Salvador Dali Christ of Saint John of the Cross 1951


https://twitter.com/itscarterhughes/status/1909334208536846529
MAGA
https://twitter.com/gaborgurbacs/status/1909348105675211192
Bessent
Almost 70 countries have now approached us wanting to help rebalance global trade.
On behalf of @POTUS, I'm glad to join @USTradeRep to open talks with Japan as we work to enact the President’s vision for a new Golden Age of Global Trade.pic.twitter.com/PGUGjh7JkH
— Secretary of Treasury Scott Bessent (@SecScottBessent) April 7, 2025
GOAT
https://twitter.com/iam_smx/status/1909347460960653353
Rubio
Sec of State Rubio is becoming one of my favorites
pic.twitter.com/SVmBTX6bBh
— G-PA (@IndianaGPA) April 7, 2025
Bondi
NOW – AG Pam Bondi Sounds Off on Rogue Judges, Vows Criminal Alien Deportations Will Continue
Attorney General Pam Bondi just torched the rogue judges attempting to block President Trump's deportation efforts.
She made it clear: Criminal aliens are getting deported whether… pic.twitter.com/7Y80QhRWj4
— Overton (@overton_news) April 8, 2025


Won’t surprise too many people. And that’s not good at all.
• Trump Assassination ‘Justified’ For Half of Left-Leaning Americans (RT)
More than half of all left-leaning Americans believe there would be some justification for the assassination of US President Donald Trump, according to a new survey. The alarming finding was reported on Monday by the Network Contagion Research Institute (NCRI). The organization monitors radical ideologies and examines what it refers to as “assassination culture” in America. The nonprofit conducted an opinion poll to assess whether American citizens would condone lethal attacks on Trump and his government efficiency tsar, Elon Musk. Among the 1,264 individuals surveyed, 31% and 38% expressed at least some justification for murdering Musk and Trump, respectively. The figures increased to 48% and 55% among respondents identifying as center or left-leaning. In the latter group, 9.1% would deem the assassination of Musk to be “completely justified,” while 13.2% said the same about Trump.
A majority of 57.6% indicated that attacking Tesla dealerships to protest Musk’s involvement with the Trump administration was at least somewhat acceptable. Commenting on the poll’s findings and claims that Democratic leaders have “incited” the situation, Musk branded the political organization “the party of violence.” He previously characterized arson attacks on Tesla-affiliated businesses in the US and abroad as “terrorism.” Last weekend, thousands of Americans marched in various cities to protest Trump’s policies and his support for Musk’s approach to reducing government spending. Critics have labeled the activities of the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE), led by Musk, as an “illegal power grab” orchestrated by the president.
Trump barely escaped death during a campaign rally in Butler, Pennsylvania last July, when a shooter opened fire at him, killing and injuring several supporters of the Republican candidate. The NCRI said its survey confirms broader “troubling trends” within US political culture, suggesting that the endorsement of violence is rooted in a particular far-left ideology. The institute also posits that this ideology fuels the online “memeification” of Luigi Mangione, the alleged murderer of UnitedHealthcare CEO Brian Thompson. Some Americans view Mangione, against whom the Trump administration is seeking the death penalty, as a folk hero, arguing that his actions could be seen as justifiable vigilantism against a predatory corporate healthcare system.

Went into effect at midnight.
• Trump Slaps ‘Proud’ China With 104% Tariffs (RT)
The US has hiked tariffs on all Chinese imports to a staggering 104%, escalating the ongoing trade conflict and wiping out another $1.5 trillion from US stock markets on Tuesday. China was originally set to face a 34% tariff increase on Wednesday, as part of President Donald Trump’s “reciprocal” measures targeting virtually all US trade partners. However, after Beijing responded with a proportional 34% duty of its own, the US president raised the blanket tariff to a total of 104%. “After all of the abuses they’ve perpetrated, China is attempting to impose additional unjustified tariffs,” Trump said at a National Republican Congressional Committee dinner in Washington on Tuesday. That’s why additional tariffs on Chinese goods are in place, effective midnight tonight at 104 percent. Until they make a deal with us, that’s what it’s going to be.
The White House published an amendment to the April 2 executive order in which Trump declared a national emergency over the US trade deficit and imposed a baseline tariff on all imports to the US. The administration said that nearly 70 countries had sought negotiations to mitigate the impact of the tariffs, as Trump pursues “tailored deals” with individual nations. The president went on to say that Beijing will have to “make a deal at some point,” claiming that “they just don’t know how to get it sorted because they’re proud people.” Until then, he added, China “will now pay a big number to our Treasury.” “Right now, China is paying a 104 percent tariff, think of it… Now, it sounds ridiculous, but they charged us for many items 100 percent, 125 percent,” Trump said. “They’ve ripped us off left and right. But now it’s our turn to do the ripping.”
Beijing previously condemned the escalating trade war as a form of “blackmail” and “economic bullying.” A spokesperson for the Commerce Ministry said on Tuesday that “China will fight till the end if the US side is bent on going down the wrong path.” The latest escalation has had a significant impact on US and global stock markets. Major indices such as the S&P 500, Dow Jones, and Nasdaq suffered further declines after a brief surge earlier this week, wiping out an estimated $1.5 trillion from US markets on Tuesday. Trump acknowledged that the fallout from his move was “somewhat explosive,” but defended his strategy, claiming that “sometimes you have to mix it up a little bit.” He insisted that the tariffs are necessary to address trade “abuses” and to promote domestic manufacturing, adding that the US is already generating $2 billion a day from the tariffs.
BOOM: Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent Just Warned China They're Bluffing—and Holding a Losing Hand
China threatened more tariffs after Trump hit back with his own. But Bessent says they’re playing poker with a pair of twos.
“That is a losing hand for them.”
He says Trump has… pic.twitter.com/JSNdRpOAQs
— Overton (@overton_news) April 8, 2025

A good fried pointed to this Moon of Alabama piece from a few days ago. It gives the impression that the Trump team is being sloppy with the tariffs. The only thing is, they say their numbers come “including Currency Manipulation and Trade barriers”. And those are not very clearly defined. But the impression of sloppy is still not a good thing.
• White House Lacks Financial Literacy – ‘Tariffs’ Show (MoA)
‘The foundation of American economic prosperity is a society empowered with the knowledge and tools to make informed financial decisions to achieve the American Dream. … ‘ I welcome that message. Teaching financial literacy must start at the top. The members of the Trump administration obviously lack the knowledge and tools to make informed financial decisions. It is the only possible explanation for how they came up with these numbers:
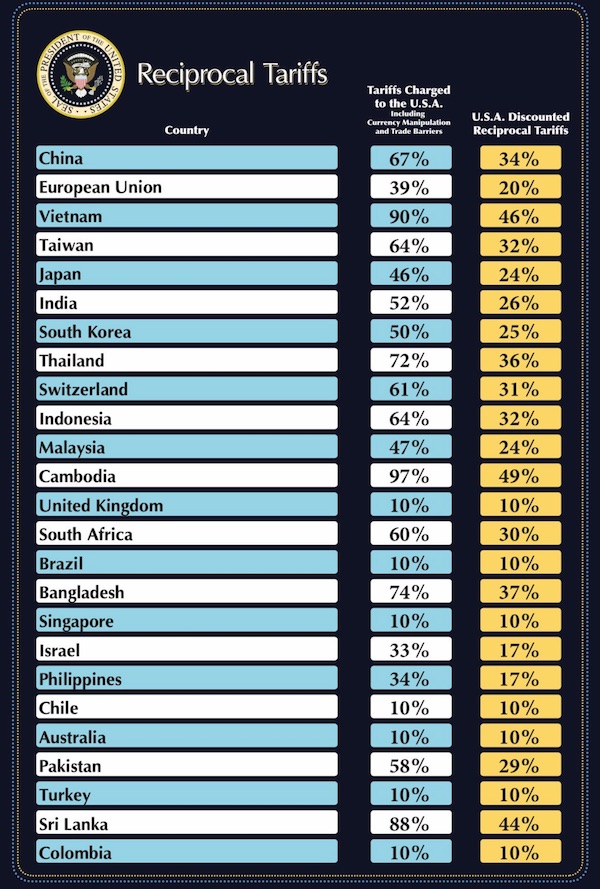
China does not have a 67% tariff on U.S. goods (it’s 7.3%). The EU does not have a 39% tariff on U.S. goods (it’s 5.2%). The numbers are bollocks. So where do they come from? The official explanation from the U.S. Trade Representative is here. Its baloney:
“James Surowiecki @JamesSurowiecki – 0:22 UTC · Apr 3, 2025 “Just figured out where these fake tariff rates come from. They didn’t actually calculate tariff rates + non-tariff barriers, as they say they did. Instead, for every country, they just took our trade deficit with that country and divided it by the country’s exports to us. So we have a $17.9 billion trade deficit with Indonesia. Its exports to us are $28 billion. $17.9/$28 = 64%, which Trump claims is the tariff rate Indonesia charges us. What extraordinary nonsense this is.
…
Even given that it’s Trump, I cannot believe they said “We’ll just divide the trade deficit by imports and tell people that’s the tariff rate.” And then they decided to set our tariffs by just cutting that totally made-up rate in half! This is so dumb and deceptive. .. it’s actually worse than I thought: in calculating the tariff rate, Trump’s people only used the trade deficit in goods. So even though we run a trade surplus in services with the world, those exports don’t count as far as Trump is concerned.”The last point is a major one, for China, but especially for the EU :
“EU-US trade in goods and services reached an impressive €1.6 trillion in 2023. This means that every day, €4.4 billion worth of goods and services cross the Atlantic between the EU and the US. … The total bilateral trade in goods reached €851 billion in 2023. The EU exported €503 billion of goods to the US market, while importing €347 billion; this resulted in a goods trade surplus of €157 billion for the EU. Total bilateral trade in services between the EU and the US was worth €746 billion in 2023. The EU exported €319 billion of services to the US, while importing €427 billion from the US; this resulted in a services trade deficit of €109 billion for the EU. …EU-US goods and services trade is balanced: the difference between EU exports to the US and US exports to the EU stood at €48 billion in 2023; the equivalent of just 3% of the total trade between the EU and the US.”
Despite that Trump has decreed a 20% on all goods from the EU. The natural countermeasure from the EU will be to put a 20+% tariff on all import of U.S. services. Trump also decreed a minimum 10% tariff on imports from every country. Products made by the penguins of the uninhabited Heard and McDonald Islands in the Antarctic will now come with a 10% surcharge.”
There is really no economic reasoning behind these numbers. “Arnaud Bertrand @RnaudBertrand – 4:16 AM · Apr 3, 2025 “To illustrate just how nonsensically these tariffs were calculated, take the example of Lesotho, one of the poorest countries in Africa with just $2.4 billion in annual GDP, which is being struck with a 50% tariff rate under the Trump plan, the highest rate among all countries on the list…. As a matter of fact Lesotho, as a member of the Southern African Customs Union (SACU), applies the common external tariff structure established by this regional trade bloc. … So since the tariffs charged by these 5 countries on U.S. products are exactly the same, they must all be struck with a 50% tariff rate by the U.S., right? Not at all: South Africa is getting 30%, Namibia 21%, Botswana 37% and Eswatini just 10%, the lowest rate possible among all countries.
Looking at Lesotho specifically, every year the U.S. imports approximately $236 million in goods from Lesotho (primarily diamonds, textiles and apparel) while exporting only about $7 million worth of goods to Lesotho (https://wits.worldbank.org/CountryProfile/en/Country/LSO/Year/2022/TradeFlow/EXPIMP/Partner/by-country). Why do they export so little? Again this is an extremely poor country where 56.2% of the population lives with less than $3.65 a day (https://databankfiles.worldbank.org/public/…), i.e. $1,300 a year. They simply can’t afford U.S. products, no-one is going to buy an iPhone or a Tesla on that sort of income… The way the tariffs are ACTUALLY calculated appears to be based on a simplistic and economically senseless formula: you take the trade deficit the U.S. has with a country, divide it by that country’s exports to the U.S and declare this – falsely – “the tariff they charge on the U.S.”
And then as Trump did in his speech last night, you magnanimously declare that you’ll only “reciprocate” by charging half that “tariff” on them. As such, for Lesotho, the calculation goes like this: ($236M – $7M)/$235M = 97%. That’s the “tariff” Lesotho is deemed to charge this U.S. and half of that, i.e. roughly 50% is what the U.S. “reciprocates” with. It’s extremely easy to see why this makes no sense at all. ”
Lesotho has a comparative advantage over the U.S. as it can dig up and sell diamonds. But it lacks the purchasing power to buy U.S. goods and services. The calculations by the Trump administration ignore those basic facts. No tariffs were by the way introduced against Belarus, Russia and North Korea. This because of sanction, the U.S. has allegedly no trade relation with them. (Other than buying enriched Uranium for its nuclear power stations?) Did the Trump administration anticipate how this nonsense will explode in its face? It is Smoot-Hawley writ large.

“If you don’t believe that what Donald Trump is trying to do on debt, budget, workforce, trade, then come up with a better agenda. And show why it will work and why his will fail..”
• Don’t Like Trump’s Plan for the Economy? Let’s Hear Yours (Victor Davis Hanson)
Hello, this is Victor Davis Hanson for The Daily Signal. I’d like to talk about the economy and politics very quickly. Whether you like it or I like it or whether the administration likes it or whether the Congress or the American people like it, the success or failure of President Donald Trump will hinge on the status of the economy. It will overshadow the miraculous achievement on the border, where he went from a rate of about 2 million people a year to almost zero illegal immigration. It will even outrank the question of peace and stability in Ukraine or the Middle East. It’ll outrank everything. So, here’s my question. There is now outrage, hysteria over the last 24 hours to 48 hours that Donald Trump has outlined his tariff program to bring down the nearly $1 trillion trade deficit, and the stock market has taken hits.
So, here’s my question, though, when Sen. Cory Booker stands up for 25 hours, does he give an alternate agenda on the economy? Does Rep. Nancy Pelosi talk about the economy? She used to. Does The Wall Street Journal, when they criticize Donald Trump, why don’t they get a columnist and say, “These are the 10 points that are preferable in addressing our economic challenges”? Now, what are our economic challenges? Well, the first is debt. We owe $37 trillion. We’re paying $3 billion a day in interest. We’re running a $1.7 trillion deficit. So, if you were on the left and you were part of the machine that borrowed $7 trillion under President Joe Biden, created these huge new programs, why don’t you make an argument? Just say, “I believe in modern monetary theory. I believe, if we can just get down to 1% or 2% interest, you can service any debt because the bondholders, they’re wealthy anyway. So, that’s what we’ve been doing. And I don’t—I believe money’s a construct. It’s just an idea. So, there is no such thing as, you know, red or blue ink—any of that. So, just keep spending. There’s no problem—$37, $40 trillion.” Say that.
Or, if you’re on the right, say, “I prefer to look at the debt in a different way. If you’re going to cut, why select particular fraud, waste, and abuse areas? Why not just go across the board and treat everybody the same with a 4% or 5% or 10% cut?” Or, if you don’t believe in cutting government to reduce the debt, then say, “Let’s just go completely laissez-faire and let’s grow the economy so it’s growing at 4% or 5% gross domestic product. And it will solve the problem.” Or, if you’re in the middle and you’re an independent, why don’t you just say, “We had three balanced budgets. We were reducing the debt because former House Speaker Newt Gingrich controlled taxes and former President Bill Clinton controlled spending. And he was able to find an incentive plan to increase revenue and Bill Clinton decreased spending. OK? Why not we go back and follow their model?”
I really like how he explains this, he lets you make your own decision and just gives you the information about Tariffs. This is actually the best one. pic.twitter.com/jaiatOzwgf
— Johnny Midnight
(@its_The_Dr) April 7, 2025
But the problem is none of these areas—right, center, and left—nobody in these disciplines is offering any alternative agenda. It’s just attack Trump, Trump, Trump, Trump. Let’s go to trades. So, we have, again, about a trillion-dollar trade deficit. We haven’t had balanced trade for 50 years. Our opponents, challengers, allies, whatever you want to call them, feel that protected tariffs in China, in India, in Europe, in South Korea, in Japan have been very conducive to their economic miracle—postwar miracles. And they feel that there must be some wisdom in them because they continue to perpetuate them. They have not run deficits for a half-century. They’re not, in terms of GDP, debt, quite like we are. So, maybe you can argue that tariffs are just an American problem. An obsession. And they don’t really matter. Or you can say that we should have reciprocal tariffs based on each one. But tell us what you want to do.
Why don’t you just say that if you—and I have read this from scholars as diverse as the American Enterprise Institute, the Cato Institute. This is just a construct, trade deficits, they don’t matter. Because the people, if they run up a surplus, they buy our bonds or they invest, and it’s a circular process—just say that. Or, if you believe that trade deficits matter, then you say, “Well, the answer is not through tariffs. It’s through greater productivity. And here’s how I want to do it.” But again, there’s nothing. And then we get, finally, into foreign investment. Donald Trump is bragging, I think justifiably so, that he may have $3 to $5 trillion in foreign investment. Nobody says a word about it. Nobody says this many trillion dollars will result in this many new jobs created. No, they just kind of ignore it. So, give us a reason why. Just say, “You know, the new massive amounts of foreign aid will have no effect on either our trade deficit or our budget deficit. It’s just a construct that Trump says.”
Or say that it will but it won’t nullify the pernicious effects of tariffs. But what I’m getting at, in conclusion, is what if Cory Booker had said, “I’m going to speak for 25 hours on why Donald Trump’s trade, debt, and federal workforce investment are all wrong. And here’s da, da, da, da”? Or what if House Minority Leader Hakeem Jeffries said, “Here is our contract for America on the economy. The economy”? No one is giving any alternatives. No one is talking in any way that they have an antithetical and a better plan than Donald Trump. So, what we’re left with is just naysaying, nihilism, criticism. And the American people are confused. If you don’t believe that what Donald Trump is trying to do on debt, budget, workforce, trade, then come up with a better agenda. And show why it will work and why his will fail. But don’t just scream and yell and cause all hysteria and go to street theater because that’s no answer. It only amplifies the problem.

Guess they can try.. But so could anyone.
• US Chamber of Commerce Considers Block on Trump’s New Import Tariffs (Sp.)
The US Chamber of Commerce, the country’s most powerful corporate lobby, is considering filing a lawsuit against the administration of US President Donald Trump to block the entry of new import tariffs into force, the Fortune magazine reported, citing sources familiar with the discussions of the lawsuit. The Chamber of Commerce may claim that Trump’s use of emergency powers to impose tariffs was illegal. According to the publication, some of the organization’s largest members are calling for the lawsuit. Sources also say that other organizations might join the lawsuit. The head of the US Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) Elon Musk personally asked US President Donald Trump to reconsider new US tariffs on imports from a number of countries, the Washington Post reported, citing two sources.
According to the publication, over the weekend, when Elon Musk unleashed a stream of messages on social media criticizing one of the White House’s top advisers, trade aide Peter Navarro, for Trump’s aggressive tariff plan, he personally approached the president. The attempt, however, has not yet been successful: Trump on Monday threatened to add new 50% tariffs on imports from China on top of those already announced if Beijing did not abandon its retaliatory measures, the newspaper said. On Sunday, Musk announced his support for the creation of a free trade area with the EU, despite President Trump’s previously imposed trade tariffs against the union. The US President signed an executive order on April 2 introducing “reciprocal” tariffs on imports from other countries, calling it a “liberation.” The basic minimum rate will be 10%, and 20% for goods from the European Union. The US President promised budget revenue from tariffs of $6-$7 trillion.

They have no idea what to do, zero consensus.. And all 27 of them will have to agree.
• EU Commission Eyeing 25% Tariffs on US Goods (Sp.)
The European Commission is proposing to impose reciprocal tariffs of up to 25% on a number of goods from the United States, in particular on clothing, yachts, fruit juices, nuts and diamonds, the RMF FM radio reported. Bourbon was excluded from the preliminary list after protests from France and Italy, which feared that the United States would impose 200% duties on wine, prosecco and champagne, the report said on Monday. EU countries are expected to vote on this proposal on Wednesday, the report added. However, the commission is still counting on negotiations with Washington, and it has proposed reciprocal zero tariffs on industrial products, including cars, the report read.
At the same time, French Minister Delegate for Europe Benjamin Haddad said that Paris is in favor of a tough response to the US tariffs and will support the European Commission’s decision to impose 25% tariffs on some US imports. On April 2, US President Donald Trump announced reciprocal tariffs on imports from other countries. For the UK the baseline rate of 10% was set. However for each country the tariff will be calibrated and will be half of what they charge companies importing US goods. Trump said this will be a “declaration of economic independence” for the United States. The EU is subject to 20% tariffs.

Ursula von der Leyen is afraid of the White House.
• Von der Leyen Endorses Meloni As Main Tariff Negotiator (Sp.)
As the White House prepares to receive the Italian PM on April 17, Ursula von der Leyen believes Giorgia Meloni is the only EU leader who can facilitate dialogue with Trump, the WP reports, citing Italian officials. European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen supports the upcoming visit of Italian Prime Minister Giorgia Meloni to Washington and believes that she is the one who is capable of facilitating dialogue between the European Union and US President Donald Trump, The Washington Post newspaper reported, citing an Italian official. On Tuesday, White House press secretary Karoline Leavitt said that Trump would receive Meloni in Washington on April 17.
“Von der Leyen is telling [Meloni] that if there’s one leader more in contact with the US, who’s capable of facilitating the conversation between the EU – not just Italy – and Trump, that’s her,” the official was quoted as saying by the newspaper on Tuesday. Von der Leyen was in favor of Meloni’s trip to Washington, the report added.

“..returning to tariffs as the source of government revenues and abandoning the income tax. This is consistent with correct economics and with freedom. Such a change would be possibly the most important reform in American history.”
• The Tariff Issue (Paul Craig Roberts)
The tariff controversy is being colored in the most scary ways possible, because the Democrats, media, and ruling establishment want rid of Trump. It is also important to understand that tariffs are not the only way to limit imports. There are other means, such as quotas. Quotas on imports into the US of Japanese cars were part of the US auto producers bailout negotiated in the final year of the Carter administration. I will attempt to put the issue in a correct perspective. It is not Trump’s intention, at least at the present time, to institutionalize a tariff regime. Trump is using tariffs as a threat to secure agreements that he thinks are in America’s interests. So far 50 countries have, according to reports, agreed to remove their tariffs on US goods. The countries responding aggressively seem to be China and our European allies.
I explained yesterday how Trump could better have gone about his task. Nevertheless, as the Commerce Secretary said, Trump’s tariffs are not expected to extend beyond a few weeks or a few months of negotiation. During this time there could be supply disruptions. Apparently, Trump is aware and has released an 11-page appendix that exempts all sorts of imported items that US producers require to continue their operations. Whatever disruption does occur, should be small compared to the Covid lockdown supply disruption, the basic cause of the current inflation. The Covid disruption was pointless and counterproductive. The tariff disruption, if there is one, is the cost of establishing a fair and uniform trading system. So, Trump is not being arbitrary or on a rampage to destroy international trade. Tariff negotiations, especially with so many countries and products can go on for years.
Trump might think that he only has two years to get anything done before the Democrats steal the midterm elections and bring his renewal of America to a halt. President Trump has spoken of tariffs in a wider and much more important context. Over most of American history until the First World War, tariff revenues were the source of government revenues. An income tax was unconstitutional and a violation of freedom. The definition of a free person is a person who owns his own labor. A slave does not own his own labor, and a serf only owns part of his labor. A person required to pay an income tax does not own that part of his labor that he must provide to government in order to avoid imprisonment. The difference between a medieval serf and an American taxpayer is the serf paid the tax in kind as hours worked, and the American pays the tax in money as a percentage of his income.
Classical economists, real economists unlike the faux ones of today, understood that factors of production–labor and capital–should not be taxed, because the supply of both to the economy is reduced by taxation. Supply-side economics is based on this principle. Thus, its emphasis on lowering the marginal rates of taxation. Reducing the supply of factors of production, reduces the economic growth rate and the national income. The century that the US economy has labored under income tax has costs us substantially in lost income. The classical economists said that taxation should fall on consumption not on factors of production. Traditionally, imported items are finished goods–German cars, French wines and perfumes. High priced goods are for the wealthy, so tariffs fall on the rich. The working class does not indulge in Porsche cars and Clicquot champagne. However, for about 30 years much of our imports have consisted of the offshored production of US firms.
When Apple, for example, brings its products made in China to the US to be marketed, they come in as imports and worsen the US trade deficit. Instead of beating up on China, Trump should call the US corporations that offshore their production for US markets to a White House conference and point out to them the consequences of their policy: the shrinkage of the American middle class, the loss of tax base, decaying infrastructure, and loss population of America’s former manufacturing cities, the pressure on city and state pension systems, the pressure of lower ratings on municipal bonds. Trump should ask the executives if they went too far in maximizing profits that benefitted a relatively few at the expense of the many, and what they think they should do about it. Capitalism ceases to serve the general interest when it separates Americans from the incomes associated with the production of the goods and services that they consume.
Trump has spoken of returning to tariffs as the source of government revenues and abandoning the income tax. This is consistent with correct economics and with freedom. Such a change would be possibly the most important reform in American history. It would be a difficult reform to achieve, because ideological, not economic, considerations intervene. Taxing the rich became the agenda of mass democracy. Taxing the rich was not seen as punishing a person for being successful. A successful person was portrayed as having become rich by exploiting labor. As fortunes were “stolen” by exploiting labor or resulted from government preference or legal privilege, income taxation was perceived as an instrument of justice. It is certainly perceived that way today by the liberal/left and the Democrat Party.
As an income tax is emotionally satisfying to the liberal/left, we are stuck with slower economic growth and less national income. It is disturbing that the liberal/left agenda has made American politics so highly partisan. What we see today is literal hatred of Trump, Republicans, conservatives, and white heterosexuals by the liberal/left. Hatred makes democracy dysfunctional. Politics cannot function as each side is intent on destroying any achievement by the other side. As democracy ceases to function, dictatorship becomes the means of governance. The liberal/left’s agenda to remake America by destroying its roots and recasting it into a different kind of society means the death of democracy and the rise of dictatorship. This is our real problem.

“Prime Minister Abe knew what President Trump was trying to achieve. In turn, President Trump knew Abe would remain a fierce Japan-first trade competitor to the America-first program..”
• President Trump Bestows Great Honor on Nation of Japan (CTH)
The decades long relationship between former Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe and President Donald Trump permeates through a recent announcement that Japan will be the first nation to enter the new era of trade negotiations with the United States. Shinzo Abe was assassinated in July 2022, as he traveled throughout Japan gaining support for increased national military development. As businessmen and later politicians Donald Trump and Shinzo Abe (RIP) had a decades long friendship grounded in mutual respect and competition. To understand the dynamic of President Trump giving the nation of Japan the position as the first nation to enter new trade negotiations, a high honor, is to understand the business relationship between the U.S and Japan in the post-World War II (40 yr) period between 1950 and 1990. The formative years for both Japanese industry and President Trump’s business empire.
For Europe the U.S. gave them money through the Marshall Plan, a process of one-way tariffs which helped them rebuild their nations. For Japan we gave them W Edwards Demming, an industrial engineer and extraordinarily brilliant mind in the processes of efficiency and industrial production. In essence, to generate the reindustrialization of both economies, we gave the EU a fish (money), but we taught Japan how to fish; how to be create and build exceptional industry. In the decades that followed, the EU rebuilt their capitalistic industrial base from the trade and tariff money we permitted them to exploit. The EU rebuilt from their historic systems, upgrading to newer industrial technology. Japan, however, learned deeper more technical skills from the Demming process of industrial capacity building, a critically strong excellence in quality manufacturing and attention to specific details in all processes.
It did not take long before the results of quality in design and Japanese manufacturing surfaced in the sector of automobiles, and later consumer electronics. The U.S. auto industry was slow to adapt to the Japanese quality focus and began losing market share to Toyota, Datsun, Nissan and Honda. Throughout this period, President Trump and Shinzo Abe were on opposite sides of the industrial competition. Trump railing about Japan, and later aggregate Asia exploiting our generosity; Abe smiling and joking with his friend that despite Trump’s grievances, tomorrow Eric will be purchasing 1,500 Sony televisions for his next Hotel. And so it went…. The friendship grew, the competition was intense but incredibly respectful, and both Shinzo Abe and Donald Trump became men of great influence whose partnership in competition was always visible.
Prime Minister Abe knew what President Trump was trying to achieve. In turn, President Trump knew Abe would remain a fierce Japan-first trade competitor to the America-first program. Tremendous respect and mutual admiration underpinned their geopolitical efforts. No single picture better exemplified the nature of Trump and Abe as the G7 summit picture taken in Canada as the ripple effects of Trump’s first-term trade and tariff program against China (mostly) started to hit the global economy. As China started to feel the pressure from President Trump forming new ASEAN partnerships, China started pulling back from ordering heavy industrial goods from Europe. The EU, specifically the German economy, felt the lessening of Chinese manufacturing via diminished orders. However, a respectful Japan positioned their trade agreements for benefit, but also for benefit of American workers.
Prime Minister Shinzo Abe knew there was nothing to fear from President Trump’s global trade reset. Unless, that is, you were a nation taking unfair advantage of the generosity provided by America. It makes total sense in the big picture for President Trump to honor the legacy of Shinzo Abe, and the respectful connections to Japan by granting them the first position in the schedule of the global trade reset. Total sense.

Musk’s private war with Navarro doesn’t define his relationship with Trump.
• Musk Wants Trump To Cancel Tariffs – WaPo (RT)
Elon Musk has made direct appeals to US President Donald Trump, urging him to reconsider his decision to impose steep tariffs on American trade partners, the Washington Post reported on Tuesday. According to the outlet, many business and tech leaders who supported Trump’s candidacy have also criticized the move, calling it overly aggressive. Trump unveiled sweeping new tariffs on global imports last week, including a 34% duty on Chinese goods. In response, Beijing pledged to retaliate with a matching 34% tariff on American exports – prompting Trump to threaten an additional new 50% tariff. Over the weekend, Tesla and SpaceX CEO Musk – who serves as Trump’s government efficiency czar – fired off a series of social media posts criticizing White House trade adviser Peter Navarro, a central architect of the president’s aggressive tariff strategy.
“A PhD in Econ from Harvard is a bad thing, not a good thing,” Musk wrote. Musk also reportedly reached out to Trump personally. The attempted intervention has so far failed to yield results, two people familiar with the matter told the Washington Post. As the head of Tesla, Musk has long viewed tariffs as harmful to the company’s goals, given that both the US and China serve as major manufacturing bases and key markets. Many business leaders who supported Trump’s candidacy were also frustrated by their inability to influence the policy and suggested that a basic 10% rate combined with negotiations with other countries would have been sufficient, according to the Post.
People close to Musk reportedly made direct appeals to allies within the Trump administration, including Vice President J.D. Vance and Musk himself, advocating for what they saw as more rational, pro-free-trade policies. One of Musk’s associates, investor Joe Lonsdale, posted on X that he had recently urged “friends in the administration” to reconsider, warning that tariffs would harm American companies more than Chinese ones. Over the weekend, a group of business leaders began organizing an informal coalition to lobby members of the Trump administration for more moderate trade policies, one person familiar with the effort told the Post. Trump has defended his actions, stating that “sometimes you have to take medicine to fix something,” and promised that jobs and investment would return to the United States, making it “wealthy like never before.”

They’re the big losers.
• Billionaires Slam Trump Tariffs (RT)
A host of American financiers and billionaire investors have criticized President Donald Trump over the sweeping tariffs he announced last week, calling the measures “poorly advised” and warning of serious consequences for the US economy. On April 2, Trump imposed a minimum 10% tariff on all imports and introduced “reciprocal” duties ranging from 11% to 50% on dozens of countries he accused of maintaining unfair trade imbalances. China responded with a reciprocal tariff of 34% on US imports, while a number of other nations signaled willingness to negotiate with Washington but threatened countermeasures if talks fail. Global markets have reacted sharply, with major indexes in the US, Europe, and Asia falling for three straight days.
JPMorgan Chase CEO Jamie Dimon slammed the tariffs in his annual letter to shareholders, warning they “will probably increase inflation” and the risk of recession, with the negative effects difficult to reverse. Ken Langone, billionaire co-founder of retailer Home Depot, criticized the tariffs as too high and rushed. In an interview with the Financial Times published on Monday, he described the additional 34% tariff on China – on top of the existing 20% – as “too aggressive, too soon,” and called the 46% levy on Vietnam “bullshit.” “I don’t understand the goddamn formula,” Langone said, urging a more measured approach, such as a 10% across-the-board tariff with waivers negotiated on a case-by-case basis. He added that he expects Trump to eventually pursue talks with trade partners because “right now, what everybody’s terrified of is a tariff war.”
Hedge fund investor Stanley Druckenmiller, a close mentor to Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent, posted a brief statement on X on Sunday: “I do not support tariffs exceeding 10%.” Billionaire investor Bill Ackman called the tariffs an “economic nuclear war” in a post on X. He called for a 10% flat tariff for “the privilege” of access to the US market but suggested pausing the reciprocal duties for 90 days to allow private negotiations. He lambasted Trump for relying on advisers for economic calculations, which he labeled incompetent. “The global economy is being taken down because of bad math,” he wrote.
Even tech mogul Elon Musk, Trump’s government efficiency czar, joined the criticism. He posted a series of comments on social media targeting White House trade adviser Peter Navarro, a key architect of the tariff plan, saying he “ain’t built sh*t” with the policy. Musk’s brother, Tesla board member Kimbal Musk, also condemned the tariffs, calling them a “structural, permanent tax on the American consumer.” Treasury Secretary Bessent said on Monday that Washington is open to “meaningful negotiations” in the coming weeks with trade partners, but only those who have responded “positively” to Trump’s tariffs. He criticized China for its response levies, accusing Beijing of “choosing to isolate itself by retaliating and doubling down on previous negative behavior.” China, in turn, described the new US tariffs as “economic bullying” and warned they could destabilize the entire global trade system.

“..any tax proposals or initiatives Bessent may pursue would be aligned with “his full support for President Trump’s America First Economic Agenda.”
• Officials Quietly Drafting Plan To Cushion Trump Tariff Fallout – Bloomberg (RT)
US officials are exploring ways to mitigate the potentially harmful effects of the sweeping tariffs announced by President Donald Trump, Bloomberg reported on Tuesday, citing sources in Washington. The talks are reportedly being held without Trump’s knowledge and reflect internal unease over his shift in trade policy. Last week, Trump imposed a minimum 10% tariff on all imports and introduced “reciprocal” duties ranging from 11% to 50% on dozens of countries he accused of maintaining unfair trade imbalances. The new measures included an additional 34% duty on imports from China, on top of an existing 20% rate implemented earlier, and a 20% levy on goods from the EU, among others.
On Monday, Trump threatened to slap a further 50% tariff on all Chinese imports unless Beijing reverses the 34% hike it announced in response to the new US levies. A number of other countries have slammed Trump’s tariffs over the past few days and vowed to implement countermeasures. According to Bloomberg, Trump administration officials fear that retaliatory tariffs will damage US exports, hurting American firms trying to sell goods abroad. Sources said discussions are underway about a potential exporter tax credit, which would serve as a subsidy for US firms selling products and services overseas. The credit, which would require congressional approval, could be issued at the end of the year.
Officials are also reportedly weighing a credit for importers to shield US companies from rising costs when sourcing goods from countries affected by Trump’s tariffs. These measures would aim to soften the economic blow to both exporters and importers once the tariffs take full effect. Sources told Bloomberg that neither Trump nor Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent has been formally briefed on the deliberations, and the proposals have yet to receive full backing from the administration’s economic team. A Treasury spokesperson confirmed the discussions but stressed that any talk of “specific provisions” are “still early.” The spokesperson added that any tax proposals or initiatives Bessent may pursue would be aligned with “his full support for President Trump’s America First Economic Agenda.” The White House declined to comment on the report.
Trump’s tariffs and the threat of retaliation have raised fears of a global trade war. Several investment banks have raised their recession risk forecasts for both the US and global economies over the past week. Stock markets have been rattled, with major indexes in the US, Europe, and Asia all trading lower the past three days. Despite the criticism, Trump has defended the tariffs as essential to correcting trade imbalances. On Monday, he claimed on social media that the measures were working and delivering significant economic benefits to the US.

$3,000 for an iPhone? Make a deal with India.
• Apple Staged Emergency iPhone Airlift From India (RT)
Apple transported five planeloads of iPhones and other devices from India to the US within a three-day period in late March, according to a report by the Times of India, quoting unnamed senior officials. The move was reportedly made to evade a new 10% reciprocal tariff introduced by US President Donald Trump, which came into effect on April 5. The company’s factories in India, China, and other key locations have shipped their products to the US in anticipation of higher tariffs, a source was quoted as saying in the report. The existing stock, which was imported at lower rates, will protect the company from higher costs for a while, until new shipments are made under the new tariffs, a source told the paper.
Although production has been partly shifted to Vietnam and India, the majority of iPhones are still manufactured in China. However, these countries are now facing tariffs as well, with Vietnam and India being hit with tariffs of 46% and 26%, respectively. Chinese products currently face a 34% import tax in the US. Apple is analyzing how different tariff structures across manufacturing locations will affect its supply chain, according to market watchers. Apple sells more than 220 million iPhones a year; its biggest markets include the US, China, and Europe, according to market data.
The cheapest iPhone 16 model was launched in the US at $799. This could now rise by 43% to $1,142. if Apple passes on the burden to consumers, Reuters said, citing calculations based on projections from analysts at Rosenblatt Securities. Apple currently does not plan to increase retail prices anywhere in the world, the Times of India added. Earlier today, a Wall Street Journal report said Apple is ramping up efforts to export more iPhones from India to the US in an attempt to mitigate the effects of the high tariffs on Chinese products imposed by Trump.

The welcoming app to facilitate the entry of illegals.
• More Than 900k “Biden-App”Migrants Told to ‘Self-Deport’ (NYP)
The Department of Homeland Security is urging nearly 1 million asylum seekers who entered the US through the CBP One app to “immediately” begin to “self-deport.” “Canceling these paroles is a promise kept to the American people to secure our borders and protect national security,” a DHS spokesperson said, following anecdotal reports from migrants that they had been told to return to their countries of origin. The CBP One smartphone app launched in January 2023 and through December 2024 was used to admit more than 936,500 people claiming persecution in their homelands, according to DHS data. Users were granted permission to live and work for two years in the US as they awaited the outcome of often backlogged local immigration proceedings. “Formal termination notices have been issued, and affected aliens are urged to voluntarily self-deport using the CBP Home App. Those who refuse will be found, removed, and permanently barred from reentry,” the DHS spokesperson said.
President Joe Biden’s administration launched the app to tamp down record-high illegal border crossings, but congressional Republicans accused Biden of illegally exceeding the traditional “parole” authority, which they said could not be granted categorically. The Trump DHS spokesperson said: “The Biden Administration abused the parole authority to allow millions of illegal aliens into the US which further fueled the worst border crisis in US history.” Precise data about the number of people impacted by the move are unclear for a variety of reasons — including the fact that some may have already been granted asylum, while others may be shielded by additional legal protections. The CBP One app was launched with a goal of facilitating the orderly movement of would-be illegal border crossers into the US from northern Mexico. Although geared to nationalities such as Haitians and Venezuelans flocking to the southwest border, Mexicans and citizens of other countries could participate.
Migrants who entered the US as part of programs for Afghan and Ukrainian citizens are not impacted by the latest announcement, according to DHS. DHS Secretary Kristi Noem also is revoking parole for 532,000 Cubans, Haitians, Nicaraguans and Venezuelans who flew to the US at their own expense with a financial sponsor — effective April 24. Additionally, the Trump administration is moving to end Temporary Protected Status (TPS) for 600,000 Venezuelans and about 500,000 Haitians — though that effort is paused by litigation. TPS grants 18-month reprieves for residents of designated countries and can apply to all residents of a particular nationality living within the US at the time of the protection’s declaration.
Illegal US-Mexico border crossings have plummeted since Trump took office in January with pledges to launch the largest mass deportation campaign in American history. That drive initially has focused on migrants accused of committing crimes — with Trump coercing their home countries to accept deportation flights, while sending some to Guantanamo Bay, Cuba, and others to a mega-prison in El Salvador.

If you can keep out the politics, their infrastructure may be useful…
• USAID Operations Rebooted in Several Crisis Zones (Sp.)
US President Donald Trump and the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) chief Elon Musk have repeatedly accused USAID of fraud, while Secretary of State Marco Rubio said the agency had long “strayed from its original mission.” At least 6 previously terminated USAID programs are being revived for emergency food assistance funding in Lebanon, Syria, Somalia, Jordan, Iraq, and Ecuador, Reuters reported. The move reportedly followed pressure from inside the administration and from Congress. US president Donald had previously frozen foreign aid and dismissed hundreds of USAID employees as part of DOGE-led efforts to slash federal programs and departments with little oversight, with Elon Musk calling labelling the agency a “criminal organization.” By bankrolling so-called civil society groups, USAID has long functioned as a covert enabler of American influence, sowing unrest and paving the way for regime change while packaging it all as “promoting democracy.”

Turns out, he’s not (more powerful than) the president after all…
• Judge Boasberg Scraps Trump Hearing On Deportations After Scotus Ruling (JTN)
U.S. District Judge James Boasberg on Tuesday canceled a deportation hearing for the Trump administration after the Supreme Court ruled the U.S. could continue to carry out deportations under the 1798 Alien Enemies Act. The hearing was to determine whether Boasberg would change the temporary restraining order he issued last month to block those deportations into a longer preliminary injunction, according to ABC News. On Monday, the Supreme Court ruled 5-4 that the Trump administration could use the 1798 Alien Enemies Act to deport suspected gang members of Tren de Aragua. The ruling overturns Boasberg’s March 15 order that temporarily blocked deportations under the wartime act, by granting the Trump administration’s request to vacate temporary restraining orders Boasberg placed on the order.
Miller
NOW – Stephen Miller Declares Supreme Court Ruling Trump’s Biggest Legal Victory To Date—Boasberg HUMILIATED, Deportation Powers UNLEASHED
“Those monsters can now be hunted down and expelled from this country with speed, force, and efficiency.”
Stephen Miller just reignited the… pic.twitter.com/LhIRU874O4
— Overton (@overton_news) April 8, 2025

“..his job isn’t to create policy—that duty belongs to the Executive Branch and Congress,” he said. “Instead, Judge Boasberg was charged with applying the relevant law to the facts of the case..”
• Legal Experts Sound Alarm On Judge Blocking Trump’s Deportations (DC)
As U.S. District Court Judge James Boasberg continues to be a thorn in the side of the Trump administration’s effort to deport gangbangers, legal experts have begun to raise questions about his handling of the case. The Barack Obama-appointed judge in March blocked President Donald Trump from using wartime authorities to send suspected Tren de Aragua gangbangers to a mega-prison in El Salvador, prompting incredible pushback from the president himself. As the challenge to the deportations play out in court, some legal experts have argued Boasberg should recuse himself from the case entirely, while others say he appears to be “making policy from the bench.” Critics have pointed to the fact that Boasberg’s daughter, Katharine Boasberg, works for an organization whose founder openly celebrated her father’s decision to halt the deportations.
“Under Canon 3 (C) (1) of the ‘Code of Conduct for United States Judges’ it states that judges must disqualify themselves from a case ‘in which the judge’s impartiality might reasonably be questioned,’” Hans von Spakovsky, a senior legal fellow at the Heritage Foundation, said to the Daily Caller News Foundation. “Given that his daughter works directly for an organization that supports illegal aliens, opposes deportation of aliens, and has voiced its support for Boasberg’s action in this very case, the impartiality of his judgment is obviously open to be reasonably questioned.” “He should have recused himself given his immediate family’s involvement in advocacy for illegal immigration,” Spakovsky continued.
The debate began on March 15, when Trump officially invoked the Alien Enemies Act of 1798, a seldom-used wartime authority, to expeditiously arrest and deport Tren de Aragua gang members. Boasberg quickly issued a temporary block on the flights and ordered any deportation flights in the air to turn around. However, three planes carrying 238 suspected and confirmed Tren de Aragua gangbangers and 23 MS-13 gang members managed to land at the El Salvador International airport. The Trump administration immediately ripped Boasberg for the decision. “Tonight, a DC trial judge supported Tren de Aragua terrorists over the safety of Americans,” Attorney General Pam Bondi stated after Boasberg’s order. “This order disregards well-established authority regarding President Trump’s power, and it puts the public and law enforcement at risk.”
In a court filing the following Monday, the Justice Department appealed the order and called for Boasberg to be reassigned. The administration further ripped the judge for “highly unusual and improper procedures” and accused the court of a “hasty public inquiry” into sensitive national security matters involving a criminal syndicate. “If a President doesn’t have the right to throw murderers, and other criminals, out of our Country because a Radical Left Lunatic Judge wants to assume the role of President, then our Country is in very big trouble, and destined to fail!” Trump posted on Truth Social. Questions over possible conflicts of interest arose after Boasberg’s family connections to a liberal organization surfaced. His daughter, Katharine, works for Partners in Justice, a nonprofit group based in New York City that provides client advocates to public defenders.
The group removed her biography from its website after Boasberg was assigned to the Alien Enemies Act case, according to the New York Post, but an archive of the page was saved. Before landing at Partners for Justice, Katharine worked at the Center for Justice Innovation, a left-wing organization that advocates for “racial justice” in the court system. Emily Galvin-Almanza, the founder and executive director of Partners in Justice, said Boasberg’s decision to block the wartime deportations was done “rightly” and she previously took to social media to rip the Laken Riley Act, a law mandating federal immigration authorities detain illegal migrants who commit theft-related crimes. The Code of Conduct for U.S. Judges makes clear that judges must recuse themselves from a case “in which the judge’s impartiality might reasonably be questioned,” including instances when a child of a judge is “known by the judge to have an interest that could be substantially affected by the outcome of the proceeding.”
However, there is debate over whether Boasberg fits this description. “Generally the employment of an adult child of a judge does not mandate recusal, even if the adult child is employed by a law firm representing a party in the case,” Richard Painter, a law professor for the University of Minnesota, said to the Daily Caller News Foundation. “However, if the adult child is at all involved in the representation of a party, recusal of the judge is generally required.” “Although nonprofits that don’t provide legal representation do not represent parties, I would apply the same rule,” Painter continued. “The involvement of an adult child’s employee in a matter is not sufficient grounds for recusal, but the involvement of the adult child herself is.”
Appointed to the bench by President Barack Obama in 2011, Boasberg has since presided over a number of high-profile court cases over the years, including those involving the Trump administration. In addition to the Alien Enemies Act case, the 62-year-old judge is also ruling over a lawsuit challenging top government officials’ use of Signal to discuss sensitive military operations in Yemen. Boasberg ripped the administration for allowing the deportation flights on March 15 to continue on to their destination in El Salvador, ostensibly in defiance of his order, and has demanded the DOJ answer a litany of questions regarding the flights. The administration has pointed out the judge’s written order didn’t get released until after the flights were already over international waters. While hesitant to declare whether Boasberg has any conflicts of interest in the deportation case, Matt O’Brien, a former immigration judge, questioned the immense scope of his ruling.
“The real problem with Judge Boasberg’s ruling isn’t any kind of bias. Rather, it is that, in this particular case, he rendered a decision which appears to have been intended to effectuate a specific policy outcome,” O’Brien, who now serves as Director of Investigations for the Immigration Reform Law Institute, said to the Daily Caller News Foundation. “However, his job isn’t to create policy—that duty belongs to the Executive Branch and Congress,” he said. “Instead, Judge Boasberg was charged with applying the relevant law to the facts of the case. Rather than doing his job he engaged in judicial activism (making policy from the bench).” Similar to O’Brien, the administration and other Republicans have voiced consternation over the level of authority a single district court judge is able to wield over an entire administrative branch of government.
Senate Judiciary Committee Chairman Chuck Grassley, a top ally of the president, introduced legislation in March that calls for limiting federal court orders to parties directly before the court. If passed and signed into law, such a move would essentially squash universal injunctions and rein in the scope of judicial activism. The desire to see such reforms in the judiciary appears to be quite high within the GOP. Grassley’s bill, which was very recently introduced, already touts more than 20 co-sponsors in the upper chamber. “And by engaging in such behavior, Judge Boasberg intruded upon powers that the Constitution and the Immigration and Nationality Act very clearly assigned to the Executive Branch,” O’Brien said. “That upends our system of checks and balances and throws the whole machinery of government off kilter.”




Jesus
AI reveals 'true face of Jesus' based on the Turin Shroud pic.twitter.com/5plpMfkubu
— Massimo (@Rainmaker1973) April 8, 2025
85 million
BREAKING: 85-Million-Person Study Finds Increased Risks of Stroke, Heart Attack, Coronary Artery Disease, and Arrhythmia Following COVID-19 Vaccination
Big data shows big damage to the vaccinated population. COVID-19 mRNA and viral vector injections linked to stroke (+240%),… pic.twitter.com/k5jrpTBrW6
— Peter A. McCullough, MD, MPH® (@P_McCulloughMD) April 8, 2025
Cancer
https://twitter.com/VigilantFox/status/1909374230585635102
DMSO
Dr. Pierre Kory highlights DMSO, an industrial solvent like chlorine dioxide, accidentally found to treat diseases, especially strokes. He’s told his wife to rub it on his neck if he shows neurologic deficits, citing cases of stroke reversal. Though it sounds unusual, he believes… pic.twitter.com/LojVUlMC7Z
— Camus (@newstart_2024) April 7, 2025
Pasta
Why pasta and breads feel different in Italy when eaten. pic.twitter.com/RLuqp14u66
— Suhr Majesty™ (@ULTRA_MAJESTY) April 6, 2025
3D cube
https://twitter.com/gunsnrosesgirl3/status/1909527032414757129
Capy
Good morning…
While the markets melt down, remember to take some time to relax pic.twitter.com/fYfE4bPX7Z
— Mario Nawfal (@MarioNawfal) April 7, 2025
Ripley
This is Ripley. He was nervous about taking the stairs. May have panicked a bit. 12/10 pic.twitter.com/zUBfQFaHXj
— WeRateDogs (@dog_rates) April 7, 2025
Puddle
The man, who prepared a small puddle in the forest, wondered and recorded the creatures that would benefit from this water;
— Enezator (@Enezator) April 7, 2025

Support the Automatic Earth in wartime with Paypal, Bitcoin and Patreon.