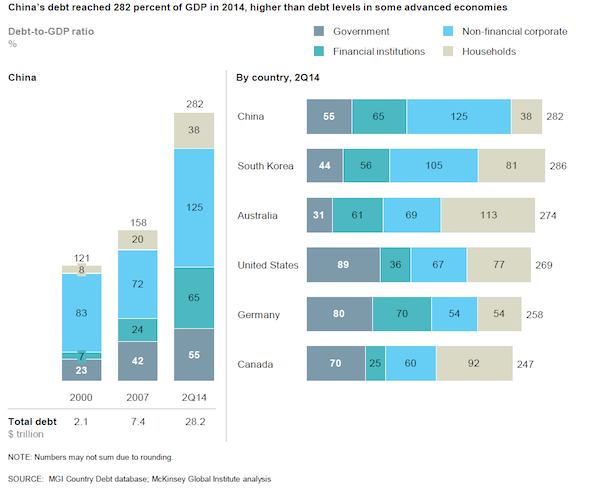
Claude Monet Hollowed Cliff near Étretat 1883

But we’ve given them all the power…
• The Real Threat To The Fed’s Independence Is Wall Street, Not Trump (WM)
[..] the real threat to the Fed’s independence isn’t coming from Trump—it’s coming from Wall Street. The Fed’s structural flaws have led to regulatory capture, which compromises its ability to set monetary and regulatory policy in a manner that isn’t tilted to favor those at the very top of the economic ladder. Trump may have broken a norm by commenting on monetary policy, but the Fed’s status quo is unaccountable, opaque decision-making shaped by deep conflicts of interest with the very financial institutions the Fed is ostensibly supposed to supervise. Consider, for instance, the abrupt resignation in March of David Cote from the New York Fed’s board of directors—a move that came as a shock to many Fed watchers.
Cote was one of just a couple people responsible for choosing the next president of the New York Fed, the most powerful economic policymaking position in the country that Trump doesn’t control. Yet before the search for New York Fed President Bill Dudley’s successor had formally concluded, Cote left the board to pursue “new business opportunities that could affect his eligibility to serve”—later revealed to be helping Goldman Sachs undertake an ambitious corporate acquisition strategy. The New York Fed claims that Cote and his fellow board members had already decided on former San Francisco Fed President John Williams to succeed Dudley by the time that Cote announced his resignation, but that means that Cote was simultaneously negotiating a new gig at Goldman Sachs while selecting one of Goldman’s top regulators.
The entire ordeal served as an unsettling reminder of the cozy relationship between the Federal Reserve and the biggest behemoth on Wall Street. Prior to being selected as New York Fed president in 2009, Dudley was Goldman Sachs’s chief economist. In 2008, Goldman Sachs Director Stephen Friedman chaired the New York Fed’s board of the directors at the same moment that it was reviewing Goldman’s application to become a bank holding company. In 2014, leaked tapes exposed New York Fed regulators pressuring one of their examiners to back off of a finding that would have imperiled Goldman Sachs’s ability to engage in a deal with Banco Santander. And in 2015, the Fed chose three consecutive men with strong ties to Goldman Sachs to be new Federal Reserve Bank presidents.

Only if we let them.
• The Trillion-Dollar Question: Can The Tech Giants Keep Growing? (G.)
It has been a tumultuous couple of weeks for America’s high-flying technology stocks, even by their own unique standards. Their shares have been soaring since the start of the year, despite being buffeted by trade war fears as President Trump talked of limiting Chinese investments in the US and restricting American technology imports to China. But now there are signs that cracks may be starting to appear in some of the biggest firms in the sector. Facebook suffered the biggest ever one-day drop in a company’s market value – losing more than £90bn – after its growth slowed in the wake of the Cambridge Analytica scandal. Twitter lost 20%, or $5bn, as it reported a surprise fall in active monthly users, while streaming service Netflix missed its targets for subscriber numbers.
On the other hand, electric car specialist Tesla managed to head in the right direction despite making a $717m second-quarter loss, as its controversial chief executive, Elon Musk, regained investor confidence after apologising for previous outbursts. That was in marked contrast to a conference call for the company’s previous set of figures, when he accused a Wall Street analyst of “boring bonehead questions” and ignored queries from investors. But the pick of the bunch remains Apple, which beat Amazon and Google to reach the landmark $1 trillion valuation on Thursday.
Despite the recent rollercoaster ride, the five key tech stocks, known as the “Faangs” – Facebook, Amazon, Apple, Netflix, and Alphabet-owned Google – have reached breathtaking heights. The total value of the five companies amounts to a staggering 19% of total US GDP. But their surge in value has prompted fears of a re-run of the dotcom boom of the late 1990s, when technology businesses dominated the stock market before coming crashing to earth. Russ Mould at investment group AJ Bell says: “That [19%] compares to the 15.5% of US GDP reached by the five biggest companies by value at the US stock market’s peak in the fourth quarter of 1999, just before the technology, media and telecoms bubble burst and that particular mania came to grief.”

“That’s my theory about what Russia is up to. If you have a better one, let’s hear it?”
The Guardians of the Galaxy at National Public Radio were beside themselves Wednesday night reporting that “the lights are blinking red for a 2018 election attack by Russia.” Well, isn’t that an interesting set-up? In effect, NPR is preparing its listeners in advance to reject and dispute the coming midterm election if they’re not happy with the results. Thus continues America’s institutional self-sabotage, with the help of a news media that’s become the errand boy of the Deep State.
What do I mean by the Deep State? The vested permanent bureaucracy of Washington DC, and especially its vastly overgrown and redundant “Intel Community,” which has achieved critical mass to take on a life of its own within the larger government, makes up its own rules of conduct, not necessarily within the rule of law, and devotes too much of its budget and influence defending its own prerogatives rather than the interests of the nation.
Personally, I doubt that President Putin of Russia is dumb enough to allow, let alone direct, his intel services to lift a finger “meddling” in the coming US midterm election, with this American intel behemoth vacuuming every digital electron on earth into the NSA’s bottomless maw of intercepted secrets. Mr. Putin must have also observed by now that the US Intel Community is capable of generating mass public hallucinations, to the beat of war-drums, and determined not to give it anything to work with. That’s my theory about what Russia is up to. If you have a better one, let’s hear it?

Turkey double-crossed the US in a prisoner swap deal. Bad idea of course. Erdogan wants Gulen, but this is not the way.
• IMF Option Looms Larger For Turkey Amid Row With US (AL M.)
While the climate of uncertainty is discouraging investments, inflation is eroding real incomes and curbing domestic consumption. As a result, the shrinking demand is bearing on economic growth, which has relied largely on the domestic market. The Turkish economy, which grew 7.4% in 2017, is expected to slow in the third quarter before beginning to contract.
The growing uncertainties are discouraging also the inflow of hot money from abroad, which Turkey desperately needs. Moreover, existing foreign investors have been fleeing the Turkish stock market, albeit slowly — a trend that contributes to sustaining the high prices of foreign exchange, especially the dollar. Accordingly, Turkey’s risk premium — reflected in credit default swaps (CDS) — is on the rise. Turkey’s CDS, which had stood at 166 basis points Feb. 1 and 199 basis points May 1, hit a record high of 334 basis points on the evening of Aug. 1 — up from 321 points in the morning. The increasing risk premium means that Turkey will now face higher interest rates when it tries to borrow from foreign creditors.
The country’s external financing needs for the next 12 months amount to $230 billion, including $180 billion to roll over external debts and $50 billion to cover its gaping current account deficit. Hence, the question of how the required funds will be secured and at what cost is crucial. The tensions with Washington came amid this already serious crunch, exacerbating the woes of Erdogan’s regime. The row over Brunson had flared last week, as both President Donald Trump and Vice President Mike Pence threatened sanctions unless Ankara took “immediate action” to release the pastor, who is being held on what Washington sees as bogus charges of espionage and collaboration with terrorist groups.
The warnings had an immediate economic effect, pushing up Turkey’s risk premium, as pundits sought to predict the scope of the upcoming sanctions. Some suggested that Washington’s hardening stance would bear on the flow of foreign capital to Turkey and the support it might seek from the IMF, while others saw trouble looming over Halkbank, the Turkish public lender embroiled in a scheme to evade US sanctions against Iran. Ultimately, Washington announced sanctions on Interior Minister Suleyman Soylu and Justice Minister Abdulhamit Gul under the 2016 Magnitsky Act, which targets individuals and entities involved in human rights abuses. According to Bloomberg, this “could be just the start of what would look like a US assault on Turkey’s vulnerable economy,” including a potentially hefty fine on Halkbank.

There’s Mark Warner again, the guy who with Comey screwed up the Assange deal with the DOJ.
• Beware the Slippery Slope of Facebook Censorship (Matt Taibbi)
You may have seen a story this week detailing how Facebook shut down a series of accounts. As noted by Politico, Facebook claimed these accounts “sought to inflame social and political tensions in the United States, and said their activity was similar — and in some cases connected — to that of Russian accounts during the 2016 election.” Similar? What does “similar” mean? The death-pit for civil liberties is usually found in a combination of fringe/unpopular people or ideas and a national security emergency. This is where we are with this unsettling new confab of Facebook, Congress and the Trump administration.
Read this jarring quote from Sen. Mark Warner (D-VA) about the shutting down of the “inauthentic” accounts: “Today’s disclosure is further evidence that the Kremlin continues to exploit platforms like Facebook to sow division and spread disinformation… I also expect Facebook, along with other platform companies, will continue to identify Russian troll activity and to work with Congress…” This was in a story in which Facebook stated that it did not know the source of all the pages. They might be Russian, or they might just be Warner’s idea of “sowing division.” Are we comfortable with that range of possibilities?
[..] Facebook was “helped” in its efforts to wipe out these dangerous memes by the Atlantic Council, on whose board you’ll find confidence-inspiring names like Henry Kissinger, former CIA chief Michael Hayden, former acting CIA head Michael Morell and former Bush-era Homeland Security chief Michael Chertoff. (The latter is the guy who used to bring you the insane color-coded terror threat level system.) These people now have their hands on what is essentially a direct lever over nationwide news distribution. It’s hard to understate the potential mischief that lurks behind this union of Internet platforms and would-be government censors. As noted in Rolling Stone earlier this year, 70 percent of Americans get their news from just two sources, Facebook and Google. As that number rises, the power of just a few people to decide what information does and does not reach the public will amplify significantly.

Makes sense. But too much of the whole thing doesn’t.
• Why Theresa May Must Stop The Brexit Clock (O.)
May’s cabinet colleagues, fanning out across the continent like Patton’s Third Army to advance her Chequers compromise, do not appear to have fared any better. Especially embarrassing are the efforts of Jeremy Hunt, the new foreign secretary. He gravely warned puzzled Europeans last week that Britain was heading for “no-deal by accident” by pushing itself off a cliff. The UK would not “blink first”, he added. Perhaps Hunt thinks he is Clint Eastwood. It matters not. On Brexit, this government has its eyes tight shut. It is blind to the consequences – and the waiting chasm. Blinking does not come into it. What part of the EU’s unchanging position on the principles governing Britain’s future relationship with Europe does May’s government not understand?
For two years or more, Barnier, the chief negotiator, firmly backed by 27 governments, has been telling London there can be no compromise and no fudge that weakens the integrity of the single market, pan-European customs and legal regulations and Europe’s borders. Yet May’s Chequers plan, seeking exceptional (and unworkable) arrangements, blithely ignores all that. In case the European public did not appreciate what was at stake, or was taken in by chauvinistic Tory claims of EU vindictiveness and dogmatism, Barnier published an op-ed in 20 European newspapers last week. Amid Brexit’s baffling complexities, his concision and clarity were refreshing. He explained the EU’s justified fears about the impact of Brexit on Europe and why it cannot reasonably be expected to bow to May’s demands for special treatment:
“The UK knows well the benefits of the single market. It has contributed to shaping our rules over the last 45 years. And yet some UK proposals would undermine our single market, which is one of the EU’s biggest achievements. The UK wants to keep free movement of goods between us, but not of people and services. And it proposes to apply EU customs rules without being part of the EU’s legal order. The UK wants to take back sovereignty and control of its own laws, which we respect, but it cannot ask the EU to lose control of its borders and laws,” Barnier wrote.

Oh, yeah, they’re going to blame it on the EU.
• UK Trade Minister Fox Says EU Is Pushing Britain To No-Deal Brexit (R.)
British trade minister Liam Fox said “intransigence” from the European Union was pushing Britain toward a no-deal Brexit, in an interview published on Saturday by the Sunday Times. With less than eight months until Britain quits the EU, the government has yet to agree a divorce deal with Brussels and has stepped up planning for the possibility of leaving the bloc without any formal agreement. Fox, a prominent Brexit supporter in Prime Minister Theresa May’s cabinet, put the odds of Britain leaving the European Union without agreeing a deal over their future relationship at 60-40. “I think the intransigence of the commission is pushing us toward no deal,” Fox told the Sunday Times after a trade mission in Japan.
“We have set out the basis in which a deal can happen but if the EU decides that the theological obsession of the unelected is to take priority over the economic wellbeing of the people of Europe then it’s a bureaucrats’ Brexit — not a people’s Brexit — (and) then there is only going to be one outcome.” It was up to the EU whether it wanted to put “ideological purity” ahead of the real economy, Fox said. If Britain fails to agree the terms of its divorce with the EU and leaves without even a transition agreement to smooth its exit, it would revert to trading under World Trade Organization rules in March 2019.

All sociopaths do it. They are defined by their lack of empathy.
• Separating Children From Their Parents Puts UK Government To Shame, Too (O.)
Donald Trump’s policy of forcibly separating immigrant parents and children at the US border has been greeted with shock and abhorrence. Around the world, people have listened to audio of young children sobbing for their parents while federal agents crack jokes and heard the stories of children locked up in cages in the richest country in the world. Even the prime minister broke with her usual timidity about Trump’s transgressions to call his family separation policy “deeply disturbing”. What hypocrisy. Less noticed – although no less inhumane – is the British government’s policy of separating parents from their young children as part of immigration detention, all conducted on Theresa May’s watch, first as home secretary, then as prime minister.
Charities such as Bail for Immigration Detainees (BID) have for years been raising the cases of children, many of whom are British citizens, taken into care because their parents have been detained, or even deported, without them. In recent months, a long list of cruelties meted out in the name of the government’s “hostile environment” policy has come to the public’s attention: people who’ve lived in Britain legally for decades, paying their taxes, suddenly denied life-saving NHS care; young people who’ve grown up in Britain facing many thousands of pounds in fees and a multi-year slog to get permanent residency; children raised in care facing the risk of deportation as an adult to a country they don’t know. Any sense of basic justice or human compassion seems to have eluded the Home Office.
But separating tiny children from their parents is cruelty of a whole different order. Today, we report on the case of Kishi, a young mother who dropped her two-year-old off at nursery in order to attend an appointment at an immigration reporting centre. There, she was restrained by immigration security officials and taken to an immigration removals centre. No arrangements were made for her toddler, who was put into emergency foster care when no one came to pick her up, and Kishi was not told where her daughter was for two days. It was another month before she saw her. Kishi and her child are not alone. BID says more than 300 children were removed from their parents in the last 12 months, an increase of 16% on the previous year. Many of those will have been taken into care as a result. The Home Office does not keep records on this; perhaps because it contravenes its own guidance, which says children must not be separated from their parents for immigration purposes if it means they will be taken into care.

Sometimes I think in Britain it’s not only the economists.
• Britain’s Economics Students Are Dangerously Poorly Educated (G.)
This month, the pressure group Rethinking Economics said Britain’s universities were failing to equip economics students with the skills that businesses and the government say they need. Following extensive interviews with employers, including organisations such as the Bank of England, it found that universities were producing “a cohort of economic practitioners who struggle to provide innovative ideas to overcome economic challenges or use economic tools on real-world problems”. Moreover, the group said, “when political decisions are backed by economics reasoning, as they so often are, economists are unable to communicate ideas to the public, resulting in a large democratic deficit.”
You could easily level that criticism at the economists forecasting the impact of AI. What are people supposed to think when those who study the field come up with such wildly varying predictions? More importantly, what will politicians think they should do? Nothing, probably, given the confusion. The Rethinking group is concerned that university departments only train, rather than educate, huge numbers of graduates for econometrics jobs across the banking, insurance and consulting sectors. In our increasingly student-led system, these young people don’t want to mess around with history or modules on inequality. They are on a mission to make money for themselves in the private sector.
If they were diverted into discussions of economic history, they might find out we are about to repeat the mistakes of the past and trigger another financial crisis. Even more inhibiting, their course might show that higher inequality dampens workers’ incentives to increase productivity, and might prompt them to ask why young economists in the City are paid colossal amounts of money to analyse bond yields or forecast oil prices. Pay them less, share the money around, and productivity might improve. Failing that, let a robot do their job.

John put something like dictatorship in the title. Bit much.
• How Reality Is Being Redefined (Slog)
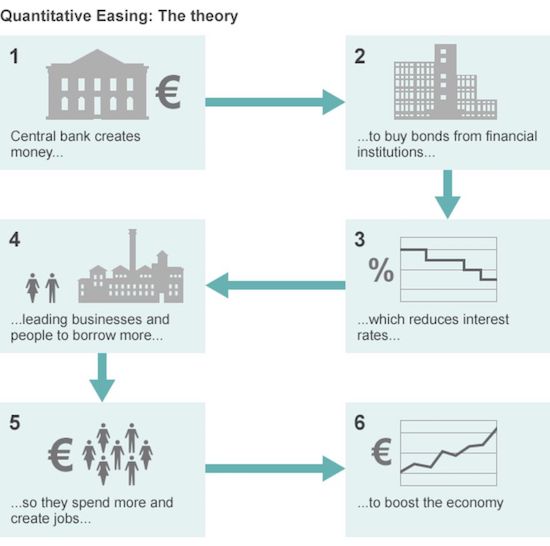
The last burgeoning growth sector on the Planet is the pursuit of redefinition. The idea is first to confuse, then create a climate of acceptance, and finally do away with every form of liberty that stands in the way of power. Both Capital and Labour are actively following the same road. It will be the end of the road for citizen freedom unless they’re both stopped. John Williams at Shadowstats.com reckons that the real unemployment rate in the US is 21.4%. Unimpressed by the US State’s insane assumption that all those no longer able to claim unemployment welfare “have found a job”, Mr Williams provides further fuel for my longstanding thesis that no real recovery can occur – if more and more mass-market consumers work fewer and fewer hours for less and less money or have no job at all – because their personal disposable income is disappearing out of sight. The term ‘in employment’ has been redefined.
When he arrived at the UK Treasury as Chancellor, George Osborne immediately gave notice that he’d be switching from the higher RPI measure of inflation (then at 5.2%) to the lower CPI at 4.5%. That doesn’t sound like much, but one has to remember two things: first, that is a 14% difference in levels that makes inflation look much lower; and second, over time the different impression given is huge: from 1996 to 2011, under the RPI system prices rose 53.6%….but using the CPI method, it only came to 35.6%. Significantly, the CPI system excludes financial services costs and government charges to the consumer. Just fancy that. So the term ‘inflation’ has been redefined.
Within two years of taking office, the Conservative-led coalition’s leader David Cameron started claiming that “the Government’s long-term economic plan is working to create more jobs”. Government Party Political Broadcasts showed the statistics, and yes, it certainly looked that way. But “a job” to most people over the last half century meant 38-40 hours a week with a month’s notice. When analysed, these new jobs were averaging 20 hours a week, often at unsocial hours and frequently on no contracts at all. They typically demand, for example, that the “employee” be ready to come into the workplace without notice. When using the weasel term ‘job’, Cameron was comparing meat and two veg with bread and dripping. So the term ‘job’ has been redefined.

One thing: people earning a low income ‘rate’ is much higher than 10.6%, and up by much more than 2% in 10 years. Lost in translation?
• Greece’s Unemployment Highest in Developed World (GR)
Greece tops all countries in the developed world in unemployment according to the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development’s (OECD) Employment Outlook 2018. Greece has suffered a dramatic spike in unemployment, with the 2017 total climbing to 21.7% of the working population, more than double the 2006 figure.
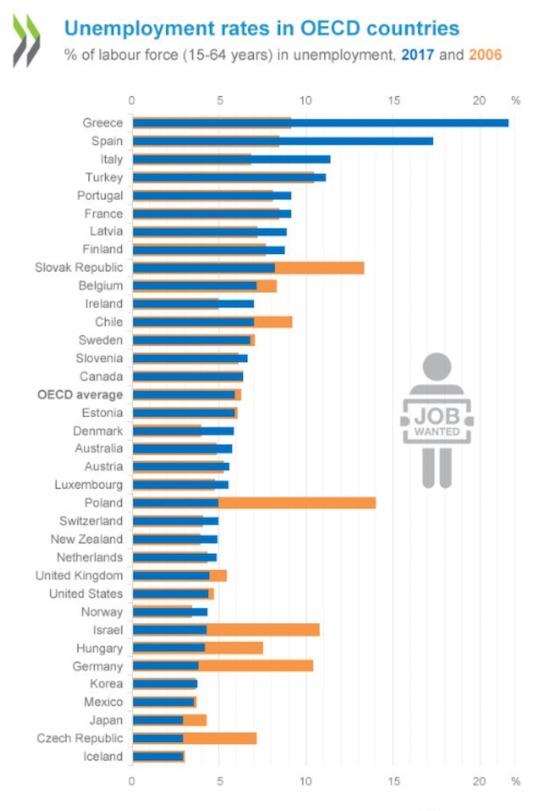
Large increases in unemployment and an underutilized workforce were accompanied by falling output, very high debt, a serious GDP deficit and deflation, the report says. Along with its impact on employment levels, the financial crisis caused a reduction in wage growth in a lot of countries, leading to a drop in living standards for many.

The proportion of working-age people earning the “low-income” rate jumped to 10.6%, up from 9.56% a decade earlier. Although Korea, Mexico, and Chile have seen a decrease in the number of low-income households, most of the countries hit hardest by the euro crisis, such as Greece, Italy, Spain and Slovenia, have suffered a 2% rise.

Thank you Brussels and Berlin.
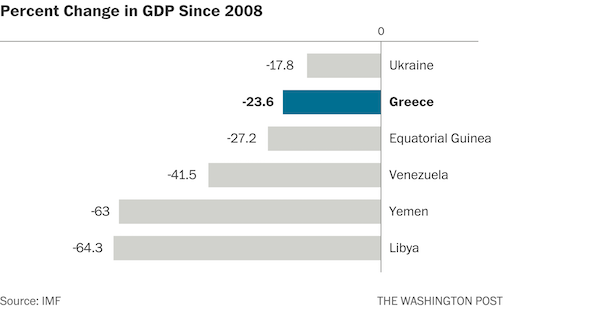
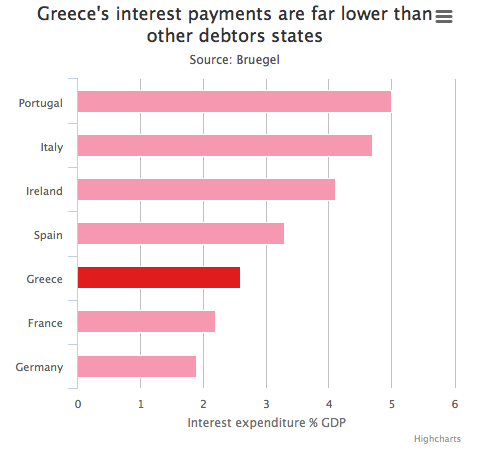
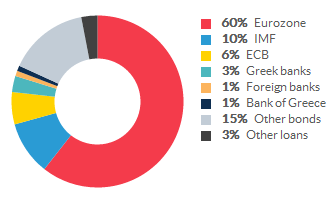
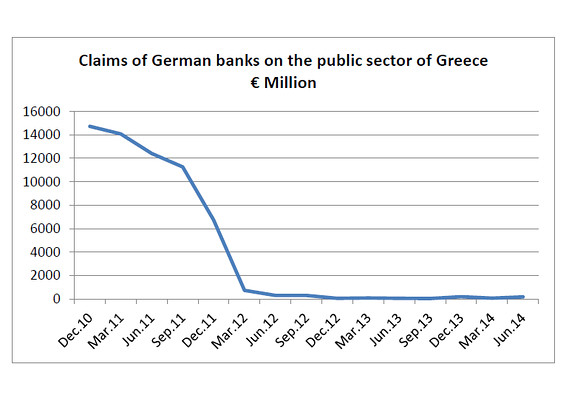
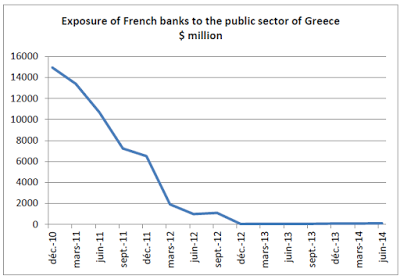
• Greece: An Economy That Has Shrunk So Much It Looks War-Torn (WaPo)
The point is that this kind of economic collapse is usually the symptom of a broader state collapse. Which is why it almost never happens in rich countries. That’s clear enough if you look at the late Angus Maddison’s historical GDP per capita numbers. Going back to 1900, there have been only three general times when European economies have shrunk over a 10-year period as much as Greece’s has since 2008: after World War I, after World War II and after the fall of communism. Most of the exceptions to this involve other wars – in particular, the Balkan wars of the 1910s, the Spanish Civil War, the Greek Civil War and the Yugoslav wars of the 1990s — but there is one that largely took place during peacetime. That was Weimar Germany’s hyperinflation.
It’s worth pointing out what isn’t here: the Great Depression. That wasn’t quite as bad in Europe as it was in the United States — at its nadir in 1933, the U.S. 10-year decline was actually comparable to Greece’s today — partly due to the fact that most European countries were quicker to leave the gold standard when things did start to get more dire. That allowed them to inject enough monetary stimulus into their economies to jump-start almost immediate recoveries. The problem, of course, is that it’s a lot harder for Greece to do the equivalent of that right now. The gold standard and the euro are similar in that they are both fixed-exchange rate systems that can get countries into trouble if they are hit by a big enough shock that their economy “needs” a cheaper currency than it has under the system.
But they’re different in that it’s a lot simpler to say your currency won’t be worth as much gold as it used to than to replace all of your currency with a new one. So instead of stimulus, Greece has gotten austerity — and a lot of it. Under the terms of its just-about-to-be-completed bailout agreement, Greece is actually supposed to keep running primary budget surpluses of at least 2.2 percent of GDP until 2060. That’s right: four more decades of austerity. It’s no wonder, then, that Greece’s economy might not get back to where it was in 2008 until 2030. This is what Europe calls a success: an economy that has shrunk so much it looks war-torn.