Frank Larson Times Square, New York 1950s

The one thing that really matters now is volatility, and all the outstanding bets for or against it.
• Worst Week in 2 Years for Stocks Ends on High Note (BBG)
U.S. equities ended their worst week in two years on a positive note, but rate-hike fears that pushed markets into a correction remain as investors await American inflation figures on Feb. 14. The S&P 500 tumbled 5.2% in the week, its steepest slide since January 2016, jolting equity markets from an unprecedented stretch of calm. At one point, stocks fell 12% from the latest highs, before a furious rally Friday left the equity benchmark 1.5% higher on the day. Still, the selloff has wiped out gains for the year. Signs mounted that jitters spread to other assets, with measures of market unrest pushing higher in junk bonds, emerging-market equities and Treasuries. The Cboe Volatility Index ended at 29, almost three times higher than its level Jan. 26.
The VIX’s bond-market cousin reached its highest since April during the week, and a measure of currency volatility spiked to levels last seen almost a year ago. Pressure on equities came from the Treasury market, where yields spiked to a four-year high, raising concern the Federal Reserve would accelerate its rate-hike schedule. Yields ended the week at 2.85%, near where they started, as Treasuries moved higher when equity selling reached its most frantic levels. Commodities including oil, gold and industrial metals moved lower Friday. The dollar, euro and sterling all declined. “Sometimes making a bottom can take time,” Ernie Cecilia, chief investment officer at Bryn Mawr Trust Co., said by phone. “Investors should be at least aware, cognizant, and expect a little more volatility after we go through this period of more cathartic volatility.”
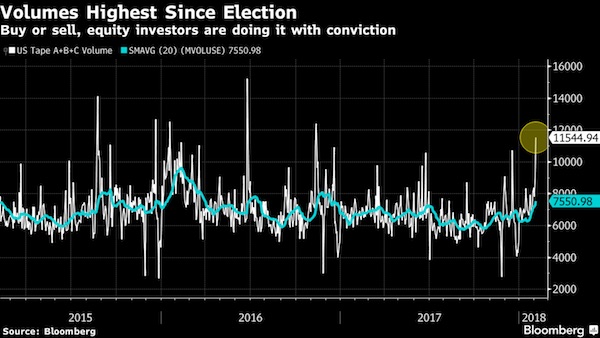

In more detail: volatility. Or in other words: how the Fed killed the market.
• By Betting On Calm, Did Investors Worsen The Stock Market Fall? (G.)
Back in 2008, the non-financial world had to digest a lot of jargon in a hurry – collateralised debt obligations (CDOs), asset-backed securities (ABSs) and the rest of the alphabet soup of derivative products that contributed to the great banking crash. This week’s diet has felt similar. As the Dow Jones industrial average twice fell 1,000 points in a day, we have had to swallow tales about the VIX, the inverse VIX, the XIV, and ETPs. Did this overdose of three-letter acronyms really cause the stock markets to swoon? Have those geniuses in the back offices of investment banks really baffled themselves – and a lot of investors – with complexity again? The short answer to the second question is: yes. The chart shows one of the most spectacular blow-ups you could hope to see.
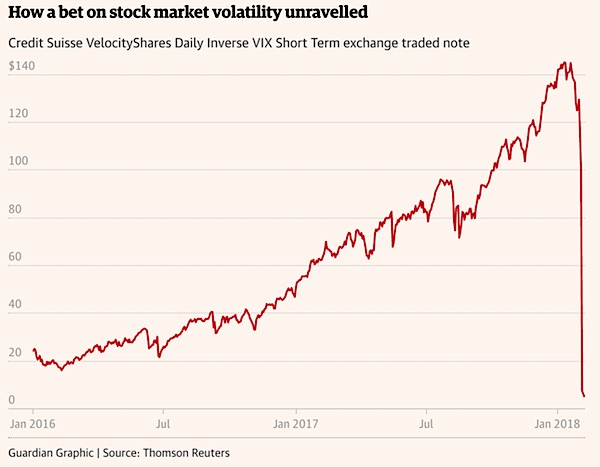
This is the XIV – it is actually the snappier name for the Credit Suisse VelocityShares Daily Inverse VIX Short Term exchange traded note – since the start of 2016. It was a beautiful investment until, suddenly, it was a disaster. What is the XIV? It was a way to bet that the S&P 500, the main US stock index, would be tranquil – in other words suffer few outbreaks of volatility. The measure of volatility is called the VIX and it is compiled and published by the Chicago Board Options Exchange by noting the prices of various option contracts in the market and then applying a mathematical formula. The VIX is more famously known as the “fear index”. In itself, the VIX is just a number – its long-term average is about 20, more than 30 is a worry, and more than 40 could herald a crisis.
For much of last year it was between 10 and 12 but on Tuesday it hit 50, before recoiling back to around 30 currently. The fun starts when products are invented to trade and speculate on how the VIX will perform. Conventional futures contracts came first. Then ETFs, or exchange-traded funds, a low-cost product that has taken the financial world by storm in the last couple of decades, followed. The XIV is slightly different (it’s a note, rather than a fund) but it comes from the same school. By trading S&P 500 options, or contracts to buy and sell the S&P at points in the future, it was structured to do the exact opposite of the VIX. If volatility in the stock market was low – as it was throughout 2016 and 2017 – owners of the XIV would do well. In the jargon, they were “short vol”. But, if volatility exploded, then the XIV would fall.

Posted a different version of this chart (from Arbeter) yesterday, coming from Market Watch.
• The Scariest Chart For The Market (ZH)
Interest-rates going up “for the right reason” is bullish, right? Each time interest rates have surged up to their long-term trendline, a ‘crisis’ has occurred…
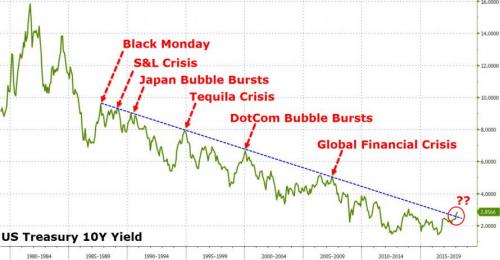
But this time is different right? Because rates are “going up for the right reason.” Hhmm, the reaction in markets each time the yield on the 10-Year Treasury yield reaches its trendline is ominous…
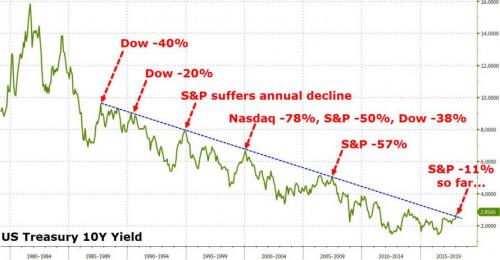
So the question is – have interest rates ‘ever’ gone up for the right reason? Or is this narrative just one more bullshit line from a desperate industry of asset-gatherers and commission-takers? It does make one wonder what the relationship between US government ‘interest costs’ and global money flow really is. Does an engineered equity tumble spark safe-haven-buying and ease the pain as deficits and debt loads soar. It would certainly help as $300bn additional budget deals are passed, The Fed has left the game, and China is threatening to be a seller not a buyer…

If everyone’s on the same side of the boat, somebody must be on the other.
• ‘Bond Vigilantes’ Are Saddled Up And Ready To Push Rates Higher (CNBC)
There’s reason to be concerned about bond vigilantes, who are no longer under “lock and key” and are free to push yields higher, Wall Street veteran Ed Yardeni told CNBC on Friday. Yardeni, a market historian, coined the term bond vigilantes in the 1980s to refer to investors who sell their holdings in an effort to enforce fiscal discipline. Having fewer buyers drives prices down — and drives yields up — in the fixed-income market. That, in turn, makes it more expensive for the government to borrow and spend. “They had been sort of put under lock and key by the central banks. The Fed had lowered interest rates down to zero in terms of short-term rates and that pushed bond yields down. And then they bought up a lot of these bond yields,” said Yardeni, president of Yardeni Research.
Now the Fed is slowly raising interest rates and starting to unwind its balance sheet. On top of that, new tax cuts were passed and a massive spending deal was just signed into law. “Now people are looking more at the domestic situation and saying, ‘You know what, maybe we need a higher bond yield,'” Yardeni said in an interview with “Power Lunch.” “They’ve saddled up, and they’re riding high. The posse is getting ready. They’re getting the message out.” Bond vigilantes last made their mark during the Clinton administration, when a bond market sell-off forced President Bill Clinton to tone down his spending agenda. Yardeni said while Clinton got the message back then, he doesn’t think the Trump administration has this time around.

Sub: Rising rates slam stocks as market volatility rages on.
• The Worst Of The Bond Rout Is Yet To Come, Says Piper Jaffray (CNBC)
It all started with bond yields. Spiking yields spilled over onto the stock market in the past week, first triggering a nearly 666-point drop on the Dow last Friday and then sparking two declines of more than 1,000 points within just 4 days. The bond rout will continue with yields on the 10-year possibly reaching 3% in the near term, according to Craig Johnson, senior technical strategist at Piper Jaffray. That is a level it has not reached since January 2014. “This is a 36-year reversal in rates,” Johnson told CNBC’s “Trading Nation” on Thursday. Bond yields, which move inversely to prices, have generally been in decline over the past 3 decades, indicating a long-term bull market for bond prices.
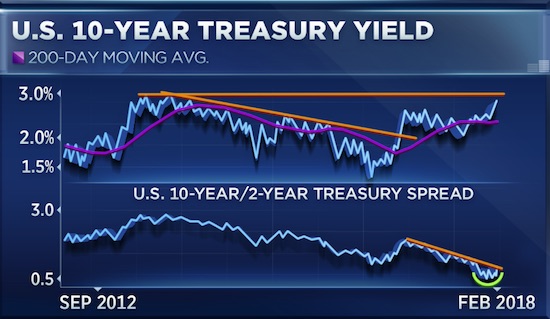
“When you reverse that downtrend from down to up you typically get a momentum response and a quick move up. That’s exactly what you’re seeing in the bond market right now,” added Johnson. “You’ve got to be careful in here right now.” The yield on 10-year Treasurys has risen at a fast clip since the U.S. election in November 2016. Bond yields held at around 1.8% prior to the election and have since moved up 100 basis points to hit a 4-year high of 2.86% this week. The uncertainty of a Trump presidency initially sent bond prices lower and yields higher at the end of 2016. Now, worries over the effect an accelerating economy and rising inflation might have on Federal Reserve policy this year have taken over. Historically, bond prices fall when interest rates rise.

No savings and huge debt means less consumer spending. Which is what 70% of US GDP is made of.
• US GDP Growth Is Not As Rosy As It Seems (Lebowitz)
Last Friday, GDP for the fourth quarter of 2017 was released. Despite being 0.3% short of expectations at 2.6% annual growth, it nonetheless produced enthusiasm as witnessed by the S&P 500 which jumped 25 points. One of the reasons for the optimism following the release was a strong showing of the consumer which notched 2.80% growth in real personal consumption. The consumer, representing about 70% of GDP, is the single most important factor driving economic growth and therefore we owe it to ourselves to better understand what drove that growth. This knowledge, in turn, allows us to better assess its durability. There are three core means which govern the ability of individuals to spend. The most obvious is income and wages earned.
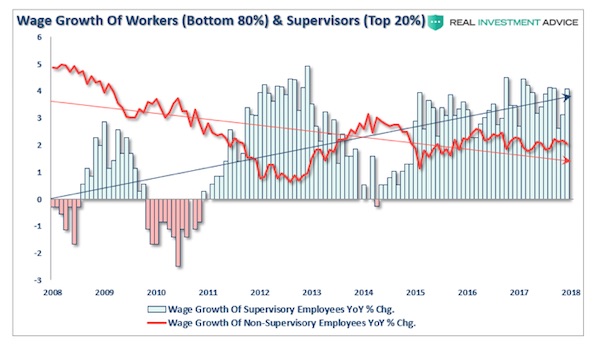
To help gauge the effect of changes in income we rely on disposable income, or the amount of money left to spend after accounting for required expenses. Real disposable personal income in the fourth quarter, the same quarter for which GDP growth data was released, grew at a 1.80% year over year rate. While other indicators of wage growth are slightly higher, we must consider that payroll gains are not evenly distributed throughout the economy. In fact as shown below 80% of workers continue to see flat to declining growth in their wages. While this may have accounted for some of the growth in consumption we need to consider the two other means of spending over which consumers have control, savings and credit card debt.
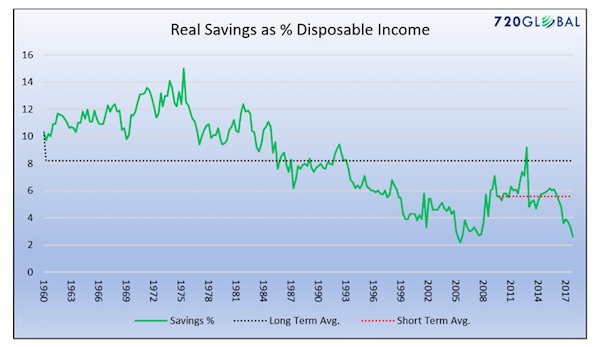
Savings: Last month the savings rate in the United States registered one of the lowest levels ever recorded in the past 70 years. In fact, the only time it was lower was in a brief period occurring right before the 2008/09 recession. At a rate of 2.6%, consumers are spending 97.4% of disposable income. The graph below shows how this compares historically. [..] the savings rate is less than half of that which occurred since the 2008/09 recession and well below prior periods.
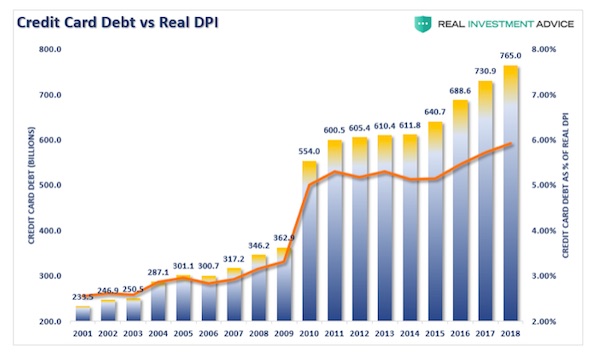
Credit Card Debt: In addition to reducing savings to meet basic needs or even splurge for extra goods, one can also use credit card debt. Confirming our suspicion about savings, a recent sharp increase in revolving credit (credit card debt) is likely another sign consumers are having trouble maintaining their standard of living. Over the last four quarters revolving credit growth has increased at just under 6% annually which is almost twice as fast as disposable income. Further, the 6% credit card growth rate is about three times faster than that of the years following the recession of 2008/09.

The liquidity super machine is stalling.
• 2018 Won’t Kill The Speculators. But It Will Teach Them A Lesson Or Two (Xie)
A decade of massive, synchronised monetary and fiscal stimulus has led to the greatest asset bubble in history, to the tune of about $100 trillion, nearly 1.5 times the world’s GDP. Compared to 2-3% of GDP growth in the global economy, we should be mindful of the potential and huge cost associated with it. Even though the US stock market is more expensive than in 1929 or 2000, and China’s property valuation is higher than Japan’s a quarter-of-a-century ago, fear-driven selloffs have been rare and brief, leading to the belief that high asset prices are the new normal. Massive amounts of financial and business activities, especially in technology, are predicated on high asset prices going higher. The unusual longevity and resilience of high asset prices are largely because government actions — not herd behaviour in the market — are force-feeding the bubble.
Government actions will lose their grip only when growth expectations crash or inflation flares up. Neither is a major risk for 2018. Hence, 2018 won’t kill the speculators of the world. But 2018 will teach them a lesson or two. High-risk assets such as internet stocks and high-end properties will struggle like never before in the past decade. US interest rates will rise above inflation for the first time in a decade. And China is tightening, especially in the property sector, out of fear of a life-threatening financial crisis. China accounts for about half of global credit growth. The interaction between the US Federal Reserve’s quantitative easing and China’s credit targeting has been the liquidity super machine. It is stalling in 2018. The asset bubble demands that the excess liquidity-money supply rises faster than GDP to sustain it.
This year may see global money supply line up with GDP. The Fed is likely to raise interest rates from the current 1-1.25% and take the level to 2.5%. This is still low compared with the 4.5-5% nominal GDP growth rate. But the US stock market is more expensive than it was in 1929 or 2000. When the interest rate surpasses inflation, it will become wobbly. Policymakers are caught between a rock and a hard place. The structural problems that led to the 2008 crisis are still here. The global economy grows ever more dependent on asset bubbles. If the global asset bubble bursts, the economy will slide into recession. Hence, when a market wobbles — as it probably will in 2018 — policymakers will come out to soothe market sentiment and may even temporarily reverse the tightening.

The EU is a feudal neo-liberal machine. There is no such thing as Soical Europe anywhere but in words. It’s about keeping the poor down, and dependent on your money.
• Minimum Wage Awkward Pillar Of Emerging Social Europe (AFP)
Twenty-two out of 28 EU states have introduced a minimum wage, trumpeted as a key pillar in the construction of a social Europe. But huge disparities from one country to the next are fuelling resistance from opponents who see the policy as dragging down competitiveness, sovereignty as well as levelling down salaries. Brexit, as an expression of eurosceptic populism, has jolted the European Commission into going on the offensive as it looks to show the European Union is not just a common market but a bloc with a social dimension. A November 17 Social Summit for Fair Jobs and Growth last year set the ball rolling as all 28 EU members signed up to a Europe-wide charter on social rights, laying down 20 basic principles including statutory minimum wages as a mainstay of a policy framework to boost convergence.
“Adequate minimum wages shall be ensured, in a way that provide for the satisfaction of the needs of the worker and his/her family in the light of national economic and social conditions, whilst safeguarding access to employment and incentives to seek work,” according to the guidelines. But the non-binding declaration is, as such, merely symbolic, not least because “European treaties stipulate clearly that salaries come under the national purview,” notes Claire Dheret, head of employment and social Europe at the Brussels-based European Policy Centre (EPC). To date, the Gothenburg charter is being respected only partially, even if all but six EU states have a legal minimum wage, as witnessed by Eurostat data highlighting starkly varying levels from Bulgaria’s 460 leva (€235; $270) a month gross to €1,999 in Luxembourg, that is, nine times as much.
Even so, the discrepancy does shrink to around a factor of three when the cost of living in each state is taken into account. But the Eurostat data shows up major discrepancies between eastern and western states. Ten of the former pay a minimum of less than €500, whereas seven western EU members have set rates surpassing €1,300 euros. Five southern states pay between €650 and €850. The six without an official minimum, which have their own arrangements to cover the basic needs of low earners are Austria, Cyprus, Denmark, Finland, Italy and Sweden.


We can repeat this every day: the mess gets messier.
• Relations Between Britain And The EU Sink To A New Low (Ind.)
David Davis has been dragged into renewed war of words with Brussels over the Brexit transition period, accusing the EU of having a “fundamental contradiction” in its approach and wanting to “have it both ways” after a week of fruitless talks. Relations between Britain and the European Commission sank to a new low on Friday after Michel Barnier, the EU’s chief negotiator, casually claimed at a press conference the UK had cancelled an important meeting due to a “diary clash”. UK officials behind the scenes took offence to the claim and said the meeting had not been cancelled at all and instead took place in the afternoon. Mr Barnier sealed the state of mutual incomprehension, telling reporters in Brussels that he had “problems understanding the UK’s position” on the transition period.
In a statement issued on Friday afternoon after Mr Barnier’s press conference – a solo affair in contrast to previous joint outings – Mr Davis said the EU could not “have it both ways” on the transition period. “Given the intense work that has taken place this week it is surprising to hear that Michel Barnier is unclear on the UK’s position in relation to the implementation period,” he said. “As I set out in a speech two weeks ago, we are seeking a time-limited period that maintains access to each other’s markets on existing terms. “However for any such period to work both sides will need a way to resolve disputes in the unlikely event that they occur.

And collapsing social services, health care etc. It’s a choice, not a flaw.
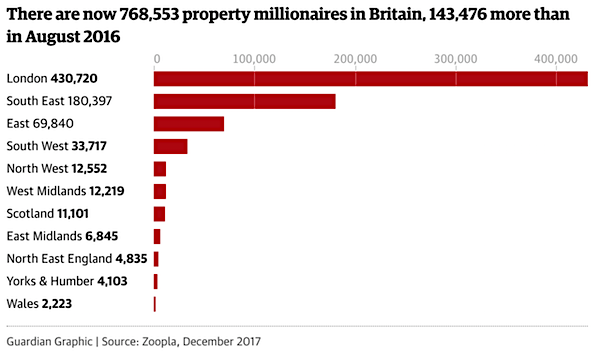
• UK Has More Than 750,000 Property Millionaires (G.)
There are now more than 750,000 property millionaires in Britain, and in some towns in the south of England half of all homes cost more than £1m, according to analysis by website Zoopla. Despite a slowing property market, Zoopla estimated that the number of property millionaires has climbed to 768,553, a rise of 23% since August 2016. The figures underscore the hugely lopsided nature of the UK property market. Yorkshire and Humberside has 4,103 property millionaires, and Wales 2,223, while in London the figure is 430,720. The figures suggest that while one in 20 people in the capital are paper property millionaires, the same can be said for only one in every 1,400 people in Wales. Zoopla did not take into account the mortgage debt attaching to properties, just the number of properties valued at over £1m.
Outside London, Guildford in Surrey is the town with the most property millionaires, estimated at 5,889, followed by Cambridge and Reading. But Beaconsfield in Buckinghamshire emerges as having the greatest concentration of property wealth in just one town. Zoopla found that 49% of all the houses in the town of 12,000 people nestled below the Chiltern Hills are valued at more than £1m. Agents in the town – dubbed Mayfair in the Chilterns – are currently marketing an opulent six-bed home in Beaconsfield’s “golden triangle” for £6m, boasting a cinema, wine-tasting room and its own six-person smoke-mirrored passenger lift opening on to a galleried balcony with a “Sexy Crystals” chandelier. There is a separate annexe for staff.

The EU plays the ultimate card: Scotland. The UK has no rebuttal. None. Nada.
• Brexit Plan To Keep Northern Ireland In Customs Union Triggers Row (G.)
Officials from the UK and EU are drawing up a plan to in effect keep Northern Ireland in the customs union and the single market after Brexit in order to avoid a hard border. The opening of technical talks followed a warning from Brussels that keeping the region under EU laws was currently the only viable option for inclusion in its draft withdrawal agreement. The development, first reported by the Guardian on Friday and later confirmed by the EU’s chief negotiator, Michel Barnier, triggered an immediate row. Scotland’s first minister, Nicola Sturgeon, tweeted: “If NI stays in single market, the case for Scotland also doing so is not just an academic ‘us too’ argument – it becomes a practical necessity. Otherwise we will be at a massive relative disadvantage when it comes to attracting jobs and investment.”
Anne-Marie Trevelyan, a Tory MP and officer in the European Research Group of Brexit-supporting Conservatives, accused Barnier of “playing hardball”. “I am surprised that the media are reporting his comments as if they are the only voice and hard fact,” she said. “Perhaps Mr Barnier could remember that the UK is in negotiations, which is a two-way discussion.” “It is important to tell the truth,” Barnier said. “The UK decision to leave the single market and to leave the customs unions would make border checks unavoidable. Second, the UK has committed to proposing specific solutions to the unique circumstances of the island of Ireland. And we are waiting for such solutions. “The third option is to maintain full regulatory alignment with those rules of the single market and the customs union, current or future, that support north-south cooperation, the all-island economy and the Good Friday agreement. “It is our responsibility to include the third option in the text of the withdrawal agreement to guarantee there will be no hard border whatever the circumstances.”

The present European commissioner for migration and home affairs is reported to have taken €40 million in bribes. He should lose his job, today.
• Greek PM Steps In To Police Exploding Novartis Bribery Investigation (FPh)
Just days after 10 former ministers in Greece were implicated in bribery allegations against Novartis, the country’s prime minister is calling for a special parliamentary committee to investigate the charges, which have been pegged as slanderous by some politicians pulled into the widening scandal. Meanwhile, three former Novartis executives believed to have provided the meat of the allegations have come under fire, even as their lawyer fights to shield their identities. The investigation targeting Novartis’s Greece offices has been going on since last January, but it blew up earlier this week when news emerged that the case would be submitted to the Greek parliament, which would then decide whether to prosecute the 10 politicians. Novartis is the target of allegations that it bribed doctors and government officials to help boost sales of its drugs.
Now Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras wants the special committee to look into allegations that the 10 politicians received millions of euros in exchange for fixing drug prices and granting other favors to Novartis, according to local press reports. A spokesman for Novartis told FiercePharma that the company continues “to cooperate with requests from local and foreign authorities.” Novartis has not received an indictment related to the investigation in Greece, he added. According to press accounts of the prosecutors’ report, the allegations of bribery stemmed from testimony from three witnesses who worked for Novartis. The witnesses spoke to the FBI, which joined in the investigation in Greece. The employees reported that Greece’s health minister from 2006 to 2009 took €40 million ($49 million) in exchange for ordering “a huge amount” of Novartis products, according to The Greek Reporter.
The health minister working between 2009 and 2010 allegedly accepted €120,000 ($147,000) from the company and laundered it through a computer hardware firm, the news organization added. At least one of the politicians named in the report wants the identities of the three Novartis witnesses to be revealed. Dimitris Avramopoulos, who was the health minister from 2006 to 2009 and now serves as European commissioner for migration and home affairs, held a press conference Friday during which he said he will file a lawsuit demanding the names of the witnesses be made public, according to Politico.

How dare he use the word sovereign in this context? Greece, like all other EU nations, was and is always sovereign. Demand his resignation.
• EU’s Moscovici Says Greece Will Be ‘Sovereign Country’ After Bailout (K.)
On exiting its third international bailout in August, Greece will be an “absolutely sovereign country,” European Economic and Monetary Affairs Commissioner Pierre Moscovici told a conference on Friday organized by the Stavros Niarchos Foundation Cultural Center (SNFCC), French magazine Le Nouvel Observateur and Kathimerini in Athens. “There should be no precautionary credit line,” Moscovici said. “There should be an end to the programs.” The commissioner said that Greece “did what it had to do” but that economic and structural reforms must continue. He also drew attention to an “issue of administrative competence,” without elaborating. In addition, Moscovici expressed his confidence in Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras, who he described as “smart and flexible,” adding that their relationship was “perfect.” Tsipras and Finance Minister Euclid Tsakalotos decided to “play ball,” Moscovici said. He further said Tsakalotos’s predecessor Yanis Varoufakis wreaked major political and financial damage on Greece.