NPC Fordson tractor exposition at Camp Meigs, Washington DC 1922



Zombie money.
• The World’s Awash In $5 Trillion In Excess Liquidity (Bloomberg)
If you’re worried the Federal Reserve will topple the debt markets, consider this: there’s rarely been so much cash available in the world to buy assets such as bonds. While the prospect of higher U.S. interest rates sent bonds worldwide to the biggest-ever quarterly loss, JPMorgan Chase says the excess money in the global economy – about $5 trillion – will support demand and bolster asset prices. Since 1990, there have been four periods when households, companies and investors held such a surplus. Each time, markets rallied. “The world is awash with unprecedented excess liquidity,” said Nikolaos Panigirtzoglou, a strategist at JPMorgan, the top-ranked firm for U.S. fixed-income research by Institutional Investor magazine. “Fed tightening won’t change that.”
The cash cushion has surged in recent years as the world’s central banks injected trillions of dollars into the financial system to jump-start demand after the credit crisis. Now all the extra money that’s sloshing around may help extend the three-decade bull market in bonds even as a stronger U.S. economy pushes the Fed closer to boosting rates from rock-bottom levels. Bonds suffered a setback last quarter as signs of inflation in both the U.S. and Europe sparked an exodus after yields fell to historical lows. They lost 2.23%, the most since at least 1996, index data compiled by Bank of America show. This month, worries over Greece’s financial ruin and China’s stock-market meltdown have pushed investors back into the safety of debt securities. Yet Wall Street is still bracing for a selloff, especially in U.S. Treasuries, once the Fed moves to raise rates that it’s held near zero since 2008.
The U.S. 10-year note, the benchmark used to determine borrowing costs for governments, businesses and consumers, yielded 2.45% as of 9:12 a.m. Monday in London. Forecasters surveyed by Bloomberg say the yield will approach 3% within a year. Although JPMorgan provided plenty of caveats, the company’s analysis suggests it might not play out that way. Helped by bond-buying stimulus in the U.S., Japan and Europe, and increased bank lending in emerging markets, the amount of cash in circulation now totals $67 trillion globally, compared with about $62 trillion of estimated demand, data compiled by the bank show. That happens when the amount of money in the world exceeds the value of the global economy, financial assets and the cash that individuals hoard in response to risk.

How real is the deal?
• Greece Capitulates to Creditors’ Demands to Cling to Euro (Bloomberg)
Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras surrendered to European demands for immediate action to qualify for up to €86 billion euros ($95 billion) of aid Greece needs to stay in the euro. After a six-month offensive against German-inspired austerity succeeded only in deepening his country’s economic mess and antagonizing his European counterparts, there was no face-saving compromise on offer for Tsipras at a rancorous summit that ran for more than 17 hours. “Trust has to be rebuilt, the Greek authorities have to take on responsibility for what they agreed to,” German Chancellor Angela Merkel said after the meeting ended just before 9 a.m. in Brussels Monday. “It now hinges on step-by-step implementation of what we agreed.”
The agreement shifts the spotlight to the parliament in Athens, where lawmakers from Tsipras’s Syriza party mutinied when he sought their endorsement two days ago for spending cuts, pensions savings and tax increases. They have until Wednesday to pass into law key creditor demands, including streamling value-added taxes, broadening the tax base to increase revenue and curbing pension costs. While the summit agreement averted a worst-case outcome for Greece, it only established the basis for negotiations on an aid package, which would also include €25 billion to recapitalize its weakened financial system.

“The government is trying to get the least bad, the least catastrophic deal..”
• Greek Fury Meets Resignation at Demands for Concessions
Greek officials and media reacted with fury to the latest European demands for spending cuts and tax hikes, with some resorting to imagery from World War II and the U.S.- led war on terror to describe their predicament. Greece is being “waterboarded” by euro-area leaders, Nikos Filis, the parliamentary spokesman for the ruling Coalition of the Radical Left, or Syriza, said on ANT1 TV Monday morning. He accused Germany of “tearing Europe apart” for the third time in the past century. Newspapers leveled similar allegations at Germany, which led the hard-line camp at all-night talks that ended with an agreement on the terms needed to open a third bailout for Europe’s most-indebted country. EC President Donald Tusk, announcing the deal after 17 hours of negotiations, said it would entail “strict conditions” and end the threat of Greece exiting the euro.
“The government is trying to get the least bad, the least catastrophic deal,” Labor Minister Panos Skourletis said on ERT TV. “Talk of a Grexit shouldn’t take place when Greece has its back to the wall.” The tone of Greek reaction illustrates the obstacles for Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras as he seeks domestic approval for a deal that creditors called the country’s last chance to stay in the euro. European leaders insisted Greece’s parliament now approve measures including placing state assets in a dedicated fund in exchange for as much as €86 billion in new financing. “The agreement is difficult, but we averted the transfer of public property abroad, we averted the plan to cause a credit crunch and the collapse of the financial system,” Tsipras said after the summit.
“We put up a hard fight for the past six months and we fought to the end in order to get the best out of it, to get a deal which will allow the country to stand on its feet and the Greek people to keep fighting.” According to the initial text for a deal presented to European leaders, Greece needs to pass laws by July 15 to raise sales taxes, cut pension payments, alter the bankruptcy code and enforce automatic spending cuts if the next budget misses its targets. A key sticking point was the involvement of the IMF, which Tsipras at one point called “criminal.” Those measures will be difficult for Tsipras to sell to a public that voted decisively in a July 5 referendum to reject an earlier austerity package that was less onerous than the measures under discussion now. The premier, who was elected on an anti-austerity platform in January, also faces the challenge of keeping Syriza together through upcoming parliamentary votes.

“Everybody on earth with a smartphone understands what happened to democracy last night.”
• Greece Wins Euro Debt Deal – But Democracy Is The Loser (Paul Mason)
The eurozone took itself to the brink last night, and we will only know for certain later whether its reputation and cohesion can survive this. The big powers of Europe demonstrated an appetite to change the micro-laws of a smaller country: its bakery regulations, the funding of its state TV service, what can be privatised and how. Whether inside or outside the euro, many small countries and regions will draw long-term negative lessons from this. And from the apparently cavalier throwing of a last-minute Grexit option into the mix by Germany, in defiance of half the government’s own MPs. It would be logical now for every country in the EU to make contingency plans against getting the same treatment – either over fiscal policy or any of the other issues where Brussels and Frankfurt enjoy sovereignty.
Parallels abound with other historic debacles: Munich (1938), where peace was won by sacrificing the Czechs; or Versailles (1919), where the creditors got their money, only to create the conditions for the collapse of German democracy 10 years later, and their own diplomatic unity long before that. But the debacles of yesteryear were different. They were committed by statesmen. People who knew what they wanted and miscalculated. It was hard to see last night what the rulers of Europe wanted. What they’ve arguably got is a global reputational disaster: the crushing of a left-wing government elected on a landslide, the flouting of a 61 per cent referendum result. The EU – a project founded to avoid conflict and deliver social justice – found itself transformed into the conveyor of relentless financial logic and nothing else.
Ordinary people don’t know enough about the financial logic to understand why this was always likely to happen: bonds, haircuts and currency mechanisms are distant concepts. Democracy is not. Everybody on earth with a smartphone understands what happened to democracy last night.

Nice!
• How The Greeks Could Have The Last Laugh: Adopt The Renminbi (David McWilliams)
The other day Enda Kenny speculated aloud that Greece should follow Ireland. Michael Noonan thinks that too. Apparently, they should do what we did and, if Greece did, there’d be no problems. Maybe we should examine this proposal because what is on the table for Greece right now makes little sense. Is there an alternative for an inventive Greece – one that might follow Ireland’s blueprint? Before we answer that, let’s examine what’s on the table for Greece right now. The German/EU offer maintains that the price for staying in the Euro is possibly 10 to 15 years of austerity with no alternative industrial model. There should be no debt forgiveness and there should be years of low to zero growth as the Greeks grind out a meagre existence largely from tourist euros.
Because there is no capital, this will occur at a time when Greek tourist assets will plummet and those that are worth something, such as tourist hotels, will be bought off by German and other investors for half nothing. In time, the Greeks will end up as workers in the tourist industry, working for foreign owners of the assets. The profits from these assets will be repatriated back to Germany, boosting the German current account surplus, while the wages for this labour will be spent in Greece on imported goods, which may or may not be made in Germany. Basically Jamaica with ouzo! Over time, the Greek standard of living will remain low and Greek people with talent will have no choice but to emigrate. There may be some pick-up in the economy but as long as there is huge debt-servicing costs, this pick-up will largely go to servicing past debts.
If there is some new EU loan made available to Greece, this will simply be borrowing from tomorrow not to pay for today but to pay for yesterday. The Greeks should do all this in order to have the privilege of paying for this stuff in the Euro. It seems a high price to pay for a currency, don’t you think? But the alternative is, according to the EU, to revert to the drachma, watch the currency fall, watch the drachma value of Greece euro debts rise, allow the national balance sheet to implode and ensure that the banks collapse. In other words, flirt with short-term Armageddon.
[..] Okay, but how can Greece get lots and lots of foreign investment into the country while still using a currency that is strong and in so doing, change irrevocably their economy? How can they move onto a higher productivity level without all these debt repayments? They can do it by adopting the Chinese Renminbi! Yes, you read it right. There’s no point for the Greeks in going back to the drachma if that will destroy its banking system. Why not do what Ireland has done over the years and adopt some other country’s currency? What’s in it for China? Everything!

“Imagine that the euro had never been introduced … do you seriously think that we would have a crisis as deep as what we have seen over the past seven years in Europe?”
• The Euro – A Fatal Conceit (MM)
Imagine that the euro had never been introduced and we instead had had freely floating European currencies and each country would have been free to choose their own monetary policy and fiscal policy. Some countries would have been doing well; others would have been doing bad, but do you seriously think that we would have a crisis as deep as what we have seen over the past seven years in Europe? Do you think Greek GDP would have dropped 30%? Do you think Finland would have seen a bigger accumulated drop in GDP than during the Great Depression or during the banking crisis of 1990s? Do you think that European taxpayers would have had to pour billions of euros into bailing out Southern European and Eastern European governments? And German and French banks!
Do you think that Europe would have been as disunited as we are seeing it now? Do you think we would have seen the kind of hostilities among European nations as we are seeing now? Do you think we would have seen the rise of political parties like Golden Dawn and Syriza in Greece or Podemos in Spain? Do you think anti-immigrant sentiment and protectionist ideas would have been rising across Europe to the extent it has? Do you think that the European banking sector would have been quasi paralyzed for seven years? And most importantly do you think we would have had 23 million unemployed Europeans? The answer to all of these questions is NO!
We would have been much better off without the euro. The euro is a major economic, financial, political and social fiasco. It is disgusting and I blame the politicians of Europe and the Eurocrats for this and I blame the economists who failed to speak out against the dangers of introducing the euro and instead gave their support to a project so economically insane that it only could have been envisioned by the type of people the British historian Paul Johnson called “Intellectuals”.

It’ll happen yet anyway.
• A Greek Exit Could Not Be More Costly Than The Current Path (Mitchell)
It appears the Germans (with their Finish and Slovak cronies) have lost all sense of reason, if they ever had any. Germany has the socio-pathological excuse of having suffered from an irrational inflation angst since the 1930s and has forgotten its disastrous conduct during the 1930s and 1940s and also the generosity shown it by allied nations who had destroyed its demonic martial ambitions. Finland and Slovakia have no such excuse. They are just behaving as jumped-up, vindictive show ponies who are not that far from being in Greece’s situation themselves. Sure the Finns have a national guilt about their own notorious complicity with the Nazis in the 1940s but what makes them such a nasty conservative allies to the Germans is an interesting question.
It also seems to be hard keeping track with the latest negotiating offer from either side. But the trend seems obvious. The Greeks offer to bend over further and are met by a barrage of it is going to be hard to accept this , followed by a Troika offer (now generalised as the Eurogroup minus Greece which is harsher than the last. And so it goes from ridiculous to absurd or to quote a headline over the weekend. From the Absurd to the Tragic, which I thought was an understatement. There are also a plethora of plans for Greece being circulated by all and sundry, most of which hang on to the need for the nation to run primary fiscal surpluses, with no reference to the scale of the disaster before us (or rather the Greek people). It is surreal that this daily farce and public humiliation (like the medieval parading of recalitrants in stocks) is being clothed as “governance”. Only in Europe really.
We now know that the Eurogroup is not content to destroy the credibility of the Greek government and have the Greek prime minister come cap in hand begging for money and agreeing to turn his back on the sentiments of his own people, expressed so strongly last Sunday. The latest document from the Recession Cult has demanded even deeper measures from Athens, which Euclid Tsakalotos has apparently acceded to.
They now want a primary surplus target of 3.5% of GDP by 20183 , much deeper pension cuts, widespread product market deregulation, a more comprehensive privatisation program (so that the northern capital owners can get their hands on Greek assets for cheap), massive deregulation of the labour market, wind-back legislation since the beginning of 2015 which have not been agreed with the institutions and run counter to the program commitments and put all of that on top the harsh austerity that has already been pushed leading into the referendum. The sentiment is that Germany is not going for an exit for Greece but total submission and probably a new government by the end of the week .

One man has not given up.
• Dr Schäuble’s Plan for Europe: Do Europeans Approve? (Yanis Varoufakis)
Article to appear in Die Zeit on Thursday 16th July 2015 – Pre-publication summary: Five months of intense negotiations between Greece and the Eurogroup never had a chance of success. Condemned to lead to impasse, their purpose was to pave the ground for what Dr Schäuble had decided was ‘optimal’ well before our government was even elected: That Greece should be eased out of the Eurozone in order to discipline member-states resisting his very specific plan for re-structuring the Eurozone.
This is no theory. How do I know Grexit is an important part of Dr Schäuble’s plan for Europe? Because he told me so!
I wrote this article not as a Greek politician critical of the German press’ denigration of our sensible proposals, of Berlin’s refusal seriously to consider our moderate debt re-profiling plan, of the European Central Bank’s highly political decision to asphyxiate our government, of the Eurogroup’s decision to give the ECB the green light to shut down our banks.
I wrote this article as a European observing the unfolding of a particular Plan for Europe – Dr Schäuble’s Plan. And I am asking a simple question of Die Zeit’s informed readers:
Is this a Plan that you approve of?
Do you consider this Plan good for Europe?

#ThisIsACoup
• Killing the European Project (Paul Krugman)
Suppose you consider Tsipras an incompetent twerp. Suppose you dearly want to see Syriza out of power. Suppose, even, that you welcome the prospect of pushing those annoying Greeks out of the euro. Even if all of that is true, this Eurogroup list of demands is madness. The trending hashtag ThisIsACoup is exactly right. This goes beyond harsh into pure vindictiveness, complete destruction of national sovereignty, and no hope of relief. It is, presumably, meant to be an offer Greece can’t accept; but even so, it’s a grotesque betrayal of everything the European project was supposed to stand for.
Can anything pull Europe back from the brink? Word is that Mario Draghi is trying to reintroduce some sanity, that Hollande is finally showing a bit of the pushback against German morality-play economics that he so signally failed to supply in the past. But much of the damage has already been done. Who will ever trust Germany’s good intentions after this? In a way, the economics have almost become secondary. But still, let’s be clear: what we’ve learned these past couple of weeks is that being a member of the eurozone means that the creditors can destroy your economy if you step out of line. This has no bearing at all on the underlying economics of austerity.
It’s as true as ever that imposing harsh austerity without debt relief is a doomed policy no matter how willing the country is to accept suffering. And this in turn means that even a complete Greek capitulation would be a dead end. Can Greece pull off a successful exit? Will Germany try to block a recovery? (Sorry, but that’s the kind of thing we must now ask.) The European project — a project I have always praised and supported — has just been dealt a terrible, perhaps fatal blow. And whatever you think of Syriza, or Greece, it wasn’t the Greeks who did it.

“Here you have the advanced countries trying to undermine a global effort to stop tax avoidance. Can you have a better image of hypocrisy?”
• Germany Showing ‘Lack Of Solidarity’ Over Greece: Stiglitz (AFP)
Prominent economist and Nobel laureate Joseph Stiglitz accused Germany on Sunday of displaying a “lack of solidarity” with debt-laden Greece that has badly undermined the vision of Europe. “What has been demonstrated is a lack of solidarity by Germany. You cannot run a eurozone without a basic modicum of solidarity. It is really undermining the common sense of vision, the sense of common solidarity in Europe,” the Colombia University professor and former World Bank chief economist told AFP. “I think it s been a disaster. Clearly Germany has done a serious blow, undermining Europe,” he said.
“Asking even more from Greece would be unconscionable. If the ECB allows Greek banks to open up and they renegotiate whatever agreement, then wounds can heal. But if they succeed in using this as a trick to get Greece out, I think the damage is going to be very very deep.” Stiglitz is in the Ethiopian capital Addis Ababa for this week s international development financing summit, which is presented as crucial for United Nations efforts to end global poverty and manage climate change by 2030. He is supporting the creation of an international tax organisation within the UN to fight against tax evasion by multinationals, although this has yet to win Western agreement.
International tax rules that allow large companies to avoid tax end up costing developing countries $100 billion every year, according to Oxfam. “European leaders and the West in general are criticising Greece for failure to collect taxes,” Stiglitz said. “The West has created a framework for global tax avoidance… Here you have the advanced countries trying to undermine a global effort to stop tax avoidance. Can you have a better image of hypocrisy?”

Very strong from Zuesse.
• How Fascist Capitalism Functions: The Case Of Greece (Zuesse)
There is democratic capitalism, and there is fascist capitalism. What we have today is fascist capitalism; and the following will explain how it works, using as an example the case of Greece. Mark Whitehouse at Bloomberg headlined on 27 June 2015, “If Greece Defaults, Europe’s Taxpayers Lose,” and presented his ‘news’ report, which simply assumed that, perhaps someday, Greece will be able to get out of debt without defaulting on it. Other than his unfounded assumption there (which assumption is even in his headline), his report was accurate. Here is what he reported that’s accurate: He presented two graphs, the first of which shows Greece’s governmental debt to private investors (bondholders) as of, first, December 2009; and, then, five years later, December 2014.
This graph shows that, in almost all countries, private investors either eliminated or steeply reduced their holdings of Greek government bonds during that 5-year period. (Overall, it was reduced by 83%; but, in countries such as France, Portugal, Ireland, Austria, and Belgium, it was reduced closer to 100% — all of it.) In other words: by the time of December 2009, word was out, amongst the aristocracy, that only suckers would want to buy it from them, so they needed suckers and took advantage of the system that the aristocracy had set up for governments to buy aristocrats’ bad bets — for governments to be suckers when private individuals won’t.
Not all of it was sold directly to governments; much of it went instead indirectly, to agencies that the aristocracy has set up as basically transfer-agencies for passing junk to governments; in other words, as middlemen, to transfer unpayable debt-obligations to various governments’ taxpayers. Whitehouse presented no indication as to whom those investors sold that debt to, but almost all of it was sold, either directly or indirectly, to Western governments, via those middlemen-agencies, so that, when Greece will default (which it inevitably will), the taxpayers of those Western governments will suffer the losses. The aristocracy will already have wrung what they could out of it.
Who were these governments and middlemen-agencies? As of January 2015, they were: 62% Euro-member governments (including the European Financial Stability Facility); 10% IMF, and 8% ECB; then, 17% still remained with private investors; and 3% was owned by “other.” Whitehouse says: “Ever since the region’s sovereign-debt crisis first flared in 2010, European nations have been stepping in for Greece’s private creditors – largely German and French banks — by lending the country [Greece] the money to pay them off. Thanks to this bailout [of ‘largely German and French banks’], banks and [other private] investors have much less at stake than before.”
So: what got bailed-out was private investors, not ‘the Greek people’ (such as the ‘news’ media assert, or try to suggest). For example, a reader’s comment to Whitehouse’s article says: “A reasonable assumption is that a large part of the Greek debt to the Germans was the result of Greek consumption of German goods and services bought with the German provided credit. In that case, the Germans have lost the Greek goods and services that could have potentially been bought with the money that is owed to them.” But this is entirely false: that “consumption” was by the aristocracy, not by the public, anywhere or at any time. After all: It’s the aristocracy that get bailed-out — not the public, anywhere.

“..we are studying the possibility of organising direct deliveries of energy resources to Greece, starting shortly.”
• Russia Considering Direct Fuel Deliveries To Help Greece (AFP)
Russia is considering direct deliveries of fuel to Greece to help prop up its economy, Energy Minister Alexander Novak said Sunday, quoted by Russian news agencies. “Russia intends to support the revival of Greece’s economy by broadening cooperation in the energy sector,” Novak told journalists, quoted by RIA Novosti news agency. “Accordingly we are studying the possibility of organising direct deliveries of energy resources to Greece, starting shortly.”
Novak said that the energy ministry expected “to come to an agreement within a few weeks,” but did not specify what type of fuel Russia would supply. Greece’s left-wing leadership has made a show of drawing closer to Moscow in recent months as the spat with its international creditors has grown more ugly. In June, Greek Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras during a visit to Russia sealed a preliminary agreement for Russia to build a €2 billion gas pipeline through Greece, extending the TurkStream project, which is intended to supply Russian gas to Turkey.

Greek politics will get a shake-up. But only Syriza can govern.
• Greek Government’s Majority In Question, Says Labor Minister (Reuters)
The strength of the Greek government’s majority is in question and no-one can blame lawmakers who won’t agree to the terms of a cash-for-reforms deal with the country’s creditors, Labor Minister Panos Skourletis said on Monday. Eurozone leaders argued late into the night with near-bankrupt Greece at an emergency summit, demanding that Athens enact key reforms this week to restore trust before they will open talks on a financial rescue. “Right now there is an issue of a governmental majority (in parliament),” Skourletis told state TV ERT. “I cannot easily blame anyone who cannot say ‘yes’ to this deal.” “We aren’t trying to make this deal look better, and we are saying it clearly: this deal is not us,” he added.

This is a question?
• Was This Humiliation Of Greeks Really Necessary? (Helena Smith)
In return for a third bailout – this time staggered over three years and amounting to €53bn – Greeks essentially have been told to walk through the valley of the shadow of death. And that is the good scenario. The alternative – Grexit – would have bypassed purgatory but taken crisis train passengers straight to hell. Greeks know that the next 48 hours will define them and Europe, too. But whatever happens, they also know the choice is one between a complete march into the unknown or a conscious decision to take measures that – for a time, at least – will inflict further damage on a country already hollowed out by the eviscerating effects of austerity. Either way, the future is bleak.
In this, Tsipras’s brinkmanship has not helped: trust is so eroded between the leadership in Athens and creditors abroad that aid, if given, will not be handed magnanimously. Almost everyone I know now fears that Greece will be left to rot in the eurozone. Politically, there is tumult on the horizon. That, in the early hours of Saturday, so many government MPs refused to give their vote to the proposed package of pension and budget cuts, tax rises and administrative reform does not portend well. Many Greeks may now credit Tsipras for convincing Europe’s fiscally obsessed creditors that the country’s debt burden remains the cause of its woes (as indeed it does), but that will not cut much ice with hardliners in his party.
Events have moved at such giddying speed that ironically most Greeks do not appear to blame Tsipras for ignoring the resounding rejection that he himself had urged when the economic demands of lenders were put to popular vote last weekend. The referendum, like so much else, has become part of the blanket of crisis. That the measures were less severe than the ones the government ultimately accepted has, in a further irony, been similarly played down. Greece, in truth, has skated so close to the edge – apocalyptic scenarios more real than ever before – that Tsipras’s spectacular U-turn has come as a welcome relief. Across an ever-fractious political spectrum, he has been applauded for putting his country before his party.
In the event of financial rescue, the hope is that Tsipras finally tackles the maladies that have so pervasively held back the country’s potential. Like no other party in power, Syriza is well placed to tackle the age-old malignancies of tax evasion, cronyism and corruption. But the leader will also face conflict on the streets. In the back alleys of Athens, where activists work in dark offices stacked with freshly painted placards and banners – the ammunition of the war against austerity – the battle is already on. “There will be demonstrations every day,” vowed Petros Papakonstantinou of the anti-capitalist bloc Antarsya. “And we will press for a general strike. That won’t be easy when the left is in power.”

In fine form.
• Greek Deal Makes Versailles Look Like A Picnic – Steve Keen (BallsRadio)
This interviewed was recorded before the deal was supposedly struck, but the sentiment still stands. Just how much does Greece have to give away. Too much says economist Steve Keen.

“Even as its economy collapses and the government makes cuts in welfare spending, Greece’s military budget remains among the largest in the European Union..”
• Greece Today, America Tomorrow? (Ron Paul)
The drama over Greece’s financial crisis continues to dominate the headlines. As this column is being written, a deal may have been reached providing Greece with yet another bailout if the Greek government adopts new “austerity” measures. The deal will allow all sides to brag about how they came together to save the Greek economy and the European Monetary Union. However, this deal is merely a Band-Aid, not a permanent fix to Greece’s problems. So another crisis is inevitable. The Greek crisis provides a look into what awaits us unless we stop overspending on warfare and welfare and restore a sound monetary system. While most commentators have focused on Greece’s welfare state, much of Greece’s deficit was caused by excessive military spending.
Even as its economy collapses and the government makes (minor) cuts in welfare spending, Greece’s military budget remains among the largest in the European Union. Despite all the handwringing over how the phony sequestration cuts have weakened America’s defenses, the United States military budget remains larger than the combined budgets of the world’s next 15 highest spending militaries. Little, if any, of the military budget is spent defending the American people from foreign threats. Instead, the American government wastes billions of dollars on an imperial foreign policy that makes Americans less safe. America will never get its fiscal house in order until we change our foreign policy and stop wasting trillions on unnecessary and unconstitutional wars.
Excessive military spending is not the sole cause of America’s problems. Like Greece, America suffers from excessive welfare and entitlement spending. Reducing military spending and corporate welfare will allow the government to transition away from the welfare state without hurting those dependent on government programs. Supporting an orderly transition away from the welfare state should not be confused with denying the need to reduce welfare and entitlement spending.

New Zealand better beware. Wait till housing collapses on top of the logging and dairy crashes.
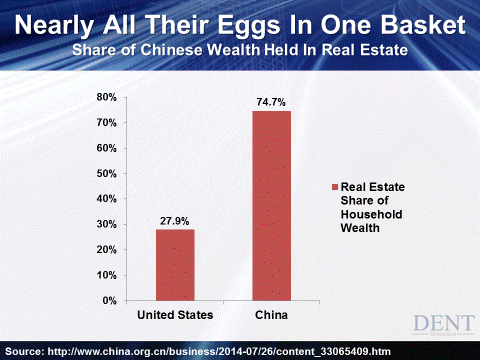
• Chinese Buyers Turn Kiwis Into Renters In Their Own Country (NZ Herald)
Mainland Chinese money snapped up at least 80% of residential sales in parts of Auckland in March but were nearer 90% in May, a whistle blower from the industry says. The Herald reported at the weekend Labour data that showed people of Chinese descent accounted for 39.5% of the almost 4000 Auckland transactions between February and April. Yet Census 2013 data showed ethnic Chinese who are New Zealand residents or citizens account for only 9% of Auckland’s population. The property insider – who wanted to protect their identity because they feared for their job – said the situation was much more serious than the Labour data suggested. The numbers should be more than doubled due to the weight of capital coming out of Mainland China, the whistle blower said.
One big Auckland real estate agency, where many salespeople are of Chinese ethnicity, was selling almost every single property throughout many suburban areas to people living in China, the insider said. In some cases, those buyers had a New Zealand connection “but it’s one group disenfranchising the other. It’s really taken off in the last 18 months. I’ve been studying the figures since October.” “The Kiwis, South Africans and British have dropped out of the market because they just can’t compete with the Chinese. The people living in China buy the places the Kiwis are trying to get, then those places are rented out the next day,” the insider said. That showed the person is in an important position in the property sector with extensive access to information unavailable to the public revealing who the buyers really are.
“We’re becoming tenants in our own country. It’s utterly outrageous. The Chinese are interested in Panmure, Ellerslie, Greenlane, Epsom, Remuera, the North Shore – not so much the west.” In some cases, a single Chinese resident was spending up to $15 million on Auckland properties and the higher the bidding at auctions went, the happier they were. “They simply don’t care how much they pay. It’s not related to the CV. If they pay another $400,000 more, that’s $400,000 they’re better off as it’s $400,000 they have shifted out of Mainland China. If they continue vacuuming up all the existing properties at the current rate of consumption, what will that do? The Chinese will outbid everyone at the auction. I’m sick of the phone bidder from Guangzhou. I’m relieved that someone at last is talking about this,” the insider said of Twyford’s data.

“..it implies that this is a capital movement rather than just individuals looking to park money.“
• China’s Rich Seek Shelter From Stock Market Storm In Foreign Property (Guardian)
Real estate agents in Australia, Britain and Canada are bracing for a surge of new interest in their already hot property markets, with early signs that wealthy Chinese investors are seeking a safe haven from the turmoil in Shanghai’s stock markets. Sydney agent Michael Pallier said in the past week alone he has sold two new apartments and shown a A$13.8m (US$10.3m) house in the harbourside city to Chinese buyers looking for an alternative to stocks. “A lot of high-net-worth individuals had already taken money out of the stock market because it was getting just too hot,” Pallier, the principal of Sydney Sotheby’s International Realty, said. “There’s a huge amount of cash sitting in China and I think you’ll find a lot of that comes to the Australian property market.”
Around 20% has been knocked off the value of Chinese shares since mid-June, although attempts by authorities to stem the bleeding are having some effect. Many wealthy Chinese investors had already cashed out. Major shareholders sold 360bn yuan (US$58bn) in the first five months of 2015 alone, compared with 190bn yuan in all of 2014 and an average of 100bn yuan in prior years, according to Bank of America Merrill Lynch. While much of that money may initially be parked in more liquid assets like US Treasury bonds and safe-haven currencies such as the Swiss franc, there is growing evidence that foreign property sales may receive a boost.
“There is anecdotal evidence that Chinese buyers have intensified their interest in safe-haven global property markets, including London, as a result of the recent stock market volatility,” said Tom Bill, head of London residential research at Knight Frank. Ed Mead, executive director of realtor Douglas & Gordon in London, said his firm had seen two buyers from China looking to buy whole blocks of flats. “It is unusual to see the Chinese block buying, it implies that this is a capital movement rather than just individuals looking to park money.“

“../Beijing’s panicky policy actions may reveal that the economy is in worse shape than is being let on.”
• How China’s Stock-Market Muddle May Spread (MarketWatch)
Despite China’s troubled stock markets finding a floor last week, do not expect any quick return to normality. The dramatic stock rout and subsequent heavy-handed interference by authorities will not be easily forgotten. It has not just rattled investor confidence, but also damaged the political credibility of President Xi Jinping. For China’s legions of retail investors, the heavy losses have been compounded by wholesale stock suspensions — with half of Shenzhen and Shanghai stocks still not trading. This is a likely to fuel anxiety so long as investors are trapped in stock positions with no liquidity. It is also likely to lead to a sea change in investor mood from only weeks earlier, when some were even selling the roof over their head to buy equities.
There may be a nasty surprise when the first post-suspension bid prices come in. Albert Edwards at Société Générale highlights the experience in 2008, when Pakistan suspended trading on the Karachi Stock Exchange to try to “put a floor” under stocks after a share-price slump. This episode left authorities’ reputation in tatters, and when the market reopened, it quickly lost another 52%. For foreign investors, many of the bizarre interventions by Beijing last week will have raised a number of other, more fundamental questions about the competence of China’s leadership and the true state of the economy. One area of renewed uncertainty is the ongoing policy commitment to allowing market forces to play a larger role in the economy, a part of Beijing’s larger reform program.
The reintroduction of a ban on initial public offerings and spate of stock suspensions set a worrying precedent and will refocus attention on political risk. This, in turn, will place a cloud of doubt over plans for liberalizing interest rates, the capital account and the domestic bond market. Foreign investors are likely to think twice as they face the risk that the government may simply suspend reforms if prices start going against them. These recent actions suggest the voices of conservatives opposed to market reforms are in the ascendancy. Perhaps the more worrying take-away is that Beijing’s panicky policy actions may reveal that the economy is in worse shape than is being let on.

More losses.
• China’s Market-Tracking ETFs Roiled By Share Suspensions (FT)
A wave of stock suspensions has played havoc with exchange traded funds tracking Chinese markets, causing wild price swings and big price gaps between passive funds and the assets they track. More than 1,400 companies — more than half of all listings — are on trading halts in China, in an effort to shield themselves from the dramatic equity market sell-off that has wiped trillions of dollars off the value of Chinese stocks. The suspensions have left a number of ETFs holding frozen shares or derivatives linked to them, even as the funds themselves continue to trade. One Hong Kong-listed ETF that tracks China’s small-cap board, the ChiNext, traded every day last week, despite more than two-thirds of the underlying shares it reflects being suspended.
On Friday, the CSOP ChiNext ETF jumped by a fifth, while the index itself rose only 4.1%. Concerns have been growing globally over the potential mismatch between the liquidity of the underlying collateral that ETFs hold and that of their units. The Bank of International Settlements warned last month that the growth of passive funds may have created a “liquidity illusion” in bonds, although analysts say the problems currently facing Chinese equity ETFs are specific to the idiosyncrasies of that market. Chinese shares have tumbled in the past month, as millions of retail investors unwind leveraged bets on the market. Beijing has responded with various supportive measures, including bans on short selling, and on stock sales by large shareholders.
The central bank has also been funnelling money to brokerages to help them buy equities. Trading volumes for many China-tracker ETFs have doubled over the past two weeks, as market volatility has risen. ETFs have experienced wild daily price swings as investors use passive funds for price discovery of suspended Chinese assets. Last Thursday, the Deutsche X-Trackers Harvest CSI 300 ETF, which trades in New York, rose 20%. The extent of share suspensions has made ETFs “one of the only tradable instruments” for global investors looking to manage their exposure to Chinese stocks, said Warren Deats, head of Asia-Pacific portfolio trading at Barclays. Such funds are performing like futures contracts, he added, with investors using them to estimate the true level of the market — a view echoed by fund providers.