Jack Delano Spectators at annual barrel rolling contest, Presque Isle, ME 1940



Envy of the entire world. “We introduced currency controls, we let the banks fail, we provided support for the poor, and we didn’t introduce austerity measures like you’re seeing in Europe.”
• Iceland Sentences 26 Bankers To A Combined 74 Years In Prison (USUncut)
In a move that would make many capitalists’ head explode if it ever happened here, Iceland just sentenced their 26th banker to prison for their part in the 2008 financial collapse. In two separate Icelandic Supreme Court and Reykjavik District Court rulings, five top bankers from Landsbankinn and Kaupping — the two largest banks in the country — were found guilty of market manipulation, embezzlement, and breach of fiduciary duties. Most of those convicted have been sentenced to prison for two to five years. The maximum penalty for financial crimes in Iceland is six years, although their Supreme Court is currently hearing arguments to consider expanding sentences beyond the six year maximum.
After the crash in 2008, while congress was giving American banks a $700 billion TARP bailout courtesy of taxpayers, Iceland decided to go in a different direction and enabled their government with financial supervisory authority to take control of the banks as the chaos resulting from the crash unraveled. Back in 2001, Iceland deregulated their financial sector, following in the path of former President Bill Clinton. In less than a decade, Iceland was bogged down in so much foreign debt they couldn’t refinance it before the system crashed. Almost eight years later, the government of Iceland is still prosecuting and jailing those responsible for the market manipulation that crippled their economy. Even now, Iceland is still paying back loans to the IMF and other countries which were needed just to keep the country operating.
When Iceland’s President, Olafur Ragnar Grimmson, was asked how the country managed to recover from the global financial disaster, he famously replied, “We were wise enough not to follow the traditional prevailing orthodoxies of the Western financial world in the last 30 years. We introduced currency controls, we let the banks fail, we provided support for the poor, and we didn’t introduce austerity measures like you’re seeing in Europe.” Meanwhile, in America, not one single banking executive has been charged with a crime related to the 2008 crash and U.S. banks are raking in more than $160 billion in annual profits with little to no regulation in place to avoid another financial catastrophe.

Sweden, Norway, New Zealand, Australia. And the rest of the emerging markets.
• HSBC: These Are the Economies That Could Run Into Trouble (Bloomberg)
“Forecasters spend much of their time finessing central projections. But sometimes by focusing on the most likely outlook for growth we lose track of vulnerabilities that are accumulating,” HSBC Economist James Pomeroy writes in the latest edition of the bank’s “Macro Health Check.” And while global markets may have stabilized since the volatile days of summer, there seems to be no shortage of potential vulnerabilities worth keeping an eye on. Here are the major trends Pomeroy is watching:
• Weakness in Asia: Lower commodity prices as well as capital flight is hurting a number of Asian economies, not to mention lowering their growth prospects. In particular, HSBC says it’s newly concerned about Malaysia and Indonesia thanks to their proximity to China – both geographically and in terms of trade. As Pomeroy puts it: “The downturn in Chinese data has hit sentiment. Currencies have weakened and borrowing costs have risen, putting the sustainability of the corporate sector at risk.”
• Bubbles in developed economies: Asset prices that are historically high as well as household debt levels well above the norm is concerning, according to Pomeroy. He notes that in Sweden and Norway, high levels of household debt and rising house prices are combining with central banks that have already cut interest rates to record lows. “This leaves them vulnerable to financial stability risks that could leave the economies exposed to any downturn or, at some later stage, a rise in rates,” he says.
• Commodities continue to struggle: Energy is still a huge topic for the world and emerging markets in particular, with Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates on track to see big hits to their economies, the HSBC economist noted. There are also worries over the macroeconomic backdrops in countries like Brazil, Russia, Colombia, and Chile, where 50% of exports are commodities -related, Pomeroy adds.
Based on these concerns, HSBC presents a “diagnosis” showing how a number of economies are and are not seeing impacts from these and other macro factors. New entries on the bank’s list of concerns include the previously-mentioned Malaysia, Indonesia, Sweden and Norway, while New Zealand also makes the cut thanks to its links to China, rising asset prices and tumbling milk prices. “Although low risk, New Zealand may be one to watch,” Pomeroy says.

Losing money way before the oil price crash… “..cash flow from operations has not covered capital expenditure since 2010 at some of the most prominent exploration and production companies since 2010..”
• Jim Chanos Nails the Link Between Debt and Energy (Bloomberg)
“Energy Investments After The Fall: Opportunity Or Slippery Slope?” So begins the latest presentation from renowned short-seller Jim Chanos. What follows is a powerful outlining of the spirally debt dynamics now dominating the future of the oil industry. At the heart of Chanos’s thesis is the contention that years of low interest rates, cheap financing, over-eager investors and ambitious managers have helped propel the boom in U.S. shale and imbue it with near unstoppable momentum; U.S. oil production is expected to grow 6% in 2015 despite a stunning 59% drop in the U.S. rig count over the past year. The extent of the capital market’s support for energy over the past half-decade is laid bare in the financial figures.
According to Chanos, cash flow from operations has not covered capital expenditure since 2010 at some of the most prominent exploration and production companies since 2010, meaning the firms have consistently outspent their income. That trend is present even at the larger “big oil” firms such as Exxon, Chevron and Royal Dutch Shell, Chanos claims, with cash flow following distributions to shareholders also firmly in the red. The question hovering over the energy sector now is whether the continuous flow of capital investment that has propped up shale firms for so long continues. There are signs that it might not. Spreads on the bonds issued by energy companies are currently 480 basis points wider than average yield on the debt of junk-rated companies, meaning investors are (finally) demanding extra return to compensate them for the added risk of E&P.
Many oil companies have large revolving credit facilities from which they could draw financing to help replace the hole left by suddenly skittish investors – an argument that has been picked up by energy bulls and managers with some aplomb. However, Chanos says that even the most reliable E&P firms will be reluctant to tap such revolvers, given the negative publicity around such a move. And while banks have so far largely continued to renew and extend credit lines to energy firms (opting perhaps to keep such companies afloat rather than cut them off and suffer the consequences on their own balance sheets) those renewals have been accompanied by a tightening of terms. It’s a reversal of an historic trend that has seen the balance of power firmly in favor of energy firms as the sheer amount of investors and bankers willing to lend to exploratory shale has meant the vast majority of debt and loans sold and issued in recent years came with far fewer protections for lenders, known as “covenants.”

Trouble brewing. A very imbalanced society.
• Saudis Risk Draining Financial Assets in 5 Years, IMF Says (Bloomberg)
Saudi Arabia may run out of financial assets needed to support spending within five years if the government maintains current policies, the IMF said, underscoring the need of measures to shore up public finances amid the drop in oil prices. The same is true of Bahrain and Oman in the six-member Gulf Cooperation Council, the IMF said in a report on Wednesday. Kuwait, Qatar and the United Arab Emirates have relatively more financial assets that could support them for more than 20 years, the Washington-based lender said. Saudi authorities are already planning spending cuts as the world’s biggest oil exporter seeks to cut its budget deficit.
Officials have repeatedly said that the kingdom’s economy, the Arab world’s biggest, is strong enough to weather the plunge in crude prices as it did in similar crises, when its finances were under more strain. But the IMF said measures being considered by oil exporters “are likely to be inadequate to achieve the needed medium-term fiscal consolidation,” the IMF said. “Under current policies, countries would run out of buffers in less than five years because of large fiscal deficits.” Saudi Arabia accumulated hundreds of billions of dollars in the past decade to help the economy absorb the shock of falling prices. The kingdom’s debt as a percentage of GDP fell to less than 2% in 2014, the lowest in the world.
The recent decline in the price of crude, which accounts for about 80% of Saudi’s revenue, is prompting the government to delay projects and sell bonds for the first time since 2007. Net foreign assets fell to the lowest level in more than two years in August, with the kingdom fighting a war in Yemen and avoiding economic policies that could trigger social or political unrest. The IMF expects Saudi’s budget deficit to rise to more than 20% of gross domestic product this year after King Salman announced one-time bonuses for public-sector workers following his accession to the throne in January. The deficit is expected to be 19.4% in 2016.

Pension funds, mom and pop.
• Who on Wall Street is Now Eating the Oil & Gas Losses? (WolfStreet)
Banks, when reporting earnings, are saying a few choice things about their oil-and-gas loans, which boil down to this: it’s bloody out there in the oil patch, but we made our money and rolled off the risks to others who’re now eating most of the losses. On Monday, it was Zions Bancorp. Its oil-and-gas loans deteriorated further, it reported. More were non-performing and were charged-off. There’d be even more credit downgrades. By the end of September, 15.7% of them were considered “classified loans,” with clear signs of stress, up from 11.3% in the prior quarter. These classified energy loans pushed the total classified loans to $1.32 billion. But energy loans fell by $86 million in the quarter and “further attrition in this portfolio is likely over the next several quarters,” Zions reported.
Since the oil bust got going, Zions, like other banks, has been trying to unload its oil-and-gas exposure. Wells Fargo announced that it set aside more cash to absorb defaults from the “deterioration in the energy sector.” Bank of America figured it would have to set aside an additional 15% of its energy portfolio, which makes up only a small portion of its total loan book. JPMorgan added $160 million – a minuscule amount for a giant bank – to its loan-loss reserves last quarter, based on the now standard expectation that “oil prices will remain low for longer.” Banks have been sloughing off the risk: They lent money to scrappy junk-rated companies that powered the shale revolution. These loans were backed by oil and gas reserves.
Once a borrower reached the limit of the revolving line of credit, the bank pushed the company to issue bonds to pay off the line of credit. The company could then draw again on its line of credit. When it reached the limit, it would issue more bonds and pay off its line of credit…. Banks made money coming and going. They made money from interest income and fees, including underwriting fees for the bond offerings. It performed miracles for years. It funded the permanently cash-flow negative shale revolution. It loaded up oil-and-gas companies with debt. While bank loans were secured, many of the bonds were unsecured. Thus, banks elegantly rolled off the risks to bondholders, and made money doing so. And when it all blew up, the shrapnel slashed bondholders to the bone.
Banks are only getting scratched. Then late last year and early this year, the hottest energy trade of the century took off. Hedge funds and private equity firms raised new money and started buying junk-rated energy bonds for cents on the dollar and they lent new money at higher rates to desperate companies that were staring bankruptcy in the face. It became a multi-billion-dollar frenzy. They hoped that the price of oil would recover by early summer and that these cheap bonds would make the “smart money” a fortune and confirm once and for all that it was truly the “smart money.” Then oil re-crashed.

Coming from a steel man, this can only mean it’ll be much worse.
• China Steel Output May Collapse 20%, Baosteel Chairman Says (Bloomberg)
China’s steel industry, the largest in the world, is bleeding cash and every producer is feeling the pain, according to the head of the country’s second-biggest mill by output, which raised the prospect that nationwide production may shrink 20%. Losses for the industry totaled 18 billion yuan ($2.8 billion) in the first eight months of the year compared with a profit of 14 billion yuan in the same period a year earlier, Shanghai Baosteel Group Corp. Chairman Xu Lejiang said on Wednesday. Output may eventually contract by a fifth, matching the experience seen in the U.S. and elsewhere, he said. After decades of expansion, China’s steel industry has been thrown into reverse as local demand contracts for the first time in a generation amid slowing economic growth and a property downturn.
The slowdown has pummeled steel and iron ore prices and prompted Chinese mills to seek increased overseas sales, boosting trade tensions. The country is the linchpin of the global industry, accounting for half of worldwide production. “If we extrapolate the previous experience in Europe, the United States, Japan, their steel sectors have all gone through painful restructuring in the past, with steel output all contracting by about 20%,” Xu told reporters at a forum in Shanghai. “China will eventually get there as well, regardless how long it takes.” Crude-steel output in China surged more than 12-fold between 1990 and 2014, and the increase was emblematic of the country’s emergence as Asia’s largest economy. Output probably peaked last year at 823 million metric tons, according to the China Iron & Steel Association.
The country produced 608.9 million tons in the first nine months, 2.1% less than the same period last year, the statistics bureau said on Monday. “The whole steel sector is struggling and no one can be insulated,” Xu said. “The sector is facing increasing pressure on funding as banks have been tightening lending to the sector – both loans and the financing provided for steel and raw material stockpiles.” Losses in China’s steel industry are unprecedented, Macquarie Group Ltd. said in a report on Monday that summarized deteriorating sentiment in the industry. While small mills have already cut production significantly, big mills are still holding out, the bank said, forecasting further cuts.

When you can’t afford empire anymore.
• China Slowdown Sees Investment In Africa Plummet 84% (ValueWalk)
The slowdown in the world’s second-largest economy has seen Chinese cross-border investment in Africa plunge. Beijing has invested just $568 million in greenfield projects and expansion of existing projects in the first 6 months of 2015, down from $3.54 billion the previous year. That investment has been focused on China’s primary interest in Africa, namely its raw materials, writes Adrienne Klasa for The Financial Times. While overall investment plunged, investment in extractive industries almost doubled from $141.4 million to $288.9 million over the period. Chinese investment in Africa has at times been controversial, but has played a major role in regional growth. The African growth story has been complicated by global headwinds such as low prices of oil and other commodities.
Many African states rely on raw materials for large parts of their revenues. Although foreign direct investment has fallen, China has been Africa’s main trade partner since 2009. In 2013 there was more than $170 billion in trade between China and sub-Saharan Africa, compared to less than $10 billion in 2002. “FDI has dipped across the board from emerging markets into other emerging markets, and into Africa in particular,” says Vera Songwe, the IFC’s director for West and Central Africa. FDI reflects changing patterns of investment. There are some concerns that a bursting Chinese real estate bubble could see demand for African raw materials reduce even further. This could have a knock-on effect on investment in the sector, and in Africa in general.

“..if the Portuguese people have to choose between “dignity and the euro”, then dignity should prevail. “Any government that refuses to obey Wolfgang Schauble must be prepared to see the ECB close down its banks..”
• Defiant Portugal Shatters The Eurozone’s Political Complacency (AEP)
The delayed fuse on the eurozone’s debt-deflation policies has finally detonated in a second country. Portugal has joined the revolt against austerity. The rickety scaffolding of fiscal discipline and economic surveillance imposed on southern Europe by Germany is falling apart on its most vulnerable front. Antonio Costa, Portugal’s Socialist leader and son of a Goan poet, has refused to go along with further pay cuts for public workers, or to submit tamely to a Right-wing coalition under the thumb of the now-departed EU-IMF ‘Troika’. Against all assumptions, he has suspended his party’s historic feud with Portugal’s Communists and combined in a triple alliance with the Left Bloc. The trio have demanded the right to govern the country, and together they have an absolute majority in the Portuguese parliament.
The verdict from the markets has been swift. “We would be very reluctant to invest in Portuguese debt,” said Rabobank, describing the turn of events as a political shock. The country’s president has the constitutional power to reappoint the old guard – and may in fact do so over coming days – but this would leave the country ungovernable and would be a dangerous demarche in a young Democracy, with memories of the Salazar dictatorship still relatively fresh. “The majority of the Portuguese people did not vote for the incumbent coalition. They want a change,” said Miriam Costa from Lisbon University. Joseph Daul, head of conservative bloc in the European Parliament, warned that Portugal now faces six months of chaos, and risks going the way of Greece.
Mr Costa’s hard-Left allies both favour a return to the escudo. Each concluded that Greece’s tortured acrobatics under Alexis Tspiras show beyond doubt that it is impossible to run a sovereign economic policy within the constraints of the single currency. The Communist leader, Jeronimo de Sousa, has called for a “dissolution of monetary union” for the good of everybody before it does any more damage to the productive base of the European economy. His party is demanding a 50pc write-off of Portugal’s public debt and a 75pc cut in interest payments, and aims to tear up the EU’s Lisbon Treaty and the Fiscal Compact. It wants to nationalize the banks, reverse the privatisation of the transport system, energy, and telephones, and take over the “commanding heights of the economy”.
Catarina Martins, the Left Bloc’s chief, is more nuanced but says that if the Portuguese people have to choose between “dignity and the euro”, then dignity should prevail. “Any government that refuses to obey Wolfgang Schauble must be prepared to see the ECB close down its banks,” she said. She is surely right about that. The lesson of the Greek drama is that the ECB is the political enforcer of monetary union, willing to bring rebels to their knees by pulling the plug on a nation’s banking system.

Any real action will send the message that there are problems.
• ECB Haunted by Paradox as Draghi Weighs Risk of QE Signaling (Bloomberg)
Mario Draghi’s challenge on Thursday is to show that he’s readier than ever to step up stimulus, without panicking investors over the euro area’s health. In the run-up to the European Central Bank’s meeting in Malta, the institution’s president and most of his Governing Council said it’s too early to decide whether to expand their €1.1 trillion bond-buying program. Yet with economists seeing the need for a fresh boost before year-end, he’ll probably be pressured to provide reassurance that the penultimate monetary-policy session of 2015 won’t leave the ECB behind the curve. Officials sitting down to talk will have to deal with a complex scenario of mixed domestic economic signals, an uncertain global outlook, and divergent opinions on what’s needed to combat feeble inflation.
The paradox for Draghi is that when he holds his regular press conference, he may find himself addressing the risks to the recovery without yet committing to action. “The ECB seems more worried about the economy yet less inclined to act; markets are more confident in the economy yet expect something will be done,” said Francesco Papadia, chairman of Prime Collaterised Securities and a former director general of market operations at the ECB. “For Draghi, it’ll be difficult to even hint that something was discussed because it would send two messages: ‘Good, they’re doing something, and wait, the situation is worse than we thought.’

Full insanity.
• Diesel Cars Emit Up To Four Times More Toxic Pollution Than A Bus (Guardian)
A modern diesel car pumps out more toxic pollution than a bus or heavy truck, according to new data, a situation described as a “disgrace” by one MEP. The revelation shows that effective technology to cut nitrogen oxides (NOx) pollution exists, but that car manufacturers are not implementing it in realistic driving conditions. Diesel cars tested in Norway produced quadruple the NOx emissions of large buses and lorries in city driving conditions, according to a report from the Norwegian Centre for Transport Research. A separate study for Transport for London showed that a small car in the “supermini” class emitted several times more NOx than most HGVs and the same amount as a 40-tonne vehicle.
“It is crackers,” said emissions expert James Tate from the University of Leeds. His own research, which uses roadside equipment to measure passing traffic, also shows the latest diesel models cars produce at least as much NOx as far heavier buses and trucks. The issue of NOx pollution, thought to kill 23,500 people a year in the UK alone, gained prominence when VW diesels were discovered to be cheating official US emissions tests. The scandal also led to revelations that the diesels of many car manufacturers produce far more NOx on the road than in EU lab tests, though not via illegal means. The UK government say the failure to keep NOx from vehicles low in the real world means road transport is “by far the largest contributor” to the illegal levels of NOx in many parts of the country.
“It is disgraceful that car manufacturers have failed to reduce deadly emissions when the technology to do so is affordable and readily available,” said Catherine Bearder, a Liberal Democrat MEP and a lead negotiator in the European parliament on the EU’s new air quality law. “The dramatic reduction in NOx emissions from heavier vehicles is a result of far stricter EU tests, in place since 2011, that reflect real-world driving conditions. If buses and trucks can comply with these limits, there’s no reason cars can’t as well.”

VW is set to shrink a lot.
• 3 Million Volkswagen Cars Need Costly Hardware Fixes In Europe Alone (Bloomberg)
Volkswagen will need hardware fixes for about 3 million cars in Europe affected by the diesel-emission manipulations as the region’s largest automaker scrambles to meet demands from regulators. Cars featuring a 1.6-liter engine require technical tweaks, while software updates are sufficient to make the other affected engines compliant, a VW spokesman said by phone. VW said last week it will recall about 8.5 million cars across Europe through 2016 and acknowledged efforts to fix all cars might drag on until 2017. VW has also stated the fallout from the scandal will cost more than the €6.5 billion already set aside.
Worldwide some 11 million cars with diesel engines are affected by the wide-ranging emissions rigging that was uncovered by U.S. regulators and triggered the resignation of Chief Executive Officer Martin Winterkorn. Moody’s Investors Service said Wednesday that uncertainties about the potential impact on VW’s reputation, earnings and cash flows could weigh on the manufacturer’s credit profile into 2017. New CEO Matthias Mueller said last week protecting the company’s credit rating is a top priority. The manufacturer can recover from the scandal in two-to-three years if the right decisions are made now to make VW more efficient, agile and cost competitive, he said.

“The logic of the EU rules holds that burning a tree doesn’t actually create new carbon emissions; it just releases the old. The carbon balance is therefore zero.”
• The EU Is Emitting Way More Greenhouse Gases Than It Says (Quartz)
One of the planet’s exemplars in preventing climate change, the EU has instituted tough emissions rules and strong support for renewable energy. Yet this doesn’t necessarily mean more solar panels or wind turbines dotting Europe’s skyline. Nope, the EU’s biggest source of renewable energy is old-school: burning wood. There’s just one problem with this. Torching wood has the potential to warm the atmosphere faster than burning coal does. So why does Europe get nearly half of its renewable energy that way? As Climate Central argues in this three-part piece, a legal loophole in the EU’s climate rules means it turns a blind eye to tens of millions of CO2 emissions that it pumps into the atmosphere each year. Worse, this policy means European governments issue hundreds of millions of dollars in incentives to encourage power plants to burn even more wood.
The core issue lies in how to count the CO2 pollution released when wood is burned for electricity and heat. Because trees grow back, EU law deems wood a “renewable energy” just like solar or wind (a source of fuel, in other words, that can be used to meet its fairly tough climate action target of sourcing 20% of its final energy consumption to come from renewable energy by 2020). But in many ways, wood is more like coal or oil—it must be burned to generate power. This process releases a lot of CO2, which traps heat in the atmosphere, warming the planet. But since trees also absorb CO2, they act as what’s been described as a “brake” on the rate of global warming. The logic of the EU rules holds that burning a tree doesn’t actually create new carbon emissions; it just releases the old. The carbon balance is therefore zero.
This makes complete sense—provided the wood you’re burning comes from already-dead wood that would release its carbon as it decomposed anyway. This includes dust and chips from sawmills, for example. And since the energy created when that wood is burned isn’t coming from fossil fuels, it’s ultimately a net positive for the atmosphere, as the CarbonBrief explains. However, that equation changes once you start clear-cutting forests for the sole purpose of fueling power plants. Wood tends to emit more carbon than fossil fuels to generate the same amount of energy, according to the Natural Resources Defense Council (pdf). Eventually, trees grow back and absorb this carbon. However, a growing body of peer-reviewed research suggests it can take decades—or even centuries—before a forest grows back enough to balance out the atmospheric CO2 created when its trees were burned.

Like the Bloomberg title.
• The Strongest El Niño in Decades Is Going to Mess With Everything (Bloomberg)
It has choked Singapore with smoke, triggered Pacific typhoons and left Vietnamese coffee growers staring nervously at dwindling reservoirs. In Africa, cocoa farmers are blaming it for bad harvests, and in the Americas, it has Argentines bracing for lower milk production and Californians believing that rain is finally, mercifully on the way. El Nino is back and in a big way. Its effects are just beginning in much of the world – for the most part, it hasn’t really reached North America – and yet it’s already shaping up potentially as one of the three strongest El Nino patterns since record-keeping began in 1950. It will dominate weather’s many twists and turns through the end of this year and well into next. And it’s causing gyrations in everything from the price of Colombian coffee to the fate of cold-water fish.
Expect “major disruptions, widespread droughts and floods,” Kevin Trenberth, distinguished senior scientist at the National Center for Atmospheric Research in Boulder, Colorado. In principle, with advance warning, El Nino can be managed and prepared for, “but without that knowledge, all kinds of mayhem will let loose.” In the simplest terms, an El Nino pattern is a warming of the equatorial Pacific caused by a weakening of the trade winds that normally push sun-warmed waters to the west. This triggers a reaction from the atmosphere above. Its name traces back hundreds of years to the coast of Peru, where fishermen noticed the Pacific Ocean sometimes warmed in late December, around Christmas, and coincided with changes in fish populations. They named it El Nino after the infant Jesus Christ. Today meteorologists call it the El Nino Southern Oscillation.
The last time there was an El Nino of similar magnitude to the current one, the record-setting event of 1997-1998, floods, fires, droughts and other calamities killed at least 30,000 people and caused $100 billion in damage, Trenberth estimates. Another powerful El Nino, in 1918-19, sank India into a brutal drought and probably contributed to the global flu pandemic, according to a study by the Climate Program Office of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. As the Peruvian fishermen recognized in the 1600s, El Nino events tend to peak as summer comes to the Southern Hemisphere. The impact can be broken down into several categories. Coastal regions from Alaska to the Pacific Northwest in the U.S., as well as Japan, Korea and China may all have warmer winters. The southern U.S., parts of east Africa and western South America can get more rain, while drier conditions prevail across much of the western Pacific and parts of Brazil.

Strong graphs. More El Niño.
• The Graphic That Shows Why 2015 Global Temperatures Are Off The Charts (SMH)
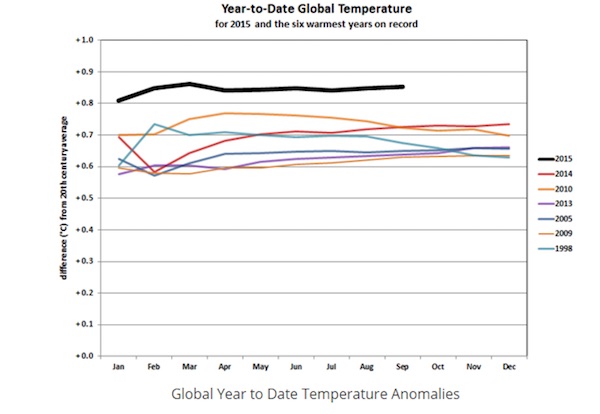
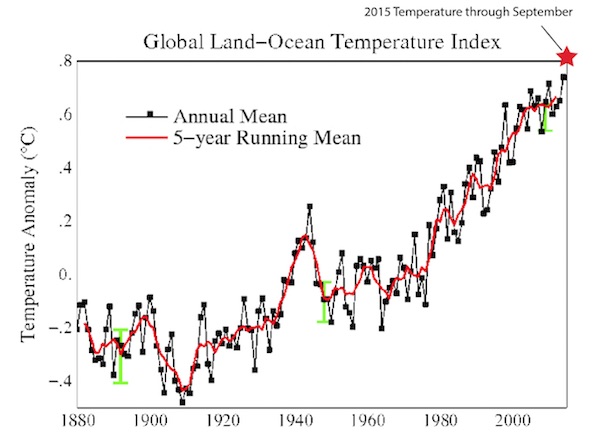
If there is one chart that might finally put to rest debate of a pause or “hiatus” in global warming, this chart created by the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration has just supplied it. For years, climate change sceptics relied on a spike in global temperatures that occurred during the monster 1997-98 El Nino to say the world had stopped warming because later years struggled to set a higher mark even as greenhouse gas emissions continued to rise. Never mind that US government scientists found the hiatus was an illusion because the oceans had absorbed most of the extra heat that satellites could tell the Earth was trapping. Nor that 2005, 2010 and 2014 all set subsequent records for annual heat.
Those record years were too incrementally warmer compared with the 1997 mark to satisfy those who wanted to believe climate change was a hoax. But it is 2015, which is packing an El Nino that is on track to match the record 1997-98, that looks set to blow away previous years of abnormal warmth. “This one could end the hiatus,” said Wenju Cai, a principal research scientist specialising in El Nino modelling at the CSIRO. “Whether it beats [the 1997-98 El Nino] will be academic – it’s already very big.” NOAA data released overnight backs up how exceptional this year is in terms of warming, with September alone a full quarter of a degree above the corresponding month in 1997. As the chart above shows, for the first nine months, 2015 has easily been the hottest year on record, with sunlight second.
[..] El Ninos typically add 0.1-0.2 degrees to the background global warming. US climate expert John Abraham has estimated how year-to-date temperatures are adding another step-up to temperatures, as seen in this chart published by Think Progress. Climate change sceptics will probably not concede in their battle to avoid action to curb emissions. Satellite or meteorological data must have been manipulated, the oceans might be producing chemical compounds never detected before that counter carbon dioxide, or perhaps the sun is about to burn a lot less brightly. Still, they now have one more inconvenient chart they have to find a reason to ignore.

114 people. That’s the whole story. But the UK won’t have none of it.
• UK Must Resettle Refugees Who Arrived On Cyprus Military Base: UN (Guardian)
The UN refugee agency, the UNHCR, has said that the UK is legally obliged to resettle more than a hundred Syrian refugees who arrived by boat at a British military base in Cyprus, contradicting claims from the Ministry of Defence (MoD) that they were a Cypriot responsibility. Two overloaded wooden boats carrying 114 refugees from Syria, including 28 children, have been transferred to a temporary reception area in the sovereign base at Akrotiri on the southern coast of the Mediterranean island. According to the Cypriot coastguard, the refugees were abandoned offshore by people smugglers and left to fend for themselves.
The arrival on British territory of asylum seekers fleeing the Syrian conflict intensifies the scrutiny on the UK’s response to Europe’s worst refugee crisis since the second world war. David Cameron has offered to take in 20,000 Syrian refugees over five years – significantly less than most other western European countries, though the government has pointed out it gives more aid for refugee camps along Syria’s borders. Reacting to the arrivals at Akrotiri, the MoD said: “At the moment our key priority is ensuring everybody on board is safe and well. We have had an agreement in place with the Republic of Cyprus since 2003 to ensure that the Cypriot authorities take responsibility in circumstances like this.”
Asked whether the refugees would be able to claim asylum in Britain, an MoD official said: “That’s not our understanding.” A spokeswoman for the Home Office also stated: “The resettlement of refugees landing on the southern bases in Cyprus is not the responsibility of the United Kingdom.” But the UNHCR said in a statement that the 2003 UK-Cyprus memorandum made it clear that “asylum seekers arriving directly on to the SBA [Sovereign Base Area] are the responsibility of the UK but they would be granted access to services in the republic at the cost of the SBA.”

They’ll throw -promises of- more money around. And that’ll be it, again.
• EU Calls Mini-Summit On Refugee Crisis As Slovenia Tightens Border (Guardian)
The EU has called a mini summit with Balkan countries on the migrant crisis as Slovenia became the latest state to buckle under a surge of refugees desperate to reach northern Europe before winter. The leaders of Austria, Bulgaria, Croatia, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Romania and Slovenia will meet in Brussels on Sunday with their counterparts from non-EU states Macedonia and Serbia, the office of EC president Jean-Claude Juncker said. “In view of the unfolding emergency in the countries along the western Balkans migratory route, there is a need for much greater cooperation, more extensive consultation and immediate operational action,” a statement said. The continent has been struggling to find a unified response on how to tackle its biggest migration crisis since 1945.
More than 600,000 migrants and refugees, mainly fleeing violence in Syria, Iraq and Afghanistan, have braved the dangerous journey to Europe so far this year, the UN said. Of these, more than 3,000 have drowned or gone missing as they set off from Turkey in inflatable boats seeking to reach Greece, the starting point for the migrants’ long trek north. With the crisis showing no sign of abating, France’s interior minister Bernard Cazeneuve reinforced security in the port city of Calais from where migrants and refugees try to cross to Britain. He also announced that women and children would be given heated tents, as arrivals in a makeshift camp face a dip in temperature.

EU police? Don’t think that exists. So, German and French cops patrolling in Slovenia? Really?
• Slovenia Asks For EU Police Help To Regulate Migrant Flow (Reuters)
Slovenia has asked the European Union for police to help regulate the inflow of migrants from Croatia, Interior Minister Vesna Gyorkos Znidar told TV Slovenia. Over the past 24 hours, more than 10,000 migrants, many fleeing violence in Syria, have arrived in Slovenia, the smallest country on the Balkan migration route, on their way to Austria. “Slovenia has already asked other EU member states for police units,” Znidar said late on Wednesday. European Commissioner for Migration and Home Affairs Dimitris Avramopoulos on Thursday will visit Slovenia to discuss the migrant crisis, while Commission President Jean-Claude Juncker called an extraordinary meeting of several European leaders for Sunday.
Juncker invited the leaders of Austria, Bulgaria, Croatia, the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Romania, Serbia and Slovenia. Slovenia’s parliament has given more power to the army which is helping police control the border, while the country also plans to rehire retired police to help. Huge number of migrants started coming to Slovenia on Saturday after Hungary on Friday sealed its border with Croatia with a bottleneck building up through the Balkans.

I’m all for it, but not for the We Must.. It will take a lot more than that.
• A Cultural Revolution To Save Humanity (Serge Latouche)
We’ve reached a point that means we can no longer go on as we are doing! Everyone’s talking about crisis and it’s slightly paradoxical because I’ve always been hearing about a crisis ever since 1968 when there was a cultural crisis, then in 1972, with the publication of the work by The Club of Rome, there was talk of an ecological crisis, then there was the neoliberal counter-revolution and the social crisis with Margaret Thatcher and Reagan, and now there’s the financial crisis and the economic crisis after the collapse of Lehmann Brothers. Finally, all these crises are getting mixed up and we re seeing a crisis of civilisation, an anthropological crisis. At this point, the system can no longer be reformed – we have to exit from this paradigm – and what is it? It s the paradigm of a growth society.
Our society has been slowly absorbed by an economy based on growth, not growth to satisfy needs – and that would be a good thing – but growth for the sake of growth and this naturally leads to the destruction of the planet because infinite growth is incompatible with a finite planet. We need a real reflection when we talk about an anthropological crisis. We need to take this seriously because we need a decolonisation of the imagination. Our imagination has been colonised by the economy. Everything has become economics. This is specific to the West and it’s fairly new in our history. It was in the seventeenth century when there was a great ethical switch with the theory expounded by Bernard Mandeville. Before, people said that altruism was good and then: “no, we have to be egoists, we have to make as much profit as possible; greed is good . Yes – to destroy our “oikos (our home) more quickly. And we have actually got to that point.

“Monstromart’s slogan was “where shopping is a baffling ordeal”.
• Why Too Much Choice Is Stressing Us Out (Guardian)
Once upon a time in Springfield, the Simpson family visited a new supermarket. Monstromart’s slogan was “where shopping is a baffling ordeal”. Product choice was unlimited, shelving reached the ceiling, nutmeg came in 12lb boxes and the express checkout had a sign reading, “1,000 items or less”. In the end the Simpsons returned to Apu’s Kwik-E-Mart. In doing so, the Simpsons were making a choice to reduce their choice. It wasn’t quite a rational choice, but it made sense. In the parlance of economic theory, they were not rational utility maximisers but, in Herbert Simon’s term, “satisficers” – opting for what was good enough, rather than becoming confused to the point of inertia in front of Monstromart’s ranges of products.
This comes to mind because Tesco chief executive Dave Lewis seems bent on making shopping in his stores less baffling than it used to be. Earlier this year, he decided to scrap 30,000 of the 90,000 products from Tesco’s shelves. This was, in part, a response to the growing market shares of Aldi and Lidl, which only offer between 2,000 and 3,000 lines. For instance, Tesco used to offer 28 tomato ketchups while in Aldi there is just one in one size; Tesco offered 224 kinds of air freshener, Aldi only 12 – which, to my mind, is still at least 11 too many. Now Lewis is doing something else to make shopping less of an ordeal and thereby, he hopes, reducing Tesco’s calamitous losses. He has introduced a trial in 50 stores to make it easier and quicker to shop for the ingredients for meals.
Basmati rice next to Indian sauces, tinned tomatoes next to pasta. What Lewis is doing to Tesco is revolutionary. Not just because he recognises that customers are time constrained, but because he realises that increased choice can be bad for you and, worse, result in losses that upset his shareholders. But the idea that choice is bad for us flies in the face of what we’ve been told for decades. The standard line is that choice is good for us, that it confers on us freedom, personal responsibility, self-determination, autonomy and lots of other things that don’t help when you’re standing before a towering aisle of water bottles, paralysed and increasingly dehydrated, unable to choose.
That wasn’t how endless choice was supposed to work, argues American psychologist and professor of social theory Barry Schwartz in his book The Paradox of Choice. “If we’re rational, [social scientists] tell us, added options can only make us better off as a society. This view is logically compelling, but empirically it isn’t true.”