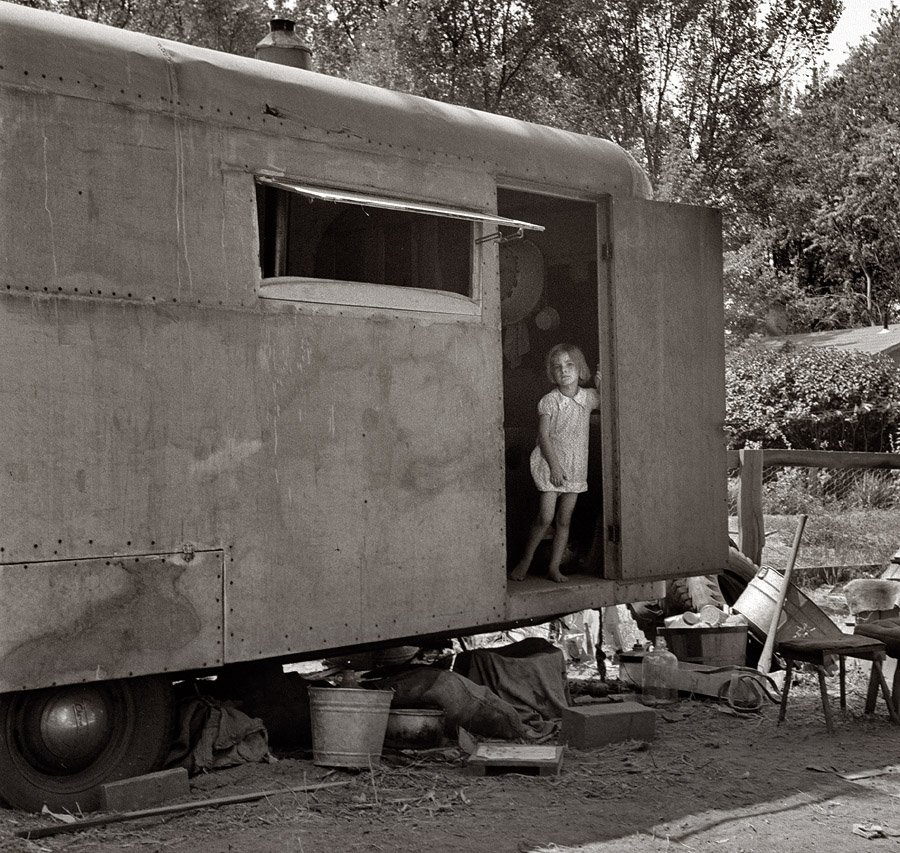
Walker Evans Vicksburg, Mississippi. “Vicksburg Negroes and shop front.” 1936



I think it’s more that we need to protect them from our own greed.
• We Must Protect Our Children From Austerity (Guardian)
The definition of a decadent society is one that destroys its own future, knowing full well the terrible consequences. On that basis, Britain is truly degenerate. Just look at how it trashes its children and teenagers. Our young are the very people on whom the rest of us will one day come to depend – to care for us, and to earn the country’s income. Rather than mere lifestyle accessories, to be slotted in alongside handbags and cars, they represent our best hope. This human truth has sustained societies around the world and down the ages. Yet in austerity Britain, children have been chucked to the bottom of the pile. They have been robbed of their rightful benefits. And the support they could once draw upon – everything from Sure Start centres to youth clubs to mental-health workers – has been hacked back.
Hyperbole? I really wish it were. Instead, I am merely repeating what professionals in field after field, from social care to mental health, are saying – and what the expert analysis shows. The landmark study of the social effects of David Cameron’s austerity was produced at the start of this year by a team of academics led by Professor John Hills at the London School of Economics. They found that the biggest victims of the spending cuts made since 2010 were children, and their parents: “Tax-benefit reforms hit families with children under five harder than any other household type. Those with a baby were especially affected.” None of this was accidental. Treasury officials stick each prospective change in tax and benefits under a Whitehall microscope – which is why so few budgets are an omnishambles.
When making their cuts, Cameron and George Osborne would have known that children and babies would suffer most – and proceeded regardless. Remember that next time you catch some commentator talking with great gravitas but little policy detail about the new compassionate Conservatism. Two things stand out in Cameron’s assault on children: it is precisely the opposite of what he promised, and exactly the reverse of what he himself knows any prime minister should be doing. Before coming to office, the Conservative leader unveiled a poster of a handsome tot: “Dad’s nose, mum’s eyes, Gordon Brown’s debt.” The whole point of cuts was “because we believe children like this deserve better”. One parliament later, the Trussell Trust reports that more than a third of the one million food parcels it gave out last year were for children.
Read more …

Due to our own lack of morals?!
• Greek Hospitals Out Of Painkillers, Scissors And Sheets Due To Austerity (RT)
Hospitals across Greece are lacking the most essential supplies, including painkillers, scissors and sheets, as years of economic meltdown have left the country’s healthcare system in a desperate state. The number of uninsured Greeks has reached 2.5 million compared to 500,000 in the pre-crisis year of 2008, the Times reported. Healthcare spending has dropped by 25% since 2009, leading to shortages of medical equipment and a lack of funds to pay nurses’ salaries. The country spends around €11 billion annually on its public healthcare system, which is one of the lowest rates in the EU.
According to media reports, some Greek patients have had to undergo painful medical procedures without anesthetics. People have also been turned away from hospitals, as they didn’t even have the equipment to measure their blood pressure, the newspaper learned. On one occasion, a patient was even asked to bring his own sheets to the infirmary from home. A trainee surgeon at KAT state hospital in Athens described the situation at his hospital as being at the “breaking point”. “There is no money to repair medical equipment, no money for ambulances to use for petrol, no money to hire nurses and no money to buy modern surgical supplies,” he told the Times.
In April, the new Syriza government vowed to battle the “barbaric conditions” in public hospitals, as well as corruption in the healthcare sector. Despite money shortages, Greek authorities abolished the €5 fee to visit state hospitals and have pledged to hire an additional 4,500 healthcare workers. “We want to turn the health sector from a victim of the bailouts, a victim of austerity, into a fundamental right for every resident of this country and we commit to do so at any cost,” Alexis Tsipras, the Greek Prime Minister, said. “We will not tolerate the exploitation of human pain,” Tsipras stressed.
Read more …

“..the creditors are responsible for the current mess by insisting on an economically illiterate adjustment programme.”
• The Key To A Greek Economic Revival Has To Be An End To Austerity (Münchau)
It is all up to Alexis Tsipras now. The Greek prime minister will decide soon whether or not he wants a deal with his creditors that would allow Athens to service its debt. If he says “no”, Greece will default. At that point, it is possible the country will have to leave the eurozone. What should he do? He will know his own political constraints. I will focus on the economics. The short answer is: if the deal is reasonable, he should accept. So where is the line between reasonable and unreasonable? The rough answer is whatever it takes to end the uncertainty. No investor is going to put their money into Greece so long as there is a threat of Grexit – a Greek exit from the eurozone. For an agreement to be viable, it would need to reduce the probability of Grexit to zero.
The same applies to the policies needed if Mr Tsipras says “no”. On that day he would need a brilliant economic plan. So what economic criteria should he apply to evaluate any offer? The single most important part of the agreement concerns the fiscal adjustment that Greece’s creditors are asking Athens to undertake. The variable to look out for is the primary surplus – the fiscal balance before payment of interest on debt: essentially the money a country has for debt servicing. There is no such thing as an objectively right or wrong number. But experience shows that large primary surpluses are politically unsustainable. It was the unsustainability of the previous agreement between Greece, its European creditors and the IMF that brought Syriza to power.
I heard a respected expert on this issue recently proclaim that a primary surplus of 2.5% of gross domestic product would probably work. The Greeks have demanded 1.5%, which is a reasonable opening bid. One of the so-called “non-papers” – the documents officials leak without leaving fingerprints – that are circulating among the negotiators had mentioned a figure of 3.5%, which strikes me as too high. A primary surplus of 4.5%, as was demanded from 2016 onwards by the previous loan agreement, is plainly ludicrous.
Greek economic mismanagement brought about the crisis in 2010, but the creditors are responsible for the current mess by insisting on an economically illiterate adjustment programme. They had not taken into account the fact that Greece is a relatively closed economy. This means that most of its GDP is produced and consumed at home. If you force such an economy into extreme austerity during a recession, it stays trapped. The key to a Greek economic revival has to be an end to austerity. This is why Grexit is not necessarily a solution, either, since it might bring even more fiscal consolidation. Greece would be cut off from international capital markets and unable to run a deficit.
Read more …

” Relative to the rest of the countries on the eurozone periphery, Greece was subjected to at least twice the austerity. There is nothing more to it than that.”
• Austerity Is the Only Deal-Breaker (Yanis Varoufakis)
A common fallacy pervades coverage in the world’s media of the negotiations between the Greek government and its creditors. The fallacy, exemplified in a recent commentary by Philip Stephens of the Financial Times, is that, “Athens is unable or unwilling – or both – to implement an economic reform program.” Once this fallacy is presented as fact, it is only natural that coverage highlights how our government is, in Stephens’s words, “squandering the trust and goodwill of its eurozone partners.” But the reality of the talks is very different. Our government is keen to implement an agenda that includes all of the economic reforms emphasized by European economic think tanks.
Moreover, we are uniquely able to maintain the Greek public’s support for a sound economic program. Consider what that means: an independent tax agency; reasonable primary fiscal surpluses forever; a sensible and ambitious privatization program, combined with a development agency that harnesses public assets to create investment flows; genuine pension reform that ensures the social-security system’s long-term sustainability; liberalization of markets for goods and services, etc. So, if our government is willing to embrace the reforms that our partners expect, why have the negotiations not produced an agreement? Where is the sticking point?
The problem is simple: Greece’s creditors insist on even greater austerity for this year and beyond – an approach that would impede recovery, obstruct growth, worsen the debt-deflationary cycle, and, in the end, erode Greeks’ willingness and ability to see through the reform agenda that the country so desperately needs. Our government cannot – and will not – accept a cure that has proven itself over five long years to be worse than the disease. Our creditors’ insistence on greater austerity is subtle yet steadfast. It can be found in their demand that Greece maintain unsustainably high primary surpluses (more than 2% of GDP in 2016 and exceeding 2.5%, or even 3%, for every year thereafter).
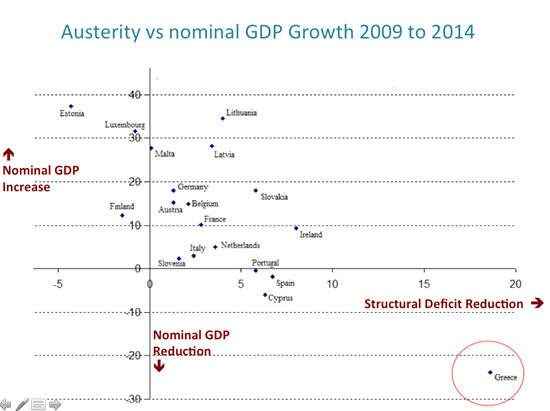
To achieve this, we are supposed to increase the overall burden of value-added tax on the private sector, cut already diminished pensions across the board; and compensate for low privatization proceeds (owing to depressed asset prices) with “equivalent” fiscal consolidation measures. The view that Greece has not achieved sufficient fiscal consolidation is not just false; it is patently absurd. The accompanying figure not only illustrates this; it also succinctly addresses the question of why Greece has not done as well as, say, Spain, Portugal, Ireland, or Cyprus in the years since the 2008 financial crisis. Relative to the rest of the countries on the eurozone periphery, Greece was subjected to at least twice the austerity. There is nothing more to it than that.
Read more …

Heart rendering. “Maybe the crisis makes us better people — but these better people will die if the crisis continues.” “They can take their money,” he said, using an expletive. “I feel ashamed to be a European.”
• Greece Is All But Bankrupt (NY Times)
Bulldozers lie abandoned on city streets. Exhausted surgeons operate through the night. And the wealthy bail out broke police departments. A nearly bankrupt Greece is taking desperate measures to preserve cash. Absent a last-minute deal with its creditors, the nation will run out of money early next month. Two weeks ago, Greece nearly defaulted on a debt payment of €750 million to the IMF. For the rest of this month, Greece should be able to cover daily cash deficits of around €100 million, government ministers say. Starting June 5, however, these shortfalls will rise sharply, to around €400 million as another I.M.F. obligation comes due. They will then double in size on June 8 and 9. “At that point it is all over,” said a senior Greek finance official.
On Sunday, the interior minister, Nikos Voutsis, said that there would not be enough money to pay the I.M.F. if there was no deal by June 5. In a society that has lived off the generosity of the government for decades, the cash crisis has already had a shattering impact. Universities, hospitals and municipalities are struggling to provide basic services, and the country’s underfunded security apparatus is losing its battle against an influx of illegal immigrants. In effect, analysts say, Greece is already operating as a bankrupt state. The government’s call to conserve funds has been far-reaching. All embassies and consulates — as well as municipalities throughout the country — have been told to forward surplus funds to Athens. Hospitals and schools face strict orders not to hire doctors and teachers.
And national security officials complain they are under intense pressure to keep air and sea missions to a minimum, at a time when migrants from Africa and the Middle East are rushing to Greece’s shores. Even the swelling ranks of investment bankers, lawyers and consultants advising the Finance Ministry have been told that, for now at least, their work is to be considered pro bono. Since its first bailout in 2010, Greece has been forced by its creditors to cut spending by €28 billion — quite a sum in a €179 billion economy. A proportional dose of austerity applied to the United States, for example, would come to $2.6 trillion.
=============
Sitting at his desk at the start of yet another 20-hour-plus workday, Theodoros Giannaros, the head of Elpis Hospital in Athens, chain-smoked cigarettes and signed off on a pile of spending requests that he said he knew would not be fulfilled. Since he started work at the hospital in 2010, Mr. Giannaros has seen his salary shrink to €1,200 a month, from €7,400. His annual budget, once €20 million, is now €6 million, and the number of practicing doctors has been reduced to 200 from 250. Like almost everyone in Greece, he is making do with less. The hospital recycles instruments; buys the cheapest surgical gloves on the market (they occasionally rip in the middle of operations, he says); and uses primarily generic drugs. “We have learned that we can live with a lot of money and survive with nothing,” he said.
“Maybe the crisis makes us better people — but these better people will die if the crisis continues.” Mr. Giannaros, who is 58, says he recently suffered a heart attack from the constant stress. But he says it is his surgeons he worries about most. In aging, depression-ridden Greece, treating the 150 or so patients that come to his hospital each day has put an extraordinary strain on his shrinking corps of doctors. The fact that many have begun to strike because they are not getting paid for overtime makes matters worse. Striding across the hospital grounds, Mr. Giannaros waved over his star surgeon, Dimitris Tsantzalos. How many operations did you do last year, he asked. “About 1,500,” said Dr. Tsantzalos, who, with his strapping build, seems younger than his 63 years. Recently he says he put in a month of consecutive 20-hour days and, not surprisingly, confesses to exhaustion. “I am burnt out,” he said. “It’s very dangerous for the patients.”
A week later, a tragedy struck Mr. Giannaros: His 26-year-old son, Patrick, committed suicide by jumping in front of an Athens subway train. “There was just an emptiness in front of him,” Mr. Giannaros said between wrenching sobs in a brief telephone conversation. “The emptiness of the future they have taken away from us.” His son had finished university studies and, unable to find work in a country where more than half the young are jobless, was helping Mr. Giannaros at the hospital. “He saw no future, no way to help his family,” Mr. Giannaros said. “Now God has found him a job — as an angel.” While Mr. Giannaros said he understood the importance of staying current with important creditors like the I.M.F., he said enough was enough. “They can take their money,” he said, using an expletive. “I feel ashamed to be a European.”
Read more …

Nothing new.
• The World Is Drowning In Debt, Warns Goldman Sachs (Telegraph)
The world is sinking under too much debt and an ageing global population means countries’ debt piles are in danger of growing out of control, the European chief executive of Goldman Sachs Asset Management has warned. Andrew Wilson, head of Europe, Middle East and Africa (EMEA), said growing debt piles around the world posed one of the biggest threats to the global economy. “There is too much debt and this represents a risk to economies. Consequently, there is a clear need to generate growth to work that debt off but, as demographics change, new ways of thinking at a policy level are required to do this,” he said.
“The demographics in most major economies – including the US, in Europe and Japan – are a major issue – and present us with the question of how we are going to pay down the huge debt burden. With life expectancy increasing rapidly, we no longer have the young, working populations required to sustain a debt-driven economic model in the same way as we’ve managed to do in the past.” Mr Wilson used Japan, where gross government debt has climbed above 200pc of gross domestic product (GDP), as an example of where the ageing population could demographics were working against them. “[This] is evidently not sustainable over the long term,” he said.
The Organisation of Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has also sounded out a warning about Japan’s growing debt pile. The think-tank said gross government debt was on course to balloon to more than 400pc by 2040 if the government did not carry out reforms. Angel Gurria, the OECD’s secretary-general, said monetary stimulus and stronger growth alone would not be enough to haul the economy out of its two-decade malaise. “Japan’s future prospects depend on ensuring fiscal sustainability over the long term. With a budget deficit of around 8pc of GDP, the debt ratio is set to rise further into uncharted territory,” he said.
Others have warned privately that Japan’s debt mountain is unsustainable. “The crunch point is when it starts to run a current account deficit,” said one senior banker. “When they stop running a current account surplus and they need our money to survive, we’re not going to lend to them at 30 or 40 basis points.”
Read more …

Why insist on calling them investors?
• Investors Are Playing A ‘Greater Fool’ Game (George Magnus)
Speculative euphoria, even when encouraged by central banks, is defined by the way it ends — not with a whimper but with a bang. In this context, the so-called Bund “tantrum” may be no more than a hiccup in the context of deeply anomalous financial market conditions. Investors are still chasing low or negative yields in bond markets, fairly or fully valued equity markets, and rising property markets. Yet, it seems increasingly that, long-term investors aside, they are playing a greater fool game. One of the biggest anomalies in global financial markets is the persistence of zero real, or inflation-adjusted, policy rates in most advanced economies and zero or negative real bond yields alongside a surge in the volume of public and private debt that shows no sign of subsiding.
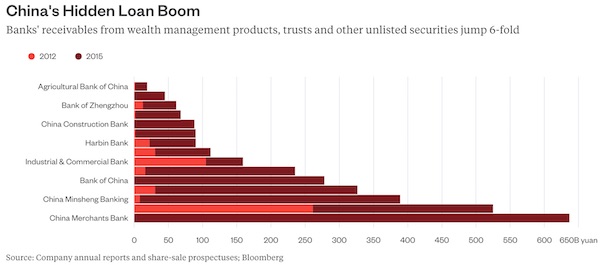
The Bank for International Settlements has mapped a 50% rise in debt outstanding in the world’s 12 largest economies since 2007 to more than $125tn at the end of 2014. A recently published McKinsey report on debt, covering 47 countries, highlighted an increase over the same period of $57tn to about $200bn, or a rise of about 20% of GDP to just under 290% of GDP. While developed markets accounted for the lion’s share of the build-up in debt up to the financial crisis and still dominate the aggregate debt-to-GDP league table, it is in emerging countries, least affected by the financial crisis, that debt has erupted since 2008. The most significant shift has occurred in Asia ex Japan, especially China, where aggregate debt to GDP has quadrupled over the past decade and the limits to debt capacity are fast approaching.
While domestic credit rises at twice the rate of money GDP growth, the toxic combination of rising leverage and slowing growth will continue to erode the nation’s ability to sustain debt accumulation. Eventually the authorities will have to clamp down on credit expansion. Global bond and equity markets remain largely oblivious to the relentless rise in indebtedness. The commonly accepted but also questionable narrative is that the Fed is severely constrained when it comes to raising policy rates, the ECB and the Bank of Japan remain committed to quantitative easing, and China is accelerating the pace of monetary accommodation. Cheap money, therefore, is around for the foreseeable future, and asset price inflation, even with occasional wobbles, is a given.
Read more …

A problem only for the perpetual growth crowd. Why should productivity always grow? That just leads to tinkering with things like our food.
• Weak Productivity Turns Into A Problem Of Global Proportions (FT)
Output per worker grew last year at its slowest rate since the millennium, with a slowdown evident in almost all regions, underscoring how the problem of lower productivity growth is now taking on global proportions. The Conference Board, a think-tank, said that based on official data on output and employment from most countries, only India and sub-Saharan Africa enjoyed faster labour productivity growth last year. Globally, the rate of growth decelerated to 2.1% in 2014, compared with an annual average of 2.6% between 1999 and 2006, it said.
Bart van Ark, the Conference Board’s chief economist, said total factor productivity, which takes account of skill levels and investment as well as the number of workers, fell 0.2% in 2014. “This is a global phenomenon and so we have to take it very seriously,” he said. Economists are increasingly identifying the problem of low global productivity as one of the greatest threats to improved living standards, in rich and poor countries alike. The fact that companies have become less efficient at converting labour, buildings and machines into goods and services is beginning to trouble policy makers around the world.
Janet Yellen cited weak US productivity as a cause of “the tepid pace of wage gains in recent years” on Friday. Also last week, George Osborne, UK chancellor, set higher productivity as the most important economic priority of the new government. “Our future prosperity depends on it,” he said. Raising productivity is seen as one of the only ways to improve living standards, at a time when advanced and some emerging economies are seeing ageing populations and a rapidly increasing retirement rate. Without stronger productivity growth, the world may have to get used to much lower rates of economic expansion.
Read more …

“Two years later, debt restructuring was on the table. And there it remains.”
• Greece, The EU And The IMF Are Dancing With Death (Coppola)
Over the last few months, the world has been watching with interest and growing concern the intricate moves in the deadly dance of Greece, the EU and the IMF. The latest move in the dance comes from Greece itself. The Interior Minister has announced that Greece cannot meet scheduled debt repayments to the IMF in June. This does not mean that Greece intends not to pay. Rather, it is warning that intransigence by the EU may force it into an IMF default. It is not the first time Greece has used the “IMF default” tactic. At the beginning of May, Greece said it couldn’t pay an IMF loan repayment. Then, in a surprising move, it drained its SDR reserve account at the IMF to make the payment.
This is effectively a short-term loan at a low interest rate from the IMF to Greece. And it is Ponzi finance – lending to a borrower so that he can service existing debts to the same lender. Using the SDR account solved Greece’s immediate cash shortfall, buying time for further negotiations. But it stores up further problems in the future. The SDR account will have to be topped up at some point. Interestingly, the IMF appears to have advised Greece to use the SDR account for the payment. And this makes me wonder what strategy the IMF is playing. It seems to have decided to cooperate with Greece. Superficially, the IMF’s aim is to recover the money it has already lent to Greece. But it has another, much larger concern. The Greek crisis is threatening the IMF’s own credibility.
The IMF’s involvement in the Greek bailout was controversial from the start. It broke its own rules in order to lend to Greece in 2010, arguing that systemic risks justified lending to a country whose debt was not by any stretch of the imagination sustainable over the medium-term. It was severely criticized by members of its own board of directors, notably by emerging-market representatives who were understandably miffed at what appeared to be special treatment accorded to Greece, or more accurately, to the Eurozone’s banks. The Brazilian representative, Paulo Nogueiro Batista, observed that the program: …may be seen not as a rescue of Greece, which will have to undergo a wrenching adjustment, but as a bailout of Greece’s private debtholders, mainly European financial institutions.
And the Swiss representative tellingly asked why debt restructuring with losses for creditors was not on the table. Two years later, debt restructuring was on the table. And there it remains. The 2012 “private sector involvement” (PSI) restructuring wrote down up to 80% of the net present value of Greece’s private sector debts. But much of the debt had already been transferred to the public sector, not only as a result of the 2010 bailout but also through subsequent IMF and EU loans and ECB support of Greece’s banks. The PSI restructuring reduced Greece’s debt to just over 150% of its GDP. Everyone knew that this was inadequate. Everyone knew that the official sector would have to suffer a haircut as well, and the longer it was delayed, the more costly it would be.
Read more …

One every day.
• Greek PM Convenes Emergency Meeting Of His Bailout Team (Guardian)
The high-stakes game of brinkmanship between Greece and its creditors intensified on Monday after the Greek prime minister convened an emergency meeting of his political negotiating team to avert a looming financial crisis. Amid mounting fears that Athens is close to running out of money, Alexis Tsipras said technical talks would resume to find a deal. To defuse tensions, he announced that Greece would honour its debts, though he failed to give details about how he would find the €1.6bn (£1.14bn) needed in two weeks’ time to repay an IMF loan. “We are very close to a deal,” the finance minister, Yanis Varoufakis, told reporters in Athens.
“There are many different Germans, just as there are many different Greeks,” Varoufakis added, responding to reports that Berlin would not be prepared to retreat in what has become an all-out tug of war between the two governments. Technical teams tasked with negotiating the framework of a cash-for-reform deal to keep the debt-stricken nation afloat, are now scrambling to break the deadlock of almost four months of fruitless talks. Both sides have signalled they will focus on VAT increases, expected to raise as much as €1bn for the Greek economy, when they reconvene in Brussels on Tuesday. Also on the table are pension reform, labour deregulation and the ever-incendiary topic of the primary surplus. Tsipras’s anti-austerity administration has argued vociferously that demands for a budget surplus higher than 1.5% will exacerbate the country’s economic death spiral.
Read more …

The ‘hard left’ already almost won the day. Tsipras’ room to move is shrinking.
• Greece’s Governing Left Divided Over Debt Terms (WSJ)
As financial pressure mounts on Greece to sign a deal with its foreign lenders, Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras is facing what may be his biggest problem yet: the struggle within the ruling Syriza party over whether to swallow creditors’ tough terms or default. Dissent is spreading within left-wing Syriza against the economic policies Greece is likely to have to enact in return for fresh bailout funding from other eurozone governments and the IMF. The Syriza-led coalition government holds only a thin majority of 12 seats in Greece’s 300-seat Parliament, so a rebellion against a deal could easily cost Mr. Tsipras his governing majority.
Greece’s lenders are particularly worried about vocal threats by Syriza’s Left Platform, a hard-line leftist faction within the party, to reject any deal that crosses ideological “red lines” by cutting pensions or workers’ rights. Mr. Tsipras’s difficulty in selling a painful compromise to Syriza’s hard left, as well as to other parts of his ideologically diverse party, has become the largest obstacle to a deal. European officials and analysts -and privately even Greek government officials- say they don’t know whether the roughly 30 lawmakers who make up Left Platform will vote as defiantly as they talk if creditors’ terms are put before the Athens Parliament. Greece needs to agree on a list of economic policies with lenders in time to avoid defaulting on a series of loan repayments to the IMF in mid-June.
Although the government probably has enough cash to repay a €300 million loan due June 5, it almost certainly can’t meet three further payments totaling about €1.25 billion on June 12, 16 and 19, European officials say. Greece needs a deal as soon as possible so it can service its IMF debts, government spokesman Gabriel Sakellaridis told reporters on Monday. “To the extent that we are in a position to pay our obligations, we will pay our obligations,” he said, adding: “It’s the government’s responsibility to be in a position to pay its obligations.” The European Central Bank has told eurozone governments it would allow Greek banks to buy more short-term Greek government debt if an economic-overhaul agreement between Athens and creditors is imminent. That would allow Greece to survive until July, when further debts fall due and fresh bailout loans will be needed.
Read more …

That’s just lip service. We all know by now it’s about politics only.
• IMF’s Blanchard Says Greek Budget Proposals Will Not Provide (Reuters)
Greece’s budget proposals are not enough to ensure a surplus this year, the IMF’s chief economist was quoted as saying on Monday. Greece was supposed to have a 3% budget surplus in 2015, but that looks unrealistic now, Olivier Blanchard told the French financial newspaper Les Echos in an interview. Lowering that surplus would lead to new financing needs, for which Greece would again need European help. That could work only if, in exchange, Greece presented a coherent programme, he said. “Considering that the most recent estimates mention a substantial budget deficit, we need credible measures to transform this into a surplus and maintain this surplus in the future,” Blanchard was quoted as saying. “This is far from being the case at the moment.”
Three weeks ago, the European Commission slashed Greek growth and surplus projections and said it expected Greece’s primary surplus – the budget balance before debt servicing costs – would be only 2.1% this year, rather than the 4.8% projected just three months earlier. It also expects the 2015 headline budget balance will deteriorate from a 1.1% surplus to a 2.1% deficit and expects the 1.6% surplus forecast for 2016 will turn into a 2.2% deficit unless policies change. “What is obvious is that the (Greek) pension system is often too generous and that there are still too many civil servants,” Blanchard told the newspaper at a central bankers’ meeting in Sintra, Portugal.
Read more …

“..French and German leaders do not have much in common with David Cameron”.
• Germany And France Agree Closer Eurozone Ties Without Treaty Change (Guardian)
Germany and France have forged a pact to integrate the eurozone without reopening the EU’s treaties, in a blow to David Cameron’s referendum campaign. Sidestepping Britain’s demands to renegotiate the Lisbon treaty and Britain’s place in the EU, the German chancellor, Angela Merkel, and the French president, François Hollande, have sealed an agreement aimed at fashioning a tighter political union among the single-currency countries while operating within the confines of the existing treaty. The Franco-German proposals are to be put to an EU summit in Brussels next month, where Cameron is also to unveil his shopping list of changes needed if he is to win support for keeping Britain in the EU.
The Franco-German accord, disclosed by Le Monde newspaper, calls for eurozone reforms in four areas “developed in the framework of the current treaties in the years ahead”. Cameron has persistently called for a reopening of the treaties to enable the eurozone to integrate more closely while providing the British with a chance to reshape the UK’s relations with the EU and repatriate powers from Brussels. EU members and senior officials in Brussels have repeatedly voiced their reluctance to reopen the Lisbon treaty – the EU’s fundamental constitutional document. The Franco-German initiative, likely to be endorsed by the 25 June summit, would definitively close the door on treaty renegotiation.[..]
The Franco-German pact, agreed as the Greek debt crisis comes to a head, was finalised last week on the fringes of the EU summit in Latvia and sent to Juncker at the weekend, Le Monde reported. The summit in Riga last Friday was Cameron’s first opportunity since re-election to present his ideas to fellow EU leaders. But it appeared that Merkel and Hollande had bigger fish to fry. Juncker is preparing policy options for the June summit on how to integrate the eurozone fiscally and politically as it struggles to emerge from more than five years of crisis. The Franco-German proposals are likely to settle the direction of policy.
They talk of economic, fiscal and social convergence, combining German insistence on monetary stability with French demands for greater investment. “Additional steps are necessary to examine the political and institutional framework, common instruments and the legal basis” (of the eurozone) by the end of next year, said the document, according to Le Monde. The following year, 2017, Germany and France have general elections, narrowing the scope for negotiations with Britain. The Franco-German policy proposal, said Le Monde, “shows that French and German leaders do not have much in common with David Cameron”.
Read more …

Brexit gets closer.
• UK’s Cameron Tells EC President That Europe Must Change (Reuters)
British Prime Minister David Cameron told the president of the European Commission that the country needed a new deal on Europe, before he presses his case for reforms to the bloc with other national leaders this week. Talks between Cameron and EC President Jean-Claude Juncker over dinner on Monday focused on reforming the European Union and renegotiating the UK’s ties with Brussels, a government spokeswoman said. “The prime minister underlined that the British people are not happy with the status quo and believe that the EU needs to change in order to better address their concerns,” she said. Juncker reiterated he wanted to find a “fair deal for the UK and would seek to help”, she said, and they agreed more discussions would be needed to find a way forward.
Cameron promised before the British national election earlier this month he would renegotiate Britain’s role in Europe, and hold a referendum on the country’s continuing membership of the bloc by the end of 2017. He launched his reform drive at a summit of EU and ex-Soviet states in Latvia last week, saying he was confident of winning concessions although it would not be easy. Cameron has said changes to rules on welfare benefits were an absolute requirement in any renegotiation. He wants to force EU migrants to wait four years before accessing a range of welfare benefits in Britain, and to win the power to deport out of work EU jobseekers after six months.
Read more …

“..bringing criminal charges against individuals and even sending some of them to jail would not disrupt the economy.”
• Banks as Felons, or Criminality Lite (NY Times)
As of this week, Citicorp, JPMorgan Chase, Barclays and Royal Bank of Scotland are felons, having pleaded guilty on Wednesday to criminal charges of conspiring to rig the value of the world’s currencies. According to the Justice Department, the lengthy and lucrative conspiracy enabled the banks to pad their profits without regard to fairness, the law or the public good. Besides the criminal label, however, nothing much has changed for the banks. And that means nothing much has changed for the public. There is no meaningful accountability in the plea deals and, by extension, no meaningful deterrence from future wrongdoing.
In a memo to employees this week, the chief executive of Citi, Michael Corbat, called the criminal behavior “an embarrassment” — not the word most people would use to describe a felony but an apt one in light of the fact that the plea deals are essentially a spanking, nothing more. As a rule, a felony plea carries more painful consequences. For example, a publicly traded company that is guilty of a crime is supposed to lose privileges granted by the Securities and Exchange Commission to quickly raise and trade money in the capital markets. But in this instance, the plea deals were not completed until the S.E.C. gave official assurance that the banks could keep operating the same as always, despite their criminal misconduct. (One S.E.C. commissioner, Kara Stein, issued a scathing dissent from the agency’s decision to excuse the banks.)
Also, a guilty plea is usually a prelude to further action, not the “resolution” of a case, as the Justice Department has called the plea deals with the banks. To properly determine accountability for criminal conspiracy in the currency cases, prosecutors should now investigate low-level employees in the crime — traders, say — and then use information gleaned from them to push the investigation up as far as the evidence leads. No one has thus far been named or charged. Nor has there been any explanation of how such lengthy and lucrative criminal conduct could have gone unsuspected and undetected by supervisors, managers and executives. The plea deals leave open the possibility of further investigation, but the prosecutors’ light touch with the banks makes it doubtful they will follow through.
Read more …

By their own main scientist.
• China Warned Over ‘Insane’ Plans For New Nuclear Power Plants (Guardian)
China’s plans for a rapid expansion of nuclear power plants are “insane” because the country is not investing enough in safety controls, a leading Chinese scientist has warned. Proposals to build plants inland, as China ends a moratorium on new generators imposed after the Fukushima disaster in March 2011, are particularly risky, the physicist He Zuoxiu said, because if there was an accident it could contaminate rivers that hundreds of millions of people rely on for water and taint groundwater supplies to vast swathes of important farmlands.
China halted the approval of new reactors in 2011 in order to review its safety standards, but gave the go-ahead in March for two new units, part of an attempt to surpass Japan’s nuclear generating capacity by 2020 and become the world’s biggest user of nuclear power a decade later. Barack Obama, the US president, recently announced plans to renew a nuclear cooperation deal with Beijing that would allow it to buy more US-designed reactors, and potentially pursue the technology to reprocess plutonium from spent fuel. The government is keen to expand nuclear generation as part of a wider effort to reduce air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, and cut dependence on imported oil and gas.
He, who worked on China’s nuclear weapons programme, said the planned rollout is going far too fast to ensure it has the safety and monitoring expertise needed to avert an accident. “There are currently two voices on nuclear energy in China. One prioritises safety while the other prioritises development,” He told the Guardian in an interview at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, where he is still working aged 88. He spoke of risks including “corruption, poor management abilities and decision-making capabilities”. He said: “They want to build 58 (gigawatts of nuclear generating capacity) by 2020 and eventually 120 to 200. This is insane.”
Read more …

“These are the only choices for the masses: whether to be a “doomer” or a “wisher.”
• Yesterday’s Tomorrowland (Jim Kunstler)
America takes pause on a big holiday weekend requiring little in the way of real devotions beyond the barbeque deck with two profoundly stupid movie entertainments that epitomize our estrangement from the troubles of the present day. First there’s Mad Max: Fury Road, which depicts the collapse of civilization as a monster car rally. They managed to get it exactly wrong. The present is the monster car show. Houston. Los Angeles. New Jersey, Beijing, Mumbai, etc. In the future, there will be no cars, gasoline-powered, electric, driverless, or otherwise. Mad Max: Fury Road is actually a perverse exercise in nostalgia, as if we’re going to miss being a nation of savages in the driver’s seat, acting out an endless and pointless competition for our little place on the highway.
The other holiday blockbuster is Disney’s Tomorrowland, another exercise in nostalgia for the present, where the idealized human life is a matrix of phone apps, robots, and holograms. Of course, anybody who had been to Disneyland back in the day remembers the old Tomorrowland installation, which eventually had to be dismantled because its vision of the future had become such a joke — starting with the idea that the human project’s most pressing task was space travel. Now, at this late date, the monster Disney corporation — a truly evil empire — sees that more money can be winkled out of the sore-beset public by persuading them that techno-utopia is at hand, if only we click our heels hard enough.
Another theme running through both films is the idea that girls can be what boys used to be, that it’s “their turn” to be masters-of-the-universe, that men are past their sell-by date and only exist to defile and humiliate females. That this message is really only a mendacious effort to rake in more money by enlarging the teen “audience share” for the reigning wishful fantasy du jour is surely lost on the culture commentators, who are so busy these days celebrating the triumph and wonder of transgender life. The reviewers are weighing these two movies on the popular pessimism / optimism scale. These are the only choices for the masses: whether to be a “doomer” or a “wisher.” Both positions are cartoon world-views that don’t provide much guidance for continuing the project of civilization, in case anyone is actually interested in that.
Read more …

“We got the dietary guidelines wrong. They’ve been wrong for decades.”
• Flawed Science Triggers U-Turn On Cholesterol Fears (Daily Mail)
For decades they have been blacklisted as foods to avoid, the cause of deadly thickening of the arteries, heart disease and strokes. But the science which warned us off eating eggs – along with other high-cholesterol foods such as butter, shellfish, bacon and liver – could have been flawed, a key report in the US has found. Foods high in cholesterol have been branded a danger to human health since the 1970s – a warning that has long divided the medical establishment. A growing number of experts have been arguing there is no link between high cholesterol in food and dangerous levels of the fatty substance in the blood. Now, in a move signalling a dramatic change of stance on the issue, the US government is to accept advice to drop cholesterol from its list of ‘nutrients of concern’.
The US Department of Agriculture panel, which has been given the task of overhauling the guidelines every five years, has indicated it will bow to new research undermining the role dietary cholesterol plays in people’s heart health. Its Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee plans to no longer warn people to avoid eggs, shellfish and other cholesterol-laden foods. The U-turn, based on a report by the committee, will undo almost 40 years of public health warnings about eating food laden with cholesterol. US cardiologist Dr Steven Nissen, of the Cleveland Clinic, said: ‘It’s the right decision. We got the dietary guidelines wrong. They’ve been wrong for decades.’ Doctors are now shifting away from warnings about cholesterol and saturated fat and focusing concern on sugar as the biggest dietary threat.
Read more …

Regard: your future.
• EU Dropped Pesticide Laws Due To US Pressure Over TTIP (Guardian)
EU moves to regulate hormone-damaging chemicals linked to cancer and male infertility were shelved following pressure from US trade officials over the Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership (TTIP) free trade deal, newly released documents show. Draft EU criteria could have banned 31 pesticides containing endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs). But these were dumped amid fears of a trade backlash stoked by an aggressive US lobby push, access to information documents obtained by Pesticides Action Network (PAN) Europe show. On 26 June 2013, a high-level delegation from the American Chambers of Commerce (AmCham) visited EU trade officials to insist that the bloc drop its planned criteria for identifying EDCs in favour of a new impact study.
Minutes of the meeting show commission officials pleading that “although they want the TTIP to be successful, they would not like to be seen as lowering the EU standards”. The TTIP is a trade deal being agreed by the EU and US to remove barriers to commerce and promote free trade. Responding to the EU officials, AmCham representatives “complained about the uselessness of creating categories and thus, lists” of prohibited substances, the minutes show. The US trade representatives insisted that a risk-based approach be taken to regulation, and “emphasised the need for an impact assessment” instead.
Read more …