Vincent van Gogh The Parsonage Garden at Nuenen in Spring 1884 (stolen yesterday)

More countries are demanding people wear face masks, even the CDC in the US talks about making it obligatory, but masks are no more available in many places than tests are. We’re three months into this thing -though I know for most people it’s been just 2 weeks-, and we’re still debating this.
In the US, half the people have it easy, they can just blame everything on Trump, it’s a entire industry, even though his approval numbers rise at the same time. But in all those other countries, who do you blame when you have face the coordinated efforts to praise your government of the day? Life isn’t easy. Maybe you can blame Trump too.
Meanwhile, we’re sadly waiting for US cases and death numbers to explode. 15,000 new cases and close to 1,000 new deaths is devastating, but nowhere near what we expect the trend to become.

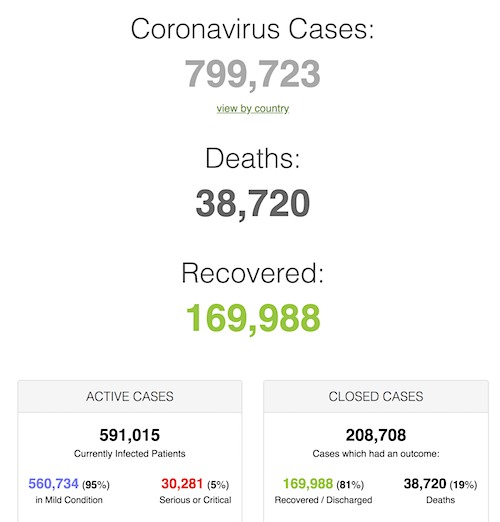
• Cases 799,723 (+ 64,792 from yesterday’s 734,931)
• Deaths 38,720 (+ 3,940 from yesterday’s 34,780)

From Worldometer yesterday evening -before their day’s close-. Note: Turkey’s in the ascendancy (though not in the zodiac)
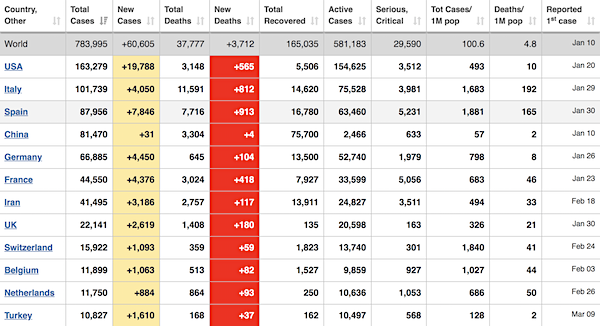
From Worldometer -NOTE: mortality rate for closed cases is at 19% –
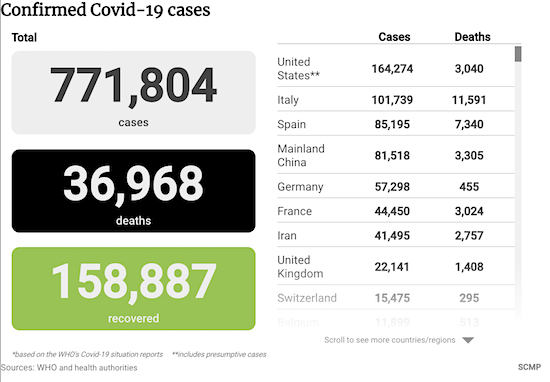
From SCMP:
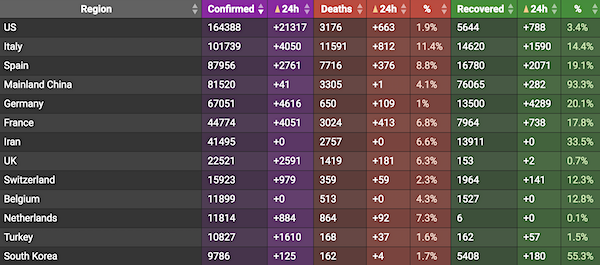
From COVID2019Live.info:

Sharyl Attkisson noticed something too. Fauci must be more careful.
• Fauci Offers More Conservative Death Rate In Academic Article Than In Public Briefings (JTN)
You’ve probably heard that COVID-19 is far deadlier than the flu. But it could turn out to be more akin to a severe flu season. Surprisingly, both of those assessments come from the same authority at the same time: Dr. Anthony Fauci, the nation’s chief infectious disease specialist. Fauci, the director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, has repeatedly cited more jarring figures in public. For instance, Fauci declared in March 11 congressional testimony that the current coronavirus “is 10 times more lethal than the seasonal flu,” which would be about 1 percent. His testimony generated news headlines that blared across the internet and television news, and it remains frequently cited today. But among his learned colleagues in academia, he has provided the more conservative analysis.
“[T]he case fatality rate may be considerably less than 1%,” Fauci wrote in an article published in the New England Journal of Medicine on March 26. “This suggests that the overall clinical consequences of COVID-19 may ultimately be more akin to those of a severe seasonal influenza (which has a case fatality rate of approximately 0.1%) or a pandemic influenza (similar to those in 1957 and 1968) rather than a disease similar to SARS or MERS, which have had case fatality rates of 9 to 10% and 36%, respectively.” A day after the NEJM article was published, Fauci was back to repeating the higher fatality number in public rather than “considerably less than 1%.” “The mortality of [COVID-19] is about 10 times [flu],” Fauci told Comedy Central host Trevor Noah on March 27.

A lot of things won’t happen without kickbacks. The system is one sick puppy.. and no reform in sight, since both parties are beholden to the industry as a whole.
• Hospital Equipment Shortages Renew Spotlight On Supply Chain Middlemen (JTN)
Healthcare providers facing medical equipment shortages and exorbitantly high drug prices during the coronavirus outbreak are captive to kickback-receiving “middlemen” who lock up hospitals in exclusive contracts that enable price gouging and supply bottlenecks, according to a network of physician advocacy groups representing 3,000 physicians. Nearly 90% of U.S. mayors who responded to a national survey released Friday by the U.S. Conference of Mayors said they lack enough protective equipment for their coronavirus medical workers, and 85% said they do not have enough ventilators for their hospitals.
Dr. Marion Mass, a Duke-educated physician who founded Practicing Physicians of America (PPA), told Just the News that so-called “safe harbor” (legal protection) provisions allowing for payments from medical equipment and drug manufacturers to pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) and group purchasing organizations (GPO) — what Dr. Mass calls the “middlemen” between providers and manufacturers — amount to “kickbacks.” The “safe harbor” payments are overseen by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), monitored by the HHS Inspector General (IG), and are currently protected by law, but Dr. Mass and her physician network argue they should be repealed.

“After significant consolidation, four behemoth GPOs now control 90% of the entire chain of hospital and nursing home supplies, and we are in the grip of an unspeakably corrupt, pay-to-play system of financial kickbacks,” Mass wrote in a white paper co-authored by the Physicians for Reform and Texas Public Policy Foundation. “If the law that established the ‘safe harbor’ for kickbacks to the GPOs (and extended to PBMs in 2003) was repealed, the cost for medical supplies and medications would fall by an estimated 25% to 30%. The cost of prescription medications would fall by 35% to 43%. Additional declines in prices are projected as true competition replaces a rigged marketplace. We estimate this reform would save Medicare and Medicaid an estimated $75 billion each year.”

DiMartino Booth tweet: “(Bloomberg) 3 days after President Trump signed $2T stimulus, Kohl’s, Macy’s & Gap joined growing number of retailers to halt pay for much of their workforce while preserving some benefits. With these furloughs, total number of employees out a paycheck at major US chains >500,000”
• US COVID19 Job Losses Could Be 47 Million, Unemployment May Hit 32% (CNBC)
Millions of Americans already have lost their jobs due to the coronavirus crisis and the worst of the damage is yet to come, according to a Federal Reserve estimate. Economists at the Fed’s St. Louis district project total employment reductions of 47 million, which would translate to a 32.1% unemployment rate, according to a recent analysis of how bad things could get. The projections are even worse than St. Louis Fed President James Bullard’s much-publicized estimate of 30%. They reflect the high nature of at-risk jobs that ultimately could be lost to a government-induced economic freeze aimed at halting the coronavirus spread. “These are very large numbers by historical standards, but this is a rather unique shock that is unlike any other experienced by the U.S. economy in the last 100 years,” St. Louis Fed economist Miguel Faria-e-Castro wrote in a research paper posted last week.
There are a couple of important caveats to what Faria-e-Castro calls “back-of-the-envelope” calculations: They don’t account for workers who may drop out of the labor force, thus bringing down the headline unemployment rate, and they do not estimate the impact of recently passed government stimulus, which will extend unemployment benefits and subsidize companies for not cutting staff. However, the jobless picture already looks bleak. A record 3.3 million Americans filed initial jobless claims for the week ended March 21. Economists surveyed by Dow Jones expect another 2.65 million to join them this week. Friday’s nonfarm payrolls count for March is expected to show a decline of just 56,000, but that’s largely due to a statistical distortion [..]


Pelosi falls innto the Chuck Todd “blood on his hands” trap. It’s a cheap political game that should not now be played. Sure, Trump was way off. But so were his advisers (Fauci), all other western and other leaders, and Pelosi herself, who was busy fiddling with impeachment when she could have been focusing on what she now says Trump should have been doing.
• Trump Rips Pelosi For Criticizing His Handling Of Coronavirus Pandemic (NYP)
President Trump unleashed on House Speaker Nancy Pelosi in an early morning phone interview on “Fox & Friends,” slamming her comments about his “deadly” handling of coronavirus. Speaking to the Fox News hosts Monday morning, the commander-in-chief described the California Democrat as “a sick puppy,” who has “a lot of problems,” when asked about Pelosi’s criticism of his response to the virus. Trump added that her remarks were “a horrible thing to say.” “When I stopped some very, very infected, very, very sick people — thousands coming in from China — earlier than anyone thought [was necessary], including the experts.
Nobody thought we should do it, except me,” Trump said, adding that he was praised by government infectious disease expert Dr. Anthony Fauci for his decision to close the borders. “If I didn’t do that, you would’ve had deaths like you have never seen before,” he continued before knocking Pelosi for not crediting him for the move. Trump went on to call San Francisco, a city that is part of Pelosi’s district, a “slum,” adding that the federal government may need to address the city’s problems. Speaking about Pelosi’s impeachment crusade against the president — which passed the House but failed in the Senate — Trump said, “Don’t forget, she was playing the impeachment game where she ended up looking like a fool.”
On Sunday, Pelosi slammed Trump’s response to the pandemic, telling CNN, “We should be taking every precaution. What the president, his denial at the beginning was deadly.” “As the president fiddles, people are dying. And we just have to take every precaution,” she continued. CNN host Jake Tapper pressed the speaker on whether she believed Trump’s downplaying of the crisis had cost American lives, to which Pelosi responded, “Yes, I am. I’m saying that.”

More games. Scheduled to take at least another month. Posing and posturing.
• Pelosi Aims To Move Fast On Next Rescue Package (Pol.)
House Democrats are moving rapidly on ambitious plans for a fourth coronavirus relief package, with Speaker Nancy Pelosi eager to put her imprint on legislation that she says could be ready for a vote in the coming weeks. Pelosi told reporters Monday that Democrats are in the early stages of drafting another major bill that will not only shore up health systems and protect frontline health care workers but could include substantial investments in infrastructure. “Our first bills were about addressing the emergency. The third bill was about mitigation. The fourth bill would be about recovery. Emergency, mitigation, recovery,” Pelosi said on a conference call. “I think our country is united in not only wanting to address our immediate needs — emergency, mitigation, and the assault on our lives and livelihoods — but also, how we recover in a very positive way.”
But Democrats’ approach could put them on a collision course with senior Republicans, who say they are very much in wait-and-see mode when it comes to another potential multi-trillion-dollar bill and are warning Pelosi not to try to jam the Senate with a progressive plan. “They’re approaching it — it seems like — as an opportunity to pass their political and ideological agenda. We’re approaching it as, ‘How do we protect the public health and our economy?’ And those are pretty divergent goals,” said Sen. John Cornyn (R-Texas) [..]

RussiaRussiaRussia is speeding up those hospital boats just to make here look bad. Actually, I don’t want to talk about Maddow.
• Rachel Maddow’s Recent Predictions Get Roasted (JTN)
MSNBC host Rachel Maddow on March 20 cast doubt on the notion that two Navy hospital ships would soon reach ports on the East and West coasts to relieve hospitals combatting the coronavirus pandemic as President Trump had promised. The ships have since arrived at their respective destination ports in California and New York where they will serve non-COVID-19 patients in an effort to decrease pressure on the hospitals ashore. “In terms of the happy talk we’ve had on this front from the federal government, there is no sign that the Navy hospital ships that the president made such a big deal of, the Comfort and the Mercy, there’s no sign that they’ll be anywhere on site helping out anywhere in the country for weeks yet,” Maddow said on her television show.
“The president said when he announced that those ships would be put into action against the COVID-19 epidemic, he said one of those ships would be operational in New York harbor by next week. That’s nonsense, it will not be there next week,” Maddow asserted. The USNS Comfort arrived in New York harbor on Monday March 30, while the USNS Mercy arrived in the Port of Los Angeles on Friday March 27 and began accepting patients on Sunday March 29. Republicans on Monday highlighted the Maddow clip.
FLASHBACK: MSNBC's Rachel Maddow: "nonsense" hospital ship will be in NYC soonhttps://t.co/fkfH6uf12m pic.twitter.com/7lSMTLPVs2
— RNC Research (@RNCResearch) March 30, 2020
It isn’t the first time the popular liberal host has faced criticism — both on the left and the right — for her prognostication or promotion. Maddow was criticized in March 2017 when she over-hyped a story about Donald Trump’s 2005 tax returns, underwhelming many viewers once she finally divulged the information she had been teasing. “In positioning it as a grand revelation, a vital step in comprehending Trump’s corruption, MSNBC created an exceedingly cynical spectacle,” Willa Paskin wrote on Slate.com.

Lesson in federalism. There are lots of things the federal government can’t do that are normal in other countries.
• Political Distancing (Turley)
New York Governor Andrew Cuomo called on the federal government to take control of the medical supply market. Illinois Governor J.B. Pritzker demanded that President Trump take charge and said “precious months” were wasted waiting for federal action. Some critics are even more direct in demanding a federal takeover, including a national quarantine. It is the legal version of panic shopping. Many seem to long for federal takeovers, if not martial law. Yet like all panic shopping, they are buying into far more than they need while not doing as much as they could with what they have. For decades, governors tried to retain principal authority over public emergencies, but they did very little with those powers.
While many are doing impressive work now, some governors seem as eager to contain the blame as the coronavirus. Call it political distancing. Even if Trump nationalized the crisis by deploying troops, imposing price controls, and forcing production of ventilators, the Constitution has left most police authority and public health safety to the states in our system of federalism. The Framers believed liberties and powers were safest when held closest to citizens in local and state governments. Elected officials at the local and state levels are more readily held accountable than unknown Washington bureaucrats. Of course, with authority comes responsibility, and the latter notion is not always as welcomed as the former.
Despite all the hyperbole of the last few days, the federal authority of the president to act is much more limited than many appear to believe. Trump cannot, and should not, simply take over the crisis. While he may want to “open for business” by Easter, he has no clear authority to lift state orders for citizens to stay at home. His greatest authority is supplying assistance in the production and delivery of necessary resources such as ventilators. While he can put conditions on some assistance, he cannot commandeer the authority of governors in their responses to the pandemic.

The virus will change the entire country. But people find it hard to comprehend. Wolf Richter doing well. “Nothing Goes to Heck in a Straight Line”
• Many Brick & Mortar Stores Will Not Reopen, CMBS will Default (WS)
Macy’s announced today that it would lay off “the majority” of its 123,000 employees after it had closed all its Macy’s, Bloomingdale’s and Bluemercury stores on March 18. Even before the lockdowns, its headcount was already down 17% from four years ago, in line with the decline of its brick-and-mortar operations. It said these stores would “remain closed until we have clear line of sight on when it is safe to reopen.” Whenever that may be. But “at least through May,” the furloughed employees who were already enrolled in its health benefits program “will continue to receive coverage with the company covering 100% of the premium.” And it said, “We expect to bring colleagues back on a staggered basis as business resumes.” That is, if business at these brick-and-mortar stores resumes.
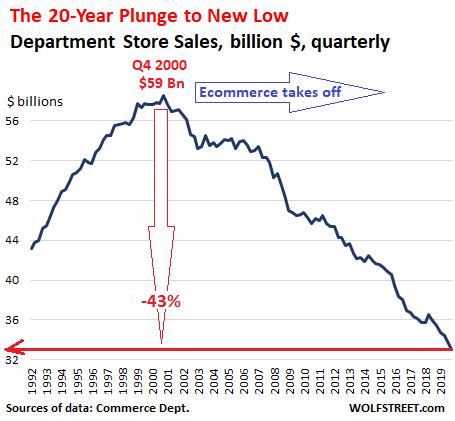
Department stores have been on a 20-year downward spiral that has ended for many of them in bankruptcy court where they got dismembered and sold off in pieces. The survivors, which have been shuttering their brick-and-mortar stores for years, are now getting hit by the lockdowns. The chart depicts the brick-and-mortar business that Macy’s, Nordstrom, Kohl’s, JCPenney, Neiman Marcus, Sears, Bon-Ton Stores, Barney’s and others are in – or were in. Over the past 20 years, department store revenues declined by 43%. And now they’re getting whacked for good by the lockdowns. That declining line of revenues is going to make a 90-degree downward kink in Q1, Q2 and Q3, to violate the WOLF STREET beer-bug dictum that “Nothing Goes to Heck in a Straight Line”:
As many brick-and-mortar stores have shut down, and as people are fearful about going to those stores that are still open (such as grocery stores), ecommerce sales have exploded. Americans have long been reluctant to buy groceries online. But that has changed overnight. Amazon, Walmart and other online retailers have gone on a hiring binge to deal with the onslaught of online buying, including the stuff people normally bought in grocery stores. Online retail is the huge winner of COVID-19. When the Q1 and Q2 ecommerce revenues emerge, we will see a historic spike in online sales even as brick-and-mortar sales went straight to heck.

More from Wolf. Depression.
• How Will COVID-19 Impact US Manufacturing? First Indications Are Ugly (WS)
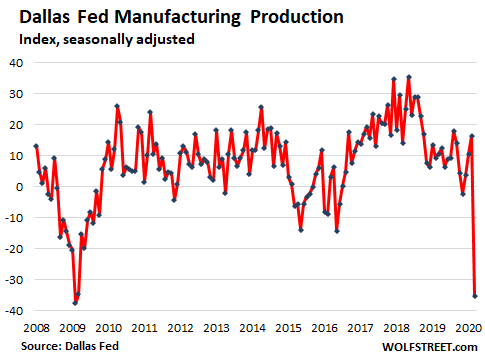
Most of the economic data is released weeks and months after the fact. But surveys of manufacturing and service companies foreshadow what will happen with the official data when it finally appears. The Texas manufacturing production index, for which data was collected between March 17 to 25 from 110 Texas-based unnamed manufacturers, plunged from +16.4 in February to -35.3 in March, the largest month-to-month drop in the history of the index going back to 2004, the Dallas Fed reported this morning:
Many manufactures in Texas supply the oil and gas industry, where mayhem had broken out long before the coronavirus lockdowns started impacting the economy. Manufacturer’s perceptions of broader business conditions collapsed from an already low 1.2 reading in February to -70.0, the lowest in survey history. The report observed laconically: “Perceptions of broader business conditions turned quite pessimistic in March”:
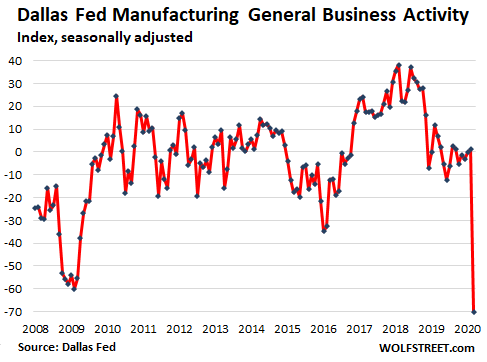
The price of crude-oil grade West Texas Intermediate (WTI) has now plunged into the range of $20 per barrel, which is catastrophic for the entire oil and gas sector. This is down from a range of $80 to $110 per barrel from 2010 through mid-2014. In an effort to stay alive a little longer, exploration-and-production companies and oil-field services companies are cutting operations, and as they’re running out of funds, they are slashing orders for equipment and supplies. And this ripples through the Texas economy. The comments made by the executives in the survey ranged from: “We are mostly just concerned.” …to something more apocalyptic: “If we see this downward trend continue, we will run out of cash within four months. New orders and inquiries have stopped instantly. Our work in-house will be finished mid to end of April, with no new orders coming in, all due to this real or imagined shutdown. I believe the country will be in a depression by the fall unless the work environment changes dramatically.”

Cruise companies lining up for bailouts. Support people instead. The companies go, but the people will remain.
• “We Are Temporarily A Company With No Product And No Revenue” (WS)
TUI, the global travel and vacation giant that owns six European airlines, 1,600 travel agencies, over 300 hotels and 14 cruise ships, desperately needs help. And it appears to have got it. On Friday, the company announced that the German government had approved a €1.8 billion loan to help keep the group afloat as COVID-19 brings the global travel sector to a literal standstill. The bridge loan, which still needs to be approved by TUI’s creditors, would be one of the biggest ever issued through German state-owned lender KfW. “We are currently facing unprecedented international travel restrictions. As a result, we are temporarily a company with no product and no revenue. This situation must be bridged,” TUI CEO Fritz Joussen said in a statement. The same could be said for millions of companies around the world. But unlike TUI, many of them don’t have the ear of their national government.
Even as giant travel companies like TUI line up with airlines and cruise owners for multi-billion dollar bailouts, huge question marks loom over the global travel industry’s future. The World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), in its updated assessment of the potential impact of COVID-19 — based on the optimistic assumption that the tourism industry will experience a swift recovery over the next 3-4 months — projects that for the whole year 2020, tourist arrivals will have fallen 20-30% from 2019, and international tourism revenues will have plunged by $300 billion to 450 billion, almost one third of the $1.5 trillion generated in 2019. Taking into account past market trends, this would mean that between five and seven years’ worth of accumulated industry growth will have been wiped out in one fell swoop.

Why on earth does Airbnb need a $250 million war chest?
• Airbnb To Pay Out $250 Million To Hosts To Help Ease Cancellation Pain (R.)
U.S. home rental firm Airbnb said on Monday it was allocating $250 million to help offset losses by hosts around the world whose guests have canceled bookings in the face of the coronavirus pandemic. The aid, which will pay hosts 25% of their normal cancellation fees, is being offered globally except for China, the company said in a letter sent to hosts by Chief Executive Brian Chesky. The payments apply to the cancellation of reservations with check-in dates between March 14 and May 31. Because hosts can choose different cancellation policies – some requiring a penalty payment, with others allowing free cancellation up to a certain date before check-in – not all canceled reservations will qualify.
Airbnb had earlier announced that guests would receive a full refund for the cancellation of reservations made on or before March 14 for check-in between March 14 and April 14, which angered many hosts. Airbnb also said that hosts could cancel reservations without a charge. Airbnb said it is funding the program for hosts itself and will begin to issue the payments in April. Airbnb’s revenue in 2019 exceeded $4.8 billion, up 35% on the year, and it has $3 billion in cash, a source told Reuters last week. [..] Airbnb also said it is creating a $10 million relief fund for its Superhosts – so-named for meeting certain requirements including good ratings – who rent out their own home and need help paying their rent or mortgage, and some Experience hosts who charge for sharing an experience like food tours.

Not much has changed. China still cares little about credibility.
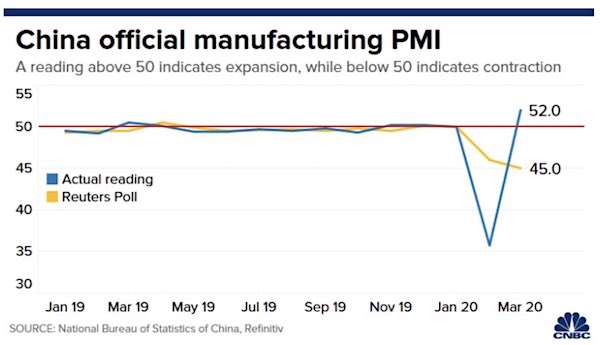
• China Says Manufacturing Activity Expanded In March (CNBC)
China on Tuesday said the official Purchasing Manager’s Index for March was 52.0, beating expectations for an economy hit by the coronavirus outbreak. Analysts polled by Reuters had expected the official PMI to come in at 45 for the month of March. In February, the official PMI hit a record low of 35.7. PMI readings above 50 indicate expansion, while those below that level signal contraction. China’s National Bureau of Statistics said in its announcement of the PMI reading that there was continued improvement in the prevention and control of the outbreak in March, with a significant acceleration in the resumption of production. Sub-indices for production, new orders and employment expanded, the bureau said.
The bureau attributed the expansionary PMI reading to the low base in February, but cautioned that it does not mean that the country’s economic activities have returned to normal levels. Earlier this year, manufacturing activity slowed dramatically in China as the government instituted large-scale lockdowns and quarantines to contain the spread of the coronavirus disease, formally known as COVID-19. Qian Wang, Asia Pacific chief economist at Vanguard Investment Strategy, said March’s manufacturing PMI reading was “totally expected” as activity improved during the month. “In February, the Chinese economy was at a full stop. It doesn’t take much to rise from such a low base,” she told CNBC’s “Street Signs.”

The EU will have to throw out Hungary.
– State of emergency w/o time limit
– Rule by decree
– Parliament suspended
– No elections
– Spreading fake news + rumors: up to 5 yrs in prison
– Leaving quarantine: up to 8 yrs in prison
• Hungary’s Viktor Orbán Wins Vote To Rule By Decree Indefinitely (Pol.)
The Hungarian parliament on Monday voted by a two-thirds majority to allow the government of Prime Minister Viktor Orbán to rule by decree without a set time limit. While the new legislation remains in place, no elections can be held and Orbán’s government will be able to suspend the enforcement of certain laws. Plus, individuals who publicize what are viewed as untrue or distorted facts — and which could interfere with the protection of the public, or could alarm or agitate a large number of people — now face several years in jail. In the vote, 137 members of parliament were in favor, 53 against and 9 did not cast a ballot. The new rules can only be lifted with another two-thirds vote of the parliament and a presidential signature.
The legislation has elicited deep concern both among civil rights groups in Hungary and international institutions, with officials from the Council of Europe, United Nations and Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe publicly expressing fears about the bill. The legislation also drew criticism from members of the European Parliament. Critics say that emergency measures to address the coronavirus crisis should be temporary and time-limited to allow for checks and balances. Hungary is currently facing Article 7 proceedings under the EU Treaty, used when a country is considered at risk of breaching the bloc’s core values.
“Civil society, journalists and international and European organizations will have to step up their efforts even more in this new situation to ensure that the potential for grave abuses by government overreach are monitored, documented and responded to,” Márta Pardavi, co-chair of the Hungarian Helsinki Committee, a human rights NGO, said following the passage of the bill. “It’s now essential that the idea that executive power cannot be unlimited is reinforced by action,” she said. “The health crisis cannot be allowed to turn into a constitutional crisis.”

To make sure they have access to health care.
The opposite of Orban.
• Portugal Gives Migrants, Asylum-Seekers Full Citizenship Rights (CNN)
Portugal has temporarily given all migrants and asylum seekers full citizenship rights, granting them full access to the country’s healthcare as the outbreak of the novel coronavirus escalates in the country. The move will “unequivocally guarantee the rights of all the foreign citizens” with applications pending with Portuguese immigration, meaning they are “in a situation of regular permanence in National Territory,” until June 30, the Portuguese Council of Ministers said on Friday. The Portuguese Council of Ministers explained that the decision was taken to “reduce the risks for public health” of maintaining the current scheduling of appointments at the immigration office, for both the border agents and the migrants and asylum seekers.
Portugal declared a State of Emergency on March 18 that came into effect at midnight that day and was due to last for 15 days. Portuguese Prime Minister Antonio Costa said during a news conference that “democracy won’t be suspended.” The country was a dictatorship for decades, with democracy being restored in 1974. President Marcelo Rebelo de Sousa called the Covid-19 pandemic “a true war,” which would bring true challenges to the country’s “way of life and economy.” Rebelo de Sousa also praised the behavior of Portuguese citizens, “who have been exemplary in imposing a self-quarantine,” reflecting “a country that has lived through everything.”

Mass gatherings. Religious, soccer, carnival. That’s where most infections originate in Europe.
• Five Days Of Worship That Set A Virus Time Bomb In France (R.)
From the stage of an evangelical superchurch, the leader of the gospel choir kicked off an evening of prayer and preaching: “We’re going to celebrate the Lord! Are you feeling the joy tonight?” “Yes!” shouted the hundreds gathered at the Christian Open Door church on Feb. 18. Some of them had travelled thousands of miles to take part in the week-long gathering in Mulhouse, a city of 100,000 on France’s borders with Germany and Switzerland. For many members of this globe-spanning flock, the annual celebration is the highpoint of the church calendar. This time, someone in the congregation was carrying the coronavirus. The prayer meeting kicked off the biggest cluster of COVID-19 in France – one of Europe’s hardest-hit countries – to date, local government said.
Around 2,500 confirmed cases have been linked to it. Worshippers at the church have unwittingly taken the disease caused by the virus home to the West African state of Burkina Faso, to the Mediterranean island of Corsica, to Guyana in Latin America, to Switzerland, to a French nuclear power plant, and into the workshops of one of Europe’s biggest automakers. Weeks later, Germany partially closed its border with France, suspending a free-movement pact that has been in place for the past 25 years. The church cluster was a key factor, two people familiar with the German decision told Reuters. Church officials told Reuters that 17 members of the congregation have since died of complications linked to the disease.
[..] As the faithful gathered on a clear Tuesday evening in the church, an old shopping centre converted into a 2,500 seat auditorium, the disease seemed remote. France had 12 confirmed cases, according to World Health Organization (WHO) data. There were none in the Mulhouse area. France, like other governments in northern Europe, had imposed no restrictions on big meetings. There was no alcohol gel for the congregations to clean their hands, no elbow bumps instead of handshakes. “At the time, we viewed COVID as something that was far off,” said Jonathan Peterschmitt, son of the lead pastor and grandson of the church’s founder. His father, Samuel, was unavailable for an interview because he had been sickened by the virus, his son and a church spokeswoman said.

“The world is still here. We’re just going to have to learn to live in it differently.”
• People Get Ready! (Kunstler)
The cable news announced the other day that Covid-19 patients placed in critical care may have to be on ventilators for 21 days. Only a few years ago, I went in for an ordinary hip replacement. A month or so later, I got the hospital billing statement. One of the line-items went like this: Room and board: 36 hours…$23,482.79. I am not jiving you. That was just for the hospital bed and maybe four lousy hospital meals, not the surgery or the meds or anything else. All that was billed extra. Say, what…? Now imagine you have the stupendous good fortune to survive a Covid-19 infection after 21 days on a ventilator and go home. What is that billing statement going to look like? Will the survivors wish they’d never made out of the hospital alive?
Right now, we’re in the heroic phase of the battle against a modern age plague. The doctors, nurses, and their helpers are like the trembling soldiers in an amphibious landing craft churning toward the Normandy beach where the enemy is dug in and waiting for them, with sweaty fingers on their machine guns and a stink in the pillbox. Some of the doctors and nurses will go down in the battle. The fabled fog-of-war will conceal what is happening to the health care system itself, while the battle rages. After that, what? One thing will be pretty clear: That the folks in charge of things gave trillions of dollars to Wall Street while tens or perhaps hundreds of thousands of Covid-19 survivors got wiped out financially with gargantuan medical bills.
Do you think the Chargemaster part of the hospital routine will just stop doing its thing during this emergency? The billings will continue – just as the proverbial beatings will continue until morale improves! In the aftermath, I can’t even imagine the ‘splainin’ that will entail. The rage may be too intense to even get to that. For some, it may be time to lubricate the guillotines? Meantime, of course, the global economy has shut down which suggests to me, anyway, that any prior frame of reference you may have had about money and business and social normality goes out the window. The world is still here. We’re just going to have to learn to live in it differently.

“..the Netherlands will “no longer be a rich country in the North if the South falls.”
• Italian Politicians Criticize Netherlands Over Lack Of Solidarity (NLT)
A group of 12 Italian politicians lambasted the Netherlands on Tuesday, angered by Dutch reticence to support European financial assistance to countries most affected by coronavirus. The Netherlands blocked emergency aid to EU member states, despite “using its tax system to withdraw tax revenue from major European countries for years,” they wrote in an open letter published in German newspaper Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung. At issue are “coronabonds”, where the funds raised from selling such bond instruments would be used to help all member states overcome economic hurdles during the ongoing health crisis. The money could then be invested in supporting any EU member state, while repayment obligations would be the responsibility of the entire EU.
Nine nations supported the plan. “However, the Netherlands are currently leading a group of countries that oppose this strategy, and Germany also seems to want to follow this group,” the politicians said, accusing the Dutch tax regime of siphoning money away from other member states which would otherwise have allowed them to assist “the socially week… who are most affected by the crisis today.” The politicians, led by Member of Europea Parliament Carlo Calenda, called for the German public to recall the unified support it had to rebuild after World War II, up through the country’s reunification. “The Dutch attitude is an example of a lack of ethics and solidarity in every respect.”
That sentiment was echoed by the leader of Dutch political party ChristenUnie, one of the parties in the governing coalition led by Prime Minister Mark Rutte. “[Italy] is in ruins. The first message, in my opinion, would be: we are going to help you,” said Gert-Jan Segers. He also called for an approach like the U.S. Marshall Plan which promoted the reconstruction of European nations after the War. The large European rescue fund could be structured similarly to the billions of deutschmarks Germany needed even though it “could never have repaid the accumulated debts,” the Italians stated. Former Dutch Central Bank leader Nout Wellink was also critical of the Dutch approach, saying that the crisis and the debt needed to get past it is “a shared responsibility.” He said, “the Netherlands will “no longer be a rich country in the North if the South falls.”

It must be possible to run the Automatic Earth on people’s kind donations. These are no longer the times when ads pay for all you read, your donations have become an integral part of it. It has become a two-way street; and isn’t that liberating, when you think about it?
Thanks everyone for your wonderful and generous donations over the past days.




Jennifer Baer

Support us in virustime. Help the Automatic Earth survive. It’s good for you.