Harris&Ewing Goat team, Washington, DC 1917



Because it has no morals.
• A Perfect Storm Of Crises Blows Apart European Unity (Guardian)
The time was shortly after 3am when David Cameron descended from level 80 of the vast Justus Lipsius building in Brussels on Friday. The birds were singing as he was whisked away for a much-curtailed sleep at the British ambassador’s residence, five minutes up the road. The prime minister is no novice when it comes to long and tedious discussions at European summits. But what he had just witnessed over a seemingly never-ending dinner with the other 27 EU leaders was something different altogether. The immediate crisis under discussion was migration and what the EU should do to handle the many thousands who have crossed the Mediterranean from Africa and the Middle East and arrived via Italy and the western Balkans over recent months.
Increasingly, Europe is a magnet for those seeking a better life. But the EU does not know how to react and the problems are spreading. Last week a strike by French workers at Calais caused huge tailbacks on motorways leading to both the ferry port and Channel tunnel as hundreds of migrants – mainly from east Africa, the Middle East and Afghanistan – tried to take advantage of queueing traffic by breaking into lorries bound for the UK. Against this background, a supposedly cordial working dinner, held high in the Council of Ministers building, rapidly descended into personal insults and finger-jabbing – which an exhausted-looking Cameron later summed up as “lengthy and, at times, heated discussions”.
Matteo Renzi, the Italian prime minister, was incensed by the refusal of several countries, including Hungary, which has taken in 60,000 refugees since the beginning of the year, and the Czech Republic, to agree to take part in a compulsory refugee-sharing scheme to help ease Italy’s burden. Cameron kept fairly quiet. The UK has opted out of EU asylum policy and Renzi, who was in an emotional state, did not need to be reminded of its non-participation. But others took up the cudgels as the row intensified across the table. Dalia Grybauskaite, the Lithuanian president, told Renzi in no uncertain terms that her country would not take part either. Bulgaria, one of the EU’s poorest countries, took a similar line. Disputes flared. European commission president Jean-Claude Juncker, prime mover behind the idea of compulsory burden sharing, and council president Donald Tusk tore strips off each other over what should be done, as inter-institutional solidarity broke down.
Read more …

They don’t seem to realize that though.
• The Losses For The EU Lenders Are Truly Eye-Watering (Muscatelli)
Greece is on the brink. Even if a last-minute deal is found it is clear that the solutions proposed are little more than a way to delay the crisis. A more comprehensive resolution of the Greek tragedy needs to address the medium-term (non-)sustainability of the Greek debt position. Economists know that negotiations usually break down when there is uncertainty in bargaining. When the two sides are uncertain as to what gains and losses the other side can make through any deal or by walking away. In this case, part of the uncertainty is political, because the Greek and other EU governments don’t fully know what might be acceptable to their electorates. But a good part of the uncertainty at this bargaining table is economic. Because we are in totally uncharted waters.
Monetary unions can be, and have been, dissolved before in history but, except in the aftermath of wars, not usually in anger. There are several sources of uncertainty for both sides in the dispute. First, if Greece leaves the Eurozone, at one level it will have greater freedom to walk away from at least some its debt, or to restructure it in a way which suits its short-term economic need. It could plan a moderate primary surplus. The problem for the Greek government is that it will inherit a broken banking system and there will be great uncertainty on whether a devaluing new Drachma could benefit its net trade position, with an impaired financial system, and shut out from world capital markets. Greece is not Iceland, and there is less social consensus on how to share the short-run burden of economic adjustment in a Grexit scenario.
Second, the losses for the EU lenders are truly eye-watering. The two bail-out packages for Greece amount to €215.8 billion. Of these €183.8 billion came from other EU countries and the rest from the IMF. The biggest shares of the support through the European Financial Stability Facility came from Germany and France. None of this includes the cost of support given to the Greek banking system via the ECB. The IMF would suffer considerable losses too (the UK’s main exposure is through this channel). The impact of Grexit and a partial or full debt repudiation on the rest of the EU would be considerable. Paradoxically by triggering a Grexit rather than an orderly debt restructure, the EU lenders may lose more of their current bail-out. So why are they not more accommodating? Because if it stays in, Greece will need a further bail-out, as no-one believes the current plan is sustainable. It’s that uncertainty again.
Read more …

Dead on. 1- 2 = -1.
• The Greek Butterfly Effect: Forcing The Issue of Math (Northman Trader)
Many times nothing happens for a long time. Then all of a sudden everything happens at once. Like a dam break. It builds slowly and then it bursts. Example: Who would have ever thought the Confederate flag would be taken down across the South during the same week that a rainbow flag is symbolically hoisted across the entire country? Just because things seem unthinkable doesn’t mean they won’t happen. Take the global debt construct as another example. For decades the world has immersed itself in ever higher debt. The general attitude has been one of indifference. Oh well, it just goes higher. Doesn’t really impact me or so the complacent rationalize. When the financial crisis brought the world to the brink of financial collapse the solution was based on a single principle:
Make the math workable. In the US the 4 principle “solutions” to make the math workable were to:
1. End mark to market which had the basic effect of allowing institutions to work with fictitious balance sheets and claim financial viability.
2. Engage in unprecedented fiscal deficits to grow the economy. To this day the US, and the world for that matter, runs deficits. Every single year. The result: Global GDP has been, and continues to be overstated as a certain percentage of growth remains debt financed and not purely organically driven.
3. QE, to flush the system with artificial liquidity, the classic printing press to create demand out of thin air.
4. ZIRP. Generally ZIRP has been sold to the public as an incentive program to stimulate lending and thereby generate wage growth & inflation. While it could be argued it had some success in certain areas such as housing, the larger evidence suggests that ZIRP is not about growth at all.
ZIRP’s true purpose is actually much more sinister: To make global debt serviceable. To make the math work without a default. Here’s the reality: If we had “normalized” rates tomorrow the entire financial system would collapse under the weight of the math. In short: Default. Which brings us to Greece the butterfly, the truth and indeed the future: Greece for all its structural faults is the most prominent victim of fictitious numbers. From the original Goldman Sachs deal to get them into the EU based on fantasy numbers and to numerous bail-outs, the simple truth has always been the same: The math doesn’t work. It never has and it never will until there is a default on at least some of the debt. And in this context the Greek government’s move to call for a public referendum on July 5 may be a very clever strategic move as it forces the issue of math.
Read more …

“The very idea that a government would consult its people on a problematic proposal put to it by the institutions was treated with incomprehension and often with disdain bordering on contempt.”
• Intervention in 27th June 2015 Eurogroup Meeting (Yanis Varoufakis)
Colleagues, In our last meeting (25th June) the institutions tabled their final offer to the Greek authorities, in response to our proposal for a Staff Level Agreement (SLA) as tabled on 22nd June (and signed by Prime Minister Tsipras). After long, careful examination, our government decided that, unfortunately, the institutions’ proposal could not be accepted. In view of how close we have come to the 30th June deadline, the date when the current loan agreement expires, this impasse of grave concern to us all and its causes must be thoroughly examined.
We rejected the institutions’ 25th June proposals because of a variety of powerful reasons. The first reason is the combination of austerity and social injustice they would impose upon a population devastated already by… austerity and social injustice. Even our own SLA proposal (22nd June) is austerian, in a bid to placate the institutions and thus come closer to an agreement. Only our SLA attempted to shift the burden of this renewed austerian onslaught to those more able to afford it – e.g. by concentrating on increasing employer contributions to pension funds rather than on reducing the lowest of pensions. Nonetheless, even our SLA contains many parts that Greek society rejects.
So, having pushed us hard to accept substantial new austerity, in the form of absurdly large primary surpluses (3.5% of GDP over the medium term, albeit somewhat lower than the unfathomable number agreed to by previous Greek governments – i.e. 4.5%), we ended up having to make recessionary trade-offs between, on the one hand, higher taxes/charges in an economy where those who pay their dues pay through the nose and, on the other, reductions in pensions/benefits in a society already devastated by massive cuts in basic income support for the multiplying needy.
Let me say colleagues what we had already conveyed to the institutions on 22nd June, as we were tabling our own proposals: Even this SLA, the one we were proposing, would be extremely onerous to pass through Parliament, given the level of recessionary measures and austerity it entailed. Unfortunately, the institutions’ response was to insist on even more recessionary (aka parametric) measures (e.g. increasing VAT on hotels from 6% to 23%!) and, worse still, on shifting the burden massively from business to the weakest members of society (e.g. to reduce the lowest of pensions, to remove support for farmers, to postpone ad infinitum legislation that offers some protection to badly exploited workers).
Read more …

There’s more than one candidate.
• Forget Greece, Portugal Is The Eurozone’s Next Crisis (MarketWatch)
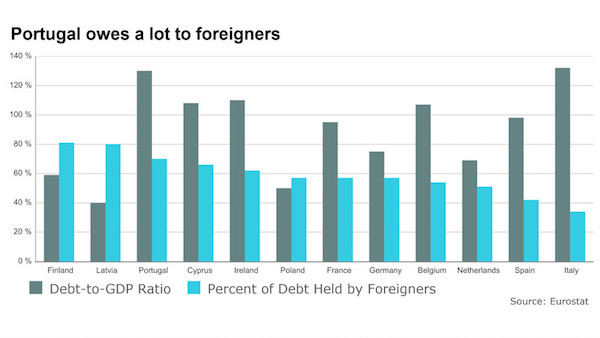
In the end, they kicked the can a little further down the road. After keeping the markets on a cliff-hanger for the last week, wondering whether the Greeks might end up getting kicked out of the eurozone, a deal of some sort looks likely. It won’t fix Greece, and it won’t fix the euro either. But it will patch the whole system up until Christmas — and that will buy everyone some time to concentrate on something else. And yet, in reality, the real crisis may not be in the east of the eurozone, but right over in the west. Portugal is the ticking time-bomb waiting to explode. Why? Because the country has run up unsustainable debts, most of the money is owed to foreigners, and with the economy still in deep trouble it may have to default as well.
The elections later this year may well trigger the second Portuguese crisis — and that will reveal how the problems in Europe involve far more than just Greece, even if that attracts most of the world’s attention. All the evidence suggests that, once the debt-to-GDP ratio climbs into the 130% bracket and above, it is basically unsustainable. Back in 2011 and 2012, when the euro crisis first flared up, three countries went bust. Of those, Greece is still in intensive care, and looks likely to remain so for the foreseeable future — the Greeks look willing to do just enough to stay in the eurozone, while the rest of Europe is willing to offer it just enough money to stay afloat while making it impossible to grow (it is a reverse Goldilocks — probably the worst of all possible solutions).
Ireland, which was always the strongest of the three bankrupt nations, is now growing again at a reasonable rate, helped along by the robust recovery in the U.K., which is still its main export market. And then there is Portugal — which is not in Greek-style permanent crisis, and yet does not seem capable of a sustainable recovery. On the surface, Portugal looks in much better shape than it did three years ago. It has exited the bailout scheme, leaving the program in May last year, after hitting European Central Bank and International Monetary Fund targets. The economy is starting to expand again. GDPt rose by 0.4% in the latest quarter, extending the run to a whole year of expansion, taking the annual growth rate up to 1.5%. It is forecast to expand by another 1.6% this year.
If Portugal can indeed recover, that would be a big win for the EU and IMF. Their catastrophic mix of internal devaluation and austerity looks to have been a complete failure in Greece, but if they can make it work in both Ireland and Portugal, the reputation of both institutions could be salvaged.
Read more …

Don’t think the ECB is smart enough to oversee the fall-out.
• Goldman’s Stunner: A Greek Default Is Precisely What The ECB Wants (Zero Hedge)
[..] if this is correct, Goldman essentially says that it is in the ECB’s, and Europe’s, best interest to have a Greek default – and with limited contagion at that – one which finally does impact the EUR lower, and resumes the “benign” glideslope of the EURUSD exchange rate toward parity, a rate which recall reached as low as 1.05 several months ago before rebounding to its current level of 1.14. Needless to say, that is a “conspiracy theory” that could make even the biggest “tin foil” blogs blush. A different way of saying what Goldman just hinted at: “Greece must be destroyed, so it (and the Eurozone) can be saved (with even more QE).” Or, in the parlance of Rahm Emanuel’s times, “Let no Greek default crisis go to QE wastel.” Goldman continues:
Greece, like many emerging markets before it, is suffering a balance of payments crisis, whereby a “sudden stop” in foreign capital inflows caused GDP to fall sharply. In emerging markets, this comes with a large upfront currency devaluation – on average around 30% across nine key episodes (Exhibit 1) – that lasts for over four years. This devaluation boosts exports, so that – as unpleasant as this phase of the crisis is – activity rebounds quickly and GDP is significantly above pre-crisis levels five years on (Exhibit 2).
In Greece, although unit labor costs have fallen significantly, price competitiveness has improved much less, with the real effective exchange rate down only ten% (with much of that drop only coming recently). This shows that the process of “internal devaluation” is difficult and, unfortunately, a poor substitute for outright devaluation. The reason we emphasize this is because, even if a compromise is found that includes a debt write-down (as the Greek government is pushing for), this will do little to return Greece to growth. Only a managed devaluation can do that, one where the creditors continue to lend and help manage the transition.
Here, Goldman does something shocking – it tells the truth! “As such, the current stand-off is about something much deeper than the next disbursement. It signals that the concept of “internal devaluation” is deeply troubled.” Bingo – because what Goldman just said in a very polite way, is that a monetary union in which one of the nations is as far behind as Greece is, and recall just how far behind Greece is relative to IMF GDP estimates imposed during the prior two bailouts..
Read more …

It’s stunning to see that when confronted with basic democracy, the press has no idea what to say or do.
• Tsipras Asking Grandma to Figure Out If Greek Debt Deal Is Fair (Bloomberg)
Economists with PhDs and hedge-fund traders can barely stay on top of the vagaries of Greece’s spiraling debt crisis. Now, try getting grandma to vote on it. That’s what Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras is doing by calling a snap referendum for July 5 on the latest bailout package from creditors. The 68-word ballot question namechecks four international institutions and asks voters for their opinion on two highly technical documents that weren’t made public before the referendum call and were only translated into Greek on Saturday.
Worse, they may no longer be on the table. International Monetary Fund chief Christine Lagarde told the BBC late on Saturday that “legally speaking, the referendum will relate to proposals and arrangements which are no longer valid.”
Tsipras’s decision means everyone from fishermen to taxi-drivers and factory workers will have to form an opinion on the package, with their country’s economic future hanging in the balance. A rejection of the bailout terms could lead to an exit from the euro area and economic calamity; accepting them would probably keep Greece in the euro, but with more austerity. “Usually in democracies, it’s the technocrats and the politicians who take care of the details, while voters are asked about broader issues and principles,” said Philip Shaw, the chief economist in London at asset manager Investec. “This is a transfer of responsibility from parliament to the voters.”
Read more …

The numbers stopped making sense long ago. Quit looking at the numbers.
• Here’s Why Any Greek Debt Deal Will Amount To Nothing (Satyajit Das)
All the heated negotiations and analysis around a bailout for Greece seem oblivious to the key problems of any settlement. Since February’s “deal,” the parties have inched close to an agreement in a prolonged battle of alternative drafts (some incorrect; other misdirected). It remains highly uncertain whether agreement can be reached. The creditors insist this is their “last and best” offer. The Greeks bluster about democracy and blackmail. Now, the Greek government has called a snap referendum on the new proposals. In its current form, the terms will represent a few concessions by the creditors, but almost total capitulation by the Greek government. Consider:
First, the agreement is likely to cover five months, necessitating a more comprehensive further program, which will inevitably require creditors to provide new financing to Greece (in effect a third bailout) if default is to be avoided. Second, the focus originally has been on the release of €7.2 billion from the existing second bailout program. If the amounts that Greece has run down from reserves, pensions and also its account at the IMF are replaced, then there is little additional new funding to Greece. It seems the European have found a little more money, by shuffling funds, whereby the amount would be a more “generous” 17 or so billion euro. But it is far from clear what Greece needs in any case.
Third, the issue of debt repayments or relief is not addressed, other than in vague terms. Greece has commitments of around 5-10 billion euro each year plus the continuing need to roll over around €15 billion in short-term Treasury bills. Greece may not have the ability to meet these obligations on an ongoing basis. This does not take into account additional funding needs of the State that may arise from budget shortfalls or the need of Greek banks.
Read more …

Oh, c’mon, I feel so awkward agreeing with Krugman….
• Europe’s Moment of Truth (Paul Krugman)
Until now, every warning about an imminent breakup of the euro has proved wrong. Governments, whatever they said during the election, give in to the demands of the troika; meanwhile, the ECB steps in to calm the markets. This process has held the currency together, but it has also perpetuated deeply destructive austerity — don’t let a few quarters of modest growth in some debtors obscure the immense cost of five years of mass unemployment. As a political matter, the big losers from this process have been the parties of the center-left, whose acquiescence in harsh austerity — and hence abandonment of whatever they supposedly stood for — does them far more damage than similar policies do to the center-right.
It seems to me that the troika — I think it’s time to stop the pretense that anything changed, and go back to the old name — expected, or at least hoped, that Greece would be a repeat of this story. Either Tsipras would do the usual thing, abandoning much of his coalition and probably being forced into alliance with the center-right, or the Syriza government would fall. And it might yet happen. But at least as of right now Tsipras seems unwilling to fall on his sword. Instead, faced with a troika ultimatum, he has scheduled a referendum on whether to accept. This is leading to much hand-wringing and declarations that he’s being irresponsible, but he is, in fact, doing the right thing, for two reasons.
First, if it wins the referendum, the Greek government will be empowered by democratic legitimacy, which still, I think, matters in Europe. (And if it doesn’t, we need to know that, too.) Second, until now Syriza has been in an awkward place politically, with voters both furious at ever-greater demands for austerity and unwilling to leave the euro. It has always been hard to see how these desires could be reconciled; it’s even harder now. The referendum will, in effect, ask voters to choose their priority, and give Tsipras a mandate to do what he must if the troika pushes it all the way. If you ask me, it has been an act of monstrous folly on the part of the creditor governments and institutions to push it to this point. But they have, and I can’t at all blame Tsipras for turning to the voters, instead of turning on them.
Read more …

Getting ugly.
• Wikileaks: Plot Against Former Greek PM’s Life, ‘Silver Drachma’ Plan (GR)
Evidence pointing to international espionage, a plot to murder former Greek Prime Minister Costas Karamanlis and a 2012 plan for Greece’s exit from the euro code-named the “Silver Drachma” are just some of the sensational findings unveiled in a report by Greek Anti-Corruption Investigator Dimitris Foukas, released on Friday and sent to the Justices’ Council for consideration. The report outlines the findings of three converging judicial investigations spanning several years, initiated after the notorious phone-tapping scandal in 2005 and revelations that the mobile phones of then Prime Minister Karamanlis and dozens of other prominent Greeks were under surveillance.
This investigation later merged with that of the “Pythias Plan’” – for the neutralization and even murder of Karamanlis – and allegations that Greek National Intelligence Service officers and former Minister Michalis Karchimakis had leaked classified state secrets and documents. Foukas cited evidence – including Wikileaks reports – supporting the existence of the Pythias Plan, which he said was designed to exert pressure on the Greek government to change its policy in crucial sectors, such as energy, arms procurements and public sector procurements. According to the report, the rapprochement between Greece and Russia provoked action by the United States to avert agreements for Russian pipelines, leading to the gradual abandonment of the plans by Athens and its commitment to the Trans-Adriatic Pipeline (TAP), as well as the cancellation of plans to acquire Russian military equipment.
Read more …

Word: “With hundreds of thousands of people depending on soup kitchens, and thousands of suicides in the years 2010-2015, the moral case for debt forgiveness seems just as strong as the technical one based on economics.”
• Greece Referendum: Why Tsipras Made the Right Move (Fotaki)
Greece will hold a referendum on July 5 on whether the country should accept the bailout offer of international creditors. The government’s decision to reject what was on offer and call the referendum is ultimately an attempt to take charge of its domestic policy and reaffirm its credibility with voters. Although Greece is hard strapped for cash this is clearly a political decision with profound consequences for the future of the European Union. It is also the right one. This is not merely useful as a negotiating tactic for obtaining a better deal with its creditors, as many commentators might suggest. The coalition of the left, Syriza, had no choice but to oppose further measures that would lock its economy into a deflationary spiral, the trappings of which are destroying Greek society.
Elected with the mandate to end the savage austerity policies already imposed, Syriza could hardly accept the further cuts demanded. These include cuts in income support for pensioners below the poverty line and a VAT hike of up to 23% on food staples. Even more onerous was the demand that Greece should deliver a sustained primary budget surplus of 1% for 2016, gradually increasing to 3.5% in the following years when its economy has already been contracting for six years. By most counts the austerity policies imposed by Greece’s creditors in 2010 in exchange for the bailout money have been an abject economic and moral failure. The IMF itself has acknowledged “a notable failure” in managing the terms of the first Greek bailout, in setting overly optimistic expectations for the country’s economy and underestimating the effects of the austerity measures it imposed.
The former IMF negotiator, Reza Moghadam, has acknowledged the fund’s erroneous projections about Greek growth, inflation, fiscal effort and social cohesion. The debt is now almost 180% of Greece’s GDP, up from 120% when the bailout program began. And this is mainly due to the fact that GDP has contracted by 25%, rather than the significantly lower projections by the IMF. The shrinking of the economy and rising unemployment levels have exceeded those that hit the US in the financial crisis of the 1930s. The human and social costs have been even more staggering in Greece. Incomes have fallen by an average of 40%, and the unemployment rate reached 26% in 2014 (and higher than 50% for youth). With hundreds of thousands of people depending on soup kitchens, and thousands of suicides in the years 2010-2015, the moral case for debt forgiveness seems just as strong as the technical one based on economics.
Yet in the terms presented to Greece by their creditors there is no commitment to reducing Greece’s crippling debt (which all commentators acknowledge is unrepayable). Nor is there any tangible proposal for rebuilding the Greek economy. Germany, France, and the EU, aided by the IMF and ECB, continue to insist on implementing policies that have so manifestly failed Greece. They do so to avoid having to justify the massive bailouts of their own financial systems – shifting the burden from banks to taxpayers – if Greece fails to make the repayments. The leading EU partners must not be seen to act leniently towards Greece as this might encourage anti-austerity parties Spain and elsewhere.
Read more …

No, the IMF should be dismantled.
• IMF Heads Must Roll Over Shameful Greek Failings (Telegraph)
Whatever the eventual outcome of the Greek debt talks, there are a number of judgments can already be made; one is that a large part of the blame for this ever deepening debacle lies at the doors of the International Monetary Fund, which from the very beginning has had both its priorities and its analysis of the situation hopelessly wrong. The IMF is meant to fix these things; instead, it has conspired to turn what should have been a containable crisis into a total disaster. With its reputation in tatters and its credibility shot to bits, it is small wonder that China and others are seeking alternative, rival models of governance for the global financial system. If this were any normal organisation, the IMF’s managing director, Christine Lagarde, would be forced to resign and someone with less of a vested interest in propping up the folie de grandeur of EMU installed in her place.
Tharman Shanmugaratnam, deputy prime minister of Singapore – measured, clever, internationally respected and impressively free- market orientated in his approach to global affairs – would make an excellent choice, though even he, as a long-standing chairman of the IMF’s policy committee, is somewhat tainted. It may require a complete outsider. Crisis management is of course what the IMF is there for; and if in the thick of a crisis, you are almost bound to get flak. Has there ever been a crisis in the IMF’s 70-year history that was not said to have done irreparable damage to the organisation’s reputation? It’s hard to think of one. Whatever it does, the IMF always gets it in the neck. Take the Russian financial crisis of 1998. The $5bn the IMF lent to help the country over its difficulties was immediately stolen and spirited away into Swiss bank accounts.
Or the pre-millennial Asian crises, where the IMF was accused of imposing a degree of austerity on afflicted nations it would never dare advocate for any G7 economy. I could go on, but it would fill the rest of the newspaper. In any case, criticism comes with the territory, which is possibly why the IMF has always been so impervious to it, and also why it repeatedly fails to learn from its mistakes. By any standards, however, the IMF’s entanglement with the eurozone crisis is a whopper of a screw-up. Nor is it something in which the IMF should have got involved in the first place. Europe, one of the richest regions in the world, should have been left to sort out its own affairs. This is more particularly the case as the Greek debt crisis is almost entirely one of the eurozone’s own making.
Read more …

Shut off the light on your way out.
• Austrians Launch Petition To Quit EU (RT)
Austrians have launched a petition to quit the EU, arguing that the nation will be better off economically if it leaves the union. To force the national parliament to consider the initiative activists need to have gathered 100,000 signatures by July 1. The petition was started by a retired 66-year-old translator, Inge Rauscher, who has collected enough signatures to launch an official campaign. The plea seeks to request that the national parliament debate the idea of a referendum on quitting the EU. However, to get that issue even discussed, the petition must gather 100,000 signatures. “We want to go back to a neutral and peace-loving Austria,” Rauscher said at the start of the campaign this week. Austrians have until July 1 to sign the petition which they can do in municipal or district offices.
Rauscher and her non-partisan Heimat & Umwelt committee (Homeland and Environment) argue that Austria will benefit from leaving the EU both economically and environmentally. She also criticized Austria’s forceful endorsement of EU sanctions against Russia, generally blaming Brussels for the economic downturn. “We are not any longer a sovereign state in the European Union. Over 80% of all essential legislation is being imposed by Brussels, not by elected commissioners. In our view, Europe is not a democracy. The European Parliament does not even have legislative powers,” Rauscher told Sputnik Radio.
An independent Austria, the committee believes, would gain an extra €9,800 per household per year, because the country will be freed from the burdens of EU bureaucracy. Recent polls show that only about one third of Austrians would be in favor of leaving the EU, according to the Local. The idea is championed by both the right-wing Freedom Party and the Euro-skeptic Team Stronach party. “This initiative is open for all political parties and we expect a broad support,” Rauscher said. “This is proved by our numerous conversations with the citizens over the past months.”
Read more …

Ari, interesting, but you kill your own argument by defining inflation as rising prices.
• The Government Must Run Deficits, Even In Good Times (Ari)
It is my view that it is very important to keep things simple and this is what I will aim to do here. I will get down to the simplest identity and build from there using empirical data. I will draw conclusions which logically follow from the data and base assumptions. But despite the elementary nature of the idea, I still think that what it will show is very informative and the conclusion it leads to is one that the current government in the UK would be appalled to consider. Although the conclusion will be surprising to some people, I believe that every step of the logic shown here is undeniably true. I would be very interested if someone can show me a faulty link in the chain. The starting point is the basic identity here:
If GDP in one year is given by £A, then the total amount of money spent on domestic goods and services is £A.
If nominal GDP the next year grows by proportion n, then GDP in year two is given by £A*(1+n) and the total amount of money spent in year two is also £A*(1+n).
What it means is that, if, for example, growth is 2% and inflation is 2%, then a total of 4% more money MUST be spent in year two than was spent in year one.
The question I will mainly be answering in the rest of this post is ‘where does this money come from?’. I will not just try to answer this question in the abstract but to quantify the effect of different sources of money. When money is spent in an economy then it contributes to nominal GDP. Nominal GDP growth is the increase in A above. The economy can be simplified to how much money was spent and how much of that leads to real growth and how much to inflation. I will try to show, using empirical data, the source of funding for our economic growth and how this leads to the conclusion that we have a big problem now. I am trying to keep things simple so I will avoid using any long equations, but to see this idea broken down into greater detail, it can be seen in the model I develop here and give an example of here (where I explain that the next crash we will have could well be a painful one).
I am not too concerned with the supply side during this discussion; it is a different issue. For example, better infrastructure and training will increase future real growth by improving productivity. There are two sides to an economy and both are important. However all of this is irrelevant for this analysis because it is just looking at the importance of demand. Deficiencies in supply will be shown in inflation figures. The supply side can expand supply to fill a certain amount of the demand as demand grows. This is dependent upon the spare capacity in the economy. If many people are out of work, then it would be easier to fulfill an increase in demand than if there is full employment. This will show in the numbers. The higher the level of GDP, the higher proportion of the extra spending that will lead to inflation.
Read more …

Not sure about this…
• Pope Francis Recruits Naomi Klein In Climate Change Battle (Observer)
She is one of the world’s most high-profile social activists and a ferocious critic of 21st-century capitalism. He is one of the pope’s most senior aides and a professor of climate change economics. But this week the secular radical will join forces with the Catholic cardinal in the latest move by Pope Francis to shift the debate on global warming. Naomi Klein and Cardinal Peter Turkson are to lead a high-level conference on the environment, bringing together churchmen, scientists and activists to debate climate change action. Klein, who campaigns for an overhaul of the global financial system to tackle climate change, told the Observer she was surprised but delighted to receive the invitation from Turkson’s office.
“The fact that they invited me indicates they’re not backing down from the fight. A lot of people have patted the pope on the head, but said he’s wrong on the economics. I think he’s right on the economics,” she said, referring to Pope Francis’s recent publication of an encyclical on the environment. Release of the document earlier this month thrust the pontiff to the centre of the global debate on climate change, as he berated politicians for creating a system that serves wealthy countries at the expense of the poorest. Activists and religious leaders will gather in Rome on Sunday, marching through the Eternal City before the Vatican welcomes campaigners to the conference, which will focus on the UN’s impending climate change summit.
Protesters have chosen the French embassy as their starting point – a Renaissance palace famed for its beautiful frescoes, but more significantly a symbol of the United Nations climate change conference, which will be hosted by Paris this December. Nearly 500 years since Galileo was found guilty of heresy, the Holy See is leading the rallying cry for the world to wake up and listen to scientists on climate change. Multi-faith leaders will walk alongside scientists and campaigners, hailing from organisations including Greenpeace and Oxfam Italy, marching to the Vatican to celebrate the pope’s tough stance on environmental issues. The imminent arrival of Klein within the Vatican walls has raised some eyebrows, but the involvement of lay people in church discussions is not without precedent.
Read more …