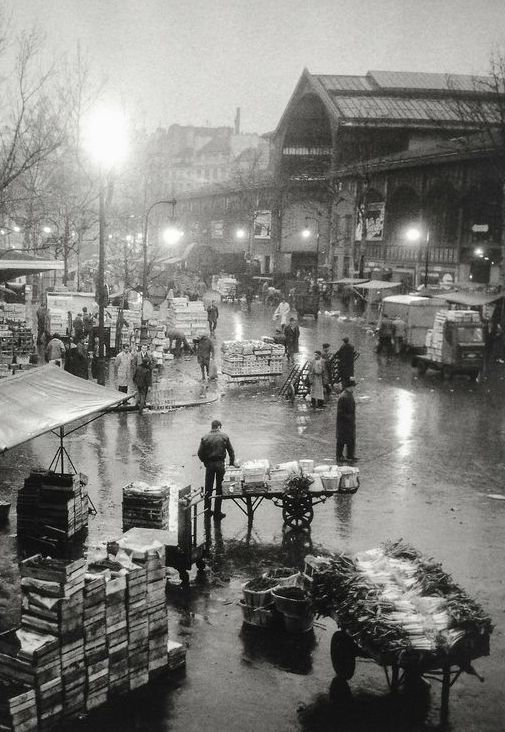
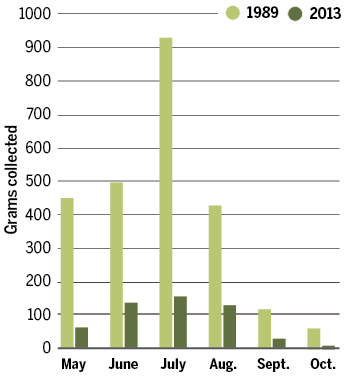Paul Almasy Les Halles, Paris 1950

The presence of a TASS reporter when Lavrov visited the White House was critized in the US media. Here’s what he wrote.
• Trump and Lavrov Meeting Round-Up (TASS)
Before meeting with Donald Trump, Sergey Lavrov held talks with the US top diplomat Rex Tillerson. Lavrov’s talks with the US president lasted for about 40 minutes behind closed doors. Moscow and Washington can and should solve global issues together, Lavrov said following his meetings with US Secretary of State Rex Tillerson and US President Donald Trump. “I had a bilateral meeting with Rex Tillerson, then the two of us were received by President Trump,” the Russian top diplomat said. “We discussed, first and foremost, our cooperation on the international stage.” “At present, our dialogue is not as politicized as it used to be during Obama’s presidency. The Trump administration, including the president himself and the secretary of state, are people of action who are willing to negotiate,” the Russian top diplomat pointed out.
Lavrov said agreement reached with Tillerson to continue using diplomatic channel to discuss Russian-US relations. According to Lavrov, the current state of bilateral relations is no cause for joy. “The reason why our relations deteriorated to this state is no secret,” the Russian top diplomat added. “Unfortunately, the previous (US) administration did everything possible to undermine the basis of our relations so now we have to start from a very low level.” “President Trump has clarified his interest in building mutually beneficial and practical relations, as well as in solving issues,” Lavrov pointed out. “This is very important,” he said. Lavrov believes Syria has areas where US might contribute to operation of de-escalation zones. “We are ready for this cooperation and today have discussed in detail the steps and mechanisms which we can manage together,” Lavrov said.
“We have confirmed our interest in the US’ most active role in those issues,” Lavrov said. “I imagine the Americans are interested in this too.” “We proceed from the fact they will take up the initiative,” he added. “We have thoroughly discussed the Syrian issue, particularly the ideas related to setting up de-escalation zones,” the Russian top diplomat said. “We share an understanding that this should become a common step aimed at putting an end to violence across Syria,” he added.
Read more …

One word: mayhem.
• $9 Trillion Question: What Happens When Central Banks Stop Buying Bonds? (WSJ)
Central banks have been the world’s biggest buyers of government bonds, but may soon stop—a tidal shift for global markets. Yet investors can’t agree on what that shift will mean. Part of the problem is that there is little agreement about how the massive stimulus policies, known as quantitative easing or QE, affected bonds in the first place. That makes it especially hard to assess what happens when the tide changes. Many expect bond yields could rise and shares fall, some see little effect at all, while others suggest it is riskier investments, such as corporate bonds or Italian government debt, that will bear the brunt. But recently, yields on European high-yield corporate bonds hit their lowest since before the financial crisis, in one potential sign that the threat of tapering has yet to affect markets.
When the unwinding begins money managers may not be positioned for it, and markets could move swiftly. In the summer of 2013, investors suddenly got spooked about the Federal Reserve withdrawing stimulus, leading to a swift bond sell off that sent yields on the 10-year Treasury up by more than 1%age point. By buying bonds after the 2008 financial crisis, central banks across the developed world sought to push yields lower and drive money into riskier assets, reducing borrowing costs for businesses. “If it’s unclear what benefits we’ve had in the buying, it’s unclear what will happen in the selling,” said Tim Courtney, chief investment officer at Exencial Wealth Advisors.
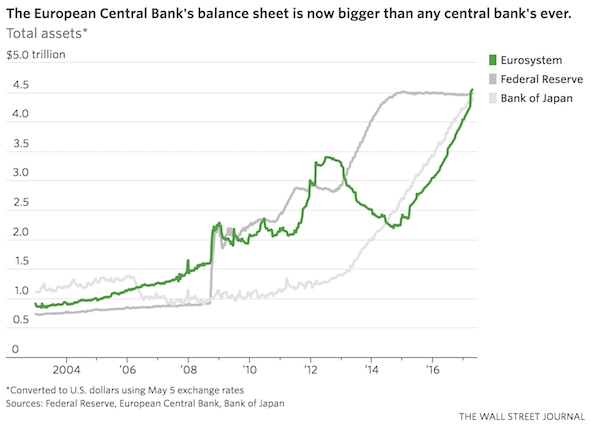
Recent data showed that the ECBholds total assets of $4.5 trillion, more than any other central bank ever. The Fed and the Bank of Japan each have $4.4 trillion, although the BOJ isn’t expected to wind down QE soon. With the world economy finally recovering, investors believe that holdings at the Fed and ECB have peaked. U.S. officials are discussing how to wind down their portfolio, which they have kept constant since 2014. The ECB’s purchases of government and corporate debt are now more likely to be tapered later in the year, analysts say, after pro-business candidate Emmanuel Macron’s victory in the French presidential election Sunday.
Read more …

Dutch politicians either don’t care about their European Union peer Greece, or they don’t know about it. Neither is a good option. They are doing so well over the backs of the Greeks they want Draghi to enact policies that will make them even richer, and the Greeks even more miserable. Oh, and of course “The euro is irrevocable” only until it isn’t.
• Draghi Stays Calm on Stimulus as Dutch MPs Warn of Risks With Tulip (BBG)
Mario Draghi kept his cool in the Netherlands – at least on monetary policy. Repeatedly pressed by Dutch lawmakers to say when he’ll start winding down euro-area monetary stimulus, the Ecb president replied that it’s still too soon to consider, despite a “firming, broad-based upswing” in the economy. “Is it time to exit? Or is it time to start thinking about exit or not? The assessment of the Governing council is that this time hasn’t come yet.” His reward was a gift of a plastic tulip in a reminder of a past European financial crisis. Draghi’s voluntary appearance at the hearing on Wednesday put him front and center in one of the nations most critical of the ECB’s ultra-loose policies, which are seen by opponents as overstepping the institution’s mandate, burdening savers and pension providers, and stoking asset bubbles.
Legislators did appear occasionally to get under his skin. The tension rose when he was quizzed multiple times him on the possibility that a government will one day have to restructure its debt, while on the topic of a nation leaving the currency bloc – as Greece came close to doing in 2015 – Draghi’s response was blunt. “The euro is irrevocable. This is the Treaty. I will not speculate on something that has no basis.” The intense questioning underscored the gap between relatively rosy economic data and the discontent among individuals who can’t see the fruits of the ECB’s €2.3 trillion bond-buying program and minus 0.4% deposit rate. It’s a challenge for Draghi, who reiterated his concern that underlying inflation remains feeble and falling unemployment has yet to boost wage growth. The region is far from healing the scars of a double-dip recession that wiped out 9 million jobs and helped the rise of anti-euro populists such as Marine Le Pen, who lost this month’s French presidential election but still managed to pick up more than a third of the vote.
Read more …

The silence before.
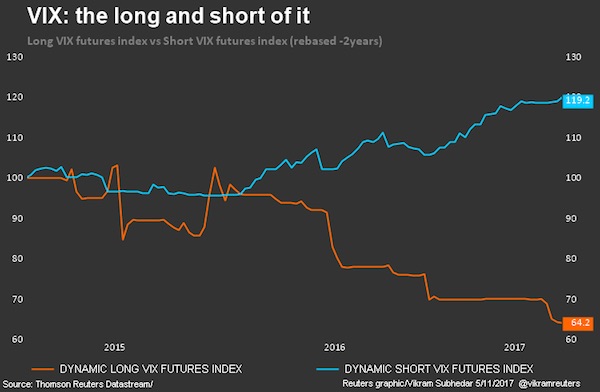
• It’s Not Just The VIX – Low Volatility Is Everywhere (R.)
The current slump in expectations of market volatility is not just a stock market phenomenon – it is the lowest it’s been for years across fixed income, currency and commodity markets around the world. It shows little sign of reversing, which means market players are essentially not expecting much in the way of shocks or sharp movements any time soon. It’s an environment in which asset prices can continue rising and bond spreads narrow further. The improving global economy, robust corporate profitability, ample central bank stimulus even as U.S. interest rates are rising, and some fading political risk from elections have all contributed to create a backdrop of relative calm.
There is little evidence of investors hedging – or seeking to protect themselves – from adverse conditions. It is most notably seen in the VIX index of implied volatility on the U.S. S&P 500 stock index, the so-called “fear index”. But implied volatility across the G10 major currencies is its lowest in three years, and U.S. Treasury market volatility its lowest in 18 months and close to record lows. The VIX, meanwhile, has dipped to lows not seen since December 2006, is posting its lowest closing levels since 1993, and is on a record run of closes below 11. By comparison, it was at almost 90 at the height of the financial crisis. Not much current “fear”, then.
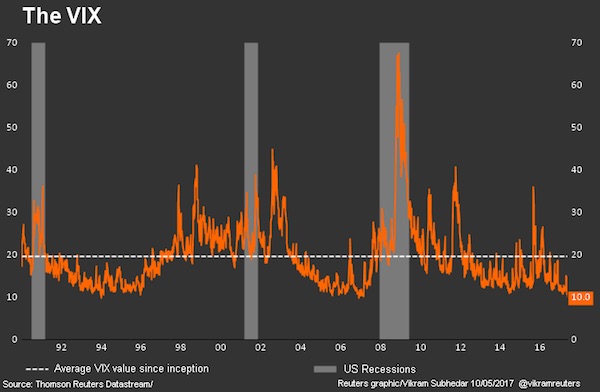
Implied volatility is an options market measure of investors’ expectation of how much a certain asset or market will rise or fall over a given period of time in the future. It and actual volatility can quickly become entwined in a spiral lower because investors are less inclined to pay up for “put” options – effectively a bet on prices falling – when the market is rising. If a shock does come the cost of these “puts” would shoot higher as investors scramble to buy them. Surging volatility is invariably associated with steep market drawdowns. According to Deutsche Bank’s Torsten Slok, an investor betting a year ago that the VIX would fall – shorting the index – would have gained around 160% today. Conversely, an investor buying the VIX a year ago assuming it would rise would have lost 75%.
Read more …

What’s that rumbling sound in the distance?
• Six Canadian Banks Cut by Moody’s on Consumers’ Debt Burden (BBG)
Six of Canada’s largest banks had credit ratings downgraded by Moody’s Investors Service on concern that over-indebted consumers and high housing prices have left lenders vulnerable to potential losses on assets. Toronto-Dominion Bank, Bank of Montreal, Bank of Nova Scotia, Canadian Imperial Bank of Commerce, National Bank of Canada and Royal Bank of Canada had their long-term debt and deposit ratings lowered one level, Moody’s said Wednesday in a statement. It also cut its counterparty risk assessment for the firms, excluding Toronto-Dominion. “Expanding levels of private-sector debt could weaken asset quality in the future,” David Beattie, a Moody’s senior vice president, said in the statement.
“Continued growth in Canadian consumer debt and elevated housing prices leaves consumers, and Canadian banks, more vulnerable to downside risks facing the Canadian economy than in the past.” A run on deposits at alternative mortgage lender Home Capital has sparked concern over a broader slowdown in the nation’s real estate market, at a time when Canadians are taking on higher levels of household debt. The firm’s struggles have taken a toll on Canada’s biggest financial institutions, which have seen stocks slide on concern about contagion. In its statement, Moody’s pointed to ballooning private-sector debt that amounted to 185% of Canada’s GDP at the end of last year. House prices have climbed despite efforts by policy makers, it said. And business credit has grown as well.
Read more …

Straight from the Monopoly printing press.
• China Holds Giant Meeting On Spending Billions To Reshape The World (CNBC)
[..] the most populous nation on the planet wants to increase its influence by digging further into its pockets — flush with cash after decades of rapid growth — to splash out with its “One Belt, One Road” policy. President Xi Jinping first announced the policy in 2013; it was later named one of China’s three major national strategies, and morphed into an entire chapter in the current five-year plan, to run through 2020. [..] The plan aims to connect Asia, Europe, the Middle East and Africa with a vast logistics and transport network, using roads, ports, railway tracks, pipelines, airports, transnational electric grids and even fiber optic lines. The scheme involves 65 countries, which together account for one-third of global GDP and 60% of the world’s population, or 4.5 billion people, according to Oxford Economics.
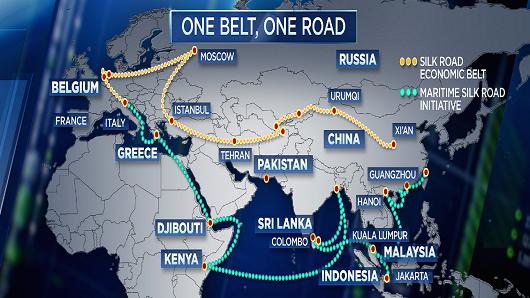
This is part of China’s push to increase global clout — building modern infrastructure can attract more investment and trade along the “One Belt, One Road” route. It could be beneficial for western China, which is less developed, as it links up with neighboring countries. And in the long run, it will help China shore up access to energy resources. The policy could boost the domestic economy with demand abroad, and might also soak up some of the overcapacity in China’s heavy industry, but analysts say these are fringe benefits. Experts say China has an opportunity to step into a global leadership role, one that the U.S. previously filled and may now be abandoning, especially after President Donald Trump pulled out of a major trade deal, the Trans-Pacific Partnership.
It’s clear China wants to wield greater influence — Xi’s speech in January at the World Economic Forum in Davos touted the benefits of globalization, and called for international cooperation. And an article by Premier Li Keqiang published shortly after also called for economic openness. But despite all the talk of global connectivity, skeptics highlight that China still restricts foreign investment, censorship continues to be an issue and concerns remain over human rights. [..] In 2015, the China Development Bank said it had reserved $890 billion for more than 900 projects. The Export-Import Bank of China announced early last year that it had started financing over 1,000 projects. The China-led Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank is also providing financing.
Read more …

The British should be happy for housing prices returning to more normal levels.
• ‘Stagnant’ Buyer Demand Puts The Brakes On UK Housing Market (G.)
The UK housing market is continuing to slow down, with falling property sales, “stagnant” buyer demand and general election uncertainty all adding up to one of the most downbeat reports issued by surveyors since the financial crash. In its latest monthly snapshot of the market, the Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors (Rics) said momentum was “continuing to ebb,” with no sign of change in the near future. Its report is the latest in a series of recent surveys suggesting that the slowdown is getting worse as household budgets continue to be squeezed and affordability pressures bite. It comes days after the Halifax said house prices fell by 0.1% in April, which meant they were nearly £3,000 below their December 2016 peak. Nationwide reported a bigger decline in April – it said prices fell by 0.4%, following a 0.3% drop in March.
Some parts of London appear to have been hit particularly hard, with estate agents and developers resorting to offering free cars and other incentives to try to tempt buyers. Rics said its members had reported that sales were slipping slightly following months of flat transactions. A lack of choice for would-be buyers across the UK appears to be one of the major factors putting a dampener on sales: the latest report said there was “an acute shortage of stock,” with the typical number of properties on estate agents’ books hovering close to record lows. New instructions continue to drop, which could make the situation worse: the flow of fresh listings to agents remained negative for the 14th month in a row at a national level, said Rics, though it added that the situation had apparently improved slightly in London.
Read more …

How dead is the left? Nice contest.
• UK Labour Party’s Plan To Nationalise Rail, Mail And Energy Firms (G.)
Jeremy Corbyn will lay out plans to take parts of Britain’s energy industry back into public ownership alongside the railways and the Royal Mail in a radical manifesto that promises an annual injection of £6bn for the NHS and £1.6bn for social care. A draft version of the document, drawn up by the leadership team and seen by the Guardian, pledges the phased abolition of tuition fees, a dramatic boost in finance for childcare, a review of sweeping cuts to universal credit and a promise to scrap the bedroom tax. Party sources said Corbyn wants to promise a “transformational programme” with a package covering the NHS, education, housing and jobs as well as industrial intervention and sweeping nationalisation. But critics said the policies represented a shift back to the 1970s with the Conservatives describing it as a “total shambles” and a plan to “unleash chaos on Britain”.
Corbyn’s leaked blueprint, which is likely to trigger a fierce debate of Labour’s national executive committee and shadow cabinet at the so-called Clause V meeting at noon on Thursday, also includes:
• Ordering councils to build 100,000 new council homes a year under a new Department for Housing.
• An immediate “emergency price cap” on energy bills to ensure that the average duel fuel household energy bill remains below £1,000 a year.
• Stopping planned increases to the pension age beyond 66.
• “Fair rules and reasonable management” on immigration with 1,000 extra border guards, alongside a promise not to “fan the flames of fear” but to recognise the benefits that migrants bring.
On the question of foreign policy, an area on which Corbyn has campaigned for decades, the draft document said it will be “guided by the values of peace, universal rights and international law”. However, Labour, which is facing Tory pressure over the question of national security, does include a commitment to spend 2% of GDP on defence. The draft manifesto, which will only be finalised after it is agreed on Thursday, also makes clear that the party supports the renewal of Trident, despite Corbyn’s longstanding opposition to nuclear weapons.
Read more …

Cycles.
• Panic! Like It’s 1837 (DB)
180 years ago today, everyone panicked. On May 10, 1837, New York banks finally realized that the easy money they were lending was unsustainable, and demanded payment in “specie,” or hard money like gold and silver coin. They had previously been accepting paper currency that for every $5 was backed by only $1 in silver or gold. Things culminated to that point after years of borrowing the paper currency to expand west, buy land, and build infrastructure. As silver came in from Mexico, banks lent out five times the amount of their deposits–fractional reserve banking. At the same time, the value of silver was falling because its supply was increasing in America. Great Britain, which had been lending much of the money, was less interested in silver because they could pay for trade with China in opium.
So even though Britain had a year earlier begun demanding payment in specie, the abundant silver in America did not hold the same weight, so to speak, it had previously. Now, reflect on this for a second. The USA was depending on loans from a country that they had successfully revolted and seceded from fewer than 50 years earlier. Britain had also provoked The War of 1812 just 25 years earlier when they wouldn’t stop attacking American ships. But somehow it still seemed like a good idea to depend on British banks to form the foundation of American development. So at the same time when American banks had to backstep their risky practices, Britain also just so happened to need 25% less cotton, which was the foundation of the American economy. This only exacerbated the trade deficit.
But still, despite whether or not Britain’s actions were nefarious, the whole situation would have been remarkably cushioned if fractional reserve banking had not been used. Because of this “easy money,” land was bought at enormous rates on credit, but credit that was not backed by actual value–only 1/5 of the actual value existed of what was being lent! President Andrew Jackson was not entirely without blame either. When he deconstructed the federal bank, he deposited the money into state banks, and encouraged them to go ahead and lend, lend, lend! Of course, when the time came for the banks to return the deposits, the money was gone. So when this massive real estate bubble burst in 1837, it caused a panic and ensuing recession that lasted until 1844. Does any of this sound familiar to you?
Read more …

The moment the ECB is allowed to buy Greek bonds again is also the moment it decides to quit its bond-buying program.
• Italy Financial Regulator Threatens EU with Return to “National Currency” (DQ)
Despite trillions of euros worth of QE, Italy has continued to suffer a 30% loss in competitiveness compared to Germany during the last two decades. And now Italy must begin to prepare itself for the biggest nightmare of all: the gradual tightening of the ECB’s monetary policy. “Inflation is gradually returning to the area of the 2% target, while in the United States a monetary tightening is taking place,” Vegas said. The German government is exerting mounting pressure on the ECB to begin tapering QE before elections in September. So, too, is the Netherlands whose parliament today treated ECB President Mario Draghi to a rare grilling. The MPs ended the session by presenting Draghi with a departing gift of a solar-powered tulip, to remind him of the country’s infamous mid-17th century asset price bubble and financial crisis.
For the moment Draghi and his ECB cohorts refuse to yield, but with the ECB’s balance sheet just hitting 38.7% of Eurozone GDP, 15 %age points higher than the Fed’s, they may ultimately have little choice in the matter. As Vegas points out, for Italy (and countries like it), that will mean having to face a whole new situation, “in which it will no longer be possible to count on the external support of monetary leverage.” This is likely to be a major problem for a country that has grown so dependent on that external support. According to the Bank for International Settlements, in 2016, international banks in particular those in Germany reduced their exposure to Italy by 15%, or over $100 billion, half of it in the last quarter of the year. ECB intervention helped plug the shortfall, at least for a while.
But the ECB has already reduced its monthly purchases of European sovereign debt instruments, from €80 billion to just over €60 billion. As the appetite for Italian government debt falls, the yields on Italian bonds will rise. The only market participants seemingly still willing and able (for now) to increase their purchase of Italian debt are Italian banks. In his address, Vegas proposed introducing a safeguard threshold of €100,000 for the banks’ bondholders, many of whom are ordinary Italian citizens, with combined holdings worth some €200 billion, who were told by the banks that their bonds were a secure investment. Not any more. “The management of crises may require timely intervention that is not compatible with the mechanisms in Frankfurt and Brussels,” Vegas added.
To get his point across, he issued a barely veiled threat in Frankfurt and Brussels’ direction — that of Italy’s exit from the Eurozone, a prospect that should not be altogether discounted given the recent growth of anti-euro sentiment and rising political instability in Italy. So he threatened: “Merely the announcement of a return to a national currency would provoke an immediate outflow of capital that would seriously jeopardize Italy’s ability to refinance the world’s third biggest public debt.”
Read more …

In other words: any positive numbers you may read about Greek GDP are false.
• Greek Capital Controls To Stay Till At Least End Of 2018 (K.)
Greece will spend at least three-and-a-half years under the restrictions of capital controls as their abolition is not expected to come any earlier than the end of 2018, according to a competent credit sector source. The next step in terms of their easing will come after the completion of the bailout review and the disbursement of the funding tranche, provided banks see some recovery in deposits. Sources say that the planning provides primarily for helping enterprises by increasing the limit on international transactions concerning product imports or the acquisition of raw materials. Almost two years after the capital controls were imposed, by next Tuesday, according to the agreement with the creditors, the Bank of Greece and the Finance Ministry have to present a road map for the easing of restrictions.
The road map is already being prepared and according to sources it will not contain any dates for the easing of controls but rather will record the conditions necessary for each step to come. Kathimerini understands that the conditions will be the following: the return of deposits, the reduction of nonperforming loans, the state’s access to money markets, the country’s inclusion in the ECB’s QE program, and the settlement of the national debt. “Ideally, by end-2018 we will be able to speak of an end to the controls. In any case, the restrictions on deposits will be the last to be lifted,” notes a senior banking source, referring to the cash withdrawal limit that currently stands at €840 per 14 days. The Hellenic Bank Association’s Executive Committee will meet on Wednesday to discuss proposals for the gradual easing of restrictions.
The bankers’ proposals will constitute an updated version of those tabled in November 2016; they will likely include the introduction of a monthly limit of 2,000 euros for cash withdrawals and an increase in the withdrawal limit for funds originating from abroad from 30% to 60%. The drop in deposits over the first quarter of the year will make it harder for such proposals to be implemented for the time being.
Read more …

Saving the healthcare system from Troika-induced collapse is a good idea. Not sure this is the way.
• Greek PM Tsipras Heralds ‘Landmark’ Plan For Healthcare (K.)
Speaking of an “institutional intervention of landmark significance,” Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras heralded on Wednesday the creation of a new primary healthcare system to be based on local health centers staffed with general practitioners. The aim is to set up 239 such centers by the end of the year, employing 3,000 family doctors and nursing staff, Tsipras said in a speech at a health center in Thessaloniki. The first 60 of those centers are to start operating by the summer, the premier said, noting that poorer areas will be prioritized. “If you were to ask me what I want to be left behind after the years of governance by SYRIZA and ANEL,” he said, referring to junior coalition partner Independent Greeks, “I would say a very essential landmark health sector reform with the creation of primary healthcare.”
Tsipras also took the opportunity to lash out at the political opposition, accusing previous governments of having a plan for “the passive privatization of the health sector.” As for the national federation of Greek hospital workers (POEDIN), which has railed against the current government for cutbacks in the health sector, Tsipras hit back, calling it “a trade union that has secured privileges.” The prime minister added that his government remained determined to fight corruption in the health sector, referring to alleged scandals embroiling the Hellenic Center for Disease Control and Prevention (KEELPNO) and the Swiss pharmaceuticals firm Novartis. “Everything will come to light,” he said.
Read more …

Erdogan’s at the White House today, or is that tomorrow?!
• Turkish Coast Guard Publishes Maps Claiming Half Of The Aegean Sea (KTG)
The Turkish Coast Guard published alleged official maps and documents claiming half of the Aegean Sea belong to Turkey. In this sense, Ankara claims to won dozens of Greek islands, the entire eastern Aegean from the island of Samothraki in the North to Kastelorizo in the South. The maps and claims have been uploaded on the website of the Turkish Coast Guard in the context of a 60-page report about the activities of the TCG in 2016. On page 7 and 13 of the report, the maps allegedly show Turkey’s Search And Rescue responsibility area. The maps show half of the Aegean Sea and also a very good part of the Black Sea, where Turkey’s SAR area coincides with the Turkish Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ). Turkey did not signed the convention in order to not be obliged to recognize the Greek EEZ.
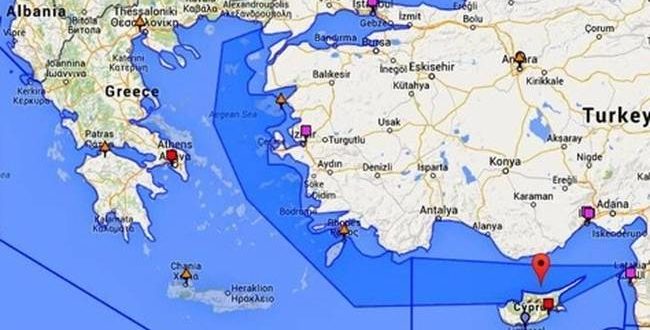
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea treaty, is the international agreement that resulted from the third United Nations Conference on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS III), which took place between 1973 and 1982. The Law of the Sea Convention defines the rights and responsibilities of nations with respect to their use of the world’s oceans, establishing guidelines for businesses, the environment, and the management of marine natural resources. The most significant issues covered were setting limits, navigation, archipelagic status and transit regimes, exclusive economic zones (EEZs), continental shelf jurisdiction, deep seabed mining, the exploitation regime, protection of the marine environment, scientific research, and settlement of disputes. Turkey started to claim areas in the Aegean Sea after 1997 when a Turkish ship sank near the Greek islet of Imia and Ankara sent SAR vessels.
Read more …

Sea Watch seems to go a bit far.
• Libya Intercepts Almost 500 Migrants After Sea Duel (AFP)
Libya’s coastguard on Wednesday intercepted a wooden boat packed with almost 500 migrants after duelling with a German rescue ship and coming under fire from traffickers, the navy said. The migrants, who were bound for Italy, were picked up off the western city of Sabratha, said navy spokesman Ayoub Qassem. The German non-governmental organisation “Sea-Watch tried to disrupt the coastguard operation… inside Libyan waters and wanted to take the migrants, on the pretext that Libya wasn’t safe,” Qassem told AFP. Sea-Watch posted a video on Twitter of what it said was a Libyan coastguard vessel narrowly cutting across the bow of its ship.
“This EU-funded Libyan patrol vessel almost crashed (into) our civil rescue ship,” read the caption. Qassem also said the coastguard had come under fire from people traffickers, without reporting any casualties. The 493 migrants included 277 from Morocco and many from Bangladesh, said Qassem, and 20 women and a child were aboard the boat. All were taken to a naval base in Tripoli. There were also migrants from Syria, Tunisia, Egypt, Sudan, Pakistan, Chad, Mali and Nigeria, he added. According to international organisations, between 800,000 and one million people, mostly from sub-Saharan Africa, are currently in Libya hoping to make the perilous Mediterranean crossing to Europe.
Read more …

No insects, no bats, no birds, etc etc.
• Where Have All The Insects Gone? (Sciencemag )
Entomologists call it the windshield phenomenon. “If you talk to people, they have a gut feeling. They remember how insects used to smash on your windscreen,” says Wolfgang Wägele, director of the Leibniz Institute for Animal Biodiversity in Bonn, Germany. Today, drivers spend less time scraping and scrubbing. “I’m a very data-driven person,” says Scott Black, executive director of the Xerces Society for Invertebrate Conservation in Portland, Oregon. “But it is a visceral reaction when you realize you don’t see that mess anymore.” Some people argue that cars today are more aerodynamic and therefore less deadly to insects. But Black says his pride and joy as a teenager in Nebraska was his 1969 Ford Mustang Mach 1—with some pretty sleek lines. “I used to have to wash my car all the time. It was always covered with insects.”
Lately, Martin Sorg, an entomologist here, has seen the opposite: “I drive a Land Rover, with the aerodynamics of a refrigerator, and these days it stays clean.” Though observations about splattered bugs aren’t scientific, few reliable data exist on the fate of important insect species. Scientists have tracked alarming declines in domesticated honey bees, monarch butterflies, and lightning bugs. But few have paid attention to the moths, hover flies, beetles, and countless other insects that buzz and flitter through the warm months. “We have a pretty good track record of ignoring most noncharismatic species,” which most insects are, says Joe Nocera, an ecologist at the University of New Brunswick in Canada. Of the scant records that do exist, many come from amateur naturalists, whether butterfly collectors or bird watchers.
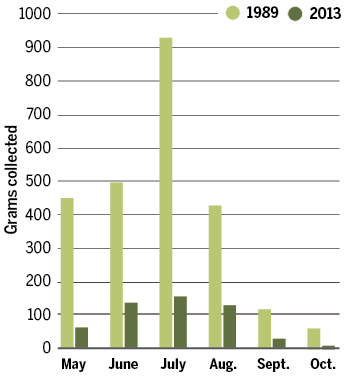
Now, a new set of long-term data is coming to light, this time from a dedicated group of mostly amateur entomologists who have tracked insect abundance at more than 100 nature reserves in western Europe since the 1980s. Over that time the group, the Krefeld Entomological Society, has seen the yearly insect catches fluctuate, as expected. But in 2013 they spotted something alarming. When they returned to one of their earliest trapping sites from 1989, the total mass of their catch had fallen by nearly 80%. Perhaps it was a particularly bad year, they thought, so they set up the traps again in 2014. The numbers were just as low. Through more direct comparisons, the group—which had preserved thousands of samples over 3 decades—found dramatic declines across more than a dozen other sites.
Such losses reverberate up the food chain. “If you’re an insect-eating bird living in that area, four-fifths of your food is gone in the last quarter-century, which is staggering,” says Dave Goulson, an ecologist at the University of Sussex in the United Kingdom, who is working with the Krefeld group to analyze and publish some of the data. “One almost hopes that it’s not representative—that it’s some strange artifact.”
Read more …