DPC Near Lewiston, Minnesota – The Pulpit. 1899



Is the mood changing? This just in from a Greek friend: “Varoufakis has to shut up, now, not at some point; it turned out that he is a narcissist and an idiot as well”
• Varoufakis Faces Criminal Prosecution Over ‘Plan B’ Currency Plot (Telegraph)
Greece’s state prosecutors have set their sights on former finance minister Yanis Varoufakis who faces possible criminal charges over plans to set up a parallel payments system inside the monetary union. The Greek parliament received two sets of legal complaints about the economist’s “surreptitious” blueprint to introduce a euro-denominated alternative currency as a precursor to an exit from the eurozone. The cases were bought to the parliament by the Supreme Court following complaints from a Greek lawyer and mayor, and separately by a group of opposition conservative parliamentarians. As an MP, Mr Varoufakis has immunity over criminal prosecution. But this could now be overturned by the Greek parliament which is set to review the allegations.
The self-styled “erratic Marxist” convened a five-man team to oversee clandestine plans to introduce “parallel liquidity” in Greece in order ease the credit strangulation imposed by the ECB. Mr Varoufakis’ team included respected US economist James K. Galbraith, and touted the use of smartphone apps to allow the state to continue making its domestic obligations to suppliers and collecting tax revenues. Mr Galbraith could also be facing a criminal trial over his involvement. Controversy centres over whether or not the finance minister ordered a childhood friend and now professor at Columbia University to “hack” into government computer systems to gain access to sensitive taxpayer information and duplicate files for use under the parallel system.
In a recorded phone conversation to private investors, the finance minister is heard saying his team “decided to hack into my minister’s own software programme” to make the copies of taxpayer files and pin codes. Mr Varoufakis has since said the nascent plans were all carried out within “the laws of the land, and at keeping the country in the eurozone”. Following the news, Mr Varoufakis told The Telegraph he feared being hung up on charges of “treason” by political forces in the country. “It is all part of an attempt to annul the first five months of this government and put it in the dustbin of history,” he said on Sunday. The former minister said he was tasked with the responsibility to devise the contingency plan by prime minister Alexis Tsipras as early as December.
He maintains the “Plan B” was fully disclosed to finance ministry officials and journalists when he resigned from office earlier this month. Nevertheless, the airing of a private audio recording has caused a fresh political storm in the country. Brussels has been forced to deny accusations it controls of Greece’s public revenues body, the equivalent of Britain’s Inland Revenue. During the conversation held by the Official Monetary and Financial Institutions Forum and co-hosted by former Tory chancellor Norman Lamont, Mr Varoufakis said the Troika was “fully and directly” in charge of the country’s Secretariat of Public Revenues, forcing him to devise a way to access its computer network. But the European Commission denied the allegations as “false and unfounded”.

I’m curious to see how far they think they can take this.
• Greek Supreme Court Prosecutor Takes Action Over Varoufakis Affair (Kath.)
Supreme Court prosecutor Efterpi Koutzamani on Tuesday took two initiatives in the wake of revelations by former Finance Minister Yanis Varoufakis that he had planned a parallel banking system: she forwarded to Parliament two suits filed against the former minister last week by private citizens and she appointed a colleague to determine whether any non-political figures should face criminal charges in connection with the affair. The legal suits were filed last week by Apostolos Gletsos, the mayor of Stylida in central Greece and head of the Teleia party, and Panayiotis Giannopoulos, a lawyer. Giannopoulos is suing Varoufakis for treason over his handling of talks with Greece’s creditors. Gletsos, for his part, accuses Varoufakis of exposing the Greek state to the risk of reprisals.
As there is a law protecting ministers, the judiciary cannot move directly against Varoufakis. It is up to Parliament to decide whether his immunity should be lifted so he can stand trial. The first step would be to set up an investigative committee. A third suit was expected to go to Parliament after a group of five lawyers said they were seeking an investigation into whether any non-political figures should face criminal charges in connection with the Varoufakis affair. The charges would involve violation of privacy data, breach of duty, violation of currency laws and belonging to a criminal organization. It was the lawyers’ move that prompted Koutzamani to order an investigation.
In a telephone call with investors, during which Varoufakis detailed his plan for a parallel banking system, he said he recruited a childhood friend, a professor at Columbia University, to hack into the ministry’s online tax system. Varoufakis did not name the head of the General Secretariat for Information Systems, Michalis Hatzitheodorou, but the description of his role at the ministry and his background suggested he was referring to him. In a statement on Tuesday, Hatzitheodorou rebuffed as “absolutely false” reports regarding any type of intervention in the ministry’s information systems. The GSIS, and the current general secratary, have not planned much less attempted any type of intervention in its systems, the statement said.
It added that the GSIS has enacted procedures with strict specifications which guarantee the security of personal data and make such interventions by anyone impossible. In a related development, European Commission spokeswoman Mina Andreeva on Tuesday described as “false and unfounded” Varoufakis’s claims that Greece’s General Secretariat for Public Revenues is controlled by the country’s creditors.

“Greece is playing it correctly. Agree to everything. Give Germany no excuse to do what they want. Get the money.”
• One Veteran FX Trader: ‘Greece Is Playing It Correctly’ (Zero Hedge)
Some interesting, and contrarian, observations from former FX trader and fund manager, and current Bloomberg commentator, Richard Breslow on Greece – which for all the bashing, may be doing just what it is supposed to be doing. From Breslow:
Greece Has More Friends Than You Think
As frustrating as trading the EUR has been over the last four months, traders in fact are the lucky ones. We can play the range. We can stop out, improve our average, buy options protection or change our minds. We can go trade something that is easier at the moment and decide to come back to the EUR later. Most of Europe has no such luxury. They are stuck in the trade. They are stuck with unemployment rates that are destroying their social fabric. They are stuck with aggregated euro-zone numbers that hide a recession in Finland or a depression in Greece. Every time the EUR rallies, true economic recovery remains merely a projection on an economist’s drawing board. The only way to save the EUR is to devalue it. Everyone is trying in their own way to tell the Germans this reality. So far with little effect.
Economist after Nobel-winning economist apoplectically argue that the conditions being imposed on Greece are unrealistic (how’s that for being diplomatic.) What is playing out is a charade. Most Europeans and the IMF know this as well. Marek Belka in the Sunday Telegraph offered the politician’s solution of dealing with debt relief, “I would call it a debt reprofiling, rather than debt relief which is the same but sounds better and politically more acceptable.” He did go on to agree that “Either way, I think at one point sooner or later Greece needs it.” Greece is playing it correctly. Agree to everything. Give Germany no excuse to do what they want. Get the money.
This is why France, among others, want this all agreed as quickly as possible, because they know this deal is not how it will end, but an end that keeps the EUR together must be found. The Germans know it too. They also know that they have been had and it is their own fault. Too many times in post French Revolution European history, they have opted for injustice over what they perceived as disorder. But Greece is no revolution, yet. It is a long series of mistakes by many actors across the continent and the viable solution won’t be found here without an admission of mutual culpability.

They bet on Germany paying Greek debt.
• Why Greece’s Lenders Need to Suffer (NYT Magazine)
There is definitive proof, for anyone willing to look, that Greece is not solely or even primarily responsible for its own financial crisis. The proof is not especially exciting: It is a single bond, with the identification code GR0133004177. But a consideration of this bond should end, permanently, any discussion of Greece’s crisis as a moral failing on the part of the Greeks. GR0133004177 is the technical name for a bond the Greek government sold on Nov. 10, 2009, in a public auction. Every business day, governments and companies hold auctions like this; it is how they borrow money. Bond auctions, though, are not at all like the auctions we’re used to seeing in movies, with the fast talkers and the loud hammers. They happen silently, electronically.
Investors all over the world type a number on their keyboards and submit it as their bid: the amount of interest they would insist on receiving in exchange for the loan. Just as with mortgages and credit cards, the riskier a loan is, the higher the rate would need to be, compensating the lender for the chance that the borrower in question will fail to pay it back. [..] On that day in 2009 when GR0133004177 was issued, investors had every reason to assume that this was an especially risky loan. The Greek government wanted 7 billion euros, or $10.5 billion, which would not be paid back in full until 2026. These were all sophisticated investors, who were expected to think very carefully about the number they typed, because that number had to reflect their belief in the Greek government’s ability to continually pay its debts for the next 17 years.
I was shocked, looking back, to see the winning number: 5.3%. That is a very low interest rate, only a couple of percentage points above the rate at which Germany, Europe’s most creditworthy nation, was borrowing money. This was a rate that expressed a near certainty that Greece would never miss a payment. In hindsight, of course, we know that the investors should not have lent Greece anything at all, or, if they did, should have demanded something like 100% interest. But this is not a case of retrospective genius. At the time, investors had all the information they needed to make a smarter decision. Greece, then as now, was a small, poor, largely agrarian economy, with a spotty track record for adhering to globally recognized financial controls. Just three weeks earlier, a newly elected Greek prime minister revealed that the previous government had scrupulously hidden billions of dollars in debt from the rest of the world. In fact, the new leader revealed, Greece owed considerably more money than the size of its entire annual economy.
Within a month of the bond sale, faced with essentially the same information the investors had, Moody’s and the other ratings agencies downgraded the country’s credit rating. In less than six months, Greece was negotiating a bailout package from the IMF. The original sin of the Greek crisis did not happen in Athens. It happened on those computer terminals, in Frankfurt and London and Shanghai and New York. Yes, the Greeks took the money. But if I offered you €7 billion at 5.3% interest, you would probably take the money, too. I would be the one who looked nuts. And if I didn’t even own that money – if I was just watching over it for someone else, as most large investors do – I might even go to jail.

“..our simple idea was to allow the multilateral cancellation of arrears between the state and the private sector using the tax office’s existing payments platform.”
• Something Is Rotten In The Eurozone Kingdom (Yanis Varoufakis)
A paradox lurks in the foundations of the eurozone. Governments in the monetary union lack a central bank that has their back, while the central bank lacks a government to support it.\ This paradox cannot be eliminated without fundamental institutional changes. But there are steps member states can take to ameliorate some of its negative effects. One such step that we contemplated during my tenure at the Greek ministry of finance focused on the chronic liquidity shortage of a stressed public sector and its impact on the long-suffering private sector. In Greece, where the central bank is unable to support the state’s endeavours, government arrears to the private sector — both companies and individuals — have been a drag on the economy, adding to deflationary pressures since as far back as 2008.
Such arrears consistently exceeded 3%t of GDP for five years. The phenomenon is both the cause and consequence of delayed tax payments to the state, reinforcing the cycle of generalised illiquidity. To address this problem, our simple idea was to allow the multilateral cancellation of arrears between the state and the private sector using the tax office’s existing payments platform. Taxpayers, whether individuals or organisations, would be able to create reserve accounts that would be credited with arrears owed to them by the state. They would then be able to transfer credits from their reserve account either to the state (in lieu of tax payments) or to any other reserve account. Suppose, for example, Company A is owed €1m by the state; and it owes €30,000 to an employee — plus another €500,000 to Company B, which provided it with goods and services.
The employee and Company B also owe, respectively, €10,000 and €200,000 in taxes to the state. In this case the proposed system would allow for the immediate cancellation of at least €210,000 in arrears. Suddenly, an economy such as Greece’s would acquire important degrees of freedom within the existing European monetary union. In a second phase of development, which we did not have time to consider properly, the system would be made accessible through smartphone apps and identity cards, guaranteeing that it would be widely adopted. The envisaged payments system could be developed to create a substitute for fully functioning public debt markets, especially during a credit crunch such as the one that has afflicted Greece since 2010.
Organisations or individuals could buy credits from the tax office online using their normal bank accounts, and add them to their reserve account. These credits could be used after, say, a year to pay future taxes at a discount (for example, 10%). As long as the total level of tax credits was capped, and fully transparent, the result would be a fiscally responsible increase in government liquidity and a quicker path back to the money markets. Handing over the reins of the finance ministry to my friend, Euclid Tsakalotos, on July 6, I presented a full account of the ministry’s projects, priorities and achievements during my five months in office. The new payments system outlined here was part of that presentation. No member of the press took any notice.
But when a subsequent telephone discussion with a large number of international investors, organised by my friend Norman Lamont, and David Marsh of the London-based Official Monetary and Financial Institutions Forum, was leaked — despite the Chatham House rule we agreed with listeners, under which speakers are not identified — the press had a field day. Committed to unlimited openness and full transparency, I granted OMFIF permission to release the tapes. While I understand press excitement about elements of that exchange, such as having to consider unorthodox means of gaining access to my own ministry’s systems, only one matter is of significance from a public interest perspective. There is a hideous restriction of national sovereignty imposed by the “troika” of lenders on Greek ministers, who are denied access to departments of their ministries pivotal in implementing innovative policies. When a loss of sovereignty, arising from unsustainable official debt, yields suboptimal policies in already stressed nations, one knows that there is something rotten in the euro’s kingdom.

You can find as many different opinions on this as you like.
• Fed Expected To Push Ahead With Rate Hike Plan (Reuters)
The Federal Reserve is expected on Wednesday to point to a growing U.S. economy and stronger job market as it sets the stage for a possible interest rate hike in September. The U.S. central bank is scheduled to issue its latest policy statement at 2 p.m. EDT following a two-day meeting, spelling out how policymakers feel the economy has progressed since they last met in June. Earlier this year the Fed embraced a meeting-by-meeting approach on the timing of what will be its first rate hike since June 2006, making such a decision solely dependent on incoming economic data. With a slew of employment, inflation and GDP reports to come before its September meeting, the Fed is unlikely to hint too strongly about its plans, Barclays economists Michael Gapen and Rob Martin wrote in a preview of this week’s meeting.
But simply hewing to the language of the June policy statement, when the Fed said the economy was expanding moderately, or even strengthening the outlook a bit, “leaves the door wide open for September,” they wrote. Despite a dovish reputation, Fed Chair Janet Yellen has been among those pulling on the door handle in recent public statements, saying she felt a rate hike would be appropriate sometime this year absent a negative shock to the economy. Although another collapse in energy prices and growing economic uncertainty in China is clouding the global economic outlook, the Fed has largely looked beyond recent turmoil overseas. Instead, it has focused on the steady growth in the U.S. job market and on policymakers’ expectations that inflation will eventually rise to the central bank’s medium-term objective of 2%.

It would lead to widespread chaos.
• “Fed Rate Hike Would ‘Crush’ US Housing” (CNBC)
Demand for U.S. housing in the second half of 2015 looks so weak that the Federal Reserve will not be comfortable starting its interest rate tightening cycle, independent real estate analyst Mark Hanson said Tuesday. “Having rates at zero hasn’t done much if you take a look at the numbers, but having rates 200 basis points higher or 100 basis points higher would crush housing. I don’t think they can take that chance,” the founder of M Hanson Advisors told CNBC’s “Squawk on the Street.” Hanson said last week’s new home sales data from the Commerce Department was a sign of a lingering stimulus hangover and a “huge miss.”
The Commerce Department reported new home sales fell 6.8% to a seasonally adjusted annual rate of 482,000 units. Analysts had expected a 0.7% increase to 550,000 units. With respect to homebuilder’s pricing power, he said new home prices have been down for the last seven months. The picture in 2015 looks worse when compared with 2013, he added, noting that comparisons with 2014 data are misleading because an interest rate plunge and the stimulus cycle boosted demand that year. “When you do that, you’ll see new home sales are only up 4.65% and prices are relatively flat,” he said.

Better question: how many Chinese investors still believe in stock markets, and in governemt control over them?
• How Long Can China’s ‘Rescue Squad’ Keep Intervening? (CNBC)
One month after mainland equities started their sharp selloff, Chinese investors continue to look to the government to help stabilize markets—but just how long can officials maintain their support? Volatility in Shanghai and Shenzhen stocks subsided on Wednesday after a rough start to the week. Tuesday saw markets swing wildly between gains and losses following a precipitous 8% drop on Monday. This week’s declines has been put down to local media reports that the government may withdraw the market support measures it announced in the last bout of seesaw trading in June. But fresh confirmation that officials would remain accommodative has calmed investors down.
The China Securities Regulatory Commission announced late on Monday that local governments will increase stock purchases while the central bank injected $8 billion into money markets on Tuesday and hinted at further monetary easing. “Confidence in China’s Rescue Squad was quick to rise this time around because market-boosting measures were already in place, compared to last month when it took a while for markets to believe in the government’s defense,” said Bernard Aw, IG’s market strategist, during a phone interview. Aw expects the official support program to last for another few months at least, thanks to Beijing’s substantial war chest. Capital outflows have been on the rise with June foreign exchange reserves $299 billion lower than last year but that’s still a drop in the water of Beijing’s total $3.7 trillion reserves.
He believes Beijing is willing to tolerate a modest correction but certainly not the extent of 8% crashes. But for others, the government’s program has no end in sight. “The government entered the market when it was at high levels, around 30 times price-earnings ratio. There is no exit strategy for them; I think they’ve become long-term shareholders,” Francis Cheung, head of China and Hong Kong strategy at CLSA, told CNBC. Unless Beijing allows the market to correct to fundamentally supported levels or wait until earnings grow enough to support valuation, the government cannot stop, he warned. “Until then, we expect the market will trade between the government prescribed range of 3,400 to 4,500, the level that they intervened at the low end and the level brokers are allowed to sell stock at the high-end.”

“.. the magnitude of China’s investment slump this year is likely to have been much greater than official figures show. ”
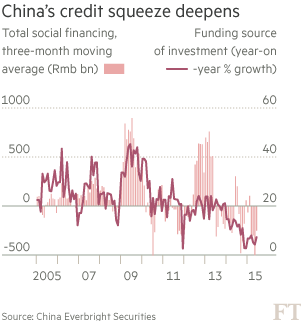
• Explainer: Key Factors Behind China’s Investment Rout (FT)
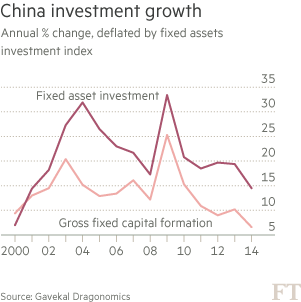
Much of the economic weakness rippling through emerging markets is “made in China”. A slump in Chinese investment growth has hammered global demand for commodities and some manufactured products, triggering a chain reaction that is depressing EM exports, deepening deflationary pressures and even sapping consumer demand. The key questions, therefore, are: what lies behind the Chinese investment rout and how long is it likely to last? First, the magnitude of China’s investment slump this year is likely to have been much greater than official figures show. Beijing’s official monthly data series tracks “fixed asset investment” (FAI), which grew by 11.4% year on year in June — not the sort of figure that might be expected to elicit alarm.
But FAI readings are inflated by several elements – such as sales of land and other assets — that do not add to the country’s productive capital stock. A cleaner measure of how much companies are investing in boosting their productive capacities – and therefore in their futures – is gross fixed capital formation (GFCF), which strips out extraneous items to capture capital goods deployment. By this yardstick, investment is tanking. Annual real growth in gross capital formation hit 6.6% in 2014, down from 10.2% in 2013 and a peak of 25% in 2009. Thomas Gatley, China corporate analyst at Gavekal Dragonomics, a research firm, estimates that so far this year GFCF may be running at around 4 to 5%. On a net basis, stripping out depreciation costs, “it is very likely that so far in 2015 net capital formation growth is at or below zero”, Mr Gatley said.
When viewed from this perspective, China’s slumping demand for iron ore, copper, alumina and other commodity imports from Latin America, Africa and elsewhere is easier to comprehend. But what are the main causes of China’s investment slump? Investment demand derives from three key sources — the property sector (25%), infrastructure (22%) and manufacturing (33%), with the remaining 20% made up of various smaller items, according to research by China Everbright Securities. Property investments have been subdued. New residential property investment rose 2.8% in the first half of this year, down from 5.9% in the first quarter, revealing a flagging momentum.

“The genie of euro zone exit has escaped in the Greek crisis and won’t easily get back in the bottle..”
• Greek Creditors Seek Third Wave Of Reforms Before Loan (Reuters)
EU officials played down the latest outbreak of logistical and security issues that have dogged talks between the creditors and Greece since Tsipras’s government took office in January, promising to free Greeks from humiliation and imposed austerity. An EU official said access for the negotiators to ministries and all relevant government bodies had been agreed. An ECB aide said some talks would take place at the Athens Hilton Hotel. The talks will mostly cover a reform programme Greece must implement to receive phased disbursements of loans, money it needs to meet its debt service obligations and help recapitalise the banks. However, an ECB policymaker said they would also cover debt relief for Athens.
ECB Executive Board member Benoit Coeure told French daily le Monde that the euro zone no longer questioned whether to restructure Greece’s debt but rather how best to go about it. “That’s why it’s important to make this restructuring, whatever form it takes, conditional on the application of measures that reinforce the economy and ensure the sustainability of Greek public finances,” he said. Coeure said five months of wrangling had caused huge economic and financial costs for Greece, and exposed how deeply flawed the euro zone’s decision-making was. He called for more integration in order to take tough decisions effectively. Germany’s Schaeuble proposed at the height of the crisis that Greece take a five-year “time out” from the currency bloc if it could not meet the conditions. “The genie of euro zone exit has escaped in the Greek crisis and won’t easily get back in the bottle,” Coeure said.

All part of the intentional gutting of an entire society.
• Greek Doctors and Nurses Looking for Jobs Abroad (GR)
The Athens Medical Association (ISA) warned about major shortages in medical staff over the next years, since an increasing number of Greek doctors, especially those working in highly specialized fields, and nurses are looking for jobs abroad and leaving the country. According to the association’s figures, more than 7,500 doctors have migrated to other countries since 2010. It was reported that in the first six months of 2015, ISA issued 790 certificates of competence, an official document required for medical sector employees who wish to work abroad. However, the report also noted that up until 2009, on average, 550 doctor were taking jobs abroad each year.
“One of the biggest losses in the crisis has been that of great minds,” ISA chief Giorgos Patoulis stated to Greek newspaper Kathimerini. “In a short time, the national healthcare system will have an aged personnel and will be unable to staff services.” Furthermore, the data showed that a total of 8,000 unemployed Greeks have been forced to look for job opportunities abroad. The Greek Nurses Union announced that it issued 349 certificates just last year, 357 in 2012 and 74 certificates in 2010.

How Reuters would like you to see the world: “former finance minister Yanis Varoufakis, who continues to heap abuse on the creditors in his blog..”
• Denials Fly In War Of Nerves Over Greek Debt Talks (Reuters)
Conflicting statements and denials flew between Athens and Brussels on Tuesday in a war of nerves highlighting the depth of mutual mistrust over a new round of negotiations on an €86 billion bailout that started this week. Any hope of a fresh start in fraught relations between Greece’s leftist government, purged of its most radical members, and the institutions representing its creditors, appeared to be dashed by the flurry of assertions and rebuttals. Differences included the pace and conduct of bailout talks, whether or not Greece needs to enact further laws before a deal, the reopening of the Athens stock exchange, and the activities of former finance minister Yanis Varoufakis, who continues to heap abuse on the creditors in his blog. [..]
Greek officials were at pains to play down what they see as the humiliating and intrusive aspects of the talks – access to ministries, the right to examine accounts and question civil servants, and the visible presence of the negotiators in Athens. The Finance Ministry official said there had been no organizational issues and all discussions were taking place at the institutions’ residence. When required, creditors’ representatives had met with Greek officials at the Bank of Greece and the State General Accounting Office. EU officials said security and logistical issues had delayed the start of the talks, originally planned for last Friday.
Also hanging over the talks is the growing disarray within Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras’s Syriza party, whose policy-setting central committee will meet on Thursday to decide whether to hold an emergency congress in September to overhaul the party or hold a referendum on the way forward. In a sign of the deepening rift within the party, three far-left members of the 11 officials on Syriza’s political committee that met on Tuesday demanded the government break off negotiations with EU/IMF creditors and return to its anti-bailout roots. Panagiotis Lafazanis, the leader of the far-left Left Platform wing of Syriza, also stepped up his attack against the pro-bailout Greek establishment, saying they were trying to “criminalize” any alternative to the bailout.
A day earlier, Lafazanis pledged in a defiant public speech that those who voted “No” to the bailout in a referendum this month would not be forgotten. On the negotiations front, the Greek official said suggestions that Greece needed to pass further reform legislation before a bailout deal were not justified by the euro summit statement or subsequent exchanges. However, euro zone officials made clear that Athens must enact measures to curb early retirement and close tax loopholes for farmers before any new aid is disbursed. Greece needs more finance by Aug. 20, when it owes a €3.5 billion payment to the ECB.

“Why, they wondered, do some things like education, medical care and live musical performances get more expensive with time, while so many other things, like manufactured goods, get cheaper?”
• Greece Isn’t a Morality Tale (Buchanan)
One of the more troubling elements of the recent drama over Greece’s debt was the urge by many to see a deficiency of national character, rather than euro-zone economics, as the problem. Right-leaning opinion, not only in Germany but around the world, put the trouble down to Greek corruption and, worse, laziness: The bad people of Greece retire too early and produce less per capita than the European average, despite working longer hours. We shouldn’t conclude much of anything from such comparisons. It’s a complete myth that economic productivity somehow reflects the average ability of people to work hard. It has far more to do with the nature of industries in different nations, and how technology has changed their productivity over time.
Nearly 20% of Greek economic output comes from tourism, which is natural enough, given the nation’s surpassing beauty. Aside from the Internet making it easier to book and advertise trips, however, tourism remains a labor-intensive activity not that different from 30 years ago. People take planes and taxis, stay in hotels, eat meals, listen to music and take excursions on boats. All of that requires a large number of people to cook and serve, entertain, clean rooms and drive taxis for long hours. The amount of these things that can be produced per hour and per person hasn’t changed a lot with time. Compare that with, say, the German automobile industry.
According to Eurostat data, the total output of the European motor-vehicle industry – German companies account for about half of it – grew in the decade before the financial crisis by about 4.4% a year. That corresponds to a doubling of output in 15 years. Much of this increase came from gains in manufacturing productivity – value created per hour of work – which in Germany, according to OECD numbers, grew by 40% over the same period. In other words, rapid economic growth in Germany and other fast-growing, developed nations has come mostly from improvements in industrial efficiency, not from some morally superior character of the workers in those nations. All this links up with a notion that economists call Baumol’s cost disease, originally proposed by William Baumol and William Bowen in the 1960s.
Why, they wondered, do some things like education, medical care and live musical performances get more expensive with time, while so many other things, like manufactured goods, get cheaper? The answer is simply that productivity improves faster in some industries than in others. As auto manufacturers make ever more and better cars – faster and with fewer workers – they can sell them more cheaply and still afford to raise wages. In contrast, a live orchestral performance today takes as long and demands as much skilled labor as it did two centuries ago. Getting good musicians requires wages that rise as fast as elsewhere in the economy, and so prices in “stagnant” sectors of this sort go up relative to others.

“..almost six years after the crisis began, the country’s European acquis is no longer a given and the European accomplishments of the last 35 years are being challenged.”
• When A Threat Becomes A Possibility (Kostis Fafoutis)
“The memorandum, whether we like it or not, is the only political text which set out specific targets, which were binding to the Greek state as a whole,” noted Yannis Stournaras in October 11, 2013, during his tenure as finance minister. Currently Bank of Greece Governor, Stournaras is still systematically taunted by those obsessed with a Greek rift with the eurozone, people whose behavior and actions, nevertheless, reaffirm his evaluation. Back in 2009, the country’s entry in the European Stability Mechanism and its guardianship was caused by the sensational collapse of Greece’s entire economic and social model developed after the fall of the military dictatorship in 1974.
The system was based on the idea of a partisan state, clientelism, under-the-table transactions and choices guided by the desire to impress or benefit certain closed, special interest groups. The structure survived either by transferring the weight onto the next generation or by taking advantage of conscientious taxpayers – salaried employees and pensioners – through a system based on tolerating and rewarding tax evasion. This was rooted in a kind of parallel economy which existed within the framework of a strange perception of democracy, where everyone enjoyed sacred rights but very few had obligations. The memorandum – for all its mistakes and weaknesses – forced the Greek state to adopt obvious changes.
These should have been implemented years ago but the political leadership did not have the willpower or strength to carry them out. Unfortunately, the memorandum was essentially decided by the lenders, and all those who had to implement it presented it as an onus imposed by the “evil” partners. Not only did they fail to present a plan of their own to exit the crisis but they never spoke of the country’s obligation – given that Greece had willingly decided to take part in a supranational organization such as the European Union and the monetary union – to undertake the cost implied by this choice. They never spoke about the fact that we have to decide whether or not we wish to become a modern western European state – which in a globalized world must constantly strive to strengthen in terms of competitiveness – or remain a democracy of cronies.
As a result, almost six years after the crisis began, the country’s European acquis is no longer a given and the European accomplishments of the last 35 years are being challenged. What’s more, a return to the drachma is no longer a threat but an openly supported possibility weighted with ideological tension, populism and the idea that it can be subverted. This position is adopted SYRIZA’s radical left wing, the extraparliamentary left and Golden Dawn. It remains to be seen whether or not it will develop into a new dividing line which will replace the equally handy, but highly confusing, memorandum-anti-memorandum dipole.

British politics has been pre-empted by an elite.
• Corbyn, Tsipras, Maggie And TINA (Andreou)
Read more …It is not a coincidence that Corbyn has been likened to Alexis Tsipras and the Syriza movement, by friend and foe alike. It is not a coincidence that Syriza has already expressed its support for him, or that he was the only one of the leadership candidates to voice his disgust at the treatment of Greece in the hands of the EU. A network is forming. Last week Tsipras, according to some commentators, was a class traitor for not pushing the nuclear button of Grexit. Now, in some cases the very same people, are suggesting Corbyn is far too radical. It confirms my instinctive conclusion: Most of the left want revolution. Most of the left would like it to happen somewhere else first, please, thanks.
Some friends, fairly, ask: How can you excuse Tsipras for signing an agreement, for compromising his principles and election promises, and at the same time criticise the other Labour candidates for proposing the same in order to get elected? I have wrestled with this issue. It makes a big difference, on the one hand, going into an election with the right ideals and motives and having to compromise, faced with powerful opposing forces and realpolitik, and on the other, selling out before you even try, because all that matters to you is getting your claws on the throne. Actually, it makes all the difference. Be careful, warns former leadership hopeful Tristram Hunt: “Britain is not Greece or Spain”.
Strange; for years, all those wishing to strengthen the notion that There Is No Alternative to neoliberal austerity, have been telling us ad nauseam that we are just like Greece and Spain. Or at least we will be, unless we happily accept the shrinking of the welfare state, the demise of free health and education, the lowering of salaries, the cruelty to migrants, the disintegration of social cohesion. And shaking this TINA narrative is precisely the point. Neoliberal austerity has become impenetrable dogma, evangelical in its fervour. All that is left to those of us who oppose it, is political guerrilla warfare; seeing the opportunity to hijack processes, like leadership elections, and make unexpected choices, like Corbyn. Greece has shown that such courses of action are the only ones that surprise elites and cause them to reveal themselves and make panicked choices. �

What politics in Europe SHOULD look like, if the EU is to survive: people first.
• Madrid’s Podemos-Backed Mayor Saves 70 Families From Eviction (TeleSur)
Madrid’s recently elected left-wing mayor announced Tuesday she had annuled eviction orders for 70 families living in social housing, while preserving over 2,000 similar rental contracts. Manuela Carmena was elected earlier in May under the banner of a local coalition Ahora Madrid, which included anti-austerity party Podemos, with a program focused on protecting housing, as the aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis in Spain led to tens of thousands of families evicted from their homes. The ruling conservative Popular Party (PP) had been governing the capital for the past 24 years. “There were 70 processes under way, but today those families have recovered their homes. Nobody is going to be thrown out on the street,” said Carmena.
The evictions followed a 2012 deal made by the Madrid social housing body EMVS to sell five blocks of public housing to the Spanish real estate developer Renta Corporación for about US$24 million. RELATED: Interview with Podemos Founder: Spain’s 2-Party System Is Dying The deal eventually fell apart, although tenants claimed they were asked by EMVS to sign new contracts including a sell-by date on their subsidized terms in the event of a sale, in order to make the flats more attractive to sell to investment funds. The city council confirmed the mayor’s decision in a statement: “The EMVS will no longer pressure the 220 families that live in five blocks owned by them in the center to leave, and it will stop the eviction processes for the 70 homes.”
It said a further 2,086 similar social rental contracts around the city would be safeguarded. Alberto Romeral, a pensioner who benefited from the measure and leader of the “Yo no me voy” (“I’m not going”) group told Reuters: “We are grateful that [Carmena] looks out for the people of the city and their problems and does not want to crush them.”

“We are the only eurozone country that actually does more trade outside the eurozone than within it…”
• British Prosperity Will Drive Ireland’s Recovery (David McWilliams)
I am on Shaftesbury Avenue in London, quite shocked. I have just put my card into an ATM to get £200 and realise that it has cost me nearly €300. I was aware that the British currency was rocketing, but this exchange rate difference is extraordinary and is brilliant news for Irish exporters. We should do a deal with the British, fix the exchange rate here and simply transport Britain’s industrial base to Ireland and hit the restart button. Of course, I am joking, but there is a startling divergence between the British economy, our biggest trading partner, and the eurozone economy that Official Ireland pretends is our biggest trading partner. Employment in Britain is growing for a start. As George Osborne claimed in his recent budget, Yorkshire has created more jobs than France.
Thankfully, the Irish economy is not a European economy in any meaningful sense. We are an Anglo-American economy with a Franco-German currency grafted onto us. Despite politicians and senior civil servants going over and back to Brussels all the time, we are actually part of the Anglosphere which maps a giant global arch from Dublin to London, across the Atlantic through North America and down to Australia and New Zealand. This is our world. This is where we trade, where our investments come from, where our people live. It is an interlinked web of culture, language and family. Granted, there are some significant differences, but if we are honest, these differences are dwarfed by commonalities. Economically, when the Anglosphere does well, we do well. Period.
In the past five years, Ireland’s economy has been dragged upwards by Britain and the US. Ireland’s youth have sought opportunities in booming Australia, Britain, Canada and the US. We head to Boston or Birmingham, not Brussels to look for work. These are the facts. We are the only eurozone country that actually does more trade outside the eurozone than within it. But this type of anomaly describes much of Irish economic policy – it’s an economic policy made up without much reference to the actual economy. However, thankfully for us, our major trading partners – Britain and the US – are motoring and they have dragged Ireland out of the mire and put us on the road to recovery.

Government sounds like amateurs.
• Imposing Losses On Hypo Bond Holders Illegal, Says Austrian Court (FT)
An attempt by Austria to slash the cost to taxpayers of Hypo Alpe Adria bank, a high-profile European casualty of the financial crisis, by imposing losses on some bondholders has been thrown out by the country’s top judges. In a ruling that came as relief for investors who feared a precedent would be set for other European bank failures, Austria’s constitutional court on Tuesday declared illegal a law that would have “bailed in” €890m in subordinated debt. The act would have breached the constitution by reversing guarantees given to bondholders by the province of Carinthia as well as treating investors unfairly, the court ruled. The law would be “repealed in its entirety”, the judges said in a statement.
Introduced last year by Michael Spindelegger, then finance minister, the law created alarm in Austria and elsewhere in Europe amid fears investors would question the value of guarantees given by other regional governments – for instance in Germany. However, investors’ relief could prove shortlived as Austria’s authorities press ahead with plans to wind up the bank under recently introduced national legislation, which has become a trial run for as-yet untested EU rules that set out who should foot the bill when banks go bust. Hypo Alpe Adria was nationalised in 2009 after ambitious international expansion plans went badly wrong. When in March it was revealed that Heta, the “bad bank” created to dispose of non-performing parts, would need a further €7.6bn in state aid, the government in Vienna refused to provide additional funding.
The bank was put into resolution, and Heta suspended bond payments. The Austrian law highlighted the pressures on European politicians to limit the impact of bank failures on stretched government finances. Mr Spindelegger “needed something to show the electorate he would prevent taxpayers bearing the cost”, said Josef Christl at Macro-Consult, a Vienna-based financial consultancy. “It was a political decision, not economically or legally based.” Tuesday’s constitutional court reversal was “a good decision for bondholders but it’s embarrassing for the government. This was not a law you would have expected from Austria and a lot of PR damage has been done,” added Franz Schellhorn, director of the Agenda Austria think-tank.

Think this insanity can last much longer?
• The Costly, Deadly Dangers of Traffic Stops in America’s Police State (Whitehead)
Incredibly, a federal appeals court actually ruled unanimously in 2014 that acne scars and driving with a stiff upright posture are reasonable grounds for being pulled over. More recently, the Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals ruled that driving a vehicle that has a couple air fresheners, rosaries and pro-police bumper stickers at 2 MPH over the speed limit is suspicious, meriting a traffic stop. Unfortunately for drivers, not only have traffic stops become potentially deadly encounters, they have also turned into a profitable form of highway robbery for the police departments involved. As The Washington Post reports, “traffic stops for minor infractions such as speeding or equipment violations are increasingly used as a pretext for officers to seize cash from drivers.”
Relying on federal and state asset forfeiture laws, police set up “stings” on public roads that enable them to stop drivers for a variety of so-called “suspicious” behavior, search their vehicles and seize anything of value that could be suspected of being connected to criminal activity. Since 2001, police have seized $2.5 billion from people who were not charged with a crime and without a warrant being issued. “In case after case,” notes The Washington Post, “highway interdictors appeared to follow a similar script. Police set up what amounted to rolling checkpoints on busy highways and pulled over motorists for minor violations, such as following too closely or improper signaling. They quickly issued warnings or tickets.
They studied drivers for signs of nervousness, including pulsing carotid arteries, clenched jaws and perspiration. They also looked for supposed ‘indicators’ of criminal activity, which can include such things as trash on the floor of a vehicle, abundant energy drinks or air fresheners hanging from rearview mirrors.” If you’re starting to feel somewhat overwhelmed, intimidated and fearful for your life and your property, you should be. Never before have “we the people” been so seemingly defenseless in the face of police misconduct, lacking advocates in the courts and in the legislatures. So how do you survive a police encounter with your life and wallet intact? The courts have already given police the green light to pull anyone over for a variety of reasons.
In an 8-1 ruling in Heien v. North Carolina, the U.S. Supreme Court affirmed that police officers can pull someone over based on a “reasonable” but mistaken belief about the law. Of course, what’s reasonable to agents of the police state may be completely unreasonable to the populace. Nevertheless, the moment those lights start flashing and that siren goes off, we’re all in the same boat: we must pull over. However, it’s what happens after you’ve been pulled over that’s critical. Survival is the key.

No, Greece is not even Europe’s biggest -moral- failure.
• 1 Dead After 1,500 Migrants Storm Eurotunnel In France For 2nd Night (RT)
At least one migrant has died when he tried to enter Eurotunnel’s French terminal near Calais on Tuesday night as about 1,500 refugees attempted to break through fences in a bid to reach UK for a second straight night. “Our teams have found a body this morning and firefighters have confirmed the person’s death,” a spokesman for Eurotunnel told France Info. BMFTV reported that the migrant of was Sudanese origin. The man was run over by a truck from the UK, Francetvinfo website reported. A police spokesman told BFMTV that they were “completely clueless” about the situation, adding that 60 officers are currently working at the scene of the incident.
According to police sources cited by Francetvinfo, migrants were attempting to break into Eurotunnel “at least three times” on Tuesday night. On Monday night about 2,000 migrants tried to breach the fences of the Calais terminal trying to get into UK. A Eurotunnel spokesman, who described the situation as “the biggest incursion effort in the past month and a half.” This is not the first migrant death in recent months. July 7 a man reportedly of Eritrean origin attempting to reach the UK from Calais was found dead on a freight shuttle, Channel Tunnel operator Eurotunnel has said. Overall, with the latest fatality, the number of deaths in Eurotunnel stands at nine, according to French media.

And we call ourselves a successful species?! (I don’t even want to go into Cecil the lion’s death)…
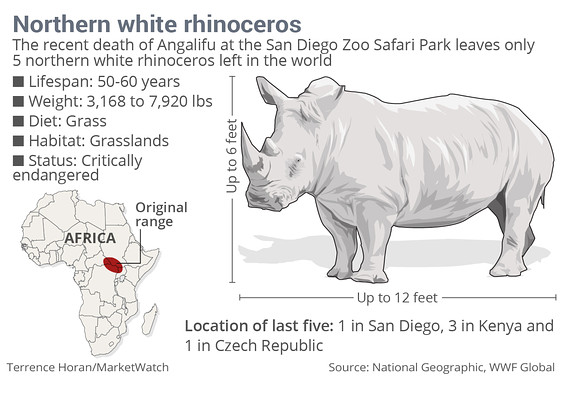
• Northern White Rhino Closer to Extinction With Czech Zoo Death (Bloomberg)
One of the world’s most endangered animals, the northern white rhinoceros, edged closer to extinction when one of the last five of its kind known to exist died in a Czech zoo. The 31-year-old female Nabire, who lived her life at the Dvur Kralove zoo, about 140 kilometers northeast of Prague, died on Monday of a ruptured cyst, the zoo said on its website Tuesday. Nabire’s death “brought another species closer to complete extinction,” zoo director Premysl Rabas said. He blamed the plight of the northern white rhinoceros on “meaningless human greed.” Northern white rhinos were last seen in the wild in central Africa in 2007. Their disappearance stemmed from demand for their horns, which are used for medical and cultural purposes in some parts of Asia and the Arab world. The last surviving male lives in Kenya with two females, and the other female lives in San Diego, according to the Czech zoo.