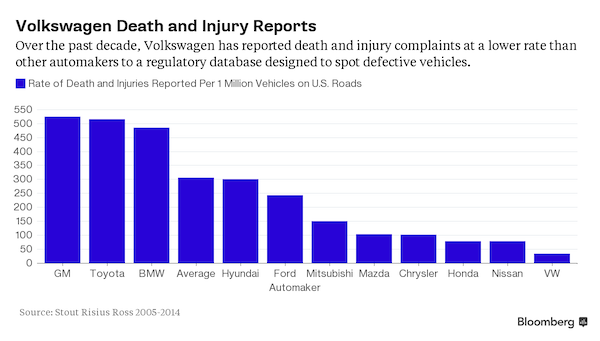
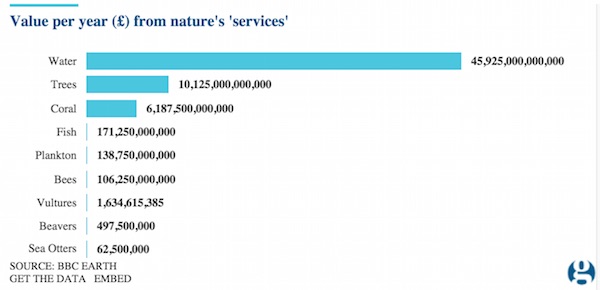
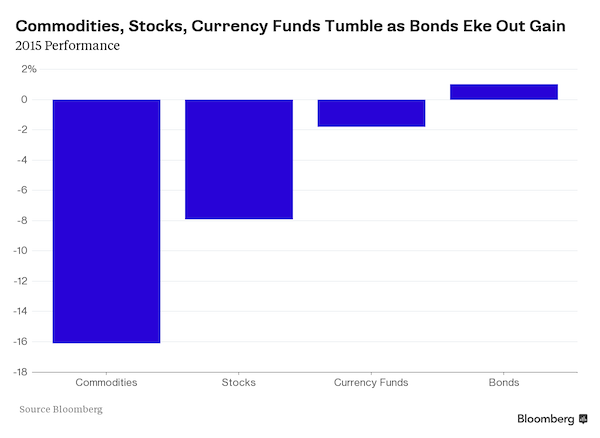
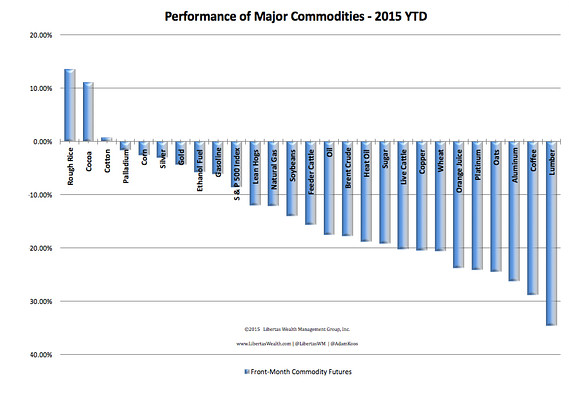
DPC League Island Navy Yard, Philadelphia. USS Brooklyn spar deck 1898



This is not reversible.
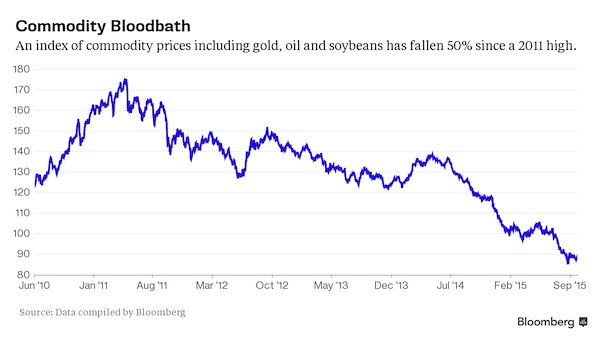
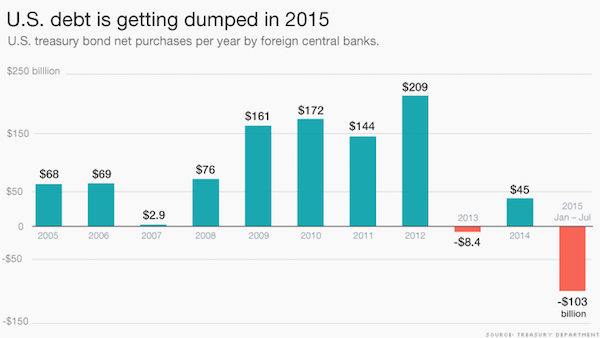
• The Biggest American Debt Selloff In 15 Years (CNN)
China has been selling U.S. debt but it’s not alone. Lots of emerging markets like Brazil, India and Mexico are also selling U.S. Treasuries. Not that long ago all these countries were all huge buyers of U.S. debt, which is viewed as one of the safest places to park money. “Five or six years ago, the big concern was that China was going to own the United States,” says Gus Faucher, senior economist at PNC Bank. “Now the concern is that China is selling them.” Foreign governments have sold more U.S. Treasury bonds than they’ve bought in the 10 consecutive months through July 2015, the most recent month of available data from the Treasury Department. Just in the first seven months of the year, foreign governments sold off $103 billion of U.S. debt, according to CNNMoney’s analysis of Treasury Department data.
Last year there was an overall increase of nearly $45 billion. It’s a reality of the global economic slowdown. When commodity prices boomed a decade ago, emerging market countries took their profits and invested them in U.S. Treasury bonds and other types of assets that are similar to cash. Now that commodity prices are falling, countries that rely on commodities – Brazil, Mexico, Indonesia – just don’t have the cash they once did to invest in safe assets like U.S. Treasury bonds. “Slow growth means that they just don’t have the same appetite for dollars because they don’t have cash to put to work,” says Lori Heinel, chief portfolio strategist at State Street Global Advisors. “The bigger issue is ‘do they have the dollars flowing into the economies to keep investing in Treasuries?'”

Interesting thought on PQE. Too little too late though.
• Inequality To Drive ‘Massive Policy Shift’: Bank of America (CNBC)
Rising income inequality and a deflationary global economic picture are going to lead to big changes in 2016, according to one Wall Street forecast. Quantitative easing and zero interest rates are on their way out in the U.S., and Michael Hartnett, chief investment strategist at Bank of America Merrill Lynch, believes they will be replaced with massive infrastructure spending. The result would benefit Main Street more than Wall Street, which has had a banner seven-year run helped by historically easy Federal Reserve monetary policy. “If the secular reality of deflation and inequality is intensified by recession and rising unemployment, investors should expect a massive policy shift in 2016,” Hartnett said in a note to clients. “Seven years after the West went ‘all-in’ on QE and ZIRP, the U.S./Japan/Europe would shift toward fiscal stimulus via government spending on infrastructure or more aggressive income redistribution.”
A reversal in trend would have a substantial impact on investing. Investors should move to assets that benefit in reflationary times, like Treasury Inflation Protected Securities, gold (which Hartnett thinks will bottom in 2016), commodities and small-cap Chinese stocks, Hartnett said. TIPs have been around flat for the year, while gold has dropped nearly 2% and commodities overall are off nearly 13%. Easy-money measures have helped boost Wall Street, with the S&P 500 up about 200% since the March 2009 lows as companies have spent some $2 trillion on stock repurchases. Dividend payments also have soared during the period, with the second quarter’s $105 billion increase the biggest in 10 years, according to FactSet.
Asset returns have jumped while global economic growth has been anemic in what Hartnett called “the most deflationary expansion of all time.” GDP gains in the U.S. have averaged barely 2% during the post-Great Recession recovery, while some economists believe a global recession could hit in 2016. The clamor for some of that asset wealth to find its way into the larger economy is growing and giving rise, according to Hartnett, to populist presidential candidates like Donald Trump and Bernie Sanders in the U.S. and similar movements around the world. “Deflation exacerbates ‘inequality’ of income, wealth, profits, asset valuations,” Hartnett wrote. “The gap between winners and losers is being driven wider and wider by excess liquidity and technological disruption (trends synonymous with the 1920s, another period infamous for ‘inequality’).”

China exports fell 20%. US exports are pluning. See the trend.
• At US Ports, Exports Are Coming Up Empty (WSJ)
One of the fastest-growing U.S. exports right now is air. Shipments of empty containers out of the U.S. are surging this year, highlighting the impact the economic slowdown in China is having on U.S. exporters. The U.S. imports more from China than it sends back, but certain American industries—including those that supply scrap metal and wastepaper—feed China’s industrial production. Those exporters have suffered this year as China’s economy has cooled. In September, the Port of Long Beach, Calif., part of the country’s busiest ocean-shipping gateway, handled 197,076 outbound empty boxes. They accounted for nearly a third of all containers that moved through the port last month. September was the eighth straight month in which empty containers leaving Long Beach outnumbered those loaded with exports.
The empties are shipping out at a faster rate at many U.S. ports, particularly those closely tied to trade with China, while shipments of containers loaded with goods are declining as exporters find it tougher to make foreign sales. That’s at least partly because the strong dollar makes American goods more expensive. Normally, after containers filled with consumer goods are delivered to the U.S. and unloaded, they return to export hubs. There, they typically are stuffed with American agricultural products, certain high-end consumer goods and large volumes of the heavy, bulk refuse that is recycled through China’s factories into products or packaging. Last month, however, Long Beach and the Port of Oakland both reported double-digit gains in exports of empty containers.
So far this year, empties at the two ports are up more than 20% from a year earlier. Long Beach’s containerized exports were down 8.2% this year through September, while Oakland’s volume of outbound loaded containers fell 12.7% from a year earlier in the January-September period. “This is a thermometer,” said Jock O’Connell at Beacon Economics. “The thing to worry about is if the trade imbalance starts to widen.” Trade figures released Tuesday in Beijing underscored China’s faltering demand. China’s imports fell 20.4% year-over-year in September following a 13.8% decline in August. As of June, U.S. exports of scrap materials were down 36% from their peak of $32.6 billion in 2011.

This is what deflation truly is: “The math is pretty simple: A lack of purchasing power for consumers has led to a lack of pricing power for companies.”
• Consumers Shutting Down As US Economy Deflates (CNBC)
The math is pretty simple: A lack of purchasing power for consumers has led to a lack of pricing power for companies. When it comes to the U.S. economy big-picture outlook, the ramifications are more complicated, and not particularly pleasant. Wednesday’s producer price index reading, showing a monthly decline of 0.5%, demonstrates a larger problem: At a time when policymakers are hoping to generate the kind of inflation that would indicate strong growth, the reality is that deflation is looming as the larger threat. Declining prices often would be treated as a net positive by consumers, but income weakness is offsetting the effects. Even Wall Street is feeling the heat. Prices for brokerage-related services and financial advice dropped 4.3% in September, accounting for about a quarter of the entire slide for final demand services.
The prospects heading into year’s end are daunting. In addition to the punk PPI number, retail sales gained by just 0.1% in September. Excluding autos, gasoline and building materials, sales actually declined 0.1%. On top of that, the August retail numbers were revised lower, with the headline rate now flat from the originally reported 0.2% gain. On the same day as the two disappointing data releases, Wal-Mart warned that the weakness is likely to extend through its fiscal year, with sales expected to be flat. The warning sent its shares tumbling 9% in morning trade, the worst performance in 15 years. All in all, then, not a great environment in which to raise rates, which the Federal Reserve hopes to do before the end of the year.
“Consumers are growing increasingly uncertain regarding their future income streams and are less willing to finance today’s spending with the prospect of tomorrow’s improved, future earnings,” Lindsey Piegza, chief economist at Stifel Fixed Income, said in a note to clients. “With gasoline prices at multiyear lows, consumers should be spending gangbusters but they aren’t.” Wage growth remains elusive for most workers, with the average hourly earnings rising just 2.2% annually. Job growth has slowed as well, with average monthly nonfarm payroll additions in the third quarter down nearly 28% from the previous quarter. The data on the ground shoot holes in a number of theories that were expected to drive the economy, market behavior and Fed policymaking.

Prices rise only in the West.
• The US Is Closer To Deflation Than You Think (CNBC)
Deflation talk these days is mostly centered on the euro zone and parts of emerging markets, but the U.S. is dancing on the brink itself. In fact, if not for a comparatively high inflation rate in the Western quadrant, the U.S. itself actually would have had a negative consumer price index rating in August, driving its economy into the same deflationary malaise found in other slow-growth regions. Of the four Census regions, only the West had a positive CPI for August, according to the most recent figures from the Bureau of Labor Statistics. And it hasn’t just been a recent occurrence. “All price growth in the U.S. in the past eight months came from the West,” the St. Louis Federal Reserve said in a report on geographic inflation influences. Inflation in the West has been a full percentage point above the other three regions, all of which experienced deflation.
Excluding the West, the national rate of inflation as measured by the CPI would have been -0.19% in August, as compared to the already anemic national rate of 0.2%, according to the St. Louis Fed. (The September reading will be released Thursday morning.) Annualized inflation in the West was 1.3% in August. In the Northeast it was -0.1%, -0.2% in the South and -0.3% in the Midwest. Much of the deflationary pressure came through falling energy prices – down 9.5% annualized in the West, 14.5% in the Midwest, 18.3% in the East and 17.1% in the South. Low inflation, and the possibility of deflation, presents a daunting conundrum for Fed officials, who have dismissed falling energy prices as transitory despite the fundamental factor of slowing global demand.
Wall Street has been waiting all year for signs the U.S. central bank would start down the path to normalizing monetary policy by raising rates for the first time in more than nine years. However, liftoff has been delayed as the FOMC has fussed over when conditions will be ideal for the move. More hawkish members want to raise because they worry the Fed will be too late once inflation accelerates, while also citing the need simply to have wiggle room for policy accommodation that the Fed does not have as long as it keeps its key rate near zero. Futures traders do not believe the Fed will hike until March 2016.

The direct result of falling consumer spending.
• Walmart Share Plunge Wipes Out $21 Billion In Market Cap In One Day (USA Today)
The Waltons had a bad – and expensive – day. Retailing giant Walmart stunned investors Wednesday when it gave disappointing guidance for growth and profit, sending its stock down 10% to $60.03. The stock drop, which was the biggest in decades, instantly wiped out more than $21 billion in shareholder wealth. That drop was bad for anyone who owns shares of Walmart. But it was especially painful for the company’s top 10 shareholders, who collectively own two-thirds of Walmart’s outstanding stock and saw $14.7 billion in wealth vanish Wednesday. The dive in Walmart shares hurt some of the wealthiest people in America including Walton family members Alice, Jim, John and S. Robson. Famed investor Warren Buffett’s Berkshire Hathaway also is a huge owner of Walmart stock.
Each was on the front line for one of the biggest implosions of a blue-chip stock in recent years. Walton Enterprises, an investment vehicle controlled by several members of the Walmart family, suffered the biggest hit. This investment vehicle owns 1.4 billion shares of Walmart, or 44% of the total shares outstanding, S&P Capital IQ says. Its holdings took a $9.5 billion hit. When you Include the holdings of other Walton family-controlled entities, such as the 197 million shares owned by S. Robson Walton and another 194 million held in the Walton Family name, the day’s loss jumps to more than $12 billion. Buffett’s Berkshire Hathaway owns 60.4 million shares of Walmart and lost nearly $405 million.
Don’t think it’s just a “rich person’s problem,” either. Walmart’s drop hit many individual investors closer to home. Index fund behemoth Vanguard is the fourth largest owner of Walmart stock because Walmart’s huge market value makes it a key holding in many index funds, which are widely held by individual investors. Vanguard’s 98.6 million shares brought home a $660 million daily loss directly to Vanguard investors. The pain of owning a big chunk of a single stock became painfully clear again Wednesday – especially if your last name is Walton.

As the no. 1 drops, so must the smaller fish.
• Wal-Mart Just Made Things Worse For Everybody Else (CNBC)
Wal-Mart shares had their worst day in 15 years Wednesday, after the world’s largest retailer said sales will be flat in fiscal 2016, while its earnings will slide to between $4.40 and $4.70 a share — down from $4.84 last year. Shares of competitors including Target, Macy’s, Kohl’s and J.C. Penney fell in sympathy, as Wal-Mart said it would invest billions into price over the next two years. With Wal-Mart already undercutting much of its peers, the move will put added pressure on its competitive set, which is already struggling to grow sales against a backdrop of steep price cuts and rock-bottom starting prices. Deflation in the retail sector was one reason why the National Retail Federation said that holiday sales will increase 3.7% this year, representing a deceleration from 2014.
Analysts and brands alike have said the holiday shopping season is already shaping up to be cutthroat, as retailers will do almost anything to get consumers to spend in their stores. “It’s a never-ending battle to capture their share of the overall spend,” Steve Barr, U.S. retail and consumer leader at PricewaterhouseCoopers, said Tuesday. It’s easy to understand why Wal-Mart, once the undisputed leader in pricing, is putting such an emphasis on delivering the best value to shoppers. According to PwC’s holiday forecast, 87% of shoppers said price is the primary driver behind their holiday spending choices. This is even more pronounced among what the consulting firm has dubbed “survivalists,” those who earn an annual income of less than $50,000.
According to PwC, 90% of survivalists said price is the No. 1 factor behind their holiday purchase decisions. Separately, a study released by coupon website RetailMeNot found consumers said a discount has to offer more than 34% off to be deemed a good deal. “I think we’ll see individuals taking advantage of the fact that prices haven’t moved against them this year,” the NRF’s chief economist, Jack Kleinhenz, said on a call after the trade group’s sales forecast.

“The most chilling words in the news release? “These are exciting times in retail given the pace and magnitude of change.”
• The Chilling Thing Wal-Mart Said About Financial Engineering (WolfStreet)
Wal-Mart had a bad-hair day. Its shares plunged $6.71, the largest single-day cliff-dive in its illustrious history. They ended the day down 10%, at $60.02, a number first kissed in 2001. Shares are 34% off their peak in January. So it wasn’t just today. But Wal-Mart didn’t do anything that special at its annual investor meeting today. It announced big “capital investments,” (we’ll get to the quotation marks in a moment), a crummy outlook, and a huge share buyback program. All of which it has done many times before. Only this time, the outlook is even worse, but the promised share buybacks are even larger. Wal-Mart proffered its strategies on how it would try to boost revenue growth in an environment where its primary customers – the 80% that got trampled by the Fed’s policies – are struggling to make ends meet.
A problem Wal-Mart has had for years. The news release hints at these new initiatives, spells out costs, and forecasts the resulting earnings debacle. Wal-Mart will goose “capital investments” by $11 billion in Fiscal 2017, on top of the $16.4 billion it’s spending on “capital investments” in fiscal 2016. This will maul earnings per share. In 2017, they’re expected to drop 6% to 12%, when the analyst community had forecast an increase of 4%. But 2019 is back in the rosy scenario of earnings growth. These capital investments aren’t computers, buildings, or new shelves. They’re largely “investments in wages and training,” which isn’t a capital investment at all, but an ordinary expense. “75% of next year’s investment will be related to people,” CEO Doug McMillon clarified.
That’s why they’ll hit earnings right away. A true capital investment would be an asset that is depreciated over time, with little earnings impact upfront. So sales in fiscal 2016 would be flat, which Wal-Mart blamed on “currency exchange fluctuations.” Would that be the strong dollar? But sales were also flat for the prior three fiscal years when the dollar was weak. Don’t lose hope, however. In the future, starting in fiscal 2017, sales would edge up 3% to 4%. To accomplish this, management is now desperately praying for inflation. The most chilling words in the news release? “These are exciting times in retail given the pace and magnitude of change.”
Then there was the announcement of a $20-billion share buyback program. $8.6 billion remaining from the $15 billion buyback program authorized in 2013 would be retired. That $15-billion program was on top of $36 billion in buyback programs over the preceding four years. Buybacks is what Wal-Mart does best.

Derivatives.
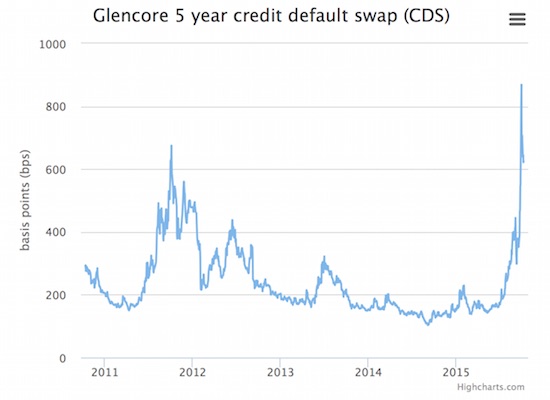
• Glencore Collapse Could Be Even Worse Than Feared (MM)
“Editor’s Note: We’re sharing this update on Glencore’s collapse with you because it’s shaping up to be even worse than Michael originally thought. Glencore still poses a “Lehman Brothers”-level risk to the global economy – but it’s now clear the world’s biggest commodities trader is on the hook for hundreds of billions in “shadow debt” that it simply refuses to address. This crisis is one small step away from upending our financial system, so here’s what you need to know…”
A lot of powerful voices have joined me in warning about the potential threat that Glencore poses to global financial markets. Bank of America, for instance, has published a report on the true size of the fallout. As you’ll see in a moment, it’s staggering. But since we talked about Glencore late last month, something insane has happened: The stock has gone up. But not for any good reason. The company has not righted the ship. The surge is only due to short-sellers covering their positions. The ugly truth is, the company is still a “shining” example of exactly what’s wrong with these markets. And I fear individual investors will get caught in the mess and wiped out on a stock like this or some of the others around it. That’s why I want to call out the misapprehensions and lies that are causing this “fauxcovery” and show you what’s next.
Because it could end up even worse than I thought…Since hitting a low of £0.69 ($1.05) per share on Sept. 28, Glencore stock has doubled to £1.29 ($1.97) per share. Even its credit default swap spreads have recovered to 650 basis points from a panic peak of 900 basis points. To place the last point in context, however, markets are pricing the company like a weak single B credit instead of a CCC credit. So while the major credit rating agencies still consider Glencore an investment-grade company, the actual credit markets have a much dimmer view of its prospects. Naturally, the company is doing everything possible to calm markets. First, last week it took the unusual step of publishing a six-page “funding factsheet” designed to dispel market concerns about its liquidity and solvency.
This factsheet shed very little light on what is really going on at the company, however. It said virtually nothing about Glencore’s derivatives contracts, other than stating that its derivatives contracts were undertaken within “industry standard frameworks.” Here’s the thing – “industry standard frameworks” normally require companies to post additional cash collateral upon the loss of an investment-grade rating, so the company’s statement should not have made anybody feel better. That suggests to me that the rise in the company’s stock price was largely a matter of short covering, not investors suddenly deciding that everything is hunky-dory in the House of Glencore.

Remember the metals bought with stored and unpaid metals as collateral?
• Unwinding Of Carry Trade May Unmask China’s True Metal Demand (Bloomberg)
The great mystery of metals is the amount used to finance the Chinese carry trade, or collateral used to borrow cheap dollars to buy yuan-backed high-interest-carrying notes. The Bank for International Settlements says this trade may be $1 trillion to $2 trillion, tying up tens of millions of metric tons of iron ore, aluminum and other metals. About a year of global copper consumption (22 million mt) equals just 5% to 10% of the estimate. The true figure will determine real China metal demand and future inventory. The impact of the Chinese metal carry trade is in the distortion of the true underlying copper demand, and a buildup in the metal’s inventory, strictly for collateral in financing. China accounts for 46% of global copper demand, according to the Word Bureau of Metals Statistics.
One question analysts must ask: What if it’s just 35%? The potential stopping of this trade, and normalization of the distorted demand, will provide understanding of China’s true copper needs and their potential growth. Nickel prices have fallen by half since year-end 2013, when they surged after No. 1 global exporter Indonesia banned exports of nonprocessed ore. Inventories are near record levels. The likely culprits for the higher inventory and price crash are the large amounts of the metal held off exchanges because they were used as collateral in a carry trade that took advantage of China’s high interest rates. A warehouse scandal at the Qingdao complex prompted banks to call in these trades, pummeling nickel prices.
The lucrative practice of using commodities as collateral to make money from interest-rate differentials inside and outside of China, a practice known as the carry trade, could cause significant pressure on commodity markets, were the trade to unravel. The Bank for International Settlements says this trade exceeds $1.2 trillion worth of commodities and could reach $2 trillion. Any major change in the direction of this trade could flood the market with more supply.


Actually, it’s a second defeat device. And that means it’s company policy, not a freak incident involving only technicians.
• VW: Secret Emissions Tool In 2016 Cars Is Separate From ‘Defeat’ Cheat (AP)
US regulators say they have a lot more questions for Volkswagen, triggered by the company’s recent disclosure of additional suspect engineering of 2016 diesel models that potentially would help exhaust systems run cleaner during government tests. That’s more bad news for VW dealers looking for new cars to replace the ones they can no longer sell because of the worldwide cheating scandal already engulfing the world’s largest automaker. Depending on what the Environmental Protection Agency eventually finds, it raises the possibility of even more severe punishment. Volkswagen confirmed to AP on Tuesday that the “auxiliary emissions control device” at issue operates differently from the “defeat” software included in the company’s 2009 to 2015 models and revealed last month.
The new software was first revealed to EPA and California regulators on 29 September, prompting the company last week to withdraw applications for approval to sell the 2016 model cars in the US. “We have a long list of questions for VW about this,” said Janet McCabe at EPA. “We’re getting some answers from them, but we do not have all the answers yet.” The delay means that thousands of 2016 Beetles, Golfs and Jettas will remain quarantined in US ports until a fix can be developed, approved and implemented. Diesel versions of the Passat sedan manufactured at the company’s plant in Chattanooga, Tennessee, also are on hold. Volkswagen already faces a criminal investigation and billions of dollars in fines for violating the Clean Air Act for its earlier emissions cheat, as well as a raft of state investigations and class-action lawsuits filed on behalf of customers.
If EPA rules the new software is a second defeat device specifically aimed at gaming government emissions tests, it would call into question repeated assertions by top VW executives that responsibility for the cheating scheme lay with a handful of rogue software developers who wrote the illegal code installed in prior generations of its four-cylinder diesel engines. That a separate device was included in the redesigned 2016 cars could suggest a multi-year effort by the company to influence US emissions tests that continued even after regulators began pressing the company last year about irregularities with the emissions produced by the older cars.

VW has provided precious little info for its clients. That’ll backfire.
• VW Customers Demand Answers And Compensation Over Emissions Scandal (Guardian)
Nine out of 10 Volkswagen drivers in Britain affected by the diesel emissions scandal believe they should receive compensation, increasing the pressure on the carmaker as it attempts to recover from the crisis. Almost 1.2m diesel vehicles in Britain are involved in the scandal, out of 11m worldwide, and VW faces a hefty bill if it is forced to make payouts to motorists. The company has put aside €6.5bn (£4.8bn) to deal with the cost of recalling and repairing the affected vehicles, but it also faces the threat of fines and legal action from customers and shareholders. There is a growing frustration among VW drivers in the UK over the lack of information about how their vehicle will be repaired, according to the consumer watchdog Which?. VW has sent letters to affected customers, arriving this week.
However, the letters state that the company is still working on its plans and another letter will be sent when these are confirmed. Paul Willis, the managing director of VW UK, told MPs on Monday that the recall of vehicles may not be completed by the end of 2016 and that it was premature to discuss compensation. However a survey by Which? has found that nine out of 10 affected motorists want compensation. Richard Lloyd, the executive director of Which?, said: “Many VW owners tell us they decided to buy their car based on its efficiency and low environmental impact, so it’s outrageous that VW aren’t being clear with their customers about how and when they will be compensated.
“Volkswagen UK must set out an urgent timetable for redress to the owners of the affected vehicles. We also need assurances from the government that it is putting in place changes to prevent anything like this happening again.” In the wake of the scandal, 86% of VW drivers are concerned about the environmental impact of their car, while 83% questioned the impact on its resale value and 73% feared the performance of their vehicle would be affected. More than half of the VW customers said they had been put off from buying a VW diesel car in the future. A total of 96% stated that fuel efficiency was an important factor in buying the diesel vehicle, while 90% said it was the seemingly limited environmental impact. Both these issues are affected by the scandal.

“..it’s unclear “why the results of so many combat sorties are so insignificant.”
• Lavrov: Unclear What Exactly US Is Doing In Syria (RT)
The Russian Foreign Ministry has questioned the effectiveness of the US-led year-long air campaign in Syria, saying it’s unclear “why the results of so many combat sorties are so insignificant.” Failing to curb ISIS, the US has now “adjusted” its program. “We have very few specifics which could explain what the US is exactly doing in Syria and why the results of so many combat sorties are so insignificant,” Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov told Russian channel NTV. “With, as far as I know, 25,000 sorties they [US-led air campaign] could have smashed the entire [country of] Syria into smithereens,” the minister noted.
Lavrov questioned the Western coalition’s objectives in their air campaign, stressing that Washington must decide whether its aim is to eliminate the jihadists or to use extremist forces to pursue its own political agenda. “Maybe their stated goal is not entirely sincere? Maybe it is regime change?” Lavrov said, as he expressed doubts that weapons and munitions supplied by the US to the so-called “moderate Syrian opposition” will end up in terrorists’ hands. “I want to be honest, we barely have any doubt that at least a considerable part of these weapons will fall into the terrorists’ hands,” Lavrov said. American airlifters have reportedly dropped 50 tons of small arms ammunition and grenades to Arab groups fighting Islamic State (IS, formerly ISIS/ISIL) in northern Syria.
US officials assure concerned parties that the fighters have been screened and are really confronting IS. “We do not want the events, when [some countries] not only cooperated with terrorists but plainly relied on them, to happen again,” Lavrov said, recalling that the French, for instance supplied weapons to anti-government forces in Libya in violation of a UN Security Council resolution. Lavrov has called on the US to “transcend themselves” and decide what is more important, either “misguided self-esteem realization” or getting rid of the “greatest threat” that is challenging humanity.

Scary.
• Two-Thirds Of British Hospitals Offer Substandard Care (Guardian)
Two-thirds of hospitals are offering substandard care, according to the NHS regulator, which also warns that pressure to cut costs could lead to a further worsening of the health service in the coming years. The Care Quality Commission also said that levels of safety are not good enough in almost three-quarters of hospitals, with one in eight being rated as inadequate. In its annual report, the watchdog detailed examples including one hospital where A&E patients were kept on trolleys overnight in a portable unit and not properly assessed by a nurse; while in another, medicine was given despite the patient’s identity not being properly confirmed. In some care homes, residents either received their medication too late or were given too much of it, leading to overdoses.
Understaffing and money problems are already contributing to a situation where 65% of hospitals, mental health and ambulance services either require improvement or are providing inadequate care.Too many patients are already receiving care that is unacceptably poor, unsafe or highly variable in its quality, from staff who range from the exceptional to those who lack basic compassion, it adds. In the report, England’s health and social care regulator raises concerns that patients could suffer as the service seeks to make the £22bn of efficiency savings by 2020 that NHS England has offered and health secretary Jeremy Hunt is pressing it hard to start delivering. “The environment for health and social care will become even more challenging over the next few years,” it states. “Tensions will arise for providers about how to balance the pressures to increase efficiency with their need to improve or maintain the quality of their care”.

As much humanity as refugees receive. “They can guard the car with 10,000 police officers if they wish..”
• Assange ‘In Constant Pain’ As UK Denies Safe Passage To Hospital For MRI (RT)
The UK has refused to grant Julian Assange safe passage to a hospital for an MRI scan and diagnosis, WikiLeaks has said, adding that he has been in “severe pain” since June. Assange’s lawyer has accused the UK of violating his client’s basic rights. WikiLeaks said that the UK government refused to satisfy Assange’s request to visit a hospital unhindered after the Ecuadorian Embassy filed one on his behalf on September 30. An MRI was recommended by a doctor, Laura Wood, back in August, according to the statement read aloud at a press conference given by Ecuadorian Foreign Minister Ricardo Patino on Wednesday.
“He [Julian Assange] has been suffering with a constant pain to the right shoulder region…[since June 2015]. There is no history of acute injury to the area. I examined him and all movements of his shoulder (abduction, internal rotation and external rotation) are limited due to pain. I am unable to elicit the exact cause of his symptoms without the benefit of further diagnostic tests, [including] MRI,” Patino read, citing a letter from the doctor. The UK’s Foreign and Commonwealth Office (FCO) issued a reply stating that Assange could not be guaranteed unhindered passage for a more thorough medical diagnosis on October 12.
Patino has criticized the decision saying that “even in times of war, safe passage are given for humanitarian reasons.” The Ecuadorian Embassy asked the UK authorities to offer a safe passage for a few hours for Assange into a London Hospital “under conditions agreed upon by UK and Ecuador,” Patino said, according to the WikiLeaks press release. “They can guard the car with 10,000 police officers if they wish,” the FM stressed, according to the press-release.

If Canada elects Harper again, forget about the country.
• Will Trudeaumania Sweep Canada’s Liberals Into Power – Again? (Guardian)
In the longest official federal election period in the nation’s history, it now appears Liberal leader Justin Trudeau may well be the nation’s next prime minister, with polls showing him establishing a commanding lead over his rivals, and the trend continuing to grow. It’s a stunning development in an election that could be described as an epic cliffhanger. Many, if not most, Canadians are eager for a change from prime minister Stephen Harper and his Conservative government, but with two worthy and eager rivals – the New Democratic party’s Thomas Mulcair and the Liberal party’s Justin Trudeau – where those change-hungry voters will place their bet has been difficult to decipher. When Harper announced the campaign in early August, it was met with immediate cynicism.
The extended campaign time (79 days as opposed to what had been the standard 37 days) gave the Conservatives an immediate advantage, given that their financial war chest is considerably larger than that of the Liberals or NDP. The Conservative strategy seemed a sound one: let the two opposition parties battle it out while the ruling party would float as much advertising as possible, handily winning over another majority. But the ruling party has faced considerable obstacles, including an astonishingly embarrassing ongoing scandal involving appointees to the unelected Senate (the Canadian version of the House of Lords) and a flagging economy. Polls have indicated many Canadians want change.
Ironically enough, one of the main reasons Canadians may have shifted their allegiances to the Liberal party leader is precisely because of the most famous negative ad campaign of the election, paid for and put into heavy rotation by the Conservatives. The ad, first rolled out in May by the Conservatives, has a group of people looking over an application by Justin Trudeau for the PM’s job. Perhaps most striking for its laughably bad acting, the ad has people concluding Trudeau is a lightweight who is “just not ready” for the job, with one concluding “nice hair, though”.
The ad attempts to suggest that not only is Trudeau simply not ready but voting for him is tantamount to a risky foray into untested waters, given the turbulent global economy and nagging threats of terror (the Cons have been playing both up at every turn). But a funny thing happened on the way through this fear-mongering: by just about any standards, Trudeau has run an excellent campaign. In late August he unveiled a campaign promise to invest billions of dollars in Canada’s roads, bridges, public transit and other public facilities. He suggested these were all necessary investments, which would help to stimulate the moribund economy, and went one step further, suggesting if he formed government, he would be open to deficit spending – moderate deficits, he cautioned, which would be over by 2019.

Europe has it coming.
• EU Need for Turkey to Halt Refugee Flow Collides With History (Bloomberg)
The EU needs Turkey more than ever to halt the flow of refugees from the Middle East – and has little to offer in return. With its decade-old bid to join the 28-nation union stalled, Turkey will be the topic without being at the table at a summit of EU leaders Thursday in Brussels. On the same mission, Angela Merkel plans to travel to Istanbul on Sunday to meet Turkish leaders. Relations have been all downhill since EU membership talks with Turkey began in 2005, years before civil war in neighboring Syria sent refugees streaming toward Europe. Turkey is stymied in part by Cyprus, its Mediterranean rival, and an anti-expansion mood in northern Europe. Meantime, a blossoming Turkish economy fed the sense that the country of 77 million could get along fine on its own.
“Many people in the EU are regretting the unproductive approach they had to the accession negotiations with Turkey, blocking the process and creating a deep sense of resentment in Ankara,” said Amanda Paul, an analyst at the European Policy Centre in Brussels. “If it were going along normally, it would be easier to reach this sort of agreement with Turkey.” Contacts are so strained that after President Recep Tayyip Erdogan went to Brussels on Oct. 5 to consider an “action plan” on migration, Turkish officials said the plan wasn’t discussed. EU Commission President Jean-Claude Juncker’s spokesman downgraded it to “an accord in principle to undertake a process.”
After Syria descended into war in 2011, European governments were content to let neighboring states such as Turkey, Lebanon and Jordan cope with the refugee influx. Only once Turkey amassed 2.2 million and they started heading northwest did European leaders wake up, finding themselves in the biggest refugee crisis since World War II. Germany, with a population of 81 million, is being roiled by this year’s expected arrival of at least 800,000 refugees, which is causing strains in Merkel’s governing coalition. “Turkey fears that even more refugees will come because the fighting in Syria isn’t letting up,” Merkel said Wednesday in a speech in eastern Germany. “I will fly to Turkey on Sunday to see how we can help on the ground so Turkey’s burden is shouldered more widely.”

“It’s just a political issue that is being ramped up by those who can use the excuse of even the smallest community as a threat to the sort of national purity of the state..”
• Refugee Rhetoric Echoes 1938 Summit Before Holocaust: UN Official (Guardian)
The dehumanising language used by UK and other European politicians to debate the refugee crisis has echoes of the pre-second world war rhetoric with which the world effectively turned its back on German and Austrian Jews and helped pave the way for the Holocaust, the UN’s most senior human rights official has warned. Zeid Ra’ad Al Hussein, the UN high commissioner for human rights, described Europe’s response to the crisis as amnesiac and “bewildering”. Although he did not mention any British politicians by name, he said the use of terms such as “swarms of refugees” were deeply regrettable. In July, the UK prime minister, David Cameron, referred to migrants in Calais as a “swarm of people”.
At this month’s Conservative party conference, the home secretary, Theresa May, was widely criticised for suggesting that mass migration made it “impossible to build a cohesive society”. In an interview, the high commissioner said the language surrounding the issue reminded him of the 1938 Evian conference, when countries including the US, the UK and Australia refused to take in substantial numbers of Jewish refugees fleeing Hitler’s annexation of Austria on the grounds that they would destabilise their societies and strain their economies. Their reluctance, Zeid added, helped Hitler to conclude that extermination could be an alternative to deportation.
Three-quarters of a century later, he said, the same rhetoric was being deployed by those seeking to make political capital out of the refugee crisis. “It’s just a political issue that is being ramped up by those who can use the excuse of even the smallest community as a threat to the sort of national purity of the state,” he said. “If you just look back to the Evian conference and read through the intergovernmental discussion, you will see that there were things that were said that were very similar.”

“..there are cases of Afghan children drowning off Greece that would touch the public deeply if publicised..”
• ‘Lesbos Is Carrying The Sins Of The Great Powers’ (ES)
Four rubber boats arrive in an hour, 40 to 50 people in each. One man nudges his two-year-old daughter towards me while he fetches his son. I try to soothe her tears. While two French doctors attend the injured, most of the new arrivals seem in good health and high spirits. Many of them, with their fashionable sportswear and smart backpacks, could be day-trippers. But it feels very different as night falls and the coach bearing me and my fellow Startup Boat activists — young volunteers trying to find tech and strategic solutions to the problems posed by the refugee crisis — takes us past a crowd of 150. None of the promised buses have arrived to take them to refugee camps at Moria and Karatape, 20 miles away.
Welcome to Lesbos, where in recent weeks 1,500-3,000 people — predominantly Syrians, then Iraqis and Afghans — have arrived daily, paying traffickers €1,200 for the short passage from Turkey. The former military camp at Moria has an official capacity of 410 but at times has housed 1,000, with hundreds camped outside. Karatape, set up specifically for Syrians, can take 1,000. While we were on Lesbos, a 24-hour period when police were off duty left Karatape at twice capacity, and food stores exhausted. The situation, says Lesbos mayor Spyros Galinos, is like “a bomb in my hands”. “I believe Lesbos is carrying the sins of great powers,” he says. “If this dot on the map could manage to accommodate such high numbers, all member states can help us.”
The problems extend beyond Syrian refugees. In Athens, young Afghan Mohammad Mirzay tells me why EU nations have made a “big mistake”, allowing Syrians the right to remain, however many countries they have travelled through, but not extending this to others. The Taliban are persecuting the Hazaras, he says, while there are cases of Afghan children drowning off Greece that would touch the public deeply if publicised. He takes me to Galatsi Olympic Hall, a venue at the 2004 Games, now designated a safe house. Families are camped in the fetid space. “Why should we be divided?” says Mirzay. “We should push in altogether. We should support ‘human’.”