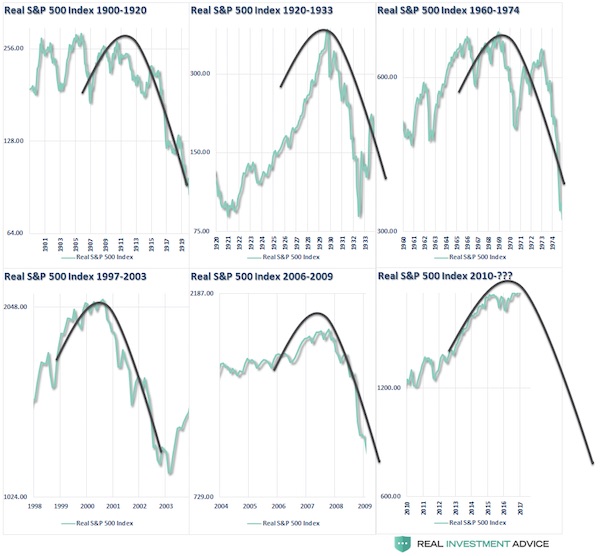
Margaret Bourke-White Great Ohio River Flood, Louisville, Kentucky 1937

Dollar shortage grows as interest rates grow.
• The Soaring Dollar Will Lead To An “Explosive” Market Repricing (ZH)
Something curious took place one month ago when the PBOC announced on April 17 that it would cut the reserve requirement ratio (RRR) by 1% to ease financial conditions: it broke what until then had been a rangebound market for both the US Dollar and the US 10Y Treasury, sending both the dollar index and 10Y yields soaring…
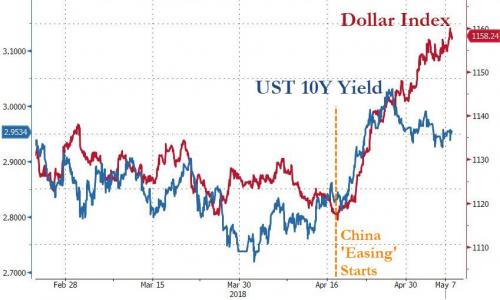
… which led to an immediate tightening in financial conditions both domestically and around the globe, and which has – at least initially – manifested itself in a sharp repricing of emerging market risk, resulting in a plunge EM currencies, bonds and stocks.
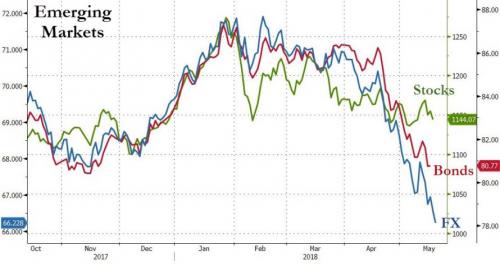
Adding to the market response, this violent move took place at the same time as geopolitical fears about Iran oil exports amid concerns about a new war in the middle east and Trump’s nuclear deal pullout, sent oil soaring – with Brent rising above $80 this week for the first time since 2014 – a move which is counterintuitive in the context of the sharply stronger dollar, and which has resulted in even tighter financial conditions across the globe, but especially for emerging market importers of oil.
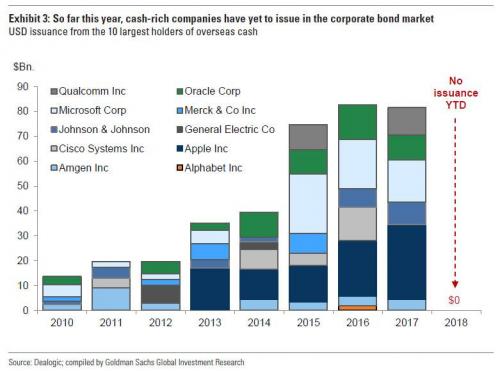
Meanwhile, all this is playing out in the context of a world where the Fed continues to shrink its balance sheet – a public sector “Quantitative Tightening (QT)” – further tightening monetary conditions (i.e., shrinking the global dollar supply amid growing demand), even as high grade US corporate bond issuance has dropped off a cliff for cash-rich companies which now opt to repatriate cash instead of issuing domestic bonds, with the resulting private sector deleveraging, or “private sector QT”, further exacerbating tighter monetary conditions and the growing dollar shortage (resulting in an even higher dollar).

Europe has no bond market left. Japan has no bond market left. All they have is central banks.
• Draghi Calls for Consolidation of Debts? (Martin Armstrong)
COMMENT: You were here in Brussels a few weeks ago. Suddenly, the ECB is talking about the need to merge the debts to prevent a crisis. So your lobbying here seems to work. – RGV, Brussels. REPLY: I do not lobby. It is rather common knowledge I have made those proposals since the EU commission attended our World Economic Conference held back in 1998 in London. I focused on the reason the Euro would fail if the debts were not consolidated. So it is not a fair statement to say I meet in Brussels to lobby for anything. I meet with people who call me in because of a crisis brewing.
So everyone else understands what this is about, the ECB President Mario Draghi has come out and proposed interlocking the euro countries to create a “stronger” and “new vehicle” as a “crisis instrument” to save Europe. He is arguing that this should prevent countries from drifting apart in the event of severe economic shocks. Draghi has said it provides “an extra layer of stabilization” which is a code phrase for the coming bond crash. He has conceded that the legal structure is difficult because what he is really talking about is the consolidation of national debts into a single Eurobond market. There is no bond market that is viable in Europe after the end of Quantitative Easing. There will be NO BID.
There is no viable bond market left in Europe. The worst debt is below US rates only because the ECB is the buyer. Stop the buying and the ceiling comes crashing down. This is why what he is saying is just using a different label. He is not calling it debt consolidation, just an extra layer of stabilization to bind the members closer together. It will be a hard sell and it may take the crisis before anyone looks at this. You have “bail-in” policies because of the same problem. If the banks in Italy need a bailout from Brussels, then other members will look at it as a subsidization for Italy which is unfair. There is no real EU unity behind the curtain which is when the debt was NEVER consolidated from day one. They wanted a single currency, but not a single responsibility for the debt.

“..20% of Italy’s industrial capacity has been destroyed, and 30% of the country’s firms have defaulted..”
• Italy’s Organic Crisis (Thomas Fazi)
The Italian Marxist Antonio Gramsci coined the term “organic crisis” to describe a crisis that differs from ”ordinary” financial, economic, or political crises. An organic crisis is a “comprehensive crisis,” encompassing the totality of a system or order that, for whatever reason, is no longer able to generate societal consensus (in material or ideological terms). [..] Gramsci was talking about Italy in the 1910s. A century later, the country is facing another organic crisis. More specifically, it is a crisis of the post-Maastricht model of Italian capitalism, inaugurated in the early 1990s.
[..] The downfall of the political establishment—and the rise of the “populist” parties—can only be understood against the backdrop of the “the longest and deepest recession in Italy’s history,” as the governor of the Italian central bank, Ignazio Visco, described it. Since the financial crisis of 2007–9, Italy’s GDP has shrunk by a massive 10%, regressing to levels last seen over a decade ago. In terms of per capita GDP, the situation is even more shocking: according to this measure, Italy has regressed back to levels of twenty years ago, before the country became a founding member of the single currency. Italy and Greece are the only industrialized countries that have yet to see economic activity surpass pre–financial crisis levels.
As a result, around 20% of Italy’s industrial capacity has been destroyed, and 30% of the country’s firms have defaulted. Such wealth destruction has, in turn, sent shockwaves throughout the country’s banking system, which was (and still is) heavily exposed to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Italy’s unemployment crisis continues to be one of the worst in all of Europe. Italy has an official unemployment rate of 11% (12% in southern Italy) and a youth unemployment rate of 35% (with peaks of 60% in some southern regions). And this is not even considering underemployed and discouraged workers (people who have given up looking for a job and therefore don’t even figure in official statistics).
If we take these categories into consideration, we arrive at a staggering effective unemployment rate of 30%, which is the highest in all of Europe. Poverty has also risen dramatically in recent years, with 23% of the population, about one in four Italians, now at risk of poverty—the highest level since 1989.

Europe gets nervous.
• Italy Has A New Government As Populist Parties Agree On New Premier (ZH)
Taking the biggest step toward forming Italy’s next government, the head of the anti-immigration League party Matteo Salvini said he’s reached a deal with Five Star leader Luidi Di Maio on forming a populist government, and picked a premier. According to a report in Corriere, Florence University law professor Giuseppe Conte was chosen as prime minister, while Matteo Salvini would be proposed as interior minister, and Five Star head Luigi and Di Maio would be labor minister. On Saturday, Il Messaggero reported that Salvatore Rossi, the Bank of Italy’s director general, could be picked as finance minister.
Today, Ansa added that according to Di Maio, Five Star will head joint ministry of economic development and labor; separately Giancarlo Giorgetti, Matteo Salvini’s right-hand man, will be proposed as economy minister, while Nicola Molteni would become minister of the infrastructure and transport and Gian Marco Centinaio would head the department of Agriculture and Tourism. ANSA added that Salvini will present the proposal to President Sergio Mattarella on Monday. As Bloomberg adds, the endgame follows a week of turmoil in Italian bonds and stocks triggered by reports about the coalition’s spending plans and rejection of European Union budget rules.
Italy’s 10-year yield spread over German bonds shot up to 165 bps on Friday, the most since October, prompting a warning from Paris. French Finance Minister Bruno Le Maire said in a Sunday interview with Europe 1 radio that “if the new government took the risk of not respecting its commitments on debt, the deficit and the cleanup of banks, the financial stability of the entire euro zone will be threatened.” Salvini fired back on Twitter, suggesting the warning was “unacceptable” interference. “Italians first!” he said, clearly referencing Donald Trump.

No crisis until now because so much was borrowed. Crisis now because so much was borrowed. It’s like a blue print for the entire world.
• Argentina: From The “Confidence Fairy” To The -Still Devilish- IMF (CF)
[..] looking at the external front, one may even be forgiven for asking: why did this crisis take so long to burst? Argentina was haemorrhaging dollars for many years, and with no sign of reversal: since 2016 the domestic non-financial sector acquired an accumulated amount of USD 41 billion in external assets. During the same period, the current account deficit totalled another USD 30 billion, in the form of trade deficit, tourism deficit, profit remittances by foreign companies and increasing interest payments. The well-known factor that allowed all these trends to last until now is the foreign borrowing spree that involved the government, provinces, firms, and the central bank, including the inflow from short-term investors for carry trade operations.
In the case of debt issuance, since 2016 the central government, provinces and private companies, have issued a whopping USD 88 billion of new foreign debt (13% of GDP). In the case of carry trade operations, since 2016 the economy recorded USD 14 billon of short-term capital inflows (2% of GDP). The favourite peso-denominated asset for this operations were the debt liabilities of the central bank called LEBAC (Letters of the Central Bank). Because of this, the outstanding stock of this instrument has now become the centre of all attention. It is important to understand the LEBACs. They were originally conceived as an inter-bank and central bank liquidity management instrument.
Since the lifting of foreign exchange and capital controls and the adoption of inflation targeting, the stock of LEBACs grew by USD 18 billion. Moreover, the composition of holders has changed significantly since 2015: At that time, domestic banks held 71% of the stock, and other investors held 29%. In 2018 that proportion has reverted to 38% banks/62% to other non-financial institution holders, which includes other non-financial public institutions (such as the social security administration) (17%), domestic mutual investment funds (16%), firms (14%), individuals (9%), and foreign investors (5%). That means that a large part of all the new issuance of LEBAC is held by investors outside the regulatory scope of the central bank, especially individuals and foreign investors. [..] these holdings could easily be converted into foreign currency, causing a large FX depreciation.

They’re talking.
• US-China Trade War ‘On Hold’ As America Backs Off On Tariffs (Ind.)
The US will hold off on imposing steep tariffs on China that ignited fears of a trade war as both sides pursue a broader deal, a top economic official said. “We’re putting the trade war on hold,” Treasury secretary Steve Mnuchin said during an appearance on Fox News Sunday. “We have agreed to put the tariffs on hold”. The announcement of a detente in the escalating trade dispute came after Chinese officials visited Washington last week, leading the White House to release an optimistic statement about both sides agreeing to take “measures to substantially reduce the United States trade deficit in goods with China” and to work on expanding trade and protecting intellectual property.
Donald Trump has railed against trade imbalances, particularly with China, as he seeks to renegotiate America’s economic relationship with other nations he accuses of exploiting the US. Breaking with some of his top economic advisers, Mr Trump announced earlier this year that he would levy tariffs on steel and aluminium. He also signed a memorandum seeking tariffs on $60bn worth of Chinese goods. [..] Mr Mnuchin signalled that America was using the leverage from tariff threats to pivot to negotiation, saying talks with Chinese officials had produced “very meaningful progress” – including a “Very productive” oval office meeting between Mr Trump and a top Chinese official.

Unintended?
• Bill Aimed At Saving Community Banks Is Already Killing Them (Dayen)
After initial reluctance, House Republicans have finally reached an agreement to move forward on a bipartisan bank deregulation bill that the Senate passed in March. Its stated aim — to help rural community banks thrive against growing Wall Street power — appears to have been enough to power it across the finish line. But banking industry analysts say the bill is already having the opposite effect, and its loosening of regulations on medium-sized banks is encouraging a rush of consolidation — all of which ends with an increasing number of community banks being swallowed up and closed down. “We absolutely expect bank consolidation to accelerate,” Wells Fargo’s Mike Mayo told CNBC the day after the Senate passed the deregulation bill in March.
The reason? Banks no longer face the prospect of stricter and more costly regulatory scrutiny as they grow. And regional banks in Virginia, Ohio, Mississippi, and Wisconsin have already taken note before the bill has even passed into law, announcing buyouts of smaller rivals. The expected consolidation simply furthers an existing trend. Community banks have been struggling for decades against an epidemic of consolidation; the number of banks in America has fallen by nearly two-thirds in the past 30 years. Ironically, the one state that has seemingly figured out how to arrest this systemic abandonment of smaller communities is North Dakota, the home state of the bill’s co-author, Democratic Sen. Heidi Heitkamp. That’s because North Dakota has a public bank.
Using idle state tax revenue as its deposit base, the Bank of North Dakota partners with community lenders on infrastructure, agriculture, and small business loans. It has thrived, earning record profits for 14 straight years, which have funneled back into state coffers. And while Heitkamp has complained that the Dodd-Frank Act has been disastrous for community banks, in North Dakota they appear to be doing well. According to a Institute for Local Self-Reliance analysis of Federal Deposit Insurance Corp. data, North Dakota has more banks per capita than any other state, and lends to small businesses at a rate that is four times the national average.

The wonders of lobbying.
• EU Blocking Cities’ Efforts To Curb Airbnb (G.)
The explosive rise of short-stay Airbnb holiday rentals may be shutting locals out of housing and changing neighbourhoods across Europe, but cities’ efforts to halt it are being stymied by EU policies to promote the “sharing economy”, campaigners say. “It’s pretty clear,” said Kenneth Haar, author of UnfairBnB, a study published this month by the Brussels-based campaign group Corporate Europe Observatory. “Airbnb is under a lot of pressure locally across Europe, and they’re trying to use the top-down power of the EU institutions to fight back.” While it might have started as a “community” of amateur hosts offering spare rooms or temporarily vacant homes to travellers, Airbnb had seen three-digit growth in several European cities since 2014 and was now a big, powerful corporation with the lobbying clout to match, Haar said.
The platform lists around 20,500 addresses in in Berlin, 18,500 in Barcelona, 61,000 in Paris and nearly 19,000 in Amsterdam. Data scraped by the campaign group InsideAirbnb suggests that in these and other tourist hotspots, more than half – sometimes as many as 85% – of listings are whole apartments. Many of the properties are also rented out year-round, removing tens of thousands of homes from the residential rental market. Even in cities where short-term lets are now restricted, about 30% of Airbnb listings are available for three or more months a year, the data indicates. In those where they are not, such as Rome and Venice, the figure exceeds 90%.
[..] local attempts to protect residents’ access to affordable housing and preserve the face of city-centre neighbourhoods are being undermined, campaigners say, by the EU’s determination to see the “collaborative economy” as a key future driver of innovation and job creation across the bloc. “The commission seems almost hypnotised by the prospect of a strong sharing economy, and not really interested in its negative consequences,” said Haar. “Commissioners talk about ‘opportunities, not threats’. The parliament, too, recently condemned cities’ attempts to restrict lettings on online platforms.”

The torture never stops. Death by a thousand cuts.
• End Of Greek Bailout Means Fresh Cuts To Salaries, Pensions (K.)
Millions of salaried workers and pensioners stand to lose at least one monthly payment within two years, in 2019 and 2020. For Greece to boast of a successful – as the government desires – exit from the third bailout program without facing any obstacles by August, the Finance Ministry has ruled out the option of avoiding a reduction to pensions from 2019 and will also be proceeding with demands to reduce the minimum tax threshold as of 2020. [..] January 2019 is when the barrage of cuts to pensions is due to start, lasting at least until 2022, with reductions to main as well as auxiliary pensions and also the abolition of family benefits. The bulk of cuts will affect some 1.1 million retirees, who will see their main pension slashed as of this December (when the January 2019 pensions are paid out) by up to 18%.
In total, in the private and public sector, the reduction of pension expenditure from this particular measure in 2019 is estimated at 2.13 billion euros. Reductions will start at 5 euros a month and may reach up to 350 euros a month. There will even be cuts to pensions where there is no personal difference, owing to the abolition of family benefits currently being paid out with the pensions in the public and private sectors. This is expected to concern around 1 million pensioners. Some 200,000 pensioners will also be affected by the cut of the personal difference from auxiliary pensions. According to the midterm fiscal plan, the reduction in 2019 will amount to savings of 232 million euros for state coffers, which is the amount pensioners will also be deprived of.
According to the government’s plans, the sum of cuts that will become evident as of this December will mean that new pensions will eventually be 30 percent below the original level before the law introduced in May 2016 by then labor minister Giorgos Katrougalos. Therefore, the vast majority of monthly pensions will hover in the 700-euro range, even for retirees who used to bring in an average of 1,300 euros.

“They’re a long way down a hole that was created by somebody else..”
• Why Boomtown New Zealand Has A Homelessness Crisis
New Zealand’s dairy-fuelled economy has for several years been the envy of the rich world, yet despite the rise in prosperity tens of thousands of residents are sleeping in cars, shop entrances and alleyways. The emerging crisis has created a milestone that New Zealanders won’t be proud of: the highest homelessness rate among the 35 high-income OECD countries. It’s a curious problem afflicting boom towns where some residents get pushed onto the streets as they can no longer afford the rocketing rents in a flourishing economy – let alone purchase a house as the price of property has soared. “I have no assets at the moment,” said 64-year-old Victor Young, who spoke to Reuters at a soup kitchen in New Zealand’s capital, Wellington.
“It’s not a kind country, it’s not an easy country. I slept in my car 20 days last year. I worked 30 hours a week.” That sentiment is something the country’s popular Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern would like to reverse. Last Thursday, across town from the Sisters of Compassion Soup Kitchen, her Labour-led government unveiled its first budget with an ambitious plan to build social infrastructure. The government has allocated NZ$3.8 billion ($2.62 billion) of new capital spending over a five-year period. This includes an extra NZ$634 million for housing, on top of the NZ$2.1 billion previously announced to fund Kiwibuild, a government building program to increase affordable housing supply.
[..] But experts say the government’s first budget underwhelms on the radical reforms the wider public wanted. “They’re a long way down a hole that was created by somebody else and they haven’t really got a great or easy solution,” said John Tookey, professor of construction management at Auckland University of Technology. He said the government’s much-vaunted Kiwibuild could come unstuck because there weren’t enough skilled workers to deliver on its ambitious target to build 100,000 homes in the next decade.

Where does this originate? WIth Theresa May of course.
• Hundreds Of Homeless People Fined And Imprisoned In UK (G.)
Growing numbers of vulnerable homeless people are being fined, given criminal convictions and even imprisoned for begging and rough sleeping. Despite updated Home Office guidance at the start of the year, which instructs councils not to target people for being homeless and sleeping rough, the Guardian has found over 50 local authorities with public space protection orders (PSPOs) in place Homeless people are banned from town centres, routinely fined hundreds of pounds and sent to prison if caught repeatedly asking for money in some cases. Local authorities in England and Wales have issued hundreds of fixed-penalty notices and pursued criminal convictions for “begging”, “persistent and aggressive begging” and “loitering” since they were given strengthened powers to combat antisocial behaviour in 2014 by then home secretary, Theresa May.
Cases include a man jailed for four months for breaching a criminal behaviour order (CBO) in Gloucester for begging – about which the judge admitted “I will be sending a man to prison for asking for food when he was hungry” – and a man fined £105 after a child dropped £2 in his sleeping bag. Data obtained by the Guardian through freedom of information found that at least 51 people have been convicted of breaching a PSPO for begging or loitering and failing to pay the fine since 2014, receiving CBOs in some cases and fines up to £1,100. Hundreds of fixed-penalty notices have been issued. Lawyers, charities and campaigners described the findings as “grotesque inhumanity”, saying disadvantaged groups were fined for being poor.

“..one of its primary effects is to generate in its victims a strong desire to go out for a beer followed by a pizza.”
• Scientists Revise Their Understanding of Novichok (Slane)
Warning: This article is likely to contain traces of satire. In the aftermath of the poisoning of Sergei and Yulia Skripal in Salisbury on 4th March, scientists are currently re-evaluating their understanding of A-234 – or Novichok as it is more commonly known. Prior to the poisoning, it had been thought that the substance was around 5-8 times more toxic than VX nerve agent, and therefore that just a tiny drop would be likely to kill a person within minutes or possibly even seconds of them coming into contact with it. In the unlikely event of a person surviving, it was believed that their central nervous system would be completely destroyed, and that they would suffer numerous chronic health issues, including cirrhosis, toxic hepatitis, and epilepsy before dying a premature and miserable death, probably within a year or so.
However, according to an anonymous source at the Porton Down laboratory, which is located just a few miles down the road from Salisbury, scientists now believe they may have completely misunderstood the properties and effects of the chemical: “All the available information we had about Novichok before March this year suggested that it was by far the most lethal nerve agent ever produced, and we had assumed that even the tiniest drop would kill a person within minutes. However, after studying the movements of the Skripals after being poisoned, we have now revised our understanding, and we now believe that one of its primary effects is to generate in its victims a strong desire to go out for a beer followed by a pizza.”
Yet it’s not only the effects of the substance that have led to this reappraisal, but also its mysterious ability to move about from location to location, seemingly at will. According to the source: “At first, differing reports of the location of the poisoning baffled us. First it was the restaurant, then it was the pub, followed by the bench, the car, the cemetery, the flowers, the luggage, the porridge, and then finally the door handle three weeks after the incident. However, we now believe we have an explanation for this phenomena. When Novichok was developed, we think it may have been given the ability to appear in one place, only to then disappear and turn up in an entirely different place.