Byron In Chinatown, Pell Street, New York 1900



The idea was always to stretch the meeting till Monday.
• Eurogroup Fails to Agree to Next Greek Bailout Steps (Bloomberg)
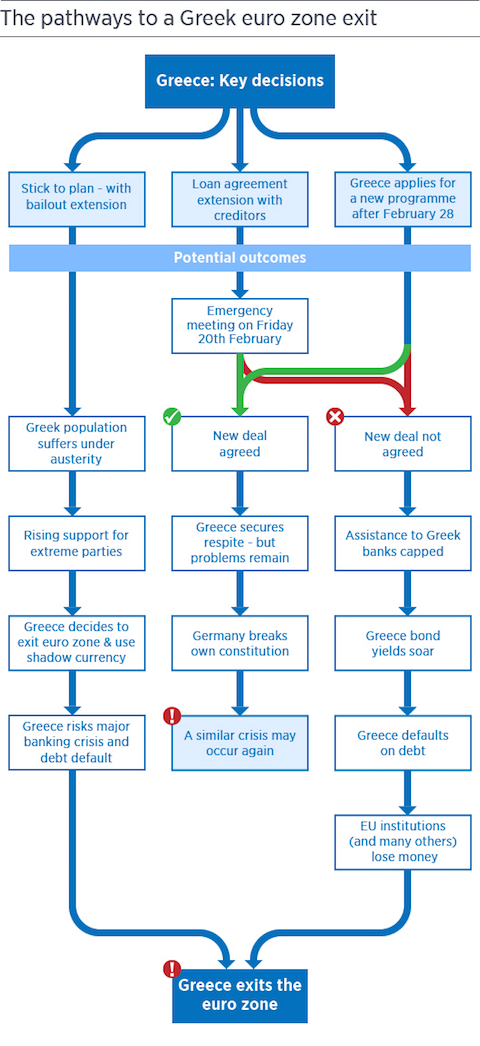
Euro-area governments left tough decisions on the future of Greece’s bailout for next week, after talks failed to bridge differences over the aid program that the Greek government blames for economic hardship. With Greece’s current bailout expiring at the end of February, finance ministers met for six hours in Brussels without signing off on any conclusions on the way forward for the region’s most-indebted nation. That leaves open how Greece can avoid running out of cash and avert a possible exit from the 19-nation currency union. Attention now shifts to a summit of European Union leaders on Thursday in Brussels, a day after German Chancellor Angela Merkel and French President Francois Hollande traveled to meet Russian President Vladimir Putin to negotiate a cease-fire in Ukraine.
Merkel had left bargaining with Greece to the finance ministers. “We understand each other much, much better now than we did this morning,” Greek Finance Minister Yanis Varoufakis told reporters after the finance chiefs broke up without a deal early Thursday in Brussels. “Europe manages to find agreements even if it’s at the last moment.” The euro fell as much as 0.3% to $1.1303 after Jeroen Dijsselbloem, the Dutch finance minister who chairs the euro group’s talks, said ministers couldn’t agree on a common approach. The euro briefly spiked to as high as 1.1352 earlier, when officials suggested an accord on steps forward was within reach.
“We covered a lot of ground but didn’t actually reach a joint conclusion on how to take the next steps,” Dijsselbloem said at a press conference. “There has to be a political agreement on the way forward.” Finance chiefs will return to Brussels on Feb. 16 to try to break the deadlock after Greek negotiators were said to have wavered on a commitment to extending the country’s existing bailout from the Troika. Greek Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras’s campaign pledge to end the bailout — and its austerity mandates — hung over the talks. Agreed language on a bailout extension was within reach, only to be rejected later by Greek negotiators who said they had to consult with superiors in Athens, German Finance Ministry spokesman Martin Jaeger said.
Read more …

There will be no extension. Syriza has said that 1000 times.
• Rejected Eurogroup Draft Spoke Of “Extending” Greek Bailout (Reuters)
A draft statement by euro zone finance ministers on how to handle Greece’s finances spoke of “extending” its current bailout deal as a “bridge” to a new package, according to a copy of the draft that was rejected by Athens. The new Greek government, elected on a mandate to end deeply unpopular international bailout terms, has insisted there can be no “extension” once that deal expires at the end of the month. But EU partners fear financial chaos without such an accord. A draft of the planned Eurogroup statement, seen by Reuters, read: “Today the Eurogroup took stock of the current situation in Greece and the state of the current adjustment programme. In this context, the Eurogroup has engaged in an intensive dialogue with the new Greek authorities.
“The Greek authorities have expressed their commitment to a broader and stronger reform process aimed at durably improving growth prospects”. At the same time, the Greek authorities reiterated their unequivocal commitment to the financial obligations to all their creditors. “On this basis, we will now start technical work on the further assessment of Greece’s reform plans. The Greek authorities have agreed to work closely and constructively with the institutions to explore the possibilities for extending and successfully concluding the present programme taking into account the new government’s plans. If this is successful this will bridge the time for the Greek authorities and the Eurogroup to work on possible new contractual arrangements. We will continue our discussions at our next meeting on Monday 16 February.”
Read more …

Mexican standoff.
• Greece And Eurozone In Stalemate Over Debt Burden (Guardian)
The Greek government’s confrontation with its eurozone creditors over its campaign to relieve its staggering debt burden while relaxing the terms of five years of austerity resulted in stalemate late on Wednesday. The first proper negotiations between Greece and eurozone finance ministers failed to make any progress or result in a joint statement. While no immediate agreement had been expected, the emergency meeting had been tipped to produce a framework for talks to be finessed over the next few days before another meeting next Monday. Jeroen Dijsselbloem, the Dutch finance minister who chaired the Brussels meeting, announced that this aim was not met. It appeared that the new leftwing government in Athens was isolated in seeking to extract better terms from Europe.
Alexis Tsipras, the new Greek prime minister, seems to have ordered his finance minister, Yanis Varoufakis, to stand firm against the pressure to make any concessions. Tsipras is due in Brussels on Thursday for his debut on the European stage at an EU summit. Following 10 days of touring Europe in a failed attempt to woo Berlin, Frankfurt and other key capitals to alter the terms of trade between Athens and the eurozone, Varoufakis went into negotiations with the other finance ministers at a specially convened session in Brussels. Entering and leaving the meeting, he was uncharacteristically taciturn.
The stalemate could see Greece running out of cash next month, unilaterally defaulting on the bailout programme with the ECB, the European Commission and the IMF, and being forced to leave the single currency. That prospect is viewed as a disaster fraught with risks in Brussels, Paris and Rome. But Berlin, whose voice matters more than most in the negotiations, is reliably said to be “extremely relaxed” about the Greek crisis and opposed to tearing up the agreements that Greece is formally bound to under the bailout terms.
Read more …

“..popular protests “across Greece and Europe” are “the source of our strength.”
• Greece Said to Offer Euro Area Four Principles for Talks (Bloomberg)
Greek Finance Minister Yanis Varoufakis presented his European counterparts with four principles for a new financing deal, according to two euro-area officials, as Greece battles to stave off a cash crunch and stay in the currency bloc. Greece wants a deal that provides for financial stability, financial sustainability and debt restructuring, while addressing Greece’s humanitarian crisis, Varoufakis said during talks Wednesday in Brussels without offering details, according to the officials, who asked not to be named because the talks are private. Finance ministers of the 19 euro nations met on Wednesday after Germany and Greece took clashing positions heading into negotiations that will continue Feb. 16 in the Belgian capital.
Dutch Finance Minister Jeroen Dijsselbloem, who heads the meetings, said the ministers wanted to hear Greece’s proposals. “I don’t expect an outcome today,” Dijsselbloem told reporters in Brussels before the talks. Extra money “is not on the table right now” and Greece needs to stick to its reform path, he said. Greece’s bailout package will expire this month if the euro area’s most-indebted nation can’t reach a deal with its creditors. Asked by a reporter before the meeting whether Greece’s exit from the euro area is on the table, Varoufakis said: “Of course not.” In Athens, thousands rallied in front of the Greek parliament in support of the government’s anti-austerity stance. Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras posted a photo of the rally on his Twitter account, saying popular protests “across Greece and Europe” are “the source of our strength.”
Read more …

“You can defend EMU policies, or you can defend your political base, but you cannot do both.”
• Germany Faces Impossible Choice As Greek Austerity Revolt Spreads (AEP)
The political centre across southern Europe is disintegrating. Establishment parties of centre-left and centre-right – La Casta, as they say in Spain – have successively immolated themselves enforcing EMU debt-deflation. Spain’s neo-Bolivarian Podemos party refuses to fade. It has endured crippling internal rifts. It has shrugged off hostile press coverage over financial ties to Venezuela. Nothing sticks. The insurrectionists who came from nowhere last year – with Trotskyist roots and more radical views than those of Syriza in Greece – are pulling further ahead in the polls. The latest Metroscopia survey gave Podemos 28pc. The ruling conservatives have dropped to 21pc. The once-great PSOE – Spanish Workers Socialist Party – has fallen to 18pc and risks fading away like the Dutch Labour Party, or the French Socialists, or Greece’s Pasok.
You can defend EMU policies, or you can defend your political base, but you cannot do both. As matters stand, Podemos is on track to win the Spanish elections in November on a platform calling for the cancellation of “unjust debt”, a reversal of labour reforms, public control over energy, the banks, and the commanding heights of the economy, and withdrawal from Nato. Europe’s policy elites can rail angrily at the folly of these plans if they wish, but they must answer why ex-Trotskyists threatening to dismantle market capitalism are taking a major EMU state by storm. It is what happens when 5.46m people lack jobs, when 2m households still have no earned income, and when youth unemployment is still running at 51.4pc, and home prices are down 42pc, six years into a depression.
It is pointless protesting that Spain’s economy is turning the corner, a contested claim in any case. There comes a point when a society breaks and stops believing anything its leaders say. The EU elites themselves have run their currency experiment into the ground by imposing synchronized monetary, fiscal, and banking contraction on the southern half of EMU, in defiance of known economic science and the lessons of the 1930s. It is they who pushed the eurozone into deflation, and thereby pushed the debtor states into accelerating compound-interest traps. It is they who deployed the EMU policy machinery to uphold the interest of creditors, refusing to acknowledge that the root cause of Europe’s crisis was a flood excess capital flows into vulnerable economies.
It is they who prevented a US-style recovery from the financial crisis, and they should not be surprised that such historic errors are coming back to haunt. The revolt in Italy has different contours but is just as dangerous for Brussels. Italians may not wish to leave the euro but political consent for the project but broken down. All three opposition parties are now anti-euro in one way or another. Beppe Grillo’s Five Star movement – with 108 seats in parliament – is openly calling for a return to the lira. Mr Grillo proclaims that Syriza is carrying the torch for all the long-suffering peoples of southern Europe, as it is in a sense. “What’s happening to Greece today, will be happening to Italy tomorrow. Sooner or later, default is coming,” he said.
Read more …

How the right wing sees things.
• Eurozone Leaders Believe Syriza Must Fail And Be Seen To Fail (Telegraph)
In current discussions of what Greece might or might not get in the way of concessions from the Eurozone, there has so far been relatively little appreciation of one basic political reality: as far as the governments of Spain, Portugal, Ireland, probably Italy and perhaps even France are concerned, Syriza must fail and must be seen to fail. Why? The reasons differ slightly between countries. The easiest case to see is perhaps Spain. In Spain, the governing party is the centre-right Partido Popular led by Mariano Rajoy. It is currently facing pressure from a far-left party, Podemos, allied to Syriza. Indeed the Podemos leader Pablo Iglesias even campaigned in partnership with Syriza and, following Syriza’s victory, at his own party’s rally he proclaimed: “Syriza, Podemos – we will win [venceremos]!”
Podemos is currently leading in the polls, ahead of an election later this year. The very last thing Rajoy can afford is for Syriza’s approach to be seen to succeed, emboldening and vindicating Podemos. As for Portugal and Ireland, where the governments stuck to bailout conditions despite the domestic pain, how would they sell concessions to Syriza to their own voters? Suppose they go back and say: “We were suckers. We shouldn’t have made all those cuts. Instead, what we really should have done was to raise the minimum wage, hire back the public sector staff that had been fired, say we weren’t going to pay our debts to our eurozone partners, cosy up to the Russians and tell the Germans they didn’t feel nearly guilty enough about World War II. Then everyone would have said we were ‘rock stars’ and and forgiven our debts.” Do you reckon that would go down well?
As for the Italians, the Syriza leaders are terribly keen to claim that Greece and Italy are in much the same position and that there should therefore be a general debt amnesty across the eurozone. The Italians, on the other hand, are less keen on this comparison. Over the weekend, the Greek finance minister stated: “Let’s face it, Italy’s debt situation is unsustainable”. The Italian Finance Minister Pier Carlo Padoan replied on Twitter that his Greek counterpart’s remarks were “out of place” and that Italy’s debt is “solid and sustainable”. If the Italians, at any point, seek any relaxation of the fiscal strictures their eurozone partners have placed upon them, you can rest assured they will not be claiming that they are just like Greece or that anything that happens in Greece sets a precedent for them.
Read more …

Letter from Spain’s oppostion leader: “..the diktats of those who still appear to be running things in Europe have failed, and the victims of this inefficiency and irresponsibility are Europe’s citizens.”
• If The Greek Olive Branch Is Rejected, Europe May Fall (Pablo Iglesias)
During his swearing-in speech as Greece’s prime minister, Alexis Tsipras was clear: “Our aim is to achieve a solution that is mutually beneficial for both Greece and our partners. Greece wants to pay its debt.” The European Central Bank’s (ECB) response to the Greek government’s desire to be conciliatory and responsible, was also very clear: negative. Either the Greek government abandons the programme on which it was elected, and continues to do the very thing that has been disastrous for Greece, or the ECB will stop supporting Greek debt. The ECB’s calculation is not only arrogant, it is incoherent. The same central bank that recognised its mistakes a few weeks ago and began to buy government debt is now denying financing to the very states that have been arguing for years that the role of a central bank should be to back up governments in protecting their citizens rather than to rescue the financial bodies that caused the crisis.
Now, instead of acknowledging that Greece deserves at least the same treatment as any other EU member state, the ECB has decided to shoot the messenger. Excesses of arrogance and political short-sightedness cost dear. The new despots who are trying to persuade us that Europe’s problem is Greece are putting the European project itself at risk. Europe’s problem is not that the Greeks voted for a different option from the one that led them to disaster; that is simply democratic normality. Europe’s threefold problem is inequality, unemployment and debt – and this is neither new nor exclusively Greek. Nobody can deny that austerity has not solved this problem, but rather has exacerbated the crisis.
Let’s spell it out: the diktats of those who still appear to be running things in Europe have failed, and the victims of this inefficiency and irresponsibility are Europe’s citizens. It is for this precise reason that trust in the old political elites has collapsed; it is why Syriza won in Greece and why Podemos – the party I lead – can win in Spain. But not all the alternatives to these failed policies are as committed as Syriza and Podemos are to Europe and to European democracy and values. The Greeks have been pushed to the point of disaster, yet the Greek government has reached out and shown great willingness to cooperate. It has requested a bridge agreement that would give both sides until June to deal with what is little short of a national emergency for the majority of the Greek population.
Read more …

Interesting to see how hard Syriza will go after these guys.
• 86 Names Missing from Greek ‘Lagarde List’ (Greek Reporter)
The notorious “Lagarde List” should include a total of 2,148 names and not the 2,062 that are listed so far, according to a report in Ta Nea newspaper. The Lagarde List is a spreadsheet containing over 2,000 names of possible Greek tax evaders with undeclared deposits at Swiss HSBC bank’s Geneva branch. It is named after former French finance minister Christine Lagarde who passed it to the Greek government in October 2010 to help them tackle tax evasion. Lagarde is now Managing Director of the International Monetary Fund. The list was hidden by Greek officials and it became known two years later when it was exposed by investigative journalist Costas Vaxevanis.
The newspaper report says that after research by the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists, there are 86 new names of Greeks who have undeclared deposits in the Swiss bank. They are all natives of Greece, but have declared residency in other countries, thereby not listed on the original list. Also, the investigation shows that there are another 41 names who are linked to the accounts of potential tax evaders already on the list. So far, very few names on the list have been audited. Former finance minister Giorgos Papaconstantinou is accused of distorting the spreadsheet and erasing names of his relatives on the list and will be referred to the Special Court.
Read more …

Even deeper into debt slavery.
• Ukraine Gets IMF-Led $40 Billion Aid Accord to Avert Default (Bloomberg)
Ukraine reached a preliminary accord to expand an International Monetary Fund-led bailout to $40 billion to avert a default as the 10-month conflict in the nation’s east damages the economy and drains resources. An IMF team, which has been in the Ukrainian capital since Jan. 8, will recommend the Washington-based lender’s board sign off on the package, Managing Director Christine Lagarde said Thursday in Brussels. The package includes contributions from other sources, including the EU, Lagarde told reporters. Ukraine, rocked by a pro-Russia insurgency in its industrial heartland, is struggling with the deepest recession since 2009, foreign reserves at an 11-year low and the world’s worst-performing currency.
The country’s fiscal and economic condition will help determine whether it remains oriented toward the U.S. and EU or is drawn into Russia’s orbit amid the worst standoff since the end of the Cold War. “It’s an ambitious program, it’s a tough program and it’s not without risk,” Lagarde told reporters. “But it’s also realistic.” Ukraine’s April 2023 Eurobond was little changed at 53.19 cents on the dollar at 10:23 a.m. in Kiev, lowering the yield two basis points to 19%. The government of Ukraine faces debt repayments of $11 billion this year and has said it will approach foreign bondholders over easier terms once IMF financing is in place. The accord still needs IMF board approval. Ukraine’s allies stepped in with funding pledges in the run-up to the IMF talks being completed.
The U.S. promised as much as $2 billion in loan guarantees, while the European Union said it would disburse €1.8 billion euros. Leaders of Russia, Ukraine, France and Germany are meeting in Minsk, Belarus on Thursday to reach a peace deal in the conflict that has killed at least 5,400 people, the United Nation estimates. The U.S., EU and Ukraine blame Russia for aiding the rebels. President Vladimir Putin denies the charges. “The hope will be to send a signal to Putin and to Ukrainians that the West stands behind Ukraine and will not let it fail financially,” Timothy Ash at Standard Bank said.
Read more …

Meaningless?!
• Ukrainian Cease-Fire Sealed After All-Night Minsk Peace Summit (Bloomberg)
The leaders of Russia, Ukraine, Germany and France agreed on a cease-fire to stem the conflict that’s devastated eastern Ukraine and triggered the worst crisis in more than 20 years between Russia and its former Cold War foes. The deal envisages a truce starting Feb. 15 and reaffirms some commitments from a failed September bid to end the conflict, Russian President Vladimir Putin told reporters in the Belarusian capital of Minsk. The accord was struck early Thursday after all-night talks between Ukrainian President Petro Poroshenko, Putin, German Chancellor Angela Merkel and French President Francois Hollande.
The collapse of previous cease-fires has stoked skepticism as to whether this one will hold. Ten months of fighting have killed more than 5,000 people, ravaged Ukraine’s economy and propelled Russia toward recession through U.S. and European sanctions. Raising pressure to deliver a settlement, the run-up to the summit was accompanied by escalating violence and calls for the U.S. to supply weapons to Ukraine’s struggling army. “The conflict will continue, even with this agreement,” Joerg Forbrig, a senior program director at the German Marshall Fund in Berlin, said by phone. “Eastern Ukraine is now basically lost to central government control.”
Read more …

“The situation in Ukraine is being used as a pretext for the active ‘repression’ of our country..”
• Putin Top Advisor: US Uses Ukraine To Get Regime Change in Russia (Zero Hedge)
Following the humiliation of tonight’s much anticipated Eurogroup meeting in which for the first time ever the ensuing disarray was so profound the panicked European finance ministers couldn’t even find a quorum consensus to produce even the tersest of official statements, there was some hope that the second round of negotiations currently taking place in Minsk to find a solution to the Ukraine civil war would at least partially redeem Europe’s faltering negotiating reputation. Alas, as of this moment, that does not appear to be the case, and as Reuters reports citing a Kiev presidential aide, that Minsk talks on Ukraine crisis could last six more hours. “We’ve got another 5-6 hours of work. At least. But we should not leave here without an agreement on an unconditional ceasefire. There’s a battle of nerves underway,” aide Valeriy Chaly said in a Facebook post.
Well, if it is indeed a “battle of nerves”, something tells who the victor will be, considering all his peers are just a little more preoccupied with the potential collapse of their artificial monetary and political union. Yet, just like the previous Minsk “agreement”, even if by some miracle there is a solution this time around, the probability peace will be maintained is slim to none. The reason is not simply because the Ukraine civil war will go on until there is a terminal partition between the pro-western West part of the country, and the pro-Russian eastern regions. The real reason may be what one of Vladimir Putin’s top security advisors, the secretary of the Security Council, Nikolai Patrushev said earlier today, when he told a Russian state newspaper that the U.S. was orchestrating events in Ukraine in a bid to overthrow Mr. Putin’s government.
He also expressed certainty that the West’s financial aid for Kiev would only bring the Ukrainian economy to a “dead end.” “The situation in Ukraine is being used as a pretext for the active ‘repression’ of our country,” Mr. Patrushev, who ran Russia’s Federal Security Service during Mr. Putin’s first eight years as president, said in an interview with the Rossiyskaya Gazeta, published Wednesday. And, if accurate, Patrushev’s assessment is that the US will not stop short of what effectively will be world war: “The Americans are trying to involve the Russian Federation in an interstate military conflict, cause regime change [in Russia] and ultimately dismember our country via events in Ukraine,” he said.
Read more …

Most won’t be able to.
• Oil Firms ‘Need Fresh Strategies’ To Operate in Future of $50 Oil (BBC)
Many oil and gas firms will need to transform the way they operate in order to grasp future opportunities in the sector, according to a report. PwC said companies should be looking to deploy fresh strategies, following a sustained fall in the price of oil. It suggested they should look to reduce costs “in a sustainable manner” and find efficiencies by keeping tax costs in control. Other suggestions included divesting non-core parts of their business. PwC argued that firms might also want to identify and invest in strategic acquisitions to secure market position in key areas. The report’s authors said the UK oil and gas sector would have been in a much better place “to weather the oil price maelstrom”, had it heeded 30%-40% cost reduction warnings which surfaced 12-18 months ago.
The report said there was still time for firms to “learn the harsh lessons of past languor” by adopting fresh strategies. But it also warned that to achieve that, they needed to get away from “short term knee-jerk reactions” seen in previous downturns – or risk damaging the long term future of the industry. PwC cited significant downsizing undertaken during the downturn of 1999-2000, arguing that the industry had struggled since then with talent retention. It said “aggressive price negotiation” and contract revisions with the oil services sector would also do little to create a collaborative environment. The report argued that companies must answer “hard questions” about whether they can continue to invest in the sector, or if they should instead “move on”.
But it stressed the need for the industry to take a long-term view, adding that “intelligent and strategic cost-cutting” could “position players well through this turmoil”. Brian Campbell, oil and gas capital projects director at PwC and co-author of the report, said: “With economists predicting low oil prices throughout 2015, UK oil and gas firms are not out of the woods by any means. “They are still at risk of an economic triple-whammy: as the falling oil price reduces income, incremental investment may no longer be economic with a risk that field life diminishes and decommissioning is accelerated. “The stark reality is that firms need to be able to operate in an environment where oil averages at $50 per barrel – only then can it be truly fit for the future.”
Read more …

Just starting.
• Global Oil Layoffs Exceed 100,000 (Bloomberg)
The promise of plentiful jobs and salaries as high as a quarter-million dollars a year lured Colombia native Clara Correa Zappa and her British husband to Perth, Australia, at the height of the continent’s oil and gas frenzy. Engineers were in high demand in 2012, when oil prices exceeded $100 a barrel, making the move across the world a no-brainer. Within two years, though, oil plunged to less than half the 2012 price and Zappa lost her job as a safety analyst. Now she’s worried her husband, who also works in the commodities industry, could also lose his job. Such anxieties are rising at a time when the number of energy jobs cut globally have climbed well above 100,000 as once-bustling oil hubs in Scotland, Australia and Brazil, among other countries, empty out, according to Swift Worldwide Resources, a staffing firm with offices across the world.
“It’s shocking,” Zappa, 29, said in a telephone interview. There is “so much pressure for him to keep his job and even work extra.” Her concerns mirror those of tens of thousands of workers who migrated to oil and gas boomtowns worldwide in the years of $100-a-barrel crude, according to Tobias Read, Swift’s chief executive officer. While much of the focus on layoffs has centered on the U.S., where the shale fields that created the glut have seen the steepest cutbacks, workers in oil-related businesses across the globe are suffering, he said. “The issue is one of uncertainty, of whether there’s a job out there,” Read said in a phone interview. “For seven years, there was a shortage of staff. Now for the first time, there’s a surplus. Currently almost no one is hiring.”
Read more …

“The idea is that the stock market is a pretty good indicator of economic demand.” Really? Nothing to do with QE?
• Goldman: Why Oil Crashed—and Why Lower Prices Are Here to Stay (Bloomberg)
Oil prices have gotten crushed for the last six months. The extent to which that was caused by an excess of supply or by a slowdown in demand has big implications for where prices will head next. People wishing for a big rebound may not want to read farther. Goldman Sachs released an intriguing analysis on Wednesday that shows what many already suspected: The big culprit in the oil crash has been an abundance of oil flooding the market. A massive supply shock in the second half of last year accounted for most of the decline. In December and January, slowing demand contributed to the continued sell-off. Goldman was able to quantify these effects.
Goldman’s model is simple on its face, looking at just two variables over time: the price of oil and the value of U.S. stocks (as measured by the S&P 500). The idea is that the stock market is a pretty good indicator of economic demand. So when stocks move in tandem with oil prices, demand is in the driver’s seat. When the price of oil moves in the opposite direction of stocks, the shock is coming from supply.
Read more …

“The message is clear that Warren’s attacks on the industry have made even moderate Democrats skittish to stand up for banks..”
• Have Banks Overplayed Their Hand Fighting Wall Street Regulation? (Bloomberg)
The financial industry is finding that winning in Washington comes at a cost. Wall Street lobbied aggressively and succeeded late last year in persuading lawmakers to roll back rules for the $700 trillion derivatives market. Instead of generating momentum for further changes to the Dodd-Frank Act, the victory sparked a populist uprising among Democrats that’s had wide-ranging consequences, including stymieing less controversial requests from regional banks like Capital One Financial Corp. “A short while ago there was bipartisan agreement on a number of common sense improvements,” said Rob Nichols, president of the Financial Services Forum that represents the chief executives of Wall Street’s biggest banks. “Unfortunately, that bipartisan agreement is gone.”
Financial companies and their employees spent $169 million on the November elections and had expectations that their bid to loosen regulations would get easier with Republicans in control of both the House and Senate. Now, there is second-guessing that banks overplayed their hand, according to lobbyists. The December win on swaps rules has become a rallying cry for Senator Elizabeth Warren, a frequent critic of Wall Street, and spurred repeated White House vows to defend Dodd-Frank. The fallout has frustrated banks, which hope it’s temporary. Democrats who previously said they wanted to revise the law now won’t even discuss it. Republicans are altering their strategy for attacking Dodd-Frank. And lobbyists have been hindered in their efforts to persuade Senate Democrats to champion changes to financial rules.
A sign of the political headwinds has been regional banks’ difficulty winning bipartisan support for a bill that would free them from stringent oversight imposed on lenders with at least $50 billion of assets. Capital One considers getting the threshold increased a top legislative goal this year, according to people with knowledge of the matter. The company’s inability to persuade Democrats to lead the charge in the Senate, particularly home state Senator Mark Warner of Virginia, has reverberated through the ranks of financial lobbyists, according to two people involved in the talks. The message is clear that Warren’s attacks on the industry have made even moderate Democrats skittish to stand up for banks, the people said. Capital One’s discussions with Warner aren’t unique, said company spokeswoman Tatiana Stead. “We have had identical and multiple discussions with his Senate colleagues and other elected officials,” she said.
Read more …

“..this whole chorus of Fed governors – yesterday’s lineup included Richard Fisher and Charles Plossner – defending the sacred “independence” of the Federal Reserve is downright Kafkaesque.”
• Audit The Fed – And Shackle It, Too (David Stockman)
The reason to be fearful about the economic and financial future is that we are in the thrall of a mainstream consensus that is downright meretricious. In attacking Rand Paul’s audit legislation, for instance, one of the time-servers on the Fed Board of Governors, Jerome H. Powell, let loose the following gem: “As recent U.S. history has shown, elected officials have often pushed for easier policies that serve short-term political interests…..” Perhaps Mr. Powell is a descendent of Rip Van Winkle – and missed the last 20 years of history while doing LBOs at the Carlyle Group and helping Congress improve upon its enviable record of fiscal management while at the Bipartisan Policy Center. But whatever he was doing—snoozing or otherwise distracted – it most assuredly was not gathering evidence that “elected officials” were putting undue pressure on the Fed for “easier policies”.
For crying out loud there is exactly zero evidence that “politicians” had anything to do with zero interest rates. And ZIRP defines the ultimate level of “ease” according to Bernanke himself, who famously described his policies as positioned at the “zero bound”. Indeed, given the very earliest expected date for “lift-off” in June, the Fed will have pinned the money market rate at zero for 80 months running. This unprecedented tsunami of “easy money”, of course, happened with nary a Congressman or Senator darkening the door at the Eccles Building. Folks, this whole chorus of Fed governors – yesterday’s lineup included Richard Fisher and Charles Plossner – defending the sacred “independence” of the Federal Reserve is downright Kafkaesque.
Rather than protecting the Fed from meddling politicians, it is the American public that desperately needs protection from the depredations of an unelected monetary politburo that runs the entire financial system. Let’s say you have saved a quarter million bucks over a lifetime of working and scrimping, but wish to keep it safe and liquid in your retirement years. Well thank you “independent” governors of the Fed for the privilege of owning a bank CD that generates 40 bps or the grand sum $2.75 per day. That’s one visit to Starbucks each morning, but forget the cappuccino. It’s just black coffee for you!
Read more …

When will this bomb burst?
• ‘No Solution To Brazil’s Crisis’ (CNBC)
Brazil’s central bank won’t be able to save the country with monetary policy, economists warned, after downgrading their 2015 growth outlook to zero as stagflation drags the once vibrant economy. “There is no near-term solution to deepening stagflation,” said Dev Ashish, Latin America economist at Societe Generale in a note on Wednesday. “Fiscal and monetary orthodoxy is not expected to yield any fruit in the near to medium term.” Annual inflation shot up to a twelve-year high of 7.1% in January, according to official data on Friday, well above the central bank’s 4.5% target range. With inflation widely expected to remain elevated, analysts in Brazil revised their 2015 gross domestic product (GDP) growth forecast to zero, according to a central bank survey this week.
South America’s largest nation is estimated to have grown less than 1% last year. Brazil’s central bank – the Banco Central do Brasil (BCP) – engaged in an aggressive tightening cycle last year to combat inflation. It pushed the benchmark short-term interest rate, the Selic, to its current multi-year high of 12.25%. Markets widely expect more rate hikes in the coming months. Analysts don’t have faith in the central bank’s toolbox. Rate hikes dampen economic growth, so the success of additional monetary tightening depends on how effectively the government manages its finances, but that depends on economic growth, SocGen said. The bank expects public debt to rise nearly 70% over the next two years on the back of weak GDP.
Read more …

Panic.
• Sweden’s Riksbank Cuts Key Rate to Negative (Bloomberg)
Sweden’s central bank cut its main interest rate below zero and unexpectedly unveiled plans to start buying government bonds to jolt the largest Nordic economy out of a deflationary spiral. The Riksbank lowered its repo rate to minus 0.10% from zero. A cut had been predicted by six of the 18 economists surveyed by Bloomberg, while the remainder forecast no change. Policy will “soon” be made “more expansionary” by buying 10 billion kronor ($1.2 billion) in government bonds with maturities of one to five years, the Stockholm-based bank said. It pledged to keep the repo rate negative until underlying inflation is close to 2%, which the bank predicts will happen in the second half of 2016. Policy makers will take further steps if necessary, the bank said.
“To ensure that inflation rises toward the target, the Riksbank is prepared to quickly make monetary policy more expansionary, even between the ordinary monetary policy meetings, should the need arise,” it said. Policy makers are delving deeper into their toolbox, joining the European Central Bank in unleashing unconventional measures as deflation risks becoming entrenched. The bank, led by Governor Stefan Ingves, last year reversed course and scrapped a policy of keeping rates up to guard against a build-up in household debt. The reluctance to ease in the face of slowing inflation and high unemployment was characterized as “sadomonetarist” by Nobel laureate Paul Krugman.
The krona slumped as much as 2.1%, and was down 1.4% at 9.62 per euro as of 10:33 a.m. in Stockholm. The yield on Sweden’s benchmark five-year note fell 10 basis points to 0.8%. Two-year yields slid to minus 0.24%. “We didn’t expect the Riksbank to buy government bonds as early as now, but rather that they would wait and see if this would be needed,” said Olle Holmgren, an analyst at SEB. “They are also maybe even clearer in signaling willingness to do even more if needed. This is softer than we thought.”
Read more …

Europe’s biggest disgrace is still not being tackled.
• Mediterranean Sinking ‘Kills 300 Migrants Bound For Europe (BBC)
At least 300 migrants are feared dead after the boats carrying them from the North African coast sank in the Mediterranean Sea, the UN says. UNHCR regional director Vincent Cochetel called the incident a “tragedy on an enormous scale”. Nine survivors who were brought to Lampedusa by the Italian coast guard are believed to be from West Africa. Initial reports on Monday suggested that at least 29 migrants had died after their dinghy overturned. The UNHCR said the migrants had departed from Libya on Saturday in four dinghies. Mr Cochetel said, “Europe cannot afford to do too little too late”, and called the tragedy, “a stark reminder that more lives could be lost if those seeking safety are left at the mercy of the sea.” In November, Italy ended a year-long operation aimed at rescuing seaborne migrants.
Known as Mare Nostrum, it was launched in October 2013 in response to a tragedy off Lampedusa in which 366 people died. The aim of the mission was to look for ships carrying migrants that may have run into trouble off the Libyan coast. There is no way of knowing for sure whether these men, women, and children would have been saved if the former Italian search-and-rescue operation known as Mare Nostrum was still running. But having spent a week on board an Italian navy frigate, I can be sure they would have done their utmost to save as many lives as possible. The EU’s Triton border patrol is not designed to do that. It cannot pre-empt trouble in international waters – it can only act when lives are immediately at risk. The Italian operation was set up differently. The naval crews knew they had one single purpose – to prevent death.
Some time back, EU leaders pledged that not a single life would again be lost as a result of these large scale tragedies at sea. The EU now runs a border control operation, called Triton, with fewer ships and a much smaller area of operations. The UNHCR says almost 3,500 people died attempting to cross the Mediterranean Sea to reach Europe in 2014, making it the world’s most dangerous sea crossing for migrants. More than 200,000 people were rescued in the Mediterranean during the same period, many under the Mare Nostrum mission prior to its abolition, and the UNHCR expects the figure to remain high in 2015. In a speech before the European Parliament in November, Pope Francis called for a “united response to the question of migration”, warning that the Mediterranean could not be allowed to become a “vast cemetery”.
Read more …

“In another development, US President Barack Obama has said he will withdraw nearly all US troops helping to combat the disease in Liberia.”
• New Ebola Cases Rise For Second Week In A Row (BBC)
The number of new cases of Ebola has risen in all of West Africa’s worst-hit countries for the second week in a row, the World Health Organization (WHO) says. This is the second weekly increase in confirmed cases in 2015, ending a series of encouraging declines. The WHO said on Wednesday that Sierra Leone had registered 76 of the 144 new cases, Guinea 65 and Liberia three. More than 9,000 people have died from Ebola since December 2013. The WHO said that the increase highlights the “considerable challenges” that must still be overcome to end the outbreak. “Despite improvements in case finding and management, burial practices, and community engagement, the decline in case incidence has stalled,” the UN health agency said in a statement. In another development, US President Barack Obama has said he will withdraw nearly all US troops helping to combat the disease in Liberia.
Read more …

“No other country has had such a high rate and number of mammal extinctions over this period, and the number we report for Australia is substantially higher than previous estimates..”
• Australia On Brink Of ‘Extinction Calamity’ (BBC)
Australia has lost one in ten of its native mammals species over the last 200 years in what conservationists describe as an “extinction calamity”. No other nation has had such a high rate of loss of land mammals over this time period, according to scientists at Charles Darwin University, Australia. The decline is mainly due to predation by the feral cat and the red fox, which were introduced from Europe, they say. Large scale fires to manage land are also having an impact. As an affluent nation with a small population, Australia’s wildlife should be relatively secure from threats such as habitat loss. But a new survey of Australia’s native mammals, published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, suggests the scale of the problem is more serious than anticipated.
Since 1788, 11% of 273 native mammals living on land have died out, 21% are threatened and 15% are near threatened, the study found. Marine mammals are faring better. “No other country has had such a high rate and number of mammal extinctions over this period, and the number we report for Australia is substantially higher than previous estimates,” said conservation biologist John Woinarski, who led the research. “A further 56 Australian land mammals are now threatened, indicating that this extremely high rate of biodiversity loss is likely to continue unless substantial changes are made. “The extent of the problem has been largely unappreciated until recently because much of the loss involves small, nocturnal, shy species with [little] public profile – few Australians know of these species, let alone have seen them, so their loss has been largely unappreciated by the community.”
Read more …