Arthur Rothstein Wasatch Mountains. Summit County, Utah 1940

It’s the investors and reporters that live in sweet spots.
• Bond Yields Moving From ‘Sweet Spot’ To Riskier Area (CNBC)
The 10-year Treasury yield is getting dangerously close to 3%, a level that some say will set off serious alarm bells for some stock investors. While the entire Treasury market is moving, the 10-year is the benchmark, the rate most widely watched by investors and the one tied to a whole range of business and consumer loans, including mortgages. On Wednesday, it rose to a fresh four-year high of 2.957%, and that helped turn a strong stock market rally after the Fed minutes into a bloodbath. The Dow closed down 166 points at 24,797. That puts the focus again on the bond market Thursday and the events that could impact trading. That would include an appearance by New York Fed President William Dudley on Thursday morning and a 7-year bond auction Thursday afternoon.
The 3% level does not necessarily have to stop the stock market’s bull run, but it is a level where the probability for losses in the S&P 500 increases, according to a new report from Bank of America Merrill Lynch. “You’re on the cusp of leaving the sweet spot, but that being said, the rising rates are not necessarily bad for the stock market. Yes, from your finance courses, a higher discount rate means you’re going to see lower valuations, all else being equal. But the ‘all else being equal’ missing ingredient is a high growth rate,” said Marc Pouey, equity and quant strategist at BofAML. Pouey said the “sweet spot” for stocks is a 10-year yield between 2 and 3%, but the fact that not only U.S. growth but global economic growth is strong makes it more likely that stocks will be able to positively navigate a zone where the 10-year is above 3%.

These buyers don’t exist.
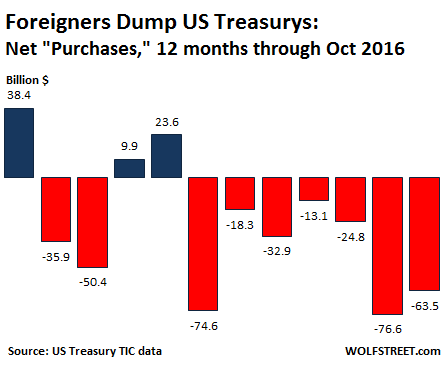
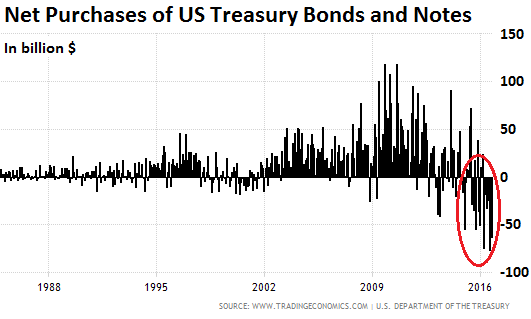
• Who Will Buy All Those Trillions of US Treasury’s? (Hamilton)
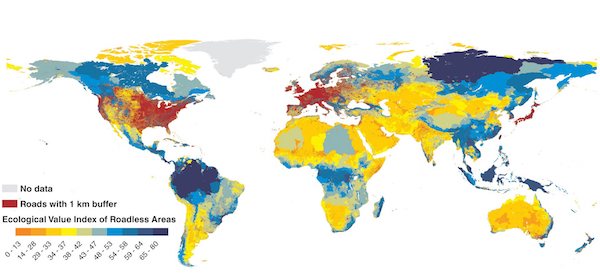
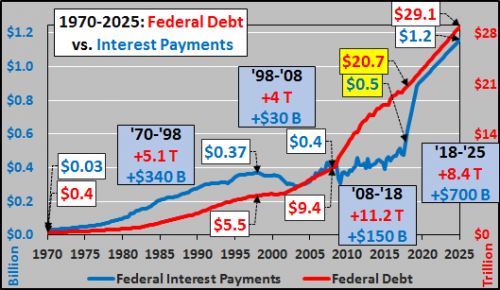
As of the latest Treasury update showing federal debt as of Wednesday, February 15…federal debt (red line below) jumped by an additional $50 billion from the previous day to $20.76 trillion. This is an increase of $266 billion essentially since the most recent debt ceiling passage. Of course, this isn’t helping the debt to GDP ratio (blue line below) at 105%.
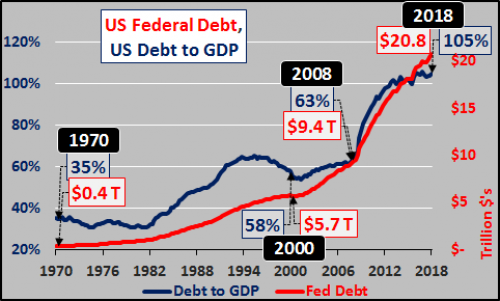
But here’s the problem. In order for the American economy to register growth, as measured by GDP (the annual change in total value of all goods produced and services provided in the US), that growth is now based solely upon the growth in federal debt. Without the federal deficit spending, the economy would be shrinking. The chart below shows the annual change in GDP minus the annual federal deficit incurred. Since 2008, the annual deficit spending has been far greater than the economic activity that deficit spending has produced. The net difference is shown below from 1950 through 2017…plus estimated through 2025 based on 2.5% average annual GDP growth and $1.2 trillion annual deficits. It is not a pretty picture and it isn’t getting better.
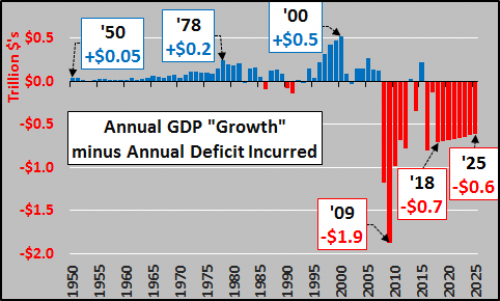
Even if we assume an average of 3.5% GDP growth (that the US will not have a recession(s) over a 15 year period) and “only” $1 trillion annual deficits from 2018 through 2025, the US still continues to move backward indefinitely.
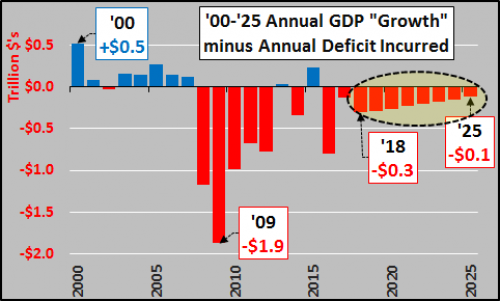
The cumulative impact of all those deficits is shown in the chart below. Federal debt (red line) is at $20.8 trillion and the annual interest expense on that debt (blue line) is jumping, now over a half trillion. Also shown in the chart is the likely debt creation through 2025 and interest expense assuming a very modest 4% blended rate on all that debt. So, for America to appear as if it is moving forward, it has to go backward into greater debt?!? If you weren’t troubled so far, here is where the stuff starts to hit the fan.

These guys can make themselves believe anything.
• A Major Misconception About The Market Exposed In One Chart (CNBC)
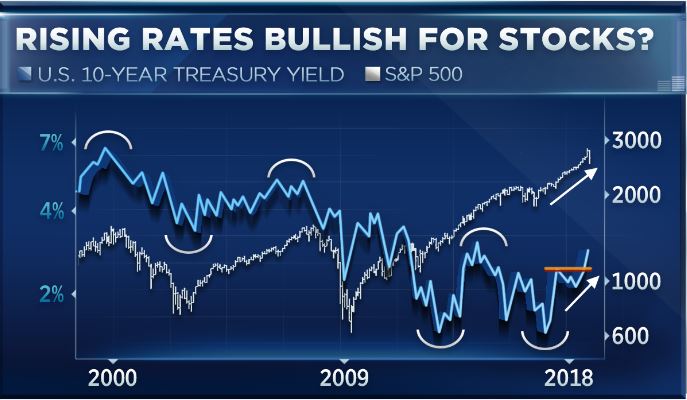
There’s one chart that could cast doubt on an age-old market adage. As Treasury yields hover around multiyear highs with the 10-year inching toward the 3% mark, Oppenheimer technician Ari Wald says that history shows that rising rates are actually bullish for the market. A more common belief is that a rising rate environment bodes ill for stocks, but Wald says the technicals point to the opposite. “The key point for us is that the direction of interest rates is equally, if not more important, than the level of interest rates,” he said Tuesday on CNBC’s “Trading Nation.” “So in general, we’re of the view that low and rising tends to be bullish for stocks and high and [falling rates] is what’s bearish.”
On a chart of the 10-year yield and the S&P 500 going back to 2000, Wald points out that since then falling interest rates have actually coincided with a drop in the market. “If you look back through history, you’ll see that it was a downturn in interest rates that coincided with market tops in 2000 and 2007, as well as what we’ve been calling the top in risk in that 2014 to 2015 period,” he said. “So we see rising rates as growth coming back into the market.” As a result, Wald believes that if investors are looking to put money to work, cyclical sectors like financials look to be a good bet right now. He cautions against bond proxies like utilities, telecom and real estate investment trusts as he believes they are going to “get hammered” in the current environment.

US housing approaches a bottleneck.
• Spiking Mortgage Rates, High Home Prices, New Tax Law, the Housing Market (WS)
The average interest rate for 30-year fixed-rate mortgages with a 20% down-payment and with conforming loan balances ($453,100 or less) that qualify for backing by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac rose to 4.64%, the highest since January 2014, according to the Mortgage Bankers Association’s Weekly Mortgage Applications Survey, released this morning. This chart shows the recent spike in mortgage rates, as reported by the MBA. There are two spikes actually: The spike off near-historic lows in the summer of 2016 (the absolute low was in late 2012) when the Fed stopped flip-flopping about rate hikes; and the spike when the subsequent rate hikes started belatedly driving up the 10-year Treasury yield late last year. It’s the 10-year yield that impacts mortgage rates. Note that, except for the brief mini-peak in 2013, the average mortgage rate would be the highest since April 2011:
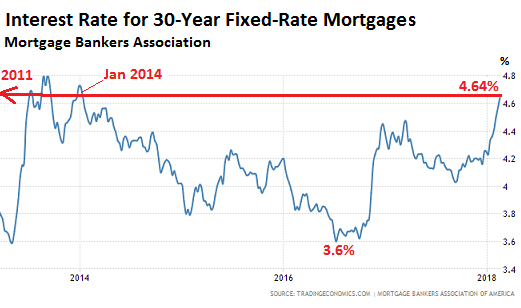
The average interest rate for 30-year fixed-rate mortgages backed by the FHA with 20% down rose to 4.58%, the highest since April 2011, according to the MBA. And the average interest rate for 15-year fixed-rate mortgages with 20% down rose to 4.02%, also the highest since April 2011. This may be far from over: “What worries investors is that if inflation increases faster than expected, the Fed may be obliged to ‘slam on the brakes’ to keep the economy from overheating by raising interest rates faster than expected,” the MBA mused separately. Home prices have skyrocketed in many markets since those years of higher mortgage rates, such as 2011 and before. The S&P CoreLogic Case-Shiller National Home Price Index has surged 40% since April 2011:
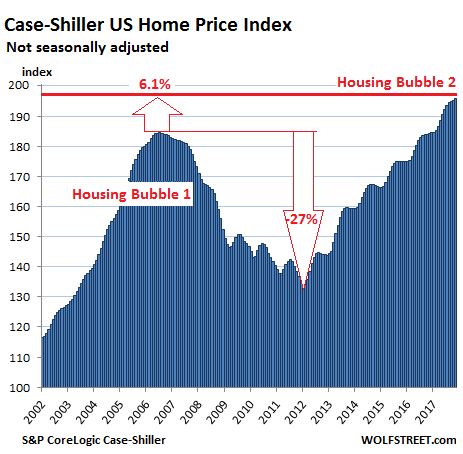
That’s the national index, which papers over the big differences in individual markets, with prices lagging behind in some markets and soaring in others. For example, in the five-county San Francisco Bay Area, according to the CaseShiller Index, home prices have surged 80% since April 2011:
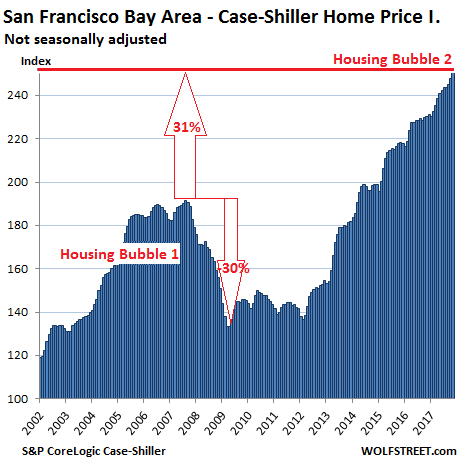
So with home prices surging for years and with mortgage rates now spiking, what gives? Today the National Association of Realtors reported that sales of existing homes fell 4.8% year-over-year in January – the “largest annual decline since August 2014,” it said – even as the median price rose 5.8% year-over-year to $240,000. I’m not sure if the new tax law, which removes some or all of the tax benefits of homeownership, has had an impact yet since it just went into effect. But the lean inventories and falling sales combined with rising prices tell a story of potential sellers not wanting to sell, and this could be exacerbated by the new tax law.
And they have a number of financial and tax reasons for not wanting to sell, including: • They’d lose some or all of the tax benefits that they still enjoy with their existing mortgages that have been grandfathered into the new law. • Given the higher mortgage rates that they would have to deal with on a new mortgage (which might exceed their existing rate by a good margin after repeated refinancing on the way down), and given the high prices of homes on the market, they might not be able to afford to move to an equivalent home, and thus cannot afford to sell.

Now try and square this with that recovery story.
• Existing US Home Sales In January See Biggest Drop In 3 Years (R.)
U.S. home sales unexpectedly fell in January, leading to the biggest year-on-year decline in more than three years, as a chronic shortage of houses lifted prices and kept first-time buyers out of the market. The supply squeeze and rising mortgage interest rates are stoking fears of a lackluster spring selling season. The second straight monthly drop in home sales reported by National Association of Realtors on Wednesday added to weak retail sales and industrial production in January in suggesting slower economic growth in the first quarter. “There may be some headwinds ahead for home resales with rising mortgage costs affecting how much the buyer can afford and this could put a damper on existing home sales and take some of the wind out of the economy’s sails,” said Chris Rupkey, chief economist at MUFG in New York.
Existing home sales dropped 3.2% to a seasonally adjusted annual rate of 5.38 million units last month, with purchases declining in all four regions. Economists polled by Reuters had forecast home sales rising 0.9% to a rate of 5.60 million units in January. Existing home sales, which account for about 90% of U.S. home sales, declined 4.8% on a year-on-year basis in January. That was the biggest year-on-year drop since August 2014. The weakness in home sales is largely a function of supply constraints rather than a lack of demand, which is being driven by a robust labor market. The shortage of properties is concentrated at the lower end of the market. While the number of previously-owned homes on the market rose 4.1% to 1.52 million units in January, housing inventory was down 9.5% from a year ago.

Everything is.
• Homeownership Is Increasingly For The Wealthy (CNBC)
The sharp drop in January home sales was not due to a shortage of homes for sale. It was due to a shortage of affordable homes for sale. While real estate economists continue to blame the pitiful 3.4-month supply of total listings (a six-month supply is considered a balanced market), a better indicator is a chart on the second-to-last page of the National Association of Realtors’ monthly sales report. It breaks down sales by price point. Sales of homes priced below $100,000 fell 13% in January year over year. Sales of homes priced between $100,000 and $250,000 dropped just more than 2%. The share of first-time buyers also declined to 29%, compared with 33% a year ago.
“Affordable inventory has been more depleted than expected and the upcoming spring homebuying season will likely be filled with bidding wars and multiple offers,” said Joe Kirchner, senior economist at Realtor.com. The biggest sales gains were in homes priced between $500,000 and $750,000, up nearly 12% annually. Apparently there are more of those homes for sale. That’s a problem, because higher price points are not where the bulk of buyers exist and especially not where most first-time buyers exist. If you look at sales distribution, about 55% of buyers are in the below $250,000 category. Just 13% are above $750,000. Unfortunately, the entry-level price point is not where most new-home builders exist either today, given the significantly higher costs of construction.
The median home price of a newly built home is around $335,000, according to the U.S. Census. The lower-price tier is, however, where investors exist. During the recession, when the supply of homes for sale was about four times what it is today, investors bought millions of properties, saving the housing market overall by putting a floor on tumbling home prices. Realtors say now is the time for those same investors to sell.

“..when US debt doubled in the past decade the Fed had no problems, and in fact enabled it. And now, it’s time to panic…”
• Dallas Fed President Kaplan Sounds Panic Over Level Of US Debt (ZH)
Nearly a decade after the US unleashed its biggest debt-issuance binge in history, doubling the US debt from $10 trillion to $20 trillion under president Obama, which was only made possible thanks to the Fed’s monetization of $4 trillion in deficits (and debt issuance), the Fed is starting to get nervous about the (un)sustainability of the US debt. The Federal Reserve should continue to raise U.S. interest rates this year in response to faster economic growth fueled by recent tax cuts as well as a stronger global economy, Dallas Federal Reserve Bank President Robert Kaplan said on Wednesday. “I believe the Federal Reserve should be gradually and patiently raising the federal funds rate during 2018,” Kaplan said in an essay updating his views on the economic and policy outlook.
“History suggests that if the Fed waits too long to remove accommodation at this stage in the economic cycle, excesses and imbalances begin to build, and the Fed ultimately has to play catch-up.” The Fed is widely expected to raise rates three times this year, starting next month. Kaplan, who does not vote on Fed policy this year but does participate in its regular rate-setting meetings, did not specify his preferred number of rate hikes for this year. But he warned Wednesday that falling behind the curve on rate hikes could make a recession more likely. [..] The most ironic warning, however, came when Kaplan predicted the US fiscal future beyond 2 years: he said that while the corporate tax cuts and other reforms may boost productivity and lift economic potential, most of the stimulative effects will fade in 2019 and 2020, leaving behind an economy with a higher debt burden than before.
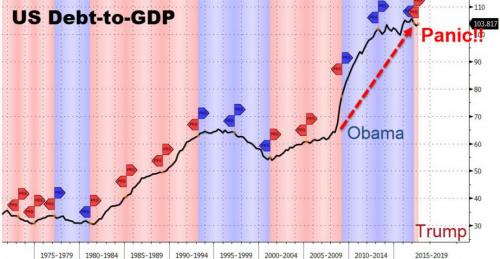
“This projected increase in government debt to GDP comes at a point in the economic cycle when it would be preferable to be moderating the rate of debt growth at the government level,” Kaplan said. A higher debt burden will make it less likely the federal government will be able to deliver fiscal stimulus to offset any future economic downturn, he said, and unwinding it could slow economic growth. “While addressing this issue involves difficult political considerations and policy choices, the U.S. may need to more actively consider policy actions that would moderate the path of projected U.S. government debt growth,” he said. So to summarize: when US debt doubled in the past decade the Fed had no problems, and in fact enabled it. And now, it’s time to panic…

Something’s in the air.
• Trump Gov’t May Make It Easier To Wipe Out Student Debt In Bankruptcy (CNBC)
Student loan borrowers may finally have their day in court. The Education Department said Tuesday it would review when borrowers can discharge student loans, an indication it could become easier to expunge those loans in bankruptcy. The department said it is seeking public comment on how to evaluate undue hardship claims asserted by student loan borrowers to determine whether there is any need to modify how those claims in bankruptcy are evaluated. As of now, “it’s almost impossible to discharge student loans in bankruptcy,” said Mark Kantrowitz, a student loan expert. “The problem was undue hardship was never defined and the case law has never led to a standardized definition.”
Meanwhile, college-loan balances in the United States have jumped to an all-time high of $1.4 trillion, according to Experian. The average outstanding balance is $34,144, up 62% over the last 10 years. Roughly 4.6 million borrowers were in default as of Sept. 30, 2017, also up significantly from previous years. The national student loan default rate is now over 11%, according to Department of Education data. Student loans are considered in default if you fail to make a monthly payment for 270 days. Your loan becomes delinquent the first day after you miss a payment. “I’m encouraged that they are asking the question,” Kantrowitz said of the Department of Education’s request for comment, although “this doesn’t necessarily mean there will be any policy changes.” And even still, bankruptcy should only be considered as a very last resort, he added.

“..what they’re doing is perpetuating a system that worked for their benefit but ended up costing jobs in most of the rest of the world..”
• Top US Treasury Official Slams China’s ‘Non-Market Behavior’ (R.)
The U.S. Treasury’s top diplomat ramped up his criticisms of China’s economic policies on Wednesday, accusing Beijing of “patently non-market behavior” and saying that the United States needed stronger responses to counter it. David Malpass, Treasury’s undersecretary for international affairs, said at a forum in Washington that China should no longer be “congratulated” by the world for its progress and policies. “They went to Davos a year ago and said ‘We’re into trade,’ when in reality what they’re doing is perpetuating a system that worked for their benefit but ended up costing jobs in most of the rest of the world,” Malpass said, at the event hosted by the Jack Kemp Foundation.
He said market-oriented, democratic governments were awakening to the challenges posed by China’s economic system, including from its state-owned banks and export credit agencies. He reiterated his view that China had stopped liberalizing its economy and was actually reversing these trends. “One of the challenges for the world is that as China has grown and not moved toward market orientation, that means that the misallocation of capital actually increases,” Malpass said. “They’re choosing investments in non-market ways. That is suppressing world growth,” he added. China said that its state-owned enterprises operate on free-market principles and is battling within the WTO’s dispute settlement system to be recognized as a “market economy” — a designation that would weaken U.S. and EU trade defenses.

Tightening the noose…
• Extending Brexit Transition Period Would Cost UK Billions More (Ind.)
Britain’s Brexit divorce bill will soar by billions of pounds if it tries to extend the transition period beyond the date suggested by Brussels, EU officials have told The Independent. Sources near the EU’s negotiating team said the UK would inevitably have to pay more – with the bill agreed by Theresa May already as high as £39bn – if it wants more time to prepare for its final break from the bloc. It came after a British Government document opened the way for a transition that could go on longer than the EU’s proposed end-date of 31 December 2020, though Downing Street was adamant the period will still be around “two years”. The prospect of a higher divorce bill, charged at millions of pounds a day, is likely to anger Tory Brexiteers as Ms May’s Cabinet gathers at Chequers today to try and hammer out a joint negotiating position for a trade deal with the EU.
Many hardline Eurosceptics are already uncomfortable with the idea of following EU rules with no say in making them – which some MPs have compared to making the UK a “vassal state”. One EU official close to talks told The Independent the financial settlement would “of course” have to be renegotiated if the transition extended into the next budget period, while another added: “Britain will have to pay for any transition beyond 2020, probably annual payments with no rebate.” In a statement published yesterday the Government said that the “period’s duration should be determined simply by how long it will take to prepare and implement the new processes and new systems that will underpin the future partnership” and that while “the UK agrees this points to a period of around two years” it “wishes to discuss with the EU the assessment that supports its proposed end date”.

Wonder who paid for the study.
• Give Antidepressants To A Million More Britons, Doctors Urged (Ind.)
More people should be offered drugs when suffering from mental health problems, according to a new study which calls into question recent concerns about over prescription. Research from Oxford University, which was published in The Lancet, found that more than one million extra people would benefit from being prescribed drugs and criticised “ideological” reasons doctors use to avoid doing so. Data from 522 trials, involving 116,000 patients, found that every one of the 21 antidepressants used were better than a placebo. In general, newer antidepressants tended to be better tolerated due to fewer side effects, while the most effective drug in terms of reducing depressive symptoms was amitriptyline – a drug first discovered in the 1950s.
“Antidepressants are routinely used worldwide yet there remains considerable debate about their effectiveness and tolerability,” said John Ioannidis of Stanford University, who worked with a team of researchers led by Andrea Cipriani. Mr Cipriani said the findings offered “the best available evidence to inform and guide doctors and patients” and should reassure people with depression that drugs can help. “Antidepressants can be an effective tool to treat major depression, but this does not necessarily mean antidepressants should always be the first line of treatment,” he told a briefing in London. The study looks at average effects and therefore should not be interpreted as showing how drugs work for every patient.

It’s clear where Der Spiegel stands: “Preparing for Chaos”, “Normal city life would be rendered impossible.”
Ironically, the bans may get support from the car industry, since many people and firms would need to buy new vehicles.
• Are Driving Bans Coming for German Cities? (Spiegel)
Emissions standards passed by the European Union in 2010 are regularly exceeded, essentially robbing residents of clean air to breathe. They have not, however, stayed quiet. Three years ago, 30 local residents launched a crusade against the city, demanding that traffic-calming measures be implemented and, ultimately, suing the city for inaction. In response, all they got were assurances that the city was looking into it or excuses that they didn’t have enough staff to deal with the problem. “Nothing has happened,” Lill says. That could change on Thursday. The Federal Administrative Court in Leipzig is set to consider whether vague plans to maintain clean air go far enough or whether problematic cities like Hamburg must ensure clean air as rapidly as possible, even if that means implementing driving bans. And there is plenty to indicate that the judges will prioritize health, just as lower courts in Düsseldorf and Stuttgart have done.
The landmark decision could very well send out shock waves affecting more than 60 municipalities in which, like Hamburg, limits on poisonous nitrogen oxide emissions are consistently exceeded. Germany’s major carmakers would also be put on notice, as would the German Chancellery and the ministries responsible. All have ignored the problem for years and are hardly prepared should the court prove stubborn. Things threaten to get even worse after that: Just a few weeks after the Leipzig ruling, the European Commission is also set to decide whether to initiate legal proceedings against Germany at the European Court of Justice for its failure to do anything about high levels of harmful emissions in its cities. Should Brussels decide to do so, it would clearly expose Berlin’s cozy relationship with the automobile industry at the expense of public health. “That would be a real disgrace for the German government,” says a state secretary in Berlin.
[..] The German government is now facing the consequences of its inactivity — or at least it will if the court rejects the appeals from Stuttgart and Düsseldorf against driving bans. Depending on the grace period the court decides on, the cities could be forced to close down their streets within three to six months. A verdict of that nature would destroy billions in value because drivers would suddenly be unable to drive into the city for work or to go shopping. Cars that already have to be marked down significantly in many places could then only be sold in foreign countries. Millions of cars would be affected by the ban and there is a possibility that even delivery vehicles and trucks belonging to craftsmen would not be permitted. Normal city life would be rendered impossible.

Did anyone actually believe they’d do something?
• Three Months On And Still No Action From Government On Plastic Pollution (Ind.)
MPs have attacked a three-month delay since the Chancellor pledged to tackle the huge environmental damage from plastic pollution – protesting that no action has followed. In his November Budget, Philip Hammond vowed to investigate new charges to make the UK a “world leader in tackling the scourge of plastic littering our planet and our oceans”. “We cannot keep our promise to the next generation to build an economy fit for the future unless we ensure our planet has a future,” he told the Commons. But, three months later, the Treasury has failed to start a consultation on what action to take, or even explain which Government department will run it. The protest comes from the Commons Environmental Audit Committee, which has – in the meantime – recommended a 25p charge is levied on all drinks sold in disposable cups, which are lined with polyethylene.
Mary Creagh, the committee’s chairwoman, said: “Pollution from single use plastic packaging is choking our oceans and devastating marine wildlife. “Three months ago, ministers promised to look at using the tax system reduce the use of throwaway plastics, but still have not published a call for evidence. “The Government has talked the talk on plastics pollution, but it has been too slow to walk the walk.” In a stinging letter, sent to Mr Hammond and Michael Gove, the Environment Secretary, the committee demands to know when ministers will set out action to curb the “700,000 plastic bottles that are littered every day”. “These are just one example of single-use plastics that can end up in our seas and oceans, killing wildlife and breaking down into harmful microplastics,” Ms Creagh added.