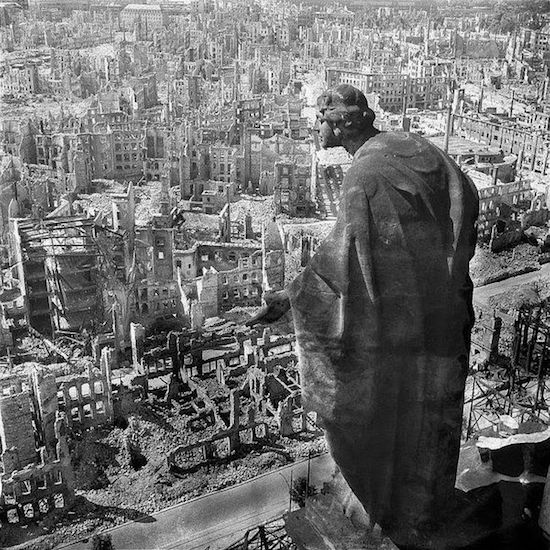
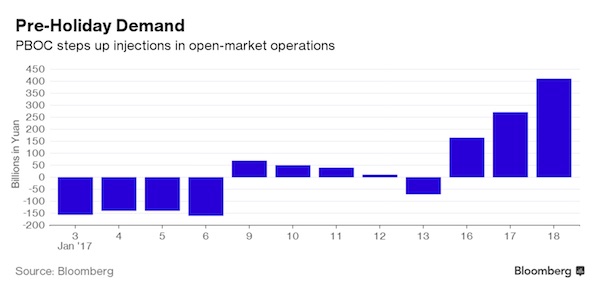
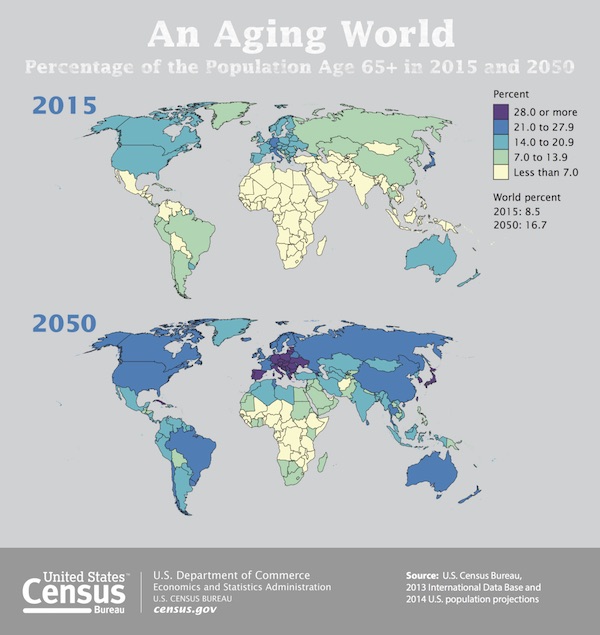
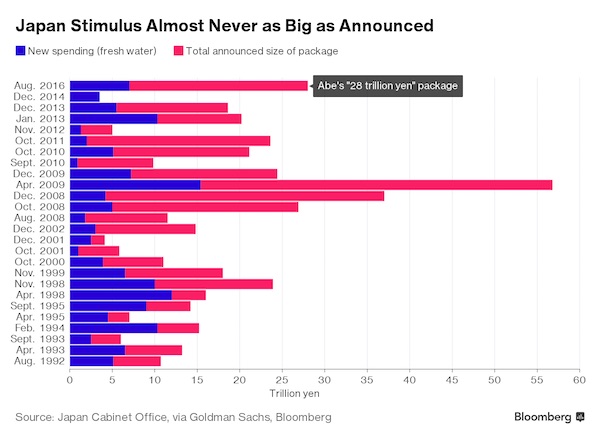
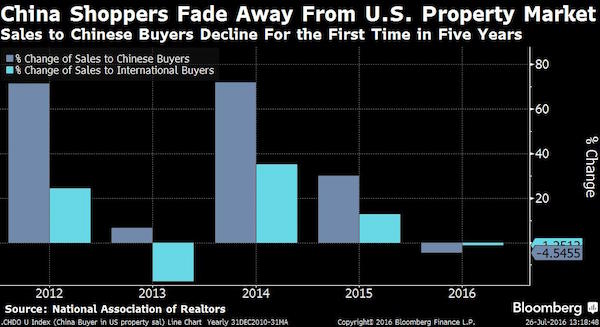
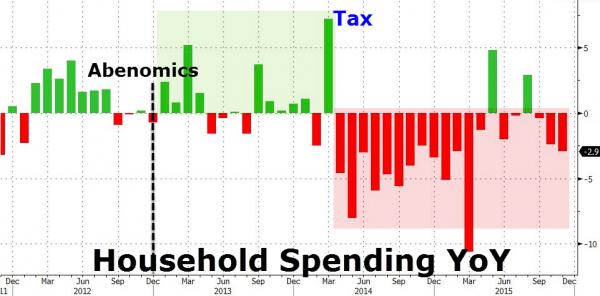
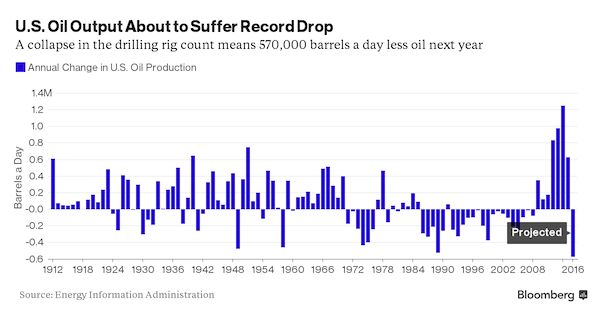
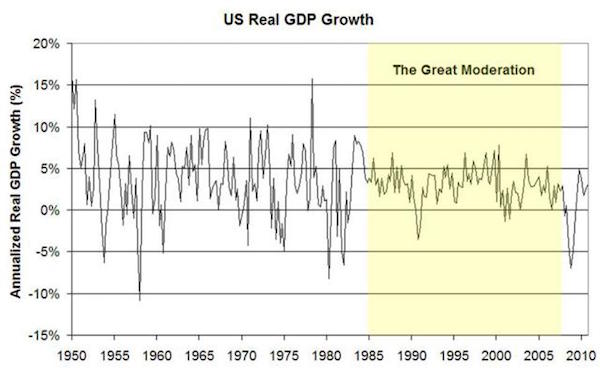
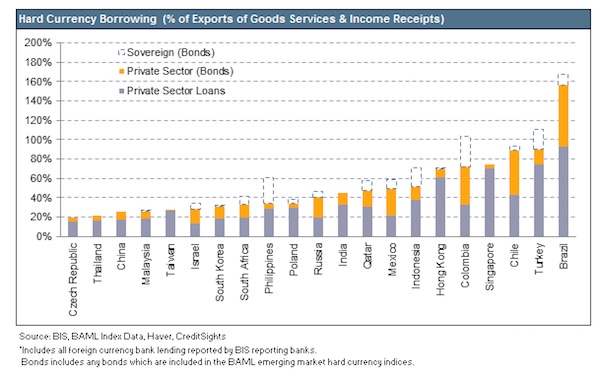
Dresden February 1945

The most striking thing about this is how utterly impossible it has become to find an objective discussion of it. I’ll go with Reuters.
• Trump Fires FBI Director Comey, Setting Off US Political Storm (R.)
U.S. President Donald Trump ignited a political firestorm on Tuesday by firing FBI Director James Comey, who had been leading an investigation into the Trump 2016 presidential campaign’s possible collusion with Russia to influence the election outcome. The Republican president said he fired Comey, the top U.S. law enforcement official, over his handling of an election-year email scandal involving then-Democratic presidential nominee Hillary Clinton. The move stunned Washington and raised suspicions among Democrats and others that the White House was trying to blunt the FBI probe involving Russia. Some Democrats compared Trump’s move to the “Saturday Night Massacre” of 1973, in which President Richard Nixon fired an independent special prosecutor investigating the Watergate scandal.
White House officials denied allegations that there was any political motive in the move by Trump, who took office on Jan. 20. Senate Democratic leader Chuck Schumer said he spoke to Trump and told him he was “making a very big mistake” in firing Comey, adding the president did not “really answer” in response. An independent investigation into Moscow’s role in the election “is now the only way to go to restore the American people’s faith,” Schumer said. Though many Democrats have criticized Comey’s handling of the Clinton email probe, they said they were troubled by the timing of Trump’s firing of him.
[..] Pushing back against critics of the move, White House officials said Deputy Attorney General Rod Rosenstein, a career prosecutor who took office on April 25, assessed the situation at the FBI and concluded that Comey had lost his confidence. Rosenstein sent his recommendation to Sessions, who concurred and they forwarded their recommendation to Trump, who accepted it on Tuesday, they said. The White House released a memo in which Rosenstein wrote: “I cannot defend the Director’s handling of the conclusion of the investigation of Secretary Clinton’s emails, and I do not understand his refusal to accept the nearly universal judgment that he was mistaken.”

The facts are classified.
• Turning Gen. Flynn into Road Kill (Robert Parry)
Not to defend retired Lt. Gen. Michael Flynn for his suspect judgment, but it should be noted that his case represents a disturbing example of how electronic surveillance and politicized law enforcement can destroy an American citizen’s life in today’s New McCarthyism. The testimony on Monday by former acting Attorney General Sally Yates and former Director of National Intelligence James Clapper offered no evidence of Flynn’s wrongdoing – those facts were deemed “classified” – yet the pair thoroughly destroyed Flynn’s reputation, portraying him as both a liar and a potential traitor. That Senate Democrats, in particular, saw nothing troubling about this smearing of the former director of the Defense Intelligence Agency and, briefly, President Trump’s national security adviser was itself troubling. Republicans were a bit more skeptical but no one, it seemed, wanted to be labeled as soft on Russia.
So, there was no skepticism toward Yates’s curious assertion that Flynn’s supposed lying to Vice President Mike Pence about the details of a phone call with Russian Ambassador Sergey Kislyak somehow opened Flynn to Russian blackmail – her core explanation for why she rushed to Trump’s White House with warnings of this allegedly grave danger. Yates also talked ominously about “underlying” information that raised further questions about Flynn’s patriotism, but that evidence, too, couldn’t be shared with the American people; it was classified, leaving it to your imagination the depth of Flynn’s perfidy. Despite the thinness of Yates’s charges – and the echoes of Sen. Joe McCarthy with his secret lists of communists that he wouldn’t release – the mainstream U.S. news media has bestowed on Yates a hero status without any concern that she might be exaggerating the highly unlikely possibility that the Russians would have blackmailed Flynn.
Her supposition was that since Vice President Mike Pence’s account of the Kislyak-Flynn conversation deviated somewhat from the details of what was actually said, the Russians would seize on the discrepancy to coerce Flynn to do their bidding. But that really makes no sense, in part, because even if the Russians did pick up the discrepancy, they would assume correctly that U.S. intelligence had its own transcript of the conversation, so there would be no basis for blackmail. Yates’s supposed alarm might make for a good spy novel but it has little or no basis in the real world. But it is hard for Americans to assess her claims because all the key facts are classified.

NATO has become an anti-ISIS vehicle. Wonder if they realize this. Turkey is a member.
• NATO Chief Finds a New Friend in Trump (Spiegel)
In Donald Trump’s eyes, NATO Secretary-General Jens Stoltenberg was actually the head of an alliance that history had made superfluous. The new American president made clear during his election campaign that he considered NATO to be a Cold War relic – cumbersome, expensive and useless. But when Stoltenberg appeared at a joint press conference during a visit to the new U.S. leader in the White House, nary a word indicated any resentment over NATO. “I said it was obsolete. It is no longer obsolete,” Trump said in a spectacular turnaround. So what happened? Stoltenberg chuckles at the question before fastening his seat belt. The Belgian air force passenger jet taxis onto the runway at the airport in Rome as it prepares to take off for Brussels. “We learn something new every day,” he says.
“Donald Trump and I discussed how NATO must further develop because the world has changed.” Above all, change means that the Europeans will have to increase their defense spending in the future – both Republican Trump and Social Democrat Stoltenberg are in agreement on the issue. In recent weeks, an alliance has formed between the two, very different men. The blustering U.S. president, who has little foreign policy experience, and the measured secretary-general from Norway are now pulling together, with both desiring more money for the alliance. Stoltenberg, 58, is now paying visits to European capitals in order to drum up the necessary funds. In two weeks, Trump plans to travel to Europe for the first time as U.S. president, and it is no coincidence that one of his first stops on May 25 will be to the massive new NATO headquarters in Brussels.
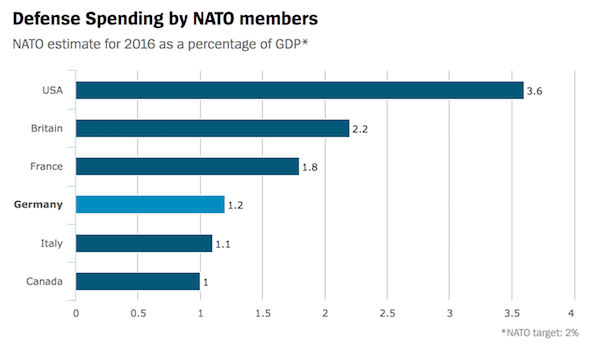
In addition to his demand for more money from other alliance members, Trump is also hoping NATO will take on a greater role in the fight against Islamic State (IS). He would like to see NATO join the U.S.-led coalition against the terrorist organization. Stoltenberg has long been of the opinion that the era of peace dividends has passed, particularly given Russia’s annexation of Crimea and the IS establishment of a “caliphate” in Syria and Iraq. But it was only with Trump’s election that his demands have gained significant momentum. Ironically, the very man who until recently considered NATO to be superfluous is now one of Stoltenberg’s closest allies.

And this flies straight in the face of Turkey’s NATO membership.
• Trump Approves Plan to Arm Syrian Kurds (NBC)
Two U.S. defense officials tell NBC News that President Donald Trump has approved a plan to arm the Syrian Kurdish militia — an important U.S. ally in Syria in the fight against ISIS. One of the officials said the move is significant because it supports the notion that the Syrian Democratic Force is the fighting force that will eventually go in to Raqqa, a city in Syria’s center which has been under ISIS control since 2014. The move also reinforces the idea that the entire Syrian Democratic Force, Syrian Kurds (YPG) and the Syrian Arab Coalition, has the backing of the U.S. Trump and members of the Cabinet spoke about it during a meeting late yesterday at the White House with Secretary of Defense James Mattis joining by video teleconference.
The order has been signed and that “allows the process to begin to function,” one official said. Once the order comes to the Pentagon, the U.S. can begin providing the Syrian Kurds with arms and equipment fairly quickly since some equipment is pre-positioned. [..] The Turks will be notified about the decision soon and the officials expect a strong reaction from them. In March, Secretary of State Rex Tillerson traveled to Turkey to meet with President Recep Tayyip Erdogan, who sees the YPG as terrorists.

Erdogan is not amused. And his recent attack on Israel won’t help.
• Turkey Hopes US Will End Support Of Syrian Kurdish YPG (R.)
Turkey hopes the United States will end its policy of supporting the Syrian Kurdish YPG militia, Deputy Prime Minister Nurettin Canikli said on Wednesday, adding that Ankara could not accept its NATO ally backing the group. Canikli’s comments are among the first official responses after U.S. officials said on Tuesday that President Donald Trump has approved supplying arms to the YPG to support an operation to retake the Syrian city of Raqqa from Islamic State. Ankara views the YPG as the Syrian extension of the outlawed Kurdistan Workers Party (PKK), considered a terrorist group by the United States, Turkey and Europe. The United States sees the YPG as a valuable partner in the fight against Islamic State in northern Syria.
“We cannot accept the presence of terrorist organizations that would threaten the future of the Turkish state,” Canikli said in an interview with Turkish broadcaster A Haber. “We hope the U.S. administration will put a stop to this wrong and turn back from it. Such a policy will not be beneficial, you can’t be in the same sack as terrorist organizations.” Turkish President Tayyip Erdogan is expected to meet Trump in Washington next week. Erdogan has repeatedly castigated the United States for its support for the YPG, saying its NATO ally should support it fully in the fight against terrorism. The Pentagon has sought to stress that it saw arming the Kurdish forces as necessary to ensure a victory in Raqqa, Islamic State’s de facto capital in Syria and a hub for planning the group’s attacks against the West.

Extremely incompetent. But the CIA doesn’t have to be competent, all it has to do is be secretive.
• Assange: ‘CIA Is Basically Useless, Incompetent’ (Exp.)
Mr Assange, declared by the Donald Trump administration as US public enemy number one, was speaking ahead of a live Spanish television interview. He told current affairs show When It’s Gone: “The CIA is basically useless. They are extremely incompetent as an organisation. “It is the organisation that gave us the end of democracy in Iran, Pinochet, the destruction of Libya, the rise of ISIS within Libya, al-Qaeda, the Syrian disaster and the Iraq war. “It is one of the most useless organisations in the world.” US intelligence agencies have concluded that Russia was behind the hack, and used Wikileaks to harm the chances of Mrs Clinton and favour Mr Trump. Mr Assange said the release was not intended to affect the election.

“This is the greatest suckers rally we’ve ever seen.”
• Stockman: There Is No Reason To Own Stocks At This Point In The Game (DR)
[..] “There will be panic in the financial markets. This is not priced in. The market isn’t expecting anything. I think it will cause some very difficult times.” The interviewer then asked what his expectations on a government shutdown would look like with Trump.” [..] “I doubt he’ll go for a shutdown by choice. The leadership is not going to stand for it. They have a false idea that Republicans can govern by keeping the Washington Monument open even if we’re bankrupting the country by piling spending. I don’t think they’re going to elect to have a shutdown. What I think is going to happen instead is they’re going to run out of borrowing authority with the debt ceiling, it is now frozen on March 15. We’re locked in at $19.8 trillion so when they run out of cash in a few months, they’ll need a majority in both houses to vote through a multi-trillion bill in both houses. They won’t have the votes.”
[..] “The market is pricing itself for perfection for all of eternity. This is crazy. We’ve got headwinds everywhere. The auto industry is now starting to roll over. The red ponzi in China has only a matter of time before it explodes. We now have debt for the household sector above where it was for the 2008 crisis. I think the market could easily drop to 1,300-1,600 by 30% or more once the fantasy ends. The government will show its true colors. We are headed for a fiscal bloodbath.” Stockman voiced his concern for clarity remarking, “This crazy notion that there is going to be a Trump tax cut and fiscal stimulus must be put to rest once and for all. It’s not going to happen. They can’t pass a tax cut that big without a budget resolution that incorporates $10 or $15 trillion of debt over the next decade. Week by week, slowly the market is beginning to figure this out.
What it means is, all of the corporate insiders are selling stock like there is no tomorrow… where institutional sales of stock have been going up since the election and what we have is the usual end of the cycle. This is the greatest suckers rally we’ve ever seen.” When asked what he would recommend to protect yourself he urged, “The main thing is, get out of the markets. These markets are unstable. They’re rigged and unsustainable… there is no reason to own stocks at this point in the game. It is so overvalued that maybe you can get another two or three out but you’re facing a 30% or 40% down. The risk versus reward is horrible. The bond market is one giant bubble because the central bank’s have been buying bonds worldwide. They’re buying a trillion and still buying a trillion or so on an annual basis. All of that is coming to a halt.”

Credit is still cheap. Even, or especially, depending on how you look at it, for zombies.
• Shale Drillers Are Outspending the World With $84 Billion Spree (BBG)
U.S. shale explorers are boosting drilling budgets 10 times faster than the rest of the world to harvest fields that register fat profits even with the recent drop in oil prices. Flush with cash from a short-lived OPEC-led crude rally, North American drillers plan to lift their 2017 outlays by 32% to $84 billion, compared with just 3% for international projects, according to analysts at Barclays. Much of the increase in spending is flowing into the Permian Basin, a sprawling, mile-thick accumulation of crude beneath Texas and New Mexico, where producers have been reaping double-digit returns even with oil commanding less than half what it did in 2014. That’s bad news for OPEC and its partners in a global campaign to crimp supplies and elevate prices. Wood Mackenzie estimates that new spending will add 800,000 barrels of North American crude this year, equivalent to 44% of the reductions announced by the Saudi- and Russia-led group.
“The specter of American supply is real,” Roy Martin, a Wood Mackenzie research analyst in Houston, said in a telephone interview. “The level of capital budget increases really surprised us.” Drilling budgets around the world collapsed in 2016 as the worst crude market collapse in a generation erased cash flows, forcing explorers to cancel expansion projects, cut jobs and sell oil and natural gas fields to raise cash. The pain also swept across OPEC, which in November relented by agreeing with several non-OPEC nations to curb output by 1.8 million barrels a day. Oil prices that initially popped above $55 in the weeks after the cut was announced have since dipped to around $46, reflecting pessimism that the OPEC-led deal can withstand the onslaught of U.S. shale.
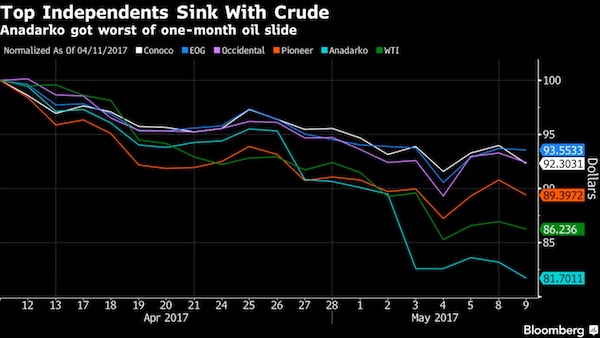
[..] EOG, the second-largest U.S. explorer that doesn’t own refineries, plans to boost spending by 44% this year to between $3.7 billion and $4.1 billion. Pioneer is eyeing a 33% increase to $2.8 billion. The sub-group that includes North American shale drillers like EOG and Pioneer is collectively targeting $53 billion in spending this year, up from $35 billion in 2016, according to the Barclays analysts. U.S. oil production is already swelling, even though output from the new wells being drilled won’t materialize above ground for months. The Energy Department’s statistics arm raised its full-year 2017 supply estimate to 9.31 million barrels a day on Tuesday, a 1% increase from the April forecast. Next year, U.S. fields will pump 9.96 million barrels a day, 0.6% more than the department estimated last month.

What are the odds anyone will be charged that May wants to keep on?
• UK Tory MPs Could Learn Fate Of Electoral Spending Inquiry By Wednesday (G.)
Dozens of Conservative MPs expect to learn shortly whether they will be charged with fraud in relation to their spending at the last election, as deadlines for the Crown Prosecution Service to make a decision approaches. MPs and their agents have been under investigation by 14 police forces for more than a year over their spending declarations at the 2015 election. They are now likely to learn their fates before the general election, possibly as soon as Wednesday as the various time limits for bringing charges are coming to an end. If it happens on Wednesday, this could be in time for Theresa May to jettison any candidates facing prosecution before the deadline for final nominations at 4pm on Thursday, but the timeline for replacements would be extremely tight.
Any decision to prosecute them would be an explosive twist in the general election with more than 20 MPs in the last parliament potentially facing charges under the Representation of the People Act. But the bar for prosecution is considered to be high, with the police having to prove intent to submit wrongful expenditure claims. Tory MPs maintain they recorded their spending as directed by the national party. The allegations centre around the declaration of spending on Conservative battle bus tour in 2015, which took activists to dozens of marginal seats before the election. This was declared as national campaign spending, with the Tories some millions below their official limit. But it emerged that the activists had been campaigning on behalf of specific Conservative MPs, rather than the party generally, leading to claims that the spending should have been record as local expenditure.

Bit of an oddity for now. But events could change that, fast.
• Anonymous Warns World To ‘Prepare’ For World War 3 (NYP)
The infamous hacktivist group Anonymous has released a chilling new video — urging people across the globe to “prepare” for World War 3 – as the US and North Korea continue to move “strategic pieces into place” for battle. “All the signs of a looming war on the Korean peninsula are surfacing,” the group says in the ominous six-minute clip, posted on YouTube over the weekend. Using their signature Guy Fawkes character, the hackers make several claims about recent military movements in the region — and alleged warnings made by Japan and South Korea about imminent nuclear attacks from the North — as they deliver their frightening prophecy. “Watching as each country moves strategic pieces into place,” the organization says, in its notorious robotic voice. “But unlike past world wars, although there will be ground troops, the battle is likely to be fierce, brutal and quick. It will also be globally devastating, both on environmental and economical levels.”
According to Anonymous, President Trump’s test of the Minuteman 3 intercontinental ballistic missile last week — coupled with a recent warning from Japanese officials to citizens, telling them to make preparations for a possible nuclear attack — are ultimately proof that all signs are pointing to a major conflict between the US and North Korea. In addition, China reportedly has urged its citizens in the Hermit Kingdom to return home as tensions continue to escalate over their nuclear weapons program. “This is a real war with real global consequences,” the group explains. “With three superpowers drawn into the mix, other nations will be coerced into choosing sides, so what do the chess pieces look like so far?”

Macron as evil incarnate.
• French Election A Catastrophe For World Peace (Paul Craig Roberts)
Marine Le Pen’s defeat, if the vote count was honest, indicates that the French are even more insouciant than Americans. The week before the election the Russian high command announced that Washington had convinced the Russian military that Washington intended a preemptive nuclear first strike against Russia. No European leader saw danger in this annoucement except Le Pen. No European leader, and no one in Washington, has stepped forward to reassure the Russians. In the US apparently only my readers even know of the Russian conclusion. Simply nothing is said in the Western media about the extraordinary risk of convincing Russia that the US is preparing a first strike against Russia. Nothing in the 20th century Cold War comes close to this. Le Pen, as Trump did prior to his castration by the military/security complex, understands that military conflict with Russia means death for humanity.
Why were the French voters unconcerned with what may be their impending deaths? The answer is that the French have been brainwashed into believing that to stand for France, as Marine Le Pen does, is to place patriotism and nationalism above diversity and is fascist. All of Europe, except for the majority of the British, has been brainwashed into the belief that it is Hitler-like or fascist to stand up for your country. For a French man or woman to escape the fascist designation, he or she must be Europeans, not French, German, Dutch, Italian, Greek, Spanish, Portuguese. Brainwashed as the French are that it is fascist to stand up for France, the French voted for the international bankers and for the EU. The French election was a disaster for Europeans, but it was a huge victory for the American neoconservatives who will now be able to push Russia to war without European opposition.

Macron as a hologram.
• Emmanuel Clinton and the Revolt of the Elites (Escobar)
So in the end the West was saved by the election of Emmanuel Macron as President of France: relief in Brussels, a buoyant eurozone, rallies in Asian markets. That was always a no-brainer. After all, Macron was endorsed by the EU, Goddess of the Market, and Barack Obama. And he was fully backed by the French ruling class. This was a referendum on the EU – and the EU, in its current set-up, won. Cyberwar had to be part of the picture. No one knows where the MacronLeaks came from – a last minute, massive online dump of Macron campaign hacked emails. WikiLeaks certified the documents it had time to review as legitimate. That did not stop the Macron galaxy from immediately blaming it on Russia. Le Monde, a once-great paper now owned by three influential Macron backers, faithfully mirrored his campaign’s denunciation of RT and Sputnik, information technology attacks and, in general, the interference of Russia in the elections.
The Macron Russophobia in the French media-sphere also happens to include Liberation, once the paper of Jean-Paul Sartre. Edouard de Rothschild, the previous head of Rothschild & Cie Banque, bought a 37% controlling stake in the paper in 2005. Three years later, an unknown Emmanuel Macron started to rise in the mergers and acquisitions department, soon acquiring a reputation as “the Mozart of finance.” After a brief stint at the Ministry of Finance, a movement, En Marche! was set up for him by a network of powerful players and think tanks. Now, the presidency. Welcome to the revolving door, Moet & Chandon-style. In the last TV face-off with Marine Le Pen, Macron did not shy from displaying condescending/rude streaks and even raked some extra%age points by hammering “Marine” as a misinformed, corrupt, “hate-filled” nationalist liar who “feeds off France’s misery” and would precipitate “civil war.”
That may in fact come back to haunt him. Macron is bound to be a carrier of France’s internal devaluation; a champion of wage “rigor,” whose counterpoint will be a boom of under-employment; and a champion of increasing precariousness on the road to boost competitiveness. Big Business lauds his idea of cutting corporate tax from 33% to 25% (the European average). But overall, what Macron has sold is a recipe for a “see you on the barricades” scenario: severe cuts in health spending, unemployment benefits and local government budgets; at least 120,000 layoffs from the public sector; and abrogation of some key workers’ rights. He wants to advance the “reform” of the French work code – opposed by 67% of French voters – ruling by decree.

Macron as a greater fool.
• Paris Afterparty (Jim Kunstler)
First mistake: Emmanuel Macron’s handlers played Beethoven’s “Ode to Joy” instead of the French national anthem at the winner’s election rally. Well, at least they didn’t play “Deutschland Über Alles.” The tensions in the Euroland situation remain: the 20%-plus youth unemployment, the papered-over insolvency of the European banks, and the implacable contraction of economic activity, especially at the southern rim of the EU. The clash of civilizations brought on by the EU’s self-induced refugee glut still hangs over the continent like a hijab. That there was no Islamic terror violence around the election should not be reassuring. The interests of the jihadists probably lie in the continued squishiness of the status quo, with its sentimental multiculture fantasies — can’t we all just get along? — so En Marche was their best bet. LePen might have pushed back hard. Macron looks to bathe France’s Islamic antagonists in a nutrient-medium of Hollandaise lite.
The sclerosis of Europe is assured for now. But events are in charge, not elected officials so much, and Europe’s economic fate may be determined by forces far away and beyond its power to control, namely in China, where the phony-baloney banking system is likely to be the first to implode in a global daisy-chain of financial uncontrolled demolition. Much of that depends on the continuing stability of currencies. The trouble is they are all pegged to fatally unrealistic expectations of economic expansion. Without it, the repayment of interest on monumental outstanding debt becomes an impossibility. And the game of issuing more new debt to pay the interest on the old debt completely falls apart. Once again, the dynamic relationship between real capital creation and the quandaries of the oil industry lurks behind these failures of economy.
In a crisis of debt repayment, governments will not know what else to do except “print” more money, and this time they are liable to destroy faith in the value of “money” the world over. I put “money” in quotation marks because the dollars, euros, yuan, and yen are only worth what people believe them to be, subject to measurement against increasingly fictional indexes of value, such as interest rates, stock and bond markets, government-issued employment and GDP stats, and other benchmarks so egregiously gamed by the issuing authorities that Ole Karl Marx’s hoary warning finally comes to pass and everything solid melts into air.
Revolving credit seemed like a good idea through the 20th century, and it sure worked to build an economic matrix based on cheap energy, which is, alas, no more. What remains is the wishful pretense that the old familiar protocols can still work their magic. The disappointment will be epic, and the result next time may be political figures even worse than LePen and Trump. Consider, though, that what you take for the drumbeat of nationalism is actually just a stair-step down on a much-longer journey out of the globally financialized economy. Because the ultimate destination down this stairway is a form of local autarky that the current mandarins of the status quo can’t even imagine.

They want it all, all of Greece. Beware.
• Germany: Greek Gold, Real Estate As Collateral If IMF Out Of Program (KTG)
The Bavarian Minister of Finance, Markus Soeder (CSU), a fierce Grexit supporter of Merkel’s CDU sister party apparently has moved away from his demand for a Greek euro exit. During a visit to Athens, Soeder said that the problems around Britain’s exit from the EU showed how difficult a Grexit would be. In addition, the Brexit already causes enough uncertainty. and Germany wants neither problems, nor uncertainty that could harm its profits especially before the parliamentary elections in autumn 2017. As Grexit is out of question, Greece should use gold reserves and real estate as collateral if the IMF stays out of the Greek program. However, Markus Soeder brought back an older idea of his, an idea he openly formulated in February 2017: that Greece pledges Gold, cash and real estate in order to get the bailout tranches, the loans by the European creditors, who love to call them financial aid.
“Soeder did not give up serious demands on Greece wile he was in Athens,” German magazine Der Spiegel writes. If the IMF does not participate in the Greek program, “new money can only be provided against collateral such as cash or real estate,” Soeder said. Soeder referred to Finland that participated in the second aid package for Greece only in 2012 and only after then Greek finance minister Evangelos Venizelos signed a bilateral agreement on colateral. “This worked,” the CSU politician said about the deal. Soeder’s demand is, however, amply theoretical, since he continues to regard an IMF participation as indispensable. He has the same problem as Federal Minister of Finance Wolfgang Schäuble (CDU): He strongly rejects further debt relief, as the IMF makes it a condition. “I have made it quite clear that a debt cut is out of question for Germany, as it the idea about issuing Eurobonds or similar.”

Brussels pisses on Greek courts.
• Greek Court Finds New Pension Cuts Illegal Under Greek, European Law (K.)
The Plenary of the State Audit Council has ruled that the cuts to main and supplementary pensions that the government and its creditors have agreed on contravene the European Convention of Human Rights, sources said on Tuesday night. The council also decided that the fiscal bill containing the cuts, to be implemented from 2019, contravenes Greek legislation as it has been tabled to the audit council without an actuarial study. A bill, outlining the pension cuts and other measures agreed with creditors is due to go to a vote in Parliament next week.

Nothing new here. WIll anything change now that an EU body finds the same many others have before them?
• Damning Findings From EU Audit Of Greek & Italian Refugee “Hotspots” (Oxfam)
1. EU Court of Auditors found “overcrowded” camps, migrants “sleeping rough”, and “scant access to basic services” According to the Court of Auditors, hotspots are seriously overcrowded, particularly on the Greek islands of Lesvos, Chios and Samos. People are fleeing from the camps, because they don’t have sufficient access to water and there are too few doctors to provide adequate health care. People also didn’t feel safe in the hotspots since fights often break out in the camps. Many of these people ended up sleeping on the streets outside the hotspots. The appalling situation in hotspots is also documented by NGOs, who have reported that people in the hotspots have been exposed to degrading conditions and had their rights denied. More than 2,000 people were forced to sleep in barely heated tents during the freezing winter.
2. Children held for months in “inappropriate conditions” against international laws and standards, the auditors say The auditors raised serious concerns about the situation of unaccompanied children in hotspots. In most hotspots children were confined either to fenced areas, or accommodated without protection from adults, exposing them to the risk of abuse. Children were held for three months or more closed in behind fences in the Moria hotspot after it was converted to a de-facto detention centre. In some hotspots, girls and boys were held together, against standard practice. NGOs have been raising concerns about this situation for months. Now the Court of Auditors has confirmed that the welfare of the children in Moria was put at risk.
3. ‘‘No framework for remedying bottlenecks or sharing lessons learnt”, the Court found Overall, the ‘hotspot approach’ has been disorganised and inconsistent, the EU auditors found. The absence of consistent guidelines for the way hotspots should be managed means that responsibilities between the various actors are not clearly defined. Conditions and services are far worse in some hotspots than in others. The unfairness of this inconsistency has been criticised by NGOs, who have also highlighted the lack of oversight over decisions and accountability for human rights violations.
Furthermore, it is difficult to track the situation of people in the hotspots and how the management of the camps affects them – because key data is not shared between authorities. Neither the length of time migrants spend in hotspots while waiting to register and complete their asylum application in Greece, nor the total number of migrants identified, registered, or receiving return orders in Italy was shared. The Court of Auditor’s recommendations to better define the roles of the different agencies involved and to appoint a manager for each hotspot exposes that management is currently lacking.
4. The auditors highlight that the “functioning of hotspots is affected by bottle-necks in the follow-up procedures” The hotspots were meant to be just a first step in the EU’s migration response. Member states should then have stepped in to facilitate the relocation and integration of these people across Europe, or facilitate their safe and dignified return. That has not happened. The set-up of the hotspots is a completely new way for national governments to cooperate with EU institutions and agencies within a member state’s territory. If follow up continues to falter, the pressure on the hotspots will only grow. This could lead to people living in the hotspots being exposed to even more suffering, and the risk that authorities will abandon acceptable legal and living standards increases. This has been evident since December, if not earlier.
5. The EU-Turkey deal “had a major impact on the functioning of hotspots” and on detentions, the auditors say The EU-Turkey deal of March 2016 had a great impact on the functioning of the hotspots, as becomes evident when we look at the details of the auditors’ report. When the deal with Turkey was announced, hotspots turned into de-facto detention centres, provoking criticism from many NGOs. But the current European approach only attempts to increase the use of detention for asylum seekers even further. The auditors have detailed the hotspots procedures in the annex to their report, and reading this makes clear how difficult it is not to be detained in the process they record.
The findings of the European Court of Auditors suggest that hotspots are being made to work at the expense of people, for the sake of fulfilling policy objectives. It is vital that safeguards are in place to ensure that people are not forced to stay in the hotspots under the conditions the EU auditors and NGOs have found to be degrading. Very close scrutiny is needed to protect the rights of those who arrive looking for safety on Europe’s shores.