Andreas Feininger Production B-17 heavy bomber 1942

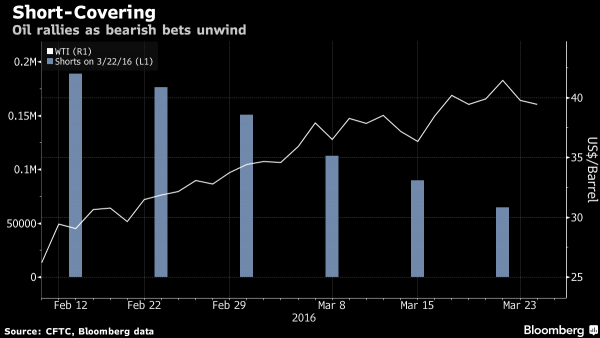
I don’t want TAE to be about warfare, but this situation is getting so absurd it’s starting to feel dangerous. Don’t believe the narrative.
• Syria and Russia Accuse Israel Of Missile Attack On Syrian Regime Airbase (G.)
Israeli war planes have bombed a Syrian regime airbase east of the city of Homs, the Russian and Syrian military have said. The Russian military said that two Israeli F-15 war planes carried out the strikes from Lebanese air space, and that Syrian air defence systems shot down five of eight missiles fired. Asked about the Russian statement, an Israeli military spokesman said he had no immediate comment. Syrian state TV reported loud explosions near the T-4 airfield in the desert east of Homs in the early hours of Monday. State TV initially reported that the attack was “most likely” American, a claim the Pentagon has denied.
Video footage on social media in Lebanon showed aircraft or missiles flying low over the country, apparently heading east towards Syria. At least 14 people, mostly Iranians or members of Iran-backed groups, were killed, the UK-based Syrian Observatory for Human Rights monitoring group said. Donald Trump warned on Sunday that the regime and its backers would pay a “high price” for the use of chemical weapons in the attack on rebel-held Douma that killed 42 people, but the Pentagon denied US forces were involved in Monday’s strikes. “However, we continue to closely watch the situation and support the ongoing diplomatic efforts to hold those who use chemical weapons, in Syria and otherwise, accountable,” a Pentagon spokesman said.
Separately, the White House put out an account of a telephone conversation between Trump and Emmanuel Macron, in which the US and French presidents “agreed to exchange information on the nature of the attacks and coordinate a strong, joint response”. Macron has said chemical weapons attacks in Syria would cross a “red line” for France and that French forces would strike if the regime was proven to have been involved. However, the French army denied responsibility for Monday’s attack.

When the easy money goes, everything follows.
• Stocks To Retest Correction Lows As Easy Money Disappears – Boockvar (CNBC)
He’s a Wall Street bear who sees more monster market moves coming — with the majority of them leaving stocks deep in the red. The Bleakley Advisory Group’s Peter Boockvar warns there’s more trouble brewing, because the era of easy money is ending, thanks to global central banks hiking borrowing costs. And as fears intensify over a trade war, Boockvar expects a solution to the tariff issue will eventually come at the expense of rising rates. “We could get that resumption of higher interest rates which would then concern the markets, and then retest the [S&P 500 Index] 2500-ish type lows,” the firm’s chief investment officer told CNBC’s “Futures Now” last week.
“We’re late cycle in the market. We’re late cycle in the economy, and you have an intensification in a tightening of monetary policy,” he said. Boockvar, a CNBC contributor, blamed the end of quantitative easing in the United States and Europe for increasing sell-off risks. “We’re a step closer to them wanting to take away negative interest rates. But there are still trillions of dollars of global bonds that have negative yielding rates,” he added. “So, it’s this rate environment that I think is becoming more of a headwind. That really is my main concern.” He doesn’t believe the situation will abate any time soon. Boockvar contended the 10-Year Treasury yield will push back toward 3 percent — preventing the S&P 500 from cracking above its Jan. 26 record high anytime soon.

Barron’s interview with Albert Edwards via ZH, who add a little David Rosenberg intro:
• Albert Edwards On The Next Recession: S&P Below 666 (ZH)
The Fed generally tightens rates until something breaks. David Rosenberg points out that since 1950 there have been 13 Fed tightening cycles, and 10 of them ended in recession (while the others have often ended in emerging market blow-ups, like the 1994 Mexican peso crisis). Surging delinquency and charge-off rates for smaller banks suggest the breaking point for the economy may come sooner than the Fed and bulls expect.
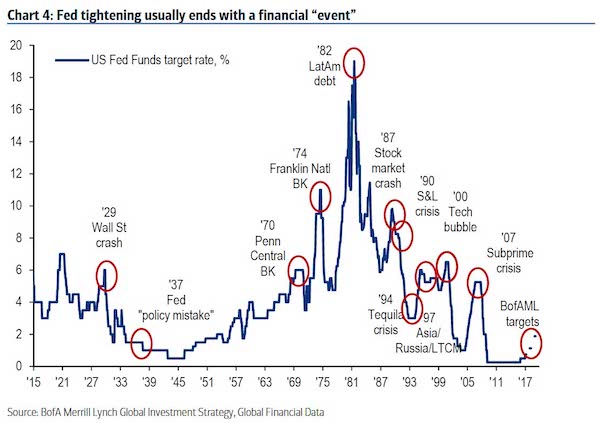
What happens to stocks during the next recession? The Federal Reserve managed to short-circuit this derating process. In 2011, when quantitative easing, or QE, really kicked in, equity re-engaged with bond yields and P/Es expanded. Like an artificial stimulant, QE inflated all asset prices away from fundamental value and from where they would otherwise have gone. We haven’t seen the lows in bond yields. In the next recession, bond yields in the U.S. will go negative and converge with those in Germany and Japan. The forward U.S. P/E bottomed at about 10.5 times in March 2009 on trough earnings. That was lower than the previous recession.
In the next recession, I would expect the P/E to bottom at about seven times, a lower low with earnings about 30% lower because of the recession. That would put the S&P lower than the 666 low of the previous crash, versus 2671 Thursday afternoon. If a recession unfolds, easy monetary policy won’t stop the market from collapsing. It will play itself out.
When will the recession hit: The Conference Board’s leading indicators look OK for now. What’s different is that problems in the real economy aren’t being reflected in the stock and bond markets. What we may see is the reverse: The stock market and parts of the credit markets collapse and cause problems in the real economy. If confidence collapses because the equity market collapses, then a recession unfolds.
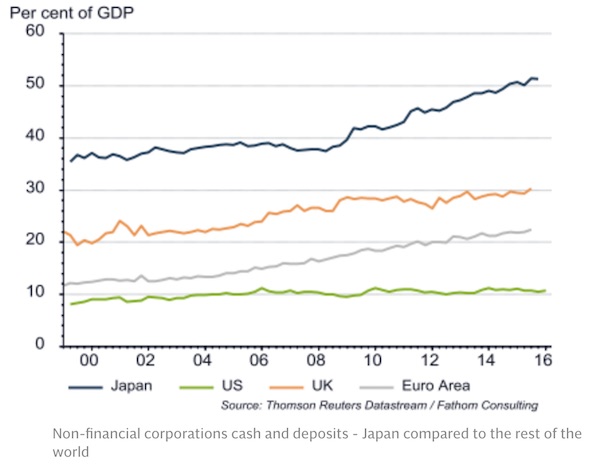
Will the US be hit harder than Japan and Europe in the next bear market? It should be. Traditionally, if the U.S. goes down 20%, the German Dax, though it is cheaper, would tend to go down a little more. Maybe this time it won’t. Japan is the one market we do like now on a long-term basis, and one of the reasons is the buildup of U.S. corporate debt during these past few years. The big bubble is U.S. corporate debt. In contrast, Japan’s corporate debt is collapsing. Over half of its companies have more cash than debt. When the Fed buys U.S. Treasuries, it pulls down all yields. There has been demand for yield, so investors look at corporate bonds as an alternative. Companies have been very keen to issue them, and they have used the money to buy back stock or as a way to enrich management. This is the way QE has washed through the system here.

“..rising expectations of a Fed policy mistake.. We could argue that mistake is 10 years old by now.
• Bad Omen for Markets From First Signs of Yield Curve Inversion
The forward curve of a closely watched proxy for the Federal Reserve’s policy rate has slightly inverted, signaling investors are either pricing in a mistake from central bankers or end-of-cycle dynamics, according to JPMorgan Chase. The inversion of the one-month U.S. overnight indexed swap rate implies some expectation of a lower Fed policy rate after the first quarter of 2020, the bank’s strategists including Nikolaos Panigirtzoglou, wrote in a note Friday. “An inversion at the front end of the U.S. curve is a significant market development, not least because it occurs rather rarely,” they said. “It is also generally perceived as a bad omen for risky markets.”
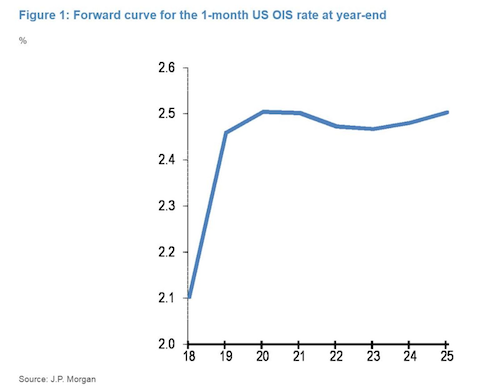
The negative market signal comes as investors grapple with higher short term borrowing costs, which have risen in the U.S. to levels unseen since the financial crisis. While the strategists admit it is difficult to discern which of the two explanations for the curve inversion carries more weight, flow data suggests it is more likely to be rising expectations of a Fed policy mistake.

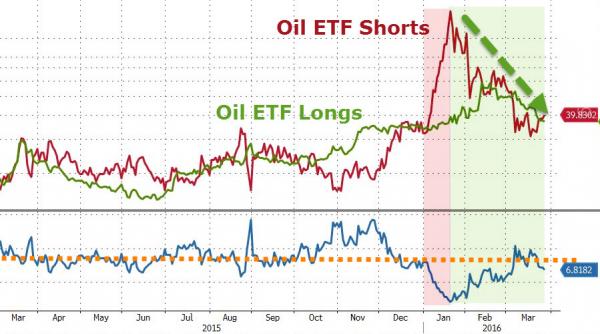
No, Bloomberg, we know that China can’t dump Treasuries. The “end of Chimerica” sounds poetic though.
• Trump’s Trade War Threatens Central Bank ‘Put’ – Deutsche (BBG)
A breakdown in the relationship between dollar weakness and Asian central bank intervention poses a risk to Treasuries, stocks and all risky assets, according to Deutsche Bank. Attempts by the Trump administration to clamp down on currency manipulation have limited the ability of central banks across the region to buy U.S. assets when the dollar weakens, and dampen the appreciation of their currencies, strategist Alan Ruskin write in a note Friday. These purchases have historically limited the greenback’s downside and acted as a “put” on Treasury market weakness, he wrote. Such central bank puts are usually associated with successive Federal Reserve chairs willing to support the wider market with loose monetary policy.
While such puts have been a continuous focus for investors, markets now risk overlooking other sources of central bank support that may be slipping as the U.S.’s “synergistic relationship with China,” comes to an end, according to Ruskin. “It is not a coincidence that in this recent period of dollar weakness, Treasury bonds were also soft,” he said. “Historically, foreign central banks of sizable current account surplus countries like China, Taiwan, Korea and Thailand would have been intervening.” According to the strategist, the “end of Chimerica” means American current account deficits are no longer financed to the same degree by Asian central bank reserve recycling of corresponding trade surpluses. That reduction in demand for Treasuries from foreign reserves is coming at a time when U.S. fiscal supply is set to increase dramatically, putting extra pressure on the country’s bond market.


This is more likely. Risky for China though, but there must be plans to shore up domestic firms.
• China Is Studying Yuan Devaluation as a Tool in Trade Spat (BBG)
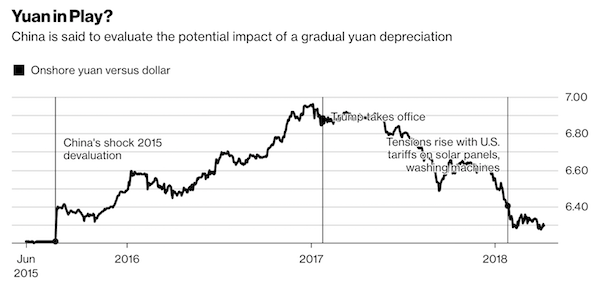
China is evaluating the potential impact of a gradual yuan depreciation, people familiar with the matter said, as the country’s leaders weigh their options in a trade spat with U.S. President Donald Trump that has roiled financial markets worldwide. Senior Chinese officials are studying a two-pronged analysis of the yuan that was prepared by the government, the people said. One part of the analysis looks at the effect of using the currency as a tool in trade negotiations with the U.S., while a second part examines what would happen if China depreciates the yuan to offset the impact of any trade deal that curbs exports. The analysis doesn’t mean officials will carry out a devaluation, which would require approval from top leaders, the people said.
The yuan erased early gains on Monday, weakening 0.1 percent to 6.3110 per dollar in onshore trading at 3:32 p.m. local time. While Trump regularly bashed China on the campaign trail for keeping its currency artificially weak, the yuan has gained about 9 percent against the greenback since he took office as China’s economic growth stabilized, the government clamped down on capital outflows and fears of a credit crisis receded. The Chinese currency touched the strongest level since August 2015 last month and has remained steady in recent weeks despite an escalation of trade tensions between the world’s two largest economies.
While a weaker yuan could help President Xi Jinping shore up China’s export industries in the event of widespread tariffs in the U.S., a devaluation comes with plenty of risks. It would make it easier for Trump to follow through on his threat to brand China a currency manipulator, make it more difficult for Chinese companies to service their mountain of offshore debt, and undermine recent efforts by the government to move toward a more market-oriented exchange rate system. It would also expose China to the risk of local financial-market volatility, something authorities have worked hard to subdue in recent years.
When China unexpectedly devalued the yuan by about 2 percent in August 2015, the move sent shock-waves through global markets. “Is it in their interest to devalue yuan? It’s probably unwise,” said Kevin Lai, chief economist for Asia ex-Japan at Daiwa Capital Markets Hong Kong Ltd. “Because if they use devaluation as a weapon, it could hurt China more than the U.S. The currency stability has helped to create a macro stability. If that’s gone, it could destabilize markets, and things would look like 2015 again.”

No really, it’s everywhere. What they can do, they will.
• YouTube Illegally Collects Data On Children – Child Protection Groups (G.)
A coalition of 23 child advocacy, consumer and privacy groups have filed a complaint with the US Federal Trade Commission alleging that Google is violating child protection laws by collecting personal data of and advertising to those aged under 13. The group, which includes the Campaign for a Commercial-Free Childhood (CCFC), the Center for Digital Democracy and 21 other organisations, alleges that despite Google claiming that YouTube is only for those aged 13 and above, it knows that children under that age use the site. The group states that Google collects personal information on children under 13 such as location, device identifiers and phone numbers and tracks them across different websites and services without first gaining parental consent as required by the US Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (Coppa).
The coalition urges the FTC to investigate and sanction Google for its alleged violations. “For years, Google has abdicated its responsibility to kids and families by disingenuously claiming YouTube — a site rife with popular cartoons, nursery rhymes, and toy ads — is not for children under 13,” said Josh Golin, executive director of the CCFC. “Google profits immensely by delivering ads to kids and must comply with Coppa. It’s time for the FTC to hold Google accountable for its illegal data collection and advertising practices.”
The group claims that YouTube is the most popular online platform for children in the US, used by about 80% of children aged six to 12 years old. Google has a dedicated app for children called YouTube Kids that was released in 2015 and is designed to show appropriate content and ads to children. It also recently took action to hire thousands of moderators to review content on the wider YouTube after widespread criticism that it allows violent and offensive content to flourish, including disturrbing children’s content and child abuse videos.

Bizarro housing.
• Number Of UK Buy-to-Let Landlords Reaches Record High (Ind.)
The number of buy-to-let investors in the UK rose to a record high of 2.5 million in the latest tax year, new research shows. The increase of 5% on the previous year comes despite the introduction of a host of extra taxes and regulations on the sector. In recent years, the government has brought in a 3% Stamp Duty levy, new stress tests for home loans, and ended mortgage interest tax relief. The number of landlords has increased 27% in the past five years, up from 1.97 million in 2011-12, research by London-focused estate agent Ludlow Thompson found.
Landlords now own an average of 1.8 buy-to-let properties each – a figure that has risen for the fifth consecutive year. The data suggests that landlords continue to see residential property, especially in London, as a strong investment, despite signs that house price growth has stalled or even gone into reverse in some areas in the last year. Investors have seen annual returns of almost 10% since 2000, Ludlow Thompson said. Chairman Stephen Ludlow said the rising number of landlords shows the enduring appeal of investing in buy-to-let. “The long-term picture for the buy-to-let market remains strong,” he said.

No chance of a second vote for now. But that may change yet.
• Public Backs Fresh Referendum On ‘Final Say’ On Terms Of Brexit Deal (Ind.)
Support is growing for a fresh referendum on the final Brexit deal, according to a new poll showing the public back the idea for the first time. The survey found that 44% of people want a vote on the exit terms secured by Theresa May, amid continued uncertainty over the withdrawal agreement. That is a clear eight points ahead of the 36% who reject a further referendum, the research conducted for the anti-Brexit Best for Britain group showed. The group pointed to evidence that “Brexit is sharpening the British public’s minds” and called for MPs to respond to the people’s growing desire for a “final say”.
The referendum would be held on the details of the deal the prime minister must strike by the autumn – on both the planned transition period and a “framework” for a permanent trade and security relationship. Eloise Todd, Best for Britain’s chief executive, said voters should be allowed to choose between the details of the future on offer outside the EU, or staying inside the bloc. “Now there is a decisive majority in favour of a final say for the people of our country on the terms of Brexit. This poll is a turning point moment,” she said. “The only democratic way to finish this process is to make sure the people of this country – not MPs across Europe – have the final say, giving them an informed choice on the two options available to them: the deal the government brings back and our current terms.

Celente rants are always good.
• Murderers & Thieves Sold Out America – Gerald Celente (USAW)
Renowned trends researcher Gerald Celente says the trade war President Trump is starting against China must be fought for America to survive. Celente explains, “We have lost 3.5 million jobs (to China). Some 70,000 manufacturing plants have closed. Why would anybody be fighting Trump to do a reversal of us being in a merchandise trade deficit of $365 billion? Tell me any two people that would do business with each other and one side takes a huge loss and keeps taking it. . . So, why would people argue and fight and bring down the markets because Trump wants to bring back jobs and readjust a trade deficit that, by any standard, is destroying the nation?” Who’s to blame for the lopsided trade deficits destroying the middle class of America?
Look no further than the politicians and corporations buying them off. Celente charges, “They sold us out. The European companies and the American companies sold us out, and the people fighting Trump are also the big retailers because they’ve got their slave labor making their stuff over there. They bring it back here and mark up the price, and they make more money. If they have to pay our people to do that work, they have to pay them a living wage and they can’t make enough profit. That’s who is fighting us. . You go back to our top trend in 2017, and it was China was going to be the leader in AI (artificial intelligence) now and beyond, and that is exactly what happened. All the corporations have sold us out. . . .The murderers and the thieves sold out America.”
Celente thinks the odds are there will not be a financial crash in 2018 “because they are repatriating all that dough from overseas at a very low tax rate and because of the tax cuts from 35% to 21%. These are the facts. In the first three months of this year, there have been more stock buybacks and mergers and acquisitions activity than ever before in this short period of time because of all that cheap money going back into the corporations. That’s what’s keeping the markets up.”

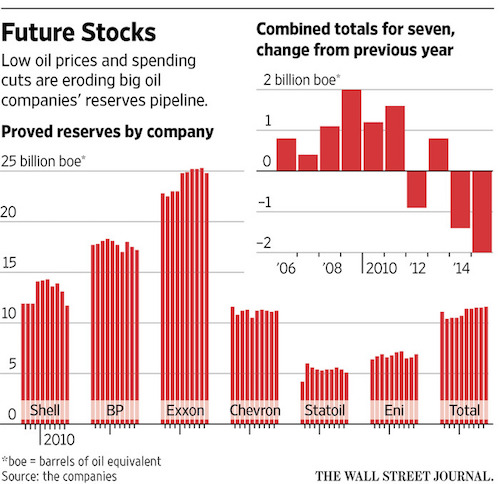
Shell’s political power will shield it.
• Shell Predicted Dangers Of Fossil Fuels And Climate Change In 1980s (Ind.)
Oil giant Shell was aware of the consequences of climate change, and the role fossil fuels were playing in it, as far back as 1988, documents unearthed by a Dutch news organisation have revealed. They include a calculation that the oil company’s products alone were responsible for 4% of total global carbon emissions in 1984. They also predict that changes to sea levels and weather would be “larger than any that have occurred over the past 12,000 years”. As a result, the documents foresee impacts on living standards, food supplies and other major social, political and economic consequences.
In The Greenhouse Effect, a 1988 internal report by Shell scientists, the authors warned that “by the time the global warming becomes detectable it could be too late to take effective countermeasures to reduce the effects or even to stabilise the situation”. They also acknowledged that many experts predicted an increase in global temperature would be detectable by the end of the century. They went on to state that a “forward-looking approach by the energy industry is clearly desirable”, adding: “With the very long time scales involved, it would be tempting for society to wait until then before doing anything. “The potential implications for the world are, however, so large that policy options need to be considered much earlier. And the energy industry needs to consider how it should play its part.”

Money trumps history.
• Indigenous People Are Being Displaced Again – By Gentrification (Latimore)
It is symptomatic of the colonial-settler prerogative that has sought to eliminate the offensive presence of the natives from any profitable territory. In 21st-century Australia, the “dispersal” that began with European invasion continues through the gentrification of city suburbs where Indigenous identities persist. In the colonial argot of the 19th century, dispersal euphemistically described a bloody practice of massacre and forced dispossession of First Nations peoples, often performed as punishment for perceived theft, or any other form of resistance to the colonisers more generally. In the early and mid-20th century, blackfullas were forcibly coerced into government reserves most commonly known as “missions”.
The overarching intent of these “protection” policies was to ensure the dissolution of First Nations culture and traditional governance structures, pushing mob to develop from “their former primitive state to the standards of the white man”, as the Aboriginal Protection Board said in 1935. When the missions began to be disbanded after the second world war, it forced significant Indigenous migration from the bush to towns and cities, where we repopulated places like Fitzroy, Brisbane’s West End and particularly Redfern in great numbers. This 1950s policy of “assimilation” was essentially a state-sanctioned experiment to force Indigenous people to give up their beliefs and traditions as they adapted to urban life.
[..] Yet the place of blackfullas in Australia’s cities is under threat. Faced with rapid gentrification and associated rental and ownership price hikes, urban Indigenous populations continue to relocate to the outer suburbs, where cheaper housing is usually located. The trend could be viewed as a contemporary iteration of the dispersals of the past – decidedly less bloody, though equally impelled by capitalistic imperatives.

Logic.
• Fish Populations In Great Barrier Reef Collapse After Bleaching Events (Ind.)
The coral bleaching events that have devastated the Great Barrier Reef in recent years have also taken their toll on the region’s fish population, according to a new study. While rising temperatures on the reef killed nearly all the coral in some sections, the effects on the wider marine community have been less clear. Now, scientists have begun to establish the long-term effects of bleaching events on the Great Barrier Reef’s fish population. This work is essential for researchers trying to understand what will happen to coral reef ecosystems as global warming makes mass bleaching events more frequent. “The widespread impacts of heat stress on corals have been the subject of much discussion both within and outside the research community,” said PhD student Laura Richardson of the ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies.
“We are learning that some corals are more sensitive to heat stress than others, but reef fishes also vary in their response to these disturbances.” Ms Richardson and her collaborators studied reefs in the northern section of the Great Barrier Reef, where around two-thirds of corals were killed in the 2016 bleaching event that followed a global heatwave. The researchers found there were “winners” and “losers” among the fish species on the reef, but overall there was a significant decline in the variety of species following bleaching. Their results were published in the journal Global Change Biology. “Prior to the 2016 mass bleaching event, we observed significant variation in the number of fish species, total fish abundance and functional diversity among different fish communities,” said co-author Dr Andrew Hoey.
“Six months after the bleaching event, however, this variation was almost entirely lost.” Predictably, the scientists noted that fish with intimate associations with corals suffered severe losses. Butterflyfish, which feed on corals, faced the steepest declines. In response to the looming threat of coral bleaching, scientists have called for “radical interventions” to save the world’s reefs. Some have suggested that more than 90% of corals could die by 2050 at the current rate of global warming.