could Become a Real Problem for Airlines (BW)
Oil futures have been on a torrid plunge in recent weeks, touching lows below $80 per barrel. Great news for airlines, right? Maybe not. For roughly the past 35 years, inexpensive jet fuel has routinely served as a siren call to airline executives. Cheap fuel spurs more flights and wild grabs for whatever business looks attainable in the travel market. Marginal routes become profitable with lower fuel prices, which, in turn, bolsters the argument that new flights can boost revenues with little cost. Cheap fuel also lets an airline experiment more radically with flight schedules in the bid to swipe market share from rivals. “If it keeps trending lower, it totally changes the economics of the industry again,” says Seth Kaplan, managing partner of Airline Weekly, an industry journal. With oil cheaper, Kaplan predicts that many airlines will probably fly their planes in off-peak periods because of the low costs associated with those extra flights. A few additional flights on the weak travel days of Tuesday and Saturday could return to some schedules.
This possibility has some Wall Street analysts in a tizzy, concerned that if oil stays cheap enough for long enough, lower prices will cause airlines to backslide on their new-found religion against deploying too much capacity. “We feel like this industry needs an oil spike now more than ever,” Wolfe Research analyst Hunter Keay wrote last week in a client note. “[C]apacity discipline of late (from some) seems theoretical at best.” Brent crude, the energy index most airline executives monitor for its correlation to jet fuel, has declined 22% this year; settling Friday at $86; a day earlier, the Brent Index scored a four-year-low, under $83. This constitutes a sharp reversal from recent years: After oil spiked to nearly $150 per barrel in July 2008, U.S. airlines radically restructured to try to cope with oil at whatever price it may be. That effort has left high or low oil prices much less important—quick swings either way are now the enemy—while turning expensive oil into somewhat of a barrier for new flying.
Read more …

If those guys are the brightest …
• Bond Market Brightest Turn Oil Analysts as Gyrations Mystify (Bloomberg)
Following the most turbulent period for U.S. bonds in more than three years, the top strategists are looking less at jobs and manufacturing and more at the price of oil for clues as to what lies ahead. Treasuries gyrated last week, with yields on benchmark 10-year notes at one point falling below 2% for the first time since June 2013, as a tumble in crude sparked concern that the global economy was on the verge of entering a deflationary spiral. Bond traders who wagered that the trillions of dollars in cash pumped into the financial system by major central banks would cause runaway inflation were forced to reverse those bets.
The moves were the latest shock in a year of surprises in the bond market. The consensus estimate among the more than 60 strategists surveyed by Bloomberg in January was for yields to rise in 2014. Instead, they fell. One of the few to get it right was FTN Financial, and its analysts say even after the rally yields are not far from fair value because cheaper energy prices will help curb gains in consumer prices. “There’s a fundamental series of questions about where we go from here,” Jim Vogel, head of interest-rate strategy at Memphis-based FTN, said in an Oct. 16 telephone interview. Vogel, who added that the 21% drop in oil prices since June “took people by surprise,” sent a note to clients last week recommending they “watch for stability in oil positions,” and noting the “strong ties” between the cost of the commodity and the government’s consumer price index.
Read more …

Schiff gets a lot more wrong than right, but this is that exception.
• “Ending QE Will Plunge US Into Severe Recession” (Zero Hedge)
“Markets are slowly coming to grips with reality is not going to be as easy as everybody thought,” Peter Schiff tells CNBC’s Rick Santelli, noting the pick up in volatility across asset classes recently. What The Fed clearly does not understand, Schiff blasts, is that “you cannot end quantitative easing without plunging the US into a severe recession.” Because of the Fed’s extreme monetary policy and the mal-investment that flows from it, Schiff says, “The US economy is more screwed up now than it’s ever been in history.” Most prophetically, we suspect, Santelli agrees that “a messy exit is a given,” and Schiff believes they know that and that is why QE4 is coming simply “because it hasn’t worked and they can’t admit it’s been a dismal failure.”
Read more …

Not sure why Bloomberg picked this title (3rd different one in a row for the same article), but the topic is relevant.
• They Studied Keynes and They’re Doing This. Why Can’t the Fed See It? (Bloomberg)
Federal Reserve policy makers are missing a key element as they assess the health of the labor market: data that includes whether those who are employed are overqualified for their job or would like to work more hours. As a result, the “significant underutilization of labor resources” that Fed officials highlighted last month as they renewed a pledge to keep interest rates low for a “considerable period” is probably even more severe than currently estimated. And the information gap means policy makers may have more difficulty gauging the right moment to raise rates off zero. “We have more slack than the official statistics suggest,” said Michelle Meyer, a senior U.S. economist at Bank of America in New York. “Because it’s difficult to measure underutilization, there’s still a lot of uncertainty as to how much slack remains, which means there’s uncertainty as to the appropriate stance of monetary policy.”
The Labor Department can put its finger on how many people are working part-time because full-time jobs aren’t available, or how many are so discouraged that they’re not even looking for employment. Other forms of underemployment — for example the graduate with an English degree who’s working as a barista –are harder to pinpoint though just as important in trying to measure whether the labor market has improved. The data shortfall sparked a discussion at a Peterson Institute for International Economics conference last month in Washington. Erica Groshen, commissioner of the Bureau of Labor Statistics, asked what additional data would be needed to help quantify labor-market slack. Betsey Stevenson, a member of President Barack Obama’s Council of Economic Advisers, pointed out that while it was possible with current data to determine whether people working less than 35 hours a week are underutilized, those putting in a longer workweek fall off the radar.
The BLS considers anyone working at least 35 hours a week to be full-time. The Census Bureau, which surveys households to get the information needed for the Labor Department to crunch the monthly jobs data, doesn’t ask full-timers whether they’d prefer a different job or additional hours. As far as anyone knows, those workers are fully employed and content.
Read more …

China’s numbers come straight out of its political agenda.
• China GDP Growth Slowest Since Global Crisis (FT)
China’s economy grew last quarter at its slowest pace since the depths of the global financial crisis, raising concerns over global growth prospects and increasing the likelihood Beijing will introduce broader stimulus measures. Gross domestic product in the world’s second-largest economy expanded 7.3% in the third quarter from the same period a year earlier, its weakest performance since the first quarter of 2009, when growth was just 6.6%. But unlike then, when the economy was in freefall as a result of the global financial crisis originating in the US, China’s growth problems this time are largely homegrown. The latest quarterly reading means China’s economy this year is almost certain to register its slowest annual pace since 1990, when the country faced international sanctions in the wake of the 1989 Tiananmen Square massacre.
A correction in China’s property sector, the most important driver of the economy for much of the past decade, is the biggest drag on growth and most analysts expect things to get worse, given huge oversupply across the country. Investment in real estate in the first nine months continued to expand but at a slower pace, rising 12.5% over the same period last year, compared with an increase of 13.2% in the first eight months. Housing sales fell in the first nine months of this year by 10.8% compared with the same period in 2013, suggesting that the property investment slowdown has further to go. Other monthly data released on Tuesday, including industrial production and consumer retail sales, showed a mild rebound in September compared with the previous two months but most analysts expect the slowdown to continue. By the end of September, Chinese factory gate prices had been in deflationary territory for 32 consecutive months, the longest period of producer price inflation in the country in the modern era.
Read more …

This looks a whole lot more realistic than official numbers, although projections 10 years into the future don’t look terribly useful in the current economic climate.
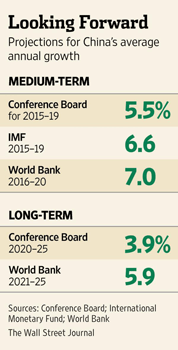
• China Growth Seen Slowing Sharply Over Next Decade (WSJ)
China’s growth will slow sharply during the coming decade to 3.9% as its productivity nose dives and the country’s leaders fail to push through tough measures to remake the economy, according to a report expected to come out Monday. Such an outcome could batter an already fragile global recovery. But the report by the business-research group the Conference Board also finds that multinational companies in China would benefit. Lean times would give foreign firms more local talent to choose from. Foreign companies and investors could also expect “more hospitable” treatment from Communist Party and government officials and a wider selection of Chinese firms they could acquire, according to the report, which was shared with The Wall Street Journal. Foreign companies should realize that China is in “a long, slow fall in economic growth,” the report said. “The competitive game has changed from one of investment-driven expansion to one of fighting for market share.”
Officials representing China’s State Council, or cabinet, referred questions to its National Bureau of Statistics, which didn’t respond. Senior officials of the Communist Party are gathering in Beijing for a major policy meeting that opens Monday and is expected to discuss the slowdown. The Conference Board forecasts that China’s annual growth will slow to an average of 5.5% between 2015 and 2019, compared with last year’s 7.7%. It will downshift further to an average of 3.9% between 2020 and 2025, according to the report. The outlook for the world’s second-largest economy is one of the most important factors affecting the global economy. For the 30 years through 2011, China grew at an average annual rate of 10.2%, a record unmatched by any major nation since at least World War II. That growth lifted hundreds of millions of Chinese out of poverty and turned the country into a major market for commodity producers in Asia, Latin America and the Middle East, and consumer and capital-goods makers from the U.S., Europe and Japan.
Read more …

“Debt gets more expensive over time, because consumer spending power declines. When prices and corporate revenue fall for a sustained period of time, wages inevitably go down, too. That makes fixed-rate debt more expensive, because you have less money instead of more to make the same regular payments.”
• Why Deflation Is So Scary (Yahoo)
If the price of a car or an iPhone drops, that’s usually good news for consumers. So it might be puzzling that investors and economists suddenly seem freaked out about the possibility of deflation, or a sustained drop in the level of all prices, on average. Deflation was a concern back in 2010 and it’s a fresh worry now as oil prices plunge, the stock market wavers and consumers put spending plans on hold. The paradox of deflation is that falling prices on a few items can generally be good for consumers, leaving more money in their pockets for other things. But falling prices on too many things can have ruinous effects on the economy that are hard to reverse. Japan suffered nearly two decades of deflation starting in the early 1990s, and deflation helped prolong the Great Depression in the 1930s. When all prices fall, consumers have a strong incentive to put off purchases – after all, everything will probably be cheaper tomorrow.
Some purchases are hard to delay – food, medical care, gasoline to get to work. But a lot of the things we buy can wait, which is why sales of cars, clothing, and appliances drop sharply when times get tough. In an economy like ours – in which consumer spending accounts for about 70% of total GDP – a powerful incentive to postpone purchases can be disastrous. When spending drops, so does corporate revenue, raising pressure to cut costs, which leads to layoffs and other personnel cutbacks. Companies are likely to freeze salaries or even cut pay for those workers remaining. Dwindling income makes consumers even more leery about spending money, worsening the whole cycle. The other mechanism for deflationary ruin is debt. One big reason lending helps the economy grow is inflation—most loans become easier to pay back over time, because the principal doesn’t grow but income used to pay it down does.
We typically think of inflation as a rise in prices, but it’s usually accompanied by an increase in workers’ wages as well, and as long as wage increases exceed price hikes, ordinary people get ahead. Home buyers, for instance, often “grow into” a mortgage that might seem onerous at first, because their income climbs as they progress through their careers. The mortgage payments on a fixed-rate loan, by contrast, remain constant. So in a typical economic environment, you gradually earn more income to make the same payment every month.
Deflation creates the opposite phenomenon: Debt gets more expensive over time, because consumer spending power declines. When prices and corporate revenue fall for a sustained period of time, wages inevitably go down, too. That makes fixed-rate debt more expensive, because you have less money instead of more to make the same regular payments. The mismatch affects companies and even governments the same way it does consumers, causing cash-flow shortages, liquidity problems and bankruptcy. Each of these ugly outcomes reinforces the others, making a deflationary spiral very hard to pull out of.
Read more …

Lower oil prices don’t look very effective vs IS.
• Islamic State Earns $800 Million a Year From Oil Sales (Bloomberg)
The Islamic State is earning about $2 million a day, or $800 million a year, selling oil on the black market, IHS Inc. estimated. The terrorist group is producing 50,000 to 60,000 barrels a day, according to an e-mailed release today from the Englewood, Colorado-based information company. It controls as much as 350,000 barrels a day of capacity in Iraq and Syria. Extremist groups typically reply on foreign donations that can be squeezed by sanctions, diplomacy and law enforcement. By tapping the region’s oil wealth, Islamic State, the group that beheaded American journalist James Foley, resembles the Taliban with oil wells. “This is financing and fueling a lot of their activities, military and otherwise,” Bhushan Bahree, a co-author of the report, said today in an interview. “For argument’s sake, let’s say their capacity were cut by half. They’ll still have $400 million coming in. This is many times more than any other source of funding we know of.”
Islamic State consumes about half its production and sells the rest for $25 to $60 a barrel, according to the report. That estimate is in line with those of U.S intelligence officials and anti-terrorism finance experts. Bombing oil-field pump stations may be the best way to cut off the flow of oil since they are stationary and difficult to replace, Bahree said. U.S.-led air strikes haven’t eliminated truck-mounted refineries that Islamic State uses to produce fuel for its war machines and to supply civilians within the territory it controls. Trafficking has encouraged middlemen to buy crude and smuggle it into Turkey, Jordan or Iraq, where it is blended with other oil and sold to unsuspecting buyers, according to the report. “It is very hard to intercept,” Bahree said. “There has probably been smuggling of all sorts of things in this place for thousands of years.” When Iraq’s regional Kurdish government tried to police long-established smuggling routes along a 1,000-kilometer (621-mile) border with what is now Islamic State territory, traffickers found new ones, he said.
Read more …

“They blame the shift on new regulations such as higher capital requirements and the Volcker rule”.
• A Little Volatility Can Be Good for You (Bloomberg)
Gyrations in financial markets are giving rise to a plaintive cry from investors: Prices are getting more volatile because new regulations are making big banks less willing to buy when others want to sell. Actually, if that’s what’s happening, it would be no bad thing. Following last week’s selloff, investors are complaining about a lack of liquidity, the ability to buy and sell assets (particularly bonds) without moving prices too much. The problem, they say, is that big U.S. banks are pulling back from market making — the buying and selling of assets to meet clients’ needs. They blame the shift on new regulations such as higher capital requirements and the Volcker rule, which aims to limit speculative trading at banks.
Investors are right that something has changed. The big banks are holding much smaller inventories of corporate bonds than they did before the 2008 crisis. In fact, dealers were net sellers of junk bonds in recent weeks, suggesting that they weren’t, in the aggregate, helping clients to unload. From the point of view of an overextended investor needing to sell, this reduction in liquidity can be scary. That said, it’s unclear that regulation is the primary cause. Banks were cutting their inventories long before Congress passed the Dodd-Frank financial reform law in 2010. And liquidity always disappears in bad times, no matter how abundant it seems in good times. Market makers are no more willing to buy than anybody else when prices appear to be in free fall. Last week’s volatility hit some securities, such as U.S. Treasury bonds, to which the Volcker rule doesn’t even apply.
Read more …

Not nearly enough.
• Forex-Rigging Fines Could Hit $41 Billion Globally (Bloomberg)
The cost for banks to settle probes into allegations traders rigged foreign-exchange benchmarks could hit as much as $41 billion, Citigroup analysts said. Deutsche Bank is seen as probably the “most impacted” with a fine of as much as 5.1 billion euros ($6.5 billion), Citigroup analysts led by Kinner Lakhani said yesterday, estimating the Frankfurt-based bank’s settlements could reach 10% of its tangible book value, or its assets’ worth. Using similar calculations, Barclays could face as much as 3 billion pounds ($4.8 billion) in fines and UBS penalties of 4.3 billion Swiss francs ($4.6 billion), they wrote in a note first sent to clients on Oct. 3. Authorities around the world are scrutinizing allegations that dealers traded ahead of their clients and colluded to rig currency benchmarks. Regulators in the U.K. and U.S. could reach settlements with some banks as soon as next month, and prosecutors at the U.S. Department of Justice plan to charge one by the end of the year, people with knowledge of the matter have said.
The Citigroup analysts made their calculations using a Sept. 26 Reuters report that the U.K. Financial Conduct Authority settlements could include fines totaling about 1.8 billion pounds. They derived their estimates for how high fines could go in other investigations from that baseline, using banks’ settlements in the London interbank offered rate manipulation cases as a guide. “Extrapolating European and, more importantly, U.S. penalties from a previous global settlement suggests to us a total potential global settlement on this key issue,” they said in the note. U.K. authorities will probably account about $6.7 billion of fines across all banks, according to the Citigroup analysts. Other European investigations will account for $6.5 billion. Penalties in the U.S. cases could be about four times greater, hitting $28.2 billion.
Read more …

Interesting case. If it forces details out into the open.
• How Goldman’s Libya Case Could Disrupt Derivatives (CNBC)
A costly legal battle between Goldman Sachs and the Libyan sovereign wealth fund could have more permanent repercussions for the global banking industry, experts have told CNBC. The Libyan Investment Authority has accused Goldman of misleading it and taking advantage of its lack of financial knowledge to make “substantial” profits on a series of derivative trades back in 2008. The bank denies the allegations and a full hearing has been touted to begin in early 2016 after a preliminary hearing was completed earlier in the month. The LIA claims the disputed derivative trades in early 2008 cost $1 billion, and carried a high degree of risk, but lost a substantial amount of value by the end of the year and expired “worthless” in 2011. Court documents allege that Goldman made profits of $350 million were made and a witness statement from a lawyer working for the LIA claims that the usual disclaimers – called non-reliance agreements – were sent after the trades were made and were never signed.
Satyajit Das, an expert on financial derivatives and risk management, told CNBC via telephone that the case has the potential to get “extremely ugly”. “This could be messy for Goldman Sachs and for a whole range of other banks,” he said, adding that this would bring up the issue of opaqueness with these sorts of trades. “It could lead to an investigation into the selling practices at banks and the types of financial products they offer.” Beyond the prospect of an investigation, industry experts are also forecasting further regulation of the complex derivatives market. Anat Admati, a professor of finance and economics at Stanford Graduate School of Business welcomed any new regulation in this space. Without commenting on this particular case, she said that investments in derivatives can be easily misunderstood by untrained investors.
Read more …

Egg meet face.
• Bank Of England Payment System Crashes Leaving Homebuyers In Limbo (Guardian)
The Bank of England apologised last night after a crucial payments system collapsed, forcing Mark Carney to launch an urgent investigation following the delay of hundreds of thousands of payments, including for homebuyers waiting for money to be transferred to pay for their new homes. The Bank of England governor promised a “thorough, independent review” after MPs demanded answers into how the system which processes payments worth an average £277bn a day had failed for nearly 10 hours. An 88-year-old woman in Sheffield was among those caught up in the collapse of the behind-the-scenes payment mechanism, which failed to open at 6am and remained shut until 3.30pm – usually the cut-off point for money to be transferred for house sales.
The Bank of England did not admit the shutdown had taken place for more than five hours after the system had been due to open, and was later forced to extend opening hours by four hours to 8pm to clear the backlog of 143,000 payments. More than 10 hours after first admitting to the problem with the clearing house automated payment system (Chaps) the Bank of England eventually apologised “for any problems caused by the delays to the settlement system”. While Chaps was down, there were fears that homebuyers and sellers around the country would be left unable to complete purchases on time and that big businesses, which also use the system, would fail to make payments. Only weeks ago the Bank said it had a new contingency plan for the collapse of the payments system. The Bank of England will subject the system to additional monitoring when it reopens at 6am on Tuesday.
Read more …

Emptier words were never heard.
• Fed’s Dudley Warns Banks Must Improve Culture or Be Broken Up (Bloomberg)
Banks must change the way employees are compensated and take other steps to fix a corporate culture that encourages misdeeds or face being broken up, said William C. Dudley, president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York. If bad behavior persists, “the inevitable conclusion will be reached that your firms are too big and complex to manage effectively,” Dudley told industry leaders in a speech yesterday at the New York Fed. “In that case, financial stability concerns would dictate that your firms need to be dramatically downsized and simplified so they can be managed effectively.” Dudley’s comments, which follow bank scandals involving Libor and foreign exchange trading, were made at a closed-doors workshop attended by senior bankers at the New York Fed on reforming Wall Street culture and behavior.
Large U.S. banks were widely blamed for taking too much risk leading up to the 2008 financial crisis, which triggered the worst economic downturn since the Great Depression. Lawmakers have since enacted a major overhaul of the rules designed to prevent banks becoming “too big to fail.” Dudley said it was fair to question if the “sheer size, complexity and global scope of large financial firms today have left them ‘too big to manage.’” Barclays Plc Chairman David Walker, who also addressed the gathering, separately said banks should be allowed to overhaul their own culture, rather than have regulators do it for them. Dudley, who has had to defend the New York Fed recently against allegations it was too soft on big Wall Street firms, suggested a number of ways to better align bank employee incentives with the interests of the general public. These include deferred compensation plans that switch emphasis to debt, rather than equity, and a centralized, industry-wide registry for tracking individual offenses.
Read more …

Chasing the dodo.
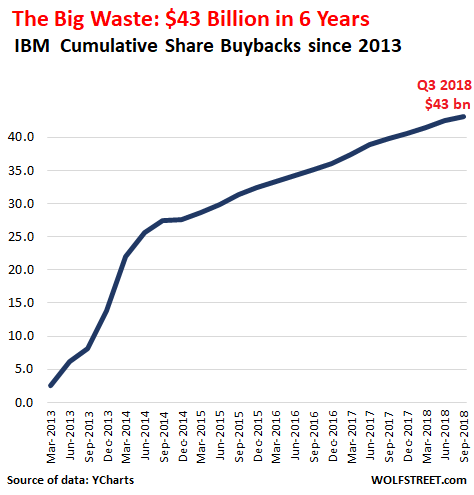
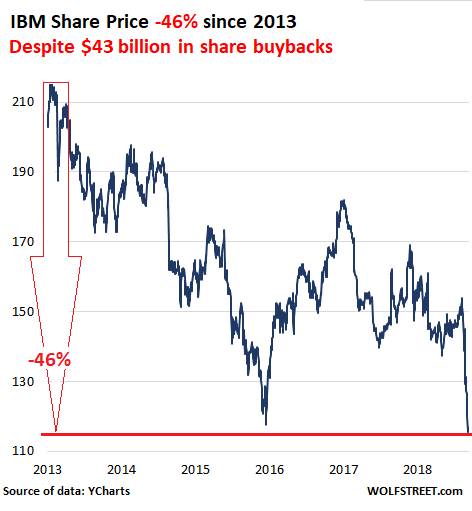
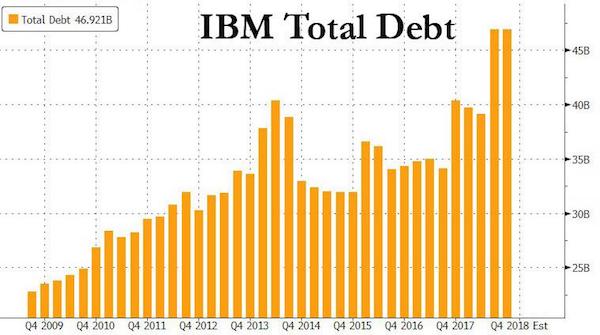
• IBM Is in Even Worse Shape Than It Seemed (BW)
Like a driver obeying the commands of a GPS system even as passengers shout that the car is clearly headed toward a ditch, IBM’s chief executive officer, Ginni Rometty, has followed the profit “roadmap” laid out by her predecessor. The company was going to reach $20 in adjusted earnings per share by 2015, damn it, even as nine straight quarters of sinking revenue made that an increasingly untenable feat of financial engineering. IBM laid off workers, fiddled with its tax rate, took on debt, and bought back a staggering number of its own shares to make the math work, even as all that left the company less able to compete with the likes of Amazon.com and Google in cloud computing.
Today Rometty finally abandoned “Roadmap 2015,” announcing that IBM cannot hit the target after all. IBM also said it will pay a chipmaker called GlobalFoundries $1.5 billion to take its chip division off its hands, while also taking a $4.7 billion charge. And IBM reported its third-quarter results—a 10th consecutive period of falling sales, marked by weaker performance in growth markets. “We are disappointed in our performance,” Rometty said in a statement. “We saw a marked slowdown in September in client buying behavior, and our results also point to the unprecedented pace of change in our industry.” In response, shares of IBM were down more than 7% on Monday morning, Oct. 20.
Read more …

Does it matter whether there’s forward guidance or not? Isn’t it just plain stupidity anyway? A much bigger problem seems to be the economic and hence political power handed over to central banks.
• ‘Forward Guidance’ Marches Global Economy Backwards (Satyajit Das)
A paucity of policy options has increased central banks’ reliance on so-called forward guidance, where policy makers telegraph likely future actions. There are two components to forward guidance. First, it communicates clear policies to which the central bank is committed. Second, the commitment is over a medium- to long time horizon. But forward guidance suffers from a number of weaknesses. A fresh batch of eurozone data out next week is likely to confirm that the economy is slowing, with both consumer confidence and flash PMIs forecast to have slumped in October. In the U.K., third-quarter GDP figures and minutes from the Bank of England’s latest policy meeting will give more clues on the health of the country’s economy.
First, a focus on any single or a narrowly based set of indicators is problematic. The Federal Reserve’s commitment to accommodative monetary policy, for example, was based on a target unemployment rate. A single indicator such as unemployment is not meaningful. It can be affected by participation rates or the definition of employment. Levels can be affected by unexpected disruptions including a government shutdown, strikes or natural catastrophes. What is relevant is the nature of employment, such as part- or full-time, and the type of job or income levels. The composition of unemployment, temporary or long-term, age and skill levels of the unemployed, also may be pertinent.
In Japan, meanwhile, the Bank of Japan’s policy targets 2% inflation. It is not entirely clear which inflation indicator is the most relevant. Core inflation ignores the effect of volatile food and energy prices, which are very relevant to Japan. Inflation in domestic goods or imported inflation, such as the result of currency movements, may have different policy implications. Forward guidance relies on the accuracy of forecasts. It implies an automatic rule-based central banking response, which could lead to a sudden and sharp change in interest rate or monetary policy. In reality, guidance is highly conditional. Environmental changes can negate any earlier policy commitment. The Fed, for instance, was forced to clarify that its unemployment target was merely a non-binding indicator. The most damning problem, as Citibank Chief Economist Willem Buiter has argued, is that central bankers have “no skin in the game.” Central banks do not stand to make or lose money from their forward commitments. Central bankers’ tenure or remuneration is also not linked to outcomes.
Read more …

Complicated talks.
• Ukraine And Russia Agree On $385 Gas Price For Winter (RT)
Moscow and Kiev have confirmed the price of Russian gas to Ukraine until the end of March at $385 per 1,000 cubic meters, according to both Ukrainian President Petro Poroshenko and Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov. “We have agreed on a price for the next 5 months, and Ukraine will be able to buy as much gas as it needs, and Gazprom is ready to be flexible on the terms,” Lavrov said Monday at a public lecture. Russia’s foreign minister dispelled rumors of two separate prices, one for winter and one for summer. “At the Europe-Asia summit in Milan, there was no talk of summer or winter gas prices, but just about the next 5 months,” the foreign minister said. Included in the $385 price is a $100 discount by Russia. Ukraine is still insisting on a further discount, asking for $325 for ‘summer prices’ after the 5-month winter period.
“We talked about how there should be two prices, like how the European spot market has two prices, a winter price when demand is high, and summer when demand is low. Our joint proposal with the EU was the following: $325 per thousand cubic meters in the summer and $385 per thousand cubic meters in the winter,“ Poroshenko said in an interview on Ukrainian television Saturday. President Poroshenko and Russian President Vladimir Putin reached a preliminary agreement in Milan on Friday for the winter period, but Russia won’t deliver any gas to its neighbor without prepayment.
Gas talks are expected to continue Tuesday in Berlin between the energy ministers of Russia, Ukraine, and the EU. On September 26, the three energy ministers agreed to provide 5 billion cubic meters to Ukraine on a “take-or-pay” contract, to help the country survive the winter months. The so-called winter plan is contingent on Ukraine starting to repay at least $3.1 billion worth of debt to Gazprom. Ukraine is still looking for funding to pay for the gas supplies as well as its $4.5 billion arrears to Russia’s state-owned gas company. Moscow reduced the debt from $5.5 billion to $4.5 billion, calculating in the discount of gas, Putin said on Friday.
Read more …

Very bright man, and talking to Russia about grand projects at a time of sanctions. On the other hand, accidents do happen.
• “Anti-Petrodollar” CEO Of French Giant Total Dies In Moscow Plane Crash (ZH)
Three months ago, the CEO of Total, Christophe de Margerie, dared utter the phrase heard around the petrodollar world, “There is no reason to pay for oil in dollars”. Today, RT reports the dreadful news that he was killed in a business jet crash at Vnukovo Airport in Moscow after the aircraft hit a snow-plough on take-off. The airport issued a statement confirming “a criminal investigation has been opened into the violation of safety regulations,” adding that along with 3 crewmembers on the plane, the snow-plough driver was also killed.
Read more …

I don’t know about the assertion that “NATO has succumbed to the socialist phenomenon”. I think it’s blunt power politics all the way, a protection racket.
• The Tragedy Of NATO: “Beware Foreign Entanglements” (Mises Canada)
Mises explained that socialism discourages production while it increases demand. Why produce only to be forced to share with others when one can demand to share in the production of others without regard to having previously produced something of value to those same others? Eventually all altruism vanishes in a sea of cynicism and nothing is produced for anyone to share. The result is a tragedy of the commons fed by moral hazard and socialism. Today we see the above destructive economic forces at work in NATO expansion. When the Soviet Union disintegrated in 1990, the reason for NATO’s existence vanished.
But rather than declare NATO to have been a success in deterring war in Europe, possibly disbanding the alliance and building a new Concert of Europe that would include Russia, NATO bureaucrats set about to expand the alliance to the east. Whereas the Concert of Europe after the Napoleonic Wars had quickly embraced France as an important member, NATO expanded to isolate Russia by absorbing its former satellite nations. The last NATO expansion prior to the disintegration of the Soviet Union had occurred in 1982 when Spain joined the alliance. At that point in time NATO was composed of sixteen nations. Starting in 1999 twelve countries have joined NATO, ten of them former members of the Warsaw Pact.
The other two, Slovenia and Croatia, were previously part of Yugoslavia, officially a non-aligned nation, but a communist dictatorship all the same. With the possible exception of Poland, none of these new members contribute much to the alliance’s military capability, meaning that the older members are shouldering their security burden. Naturally expanding NATO to the east has resulted in isolating and antagonizing Russia, who feels its security threatened. So, NATO has succumbed to the socialist phenomenon by adding new members who demand security without much of an obligation and to the moral hazard phenomenon by adding new members whose territories could be used to house American nuclear weapons, a situation that may yet provoke a major world crisis with Russia, which is precisely what NATO was formed to avoid.
Read more …

Interesting angles. 10 years since ‘Hobbit’ was found.
• Hobbit Find Rewrites Human History (BBC)
The discovery of a tiny species of human 10 years ago has transformed theories of human evolution. The claim is made by Prof Richard Roberts who was among those to have published details of the “Hobbit”. The early human was thought to have lived as recently as 20,000 years ago and so walked the Earth at the same time as our species. The Hobbit’s discovery confirmed the view that the Earth was once populated by many species of human. It’s a far cry from the old view of a linear progression from knuckle-dragging ape-like creatures to upright modern people. Prof Roberts says the discovery of a completely different species of human on the Indonesian Island of Flores that lived until relatively recently, “put paid to this cosy status quo in one fell swoop”. “It surpassed anything else I’d been involved with because it just kept running. People kept on talking about it and it became part of popular culture and a sign of a new view of anthropology. The days of the old linear models of anthropology were gone.
Dr Henry Gee, the manuscript editor who decided to publish the paper in the journal Nature, said that it gradually dawned on him just how important the discovery was. “It is the biggest paper I have been involved with,” he told BBC News.The publication of the discovery on the Indonesian Island of Flores in October 2004, caused a sensation. The news that another species of human walked among us until relatively recently stunned the world. There were even questions about whether the Hobbit, named Homo floresiensis, still existed somewhere on the island. Perhaps there were other species of humans in other very remote parts of the world yet to be discovered?There are many puzzles that remain about the Hobbit. The female skeleton was 1m (3ft) high and was a very primitive form of human. Her brain was about the size of a chimpanzee, yet there is evidence that she used stone tools.
Read more …