DPC Betsy Ross house, Philadelphia. Birthplace of Old Glory 1900



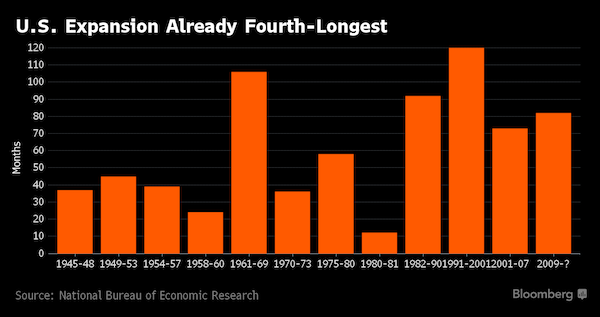
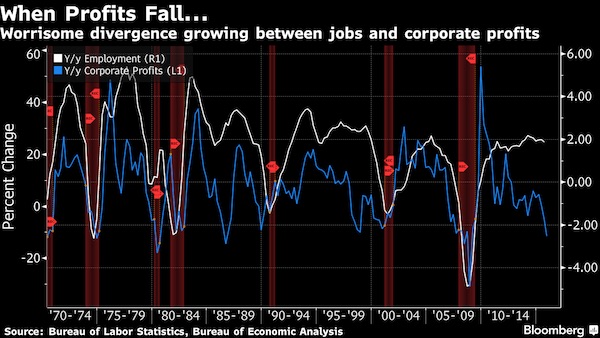
Look what the Fed bought you! “The 83-month-old expansion is already the fourth-longest in more than 150 years..”
• The Next US President Will Face A Recession (BBG)
Talk about a poisoned chalice. No matter who is elected to the White House in November, the next president will probably face a recession. The 83-month-old expansion is already the fourth-longest in more than 150 years and starting to show some signs of aging as corporate profits peak and wage pressures build. It also remains vulnerable to a shock because growth has been so feeble, averaging just about 2% since the last downturn ended in June 2009. “If the next president is not going to have a recession, it will be a U.S. record,” said Gad Levanon, chief economist for North America at the Conference Board in New York. “The longest expansion we ever had was 10 years,” beginning in 1991.
The history of cyclical fluctuations suggests that the “odds are significantly better than 50-50 that we will have a recession within the next three years,” according to former Treasury Secretary Lawrence Summers. Michael Feroli, chief U.S. economist for JPMorgan Chase & Co. in New York, puts the probability of a downturn during that time frame at about two in three. The U.S. doesn’t look all that well-equipped to handle a contraction should one occur during the next president’s term, former Federal Reserve Vice Chairman Alan Blinder said. Monetary policy is stretched near its limit while fiscal policy is hamstrung by ideological battles.
This wouldn’t be the first time that a new president was forced to tackle a contraction in GDP. The nation was in the midst of its deepest slump since the Great Depression when Barack Obama took office on January 20, 2009. His predecessor, George W. Bush, started his tenure as president in 2001 with the economy about to be mired in a downturn as well, albeit a much milder one than greeted Obama. The biggest near-term threat comes from abroad. Former IMF official Desmond Lachman said a June 23 vote by the U.K. to leave the European Union, a steeper-than-anticipated Chinese slowdown and a renewed recession in Japan are among potential developments that could upend financial markets and the global economy in the coming months. “There’s a non-negligible risk that by the time the next president takes office in January you would have the world in a pretty bad place,” said Lachman, who put the odds of that happening at 30% to 40%.

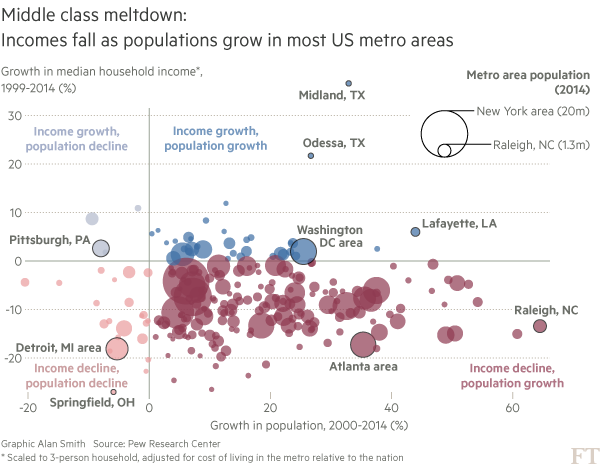
A strange combo of how great Raleigh is and how decrepit at the same time. ‘Remarkable success story’ blah blah. The FT blows up America’s economic myths, but it does so reluctantly.
• America’s Middle Class Meltdown (FT)
The erosion of America’s middle class and the resulting voter frustration that has helped fuel the presidential campaigns of Republican Donald Trump and Bernie Sanders, the populist Democratic senator from Vermont, is often portrayed as a phenomenon brought about by the collapse of well-paying manufacturing jobs over the past three decades thanks to increased automation and competition from China. But a new study by the non-partisan Pew Research Center, shared with the Financial Times, points to just how widespread the damage to America’s middle has been and how divided the country’s class structures are becoming. Median incomes fell in four-fifths of the 229 metropolitan areas studied by Pew, with the share of middle-income adults decreasing in 203 areas.
At the same time the portion of lower-income adults rose in 160 metropolitan areas between 1999 and 2014 while the share of upper-income households rose in 172. Of the metropolitan areas analysed by Pew, none saw faster population growth this century than Raleigh. Together with neighbouring Durham and the Research Triangle Park, it is celebrated as an example of how cities can transform themselves into sparky science and technology-driven hubs of innovation, or key outposts for America’s new “knowledge economy”. “It is one of the most remarkable success stories of the last 20 years, or even 30 years,” says Enrico Moretti, a University of California, Berkeley, economist and author of The New Geography of Jobs.
[..] But while Raleigh’s population continues to grow, the new data from Pew shows that the robust population growth has not necessarily translated into higher incomes for its new residents. The benefits of the boom have been shared unequally. The inflation-adjusted annual median income for a household of three in Raleigh fell by more than $10,000 to $74,283 in 2014 from $85,784 in 1999, even as its population grew by two-thirds to more than 1.3m people from just under 800,000. More surprisingly, the only income group to grow as a share of the population was its poorest. In 1999 one in five residents of the metropolitan area lived in households making two-thirds or less of the median income. By 2014 that figure had grown to one in four.

“..the Forecaster of the Month contest for April..”? Geez, that’s for real? But the point made is relevant, even if I’m not convinced the Fed ‘doesn’t get it’.
• ‘Fed Doesn’t Get It About Global Excess Supply’ (MW)
The Federal Reserve is blowing it because it thinks the economy could be overheating, but the real problem is excess supply and deflationary pressure, says Steven Ricchiuto, chief economist for Mizuho Securities USA and the winner of the Forecaster of the Month contest for April. “The dynamics of supply and demand have shifted,” Ricchiuto said in an interview. “I don’t think they get it yet,” he said of the Fed. The central bank is trying to manage the economy as if excess demand were still the major problem it was in the 1970s and 1980s. But today’s global economy suffers from a different imbalance, Ricchiuto says: Excess supply. When excess demand is the normal state of the economy, then inflation is the perennial problem.
But if the economy is stuck in a rut of excess supply, then slow growth and deflation will persist. “We should be immunizing the nation against deflation,” Ricchiuto said. But, instead, the Fed still seems to be living in the 1970s, worried that the unemployment rate will go too low and that the economy will overheat. That’s why the Fed “blew it in December” when it raised interest rates. The myopic focus on unemployment is misguided, in Ricchiuto’s view. Almost all of the economic data on the production side of the economy (such as industrial output, business sales and gross domestic product) show a tepid economy. But the labor market is doing great, comparatively. The Fed reacts to the strong job news, but ignores the rest of the story. If the Fed cared about the supply side of the economy, it would see that idle resources are pulling the economy toward stagnation and deflation.
Of course, excess supply is a global problem, not just in the U.S. Other economies are trying to reduce their excess supply the quickest way they can: Devaluing their currency in hopes that they can push the problem of excess capacity onto the country with the strongest currency. These beggar-thy-neighbor policies don’t really solve the problem, at least not quickly. Everybody around the world needs to figure out how to increase domestic demand to bring supply and demand back into balance, he said. Although the Fed doesn’t get it, many voters do, and so do candidates like Bernie Sanders, Ricchiuto said. “People are recognizing deep, fundamental flaws” in the economy. They are clamoring for policies such as more spending on infrastructure, measures to reduce the concentration of wealth, and tax reform.

In a nutshell: Banks are regulated. Blackstone is not.
• The New Kings Of Wall Street (Forbes)
In March 2015 Stephen Schwarzman got a telephone call from JPMorgan vice chairman Jimmy Lee, one of Wall Street’s legendary power brokers. Lee, who died three months later, was helping General Electric unload $30 billion in commercial real estate assets lingering on its books. GE boss Jeffrey Immelt was uncomfortable with the massive financial services business his predecessor, Jack Welch, had slowly built up. During the 2008 meltdown, frozen credit markets put GE Capital’s $101 billion in commercial paper funding in peril, bringing the mighty industrial conglomerate to its knees. Lee told Schwarzman that the real estate sale was the keystone to Immelt’s reinvention plan for the 123-year-old company.
The hang-up: finding a single buyer for a portfolio that included financing for everything from Mexican warehouses to Parisian office buildings to commercial mortgages in Australia. The billions in real estate and commercial mortgages were scattered across six countries, comprising all sorts of risks. Lee, Immelt and GE Capital boss Keith Sherin knew that Blackstone Group was the only firm with three key traits: the global reach to understand all the different assets, the resources to close a deal quickly and the financial firepower to swallow the entire package. The first call went to Blackstone’s global real estate chief, Jonathan Gray, who quickly darted over to GE’s 30 Rockefeller Center offices in Manhattan.
There Sherin offered Blackstone an exclusive look for three weeks–a minuscule period of time given the scope of the assets, but also a huge opportunity. Gray agreed, and before even getting off the elevator, he was marshaling an army of 100 Blackstone real estate professionals to tear through GE Capital’s portfolio. Four weeks later, on Apr. 10, Immelt announced that Blackstone would purchase $14 billion of GE’s assets, with Wells Fargo WFC -0.65% taking $9 billion of GE’s commercial real estate mortgages. For Immelt, Blackstone was a savior. GE’s languishing stock jumped 11% on the news. It was an even better transaction for Blackstone. The private equity firm had the inside track and thus more control over the deal terms and price, which was ultimately discounted.
“It was a perfect deal for us,” Schwarzman says. “No one else in the world is set up to buy both equity assets and real estate debt on a global basis.” Indeed, Blackstone’s massive 2015 purchase, executed flawlessly, announced to the world that the bankers at JPMorgan and Goldman Sachs–who had been the premier financiers for many decades–were no longer the kings of Wall Street. There was a new pecking order that put private equity firms on top–with Blackstone at the apex and its chairman and chief executive, Schwarzman, as the most powerful banker on the planet.

All that’s missing is a spark to start the fire.
• Italy Must Choose Between The Euro And Its Own Economic Survival (AEP)
Italy is running out of economic time. Seven years into an ageing global expansion, the country is still stuck in debt-deflation and still grappling with a banking crisis that it cannot combat within the paralyzing constraints of monetary union. “We have lost nine %age points of GDP since the peak of the crisis, and a quarter of our industrial production,” says Ignazio Visco, the rueful governor of the Banca d’Italia. Each year Rome hopefully pencils in a fall in the ratio of public debt to GDP, and each year the ratio rises. The reason is always the same. Deflationary conditions prevent nominal GDP rising fast enough to outgrow the debt. The putative savings from drastic fiscal austerity – cuts in public investment – were overwhelmed by the crushing arithmetic of the ‘denominator effect’. Debt was 121pc in 2011, 123pc in 2012, 129pc in 2013.
It came close to levelling out last year at 132.7pc, helped by the tailwinds of a cheap euro, cheap oil, and Mario Draghi’s fairy dust of quantitative easing. This triple stimulus is already fading before the country escapes the stagnation trap. The IMF expects growth of just 1pc this year. The global window is closing in any case. US wage growth will probably force the Federal Reserve to raise interest rates and wild speculation will certainly force China to rein in its latest credit boom. Italy will enter the next downturn – perhaps early next year – with every macro-economic indicator in worse shape than in 2008, and half the country already near political revolt. “Italy is enormously vulnerable. It has gone through a whole global recovery with no growth,” said Simon Tilford from the Centre for European Reform.
“Core inflation is at dangerously low levels. The government has almost no policy ammunition to fight recession.” Italy needs root-and-branch reform but that is by nature contractionary in the short-run. It is viable only with a blast of investment to cushion the shock, says Mr Tilford, but no such New Deal is on the horizon. Legally, the EU Fiscal Compact obliges Italy to do the exact opposite: to run budget surpluses large enough to cut its debt ratio by 3.6pc of GDP every year for twenty years. Do you laugh or cry? “There is a very real risk that Matteo Renzi will come to the conclusion that his only way to hold on to power is to go into the next election on an openly anti-euro platform. People are being very complacent about the political risks,” said Mr Tilford. Indeed. The latest Ipsos MORI survey shows that 48pc of Italians would vote to leave the EU as well as the euro if given a chance.
The rebel Five Star movement of comedian Beppe Grillo has not faded away, and Mr Grillo is still calling for debt default and a restoration of the Italian lira to break out of the German mercantilist grip (as he sees it). His party leads the national polls at 28pc, and looks poised to take Rome in municipal elections next month. The rising star on the Italian Right, the Northern League’s Matteo Salvini, told me at a forum in Pescara that the euro was “a crime against humanity” – no less – which gives you some idea of where this political debate is going. The official unemployment rate is 11.4pc. That is deceptively low. The European Commission says a further 12pc have dropped out of the data, three times the average EU for discouraged workers.
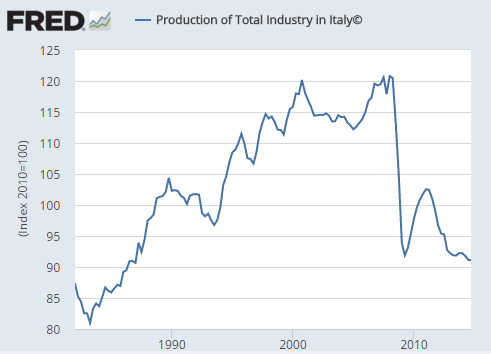
Italy’s industrial output has fallen back to the levels of the 1980s. It has been catastrophic Credit: St Louis Fed
The youth jobless rate is 65pc in Calabria, 56pc in Sicily, and 53pc in Campania, despite an exodus of 100,000 a year from the Mezzogiorno – often in the direction of London. The research institute SVIMEZ says the birth rate in these former Bourbon territories is the lowest since 1862, when the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies in Naples began collecting data. Pauperisation is roughly comparable to that in Greece. Industrial output has dropped by 35pc since 2008, and investment by 59pc. SVIMEZ warns that the downward spiral is turning a cyclical crisis into a “permanent state of underdevelopment”. In short, southern Italy is close to social collapse, and there is precious little that premier Renzi can do about it without reclaiming Italian economic sovereignty.

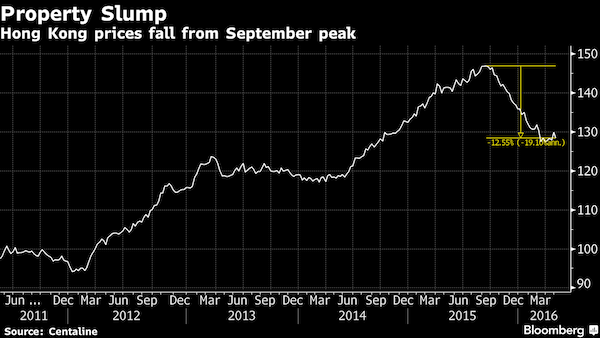
“The Chinese credit system, according to Bass, is “one of the biggest macro imbalances the world has ever seen”..”
• Hong Kong Property Market in Free Fall: Kyle Bass (BBG)
Kyle Bass, the hedge-fund manager who’s wagering on a slowdown in China’s economy, said Hong Kong’s property market is in “free fall” and the credit expansion in Southeast Asian emerging markets will unravel. “Hong Kong’s in a worse position than it was in prior to the ’97 crisis today,” Bass said at the SkyBridge Alternatives Conference in Las Vegas on Wednesday. He said credit in Asian emerging markets has grown “recklessly,” citing Malaysia and Thailand. Hong Kong property prices have declined and sales are hovering near a 25-year low as the city grapples with the repercussions of a slowing Chinese economy. Home prices have dropped about 13% from a peak in September, according to data compiled by Centaline Property Agency.
The last major housing crash in the former British colony saw prices tumble almost 50% in the 12 months from October 1997. They eventually bottomed in mid-2003 when the city was swept up by the severe acute respiratory syndrome epidemic and have almost quadrupled since then. Bass, famed for betting against U.S. subprime mortgages prior to the housing crash, is predicting losses for China’s banks and raising money to start a dedicated fund for bets in the nation. He said last week at a conference that investors putting money in Asia should ask themselves if they can handle 30% to 40% writedowns in Chinese investments.
“China may be able to not tell the truth about specific output levels, or GDP figures – they might be able to fudge those numbers for a while,” Bass said at a panel discussion, moderated by Bloomberg TV’s Erik Schatzker. “But their trading partners kind of tell the truth, and you’re already seeing what’s happening in their primary trading partners.” The Chinese credit system, according to Bass, is “one of the biggest macro imbalances the world has ever seen.” The fund manager said China is already experiencing a “hard landing as we speak.” He said he isn’t a “permanent bear” on China, instead describing himself as a pragmatist.

In lieu of welfare?! BTW, where will they borrow the money?
• China Eyes $724 Billion Of Transport Investment Over Next Three Years (R.)
China will invest around 4.7 trillion yuan ($724 billion) in transport infrastructure projects over the next three years, the country’s transport ministry said in an article posted on its website late on Wednesday. The 2016-2018 plan from China’s Ministry of Transport and National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) will see the country push forward 303 key transportation projects including railways, highways, waterways, airports and urban rail, it said. The investment splurge underlines China’s reliance on high-levels of public sector spending, credited by economists as being behind recent signs of improvement in the country’s economy, but also as creating a risk as debt levels rise.
The article, posted on the Ministry of Transport’s website, said the investment plan would improve the country’s high-speed transport networks and inter-city links to meet the demands of China’s wider economic and social development. China’s first quarter investment in infrastructure surged almost 20%, as the government looks to transport-related sectors to help support wider economic growth. The official Xinhua news agency reported earlier this month that China will invest around $12 billion this year in building aviation infrastructure.

And yes, this is where they’ll borrow, and that means shadow banks: “..Beijing has given local governments its blessings to raise funds in the bond market, much of it through local government financing vehicles (LGFVs) that skirt official spending limits..”
• Defying Debt Fears, China Bets On Infrastructure, Property (R.)
Local governments across China are binging on debt again to pump-prime their slack economies. But this time round, they are not wasting money propping up zombie factories or loss-making steel plants. Investment in industries hit by chronic overcapacity is drying up quickly. Investment in mining tumbled 18% in the first quarter from a year earlier, the most since at least the second quarter of 2004, while investment in manufacturing grew just 6%, the slowest in the same period, according to the latest data from the National Bureau of Statistics. In recent years, miners and manufacturers had tapped easy-to-access bank credit and government subsidies to fire up production even as demand began to wilt.
In a landmark move, Beijing has ordered the closure of debt-ridden zombie firms as its policy priority for 2016. In contrast, first-quarter investment in infrastructure and real estate surged 19.6% and 6.2%, respectively. The numbers reflect the government’s strategy of re-allocating capital to other engines of the economy, and in turn, providing a little respite to the steel, cement, energy and related services sectors. China will invest $11.9 billion in aviation infrastructure this year alone. It has also approved a 27.4 billion yuan high-speed rail project linking Beijing’s new airport with neighboring Hebei province. In real estate, China’s March home prices rose at the fastest clip in almost two years on the back of a boom in top-tier cities amid easy bank credit.
To boost infrastructure investment, Beijing has given local governments its blessings to raise funds in the bond market, much of it through local government financing vehicles (LGFVs) that skirt official spending limits. LGFVs have raised tens of billions of dollars through bonds in the first quarter, according to brokerage estimates, even as China skeptics warn of another debt bust. The AA-rated LGFV issuances have appealed to investors increasingly unsure of the quality of corporate paper. Overall local government bond issuances in the quarter totaled 955.4 billion yuan, according to investment firm China International Capital. Investment in infrastructure and real estate is more organized and demand-based this time, and will have a better chance of success than more speculative developments in the past, some economists say. But that’s a subject for debate.

Fun with beer. The kind of stuff to bore your guests with while serving them ‘America’.
• Budweiser’s ‘America’ No Longer Exists (MW)
Oh, Budweiser is American all right — just not in the way its cans want you to think it is. Earlier this week, the folks behind Anheuser-Busch InBev’s Budweiser brand announced their intention to relabel Budweiser as “America” from late May through the November presidential election. They’re going to sub in “US” for “AB” in the logo, switch out “King of Beers” for “E Pluribus Unum” and include the entire first stanza of “The Star-Spangled Banner” on the head of the label. Now, you could write this off by saying that A-B takes some sort of patriotic measure with Budweiser cans every year, and you’d be right, but this particular rebrand says more about Budweiser’s American tale than it likely wants to admit. For starters, “Budweiser” traces its origins back to the South Bohemia region of what is now the Czech Republic.
The city of Ceske Budejovice has been brewing beer since the 1400s, and its German-speaking residents — who called it “Budweis” — began brewing Budweiser Bürgerbräu in 1795. They began shipping that beer to the U.S. in 1875, or about a year before a German immigrant named Adolphus Busch made a trip to Bohemia and decided to name his own U.S. beer Budweiser in tribute to the Bohemian brand. Though Anheuser-Busch InBev now owns that brand, another Czech brewery — state-owned Budejovicky Budvar , founded in 1895 — has laid claim to the Budweiser name, saying it is indicative of the city where it was first made. While A-B InBev can call its beer Budweiser in North America, the United Kingdom and much of the rest of the world, Budvar has the rights to the Budweiser name in much of Europe and forces Anheuser-Busch InBev to name its version “Bud.”
When challenged in court, Budvar simply reminds folks of what Adolphus Busch himself testified in a New York courthouse in 1896: “The Budweiser beer is brewed according to the Budweiser Bohemian process. The idea was simply to brew a beer similar in quality, color, flavor and taste to the beer then made at Budweis, or in Bohemia.” If the loss of its identity in Europe didn’t sever Budweiser’s ties to the Old World, the sale of Anheuser-Busch to InBev for $52 billion back in 2008 certainly did. Not only had A-B been taken over by a company with headquarters in Belgium and Brazil — enabling it to engage in the grand American tradition of tax inversion — but cost-cutting measures reduced U.S. jobs, removed German Hallertauer Mittelfrüh hops from the equation and put pressure on suppliers of everything from rice grains to the beechwood used in “beechwood-aged” Budweiser’s touted brewing process.

“You’re gonna lift the tax-free threshold for rich people. If you lift my tax-free threshold, that changes my life. That means that I get to say to my little girls, ‘Daddy’s not broke this weekend, we can go to the pictures.’ Rich people don’t even notice their tax-free threshold lift.”
• US Anti-Poverty Campaigner Is Worried About Australia (DL)
Linda Tirado is in the green room of the ABC on Monday night during the broadcast of Q&A and she is getting madder and madder; and it’s not just from hearing #IStandWithDuncan Duncan Storrar be real in the audience that evening. Tirado, a US anti-poverty campaigner (a job we should all do), is overwhelmed by what Storrar, the 45 year-old Geelong father of two and part-time truck driver had to say about the federal government’s planned tax cuts. “You’re gonna lift the tax-free threshold for rich people. Why don’t I get it? Why do they get it?” he asked assistant treasurer Kelly O’Dwyer.
“I’ve got a disability and a low education – that means I’ve spent my whole life working off a minimum wage. You’re gonna lift the tax-free threshold for rich people. If you lift my tax-free threshold, that changes my life. That means that I get to say to my little girls, ‘Daddy’s not broke this weekend, we can go to the pictures.’ Rich people don’t even notice their tax-free threshold lift.” So, Duncan Storrar is talking, Kelly O’Dwyer is responding and Tirado is sitting in the green room, furious. She’s wondering exactly what’s been happening to Australia over the last 12 months. “Obviously I cannot tell you what a hero he is and what a sacrifice he made. To say something like that in public, to say you don’t make enough to make ends meet, that is incredibly brave.”
But she fears the change she has seen in the Australian political landscape since she was last here. She’s here as part of the Anti-Poverty Network’s conference but is keen to stay a little longer and cover the Australian election from the eyes of a survivor of the US class war. [..] “In America, we have this idea of meritocracy. If you deserve it, you will have it. If you don’t have it, it is because you don’t deserve it and the fact remains 45 million Americans are living in poverty, most of those people are in work. They’re holding down multiple jobs and we call them lazy. By definition anybody who works three jobs is not lazy and if you think so I dare you to get out of your air conditioned office and try it for yourself.”

“..a disease whose main cause is now Germany’s own current account surplus.”
• Berlin Should Be Careful What It Wishes For (FT)
Greece’s parliament this week approved reforms to the country’s creaking pensions and tax system by a larger margin than had been anticipated. But significant differences remain, notably on how large a primary budget surplus should be targeted over the next few years, and above all on the question of debt relief. The disagreement between the IMF and European governments on the latter point has come into the open. On this, the IMF is right and those Europeans who oppose relief are wrong: there can be no solution to the Greek crisis without it. Germany, driven by Wolfgang Schäuble, its finance minister, remains doggedly opposed, but even within the German government, open opposition to Mr Schäuble’s hard line has come recently from Sigmar Gabriel, economics minister.
Chancellor Angela Merkel may be tempted to ignore Mr Gabriel, whose Social Democratic party is polling poorly and whose own future as its leader is in question. German public opinion sees relief as a favour the Greeks have done little or nothing to deserve, and asks whether it will stop with Greece. The issue is not a winning one for a chancellor already under siege. Nevertheless, she would be wise to recognise the stakes for Europe as a whole. Berlin’s tenacious enforcement of austerity across the eurozone mistakes a symptom — the continued difficulties of countries like Greece — for a disease whose main cause is now Germany’s own current account surplus. The Germans have been able to persist in this illusion because without the low interest rates that Germany’s affluent voters now complain about it is doubtful whether the eurozone would have weathered the last six years at all.
Mr Schäuble might believe that the eurozone is safe come what may, even if his hard line leads to Grexit, but saving the euro will count for little if the cost is massive damage to the EU itself. Is this putting it too strongly? Perhaps it was two or three years ago but things have moved on since then. The refugee crisis has mushroomed and openly authoritarian Eurosceptic parties have profited and threaten some of the EU’s core values and principles. Euclid Tsakalotos, the Greek finance minister, warned his European counterparts recently of turning the country into a “failed state”. Even though some of his frustrated partners might think it already is, he is right: things could get much worse. It is not just about the refugee crisis although that is one factor.
There is a good deal of wishful thinking right now on this in much of central and eastern Europe. The Greeks, who despite their own deep difficulties are actually doing a great deal to help the refugees, know better: the neo-Habsburg military frontier going up across south-eastern Europe to keep out refugees will not work. There is no good alternative to helping the Greeks in the massive task that confronts them. Then there is the question of the Balkans as a whole. In Bosnia the Dayton peace settlement did one thing: it stopped the fighting. But two decades on, Bosnia remains a genuinely failed state, and Kosovo and Macedonia, too, are deeply fragile polities. The EU needs Greece to serve as a force for growth right across the Balkans and not as some kind of confirmation that the EU has decided to abandon the entire region.

Does the parliament have the guts to say no? It’s starting to look that way. EP president Schulz has refused to send the necessary documents to be appraised.
• EU Parliament Raises the Rhetoric Over Turkey’s Visa-Waiver Bid (BBG)
The European Parliament added to the war of words with Turkey over its bid for visa-free travel to Europe, highlighting the risk that a hard-fought agreement with Ankara to curb the influx of Mideast refugees will collapse. Members of the European Union assembly said Turkey must narrow the scope of its terrorism legislation to qualify for EU visa-free status. That is a prize the Turkish government sought in return for signing up to the mid-March migrant accord, which has stemmed Europe’s biggest refugee wave since World War II and eased domestic political pressure on leaders including Angela Merkel. Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan has signaled he won’t bow to the European demand over terrorism legislation, citing terror threats in Turkey that his critics say are being used as cover to jail political opponents.
Adding Turkey to a list of around 60 countries whose citizens benefit from hassle-free travel to Europe requires approval by EU governments and the 28-nation Parliament. “The liberalization can only be granted if all of the criteria are fulfilled,” Mariya Gabriel, a Bulgarian member of the Christian Democrats, the EU Parliament’s biggest faction, said during a debate on Wednesday in Strasbourg, France. Tanja Fajon, a Slovenian member of the No. 2 Socialists, said: “Turkey is very important to the solution to the migration crisis, but this does not mean that we should be making promises to Turkey without ensuring that all the conditions are fulfilled.” The EU-Turkey sparring is a test of geopolitical power that combines high politics, principles and pride.
The migrant flows into Europe via Turkey over the past year have handed Erdogan leverage over the EU, which has lambasted him for cracking down on domestic dissenters and kept Turkey’s longstanding bid for membership of the bloc largely on hold. Last Friday, when commenting on the EU call for Turkish terrorism-rule changes, Erdogan said “we are going our way and you go yours.” He also dared the bloc to “go make a deal with whoever you can.” In a further sign of Ankara’s renewed confidence in dealing with the EU, Burhan Kuzu, a former adviser to Erdogan, said earlier on Wednesday that Turkey would send refugees to Europe should the EU Parliament make a “wrong decision” in the deliberations over visa-free status for Turkey. “That is blackmail,” said Sophie in ’t Veld, a Dutch member of the EU Parliament’s Liberal group. She called Erdogan a “dictator.” Cecilia Wikstroem, a Swedish Liberal, said “something is rotten in this.”

This is Europe’s epic failure. And that is what the UK Brexit vote next month is really about: do you want to be part of this?
• European Rights Watchdog Complains About Greek Refugee Camps Conditions (R.)
Urgent measures are need to address overcrowding and poor living conditions in refugee and migrant camps in Greece, Europe’s top rights watchdog warned on Wednesday. The Council of Europe, which brings together 47 countries, said some facilities were “sub-standard” and able to provide no more than the most basic needs such as food, hygiene products and blankets. The report echoes warnings by other rights groups and aid agencies who say Greece has been unable to care properly for the more than 800,000 people reaching its shores in the last year, fleeing wars or poverty in the Middle East and Africa. The Council described dire living conditions in several sites visited on a March 7-11 trip, just before the EU and Turkey reached a deal that reduced arrivals but increased the number of people held in detention awaiting asylum decisions or deportation.
It said in its report that people who reached Greece were locked away in violation of international human rights standards and lacked legal access. At Greece’s Nea Kavala temporary transit camp, people were left burning trash to keep warm and sleeping in mud-soaked tents, according to the report. The Council called for the closure of a makeshift camp in Idomeni, where some 10,000 people have been stranded en route to northern Europe due to the closure of Macedonia’s border. Germany has taken in most of the 1.3 million refugees and migrants who reached Europe across the Mediterranean in the past year, triggering bitter disputes among the 28 EU member states on how to handle the influx. Europe’s deal with Turkey last month gave its leaders some breathing space but has come under pressure since Prime Minister Ahmet Davutoglu, one of the sponsors of the accord, stepped down.
The morality and legality of the deal has been challenged by human rights groups, however, and a provision to grant Turkish citizens visa-free travel to Europe in exchange for Ankara’s help remains politically contentious. In a separate report, a trio of European Parliamentarians on Tuesday described the poor conditions faced by people who have been returned to Turkey under the deal. “We have seen how the migration policies imposed by the European Union have terrible consequences on the lives of thousands of people,” said Cornelia Ernst, a German member of the European Parliament and a co-author of that report. “Turkey has been hired as a deportation agency, putting into practice the migration policies designed in Brussels.”