‘Daly’ Store, Manning, South Carolina July 1941



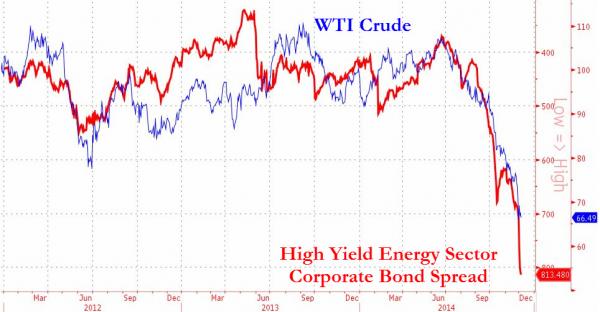
The threat here is not about the oil, it’s about the financing. Junk bonds, loans, oil stocks etc. The whole industry is leveraged up to its neck. It’s an extremely brittle system that can’t take shocks.
• Canadian Natural Resources Chairman Sees Oil Touching $30 A Barrel (NatPost)
Canada’s oil industry faces a year of “tough slugging,” including the deferment of many projects, as oil prices collapse to as little as US$30 a barrel then likely stabilize around US$70 to US$75 a barrel, oil entrepreneur Murray Edwards predicted Friday. Because of its high costs, the Canadian sector will be impacted more than many oil-producing jurisdictions around the world by OPEC’s decision Thursday to not cut oil production, said Mr. Edwards, the chairman of Canadian Natural Resources and one of Canada’s single biggest oil investors. Prices could spike down to $30, $40. It got down to $35 in 2008, for a very short period of time “On a given day you can have market fluctuations where prices fluctuate far more than the underlying economic value of the unit,” Mr. Edwards told reporters on the sidelines of a business forum here.
“Prices could spike down to $30, $40. It got down to $35 in 2008, for a very short period of time,” he said. “I don’t believe that if it spikes down that low, that it will stay that low for long, because you will see increased demand and supply respond. “The better question is where does it stabilize, and that $70-$75 area is probably not a bad place to stabilize for a period of time until you get more balance in term of growth in demand and some supply response.” Mr. Edwards said industry projects that are already under way, particularly oil sands projects with a long-term horizon and capital already invested, will likely continue. But others will be shelved until there is more clarity around future oil prices. There will also be a slowdown in conventional oil projects, particularly those that tend to produce a lot at the front end, he predicted.
Weak oil prices will force the industry to refocus and look at new way of doing things to cut costs, he said. Canadian Natural Resources, one of Canada’s top oil and gas producers, will adjust its capital spending next year to reflect weaker oil prices, he said. The company recently approved an $8.5-billion capital budget for 2015, including $2-billion in flexible capital, based on oil averaging around US$81 for West Texas Intermediate. Overtime, markets will find a new balance as low oil prices stimulate demand. “Right now we have more supply than we have demand for a period of time,” he said. “The market is now going to find a price which best reflects what it costs to produce a barrel of oil … nothing solves low prices like low prices.”
Read more …

” .. a collapse in the oil price is far more dangerous for the banks than it would have been only a few years ago.”
• Banks’ $650 Billion Bet On Oil Backfires As Brent Prices Slump (Telegraph)
British banks face losses of more than £2bn as risky loans to the oil and gas industry go sour amid the plummeting price of crude. Banks have piled into the sector over the last three years, with oil and gas accounting for £11 of every £100 of high-yield debt on the back of America’s booming shale industry. However, oil’s precipitous decline since June has left many of the lenders looking at heavy losses. Brent Crude prices fell to a low of $67.53 yesterday, the lowest level for almost five years. The price rebounded by around 2pc as of Monday afternoon but remains almost 40pc down since June. Last week, Opec leaders decided against restricting output in an attempt to squeeze North America’s shale producers – many of whom have borrowed heavily to invest. Although much of the banks’ exposure will have been hedged off, Barclays, RBS, HSBC and Standard Chartered could face a combined $3.4bn (£2bn) of impairment charges related to oil and gas exposures in the fourth quarter of the year, according to Chirantan Barua, an analyst at Bernstein.
“Nearly $650bn of high yield debt has been issued in the sector since 2011,” Mr Barua said. “While the broader high yield market is down [around] 20pc year-to-date, oil and gas has been flat with issuance running straight up to the OPEC event. [This] can’t be a good thing for a sudden stress in the market if oil prices stay at this level.” When you see $650bn of high yield issuance in a sector that has been levering up across the supply chain, any shocks in the underlying business will have risk ripples across the financial system.” While Barclays, HSBC and RBS could be sitting on losses of $1bn each, and Standard Chartered faces $400m of impairments, banks in North America could face much bigger impairment charges. US and Canadian banks that have lent heavily to the sector on the back of the US shale boom, and high-yield debt to less stable oil companies has increased substantially. This means a collapse in the oil price is far more dangerous for the banks than it would have been only a few years ago.
Read more …

“They’ll pull back and won’t drill it until the price recovers. That’s the way it ought to be.”
• Billionaire Shale Pioneer Sees Drilling Slowdown on Oil Price Drop (Bloomberg)
Billionaire wildcatter Harold Hamm, a founding father of the U.S. shale boom whose personal fortune has fallen by more than half in the past three months, said U.S. drilling will slow as producers cut back amid falling oil prices. Declining activity from Texas to North Dakota won’t be as harmful to the industry as some have feared, the chairman and chief executive officer of Continental Resources Inc. said. OPEC’s refusal to curb output last week bodes well for U.S. producers that can outlast countries in the cartel, which depend on higher oil prices. “Will this industry slow down? Certainly,” Hamm said yesterday in a telephone interview. “Nobody’s going to go out there and drill areas, exploration areas and other areas, at a loss. They’ll pull back and won’t drill it until the price recovers. That’s the way it ought to be.”
Investors have been spooked as oil has declined to a five-year low. The downturn comes after prices above $100 a barrel sparked a boom in output from U.S. shale formations that helped create a glut of supply. Hamm’s wealth, which is largely tied to the fate of Oklahoma City-based Continental, has fallen by more than $12 billion in three months, according to the Bloomberg Billionaires Index. Hamm, who helped discover the potential of North Dakota’s Bakken formation, predicted a swift recovery in oil prices, which have declined more than 36 percent since June as Saudi Arabia and its allies in the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries refused to cut production last week to help re-balance the market. The company said last month it’s sold nearly all its hedges through 2016, in a bet on a recovery in prices. West Texas Intermediate, the U.S. benchmark, fell below $65 a barrel yesterday before settling up 4.3 percent to $69.
Read more …

Well, we all like a little competition, don’t we?
• US Shale Crude Exports To Asia Grind To Halt On Flood Of Mideast Oil (Reuters)
An aggressive strategy by Mideast Gulf producers to exploit the lowest oil prices in five years to defend market share is showing signs of bearing fruit as U.S. crude exports to Asia grind to halt. Asian refineries have suspended imports of condensate, a light crude oil produced from the U.S. shale boom, just four months after they began in favor of cheaper Middle East grades, according to trade and industry sources. The suspension illustrates how competition between suppliers has heated up following a more than 40% decline in oil prices since June.
Last week Ali al-Naimi, the oil minister of OPEC kingpin Saudi Arabia, warned his fellow OPEC members they must combat the U.S. shale boom. He argued against cutting OPEC production so as to keep prices depressed and undermine the profitability of North American producers. “There’s so much oversupply that Middle East crudes are now trading at discounts and it is not economical to bring over crudes from the U.S. anymore,” said Tushar Tarun Bansal of consultancy FGE in Singapore. U.S. oil became uncompetitive against similar grades from Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates after Gulf producers began dropping prices in August to maintain their market share in an oil market glut.
Read more …

We’ll see a lot more restructuring and defaults, a lot less financing, and a lot less exploration and drilling.
• October Oil Shale Permits Drop 15%: Is The Slowdown Here? (Reuters)
U.S. oil producers have been racing full-speed ahead to drill new shale wells in recent years, even in the face of lower oil prices. But new data suggests that the much-anticipated slowdown in shale country may have finally arrived. Permits for new wells dropped 15% across 12 major shale formations last month, according to exclusive information provided to Reuters by DrillingInfo, an industry data firm, offering the first sign of a slowdown in a drilling frenzy that has seen permits double since last November. OPEC last week agreed to maintain its production quota of 30 million-barrels-per-day, despite a 30% drop in oil prices since June, triggering an additional 10% decline. That move, many analysts believe, was squarely aimed at U.S. oil producers driving the country’s energy resurgence: can they continue drilling at the current pace if prices don’t rise? “Currently, the market is focused on U.S. shale as the place where spending and production must be curtailed,” Roger Read, a Wells Fargo analyst, said in a note Friday.
“There is little doubt, in our view, that lower oil and gas prices will result in lower spending and lower shale production in 2015 to 2017.” A cutback of U.S. production could play into the hands of Saudi Arabia, which has suggested over the past few months that it is comfortable with much lower oil prices. Most analysts predict U.S. oil producers can maintain their healthy production rates in the first half of 2015 – thanks in part to investments made months ago. Some oil service companies have suggested that a slowdown might be held off, as they continue to buy key drilling components. But, the data suggests that production is likely to eventually succumb to lower prices. “The first domino is the price, which causes other dominos to fall,” said Karr Ingham, an economist who compiles the Texas PetroIndex, an annual analysis of the state’s energy economy. One of the first tiles to drop: the number of permits issued, Ingham said.
Read more …

“The day rate for a top specification drillship, which can work in water up to 12,000 feet (3,658 meters) deep, was recently quoted at as low as $400,000, down from $600,000 last year.” [..] “The global fleet of jackup rigs is forecast to grow 9% in 2015 and another 7% in 2016 .. ” Overinvestment is what you get when credit is too cheap. It turns the whole world into a casino, and everyone into a gambler. And then they all lose.
• As Crude Tumbles, Oil Drillers Seek To Temporarily Idle More Rigs (Reuters)
Offshore drillers globally are increasingly considering “warm stacking” their rigs to take them temporarily off the market, as they gear up for a slowdown in the hunt for oil with crude prices sliding to five-year lows. Rigs in warm stack maintain basic operations and most of the crew, and can be put to use once the owner gets a contract. Drillers put rigs in warm stacks to lower operational costs and also to keep them sufficiently ready for quick deployment, meaning they are hopeful a downturn won’t be a prolonged one. Rigs can also be “cold stacked”, or shut down, which typically happens when an owner does not expect to find work for an extended period of time.
“Six months ago, no one talked about stacking rigs,” said Thomas Tan, chief executive officer at Kim Heng Offshore & Marine Holdings, a Singapore-based oilfield service firm, “In the last few weeks, things have become scarier and the talk of stacking started.” Tan said his firm has received enquiries to stack dozens of rigs over the past few weeks. Kim Heng currently services four rigs in warm stack around Singapore. The company serves about 60 rigs a year in different stage of operations, including providing repair, maintenance and logistics services. “A lot of people are looking at warm stack, as they hope that the market will turn around quickly,” Tan said. “Cold stack is on their mind… but they haven’t given up hope yet.” [..]
The day rate for a top specification drillship, which can work in water up to 12,000 feet (3,658 meters) deep, was recently quoted at as low as $400,000, down from $600,000 last year. Even rates for jack-up rigs, generally working in water depth below 400 feet, have started to weaken in recent months after holding up relatively well earlier in the year. Rig orders soared in recent years when oil prices topped $100 per barrel, making it more profitable to explore in hard-to-reach underwater areas. The global fleet of jackup rigs is forecast to grow 9% in 2015 and another 7% in 2016, Oslo-based investment bank Pareto Securities estimated.
Read more …

Darwin looms over fossils. Sort of fitting.
• For Oil Companies, It’s Survival Of The Fittest (MarketWatch)
It looks like it may be a long winter on the oil patch. Companies are dusting off contingency plans that may have seemed far-fetched when oil was trading above $100 a barrel in the summer. Oil-well and land portfolios are coming under renewed scrutiny as they decide where to wait it out and where to continue production. Survival of the fittest is the term being used by investors and analysts as they try to figure out what’s next after the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries last week decided to keep its production levels unchanged, sending crude futures down 10% on Friday. Prices recovered some of those losses on Monday, with New York-traded oil closing at $69 a barrel after testing lows below $65 a barrel earlier in the session. “We are on the edge of what people are comfortable with,” said Meredith Annex, an analyst with research firm Bloomberg New Energy Finance. U.S. drilling is likely to continue if prices hold around $70 to $75 a barrel, she said.
Below $65, however, companies will cut production and move away from the newer, less developed shale plays in the U.S., and even from the fringes of the more established shale areas like the Permian basin in Texas and North Dakota’s Bakken basin, she said. The U.S. would then import more crude until prices come back up again. Analysts at Tudor Pickering Holt told investors to find shelter in “liquid names with high quality assets and healthy balance sheets that can weather the 2015 storm.” Tudor and others are expecting oil prices to stabilize around $70 a barrel in the coming weeks or months. Last week’s steep decline was probably exaggerated by thin U.S. trading around Thursday’s Thanksgiving holiday, they said. [..]
Energy is a cyclical business, and adjusting production to lower prices and lower demand is not uncommon — companies did exactly that in 2008 and 2009, when oil prices collapsed during the recession. This year, however, companies were convinced in the spring and summer that prices would remain around $90 a barrel, said Reid Morrison, energy consultant with PwC. U.S. companies are likely poring over their portfolios now to figure out which wells they can afford to shut down, to ditch, or even to sell. Idling a well, from a purely technical viewpoint, is relatively easy. But it gets complicated when companies have to factor in the financing structure and tens of thousands of land leases, each carrying different obligations and time frames, said Morrison. “Every exploration and production company is doing a detailed review of their leases and rationalizing their portfolio as we speak,” Morrison said. In some cases, selling the land lease might be the answer, he said.
Read more …

Check your pension plans!
• Beware the Vulnerable Oil Debt That Lurks in Your Junk-Bond ETFs (Bloomberg)
It pays to look a little closer at your investments in exchange-traded high-yield funds right now to find out just how exposed you are to plunging oil prices. Take State Street’s $9.8 billion junk-bond ETF that trades under the ticker JNK. It’s lost almost twice as much as a broad index of high-yield debt since the end of August, partly because its bigger allocation to energy companies has been a drag as oil prices plummet to the lowest since 2009. Individuals and institutions alike have gravitated toward ETFs as a quick way to enter infrequently-traded bond markets. Those who piled into speculative-grade bonds may not have realized their fortunes are, more than ever, tied to the outlook for oil given energy companies account for a record proportion of the market. “As oil prices have fallen further, reality has struck,” UBS analysts Matthew Mish and Stephen Caprio wrote in a Nov. 26 report. “For high yield, we expect that spreads and flows will be quite sensitive to oil prices at these levels. Further price declines would significantly raise expected default rates.”
Oil has collapsed into a bear market as the U.S. pumps crude at the fastest rate in three decades at the same time that global growth is slowing. OPEC resisted calls from members including Venezuela and Iran to reduce its production target when it met last week in Vienna, prompting West Texas Intermediate crude to fall below $65 dollars a barrel from more than $80 at the end of October and a high of $107 in mid-June. While some still like riskier U.S. bonds — such as Morgan Stanley (MS) analysts who today recommended buying the securities — the debt has suffered losses in the past five months as concern mounts that dropping energy costs will leave speculative shale drillers unable to meet their obligations.
Read more …

The stranded assets issue due to climate agreements is starting to make people nervous. Investors are preparing to get out. Lower prices might (should) be just what they need to make the decision.
• Oil Investors May Be Running Off a Cliff They Can’t See (BW)
A major threat to fossil fuel companies has suddenly moved from the fringe to center stage with a dramatic announcement by Germany’s biggest power company and an intriguing letter from the Bank of England. A growing minority of investors and regulators are probing the possibility that untapped deposits of oil, gas and coal – valued at trillions of dollars globally – could become stranded assets as governments adopt stricter climate change policies. The concept gaining traction from Wall Street to the City of London is simple. Limits on emissions of carbon dioxide will be necessary to hold temperature increases to 2 degrees Celsius, the maximum climate scientists say is advisable. Without technologies to capture the waste gases from combusting fossil fuels, a majority of known oil, gas and coal deposits would have to stay underground. Once that point is reached, they become stranded.
With representatives from more than 190 countries gathered to discuss climate rules in Lima, the argument that burning all the world’s known oil, gas and coal reserves would overwhelm the atmosphere is moving beyond the realm of environmental activists. Storebrand), a Scandinavian financial services company managing $74 billion of assets, announced last year that it would divest from 19 fossil fuels companies. That list has since expanded to 35, including 15 coal producers, 10 oil-sand miners and 10 utilities that predominantly use coal. “It was a financial and climate-related decision, and there was very much a consideration of stranded assets,” Christine Torklep Meisingset, Storebrand’s head of sustainable investments, said by phone from Oslo. “Companies that specialize in carbon-intense projects are very vulnerable to climate policy and shifting regulations.”
Read more …

“In May, Carbon Tracker reported that over $1 trillion is currently being gambled on high-cost oil projects that will never see a return if the world’s governments fulfil their climate change pledges.”
• Bank Of England Investigating Risk To Banks Of ‘Carbon Bubble’ (Guardian)
The Bank of England is to conduct an enquiry into the risk of fossil fuel companies causing a major economic crash if future climate change rules render their coal, oil and gas assets worthless. The concept of a “carbon bubble” has gained rapid recognition since 2013, and is being taken increasingly seriously by some major financial companies including Citi bank, HSBC and Moody’s, but the Bank’s enquiry is the most significant endorsement yet from a regulator. The concern is that if the world’s government’s meet their agreed target of limiting global warming to 2C by cutting carbon emissions, then about two-thirds of proven coal, oil and gas reserves cannot be burned. With fossil fuel companies being among the largest in the world, sharp losses in their value could prompt a new economic crisis. Mark Carney, the bank’s governor, revealed the enquiry in a letter to the House of Commons environment audit committee (EAC), which is conducting its own enquiry. He said there had been an initial discussion within the bank on “stranded” fossil fuel assets.
“In light of these discussions, we will be deepening and widening our enquiry into the topic,” he said, involving the financial policy committee which is tasked with identifying systemic economic risks. Carney had raised the issue at a World Bank seminar in October. News of the Bank’s enquiry comes on the day that global negotiations on climate change action open in Lima, Peru, and as one of Europe’s major energy companies E.ON announced it was to hive off its fossil fuel business to focus on renewables and networks. The UN’s Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change recently warned that the limit of carbon emissions consistent with 2C of warming was approaching and that renewable energy must be at least tripled. “Policy makers and now central banks are waking up to the fact that much of the world’s oil, coal and gas reserves will have to remain in the ground unless carbon capture and storage technologies can be developed more rapidly,” said Joan Walley MP, who chairs the EAC.
“It’s time investors recognised this as well and factored political action on climate change into their decisions on fossil fuel investments,” she told the Financial Times. Anthony Hobley, chief executive of thinktank Carbon Tracker which has been prominent in analysing the carbon bubble, said the bank’s latest move could lead to important changes. “Fossil fuel companies should be disclosing how many carbon emissions are locked up in their reserves,” he said. “At the moment there is no consistency in reporting so it’s difficult for investors to make informed decisions.” Both ExxonMobil and Shell said earlier in 2014 that they did not believe their fossil fuel reserves would become stranded. In May, Carbon Tracker reported that over $1tn is currently being gambled on high-cost oil projects that will never see a return if the world’s governments fulfil their climate change pledges.
Read more …

“The sharp drop in oil prices will help boost consumer spending ..” I don’t understand that: we’re talking about money that would otherwise also have been spent, only on gas. There is no additional money, so where’s the boost?
• Fed’s Dudley Says Oil Price Decline Will Strengthen US Recovery (Bloomberg)
The sharp drop in oil prices will help boost consumer spending and underpin an economy that still requires patience before interest rates are increased, Federal Reserve Bank of New York President William C. Dudley said. “It is still premature to begin to raise interest rates,” Dudley said in the prepared text of a speech today at Bernard M. Baruch College in New York. “When interest rates are at the zero lower bound, the risks of tightening a bit too early are likely to be considerably greater than the risks of tightening a bit too late.” Dudley expressed confidence that, although the U.S. economic recovery has shown signs in recent years of accelerating, only to slow again, “the likelihood of another disappointment has lessened.”
Investors’ expectations for a Fed rate increase in mid-2015 are reasonable, he said, and the pace at which the central bank tightens will depend partly on financial-market conditions and the economy’s performance. Crude oil suffered its biggest drop in three years after OPEC signaled last week it will not reduce production. Lower energy costs “will lead to a significant rise in real income growth for households and should be a strong spur to consumer spending,” Dudley said. The drop will especially help lower-income households, who are more likely to spend and not save the extra real income, he said. Lower energy prices have already helped speed U.S. growth. Manufacturing in the U.S. expanded in November at a faster pace than projected, according to the Institute for Supply Management’s factory index.
[..] He also tried to disabuse investors of the notion that the Fed would, in times of sharp equity declines, ease monetary conditions, an idea known as the “Fed put.” “The expectation of such a put is dangerous because if investors believe it exists they will view the equity market as less risky,” Dudley said. That could cause investors to push equity markets higher, contributing to a bubble, he said. “Let me be clear, there is no Fed equity market put,” he said.
Read more …

It’s simply a balloon deflating.
• Why The Commodities Selloff May Continue In 2015 (CNBC)
Several of the world’s key commodities – including oil, gas, gold and corn – have been suffering the worst months of trading since the commodities crash of 2008. Back then, the main reason for downturn in prices was obvious: the credit crisis and subsequent panic about global economic growth. Yet today, while global growth is more sluggish than hoped in certain parts of the world – particularly in China – the overall economic picture seems much brighter than in 2008. In 2014, the focus seems to have switched to supply, as OPEC pledges to keep supply constant despite plunging oil prices. As well as being interpreted as throwing down the supply gauntlet to the shale-rich U.S., the OPEC move has been criticised for apparently penalizing several of its members.
Ultimately, it looks like investment decisions in the developed world may be causing the commodities glut. “Increasingly the supply side counts more, as investment cycles are creating persistent gluts in some areas (e.g. oil, natural gas, iron ore, grains) and lagging investment is starting to result in tightening elsewhere (industrial metals in general, copper in particular),” commodities analysts at Citi wrote in a research note. Despite the focus on emerging markets, the Citi analysts argue that continuing weakness in 2015 will have a “Made in America” quality, and called an end to “the era of $100 a barrel oil.” With grains, better weather conditions than for years meant better-than-expected crops, which “should leave inventories chock-a-block for a good year or two,” according to Citi.
The classic, straightforward analysis of commodity supply-demand dynamics would argue that, with cheaper commodities and cheaper prices, demand from consumers who feel like they’re getting a bargain will subsequently grow, sending prices up again. Unfortunately for miners and other commodities-linked companies, who have seen share price falls already this week, this may not be the case in 2015. “This fall in prices seems demand rather than supply led and so any benefit (to consumers) will be negated by the declining world growth outlook,” Rabobank strategists argue.
Read more …

Anyone still keeping count?
• Europe Debates Third Bailout Package for Greece (Spiegel)
It’s no accident that “pathos” is a Greek word. Greek Prime Minister Antonis Samaras, at least, is a politician who is fond of sprinkling his speeches with the kind of emotional appeal that Aristotle long ago identified as an effective stylistic device. “The era of bailout packages is ending,” Samaras promised in September during an appearance in Thessaloniki. “Greece is now welcoming the new Greece.” Samaras knew the line would guarantee him applause from his audience, but the promise also came a bit prematurely. Following the announcement, Greece got a small taste of what it might mean were Greece were released from the oversight of the troika, comprised of the European Commission, the ECB and the IMF. The more often Samaras spoke of a “clean solution,” the more yields rose on long-term Greek government bonds. At the beginning of September, the rates had been 5.8%, but they soon climbed to almost 9%. It was the financial markets’ way of hinting that it is still too early to grant Greece full fiscal independence.
One high-ranking EU official compared the situation to a patient who has survived intensive care but wants to leave the hospital early. A relapse is certain and the subsequent care will be much more involved than if the patient had stayed in the hospital long enough for full recovery. Greece’s second bailout package officially ends in a month’s time, but it is already certain that the country will require additional funding from its EU partners. Last Wednesday in Paris, there was a minor uproar when troika officials made it known that they felt Greece hadn’t fulfilled conditions for the payout of the final tranche from the second bailout package. Athens’ international creditors determined the country will fall around €2 billion ($2.5 billion) short of reaching its commitment of not exceeding a budget deficit of 3% of gross domestic product. The Greeks, for their part, accused the troika of being overly critical, arguing that in the past, the situation had developed more positively than predicted by pessimists.
Read more …

More creative accounting. And another completely useless stress test. A new capitalization standard that goes into effect in 2015 was not applied to banks in 2014. Idiots.
• European Banks Seen Afflicted by $82 Billion Capital Gap (Bloomberg)
Europe’s latest bank stress test was flawed, and dozens of the region’s lenders, including Deutsche Bank and BNP Paribas, aren’t sufficiently capitalized to improve the economy’s anemic growth or withstand a repeat of the 2008 financial crisis. Those are the conclusions of analysts at Keefe, Bruyette & Woods and the Danish Institute for International Studies who looked at what would have happened if the ECB had applied a leverage minimum that will be introduced next year. A third study by the Centre for European Policy Studies showed Deutsche Bank and BNP Paribas above the cutoff, while 28 other banks that passed the stress test failed. The new standard requires banks around the world to have capital equal to 3% of total assets, complementing a system that weights them for risk.
If the ECB had used that yardstick and demanded the highest quality capital, 12 big European banks that passed the stress test would need to raise an additional €66 billion ($82 billion), according to Jakob Vestergaard, a senior researcher at the Danish institute. “Relying on risk-based measures only isn’t enough because it’s always what we thought wasn’t risky that ends up blowing up during a crisis,” said Vestergaard, who examined data collected by the ECB at the request of Bloomberg News and has published papers on leverage. “The ECB wanted to appear tough, but it still couldn’t show big German, French banks as undercapitalized for political reasons.”
The ECB didn’t subject bank leverage ratios to the stress test’s adverse economic scenario because European lenders only have to report those numbers on an informational basis starting next year, a spokeswoman for the central bank in Frankfurt said. The new international standard approved by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision won’t be fully binding until 2018. When it released test results on Oct. 26, the ECB provided leverage data that showed 14 lenders, including Deutsche Bank, were below the 3% minimum. Three more fell short after the central bank’s asset-quality review determined how many loans should be considered nonperforming. Combining the results of the independent studies, almost three times as many banks would fail the stress test if the leverage standard were used.
Read more …

And why does it take 2 years to get this out into the open?
• Leak at Federal Reserve Revealed Confidential Bond-Buying Details (ProPublica)
The Federal Reserve sprung a previously unreported leak in October 2012, when potentially market-moving information about highly confidential monetary deliberations made its way into a financial analyst’s private newsletter. The leak occurred the day before the scheduled public release of meeting minutes that shed new light on the Fed’s decision to embark on a third round of bond buying to boost the economy, ProPublica has learned. The newsletter revealed what the minutes would say the next day as well as fresh details about the Fed’s internal plans and deliberations – information that could have provided traders with an edge. Leaks from inside the Fed are considered a serious matter. In the past, they have prompted Congressional concern and triggered the involvement of federal law enforcement. In this instance, then Fed Chairman Ben Bernanke instructed the central bank’s general counsel to look into the matter.
The Federal Reserve has faced criticism in recent years for its information security practices, with some in Congress questioning whether it operates under sufficient oversight. The October 2012 leak involved deliberations of the Federal Open Markets Committee, which holds eight regularly scheduled meetings per year to set policies that control inflation and keep the economy growing. Since the 2008 economic crisis, it has involved itself more deeply in financial markets. Minutes of the committee’s meetings are released promptly at 2 p.m. three weeks after it meets. Fed watchers eagerly await the event and parse every word for clues on how financial markets will move. The Fed tightly guards nonpublic information about deliberations by the committee and the select staffers who are privy to them, about five dozen people in all. Doing so is critical to “reinforce the public’s confidence in the transparency and integrity of the monetary process,” the Fed’s policy on external communications says. [..]
The newsletter containing the leaked material came from an economic policy intelligence firm called Medley Global Advisors whose clients include hedge funds, institutional investors and asset managers. On Oct. 3, 2012, Regina Schleiger, an analyst with the firm, sent clients a “special report” titled “Fed: December Bound.” The report focused on the Sept. 12-13 open market committee meeting, where the panel had approved what’s called “QE3,” a new program of large-scale purchases of mortgage-backed and Treasury securities. Typically, the Fed chairman holds a news conference following the meetings to help explain the committee’s actions. But when Bernanke did this on Sept. 13, he did not reveal the depth of disagreement within the committee about how effective the bond-buying program would be and whether it was worth the cost. Schleiger wrote, however, that the minutes due out the next day would reveal “intense debate between Federal Open Market Committee participants.”
Read more …

Roubini’s not much of an analyst anymore, it’s all Keynes ‘austerity killed the cat’ all the way, a one dimensional focus on growth that is so abundant today. To claim, for example, that Japan’s sales tax hike in April ‘killed the recovery’ is an opinionated opinion, at best. Japan’s problems are far too deep to be either solved or aggravated by a 3% extra sales tax. But it’s the sort of opinion that gets Nouriel re-invited to Basel and all those places where the rich meet.
• The Return Of Currency Wars Will Strengthen The US Dollar Even More (Roubini)
The recent decision by the Bank of Japan to increase the scope of its quantitative easing is a signal that another round of currency wars may be under way. The BOJ’s effort to weaken the yen is a beggar-thy-neighbor approach that is inducing policy reactions throughout Asia and around the world. Central banks in China, South Korea, Taiwan, Singapore and Thailand, fearful of losing competitiveness relative to Japan, are easing their own monetary policies or will soon ease more. The European Central Bank and the central banks of Switzerland, Sweden, Norway and a few Central European countries are likely to embrace quantitative easing or use other unconventional policies to prevent their currencies from appreciating. All of this will lead to a strengthening of the U.S. dollar, as growth in the United States is picking up and the Federal Reserve has signaled that it will begin raising interest rates next year.
But if global growth remains weak and the dollar becomes too strong, even the Fed may decide to raise interest rates later and more slowly to avoid excessive dollar appreciation. You can lead a horse to liquidity, but you can’t make it drink. The cause of the latest currency turmoil is clear: In an environment of private and public deleveraging from high debts, monetary policy has become the only available tool to boost demand and growth. Fiscal austerity has exacerbated the impact of deleveraging by exerting a direct and indirect drag on growth. Lower public spending reduces aggregate demand, while declining transfers and higher taxes reduce disposable income and, thus, private consumption. In the eurozone, a sudden stop of capital flows to the periphery and the fiscal restraints imposed, with Germany’s backing, by the European Union, the IMF and the ECB have been a massive impediment to growth.
In Japan, an excessively front-loaded consumption-tax increase killed the recovery achieved this year. In the U.S., a budget sequester and other tax-and-spending policies led to a sharp fiscal drag in 2012-2014. And in the United Kingdom, self-imposed fiscal consolidation weakened growth until this year. Globally, the asymmetric adjustment of creditor and debtor economies has exacerbated this recessionary and deflationary spiral. Countries that were overspending, under-saving and running current-account deficits have been forced by markets to spend less and save more. Not surprisingly, their trade deficits have been shrinking. But most countries that were over-saving and under-spending have not saved less and spent more; their current-account surpluses have been growing, aggravating the weakness of global demand and, thus, undermining growth.
Read more …

Wages have been falling for much longer.
• Japanese Workers See Wages Drop for 16th Month (Bloomberg)
Japanese wages adjusted for inflation dropped for a sixteenth straight month as Prime Minister Shinzo Abe faces an election focused on his efforts to spur economic growth. Earning declined 2.8% in October from a year earlier, the labor ministry said today, following data last week showing households cut spending for a seventh month. Abe’s call for companies to use their cash holdings on salaries and investment has been partially met, with capital spending among manufacturers rising while wages change little. He faces voters on Dec. 14 with an economy that fell into recession following a sales-tax increase and opposition parties highlighting the difficulties of low-income earners.
“With the effect of the sales tax hike, I don’t see real wages rising in the financial year through April,” said Toru Suehiro, an economist at Mizuho Securities. “People will be asking themselves whether they feel better off, and there probably aren’t that many who think the economy has got better.” Before adjusting for inflation, average monthly pay in October rose 0.5% from a year earlier to 267,935 yen ($2,260). Large Japanese companies will raise winter bonuses by 5.8% this year, according to the preliminary results of a survey by the Keidanren business lobby group. Abe said yesterday that Keidanren has promised to lift pay next year.
Read more …

The EU shoots itself in the foot. And Russia gets angrier. Gazprom spent billions preparing the South Stream line. Dmitry Orlov said from now on to expect things from Russia that no-one expects.
• Putin: EU Stance Forces Russia To Withdraw From South Stream Project (RT)
Russia is forced to withdraw from the South Stream project due to the EU’s unwillingness to support the pipeline, and gas flows will be redirected to other customers, Vladimir Putin said after talks with his Turkish counterpart, Recep Tayyip Erdogan. “We believe that the stance of the European Commission was counterproductive. In fact, the European Commission not only provided no help in implementation of [the South Stream pipeline], but, as we see, obstacles were created to its implementation. Well, if Europe doesn’t want it implemented, it won’t be implemented,” the Russian president said. According to Putin, the Russian gas “will be retargeted to other regions of the world, which will be achieved, among other things, through the promotion and accelerated implementation of projects involving liquefied natural gas.”
“We’ll be promoting other markets and Europe won’t receive those volumes, at least not from Russia. We believe that it doesn’t meet the economic interests of Europe and it harms our cooperation. But such is the choice of our European friends,” he said. The South Stream project is at the stage when “the construction of the pipeline system in the Black Sea must begin,” but Russia still hasn’t received an approval for the project from Bulgaria, the Russian president said. Investing hundreds of millions of dollars into the pipeline, which would have to stop when it reaches Bulgarian waters, is “just absurd, I hope everybody understands that,” he said. Putin believes that Bulgaria “isn’t acting like an independent state” by delaying the South Stream project, which would be profitable for the country.
He advised the Bulgarian leadership “to demand loss of profit damages from the European Commission” as the country could have been receiving around €400 million annually through gas transit. Putin said that Russia is ready to build a new pipeline to meet Turkey’s growing gas demand, which may include a special hub on the Turkish-Greek border for customers in southern Europe. For now, the supply of Russian gas to Turkey will be raised by 3 billion cubic meters via the already operating Blue Stream pipeline, he said. Last year, 13.7 bcm of gas were supplied to Turkeyvia Blue Stream, according to Reuters. Moscow will also reduce the gas price for Turkish customers by 6% from January 1, 2015, Putin said. “We are ready to further reduce gas prices along with the implementation of our joint large-scale projects,” he added.
Read more …

And announced a 0.8% growth shrinkage for 2015.
• Russia Intervenes As Crumbling Ruble Echoes 1998 Debt Crisis (Guardian)
Russia’s central bank was forced to step in to defend the ruble on the foreign exchanges on Monday after fears over the economy’s vulnerability to a weak oil price sent the currency to a record low against the dollar. Moscow was forced to abandon its hands-off policy towards the ruble amid heavy selling, unmatched since the Russian debt default of 1998. The Russian central bank intervened when the ruble was down 6.5% on the day against the US dollar, and by the close of trading the currency had recouped more than half its earlier losses. A bounce in the oil price from a fresh five-year low and a sense that the sell-off since last week’s meeting of the Opec cartel has been overdone helped sentiment towards the Russian currency, which has been badly buffeted by a plunge of almost 40% in the cost of crude since the summer.
Data from the US suggesting that drilling activity in the shale oil sector is being affected by lower oil prices also helped the ruble by pushing down the value of the dollar. Oil is denominated in dollars, so when the US currency falls oil becomes cheaper and more attractive for holders of other currencies. With Moscow fearful that the drop in the value of the ruble makes Russia vulnerable to capital flight, Ksenia Yudaeva, the Russian central bank’s deputy chairwoman, told newswires that households should not panic. She said the rise in interest rates to 9.5% should encourage them not to convert savings into euros or dollars. “It’s necessary to explain to people that the yield they get on their deposits at the moment will guarantee a high degree of safety for their savings with regards to inflation. They should think twice before rushing out, losing the yield on their deposits, taking on currency risks and losing money on their currency conversions.”
Read more …

NATO is putting ever more attack weapons in countries it had been agreed would be neutral terrain.
• Russia Says NATO Destabilizes North Europe, Aid Draws Ire (Bloomberg)
Russia accused NATO of trying to destabilize northern Europe as the alliance’s chief said the latest aid convoy for Ukraine was another sign of Russian disrespect for its neighbor’s border. NATO military drills and its transfer of warplanes capable of carrying nuclear weapons to the Baltic states are a “reality which is extremely negative,” Interfax reported Russian Deputy Foreign Minister Aleksey Meshkov as saying today. “They are trying to shake up the most stable region in the world, the north of Europe,” Meshkov said. “In this regard, Russia’s leadership is and will be taking all steps to ensure the security of Russia and its citizens.” Ukraine and its allies blame Russia for stoking the conflict in the east of Ukraine, which has killed more than 4,300 people and left at least 10,000 wounded. The government in Moscow denies involvement. After delivering more than 1,200 metric tons of cargo to the Donetsk and Luhansk regions without consulting the government in Kiev yesterday, Russia may soon dispatch a ninth aid convoy, Tass reported, citing the Emergencies Ministry.
Read more …

Stranger than fiction. Then again, if a country seen as hostile to the US produces a movie in which the plot evolves around a plan to kill the American President, how amused would Washington be?
• North Korea Refuses To Deny Sony Pictures Cyber-Attack (BBC)
North Korea has refused to deny involvement in a cyber-attack on Sony Pictures that came ahead of the release of a film about leader Kim Jong-un. Sony is investigating after its computers were attacked and unreleased films made available on the internet. When asked if it was involved in the attack a spokesman for the North Korean government replied: “Wait and see.” In June, North Korea complained to the United Nations and the US over the comedy film The Interview. In the movie, Seth Rogen and James Franco play two reporters who are granted an audience with Kim Jong-un. The CIA then enlists the pair to assassinate him. North Korea described the film as an act of war and an “undisguised sponsoring of terrorism”, and called on the US and the UN to block it. California-based Sony Pictures’ computer system went down last week and hackers then published a number of as-yet un-released films on online download sites.
Among the titles is a remake of the classic film Annie, which is not due for release until 19 December. The Interview does not appear to have been leaked. When asked about the cyber-attack, a spokesman for North Korea’s UN mission said: “The hostile forces are relating everything to the DPRK (North Korea). I kindly advise you to just wait and see.” On Monday Sony Pictures said it had restored a number of important services that had to be shut down after the attack. It said it was working closely with law enforcement officials to investigate the matter but made no mention of North Korea. The FBI has confirmed that it is investigating. It has also warned other US businesses that unknown hackers have launched a cyberattack with destructive malware.
Read more …

It’s good to see the NZ justice system has a degree of independence. But this isn’t over. They’ll keep on trying.
• Kim Dotcom Avoids Jail After Bail Hearing (NZ Herald)
Kim Dotcom has had bail conditions tightened, although the judge who did so said there was no evidence he had breached any of the court-ordered conditions. Dotcom now has to report twice a week, rather than once, and is banned from travelling on private aircraft or sea-going vessels. Dotcom lambasted the United States and the Crown lawyers acting for it outside court, saying both seized the opportunity to have his bail revoked after he split from his former gold-plated legal team. “The court has found I have no breached any of my bail conditions. I have been probably the most compliant, exemplary candidate of bail in NZ and I am surprised, even though I am going home right now, that my bail conditions have been tightened given my excellent bail compliance.
“I think this is another case of harassment and bullying by the United States government in concert with the New Zealand government. I think this whole application was only made because my lawyers decided to resign because of a lack of funds on my part because Hollywood has seized the new family assets that have been made after the raid. “The Crown and US government have used this opportunity at a weak moment to make up the bogus case for me having breached my bail conditions.” He accused the FBI of being deceitful bringing allegations he had tried to sell a Rolls Royce or been in contact with banned co-accused. He said the evidence showed – as he claimed was true in other branches of the case – that the US would not act with openness and honesty.
“I’m now going home to play with my kids.” Judge Nevin Dawson dismissed the arguments put by the US, saying there was “no proof” he had been in contact with former Megaupload staff who are free in Europe but also facing criminal copyright charges. He said he was not compelled by accusations Dotcom acted with a “lack of candour” by using a driver licence under the name Kim Schmitz in 2009 when stopped for dangerous driving. He said “it appears to be a legitimate use of the name Kim Schmitz”. Other claims also failed to find traction with Judge Dawson, who said he was tightening conditions to take account of the wealth Dotcom had accrued since his arrest and the approaching extradition trial, set for June.
Read more …