Harris&Ewing Army Day Parade, Memories of the World War, Washington DC 1939



This won’t stop until everyone who wants to sell, has. That’s the difference between markets and central control.
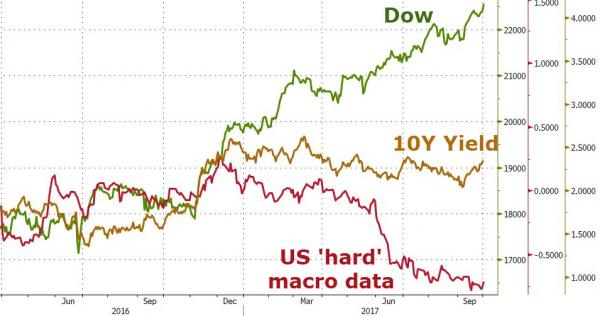
• China Stock Markets Shuttered -Again- After Falling 7% (FT)
China’s entire equity market was shuttered within half an hour of opening after falling 7% on further currency weakness as government rescue efforts failed to deter the tide of sellers. China’s stock market meltdown and currency depreciation have spooked international investors in a replay of last summer’s rout that reverberated around the globe. So far this year — just four days — the bluechip CSI 300 index is down 12%. Newly minted circuit breakers, introduced and first tripped on Monday, kicked in again on Thursday after the CSI 300 fell 7%. Trading was halted for 15 minutes after the index lost 5%, but as stocks continued to fall the full-day closure was triggered. Investors were rattled by further weakening of the renminbi, said Wang Jun at China Securities in Beijing. “It was a panicked response to the forex market,” he said.
“Accelerating exchange-rate depreciation could lead to liquidity problems. Valuations can’t help but take a pounding.” The renminbi fell to its weakest level in nearly five years on Thursday, with capital outflow pressure still heavy even after more than a year of nearly uninterrupted outflows. The renminbi was 0.6% weaker on Thursday morning at 6.5928 per US dollar after falling by roughly the same amount on Wednesday. Policymakers appear uncertain about whether to wade back in to buy stocks with state funds or to stand back. On Tuesday, the “national team” of state-owned financial institutions appeared to re-enter the stock market after remaining on the sidelines since late August. Goldman Sachs estimated in September that the government had spent Rmb1.5tn ($234bn) to support the stock market in July and August, when the main index was down by as much as 45% from its late-June high.
The “national team” owned at least 6% of tradable market capitalisation in the Shanghai and Shenzhen exchanges at the end of the third quarter. On Wednesday, the stock market had clawed back some lost ground after state media said the securities regulator would extend a ban on share sales by large shareholders. After the trading halt on Thursday, the regulator published new permanent rules restricting share purchases by large shareholders, as well as by corporate management and directors. Starting January 9, large shareholders can sell a maximum of 1% of a company’s shares every three months. They also must disclose stake-cutting plans 15 days in advance. The China Securities Regulatory Commission said the new rules should help to stem panic-selling.
Read more …

Christine Lagarde will have to speak out.
• China Jolts Markets With Sharply Lower Yuan Fix (CNBC)
China’s central bank guided the yuan lower on Thursday at the fastest pace since its shock devaluation in August, prompting a shuttering of mainland stocks and roiling markets elsewhere. The People’s Bank of China (PBOC) set the yuan reference rate at 6.5646 against the dollar, down 0.51% from Wednesday’s fix. That represents the largest daily change in the fix since August 13, according to Reuters data. The yuan had finished at 6.5554 on Wednesday. China’s central bank lets the yuan spot rate rise or fall a maximum of 2% against the dollar, relative to the official fixing rate. Thursday’s fix jolted markets, with the more freely-traded offshore yuan plunging to a record low of 6.7511 against the dollar before recovering to 6.6910 on suspected intervention. The onshore yuan rate fell to as much as 6.5932.
Equity markets in the region tumbled, with Chinese stocks closing for the day after the CSI 300 index fell more than 7%, triggering a circuit breaker. “The PBOC said the fix will be based on the previous day’s close and a softer fix is therefore not inconsistent with market forces,” said Vishnu Varathan, head of economics and markets strategy at Mizuho Bank’s Singapore office. “There is a sense in the market that the offshore market is getting carried away though and the PBOC would want to rein in excessively aggressive one-way bets,” he said. The currency moves have revived a litany of concerns in financial markets, from the health of the Chinese economy to the impact of a weaker yuan on capital outflows, which have accelerated in recent months. The more stocks fall on cues from a lower yuan, the more investors may be encouraged to yank funds out of China and park them overseas, in turn exerting further pressure on the yuan.
Read more …

Out of their hands.
• Offshore Yuan Rises From Five-Year Low as PBOC Puzzles Markets (BBG)
The offshore yuan strengthened the most in two months amid speculation the central bank propped up the exchange rate after setting a weaker fixing that sent it into a tumble. The currency swung from a 0.3% gain to a 0.7% loss and back in the space of about 30 minutes, spurring intervention speculation and creating confusion about what the central bank is trying to achieve. The yuan turmoil sent mainland shares into a spiral, forcing an early trading halt for the second day this week. “China isn’t communicating its policy intentions in a clear manner,” said Sue Trinh at Royal Bank of Canada in Hong Kong. “It is sending confusing signals to the market. And it’s disappointing that their communication policy is less than transparent.”
The offshore yuan advanced 0.44% to 6.6837 a dollar as of 12:10 p.m. in Hong Kong, according to data compiled by Bloomberg, after reaching the weakest level since September 2010. The spot rate in Shanghai plunged 0.57% to a five-year low of 6.5923. The People’s Bank of China reduced its fixing, which restricts onshore moves to a maximum 2% on either side, by 0.51% to 6.5646, the lowest since March 2011. “We saw aggressive intervention in the offshore yuan market,” said Zhou Hao at Commerzbank in Singapore. “We don’t really understand the rationale behind the market movements in the past few days. Obviously, these movements have reminded us of the market rout last year.”
Read more …

Article says 11-year low, but reality caught up.
• Global Oil Prices Hit 12-Year Low (Reuters)
Brent crude futures fell to a fresh 11-year low on Thursday as a sliding yuan and an emergency halt in China’s stock trading left Asian markets in a turmoil, while a huge supply overhang and near-record output levels also continued to drag on oil prices. China accelerated the devaluation of the yuan on Thursday, sending currencies across the region reeling and domestic stock markets tumbling, as investors feared the Asian giant was kicking off a virtual trade war against its competitors. Trading on its stock markets was suspended for the rest of the day, the second time this week, and China’s securities regulator intervened heavily by issuing rules to restrict share sales by listed companies’ major shareholders.
Tracking the weakness across financial markets, the global benchmark Brent fell to $33.09 per barrel, the weakest since 2004 and below the previous 11-year low from Wednesday. Prices, however, edged back to $33.42 by 0440 GMT. “With oil markets producing 1 million barrels a day in excess (of demand) and very little sign of any rational response from the supply side, it’s little wonder we’re seeing pressure again,” said Michael McCarthy at CMC Markets in Sydney. Global oil prices have crashed 70% since mid-2014 as near-record output from major producers such as OPEC, Russia and North America has left storage tanks brimming with supplies. Exacerbating the oil market woes is a weakening demand, especially in Asia, home to the world’s No.2 oil consumer, China, that is seeing the slowest economic growth in a generation.
“The Chinese economy actually contracted in December and that’s adding fire to fears of a more rapid slowdown in the world’s second biggest economy,” McCarthy said. Financial markets fear the yuan’s rapid depreciation may accelerate, which would mean China’s economy is even weaker than had been imagined. Offshore yuan fell to a fresh record low on Thursday since trading started in 2010. With the global economy looking shaky due to China’s slowdown, analysts said the outlook for oil remains for cheap prices for much of this year. “We think low $30’s (per barrel) is a floor, but once positioning gets so biased anything can happen,” said Virendra Chauhan at Energy Aspects in Singapore.
Read more …

China already did pre-empt the stock sale ban that was supposed to expire: “The CSRC capped the size of stakes that major investors are allowed to sell at 1% of a company’s shares for three months effective Jan. 9..”
• Shanghai Fund Manager Dumps All Holdings in ‘Insane’ Market (BBG)
A Shanghai fund dumped all its holdings as Chinese shares tumbled and triggered a circuit-breaker that halted trading in the world’s second-biggest stock market. “This is insane,” Chen Gang, CIO at Shanghai Heqi Tongyi Asset Management, said in an interview on Thursday. “We were forced to liquidate all our holdings this morning,” said Chen, whose firm manages about 300 million yuan ($45.5 million). China’s CSI 300 Index plunged 7.2% before trading was halted by automatic circuit-breakers for the second time this week, after a weaker-than-estimated yuan fixing fueled concern that slowing economic growth is prompting authorities to guide the currency lower. Many private funds and hedge funds in China have agreements with investors spelling out mandatory liquidation levels if their holdings drop below a certain value.
Chinese regulators have imposed a limit on the amount of stock major corporate shareholders can sell as authorities move to curb the nation’s market rout. The CSRC capped the size of stakes that major investors are allowed to sell at 1% of a company’s shares for three months effective Jan. 9, the regulator said in a statement on Thursday. The restriction replaces an existing six-month ban on any secondary market stock sales that is due to expire Friday, it said. Chen, who commented before the CSRC announced its new caps, said he “won’t consider getting back into the market until that overhang is gone and CSRC improves its circuit-breaker system, for instance by extending the 15-minute break to half an hour.”
The Shanghai Heqi Tongyi manager, whose fund started mid-year in 2015, regretted the timing of its launch and said it “couldn’t be worse.” Chen isn’t alone in criticizing the circuit-breaker rule introduced Monday, which many say exacerbates a liquidity squeeze as investors rush for the exits before trading halts kick in. Under the new rule, a drop of 5% suspends trading for 15 minutes, while a decline of 7% halts the market for the rest of the day. “A trading break of 15 minutes or even longer wouldn’t ease their nerves or get them a clear picture of the fundamentals,” said Polar Zhang at BOC International. “On the contrary, it’s draining liquidity as everybody tries to get out of the door before the door is closed.”
Read more …

Deflation.
• It’s All Bad News for Markets Buckling Under China, Fed, Economy (BBG)
New year, same fears. Except now they’re hitting all at once. For U.S. stocks it’s meant the worst start since the financial crisis, while volatility in Europe has exploded to levels not seen in a decade. From China’s weakening currency to the rout in oil to the withdrawal of Fed stimulus and gains in the cost of financing business, things that keep investors up at night are climbing out from under the bed again in 2016. While little of it is new, the persistence is troubling, especially when buffers such as valuations and central bank support are turning against bulls. The result has been one of the fastest retreats from risk ever by investors coming back from New Year’s holiday. Just days into 2016, Wall Street firms from Citigroup to Royal Bank of Canada have already scaled back bullish calls for American equities this year, while single-stock analysts forecast fourth-quarter profits will shrink by more than 6% after predicting an expansion in August.
“The market obviously rises on the wall of fear, but right now the fear is looking a little bit more realistic,” said Brad McMillan at Commonwealth Financial Network. Over three days, more than $2 trillion has been wiped from the value of global equities, volatility in the broadest stock gauges has jumped 13% or more, and more than 8% was shorn from the price of oil. China’s Shanghai Composite Index plunged almost 7% to start the year while everything from junk bonds to cocoa and coffee has tumbled. As has been true before, the proximate cause is China. Data showing weakness in manufacturing this week sparked a tumble in the CSI 300 Index. Markets were roiled Wednesday when the nation’s central bank unexpectedly set the yuan’s daily reference rate at the lowest level since April 2011, fueling concern over the strength of the world’s second-largest economy.
Read more …

“Almost $2.5 trillion was wiped from the value of global equities this year through Wednesday, and losses deepened in Asia on Thursday..”
• George Soros Sees Crisis in Global Markets That Echoes 2008 (BBG)
Global markets are facing a crisis and investors need to be very cautious, billionaire George Soros told an economic forum in Sri Lanka on Thursday. China is struggling to find a new growth model and its currency devaluation is transferring problems to the rest of the world, Soros said in Colombo. A return to positive interest rates is a challenge for the developing world, he said, adding that the current environment has similarities to 2008. Global currency, stock and commodity markets are under fire in the first week of the new year, with a sinking yuan adding to concern about the strength of China’s economy as it shifts away from investment and manufacturing toward consumption and services.
Almost $2.5 trillion was wiped from the value of global equities this year through Wednesday, and losses deepened in Asia on Thursday as a plunge in Chinese equities halted trade for the rest of the day. “China has a major adjustment problem,” Soros said. “I would say it amounts to a crisis. When I look at the financial markets there is a serious challenge which reminds me of the crisis we had in 2008.”
Read more …

Emerging markets will keep plummeting.
• Fears Mount Over Rise Of Sovereign-Backed Corporate Debt (FT)
More than $800bn of emerging market sovereign debt is being camouflaged by the growing use of bonds that offer implicit state backing without always appearing on government balance sheets, according to new research. The stock of so-called quasi-sovereign bonds issued in dollars and other hard currencies by emerging markets has risen sharply in the past 12 months to overtake that of all external emerging market sovereign debt by the end of 2015. The growing use of such bonds suggests that developing countries are increasingly transferring debt obligations to third parties that have taken advantage of historically low interest rates to load up with cheap debt. Emerging markets are already under strain as the US dollar strengthens against the renminbi and other emerging market currencies, making the cost of servicing debt denominated in dollars harder to bear.
Although official debt-to-GDP levels of countries such as India, Russia and China remain low by global standards, the growth of less visible debt which they might still have to guarantee in a crisis underlines the potential scale of their liabilities. “This has been a source of worry for some time, in part because it does not always appear on government balance sheets.” said Lee Buchheit, a partner at Cleary Gottlieb and expert on sovereign debt default. “Emerging markets have benefited from interest rates at historic low levels and commodity prices at historic highs,” he said: “In the last year both of these have begun to unwind. If the resulting strains on a country compel a sovereign debt rearrangement of some kind, these contingent liabilities of the sovereign will need to be addressed.”
New figures from JPMorgan and Bond Radar show that issuance of quasi-sovereign bonds outpaced that of sovereign bonds in emerging markets last year, raising the stock of such debt from $710bn in 2014 to a record $839bn by the end of 2015. By comparison, the stock of all external emerging market sovereign debt stood at $750bn at the end of last year, according to JPMorgan. The cost of selling bonds with either an explicit or implicit guarantee of the government is lower than other corporate bonds. Quasi-sovereign borrowers include 100% state-owned entities such as Mexico’s Pemex, local governments in countries such as China, and entities in which the government owns more than 50% of the equity or has more than 50% of the voting rights — a description that encompasses Brazil’s Petrobras.
However, the treatment of such debt is not uniform. Bonds issued by Pemex are included in debt-to-GDP calculations for Mexico, but this is unusual, and only 19 of the 181 quasi-sovereign bonds tracked by JPMorgan carry an explicit sovereign guarantee. [..] Emerging markets’ quasi-sovereign bonds are now suffering from the same diminishing capital flows and rising borrowing costs plaguing the developing world, thanks to the strengthening US dollar, weakening commodity prices and fears of slowing Chinese growth. Poor performance has already hurt the credit ratings of countries that back them. Last year, Standard & Poor’s and Fitch, two of the world’s three big credit rating agencies, cut Brazil’s rating to junk in part because of the growing risks associated with Petrobras. “What can really break the dam is the quasi-sovereign element in EM external debt,” says Gary Kleiman of Kleiman International, an emerging market investment consultant. “People have always assumed there is an implicit backing, but that capacity has not been called into question explicitly.”
Read more …

Paycheck to paycheck.
• A $500 Car Repair Bill Would Send Most Americans Scrambling (WSJ)
An unexpected car repair or medical bill would cause the vast majority of Americans to scramble because they lack the needed funds in their savings accounts. Only 37% of adults have the necessary savings to cover a $500 car repair or a $1,000 emergency room bill, according to a survey Bankrate.com released Wednesday. The finding is little changed from last year, when 38% said they didn’t have the cash on hand, despite a year of steady job creation and the unemployment rate falling to 5%. “Most Americans are ill-prepared for life’s inevitable curveballs,” said Sheyna Steiner, Bankrate.com’s senior investing analyst. She said that’s a concern because more than 40% of families experienced a similar unexpected cost during the past 12 months.
Without the savings, 23% of those surveyed said they would have to cut back on spending elsewhere, and 15% said they would turn to credit cards. The same share said they would have to borrow from friends or family. The data suggests that many households are still on uncertain financial footing more than six years after the recession ended. However, other figures indicate Americans are earning, and saving, more. The personal saving rate was 5.5% in November, the second-highest level since the start of 2013, the Commerce Department said last month. Lower gasoline prices and solid income gains in recent months are supporting savings. Wages increased 2.3% from a year earlier in November, the Labor Department said, even as consumer inflation held near zero.
The Bankrate survey found that preparedness for unexpected expenses varied widely by income level. Just 23% of those earning less than $30,000 annually had the needed savings, while 54% of those earning more than $75,000 annually said they would have the cash on hand.
Read more …

“In Britain we’ve already experimented with a system in which one group of people receive a guaranteed income with no obligation to work for it. But what if this was extended beyond the royal family?”
• If A Basic Income Works For The Royal Family, It Can Work For Us All (Guardian)
My first response to the notion of a universal basic income (UBI) was: “Well, really. That is never going to happen! I mean, it’s completely unaffordable. I mean, it would be political suicide for any progressive party suggesting it.” And then I may have started to froth at the mouth slightly and ask if it would be paid to refugees. Yet this year will see a UBI paid to residents of Utrecht and 19 other Dutch municipalities. Everyone will get about £150 a week, whether working or not. The unemployed won’t find themselves penalised for finding work, and the hope is that the state will spend less money snooping on benefit claimants, moving on the homeless or locking up those driven to crime. Advocates of this radical idea are keen to quash any notion that recipients of free money will just use it to lie around all day getting stoned.
This is why it is being piloted in Holland. The idea is so refreshingly contrary to the petty conditionality that is killing the welfare state that it began to fill me with optimism that there may be a few people lying in this political gutter still looking at the stars. Once upon a time, universality was the underpinning principle of welfare. Every mother got child benefit; every child got free school milk, until that was snatched away by … Oh, I can’t remember – I’m not one to bear grudges. In Britain we’ve already experimented with a system in which one group of people receive a guaranteed income with no obligation to work for it. But what if this was extended beyond the royal family? Imagine now if everyone in the UK started out with a guaranteed minimal amount of money each week.
All other benefits would be done away with, along with the stigma and entrapment that came with the old system of welfare (and the expense of policing and administering it). The idea of the UBI is so contrary to everything that has been drummed into us about preventing the “something for nothing society”, it’s worth advocating it just to see the Daily Mail and Iain Duncan Smith implode with outrage. The predictable argument that will be rolled out is that it will turn the masses from “strivers into skivers”; it will lead to welfare dependency, a lack of initiative and lots of programmes on Channel 5 called Fat Ugly People Spending Your Money on Crisps and Big Tellies.
Read more …

Vanguard for a much bigger trend.
• Macy’s To Cut Jobs, Shut Stores Amid Weak Holiday Sales (Reuters)
Macy’s said it will eliminate more than 2,000 jobs and consolidate operations after reporting weak holiday sales, highlighting a downturn in apparel demand that has likely taken a similar toll on other department stores and clothing chains. Macy’s said comparable sales at stores open for more than a year tumbled by 4.7% in November and December, far worse than what it had estimated in November, and it cut its earnings outlook for the second time in two months. Macy’s, which operates the upscale Bloomingdale’s chain as well as its namesake Macy’s department stores, estimated that 80% of the fall was due to unusually warm weather, which discouraged purchases of sweaters, coats and gloves. It also blamed the strong dollar for keeping tourists from visiting the United States and spending money at its flagship stores.
The company’s shares rose 2.8% to $37.15 in after-hours trading on Wednesday as investors cheered its plan to reduce costs by $400 million by consolidating regions and call-centers. The jobs to be eliminated include 3,000 store workers, though about half of those employees will be put in other positions, as well as hundreds of back-office and senior executive posts, the company said in a press release. “Macy’s is cutting the fat, becoming a leaner organization,” said Lisa Haddock, marketing lecturer at San Diego State University, of why the shares rose. But Haddock said Macy’s, like many other traditional bricks-and mortar retailers, faced an uncertain future as more and more consumer demand shifted online. “Macy’s doesn’t seem to have a unique spot in consumers’ minds,” she said.
Read more …

Essential: “..the banks have very good reasons not to “fulfil their purpose” today, because that purpose is not what Joe thinks it is. Banks don’t “intermediate loans”, they “originate loans”..”
• Note To Joe Stiglitz: Banks Originate, Not Intermediate (Steve Keen)
I like Joe Stiglitz, both professionally and personally. His Globalization and its Discontents was virtually the only work by a Nobel Laureate economist that I cited favourably in my Debunking Economics, because he had the courage to challenge the professional orthodoxy on the “Washington Consensus”. Far more than most in the economics mainstream—like Ken Rogoff for example—Joe is capable of thinking outside its box. But Joe’s latest public contribution—“The Great Malaise Continues” on Project Syndicate—simply echoes the mainstream on a crucial point that explains why the US economy is at stall speed, which the mainstream simply doesn’t get. Joe correctly notes that “the world faces a deficiency of aggregate demand”, and attributes this to both “growing inequality and a mindless wave of fiscal austerity”, neither of which I dispute. But then he adds that part of the problem is that “our banks … are not fit to fulfill their purpose” because “they have failed in their essential function of intermediation”:
Between long-term savers (for example, sovereign wealth funds and those saving for retirement) and long-term investment in infrastructure stands our short-sighted and dysfunctional financial sector… Former US Federal Reserve Board Chairman Ben Bernanke once said that the world is suffering from a “savings glut.” That might have been the case had the best use of the world’s savings been investing in shoddy homes in the Nevada desert. But in the real world, there is a shortage of funds; even projects with high social returns often can’t get financing.
I’m the last one to defend banks, but here Joe is quite wrong: the banks have very good reasons not to “fulfil their purpose” today, because that purpose is not what Joe thinks it is. Banks don’t “intermediate loans”, they “originate loans”, and they have every reason not to originate right now. In effect, Joe is complaining that banks aren’t doing what economics textbooks say they should do. But those textbooks are profoundly wrong about the actual functioning of banks, and until the economics profession gets its head around this and why it matters, then the economy will be stuck in the Great Malaise that Joe is hoping to lift us out of.
The argument that banks merely intermediate between savers and investors leads the mainstream to a manifestly false conclusion: that the level of private debt today is too low, because too little private debt is being created right now. In reality, the level of private debt is way too high, and that’s why so little lending is occurring. I can make the case empirically for non-economists pretty easily, thanks to an aside that Joe makes in his article. He observes that when WWII ended, many economists feared that there would be a period of stagnation:
Others, harking back to the profound pessimism after the end of World War II, fear that the global economy could slip into depression, or at least into prolonged stagnation.
In fact, the period from 1945 till 1965 is now regarded as the “Golden Age of Capitalism”. There was a severe slump initially as the economy changed from a war footing to a private one, but within 3 years, that transition was over and the US economy prospered—growing by as much as 10% in real terms in some years. The average from 1945 till 1965 was growth at 2.8% a year. In contrast, the average rate of economic growth since 2008 to today is precisely zero.
Read more …

“Schumpeterian creative destruction“: “The occurrence of a crisis greatly amplifies the impact of previous misallocations..”
• BIS Says Central Banks’ Stimulus Strategy Is Based On A False Premise (AEP)
The world’s monetary watchdog has thrown down the gauntlet. It has challenged the twin assumptions of secular stagnation and the global savings glut that have possessed – some would say corrupted – the Western economic elites. It has implicity indicted the US Federal Reserve and fellow central banks for perverting the machinery of interest policy to conjure demand that may not, in fact, be needed, and ensnaring us in a self-perpetuating “debt-trap” with a diet of ever looser money. The Bank for International Settlements (BIS) – the temple of monetary orthodoxy in Switzerland – has been waiting for this moment, combing through the archives of economic history to mount an unanswerable assault. The BIS believes it has found the smoking gun in a study of recessions in 22 rich countries dating back to the late 1960s.
The evidence suggests that the long malaise of the post-Lehman era – and the strange episode that preceded it – can be explained almost entirely by the destructive effects of boom and bust on productivity growth. Credit bubbles are corrosive. They gobble up resources on the upswing, diverting workers into low-productivity sectors and building booms. In Spain the construction share of GDP reached 16pc at the height of the “burbuja” in 2007, when teenagers abandoned school en masse to earn instant money erecting ghost towns. Parasitical wastage creeps in. “Financial institutions’ high demand for skilled labour may crowd out more productive sectors,” said the paper, acidly. The bubbles leave a long toxic legacy after the bust hits. This takes eight years or so to clear.
“The occurrence of a crisis greatly amplifies the impact of previous misallocations,” said the paper, racily titled “Labour reallocation and productivity dynamics: financial causes, real consequences”. Crippled economies have to make the switch back to healthier sectors against the headwinds of a credit crunch and a broken financial system, and typically amid austerity cuts in public investment. The BIS has long argued that a key reason why the US recovered more quickly than others is because it tackled the bad debts of the banking system early, forcing lenders to raise capital. This averted a long credit squeeze. It cleared the way for Schumpeterian creative destruction. The Europeans dallied, prisoners of their bank lobbies. They let lenders meet tougher rules by slashing credit rather than raising capital.
Europe’s unemployed have paid a high price for this policy failure. Claudio Borio, the paper’s lead author and the BIS’s chief economist, said the “hysteresis” effect of lost productivity is 0.7pc of GDP each year. The cumulative damage from the boom-bust saga over the past decade is 6pc. This more or less accounts for the phenomenon of “secular stagnation”, the term invented by Alvin Hansen in 1938 and revived by former US Treasury Secretary Larry Summers. Loosely, it describes an inter-war Keynesian world of deficient investment and demand. The theory of the global savings glut propagated by former Fed chief Ben Bernanke falls away, and so does the Fed’s central alibi. It can longer be cited as the canonical justification for negative real rates. The alleged surfeit of capital in the world proves a mirage. So does the output gap. If the BIS hypothesis is correct, there is no lack of global demand. The world faces a supply-side problem, impervious to monetary stimulus. The entire strategy of global central banks is based on a false premise.
Read more …

“..the Saudi royals would just be some broke 80-year-olds with nothing left but a lot of beard dye and Viagra prescriptions.”
• One Map That Explains the Dangerous Saudi-Iranian Conflict (Intercept)
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia executed Shiite Muslim cleric Nimr al-Nimr on Saturday. Hours later, Iranian protestors set fire to the Saudi embassy in Tehran. On Sunday, the Saudi government, which considers itself the guardian of Sunni Islam, cut diplomatic ties with Iran, which is a Shiite Muslim theocracy. To explain what’s going on, the New York Times provided a primer on the difference between Sunni and Shiite Islam, informing us that “a schism emerged after the death of the Prophet Muhammad in 632” – i.e., 1383 years ago. But to the degree that the current crisis has anything to do with religion, it’s much less about whether Abu Bakr or Ali were Muhammad’s rightful successor and much more about who’s going to control something more concrete right now: oil.
In fact, much of the conflict can be explained by a fascinating map created by M.R. Izady, a cartographer and adjunct master professor at the U.S. Air Force Special Operations School/Joint Special Operations University in Florida. What the map shows is that, due to a peculiar correlation of religious history and anaerobic decomposition of plankton, almost all the Persian Gulf’s fossil fuels are located underneath Shiites. This is true even in Sunni Saudi Arabia, where the major oil fields are in the Eastern Province, which has a majority Shiite population. As a result, one of the Saudi royal family’s deepest fears is that one day Saudi Shiites will secede, with their oil, and ally with Shiite Iran.
This fear has only grown since the 2003 U.S. invasion of Iraq overturned Saddam Hussein’s minority Sunni regime, and empowered the pro-Iranian Shiite majority. Nimr himself said in 2009 that Saudi Shiites would call for secession if the Saudi government didn’t improve its treatment of them. As Izady’s map so strikingly demonstrates, essentially all of the Saudi oil wealth is located in a small sliver of its territory whose occupants are predominantly Shiite. (Nimr, for instance, lived in Awamiyya, in the heart of the Saudi oil region just northwest of Bahrain.) If this section of eastern Saudi Arabia were to break away, the Saudi royals would just be some broke 80-year-olds with nothing left but a lot of beard dye and Viagra prescriptions.
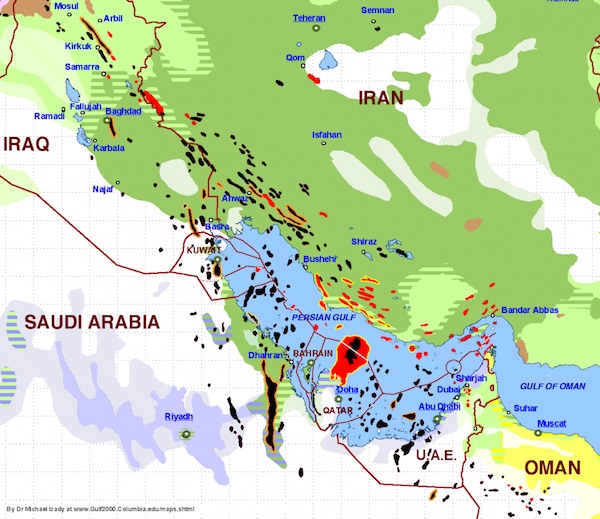
Map shows religious populations in the Middle East and proven developed oil and gas reserves. Click to view the full map of the wider region. The dark green areas are predominantly Shiite; light green predominantly Sunni; and purple predominantly Wahhabi/Salafi, a branch of Sunnis. The black and red areas represent oil and gas deposits, respectively. Source: Dr. Michael Izady at Columbia University, Gulf2000, New York
Read more …

Detailed and instructive article. Recommended reading.
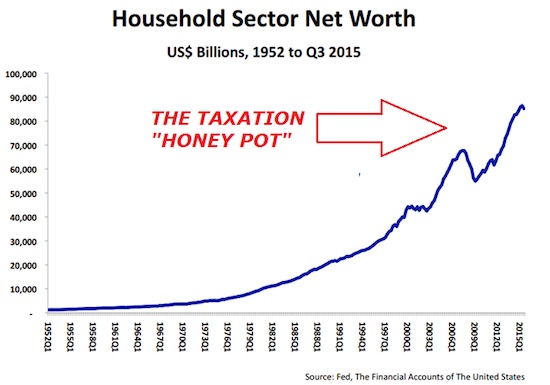
• Massive US Tax Grab Coming in 2016 at All Levels of Government (FRA)
The Financial Repression Authority sees the massive government tax grab already quietly underway accelerating in 2016 in most of the developed economies. This ‘grab’ will be a desperate political act driven by underfunded, and in a significant number of cases, unfunded public pension which will unfold at all three levels of government, Federal, State and City /Local government. It will be disguised by different focal emphasis and appear to evolve in an uncoordinated manner – but it will occur! To spot its telltale fingerprints we should expect the following words to become much more prevalent in the “public narrative” throughout 2016 and to see EACH of these which we explore in this article to increasingly and significantly extract money from taxpayer wallets:
• Capital Gains Tax,
• Property Tax,
• Global Wealth Tax (PFIC, FATCA, GATCA),
• Civil Forfeiture Fines,
• Means Testing,
• Licensing Fees,
• Usage, Tolls & Emergency Services Fees,
• Inspection Fees,
• Processing Fees,
• Fines (Police and Agency)
• Ticketing,
• School Activity, Equipment & Supply Fees,
• Inheritance Tax,
• Social Security Taxation Rate
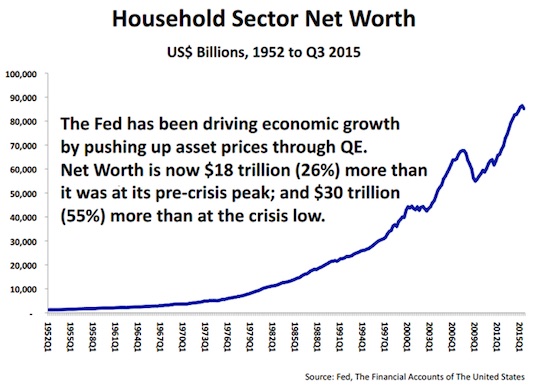
The Wealth Effect is believed by the government to have pushed up taxpayer US Household Net Worth by $30 Trillion or 55% from the Financial Crisis low. The US government is coming after that money! They see it as a “Honey Pot” that can’t be resisted.
Read more …

Build a wall with Cuba?
• Deal Paves Way For Thousands Of Cuban Immigrants Heading To US (CNN)
It’s a rare deal at a time when daily sparring over immigration is a worldwide reality. Five Central American countries and Mexico inked an agreement last week that will help thousands of stranded Cuban immigrants make their way to the United States. The group of Cubans, about 8,000 at the latest estimate, had been stuck in Costa Rica for weeks after Nicaragua closed its borders to them. Now a group of Central American countries say the Cubans will be flown to El Salvador, then transported on buses to Mexico. Then they’ll have a chance to cross into the United States. Officials have said they’ll start transporting the group of Cubans on flights this month. The first group of 180 will leave on a flight to El Salvador on Tuesday as part of a pilot program, Costa Rica’s foreign minister said Wednesday. It won’t be a free ride; the immigrants will have to pay about $550 to cover travel and visa costs, officials said.
The idea of 8,000 new immigrants showing up at America’s doorstep sounds like a large number. But experts say it’s in keeping with a trend they’ve observed. The number of Cubans coming to the United States has spiked dramatically, particularly after President Barack Obama’s announcement that relations between the United States and the island nation were on the mend. More than 43,000 Cubans entered the United States at ports of entry in the 2015 fiscal year, according to a recent Pew Research Center report, which cited U.S. Customs and Border Protection data. That represents a 78% increase over the previous year, according to Pew. Several factors are fueling the trend, said Marc Rosenblum, deputy director of the U.S. immigration policy program at the Migration Policy Institute.
These include the Obama administration’s 2009 decision to ease restrictions on Americans traveling to Cuba and sending money to families there, Cuba’s move in 2013 to relax exit controls on Cubans seeking to leave the island and – most importantly – the U.S. decision to normalize relations last year. Some fear the immigration policies that have welcomed Cubans into the United States could change now that relations between the countries are warming, Rosenblum said. “There is this concern that Cuba special privileges will be eliminated, so Cubans are trying to get out while the getting’s good,” he said. Not anymore. While the U.S. Coast Guard said last year it was seeing an increase in the number of Cubans trying to reach the United States in rafts, even more are taking a different route.
“Over the last several years, we’ve seen pretty sharp increases in the number of Cubans, especially traveling by land,” Rosenblum said. Until recently, many flew into Ecuador, which didn’t require a visa for Cubans until several months ago. From there, they trekked through Latin America until they reached the United States.
Read more …

Clueless.
• EU Fails to Defuse Passport-Free Clash in Northern Europe (BBG)
German, Danish, Swedish and European officials blamed each other – and political leaders across the continent – for the refugee overruns that have led to the reintroduction of passport checks in northern Europe. A migration crisis session in Brussels on Wednesday ended with Germany identifying Greece’s lightly policed sea border as the cause of the problem, Denmark telling refugees to go elsewhere, Sweden confessing that it’s swamped and the EU’s head office appealing for “solidarity.” “Our problem at the moment in Europe is that we do not have a functioning border-control system, especially at the Greece-Turkey border,” German deputy interior minister, Ole Schroeder, told reporters afterward.
The latest threat to no-passport travel in much of the 28-nation EU started when Sweden began stopping traffic on its border with Denmark, leading to controls on the Danish-German frontier and prompting the bloc’s home affairs commissioner, Dimitris Avramopoulos, to plead for a “return to normal as soon as possible.” The scale of the challenge was dramatized by data showing that EU governments have rehoused only 272 of a pledged 160,000 refugees, leaving Germany, Sweden, Greece and Italy as the main interim hosts of people fleeing wars in the Middle East. Sweden renewed its call for the equitable distribution of refugees, as required by EU laws passed last year, and invoked the rule – widely seen as broken beyond repair – that refugees apply for asylum in the first EU country they reach.
“We cannot do everything, we have to share responsibility among all member states,” Swedish Justice Minister Morgan Johansson said. The largest movement of people since the dislocations after World War II has stirred tensions among commercially and culturally like-minded countries in Scandinavia. “We don’t wish to be the final destination for thousands and thousands of asylum seekers,” said Danish immigration minister, Inger Stoejberg. She said Denmark is ready “at very short notice” to sanction transport operators for bringing in illegal migrants.
Read more …

Still 4,000 a day arriving in Germany every day. Or 1.46 million per year. And that’s in winter.
• Drop In Refugees Due to Weather, Not Turkey’s Crackdown, Germany Says (Reuters)
Migrant arrivals in Germany dropped significantly last month, but the reason was rough seas, not efforts by Turkey to crack down on illegal departures to Greece, German Interior Minister Thomas de Maiziere said on Wednesday. His remarks suggest that German efforts to stem the flow of arrivals with help from Turkey are not effective yet, which increases pressure on Chancellor Angela Merkel, whose popularity has fallen over her decision to welcome refugees. “Our impression is that the drop (in arrivals) is predominantly linked to the weather, namely a stormy sea in the Mediterranean,” de Maiziere, a member of Merkel’s Christian Democratic Union (CDU), told a news conference.
“We are also seeing efforts by Turkey to reduce the number of illegal migration departure from Turkey,” he said. “But we cannot confirm a sustainable, permanent, and visible reduction because of these activities and based on individual steps in December.” From 2,500 to 4,000 migrants entered Germany through Austria each day in December. That is far less than 10,000 daily arrivals recorded at the height of the crisis in autumn but still not low enough to silence Merkel’s critics. Most migrants reach Europe by making the short voyage from Turkey to Greece. Merkel wants Turkey to stem the flow and take back asylum seekers rejected by Europe.
In exchange, Turkey will get support for faster action on its bid to join the European Union and billions of euros in aid for Syrian refugees in border camps. The chancellor has rejected demands from members of her own conservatives to cap the number of refugees Germany is willing to take each year as well as calls to seal the border with Austria. Her multi-front approach to reducing the number of arrivals also includes providing aid to Syrian refugees in Lebanon and Jordan and distributing asylum seekers across the EU.
Read more …