Edward S. Curtis Mosa Mohave girl c. 1903

Another great set of graphs from Lance Roberts, who just keep churning them out. I picked these two to show how dependent economies have become on suppressing wages. Problem is, that threatens economies. You need money rolling at the ground level to keep your economy going.
• The Mean Reverting History Of Profit Growth (Roberts)
Since 2000, each dollar of gross sales has been increased to more than $1 in operating and reported profits through financial engineering and cost suppression. The next chart shows that the surge in corporate profitability in recent years is a result of a consistent reduction of both employment and wage growth. This has been achieved by increases in productivity, technology, and off-shoring of labor. However, it is important to note that benefits from such actions are finite. (Note the acceleration in profits starting with the Reagan Tax Cuts in the 1989’s. There is no evidence that cutting taxes for corporations leads to higher wages for employees.)
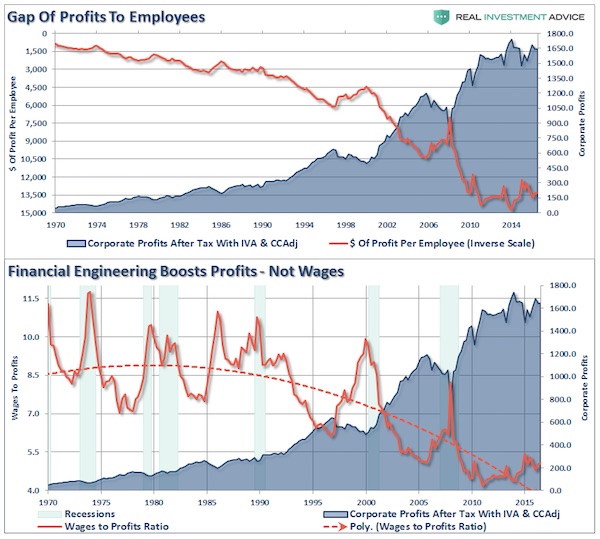
Given the economic landscape of recent years, large offsetting sectoral deficits and surpluses are not surprising, but they should not be taken as evidence that the long-term profitability of the corporate sector has permanently shifted higher. Stocks are not a claim to a few years of cash flows, but decades and decades of them. By pricing stocks as if current profits are representative of the indefinite future, investors have ensured themselves a rude awakening over time. Equity valuations are decidedly a long-term proposition, and from present levels, the implied long-term returns are quite dim.
Read more …

And then you get this…
• US Household Debt Is Rising 60% Faster Than Wages (ZH)
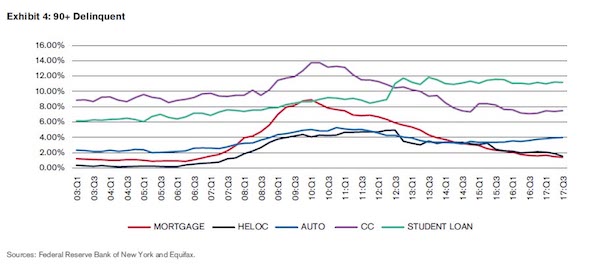
The good news: total mortgage debt has decreased since 2008, to $8.743 trillion from $9.29 trillion, but as of the third quarter of 2017, still accounts for 67.5% of overall consumer debt. The bad news: since 2008, the growth in total debt has been attributable to the auto loan and student loan sectors. Auto loan debt has increased by 50% since 2008, to slightly over $1.2 trillion from approximately $800 billion. The most dramatic growth rate, as Zero Hedge readers know well, has been in student loan debt which has grown by 122% since 2008, to $1.357 trillion from $611 billion. But a bigger concern flagged by DBRS is that the growth in consumer debt is raising concerns when viewed in the context of the existing wage stagnation hampering the current economic environment.
The rating agency cites a paper published in October 2017 by the Harvard Business Review which stated that the inflation-adjusted hourly wage has grown by only 0.2% per year since the mid-1970s and labor’s share of income has decreased to its current level of 57% from 65%. Meanwhile, in the second quarter of 2017, wages were only 5.7% higher than they were a decade earlier. In comparison, the Federal Reserve Bank of New York/Equifax data shows that consumer debt growth over the same period was 9.3%. In other words, the purchasing power of US households has been largely a function of rapidly rising debt, which over the past decade has risen 60% faster than wages. There is another concern: while overall delinquency rates have stabilized in recent years, the one stubborn outlier remains student debt, where 90+ day delinquencies have risen to more than 10%.
Read more …

“Obviously debts of this magnitude can’t and therefore won’t be repaid. Which means the coming decade will be defined by how — and how quickly — we end up defaulting.”
• We Give Up! Government Spending And Deficits Soar Everywhere (Rubino)
A recurring pattern of the past few decades involves governments promising to limit their borrowing, only to discover that hardly anyone cares. So target dates slip, bonds are issued, and the debts keep rising. This time around the timing is especially notable, since eight years of global growth ought to be producing tax revenues sufficient to at least moderate the tide of red ink. But apparently not. In Japan, for instance, government debt is now 250% of GDP, a figure which economists from, say, the 1990s, would have thought impossible. Over the past decade the country’s leaders have proposed a series of plans for balancing the budget, and actually did manage to shrink debt/GDP slightly in 2016. But now they seem to have given up, and are looking for excuses to keep spending.
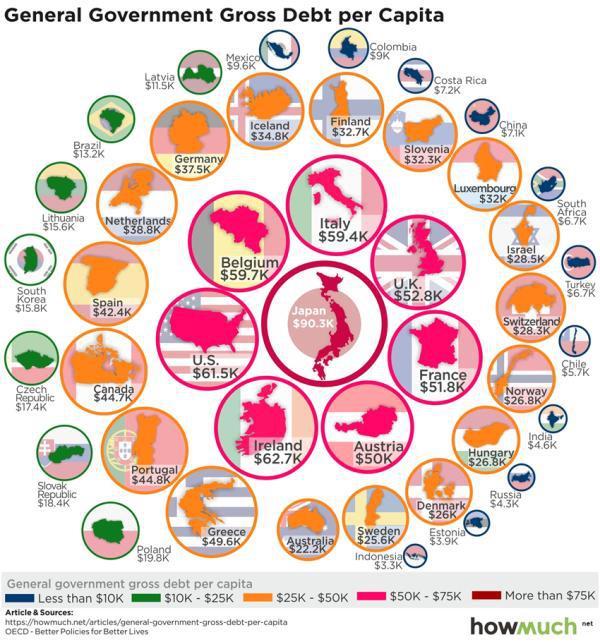
[..] To put the above in visual terms, here’s an infographic from Howmuch.com that shows per-capita government debt for the world’s major countries. Note that a Japanese family of five’s share of its government’s debt is close to $450,000 while in the US a similar family owes $300,000. That’s in addition to their mortgages, car loans, credit cards, etc. Obviously debts of this magnitude can’t and therefore won’t be repaid. Which means the coming decade will be defined by how — and how quickly — we end up defaulting.
Read more …

More of that same story.
• Lemmings In Full Stampede Toward The Fiscal Cliff (Stockman)
The lemmings are now in full stampede toward the cliffs. You can literally hear the cold waters churning, foaming and crashing on the boulders far below. From bitcoin to Amazon, the financials, the Russell 2000 and most everything else in between, the casinos are digesting no information except the price action and are relentlessly rising on nothing more than pure momentum. The mania has gone full retard. Certainly earnings have nothing to do with it. As of this morning, the Russell 2000, for instance, was trading at 112X reported LTM earnings. Likewise, Q3 reporting is all over except for the shouting and reported LTM earnings for the S&P 500 came in $107 per share. That’s of signal importance because fully 36 months ago, S&P earnings for the September 2014 LTM period posted at $106 per share.
That’s right. Three years and $1 of gain. They talking heads blather about “strong earnings” only because they think we were born yesterday. What happened in-between, of course, was the proverbial pig passing through the python. First, the global oil, commodities and industrial deflation after July 2014 took earnings to a low of $86.44 per share in the March 2016 LTM period. After that came the opposite—the massive 2016-2017 Xi Coronation Stimulus in China. The new Red Emperor and his minions pumped out an incredible $6 trillion wave of new credit, thereby artificially stimulating a global rebound and a profits recovery back to where it started three years ago.
The difference of course is that $106 of earnings back then were priced at an already heady (by historical standards) 18.6X, whereas $107 of earnings today are being priced at a truly lunatic 24.6X. After all, nothing says earnings bust ahead better than an aging business cycle, a cooling Red Ponzi, an epochal shift toward central bank QT (quantitative tightening) and a massive Washington Fiscal Cliff. Yet every one of those headwinds are self-evident and have made their presence known with a loud clang in the last few days.
Read more …

For good measure, let’s throw in some Catch 22.
• Brexit Risks Leaving Banks on the Hook for Impossible Contracts (BBG)
As far as Brexit headaches go, John McFarlane, who chairs Barclays and London’s bank lobby, says that while his firm is on top of job moves, he’s more concerned about rewriting “hundreds of thousands” of contracts. He’s not alone. Andrew Bailey, head of the U.K. Financial Conduct Authority, said “contract continuity” was among the biggest potential disruptions from a no-deal, no-transition Brexit. Both men were testifying to lawmakers Wednesday. Bank of England Governor Mark Carney and ECB President Mario Draghi have also expressed concern about the issue and the dearth of time left for a fix. A week ago, data from the European Banking Authority showed the scope of the issue, and that money is already on the move for precisely this reason: European banks have slashed their U.K. assets by $425 billion, driven by a 35% drop in derivatives exposures.
Insurance policies are affected too: Carney estimates about 20 billion pounds of insurance liabilities in Britain could be affected without swift action. The issue arises because one side or the other of a contract can meet its obligations only thanks to an authorization that’s set to disappear once the U.K. leaves the European Union in 2019. This might result in a firm being obliged by contract law to do something that regulation prohibits it from carrying out, and impossibility generally isn’t a defense against non-performance of a contract, said Simon Gleeson at Clifford Chance in London. “A bank which enters into a contract which becomes illegal to perform by reason of Brexit may well be liable in damages for its non-performance to the counterparty,” said Gleeson. “Dealing with this is so much in everyone’s interest that I’m amazed it hasn’t been addressed.”
[..] Cross-border revolving credits – credit lines that can be drawn down, repaid, then drawn down again – are among such contracts. Many of these are issued to EU companies by syndicates with members based in the U.K. For example, lenders to Volkswagen Financial Services’s €2.5 billion ($3 billion) line include London-based entities for Bank of America and Citigroup, as well as the U.K. units of the major British banks, data compiled by Bloomberg show. A lender that lost its authorization but made an advance to the company under the revolver might find itself in breach of local law in jurisdictions including Germany and France, according to Clifford Chance. On the other hand, it might be in breach of contract if it failed to make the loan.
Read more …

Because Morgan Stanley exposes itself this way. As Corbyn himself said: Yes, we’re a threat. To you.
• I’m Glad Morgan Stanley Has Warned Us About Jeremy Corbyn (Ind.)
This week, Morgan Stanley claimed that “Corbyn would be more of a danger to markets than hard Brexit”, something which I saw as supremely ironic. Because the actions of Morgan Stanley, and others like it, laid the foundations for Leave because of their role in the financial crisis: a crisis of capitalism, which ushered in seven years of austerity, falling wages and insecure work. Precisely the conditions that would encourage the majority of British people to vote against the status quo and opt for Leave. Morgan Stanley’s role in the financial crisis cannot be understated; and, given describing things as a “danger to markets” appears to be in fashion right now, let’s remind ourselves what they got up to just over a decade ago.
Essentially, they packaged up sub-prime mortgages as something called Collateralised Debt Obligations (CDOs), got credit ratings agencies – who were entirely conflicted as their clients were the investment banks – to rate these absolute garbage CDOs triple-A investments. Morgan Stanley then misled investors who bought them. Because they knew what those investments were actually worth, Morgan Stanley’s traders bought what are known as “credit default swaps” on those CDOs – effectively amounting to a bet on it defaulting. You can buy or sell a credit default swap even if you don’t own the investment. They did this thousands of times.
[..] the right-wing press, which gleefully reported on this Corbyn/Brexit warning, clearly has a short memory about what really happened. After all, the lie that Labour caused the financial crisis, and not investment banks like Morgan Stanley, was a convenient pretext for maintaining the economic status quo while cutting to public spending. This forced ordinary working people to pay for a financial crisis they did not cause. It’s little wonder that people voted Leave having been totally shafted by the system. But the opportunity to do so only arose because the narrative that “Labour crashed the economy” helped secure David Cameron a majority in 2015 on a manifesto that promised a referendum.
Read more …

Make it 2018.
• US Senate Suspends Tax Bill Votes to Friday Morning (BBG)
Senate Majority Leader Mitch McConnell said votes on the tax bill will resume at 11 a.m. on Friday as the collapse of a key compromise to win a majority for a Senate tax overhaul left Republicans scrambling to salvage the legislation. Debate over the bill may continue into the evening, McConnell said. It’s unclear when the unlimited amendment vote series known as “vote-a-rama” would begin. After seeming to gain momentum during the day, the GOP’s tax cut plan smacked into a decision from the Senate’s rule-making office that said a so-called trigger proposed by GOP holdouts didn’t pass procedural muster. At least three Republicans – Bob Corker of Tennessee, Jeff Flake of Arizona and James Lankford of Oklahoma – had tied their votes to the mechanism, which would have increased taxes if revenue targets weren’t met.
The trio is now demanding that leaders agree to other changes in the bill to avoid a huge deficit increase. Republicans have a slim majority in the Senate and can only afford to lose two members if they want to pass the tax bill without Democratic support. Adding to the difficulty was a ruling by a key fiscal referee that the tax plan would blow a $1 trillion hole in the nation’s debt – even after accounting for economic growth. The day’s events left GOP leaders contemplating a variety of potentially unpalatable measures — including making some tax cuts on the individual and corporate side end within six or seven years. The current version of the Senate bill would sunset individual breaks in 2026.
Read more …

Wait till home priced start to plummet. That’s when the scandals will break.
• Australian Banks Face Public Inquiry Amid String of Scandals
Australia’s banks will be subject to a wide-ranging public inquiry after Prime Minister Malcolm Turnbull bowed to pressure to address scandals besetting the industry. The yearlong royal commission will examine the conduct of the nation’s banks, insurers, financial services providers and pension funds, and consider whether regulators have enough power to tackle misconduct, Turnbull said Thursday. He pledged the inquiry would not put “capitalism on trial.” The announcement came just minutes after Commonwealth Bank of Australia, Australia & New Zealand Banking, Westpac and National Australia Bank dropped their opposition to an inquiry, saying in an open letter to the government that months of political squabbling over the issue risked undermining offshore investor confidence.
More than A$8 billion ($6 billion) was wiped off the market value of the big four lenders in early Sydney trading, with Commonwealth Bank declining as much as 2.7%. “Ongoing speculation and fear-mongering about a banking inquiry or royal commission is disruptive and risks undermining the reputation of Australia’s world-class financial system,” Turnbull said. The inquiry will “further ensure our financial system is working efficiently and effectively.” The main opposition Labor party has for months been demanding a royal commission into the finance industry, amid a string of scandals ranging from misleading financial advice, attempted rate-rigging and alleged breaches of anti-money laundering laws. Pressure was growing on Turnbull to hold an inquiry, with some lawmakers in his Liberal-National coalition threatening to force a vote in parliament next week.
Read more …

A big problem for Erdogan. The US takes its sanctions seriously.
• Gold Trader Implicates Erdogan In US Sanctions Breaking Case (BBC)
A controversial Turkish-Iranian gold trader has told a US court that Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan personally approved his sanction-breaking deals with Iran. Reza Zarrab, 34, is a key witness in the criminal trial of a Turkish banker whom he allegedly worked with to help Iran launder money. Mr Erdogan has denied that Turkey breached US sanctions on Iran. The case has strained relations between Ankara and Washington. In his testimony, Mr Zarrab implicated Mr Erdogan in an international money laundering scheme that he and the banker, Mehmet Hakan Atilla, ran between 2010 and 2015 that allegedly allowed Iran to access international markets despite US sanctions.
He said that he was told in 2012 by the then economy minister that Mr Erdogan, who was prime minister at the time, had instructed Turkish banks to participate in the multi-million dollar scheme. Mr Erdogan said earlier on Thursday that Turkey did not breach US sanctions on Iran, Turkish media report. His government has described the case as “a plot against Turkey”. The Turkish president is yet to respond to the new allegations about him made in court. Mr Atilla has pleaded not guilty. Nine people have been charged in total. Mr Zarrab was arrested by US officials in 2016 and accused of engaging in hundreds of millions of dollars’ worth of transactions on behalf of the Iranian government, money laundering and bank fraud. But he decided to cooperate with prosecutors and is now their star witness in the New York trial.
On Wednesday, he told the court he paid Zafer Caglayan, then Turkey’s economy minister, bribes amounting to more than €50m to facilitate deals with Iran. Turkey’s Deputy Prime Minister, Bekir Bozdag, responded to the allegations, saying that Mr Zarrab had been “pressured into committing slander”. Speaking to state-run news agency Anadolu, Mr Bozdag called the trial a “theatre”. The Turkish government had previously said that Mr Caglayan acted within Turkish and international law.
Read more …

Overcapacity export.
• From The Caucasus To The Balkans, China’s Silk Roads Are Rising (Escobar)
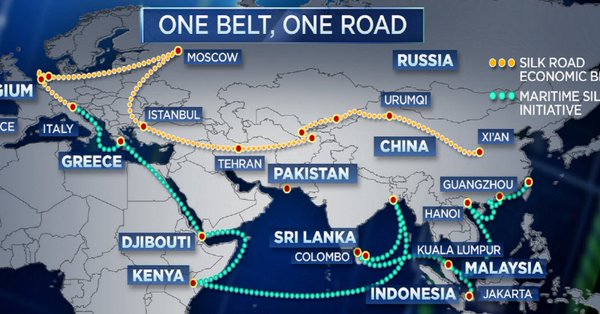
The 19th Chinese Communist Party Congress made it clear that the New Silk Roads – aka, the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) – launched by President Xi Jinping just four years ago, provides the concept around which all Chinese foreign policy is to revolve for the foreseeable future. Up until the symbolic 100th anniversary of the People’s Republic of China, in 2049, in fact. Virtually every nook and cranny of the Chinese administration is invested in making the BRI Grand Strategy a success: economic actors, financial players, state-owned enterprises (SOEs), the private sector, the diplomatic machine, think tanks, and – of course – the media, are all on board. It’s under this long-term framework that sundry BRI projects should be examined. And their reach, let’s be clear, involves most of Eurasia – including everything from the Central Asian steppes to the Caucasus and the Western Balkans.
Representatives of no fewer than 50 nations are currently gathered in Tbilisi, Georgia, for yet another BRI-related summit. The BRI masterplan details six major economic “corridors,” and one of these is the Central Asia-West Asia Economic Corridor. That’s where Georgia fits in, alongside neighboring Azerbaijan: both are vying to position themselves as the key Caucasus transit hub between Western China and the European Union. [..] The action in the Caucasus was mirrored in Europe earlier in the week as Chinese Premier Li Keqiang and Hungary’s Prime Minister Viktor Orban opened the sixth “16+1” summit, involving China and 16 Central and Eastern European nations, in Budapest. “16+1” is yet another of those trademark Chinese diplomatic “away wins.”
Some of these nations are part of the EU, some part of NATO, some neither. From Beijing’s point of view, what matters is the relentless BRI infrastructure and connectivity drive. Beijing may have invested as much as US$8 billion so far in Central and Eastern Europe. China is having a ball in the Western Balkans – especially in Serbia, in Montenegro, and in Bosnia and Herzegovina, where EU financial muscle is absent. China has invested in multiple connectivity and energy projects in Serbia – including the much-debated Belgrade-Budapest high-speed rail link. Construction of the Serbian stretch started this week, with 85% of the total cost (roughly €2.4 billion) coming from the Export-Import Bank of China.
Read more …

Dream of power are always costly.
• Paris – The Financial Capital Of West And Central Africa (Gefira)
France’s current zone of influence in Africa is the result of the policies of President Charles de Gaulle, who was unable to come to terms with his defeats in Indochina (1954) and Algeria (1962) and therefore sought to achieve the dominance of France in his former colonies. After de Gaulle, however, other presidents did not refrain from using military force and violence in Africa to defend their interests, on the pretext of protecting human rights and democracy. The French often achieved the opposite, because they made the same mistakes in their military actions as Americans made elsewhere in the world: they supported people who later became their enemies or violated human rights.
For example, it was the regime of Juvenal Habyariman in Rwanda that was supported by Paris: the French supplied Hutu combat groups with weapons, thus contributing to the Tutsi massacre. Hollande, who in Paris and Europe was perceived as a weakling, showed the face of a warrior and sent heavy units and fighter planes to Mali in 2013. This would not have been necessary if French President Sarkozy and the USA had not overthrown Qaddafi. It was Sarkozy that initiated the NATO led airstrikes against Libya. The removal of Colonel Qaddafi gave rise to the creation of the Caliphate with the help of Tuaregs in the north of Niger and Mali. After a few years since the start of the mission in Mali one wonders: has it made Europe safer?
Has the flow of migrants been stopped through Sahel countries? Are the Jihadists of African descent a lesser threat in Europe? The cost of the military action in Mali in 2013 amounted to €650 million. Operation Barkhane (as it is called) continues to this day and costs the French budget €500 million per year. Of course, democracy in Mali is a top priority for most Europeans, right? A total of 9,000 French soldiers are currently stationed in Chad, Niger, Mali, Burkina Faso, Senegal, Gabon, the Central African Republic and Djibouti. The growing military presence is intended to support the fight against terrorism and crime, in fact it is about the French elites extending their power to the south, reaching for cheap raw materials and outlet markets.
Read more …

“..if we can identify it is dark matter for sure then that is very significant. And if not, it is even more significant because they would be fresh new particles that no one had predicted before..”
• Chinese Satellite Closes In On Dark Matter Mystery (AFP)
Scientists have detected cosmic ray energy readings that could bring them closer to proving the existence of dark matter, a mysterious substance believed to comprise a quarter of our universe, a study revealed on Thursday. Likely made up of unknown sub-atomic material, dark matter is invisible to telescopes and can be perceived only through its gravitational pull on other objects in the universe. Beijing’s first astronomical satellite launched two years ago detected 1.5 million cosmic ray electrons and protons, the study said, and unprecedented measurements found curiously low-energy rays. The team of researchers from China, Switzerland and Italy, who published their first results in the journal Nature, said the data may cast light on “the annihilation or decay of particle dark matter”.
“This new unseen phenomena can bring breakthroughs,” Bai Chunli, president of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, said at a briefing. “After collecting more data, if we can identify it is dark matter for sure then that is very significant. And if not, it is even more significant because they would be fresh new particles that no one had predicted before,” Bai added, to applause from fellow scientists. The Dark Matter Particle Explorer (DAMPE) is now collecting more data from space to help researchers figure out what it could be. DAMPE was launched from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Centre in the Gobi desert in December 2015, after nearly 20 years in development. Its designers boast that DAMPE is superior to its US counterpart, the AMS-02 (Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer) that NASA installed on the International Space Station in 2011.
“Our cosmic ray detection range is 10 times that of AMS-02 and three times as accurate,” said DAMPE chief scientist Chang Jin. “Proving the existence of dark matter takes a lot of time. Now we have worked out the most precise spectrum, but we are not 100% sure that this can lead us to the location of dark matter,” he said.
Read more …




















