Edward Hopper Railroad crossing 1926

The coronavirus death toll in Europe crossed 175,000
New cases past 24 hours in:
• US + 20,103
• Brazil + 20,154
• Russia + 8,371
• UK 4,938
• India + 7,540
• Peru + 6,154
New deaths past 24 hours in:
• US + 1,529
• Brazil + 1,104
• Mexico 462
• UK 343

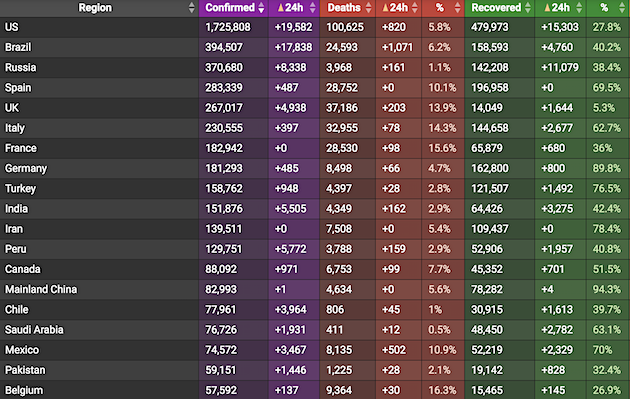
• Cases 5,813,239 (+ 103,721 from yesterday’s 5,709,518)
• Deaths 357,893 (+ 5,143 from yesterday’s 352,750)

From Worldometer yesterday evening -before their day’s close-:
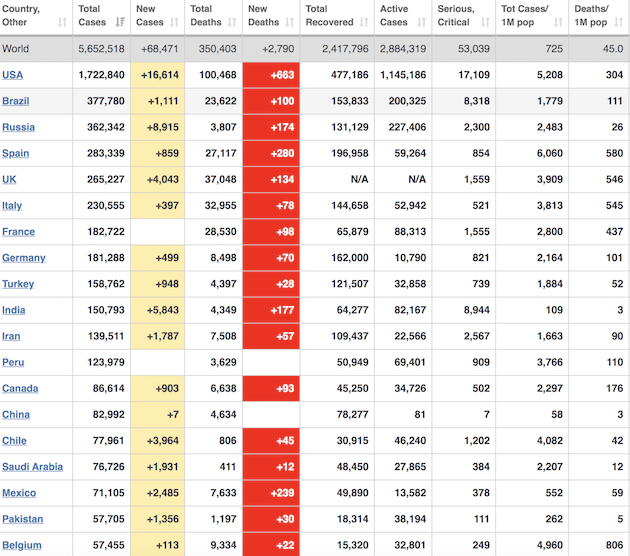
From Worldometer:
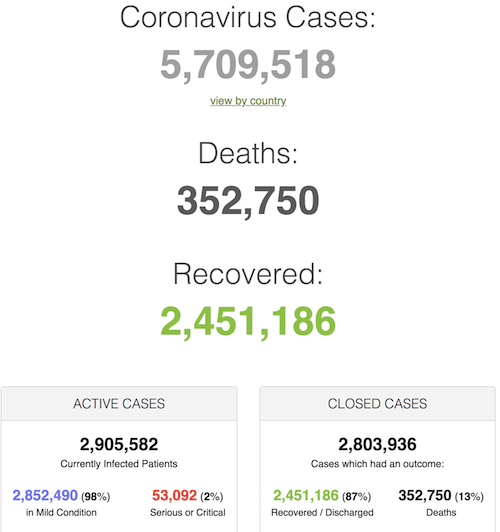
From SCMP:
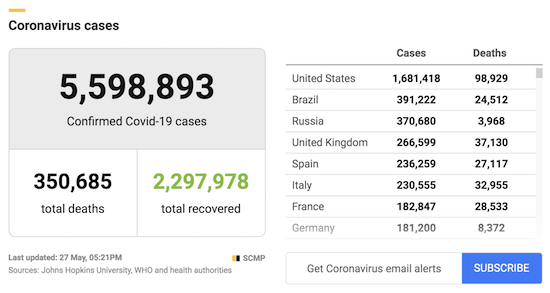
From COVID19Info.live:

One single report in the Lancet, based on data from a company nobody seems to know, has had the desired effect. France, the WHO, and now Italy and Belgium have all turned their backs on HCQ.
• Questions Raised Over HCQ Study Which Caused WHO To Halt Trials (G.)
Questions have been raised by Australian infectious disease researchers about a study published in the Lancet which prompted the World Health Organization to halt global trials of the drug hydroxychloroquine to treat Covid-19. The study published on Friday found Covid-19 patients who received the malaria drug were dying at higher rates and experiencing more heart-related complications than other virus patients. The large observational study analysed data from nearly 15,000 patients with Covid-19 who received the drug alone or in combination with antibiotics, comparing this data with 81,000 controls who did not receive the drug.
[..] The study, led by the Brigham and Women’s Hospital Center for Advanced Heart Disease in Boston, examined patients in hospitals around the world, including in Australia. It said researchers gained access to data from five hospitals recording 600 Australian Covid-19 patients and 73 Australian deaths as of 21 April. But data from Johns Hopkins University shows only 67 deaths from Covid-19 had been recorded in Australia by 21 April. The number did not rise to 73 until 23 April. The data relied upon by researchers to draw their conclusions in the Lancet is not readily available in Australian clinical databases, leading many to ask where it came from.
[..] The Lancet told Guardian Australia: “We have asked the authors for clarifications, we know that they are investigating urgently, and we await their reply.” The lead author of the study, Dr Mehra Mandeep, said he had contacted Surgisphere, the company that provided the data, to reconcile the discrepancies with “the utmost urgency”. Surgisphere is described as a healthcare data analytics and medical education company. [..] Dr Allen Cheng, an epidemiologist and infectious disease doctor with Alfred Health in Melbourne, said the Australian hospitals involved in the study should be named. He said he had never heard of Surgisphere, and no one from his hospital, The Alfred, had provided Surgisphere with data.
“Usually to submit to a database like Surgisphere you need ethics approval, and someone from the hospital will be involved in that process to get it to a database,” he said. He said the dataset should be made public, or at least open to an independent statistical reviewer. “If they got this wrong, what else could be wrong?” Cheng said. It was also a “red flag” to him that the paper listed only four authors. “Usually with studies that report on findings from thousands of patients, you would see a large list of authors on the paper,” he said. “Multiple sources are needed to collect and analyse the data for large studies and you usually see that acknowledged in the list of authors.”

This is about health care workers on the front lines, who have nothing else to protect themselves.
• India Invites Scepticism As It Sticks By Hydroxychloroquine (SCMP)
The Indian government is courting controversy by continuing to give the antimalarial drug hydroxychloroquine to health care workers on the front lines of the fight against the coronavirus, despite safety concerns that have prompted the World Health Organisation to pause a large-scale trial of the drug. Scientists at the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), the body leading the coronavirus battle in India, say their studies have shown definitively that the drug – also known as HCQ – helps to prevent infections among health care workers exposed to Covid-19. The ICMR has conducted three studies, involving control groups of between 330 and 1,300 people, in which frontline health care staff have taken the drug as a preventive measure.
Dr Suman Kanungo, ICMR’s senior epidemiologist, told This Week in Asia that further research was being carried out on a control group of 1,500 health care workers and that the results of the studies would be released within a month. He stressed the ICMR recommended the drug as a preventive measure, indirectly implying that it was not recommended as a cure for Covid-19. His comments came after the ICMR’s director general Balram Bhargava said on Tuesday that the group’s studies had shown that HCQ, when used as a preventive measure, had no side-affects. However, some experts are sceptical of the ICMR’s claims, pointing out that India is the world’s largest manufacturer of the drug and that only very limited details of the studies have been made public.
Dr Sapan Desai, CEO of the Surgisphere Corporation and a co-author of the Lancet study, said the study was based on a “specific group” of hospitalised Covid-19 patients. “[We] have clearly stated that the results of our analyses should not be over-interpreted to those that have yet to develop the disease or those that have not been hospitalised. It is in recognition of these limitations of our observational study that we recommended that RCTs [randomly controlled trials] be urgently completed,” he said.

Every government’s nightmare.
• South Korea Could Face Return To Restrictions After Spike In New Cases (G.)
South Korea has reported its biggest daily increase in coronavirus cases in 53 days, triggering warnings it may have to revert to stricter social distancing measures after appearing to have brought the outbreak under control. The Korean Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (KCDC) reported 79 new infections on Thursday with 67 of them from the Seoul metropolitan area, home to about half of the country’s population of 51 million. Officials said health authorities were finding it increasingly difficult to track the transmission routes for new infections and urged people to remain vigilant amid fears of a second wave of Covid-19 infections.
The health minister, Park Neung-hoo, pleaded with residents in and around the capital to avoid unnecessary gatherings and urged companies to allow sick employees to take time off work. “Infection routes are being diversified in workplaces, crammed schools and karaoke rooms in the metropolitan area,” Park said. The recent spike in infections has underlined the risks that come with relaxing social distancing rules, as countries seek to breathe life into their struggling economies. More than 250 new infections were traced to clubs and bars in the Itaewon district of Seoul in early May, while the latest cluster has been linked to a distribution centre in Bucheon, near Seoul, owned by the e-commerce firm Coupang.
The recent rise in cases is affecting the phased reopening of schools, only recently held up as evidence that South Korea, one of the first countries outside China to be affected, had contained the outbreak. More than 500 schools have delayed the resumption of classes over virus concerns, the education ministry said this week. Thursday’s figures followed reports of 40 new cases on Wednesday – the highest figure in seven weeks. South Korea has reported a total of 11,344 cases and 269 deaths from Covid-19.

Pompeo is a pompous fool, but how could one claim he’s mistaken here?
Hong Kong is pivotal for the banking sector that underlies trade between China and the west, between the renminbi and the USD. But because nobody wants the renminbi, it’s that much more pivotal for China.
Hong Kong is interesting for the west only when it’s independent. Once it’s part of China, why stay there?
Hong Kong as it is today, is the culmination of 200 years of development, negotiations, trust building. It will take a very long time for China to establish that somewhere else. Hong Kong has a “special trading status” with the US. Those are not handed out with every box of detergent.
• Hong Kong Is No Longer Autonomous From China, US Determines (SCMP)
In a huge blow to Hong Kong, the Trump administration informed the US Congress on Wednesday that the city is no longer suitably autonomous from China. The assessment is a crucial step in deciding whether Hong Kong will continue to receive preferential economic and trade treatment from the United States. “No reasonable person can assert today that Hong Kong maintains a high degree of autonomy from China, given facts on the ground,” US Secretary of State Mike Pompeo said in a statement. “This decision gives me no pleasure. But sound policy making requires a recognition of reality.” The State Department’s certification is a recommendation and does not necessarily lead to an immediate next step. US officials, including President Donald Trump, now must decide to what extent sanctions or other policy measures should be levelled on the city.
“While the United States once hoped that free and prosperous Hong Kong would provide a model for authoritarian China, it is now clear that China is modeling Hong Kong after itself,” Pompeo said. Under the Hong Kong Human Rights and Democracy Act passed by the US Congress in November, the administration must decide annually whether governance of Hong Kong is suitably distinct from China. Options available to the administration – which may in part depend on Beijing’s reaction, analysts said – include higher trade tariffs, tougher investment rules, asset freezes and more onerous visa rules. The move sent shock waves through China and Hong Kong policy circles. “Wow,” said Bonnie Glaser, director of the China Power Project at the Centre for Strategic and International Studies.
“I fully expect the US to proceed with sanctions on individuals and entities deemed to be undermining Hong Kong’s autonomy,” she continued. “Secondary sanctions are possible on banks that do business with entities found in violation of law guaranteeing Hong Kong’s autonomy.” Analysts noted a long-standing dilemma faced by successive US administrations: if Washington imposes sanctions on Hong Kong, it risks hurting residents of the city at least as much as it penalises Beijing. Following through on threats to change Hong Kong’s status will have a hugely negative impact on US companies operating there as well as on Hongkongers while having a minuscule effect on China, said Nicholas Lardy, a fellow at the Peterson Institute for International Economics. “And I don’t know why we want to punish the citizens of Hong Kong for something that the government in Beijing is doing,” he added.
[..] Under the Basic Law, Hong Kong’s mini constitution, the city’s government has leeway to make its own decisions, other than those involving defence and national security, where Beijing prevails. But at annual political meetings last week in Beijing, China unveiled a resolution that will initiate the legislative process for a new draft legislation banning “secession, subversion, terrorism and foreign interference”. The move will greatly expand the mainland’s power over the city and has elevated concerns that China is rapidly eliminating the “one country, two systems” principle.

They’re going to pass it, because otherwise they would lose face.
• China Approves Hong Kong Draft Security Law (NBC)
The Chinese parliament passed the first hurdle of enacting a draft security law for Hong Kong on Thursday, legislation that has prompted widespread concern about Beijing’s increasing influence on the semi-autonomous region. The annual National People People’s Congress approved the framework of the law by 2,878 votes to one, and it will now go to senior party officials in the Standing Committee of the NPC to be fleshed out. The draft law, which is set to tackle issues such as secession, subversion, terrorism and foreign interference, comes after a year of anti-government protests that at times brought Hong Kong to a standstill. It has already prompted widespread concern around the world. Secretary of State Mike Pompeo said it meant that Hong Kong no longer qualifies for its special status under U.S. law. “The United States stands with the people of Hong Kong,” he said in a statement Wednesday.

“Coming out and decertifying Hong Kong’s autonomy is not the hard decision, The hard work comes now, which is how you implement it.”
• Hong Kong’s ‘Significance Is Eroding’, As Trump Considers Next Move (SCMP)
Economists, diplomats and business figures were scrambling on Thursday to quantify the effect of Washington’s decision to deem Hong Kong “no longer autonomous” from China, with many gaming out the “nuclear option”, in which the United States revokes the city’s special trading status. Former White House officials said that the most likely immediate scenario is that US President Donald Trump approves a “variety” of sanctions, potentially on both Chinese and Hong Kong officials, by the end of the week in response to China’s national security law for Hong Kong. However, “the nuclear option is certainly on the table”, said a former senior Trump administration official, which would see Hong Kong’s status as a region apart from the rest of China removed at a later date, leaving the city vulnerable to trade war tariffs, technological export controls, visa and travel restrictions and greater financial sector scrutiny.
“Coming out and decertifying Hong Kong’s autonomy is not the hard decision,” said Evan Medeiros, who served as former president Barack Obama’s top adviser on the Asia-Pacific and who confirmed that he would have done the same. “The hard work comes now, which is how you implement it.” Should Trump go gung-ho on China, there would be no direct change to Hong Kong’s international status. It would remain a member of the World Trade Organisation (WTO) and the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation group. The direct economic impact would be sharp, but short-term, analysts said. But in the long run it will be a huge blow to Hong Kong’s image as an international commercial centre – even as a gateway to China.
“I guess the significance of Hong Kong is eroding and when I go to see the members in Shenzhen and Guangzhou and listen to discussion about the Greater Bay Area, it is pretty much one story, as if Hong Kong is insignificant,” said Joerg Wuttke, president of the European Union Chamber of Commerce for China in Beijing. “Hong Kong cannot be replicated, the unique density of professionals, the transparency of the system, the rule of law, the kind of debate possibilities, the openness. They’re definitely important for developing business in China, for many of us it’s being challenged right now,” Wuttke said.

Like either gives a damn about the UN.
• US And China Fight At United Nations Over Hong Kong (R.)
The United States and China clashed over Hong Kong at the United Nations on Wednesday after Beijing opposed a request by Washington for the Security Council to meet over China’s plan to impose new national security legislation on the territory. The U.S. mission to the United Nations said in a statement that the issue was “a matter of urgent global concern that implicates international peace and security” and therefore warranted the immediate attention of the 15-member council. China “categorically rejects the baseless request” because the national security legislation for Hong Kong was an internal matter and “has nothing to do with the mandate of the Security Council,” China’s U.N. Ambassador Zhang Jun posted on Twitter. The U.S. request coincides with rising tensions between Washington and Beijing over the coronavirus pandemic.
Washington has questioned China’s transparency about the outbreak, which first emerged in Wuhan, China late last year. China has said it was transparent about the virus. The U.S. said China’s opposition to a Security Council meeting on Hong Kong coupled with its “gross cover-up and mismanagement of the COVID-19 crisis, its constant violations of its international human rights commitments, and its unlawful behavior in the South China Sea, should make obvious to all that Beijing is not behaving as a responsible U.N. member state.” Zhang responded: “Facts prove again and again that the U.S. is the trouble maker of the world. It is the U.S. who has violated its commitments under the international law. China urges the U.S. to immediately stop its power politics and bullying practices.”

In the beginning, things will move with caution. But that may not last very long as parties realize the scope of what is happening.
• What To Expect Now US Deems Hong Kong No Longer ‘Autonomous’ (SCMP)
US President Donald Trump has to decide what actions to take after the State Department informed Congress on Wednesday that Hong Kong was no longer considered autonomous from China, an assessment that could threaten the city’s long-standing special trading status. “It’s a one-two action,” said David Stilwell, assistant secretary of the Bureau of East Asian and Pacific Affairs at the State Department on Wednesday evening. “One being the State Department making the assessment that Hong Kong no longer enjoys autonomy,” said Stilwell at a briefing to reporters, referring to US Secretary of State Mike Pompeo’s statement earlier in the day. “And then, [the second action will be] the determination by the White House as to how we’re going to respond,” Stilwell said.
The State Department did not specify how fast that decision may be. “A lot of” options are being considered, including personnel and sanctions “as determined in the United States – Hong Kong Policy Act of 1992 and in the Hong Kong Human Rights and Democracy Act [of 2019],” he said. Under the Hong Kong Human Rights and Democracy Act passed by the US Congress in November, the administration must decide every year whether governance of Hong Kong is suitably distinct from China, which is the prerequisite for the special status to continue. A revocation of Hong Kong’s special trading status with the US will put an end to the preferential economic and trade treatment the city has enjoyed and which has, at least partly, contributed to making it the financial and business hub in the region.
Some analysts and members of the business community, following the State Department’s assessment, have voiced concerns that a status change would inflict more pain on Hong Kong and its people than on Beijing. “Today’s action is best understood as another turn of the screw,” said Terry Haines, an independent political analyst and former Congressional staffer. “It is a strong signal of US government displeasure.” But, given that this is only the first step, and does not necessarily lead to US sanctions or other actions against Hong Kong, there is opportunity to lessen tension, he said. “Expect Congress to help Trump pressure China on Hong Kong autonomy, but not to force Trump’s hand or require sanctions or other actions,” he said.
In his statement earlier on Wednesday, Pompeo said “no reasonable person can assert today that Hong Kong maintains a high degree of autonomy from China, given facts on the ground.” Pompeo’s assessment came a day before Beijing could pass the national security law tailor-made for Hong Kong. The move aimed to thwart Beijing’s plan to move forward with the passage of the legislation, which is considered a violation of the Sino-British Joint Declaration, the treaty that established the principle of “one country, two systems” and which stipulates the sovereign and administrative arrangement of Hong Kong after the 1997 handover.

After being accused domestically of doing the opposite. Taiwan has always offered help.
• Taiwan Will Help Relocate Fleeing Hongkongers – President Tsai (SCMP)
Taiwanese President Tsai Ing-wen has assured Hongkongers that her government would come up with special measures to help them relocate to the island, in an apparent effort to counter claims that she is giving up on Hong Kong. Tsai said her cabinet would form an ad hoc committee to work out a humanitarian action plan for Hong Kong people. Under the plan, the Mainland Affairs Council, the island’s top mainland policy planner, would establish concrete ways for the administration to help Hongkongers “live, relocate and work in Taiwan”, Tsai said. She said a special budget and resources would be set aside for the programme, which would launched as soon as possible to address the needs of Hongkongers wanting to move amid concerns about threats to freedoms posed by the introduction of a national security law.
After months of anti-government protests in Hong Kong, the National People’s Congress is expected to pass on Thursday a resolution to set up and improve legal and enforcement mechanisms for national security in Hong Kong, a move that has been widely condemned overseas and in the city. The decision to form the committee comes after Tsai came under attack for suggesting in a Facebook post on Sunday that she might consider invoking Article 60 of the Laws and Regulations Regarding Hong Kong and Macau Affairs by suspending the “application of all or part of the provisions of the act” if the NPC bypassed Hong Kong’s Legislative Council to approve the security law. That would mean an end to the preferential treatment given to people from Hong Kong and Macau, including to visit and invest in the self-ruled island.
Opposition lawmakers said the move would effectively suspend the city’s special status, essentially shutting the door to Hong Kong people doing business, studying or fleeing to Taiwan to avoid penalties for their protest actions in the city.
They criticised Tsai for trying to “dump” Hong Kong people after using them to win January’s presidential election. Tsai’s strong support for the mass protests in Hong Kong last year – triggered by a now-shelved extradition bill – helped her win a landslide in January’s presidential poll for which she secured a second four-year term. Tsai’s suggestion also attracted concerns from civic and human rights groups in Taiwan.

More reason to bail out people, not companies.
• Suddenly Everything is Too Big to Fail – John Rubino (USAW)
Everyone needs be looking past the Coronavirus crisis and at what governments are trying to do to counter the economic destruction and massive unemployment. Is the financial cure worse than the disease? Financial writer John Rubino says look at commercial real estate as an omen of what is to come. Rubino explains, “Sooner or later you’ve got to pay your bills, and if you don’t have anybody paying your bills to you, then you go bankrupt. Commercial real estate could just be a blood bath, which take us back to all the bailouts. You can’t let a big sector go bust in this world because suddenly everything is too big to fail. There is not a major sector out there that can be allowed to go bust. Not the airlines, not commercial real estate, certainly not the banks, you name it and it has to be bailed out. That’s where the really crazy stuff starts. When people figure out we are basically bailing out everybody from home owners to student loan holders, to car loan holders and right down the line, and then we get state and local governments with this gigantic multi-trillion dollar problem . . . and the amount of debt is off the charts to bail all of these guys out, that is when the real fun starts.”
How long will the bailouts go on? Rubino says, “We are heading into a Presidential election, which means we cannot let anything major fail. If you are the Trump Administration and Congress, you can’t let something big fail because it’s a crisis right before you need to get re-elected. So, you’ve got to bail people out. That’s what California, Illinois and Chicago, New York, Kentucky and all the bankrupt and badly run states have been hoping for all along. They have been hoping there would be a big crisis that would bail them out of their horrendous mismanagement of the past 20 or 30 years. There was no way that Illinois was not going to go bankrupt in normal times . . . or Chicago. . . . Now, they can go to the federal government and say we need a trillion dollars right now or we are going to lay off all the cops and all the teachers, and they think they have a pretty good chance of getting the bailout because the alternative is poison for the people running for office . . . . If you are the Trump Administration or Congress, I don’t see how you stop bailing people out before the election.”

Not everyone in Australia wants a travel bubble, apparently.
• Flightless Kiwi Economy To Land With A Thud (Austr.)
No national leader has been as feted as Jacinda Ardern during this pandemic. Young and progressive, New Zealand’s Prime Minister was popular before the crisis. Since she imposed the favoured pandemic solution of the left — a hard lockdown, shutting practically all business and no socialising with anyone outside your home — her star has only risen. “Laughing in the face of seismic shakes, she has calmly steered her country in the face of a massacre, an eruption and a pandemic,” The Guardian cooed on Tuesday. Steering it into an economic abyss, perhaps. New Zealand’s economy is in strife. Without major change, our constitutional cousin is in decline. Its public finances are in tatters, its biggest export, tourism, has been obliterated — Air New Zealand announced 4000 job losses this week — and New Zealand police now can enter people’s homes without a warrant.
“New Zealand is going backwards, falling behind the vast ≠majority of our OECD partners in virtually every social and economic measure that matters,” said Roger Douglas, a former New Zealand Labour treasurer and the famed architect of Rogernomics. New Zealand ranks fourth last in the OECD for labour productivity growth, and last for multi-factor productivity growth, according to economist Michael Reddell, based on OECD data. Health and education are gobbling up more of the budget as the population ages, with less and less to show for it.

I think they fear other scenarios a lot more. Like the full exposure of Obamagate.
• The General Election Scenario That Democrats Are Dreading (Pol.)
In early April, Jason Furman, a top economist in the Obama administration and now a professor at Harvard, was speaking via Zoom to a large bipartisan group of top officials from both parties. The economy had just been shut down, unemployment was spiking and some policymakers were predicting an era worse than the Great Depression. The economic carnage seemed likely to doom President Donald Trump’s chances at reelection. Furman, tapped to give the opening presentation, looked into his screen of poorly lit boxes of frightened wonks and made a startling claim. “We are about to see the best economic data we’ve seen in the history of this country,” he said.
[..] Furman’s case begins with the premise that the 2020 pandemic-triggered economic collapse is categorically different than the Great Depression or the Great Recession, which both had slow, grinding recoveries. Instead, he believes, the way to think about the current economic drop-off, at least in the first two phases, is more like what happens to a thriving economy during and after a natural disaster: a quick and steep decline in economic activity followed by a quick and steep rebound. The Covid-19 recession started with a sudden shuttering of many businesses, a nationwide decline in consumption and massive increase in unemployment. But starting around April 15, when economic reopening started to spread but the overall numbers still looked grim, Furman noticed some data that pointed to the kind of recovery that economists often see after a hurricane or industrywide catastrophe like the Gulf of Mexico oil spill.
Consumption and hiring started to tick up “in gross terms, not in net terms,” Furman said, describing the phenomenon as a “partial rebound.” The bounce back “can be very very fast, because people go back to their original job, they get called back from furlough, you put the lights back on in your business. Given how many people were furloughed and how many businesses were closed you can get a big jump out of that. It will look like a V.”

How many consecutive investigations is that now?
• AG Barr Launches New ‘Unmasking’ Investigation Around 2016 Election (CNN)
Attorney General William Barr has tasked a US attorney with reviewing instances of “unmasking” done around the 2016 election, adding the weight of a senior federal prosecutor behind an issue that President Donald Trump has seized on in recent weeks to underpin unfounded allegations about his predecessor. John Bash, the US attorney in San Antonio, will be handling the review in support of the ongoing criminal investigation being led by John Durham, a Connecticut prosecutor, according to a Justice Department spokeswoman. “Unmasking inherently isn’t wrong but certainly the frequency, the motivation and the reasoning behind unmasking can be problematic.
“When you’re looking at unmasking as part of a broader investigation, like John Durham’s investigation, looking specifically at who was unmasking whom can add a lot to our understanding about motivation and big picture events,” Kerri Kupec, the department spokeswoman, said in an interview with Fox News. Earlier this month, then-acting Director of National Intelligence Richard Grenell declassified a list of names of former Obama administration officials who allegedly had requested the “unmasking” of the identify of Trump’s first national security adviser, Michael Flynn. Senate Republicans later released the list, which named Obama administration officials who “may have received” Flynn’s identity in National Security Agency intelligence reports after requests to unmask Americans.
On Fox, Kupec said that Barr had “determined that certain aspects of unmasking needed to be reviewed separately as a support” to the Durham investigation. Bash will be looking “specifically at episodes both before and after the election,” Kupec said. Bash is the latest in a string of top prosecutors Barr has assigned to handle politically charged reviews. Durham, the longtime Connecticut prosecutor, was assigned to review the origins of the Russia investigation earlier this month. Jeff Jensen, the US attorney in St. Louis, had scrutinized the handling of the Flynn prosecution and recommended earlier this month that the Justice Department drop the charges. Barr has said that he has since tasked Jensen with examining other issues, but the department has not said what those issues are.
The greatest intelligence trap
history has ever revealed! pic.twitter.com/gzyYJrIlfr— Fake News Crime Fighter (@realTT2020) January 30, 2019

Openly lying to a court.
• Former Flynn Lawyers “Find” 6,800 Documents They Failed To Produce (Solomon)
The surprises keep coming in former National Security Adviser Michael Flynn’s legal battle to overturn his conviction in the Russia probe. Just days after the FBI belatedly produced possible evidence of innocence to Flynn’s new legal team led by Attorney Sidney Powell, his old law firm on Tuesday informed the judge it had located 6,800 documents that it failed to turn over as required by a court order in 2019. Covington & Burling LLP told the court its search team failed to search all of the law firm’s records and missed the documents, mostly emails. The documents were produced to Powell on Tuesday.
“Covington determined that an unintentional miscommunication involving the firm’s information technology personnel had led them, in some instances, to run search terms on subsets of emails … rather than on the broader sets of emails that should have been searched,” Flynn’s former attorney Robert Kelner told the court in a motion. “We now have performed another search, using search terms and manual reviews, on a broader universe of material to correct the earlier error and to transfer additional documents that are part of the client file,” Kelner wrote, saying his firm was willing to assist Powell on any other matters and to address any questions the judge may have about the oversight.
“They began to get increasingly concerned that somebody like Gen. Flynn, with all his intelligence experience, was going to become a national security adviser," because he'd "instantly grasp the ramifications" of what they did, says @themarketswork
WATCH: https://t.co/DEeqXmFCMK pic.twitter.com/Hbeskm5zq2
— American Thought Leaders with Jan Jekielek (@AmThoughtLeader) May 27, 2020

Graham wants Flynn, Obama and Trump to participate, but he doesn’t seek their testimony.
• Rosenstein First Witness In Senate Judiciary’s ‘Crossfire Hurricane’ Probe (JTN)
Former acting Attorney General Rod Rosenstein will be the first witness to testify in the Senate Judiciary Committee’s investigation into the FBI’s handling of its Russia collusion probe, the panel announced Wednesday. Rosenstein is set to testify the morning of June 3 before the committee led by Chairman Sen. Lindsey Graham. The South Carolina Republican called for a formal inquiry a few weeks ago, following the release of declassified information that showed officials in the FBI’s Crossfire Hurricane probe appeared to exceed authority, or at the very least break with protocol. Among the biggest revelations in the documents was that the FBI appeared to know that then-National Security Adviser Michael Flynn had not colluded with Russia during the 2016 presidential election to influence the race’s outcome, but still interviewed him and pressed him into a guilty plea.
Graham, who is seeking subpoena authority in the probe, has said the committee will look into the appointment of retired FBI chief Robert Mueller as special counsel in the investigation. Rosenstein appointed Mueller and set the parameters of his authority. Graham said after the release of the documents — which was followed by the Justice Department asking a federal court to dismiss its Flynn case — that he would also seek testimony from former FBI Director James Comey, former FBI Deputy Director Andrew McCabe, former Director of National Intelligence James Clapper, former CIA Director John Brennan and former Deputy Attorney General Sally Yates.
The first phase of the panel’s investigation “will deal with the government’s decision to dismiss” the case against Flynn, as well as “an in-depth analysis of the unmasking requests made by Obama Administration officials against Gen. Flynn,” Graham recently said. He has also invited Flynn, former President Obama and President Trump to participate.

What the heck, let’s do some gossip.
• New Book Claims Bill Clinton Had Affair With Ghislaine Maxwell (NYP)
Bill Clinton had an affair with British-born socialite Ghislaine Maxwell, who is accused of helping recruit underage victims for notorious pedophile Jeffrey Epstein, according to a blockbuster new book. The ex-president — who denies cheating on wife Hillary Clinton with Maxwell — reportedly engaged in the romps during overseas trips on Epstein’s private plane, a customized Boeing 727 that’s since become known as the “Lolita Express.” The nation’s 42nd head of state also repeatedly sneaked out to visit Maxwell at her Upper East Side townhouse, as detailed in this exclusive excerpt. Excerpt from “A Convenient Death: The Mysterious Demise of Jeffrey Epstein,” by Alana Goodman and Daniel Halper, out June 2:
“Clinton was allegedly carrying on an affair with at least one woman in Epstein’s orbit, but she was well over the age of consent. Ghislaine Maxwell, a constant presence at the ex- president’s side during these trips, was the primary reason Clinton let Epstein ferry him around the world. “[Bill] and Ghislaine were getting it on,” a source who witnessed the relationship said in an interview. “That’s why he was around Epstein—to be with her.” The source explained that reporters have been missing the point about the Clinton- Epstein relationship by focusing on Epstein’s sex crimes. “[Clinton’s] stupid but not an idiot,” the source says, dismissing the idea that the ex- president was sexually involved with children.
Clinton’s primary interest in Epstein was the woman he once dated and who allegedly helped procure her ex-boyfriend’s future victims. “You couldn’t hang out with her without being with him,” the source said of the Epstein-Clinton relationship. “Clinton just used him like everything else,” the source explains. In this case, Epstein was being used as an alibi while he hooked up with Maxwell.
[..] while attending the Clinton Global Initiative in New York City, at the end of an Indian summer, in September 2009, a process server walked through the packed lobby of the Sheraton Hotel…and served Ghislaine Maxwell papers for a deposition,” the journalist Conchita Sarnoff recalls. “Maxwell…was huddled in a small group talking to other guests” as the server approached her. He “called out her name and…with so many people surrounding her, Maxwell was unsuspecting. She confirmed her identity and he served her notice. The deposition was in relation to Epstein’s sexual abuse case. The server left at once,” Sarnoff writes in her book, TrafficKing.

I’m old enough to remember that Black Lives Matter only became a going concern under America’s first black president.
• Minneapolis Ablaze Amid Looting (ZH)
High unemployment, crashed economy, and now social unrest rears its ugly head as America descends into chaos ahead of the summer months. Across social media, pictures and videos coming from the streets of Minneapolis on Tuesday evening are absolutely stunning. Protests broke out following the death of George Floyd, a black man who died in police custody a day earlier. This reminds us of the 2014 Ferguson Riots and 2015 Baltimore Riots, in both incidents, the trigger for unrest was a young black man killed while in police custody. Unlike 2014/15, the economy has now plunged into a depression and tens of millions of people are unemployed, as some have to resort to food banks because they’ve fallen into instant poverty, which all suggests tensions are already running high as warmer weather entices people to step outside. With no work, why not riot?
Shown below, police fired rubber bullets, tear gas, and stun grenades at protesters. The initial demonstrations started peacefully than quickly got out of hand. Some hurled blunt objects at law enforcement while damaging police cars. The early hours of the protest were peaceful, hundreds, and maybe even more than a thousand people, were seen marching across 38th Street. Some carried signs that read “Justice for George Floyd,” “I can’t breathe,” and “Black Lives Matter.”
Our Minneapolis #GeorgeFloyd protest stream is back up, now with increased quality. We will stay live for you, networks permitting:https://t.co/4DTgvFtAzQ
— Unicorn Riot (@UR_Ninja) May 28, 2020
I remember this like it was yesterday. The LA Riots. The Koreans were not playing and I can vividly recall how impressed I was by their fortitude. https://t.co/DTYRL9Pmvi
— Adryana (@RedPilledChica) May 28, 2020

We try to run the Automatic Earth on people’s kind donations. Since their revenue has collapsed, ads no longer pay for all you read, and your support is now an integral part of the interaction.
Thank you.

NEW: Here’s 11 local news stations just straight up running an Amazon scripted segment ahead of their shareholders meeting pic.twitter.com/wc8HbJT4ki
— Colin Jones (@colinjones) May 26, 2020

https://twitter.com/i/status/1265474120680181762



Support the Automatic Earth in virustime.