Horacio Coppola Calle Corientes at the corner of Reconquista, Buenos Aires 1936

Out of stocks but into what?
• Global Equity Slump Deepens as Rate Fears Grow (BBG)
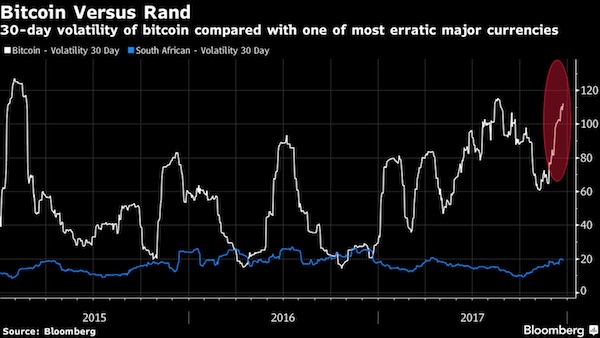
Asian equities fell and U.S. stock futures headed lower, extending the biggest selloff for global stocks in two years as investors adjusted to a surge in global bond yields. Shares sank across the region, with Japan’s benchmarks falling the most in 15 months. S&P 500 Index futures pared a drop of as much as 0.9%, signaling Friday’s rout won’t extend for another day. Shares in Hong Kong and Shanghai trimmed declines after China’s securities regulator urged brokerages to help stem the rout. Australia’s 10-year bond yield surged as the 10-year Treasury yield neared 2.87% after solid jobs data on Friday showed rising wages. The yen advanced. “It’s likely the pullback has further to go as investors adjust to more Fed tightening than currently assumed,” said Shane Oliver at AMP Capital Investors.
“The pullback is likely to be just an overdue correction, with say a 10% or so fall, rather than a severe bear market – providing the rise in bond yields is not too abrupt and recession is not imminent in the U.S. with profits continuing to rise.” The re-pricing of markets has come as investors question whether the Federal Reserve will keep to a gradual pace of monetary tightening, and whether it may need to end up boosting interest rates by more than previously expected in coming years. A higher so-called terminal rate for the Fed’s target implies higher long-term yields – raising borrowing costs across the economy. Yields on 10-year Treasuries have climbed to a four-year high from 2.40% at the start of the year. Last week’s decline for global stocks follows one of the best starts to a year on record amid hopes for ever-expanding corporate profits and growth in the world economy that’s broadening. The MSCI All Country World Index tumbled 3.4% last week, its biggest such slide since January 2016.

If anyone’s scared of inflation, they’re scared of the wrong thing. But perhaps that’s a fitting way to end a make-believe world.
• Stocks Punished As Inflation Shadow Spooks Bonds (R.)
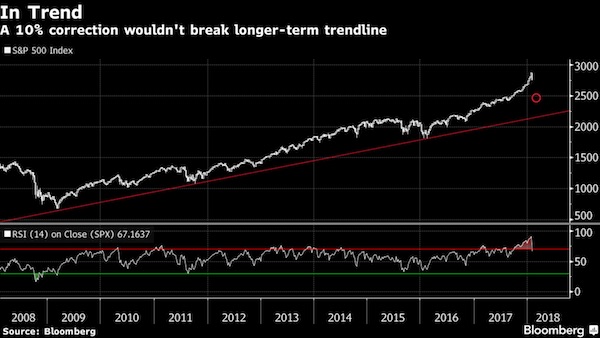
Wall Street had already been flashing expensive by many historical measures and sold off in reaction. “It has to be remembered that U.S. shares were priced for perfection at around 19 times earnings,” said Craig James, chief economist at fund manager CommSec, noting the historic average is around 15 times. “Still, U.S. companies have produced stellar earnings over the reporting period. So it is understandable that some ‘irrational exuberance’ would emerge.” With half of the S&P 500 companies having reported, 78% have beaten expectations against an average 64%. Chris Weston, chief market strategist at broker IG, noted the sudden spike in volatility caused some rules-based funds to automatically dump stock as their models required.
“There is talk that volatility targeting annuity funds could have to sell a further $30 billion of stock this week and another $40 billion should realized volatility not retreat lower,” he warned. The lift in U.S. yields provided some initial support to the dollar after a rocky start to the year, though it was starting to lose altitude again in Asian trade. Against a basket of currencies, the dollar was down a fraction at 89.123 having climbed 0.6% on Friday for its biggest single day gain in three months. The dollar backed off to 109.95 yen from an early 110.29, while the euro was barely changed at $1.2461. Any rally in the U.S. dollar is considered a negative for commodities priced in the currency, with the Thomson Reuters CRB index down 0.5%. Gold was off a touch at $1,332.04 an ounce after losing 1% on Friday.

Minskian fragility pops up its head.
• The Grand Crowded Trade Of Financial Speculation (Noland)
Even well into 2017, variations of the “secular stagnation” thesis remained popular within the economics community. Accelerating synchronized global growth notwithstanding, there’s been this enduring notion that economies are burdened by “insufficient aggregate demand.” The “natural rate” (R-Star) has sunk to a historical low. Conviction in the central bank community has held firm – as years have passed – that the only remedy for this backdrop is extraordinarily low rates and aggressive “money” printing. Over-liquefied financial markets have enjoyed quite a prolonged celebration. Going back to early CBBs, I’ve found it useful to caricature the analysis into two distinctly separate systems, the “Real Economy Sphere” and the “Financial Sphere.”
It’s been my long-held view that financial and monetary policy innovations fueled momentous “Financial Sphere” inflation. This financial Bubble has created increasingly systemic maladjustment and structural impairment within both the Real Economy and Financial Spheres. I believe finance today is fundamentally unstable, though the associated acute fragility remains suppressed so long as securities prices are inflating. [ZH: This week’s sudden burst of volatility across all asset-classes highlights this Minskian fragility]. The mortgage finance Bubble period engendered major U.S. structural economic impairment. This became immediately apparent with the collapse of the Bubble. As was the case with previous burst Bubble episodes, the solution to systemic problems was only cheaper “money” in only great quantities.
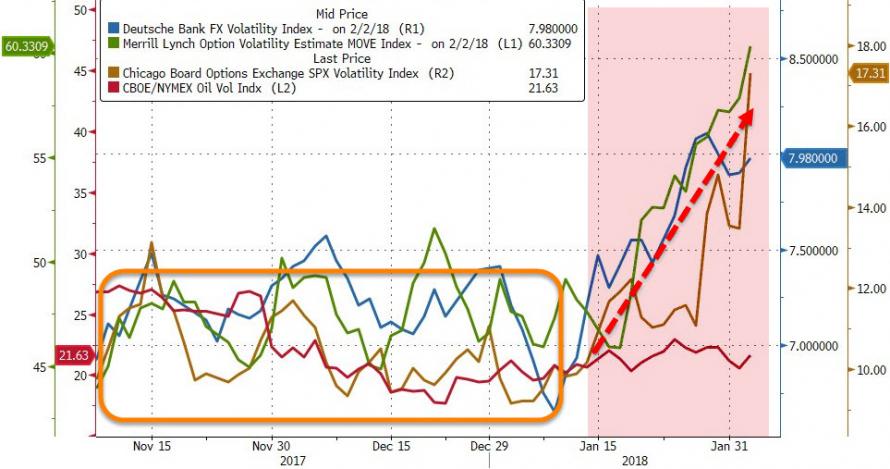
Moreover, it had become a global phenomenon that demanded a coordinated central bank response. Where has all this led us? Global “Financial Sphere” inflation has been nothing short of spectacular. QE has added an astounding $14 TN to central bank balance sheets globally since the crisis. The Chinese banking system has inflated to an almost unbelievable $38 TN, surging from about $6.0 TN back in 2007. In the U.S., the value of total securities-to-GDP now easily exceeds previous Bubble peaks (1999 and 2007). And since 2008, U.S. non-financial debt has inflated from $35 TN to $49 TN. It has been referred to as a “beautiful deleveraging.” It may at this time appear an exquisite monetary inflation, but it’s no deleveraging. We’ll see how long this beauty endures.

People need to be reassured, apparently.
• Don’t Panic. This Slump’s Just a Blip (BBG)
Is it a blip, a correction or the end of days? Stock markets in Asia tumbled Monday, extending the biggest global selloff in two years. Equity investors are fretting as Treasury yields approach 3%. On Friday, 10-year returns touched 2.85%, and the dollar rallied 0.9%. Some context, however. While the MSCI Asia ex-Japan Index’s 7.5% return in January was good, it’s not unprecedented. In January 2001, the benchmark soared 12.8%. Also, U.S. government bond yields have been on a steady rise since the start of the year, and that hasn’t stopped Asia from partying. A currency’s strength is dictated by interest rate differentials, in theory at least. And it’s unclear the dollar will get much stronger. Based on the Bloomberg Dollar Spot Index, which determines currency weights according to their relative importance to the U.S. in terms of international trade, one-third of the dollar’s value is dictated by the euro.
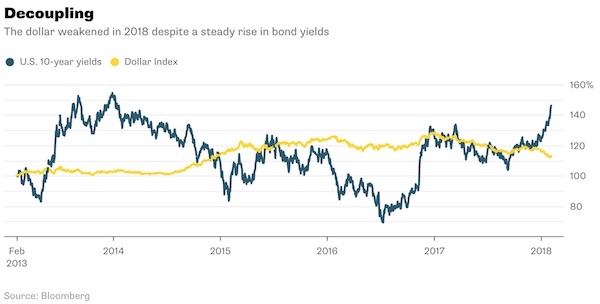
[..] But five-year bunds finally offered you something last week, after being negative since 2015. Next in line is the Japanese yen, which dictates 18% of the dollar’s value. There have been plenty of murmurings, from this columnist included, that the Bank of Japan will start stealth tightening, especially in a world of rising U.S. interest rates. After all, Japan’s central bank already owns an unprecedented 45% of the nation’s bond market; how much more entrenched can it get? Interest rates have been climbing in emerging Asia as well. Malaysia and Pakistan have both embarked on tightening cycles while the Philippines is expected to hike by 50 basis points this year. Interest rates in China and India are also on the up, as Beijing limits credit expansion and Delhi can’t stop spending. You get my point: Just because U.S. rates are strengthening doesn’t mean the dollar will necessarily follow suit.

Life in a fantasy world paid for by the Fed through taxpayers.
• This Isn’t the Start of a Major Downturn – JPMorgan (BBG)
Equities still feel like the right place to be relative to bonds for multi-asset investors, according to JPMorgan Asset Management. The pullback in risk assets among overbought conditions and stretched sentiment doesn’t look like the start of a major downturn, the money manager said. With economic and earnings growth remaining solid amid a real macro deterioration, “stretched valuations just aren’t enough to cause a big market sell-off,” said Patrik Schowitz, global multi-asset strategist at JPMorgan Asset, in a note. The firm oversees $1.7 trillion in assets. Asian equities fell and U.S. stock futures headed lower Monday, extending the biggest selloff for global stocks in two years as investors adjusted to a surge in global bond yields.
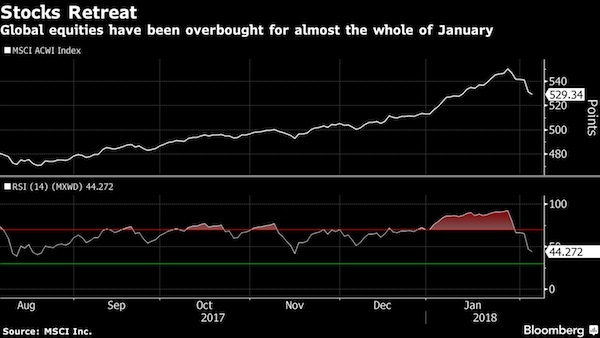
Investors are questioning whether the Federal Reserve will keep to a gradual pace of monetary tightening, and whether it may need to boost interest rates by more than previously expected in coming years. To be sure, the biggest “endogenous” risk the firm has been pointing to is rising bond yields. “The level of yields in absolute terms is not the issue, rather the velocity of the yield moves is what matters. Investors should continue to watch this closely,” said Schowitz. He said the firm has for some time flagged rising risks of a correction in risk assets on the back of increasingly more stretched positive sentiment in markets. “This move may yet turn out to be the start of something more significant, but so far it is pretty limited and it is likely that buyers will step in before we get near ‘real’ correction levels,” he said.

Because of accelerating US economic growth. Just wait five minutes.
• Gundlach: ‘Hard To Love Bonds At Even 3%’ Yield (R.)
Jeffrey Gundlach, the chief executive of DoubleLine Capital, says “it is hard to love bonds at even 3%” yield, given the backdrop for accelerating economic growth in the U.S. “It seems the tradable buy on bonds will need a flight-to-safety bid on a wave of fear washing over risk markets,” Gundlach told Reuters late on Saturday. “Hard to love bonds at even 3% when GDPNow for Q1 2018 is suggesting annualized nominal GDP growth above 7%.” The 10-year Treasury yield hit a four-year high on Friday after the latest jobs report showed solid wage gains, effectively confirming the expected rate increase at the Federal Reserve’s next meeting in March. Friday’s selloff contributed to the broad decline in U.S. government paper within the last week as inflation fears, strong economic data and an announcement of bigger Treasury auctions drove yields higher.
The yield on the 10-year Treasury note climbed 7.9 basis points to 2.852%, the highest since January 2014. “Treasury yields have been rising at a pace above 200 basis points annualized on parts of the (yield) curve since September,” said Gundlach, known as Wall Street’s Bond King. “This is partly caused by the manic mood and partly caused by the falling dollar and related rising commodities. Rates up significantly and dollar down significantly with exploding deficits is a dangerous cocktail reminiscent of 1987.” Last month, Gundlach predicted the S&P 500 may go up 15% in the first part of the year, but “I believe, when it falls, it will wipe out the entire gain of the first part of the year with a negative sign in front of it.”
On Saturday, Gundlach said: ”What matters to success this year is understanding that we entered a mania phase in 2017 that went completely out of control after September with the Bitcoin blowoff exhibiting exactly the same lunacy as the dot com blow off back in late 1999. “Similar to that period, but even more excessive this time -who’d have thought it possible – is the explosion of bullish sentiment, with some surveys registering 96%, 97%, even 100% bullish respondents. Long Island Blockchain. Kodakcoin. Cryptokitties. Sheer madness.” Gundlach said overall, the U.S. stock market is an odds-on favorite to turn in a negative return for 2018. “Whether Friday is the start of a crash or just the first chapter in the topping process is not the issue,” he said.

Highest production in 40 years.
• Oil Rally Is Unraveling On Fears Over A Rise In US Production (BBG)
Oil’s rally is unraveling on fears over a rise in U.S. production after crude’s best January in more than a decade. Futures in New York are extending declines for a second session as Baker Hughes data showed American explorers last week raised the number of rigs drilling for crude to the highest in almost six months. Short-sellers betting against West Texas Intermediate oil increased their positions for a third week, according to figures from the U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission. Crude has remained above $60 a barrel this year, extending a rally driven by the extension of an output deal until the end of 2018 by OPEC and its allies. While oil’s best start to the year since 2006 was also helped by falling U.S. inventories and a weaker greenback, Citigroup says the market is underestimating U.S. output growth as a bigger surge is forecast along with an increase capital spending.
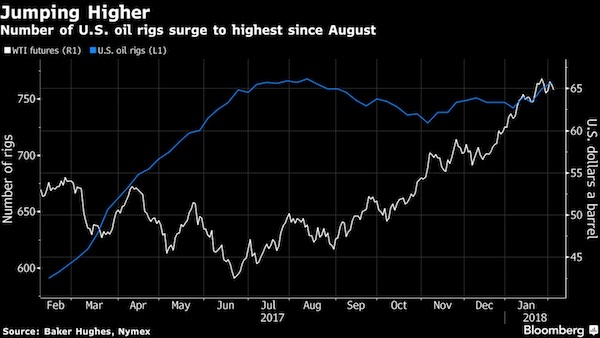
“With the higher U.S. oil rig counts and higher oil production sustaining into February, the concerns in the market seem to be valid at this point,” Barnabas Gan, an economist at Oversea-Chinese Banking Corp., said by phone from Singapore. “As these worries resurface, prices are edging lower.” [..] U.S. drillers last week added 6 rigs to raise the number of machines drilling for crude to 765, the highest since Aug. 11, Baker Hughes data showed Friday. That may lead to a further increase in U.S. crude production, which breached 10 million barrels a day to the highest level in more than four decades in November.

She starts at Bernanke’s think tank today. Good riddance.
• Yellen Says Prices ‘High’ for Stocks, Commercial Real Estate (BBG)
Outgoing Federal Reserve Chair Janet Yellen said U.S. stocks and commercial real estate prices are elevated but stopped short of saying those markets are in a bubble. “Well, I don’t want to say too high. But I do want to say high,” Yellen said on CBS’s “Sunday Morning” in an interview recorded Friday as she prepared to leave the central bank. “Price-earnings ratios are near the high end of their historical ranges.” Commercial real estate prices are now “quite high relative to rents,” Yellen said. “Now, is that a bubble or is it too high? And there it’s very hard to tell. But it is a source of some concern that asset valuations are so high.” Yellen, 71, stepped down as Fed chief on Saturday after one term, after President Donald Trump opted to replace her with Republican Jerome Powell, who’s been a Fed governor since 2012.
“I made it clear that I would be willing to serve, so yes, I do feel a sense of disappointment” about not being renominated, Yellen said. The only woman to serve as the head of the U.S. central bank described her work at the Fed as “the core of my existence.” Yellen said she’s supportive of former investment banker Powell, 64, whom she termed “thoughtful, balanced, and dedicated to public service.” The financial system is now “much better capitalized” and the banking system “more resilient” than they were entering the global financial crisis a decade ago, Yellen said. “What we look at is, if stock prices or asset prices more generally were to fall, what would that mean for the economy as a whole?” Yellen said. “And I think our overall judgment is that, if there were to be a decline in asset valuations, it would not damage unduly the core of our financial system.”
Yellen’s final act at the Fed was to hit one of the largest U.S. banks, Wells Fargo, with an unusual ban on growth that follows the lender’s pattern of consumer abuses and compliance lapses. In the interview that aired Sunday, she warned that it would be a “grave mistake” to roll back the regulations put on banks after the previous economic collapse. The current U.S. economic expansion is now approaching nine years and is the third longest in duration since 1945, according to the National Bureau of Economic Research. Yellen said the economy can continue to grow. “Yes, it can keep going,” she said. “Recoveries don’t die of old age.”

Never no holiday, Try and explain that in Europe.
• Overworked Americans Are Stuck In A Financial Groundhog Day (MW)
The U.S. had the fastest wage growth since 2009 in January. But in many other ways, American workers feel like they are working harder to achieve the same result. Does today feel a bit like yesterday, and the day before that? Feb. 2 is Groundhog Day. In the 1993 movie of the same name, Phil (Murray) wakes up at 6 a.m. only to find out that his day is actually exactly the same as the day before and the day before that. “I think people place too much emphasis on their careers,” he says. There may be a reason why that resonates with people in 2018. “Americans are doomed to relive the same reality each year: Forfeited vacation time, burnout, less time for loved ones, and negative consequences for health and well-being,” according to a report by the U.S. Travel Association’s Project Time Off. More than half of Americans (53%) are burned out and overworked, according to this survey of more than 2,000 workers by Staples Advantage, a division of office supplier Staples.
“We found that low pay and more hours is burning employees out and it causes up to half of what employees quit,” says Dan Schawbel, founder of WorkplaceTrends.com. Even so, year after year, most Americans say they are one paycheck away from the street with no emergency savings for a car repair or emergency room visit. But one reason for this exhaustion does not look like it will be changing anytime soon. Some 42% of workers took a vacation last year, according to a separate survey of more than 2,000 American adults released last year by travel site Skift using Google Consumer Surveys. (Nearly 40% only took 10 days or less.) One theory: Roughly one in four workers don’t get any paid vacation from their employers. Many are low-income workers and are the least able to afford to take an unpaid vacation day. Under the The Fair Labor Standards Act, the U.S. is also one of the few developed countries that does not require employers to provide paid time off.

At least I’m not the only one constantly saying this. Recovery is a mathematical impossibility for Greece.
• SYRIZA’s “Success Story”: Austerity By A Different Name (MintPress)
Initially, in May 2016, the Greek parliament passed a 7,500 page omnibus bill, sans any parliamentary debate, that transferred control over all of the country’s public assets to a fund controlled by the EU’s European Stability Mechanism for a period of 99 years – that is, until the year 2115. Not even Marty McFly and Doc Brown traveled that far into the future! Second, Greece’s loan commitments to the “troika” of lenders are set to continue, at the current rate of repayment, until 2059, as reported recently by the German newspaper Handelsblatt. That is the year when Greece is expected to have repaid the balance of the loans it has received, as part of its so-called “bailouts,” since 2010. The same article pointed out that the Greek government has made commitments to implement further austerity measures through 2022.
These measures — totaling €5.5 billion and agreed upon in June 2017 in what is, in essence, a fourth memorandum — include no less than 113 demands on the part of the troika, encompassing new privatizations of public assets and pension reductions. Other measures foreseen as part of this deal include a reduction in the tax- free income threshold and the further dilution of already-decimated worker rights. No increase in the also-decimated minimum wage is foreseen, nor are any new social measures to be implemented until 2023, despite Tsakalotos’ promises to the contrary. In connection with this agreement, assets slated for privatization include such strategic holdings as 25% of Eleftherios Venizelos International Airport in Athens, the remaining regional airports that have not already been privatized, Greece’s national defense industry, and the Corinth Canal.
Third, the SYRIZA-led coalition government has committed to the maintenance of annual primary budget surpluses of 3.5% through 2023, and then 2% annually through 2060. In plain language, what this means is that the state will spend less than it earns in revenues. If revenues therefore decrease, expenditures will be slashed accordingly. And, as foreseen in the 2017 deal between the Greek government and the troika, should there be shortfalls in these fiscal targets, automatic budget and spending cuts are to be immediately implemented through at least 2022. Here it should be noted that the net revenues of the Greek state declined in 2017, falling to €51.27 billion from €54.16 billion in 2016, leading in turn to a reduction in the pre-tax primary budget surplus from €2.78 billion to €1.97 billion. With state expenditures having reached €55.51 billion, Greece now faces a post-interest deficit of €4.24 billion, resulting in an increase in the country’s public debt.

WHy do people never get smallpox and measles at the same time?
• The Beautiful Cure – Immunology And The Heroes Of The Resistance (G.)
In 1989, Charles Janeway, a scientist at Yale University, had an epiphany that would revolutionise immunology. For 50 years, immunologists had subscribed to the dogma that vaccines worked by training the body to recognise molecules that were foreign to the body – “non-self” in immunological jargon. The usual way of doing this was to use vaccines to expose people to a dead or harmless version of a microbe, prompting the activation of antibodies that would be ready to swamp the germ should they encounter the alien entity a second time. But there were exceptions to the rule: sometimes, proteins separated from originating germs proved ineffective as vaccines; at other times, vaccines required the addition of an adjuvant, such as aluminium, to kickstart an immune response and no one could explain why.
What if, wondered Janeway, the presence of something that had never been in your body before was not sufficient to trigger an immune reaction? What if a second signal was required? Today, that second something is known as a pattern-recognition receptor and it is understood that there are countless varieties of them, each equipped to detect specific types of germs and switch on the appropriate immune responses. Together with an alphabet soup of other specialised cells, hormones and proteins, they form part of our innate immune system, helping us to distinguish harmful bacteria and viruses from beneficial ones, such as gut microbes essential for digestion. For Daniel Davis, professor of immunology at the University of Manchester, they constitute a “beautiful cure” more powerful than any product of a pharmaceutical laboratory.
Yet it is only in the past 30 years that immunologists such as Davis and Janeway, who died in 2003, have begun to shed light on these “wonders taking place beneath the skin”. In the process, they have found new ways to treat cancer, diabetes, arthritis and other age-related diseases. Immunologists are even beginning to understand the way in which immune responses are dependent on emotional and psychological states and the role that stress and exposure to light play in fighting disease. Given this, you would have thought that research into the workings of the immune system would be a top scientific priority. But while billions have been poured into the pursuit of the Higgs boson, immunology lacks a similar programmatic call-to-arms. Instead, Davis argues, immunology has always been a curiosity-driven science, a matter of “a few individuals following their nose”.

Filter feeders. The big boys and girls. Meaning: they ingest lots of plastic.
• Whale And Shark Species At Increasing Risk From Microplastic Pollution (G.)
Large filter feeders, such as baleen whales and basking sharks, could be particularly at risk from ingesting the tiny plastic particles, say scientists Whales, some sharks and other marine species such as rays are increasingly at risk from microplastics in the oceans, a new study suggests. Species such as baleen whales and basking sharks, which feed through filtering seawater for plankton, are ingesting the tiny particles of indigestible plastic which now appear to permeate oceans throughout the world. Some of these species have evolved to swallow hundreds or even thousands of cubic metres of seawater a day, but taking in microplastic can block their ability to absorb nutrients, and may have toxic side-effects. The new study, published in the journal Trends in Ecology and Evolution, advises more research on the megafauna of the oceans, as the effects of microplastics on them is currently not well understood.
Scientists have found, for instance through examining the bodies of beached whales, large pieces of plastic in the guts of such creatures, but the effect of microplastics, though less obvious, may be just as harmful. Elitza Germanov, a researcher at the Marine Megafauna Foundation and co-author the study, said: “Despite the growing research on microplastics in the marine environment, there are only a few studies that examine the effects on large filter feeders. We are still trying to understand the magnitude of the issue. It has become clear, though, that microplastic contamination has the potential to further reduce the population numbers of these species, many of which are long-lived and have few offspring throughout their lives.” Many species of whale, filter-feeding shark and rays are already under threat from other problems, such as overfishing and pollution. The added stress from microplastics could push some species further towards extinction, the authors of the study warned.