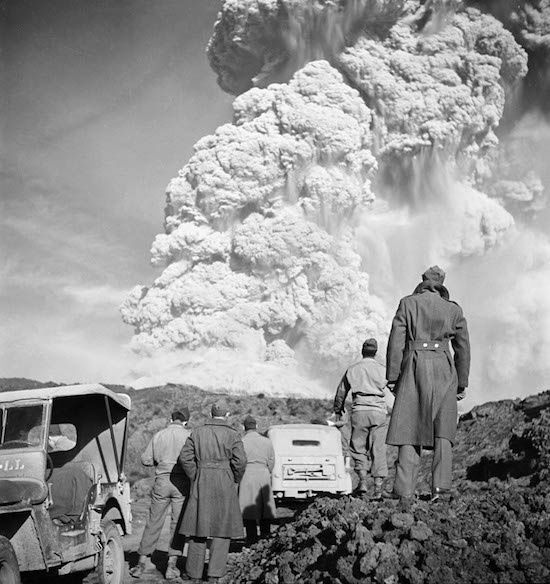
American Soldiers Observing Eruption of Mount Vesuvius 1944

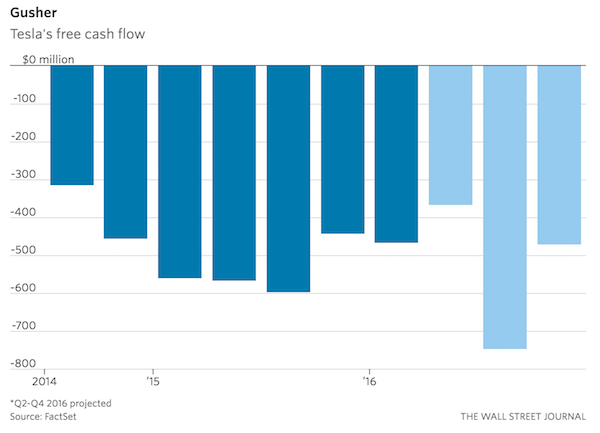
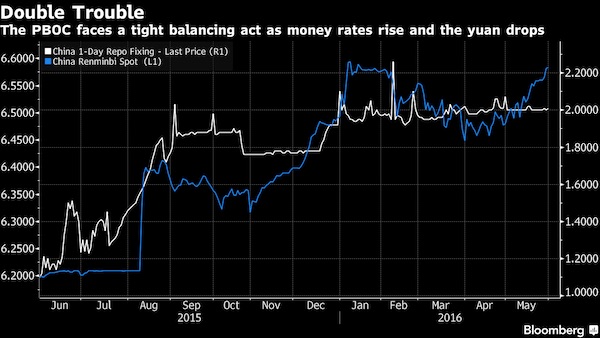
As Cohen indicates, Tillerson signed multi-billion contracts with Putin. That required a lot of trust. That trust is now being put at risk.
• ‘Russia Thinks We’re Crazy, Completely Crazy’ (ZH)
Lastly, Stephen Cohen, Professor of Russian studies at Princeton and NYU, an actual expert on China, weighed in, saying ‘Russia thinks we’re crazy, completely crazy.’ He even took some time to express his ‘disgust’ with Al Mattour, saying ‘your previous guest, I don’t mean to be rude to him. First of all, he doesn’t know what he’s talking about. And, secondly, he excludes the reality that Russia has a politics. And the politics in Russia today as we talk is […] the concern that America is preparing war against Russia. If not on Syria, then on the other two cold war fronts […] where NATO is building up in an unprecedented way. This is not good because they have nuclear weapons and because accidents happen.’
He then theorized what the conversation between Putin and Tillerson was like, pointing to the two having a history of trust together from the time Tillerson led Exxon Mobile. ‘Rex, says Putin, what in the world is going on in Washington?’ Professor Cohen, ominously, summed it up, ‘I’m not young. I’ve been doing this 40 years, sometimes as a Professor, sometimes inside. I have never been as worried as I am today about the possibility of war with Russia.’

Any day now.
• We’re Heading Straight Into a Recession – Jim Rickards (MWS)
Before the holiday weekend begins, best-selling author James Rickards joins Olivia Bono-Voznenko outside the NYSE to talk all about the markets and his latest book, “The Road to Ruin.” Jim discusses the currency wars, Trump’s turnaround on China & the Fed and an inevitable crisis amid a weak system.

Though he defines it poorly, Edwards is right that deflation is still here.
• How’s This For Grade 1 Central Bank Hubris? (Albert Edwards)
Peter Praet, the ECB’s chief economist said in a recent interview that, “Since the crisis, we have had serious concerns about deflationary risks on several occasions in the euro area, but now we can say they have disappeared.” Really? Has he seen the chart below, which shows core CPI in the Eurozone heading sharply lower and now approaching its all-time low seen at the start of 2015! Not only that, but Eurozone inflation expectations are also declining again, after surging in the aftermath of Donald Trump’s election. To be fair, Praet was focusing on the rise in headline inflation in the Eurozone, which touched 2% in February before dropping back in March to 1.5%.
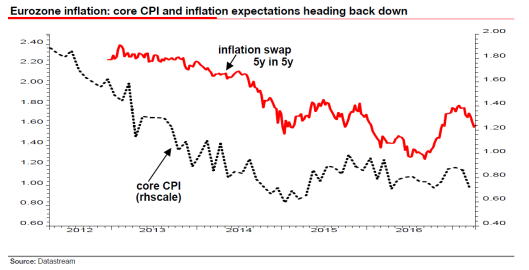
After some 18 months bobbing around the zero mark, I can understand why central bankers might be heaving a sigh of relief, but for them to take credit for a recovery in headline inflation is totally disingenuous given it has been entirely driven by a recovery in the oil price. Similarly, Janet Yellen was quoted saying the Fed is “doing pretty well” in meeting its congressionally mandated goals of low and stable inflation and a full-strength labor market. It’s this sort of comment that has led Marc Faber to want to short central bankers, the only way being to buy gold. The increasing volume of central bank hubris may even explain the recent breakout of gold to the upside! It is not just eurozone inflation expectations that seem to be in retreat. The same thing is happening in the US too (see chart below).
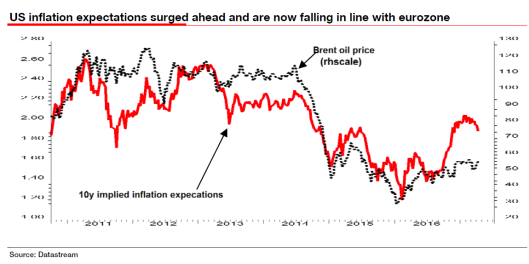
I am always surprised how dominated 10y inflation expectations are by short-term movements in the oil price and headline inflation, but it was noticeable just how rapidly inflation expectations ran up in the wake of Trump’s election – way in advance of what might have been expected by the bounce in the oil price. One might have thought the surge in the oil price from its trough some 12-18 months ago might have had more impact on wage inflation, but so far that does not seem to be the case. Despite the euphoria in the markets about the “reflation trade”, survey inflation expectations have continued to drift downwards. One thing is certain: for central banks to call victory over deflation may prove very premature indeed. Nemesis awaits.

Easter jitters.
• Wall Street Fear Gauge Hits Fresh High For The Year (CNBC)
Stocks may be in for a deeper pullback, now that the so-called fear index is finally breaking out higher. The CBOE Volatility Index (.VIX), considered the best gauge of fear in the market, closed above its 200-day moving average for the first time since the election this week. The indicator jumped more than 2% Thursday afternoon at one point to a fresh high for the year. U.S. markets are closed for trading Friday for the Easter holiday. The recent spike in fear comes just as geopolitical risk heats up. The Pentagon said Thursday U.S. military forces dropped the largest non-nuclear bomb in Afghanistan, the first time the so-called mother of all bombs has ever been used in combat. U.S. stocks fell, with the S&P 500 and DJIA closed at two-month lows Thursday. “I’d say it’s probably more of a Trump trade [reversing] than the geopolitics, but going forward I think the geopolitics is the topic the market is focusing on,” said Andres Jaime at Barclays.

Good argument: A foreign-buyer’s tax can be refunded to individuals to the extent they pay income taxes..
• The Ethical Case For Taxing Foreign Home Buyers (Gordon)
Foreign capital is playing an important role in the real estate markets of Toronto and Vancouver, and has for some time. As political leaders debate its impact and possible policy measures to alleviate its attendant issues, it is important to think clearly about the ethics of foreign ownership. Predictably, those who want to stymie or avoid policy action in this area have alluded to “xenophobia” to deter critics. Even some well-intentioned people have given credence to these claims. Yet curtailing or taxing foreign ownership is not xenophobic, especially if policy is properly designed. Xenophobia is the irrational or unjustified fear of foreigners. Concerns about the impact of foreign ownership are about flows of money, not people, and they are certainly justified in Toronto and Vancouver.
Foreign ownership raises two main ethical problems. First, those who buy based on foreign income or wealth often have access to money in ways that are unavailable to local residents. This means that locals are potentially put into disadvantageous, or unfair, competition for real estate where they live. Second, people who buy property based on foreign income or wealth may not have contributed much in Canadian taxes, which is largely what makes the property so valuable in the first place. Canadian real estate has become an attractive place to stash international money for a variety of reasons – we don’t effectively enforce money laundering regulations, we have relatively low property-tax rates and the enforcement of capital gains taxes has been lax. But real estate in Canada is ultimately attractive because of the country’s stable institutions, its public infrastructure and its social cohesion.
These latter things are paid for, or fostered by, taxes collected from Canadians – income taxes in particular. At a minimum, then, Canadians should have preferential access to property ownership, since they are paying for what makes it so valuable. It is precisely for these reasons that we see nothing ethically problematic about charging foreign students more in tuition at Canadian universities. Residential property is no different. Concerns around foreign ownership are especially potent when money is arriving from societies where corruption is widespread, and when foreign money is playing a significant role in driving up prices. Both apply in the cases of Toronto and Vancouver.
[..] We can then better design a foreign-buyer’s tax, which is needed to calm Toronto’s frenzied market. A foreign-buyer’s tax can be refunded to individuals to the extent they pay income taxes – the amount they pay in the three years following a purchase, for instance. This makes it clear that the tax need not discourage entrepreneurial talent from abroad, as claimed by Toronto Mayor John Tory. This understanding of the issue also leads straightforwardly into the proposal by many economists in British Columbia, including my colleague Rhys Kesselman. Provincial governments should introduce an annual property surtax on expensive homes that can be offset by income taxes paid, while exempting seniors with sustained CPP contribution records. This continuous surtax would powerfully target foreign ownership, and would thereby reconnect the local housing market to the local labour market.

I’ll believe it when I see it. Nobody wants to see the economy crash, they’ll stick with loose lending standards to prevent it.
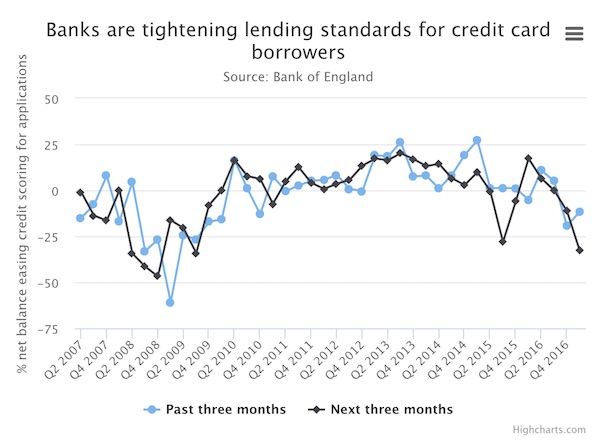
• UK Banks Crack Down On Credit Card Lending After Borrowing Binge (Tel.)
Britain’s credit card binge could be at an end as banks tighten up controls on consumer debt. Borrowing growth hit rates of more than 10pc over the past year, a pace not seen since the boom years before the financial crisis, but now banks are touching the brakes. The Bank of England has warned that a consumer debt could be more of a risk to banks than mortgage lending, should there be an economic downturn. Fierce competition to win new customers has led banks to offer more credit to customers with increasingly long interest-free periods.But banks have started tightening lending criteria for credit card applicants in a move of an intensity not seen since the depths of the financial crisis in 2008 and 2009.
A net balance of 33pc of lenders expect to tighten standards in the coming three-month period, according to Bank of England data. When unsecured loans are also included, a net balance of 27pc plan to scrutinise applications more closely. There was also a fall in the number of credit card applications approved in the first quarter of the year, and banks expect the number to remain roughly steady in the coming quarter. By contrast credit scoring criteria for secured loans, such as mortgages, is holding broadly steady. “The recent rapid growth in consumer credit could principally represent a risk to lenders if accompanied by weaker underwriting standards,” warned the Bank of England’s Financial Policy Committee this month.

After first praising it.
• CIA Director Brands Wikileaks A ‘Hostile Intelligence Service’ (G.)
Mike Pompeo, the director of the CIA, has branded WikiLeaks a “hostile intelligence service,” saying it threatens democratic nations and joins hands with dictators. In his first public remarks since becoming chief of the US spy agency in February, Pompeo focused on the group and other leakers of classified information like Edward Snowden as one of the key threats facing the United States. “WikiLeaks walks like a hostile intelligence service and talks like a hostile intelligence service. It has encouraged its followers to find jobs at CIA in order to obtain intelligence… And it overwhelmingly focuses on the United States, while seeking support from anti-democratic countries and organisations,” said Pompeo. “It is time to call out WikiLeaks for what it really is – a non-state hostile intelligence service often abetted by state actors like Russia.”
[..] Last month, WikiLeaks embarrassed the CIA and damaged its operations by releasing a large number of files and computer code from the agency’s top secret hacking operations. The data showed how the CIA exploits vulnerabilities in popular computer and networking hardware and software to gather intelligence. Counterintelligence investigators continue to try to find out who stole the files and handed them to WikiLeaks. Assange meanwhile criticized the US agency for not telling the tech industry and authorities about those vulnerabilities so they can be fixed. Pompeo said Assange portrays himself as a crusader but in fact helps enemies of the United States, including aiding Russia’s interference in last year’s presidential election.
“Assange and his ilk make common cause with dictators today. Yes, they try unsuccessfully to cloak themselves and their actions in the language of liberty and privacy; in reality, however, they champion nothing but their own celebrity. Their currency is clickbait; their moral compass, nonexistent.” However, Pompeo did not comment on how Trump has previously lavished praise on Assange for the information he has made public. Nor did Pompeo mention that he himself had cited and linked to WikiLeaks in a tweet attacking the Democratic Party. Pompeo at the time was a Republican congressman and member of the House Intelligence Committee. The CIA declined to comment on that.

Translation: get it done.
• ‘US Will Keep ‘Open Mind’ On Any IMF Aid To Greece’ (AFP)
The US government will keep an “open mind” on any new loan package from the IMF for debt-burdened Greece, a senior US Treasury official said Thursday. Despite criticism of international organizations by the Trump administration, the comments allay concerns that US Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin could veto any large new aid package for Athens. “We’re looking for the Europeans to help Greece to resolve its economic problems, and we think the IMF can play a supportive role,” the official told reporters. “And we’ll look at any potential future agreement with an open mind.” IMF chief Christine Lagarde on Wednesday said Greece and its eurozone creditors have made progress towards a new loan package that includes debt relief, but that is something the fund has been saying for months without a final deal.
Greece last week accepted a tough set of reforms demanded by its eurozone creditors in hopes of securing a new loan in time to avert a looming debt default in July, although it still must finalize the details. Athens has been deadlocked for months over reforms, and budget targets, which has put the IMF and EU at loggerheads over the need for debt relief in order to ensure an economic recovery, and the government’s ability to repay its loans. The eurozone is under heavy pressure to end the feud in order to avert a chaotic default and inflicting damage on an already stalled Greek recovery. Greece has about €7 billion in debt repayments due in July. All the key officials involved in the talks are expected to be in Washington next week to attend the IMF and World Bank annual meetings.

We waste. That’s what we’re good at.
• American Energy Use, In One Diagram (Vox)
Every year, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory LLNL produces a new energy flow chart showing the sources of US energy, what it’s used for, and how much of it is wasted. If you’ve never seen it before, it’s a bit of a mind-blower. Behold US energy in 2016: So much information in so little space! (It’s worth zooming in on a larger version.)
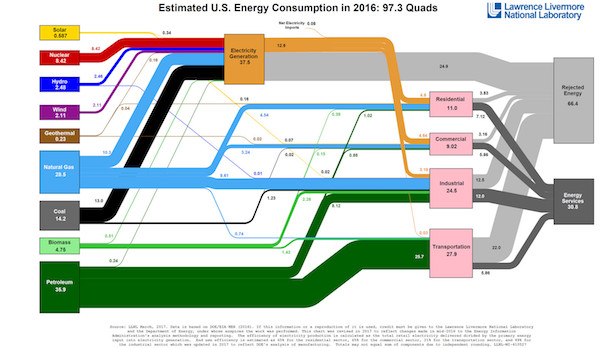
[..] a British thermal unit (BTU) is a standard unit of energy — the heat required to raise the temperature of a pound of water by 1 degree Fahrenheit. If you prefer the metric system, a BTU is about 1055 joules of energy. A “quad” is one quadrillion (a thousand trillion) BTUs. [..] a few things equivalent to a quad: 8,007,000,000 gallons (US) of gasoline, 293,071,000,000 kilowatt-hours (kWh), 36,000,000 metric tons of coal The US consumed 97.3 quads in 2016, an amount that has stayed roughly steady (within a quad or so) since 2000.
Perhaps the most striking feature of the spaghetti diagram — what everyone notices the first time they see it — is the enormous amount of “rejected” energy. Not just some, but almost two-thirds of the potential energy embedded in our energy sources ended up wasted in 2016. (And note that some scholars think LLNL is being too optimistic, and that the US is not even 31% efficient but more like 13%.) What’s more, the US economy is trending less and less efficient over time. Here’s the spaghetti diagram from 1970 (LLNL has been at this a long time):
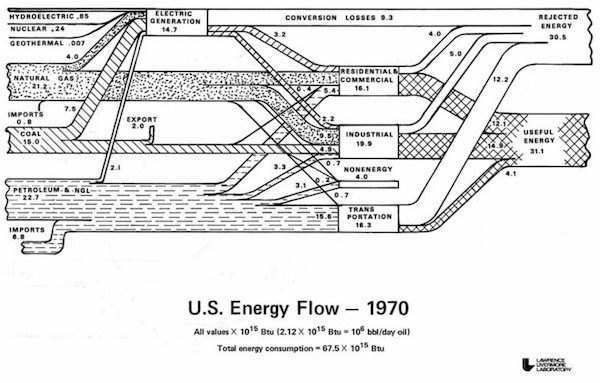
Back then, we only wasted half our energy! It’s important to put this waste in context. It is not mainly about personal behavior or inefficient energy end use — keeping cars idling or leaving the lights on, that kind of thing. That’s a part of it, but at a deeper level, waste is all about system design. The decline in overall efficiency in the US economy mainly has to do with the increasing role of inefficient energy systems. Specifically, the years since 1970 have seen a substantial increase in electricity consumption and private vehicles for transportation, two energy services that are particularly inefficient. (Electricity wastes two-thirds of its primary energy; transportation wastes about three-quarters.)
There is loss inherent in any system that converts raw materials to usable energy, or transports or uses energy, of course. That follows from the second law of thermodynamics. And it’s true both narrowly (a car is an energy system) and broadly (a city is an energy system). It’s not possible to achieve perfect efficiency, or anything close to it. But surely we can do better than 31%! Sixty-six quads is a truly mind-boggling amount of energy to vent into the atmosphere for no good purpose. It really highlights the enormous potential of better-designed systems — especially better electricity and transport systems, along with better urban systems (i.e., cities) — to contribute to the country’s carbon reduction goals. We could double our energy use, with no increase in carbon emissions, just by halving our energy waste.

I like this, and it’s high time energy became a part of economic modeling; Steve Keen is working on it too. BUT: to understand today’s predicaments, you have to look -seperately- at what has happened in financial markets. The debt binge was not a result of what went on with energy; it stood -and stands- on and by itself.
• Macroscale Modeling Linking Energy and Debt (King)
What if you realized that the fundamental economic framework of macroeconomics is insufficient to inform our most pressing concerns? The world is dynamic, in constant change, yet most economic models (even the most widely used “dynamic” model) lack fundamental feedbacks that govern long-term trends (e.g., regarding role of energy) and make assumptions that prevent the ability to describe important real-world phenomena (e.g., financial-induced recessions). Monetary models of finance and debt often assume that natural resources (energy, food, materials) and technology are not constraints on the economy. Energy scenario models often assume that economic growth, finance and debt will not be constraints on energy investment.
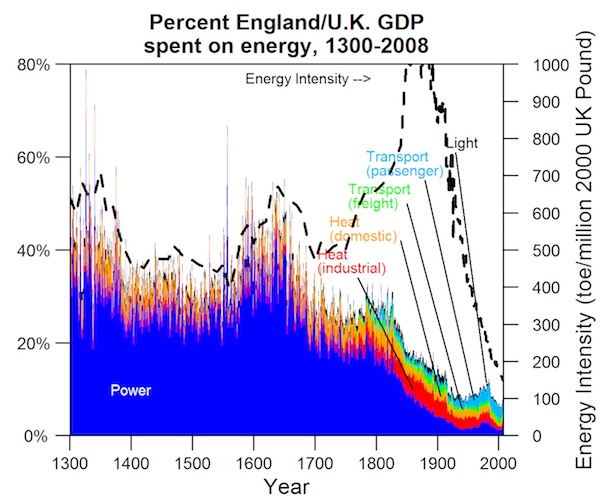
Energy and food costs have declined since industrialization, but no longer
These assumptions must be eliminated, and the modeling concepts must be integrated if we are to properly interpret the post-2008 macroeconomic situation: unprecedented low interest rates, high consumer and private debt, high asset valuations, and energy and food costs that are no longer declining. As we attempt to understand newer and more numerous options (e.g., electric cars, renewables, information) regarding energy system evolution, it is paramount to have internally consistent macro-scale models that take a systems approach that tracks flows and interdependencies among debt, employment, profits, wages, and biophysical quantities (e.g., natural resources and population). There is a tremendous research need to develop a framework to describe our contemporary and future macroeconomic situation that is consistent with both biophysical and economic principles. Unfortunately, this fundamental integration does not underpin our current thinking.
U.S. consumer costs of fundamental needs (energy, food, housing, transport) are no longer declining
• Debt is money.
• Money is created when commercial banks lend money to businesses, not when the U.S. Treasury prints money or when Federal Reserve Bank lowers interest rates. Those government and Fed actions are reactions to the creation or destruction of money (e.g., paying back loans) within the real economy.
• Businesses seek new loans when economic opportunities are present. Thus, a growing economy can support more debt.
• Economic opportunities are present when consumers have disposable income to spend (and when innovative technologies supplant old technologies, thus lowering prices, and enabling growth).
• Consumers have more money to spend when core needs (e.g., food, energy, housing) are getting cheaper relative to incomes. Thus, if these core needs are no longer getting cheaper, this is an indication of the lack of income growth to support business investment. In turn banks stop lending because there are fewer viable business opportunities.
• The conclusion is that without decreasing food and energy costs to consumers, real incomes do not rise.
• This is a viable explanation of the post-2008 economy, but one ignored by practically all policy makers, economists, and advisors!

Frontex is a disaster.
• Refugee Rescue Group Accuses EU Border Agency Of Plotting Against Them (AFP)
A Spanish group which has been rescuing migrants in the Mediterranean since 2016 accused the EU’s border control agency Frontex on Wednesday of plotting to discredit private aid organisations in order to put off donors. Allegations by Frontex that donor-funded rescue vessels may have colluded with traffickers at the end of last year prompted Italian prosecutors to begin an informal investigation into their funding sources. “The declarations by Frontex and political authorities are intended to discredit our actions and erode our donors’ trust,” said Proactiva Open Arms head Riccardo Gatti. “They are trying to say that we support the smuggling or the traffickers themselves,” he said. In a report cited in December by the Financial Times daily, Frontex raised the possibility that traffickers were putting migrants out to sea in collusion with the private ships that recover them and bring them to Italy “like taxis”.
Prosecutors then publicly wondered at the amount of money being spent, though they stopped short of opening a formal probe. “We feel there’s someone who wants to put a spoke in our wheels, though we do not really know who is behind it,” Gatti said. The organization said it had nothing to hide. “We have 35,000 donors. Some are well known – like Pep Guardiola, the current manager of Manchester City – others are anonymous,” said Oscar Camps, Proactiva Open Arms director. He said the group had so far received €2.2 million euros in donations for an op in the Med that costs between €5,000 and €6,000 a day. Pro-Activa Open Arms also heavily criticized a deal signed in February between Italy and Libya which purportedly hopes to stem the flow of migrants from the coast of North Africa to Italy.
Gatti said the deal was made with only part of the 1,700 militias he said control Libya and would therefore be ineffective. Human rights watchers have also warned the accord would put the lives of those fleeing persecution and war in greater danger. “Everything is controlled by the militias in Libya, even the coast guard, and 30 percent of the financial flows in the country come from human trafficking,” he said. The deal is in doubt after it was suspended in March by Tripoli’s Court of Appeal. Nearly 25,000 migrants have been pulled to safety and brought to Italy since the beginning of the year in a sharp increase in arrivals.

Happy Easter.
• At Least 97 Migrants Missing As Boat Sinks Off Libya (AFP)
At least 97 migrants were missing after their boat sank on Thursday off the Libyan coast, a navy spokesman said. Survivors said the missing include 15 women and five children, General Ayoub Qassem told AFP. He said the Libyan coastguard had rescued a further 23 migrants of various African nationalities just under 10 kilometres (6 miles) off the coast of Tripoli. The boat’s hull was completely destroyed and the survivors, all men, were found clinging to a flotation device, he said. Those who had disappeared were “probably dead”, but bad weather had so far prevented the recovery of their bodies, Qassem added. An AFP photographer said survivors had been given food and medical care at Tripoli port before being transferred to a migrant centre east of the capital.
Six years since the revolution that toppled dictator Moamer Kadhafi, Libya has become a key departure point for migrants risking their lives to cross the Mediterranean to Europe. Hailing mainly from sub-Saharan countries, most of the migrants board boats operated by people traffickers in western Libya, and make for the Italian island of Lampedusa 300 km away. Since the beginning of this year, at least 590 migrants have died or gone missing along the Libyan coast, the International Organization for Migration said in late March. In the absence of an army or regular police force in Libya, several militias act as coastguards but are often themselves accused of complicity or even involvement in the lucrative people-smuggling business. More than 24,000 migrants arrived in Italy from Libya during the first three months of the year, up from 18,000 during the same period last year, according to the UN High Commissioner for Refugees.

Easter feel good.
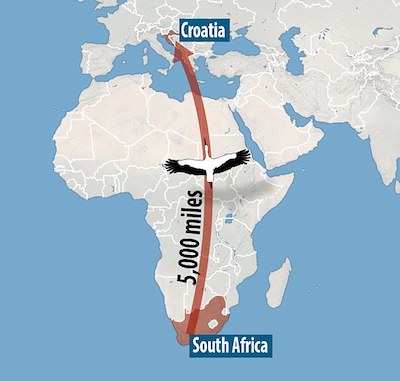
A stork has melted hearts in Croatia by flying to the same rooftop every year for 14 years – to be reunited with its crippled partner. The faithful bird, called Klepetan, has returned once again to the village of Slavonski Brod in east Croatia after a 5,000 mile migration. He spends his winters alone in South Africa because his disabled partner Malena cannot fly properly after being shot by a hunter in 1993. Malena had been found lying by the side the road by schoolteacher Stjepan Vokic, who fixed her wing and kept her in his home for years before helping her to build a nest on his roof. After placing her there, she was spotted by Klepetan 14 years ago. And now every year they are reunited in the spring. Klepetan keeps a very strict timetable, usually arriving back at the same time on the same day in March to be welcomed by locals.

But this year he was running six days late, causing panic among local media and fans of the stork couple. Such is the popularity of the pair that there is even a live feed on the main square in the capital Zagreb showing the two storks. There was huge excitement when stork-watchers saw what they thought was Klepetan circling over the nest, and then coming in to land. But the new arrival turned out to be a different stork that was attempting to woo Malena. She quickly attacked him and drove him off and continued to wait for Klepetan. Stjepan Vokic, whose roof the couple nest on, said: ‘She was pretty clear about the message, I doubt he will be back again.’ Vokic has taken care of Malena since she was first injured by hunters and says that she – like her partner – is now part of the family.
During the winter, Vokic keeps her inside the house, and then lets her go to the roof each spring where she patiently waits for her partner. This year, Malena made a rare flight and the couple were reportedly inseparable for hours. She does have the ability to make very short flights but her wing has not healed well enough for her to make the trip to Africa, or even to properly feed herself. Every summer, the pair bring up chicks, with Klepetan leading their flying lessons in preparation for the trip south in summer. The oldest recorded living stork was 39. Locals are hopeful the couple’s long relationship will continue for years to come.