Wyland Stanley Marmon touring car at Yosemite 1919



“.. if Syriza can deliver just 20% of what it promised, it will be in power for 20 years..”
• Greece: “It’s Like We Bought A Bad Franchise” (SMH)
The received wisdom is that if this summit does not strike a deal, then there is no hope of avoiding a Greek default on a €1.6 billion IMF loan, due to be repaid by the end of June. And if the loan is not repaid, Greece is likely to crash out of the euro and perhaps even the EU. International lenders are holding “hostage” €7.2 billion of new bailout cash, which will be released when Greece agrees to an economic reform package. However on Sunday the possibility was flagged that leaders could reach a broad, “in principle” deal on Monday, and hammer out the details at the very last minute when the loan is due. Neither side wants Greece to leave the eurozone. And there is said to be just a few billion euros difference in the reform packages being proffered.
But it’s not about the money, says Panagiotakis. “It’s political, it’s about who has control. If Syriza is seen as giving in to their demands, then they have no reason to continue in government. “Syriza – and Greece – doesn’t want a deal where something is given now but taken away again in three months time. Syriza wants a deal, even with compromises, that allows them to continue with policies without being kept hostage.” Syriza’s negotiators are also painfully aware that concessions that would be broadly acceptable to the Greek public may prove unacceptable to its own MPs. Depending on the degree of movement, they could lose as many as 20 MPs from their fragile coalition.
But if they secure a lasting deal, rather than a temporary fix, they will have achieved what many thought impossible. “My neighbours, friends and family say if Syriza can deliver just 20% of what it promised, it will be in power for 20 years,” Panagiotakis says. But the mood at the protest was that “rupture” with Europe was vastly preferable to more government spending cuts. “The cost of living is rising, business life has been ‘disappeared’, there’s no development,” says Bletas. “If we don’t succeed [in getting a better deal] it’s not worthwhile to stay in Europe. It’s like we bought a bad franchise.”
Read more …

Every European got poorer.
• Greece Is A Sideshow. The Eurozone Has Failed (Aditya Chakrabortty)
Workers in France, Italy, Spain and the rest of the eurozone are now being undercut by the epic wage freeze going on in the giant country in the middle. Flassbeck and Lapavitsas describe this as Germany’s “beggar thy neighbour” policy – “but only after beggaring its own people”. In the last century, the other countries in the eurozone could have become more competitive by devaluing their national currencies – just as the UK has done since the banking meltdown. But now they’re all part of the same club, the only post-crash solution has been to pay workers less. That is expressly what the EC, the ECB and the IMF are telling Greece: make workers redundant, pay those still in a job much less, and slash pensions for the elderly. But it’s not just in Greece.
Nearly every meeting of the Wise Folk in Brussels and Strasbourg comes up with the same communique for “reform” of the labour market and social-security entitlements across the continent: a not-so-coded call for attacking ordinary people’s living standards. This is what the noble European project is turning into: a grim march to the bottom. This isn’t about creating a deeper democracy, but deeper markets – and the two are increasingly incompatible. Germany’s Angela Merkel has shown no compunction about meddling in the democratic affairs of other European countries – tacitly warning Greeks against voting for Syriza for instance, or forcing the Spanish socialist prime minister, José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero, to rip up the spending commitments that had won him an election.
The diplomatic beatings administered to Syriza since it came to power this year can only be seen as Europe trying to set an example to any Spanish voters who might be tempted to support its sister movement Podemos. Go too far left, runs the message, and you’ll get the same treatment. Whatever the founding ideals of the eurozone, they don’t match up to the grim reality in 2015. This is Thatcher’s revolution, or Reagan’s – but now on a continental scale. And as then, it is accompanied by the idea that There Is No Alternative either to running an economy, or even to which kind of government voters get to choose.
Read more …

“..half the Greek workforce has no income.”
• Crisis Is The New Normal For Weary Greeks (Guardian)
As the “last-chance” talks rolled on towards another “last-ditch” summit possibly at the end of this week, weary Greeks have deadline fatigue. “Unfortunately, we’ve become hardened and accustomed to all this, including the never-ending talks,” said Christos Griogoriades, a physics and IT teacher in Greece’s northern second city of Thessaloniki. Panic about so-called “knife-edge”, “life-or-death” negotiations has become so commonplace that it is almost meaningless to a population whose major concerns are still making ends meet and scrimping for enough to eat. Griogoriades, 42, has friends who have lost good jobs and are now living back in their parents’ rural northern villages, supporting their young children on €40 a month and homegrown vegetables.
“We’ve got to the point where people here look at others, saying: ‘OK, I think I’ve got it bad but that man over there is eating from a garbage can.’ This is going to be our reality for many years, and I think the worst is yet to come.” His parents had lived through extreme post-war poverty and knew how to live very frugally. He felt the younger generation now felt condemned to live through an economic crisis that could stretch on for decades. With the Greek crisis now dragging on longer than the first world war, there have been at least a dozen emergency summits since 2009. The nation has so often been described as perched “on the edge of a cliff” and “staring into the abyss” that it has become part of the depressing new normality, just like cash-strapped hospitals, rocketing unemployment or the families with children living in flats with no running water or electricity because they cannot pay the bills.
Thessaloniki, which has long had the country’s highest jobless rates, now has 65% youth unemployment and around a third of the general workforce out of work. But unemployment is only part of the picture. Greece has around 1.5 million jobless, but a further one million people get up every day to go to work in jobs where bosses fail to pay them promptly. Salaries can trickle in three months late or even take a year to arrive in bank accounts. This means half the Greek workforce has no income. Meanwhile, whole families can depend for survival on grandparents’ shrinking pensions. While the emergency talks focus on immediate debt and repayments, many Greeks feel that little will help their daily struggle in the grim economic landscape.
Read more …

A risky game for Tsipras.
• Greece’s Red Lines Start To Blur And Bend (Guardian)
Like a husband forgiven for countless infidelities, Greek leader Alexis Tsipras is back in Brussels with a wink and a smile and, yes, another kiss and make-up proposal. Only this time, it looks like the marriage is saved. Tsipras has for the first time in several months taken the time to consider the concerns of his partners and rather than simply demanding solidarity, he has put together a plan to patch things up. What his partners want is simple, if difficult to achieve without further sacrifices. They want to close a funding gap in this year’s budget that most analysts estimate at €2bn (£1.4bn). It would appear that the leader of the leftist Syriza government has done enough to keep alive his country’s hope of staying inside the euro.
The question for his supporters at home will be, has he ditched his principled stand against further austerity, and if he has, do they care? Tackling the towering cost of the Greek pension system was once considered a no-go area. Already cut by his predecessors, Tsipras had ruled out shaving anymore from the bill. Likewise VAT was off the agenda. Now it seems he is prepared to compromise on both issues. On pensions, Athens appears to have conceded that the government’s coffers must be shielded from a wave of early retirements. According to documents supplied by Tsipras’s finance minister, Yanis Varoufakis, there are 400,000 Greeks looking to retire this year who qualify for a state pension, most of them under the existing early retirement rules. That’s a whole bunch of 60- and 61-year-olds who want to get under the wire, probably to supplement a meagre income from working or to serve as an unemployment benefit, all at a huge cost to the public purse.
Read more …

Part of the negotiations.
• Greek Offer To Creditors Runs Into Angry Backlash At Home (Reuters)
Greek lawmakers reacted angrily on Tuesday to concessions Athens offered in debt talks and parliament’s deputy speaker warned the proposals would struggle to win approval, puncturing optimism that a deal to lift Greece out of crisis might be quickly sealed. European leaders on Monday welcomed the new budget proposals from Athens as a basis for a possible agreement to unlock frozen aid and avert a default that could trigger a Greek exit from the euro zone. Stock markets also welcomed the plan, with European shares extending the previous session’s sharp rally and climbing to a three-week high on Tuesday, with growing expectations that Greece was getting closer to striking a deal.
But Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras, who was voted into office in January on a pledge to roll back years of austerity in a country battered by recession, must keep his leftist Syriza party as well as his creditors onside for a deal to stick. “I believe that this program as we see it … is difficult to pass by us,” Deputy parliament speaker and Syriza lawmaker Alexis Mitropoulos told Greek Mega TV on a morning news show. If parliament does fail to back the latest offer, which included higher taxes and welfare changes and steps to curtail early retirement, Tsipras might be forced to call a snap election or a referendum that would prolong the uncertainty.
Read more …

Tsipars walks dangerously close to the line with new concessions.
• Syriza Members Warn Tsipras Against Betrayal With Bailout Compromise (Dow Jones)
To avert a default and possible exit from the eurozone, Greek Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras must sell Germany’s chancellor, Angela Merkel, on his plan to fix Greece’s finances. Then he needs to persuade Vassilis Chatzilamprou. But out at the Resistance Festival, an annual gathering of Greece’s far left, the lawmaker from Mr. Tsipras’s left- wing Syriza party said he was in no mood for submission. “We cannot accept strict, recessionary measures,” Mr. Chatzilamprou warned. It was after midnight Sunday, and the weekend festival was winding down. “People have now reached their limits.” Syriza isn’t a traditional party but a coalition of left-wing groups with an intricate family tree formed out of doctrinal splinters and squabbles.
It is those many, disparate factions that Mr. Tsipras must also satisfy with any potential bailout agreement with Greece’s creditors. Mr. Chatzilamprou, for instance, is a member of the Communist Organization of Greece, which is an outgrowth of the Organization of Marxist-Leninists of Greece. It is distinct from the Communist Tendency, which has a Trotskyite bent. (Neither should be confused with the Communist Party of Greece, which is outside Syrzia.) That unusual composition has made it especially hard for Mr. Tspiras to strike a deal with eurozone and IMF officials. “The people who are responsible for the negotiation move within a frame that is determined by the central committee of the party,” says Alekos Kalyvis, a longtime union official who is on the committee and responsible for its economic-policy portfolio.
The negotiators have some latitude to make decisions, he said, “but this shouldn’t be interpreted as if they have a blank check from the party – neither them nor Tspiras.” Many of Syriza’s factions regard the party’s rise as a epochal moment for the left–and any compromise on a bailout as a deep betrayal of its principles. Stathis Leoutsakos, another Syriza member of Parliament, said Germany and the other creditor countries are determined to defeat Syriza. “In my opinion, their aim is to humiliate the Greek government,” he says. “They want the message that no other politics are accepted in the eurozone.”
Read more …

“Disfunction is very deeply entrenched indeed.”
• On Those Creditor ‘Red Lines’ For Greece (Peter Doyle)
Troika-Greek negotiations are reportedly down to the wire over early-retirement pensions, VAT, and labor reforms: the IMF says all are non-negotiable; Tsipras, perhaps inadvertently echoing Mrs. Thatcher, has, so far, responded “No! No! No!” These three issues converge on those at the upper end of their working lives, the 50-74 year old cohort, and are reflected in its participation and unemployment behavior. So it is worth considering data on those and the associated implications for the negotiations. Doing so suggests that these creditor red lines lack foundation Start with the obvious. Prior to 2009, Greece stands out with lower participation rates for this cohort than all but Hungary (males) and Malta (females). And the gender participation gap is also somewhat higher in Greece, but evolving.
So Greece is unusual, but why? Possibly early/generous retirement; possibly underreporting due to tax-evasion, low-pay, and/or predominance of agriculture and services; or perhaps skills outdating/mismatching and non-participation hysteresis; or public provision of education (easing the direct financial burden on parents of young adults); or health issues; and maybe slow-evolving gender cultural choices. But whatever their roots, these participation rates give rise to the political narrative of “cosseted Greeks” and they need to rise to boost incomes in Greece over the longterm. Once identified, their causes need to be fixed; the issue is “how and when?” Alongside, prior to 2009, unemployment rates in this cohort in Greece were either low (males) or middling (females); but no evident Greek stand-out.
These unemployment data clarify that relatively low participation rates in the 50-74 cohort prior to 2009 did not evidently reflect withdrawal due to lack of jobs for them to find, the “discouraged worker” effect. Instead, they were, in that sense, some kind of voluntary/structural feature of the labor market. To get a handle on the nature of those voluntary/structural characteristics of low Greek participation rates in this cohort, consider post-2008 developments. Given how much room there was for them to rise towards European “norms”, it is astonishing that participation rates barely budged despite an extraordinary battering from policy changes aimed to shift them—with average pensions, wages, and public employment cut broadly by 50, 40, and 30 percent respectively.
Greek male participation only edged up to end-2012 while Greek females continued their slow rise through early-2011. Then participation rates for both fell relative to their trends. This makes clear that any notion that the evident disfunction in the labor market in Greece—and hence the country’s long-term growth performance—is amenable even to enormous short-term parametric fixes on early-pensions, VAT, and wages in the current negotiations can be set aside. Disfunction is very deeply entrenched indeed.
Read more …

As if capital controls in a sovereign nation is something any foreigner has any legal say in.
• Greek Bank Run Fears Escalate As Capital Controls Openly Discussed (Telegraph)
Pressure is mounting on the European Central Bank to keep Greece’s flailing banking system alive for another day, amid tentative hopes Greece will finally be granted the bail-out money it needs to avoid a debt default next week. The possibility of capital controls was raised at an aborted meeting of eurozone finance ministers on Monday, with Belgium’s finance minister admitting EU officials had discussed the draconian measures to stop money bleeding out of the financial system. “There were indeed different opinions; not everybody was on the same wave length with respect to capital controls” said Johan Van Overtveldt. Germany’s finance minister Wolfgang Schaeuble is thought to have raised the possibility which was roundly dismissed by his Greek counterpart Yanis Varoufakis.
Capital controls, such as deposit withdrawal limits, can only be imposed in a country at the request of a member state government in the EU. They were last seen in the eurozone in 2013, during Cyprus’s banking crisis, after the ECB threatened to pull the plug on the country’s financial system. The remarks came as European leaders failed to agree a deal to keep the country in the eurozone after two emergency summits convened in Brussels on Monday. After the summit, German Chancellor Angela Merkel said there remained “much more to do” as Athens failed to get its reforms rubber stamped by the euro’s finance ministers earlier in the day. The Eurogroup said they needed more time to consider a revised set of Greek reforms in order to ascertain whether or not they “added up”.
Confusion reigned in Brussels as Athens was reported to have sent the wrong document to creditors at 2am on Monday morning. But in a hopeful sign, president Jeroen Dijsselbloem said the Greek plans were a “welcome step in a positive direction”. Alexis Tsipras, the Greek prime minister, said on Monday night it was now up to European authorities to find a debt deal to save Athens from default. “The ball is in the court of the European authorities,” radical leftist leader Tsipras told reporters after an emergency eurozone summit in Brussels. “Our proposal has been accepted as the basis for discussion by the institutions,” he said. “Negotiations will continue over the next two days. We don’t want a fragmented deal that is only for a limited time. We want a complete and viable solution.”
Read more …

It’ll be all too watered down. Greece needs very serious relief.
• EU Leaders Weigh Greek Debt Relief as Second Step in Aid Talks (Bloomberg)
Euro-area leaders said talk of debt relief for Greece is possible once the nation resolves the immediate financing dispute with its creditors. Easing Greece’s massive obligations won’t be decided in coming days and will instead come later in aid negotiations, French President Francois Hollande told reporters after a Brussels summit on Monday. He said creditors should commit to discussing debt changes as a “second step” after an agreement on Greece’s budget, economy and near-term financing is achieved in coming days. German Chancellor Angela Merkel took a similar line. While a third aid program is off the table for now, debt sustainability is part of the aid talks, she said.
“As far as the question of Greece’s ability to finance itself and its debt sustainability, this wasn’t discussed in detail, but it became clear that this question of being able to finance itself must be part of the deal,” Merkel told reporters after the meeting. The euro area said in 2012 that it might ease terms on some existing loans if Greece fulfilled its rescue conditions. For Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras to take advantage of those pledges, he’ll have to show his government has taken steps to fulfill its bailout obligations. As Monday’s summit took shape, leaders weighed how to present a renewed commitment to debt relief as part of talks on Greece’s bailout, according to officials familiar with the discussions.
France wants follow-on rescue arrangements to be part of any deal on how to handle the current program, the officials said. Greece will insist on a debt-relief component of any aid agreement, a Greek government official told reporters in Brussels. At the same time, the Greek official said, Greece is open to considering any type of debt arrangement that would pass muster with creditors. Maltese Prime Minister Joseph Muscat said the outlines of the debt talks are already in focus. “There is a commitment towards the realization of restructuring the Greek debt,” Muscat said in an interview after the summit. Haircuts would seem to be off the table, while three things on the agenda are the maturity of the debt, the grace period for no interest and the reduction of the coupon, he said.
Read more …

The numbers.
• The 2 Main Points Of Contention In The Greek Debt Saga (MarketWatch)
Hopes for an imminent deal between Greece and its creditors led stock markets to rally in Europe and in the U.S. on Monday, after Athens offered last-ditch proposals aimed at ending a debt deadlock that has left the country on the brink of default. The proposals received a warm, preliminary welcome from the Eurogroup, which is composed of eurozone finance ministers, which called the measures a “positive step in the process.” The Greek proposals are projected to save €2.7 billion or 1.51% of GDP in 2015, up from €2 billion in Greece’s initial proposal, according to Greek newspaper Kathimerini, which posted a copy of the official cost analysis of the Greek proposal late Monday. In 2016 the measures would save €5.2 billion or 2.87% of GDP, up from €3.6 billion in the initial proposal.
However, an agreement is still far from a done deal. And the political stakes are high. A joint poll conducted last week by Greek firm Kapa Research and German firm Infratest dimap in both countries showed that voters feel that the other side is being too rigid. In Germany, 78% of citizens polled said that the Greek government doesn’t sufficiently understand German demands. In Greece, 67% said Germany doesn’t understand the Greek position. Here are the two biggest bones of contention between Greece and its creditors:
Pensions Greece’s creditors have consistently asked the cash-strapped country to eliminate early retirement and phase out solidarity grants for all pensioners. On Monday, Greece offered to raise the retirement age gradually to 67 and curb early retirement, Reuters reported. The question, however, is how long it would take the Greek government to get the retirement age to 67 and what this would mean in absolute euro amounts. The Greek side wants to increase pension contributions now and to phase in cuts over three years, starting Jan. 1, so that vested rights can be safeguarded, according to Greek newspaper To Vima.This would create pension savings worth 0.37% of GDP for this year and 1.05% starting next year, according to the Greek proposal.
Value-added tax Greece’s creditors have been pushing the country to modify its value-added tax, or VAT, by imposing a 23% rate across the board, with the exception of food, medicine and hotels, which would be taxed at an 11% rate. A value-added tax is a consumption tax that is levied on goods and services at every stage of the supply chain. T The Greek government, on the other side, wants to keep VAT on certain basic goods and services at a lower rate. They say the objective is to protect the most financially vulnerable citizens, since the VAT is viewed as regressive, meaning that it affects low-income citizens more than the high earners.
Greece’s initial proposal was a sliding scale: 6% on medicine, books and theaters; 11% on newspapers, food, energy, water, hotels and restaurants; and 23% on all other goods and services. The creditors wouldn’t accept this, so Greece came back offering 6% on medicine and books; 13% for energy and basic foods; and 23% for everything else. This is expected to provide savings and new revenues equal to 0.38% of GDP in 2015 and 0.74% in 2016, according to the proposal. According to the Greek press, the main bone of contention is energy: Greece won’t budge from a 13% tax rate on electrical bills while the creditors are pushing for 23%. Meanwhile, last week the Greek electric power authority reported that its unpaid bills reached €1.9 billion in 2015, up from €1.7 billion in 2014.
Read more …

A tad overdone,
• Why The Words ‘Civil War’ Are No Longer A Joke In Greece (Paul Mason)
Here’s the situation as the Eurogroup on Greece is underway. On Sunday the Greek cabinet met and decided to make a further retreat on the fiscal targets their lenders want them to meet. There’s a gap of about €2bn between the two sides, and this latest move fills €1bn of it. This is by putting up the VAT rate on electricity, cutting the pensions of better-off pensioners, reducing early retirement rights quicker than planned, a one-off tax on companies with turnover above half a million, and closing tax loopholes. However, the real change is in the tone on debt relief. Alexis Tsipras has always argued that any deal done now should form the framework of a future discussion on rescheduling Greece’s debts. Until Sunday this was a red-line issue.
Now I understand the Greek government would accept a form of words that pledged to address this in future; and an un-named EU official has said this is likely. The problem is, these extra measures are effectively “left austerity” – changes of the kind the lenders don’t like, hitting the rich harder than the poor. So even if they accept they could help balance Greece’s books, they might still object that they are not sustainable. But the background to this final concession is ominous. Tsipras and his team are under huge pressure from within Syriza, and from within the 47% of voters who, when polled last week, said they would vote for Syriza. The pressure comes verbally, in constant text messages from constituents, and from a group within the parliamentary party known as the 53 group.
These are grassroots “modernised” left-wingers – and their 53+ MPs, combined with around 30 or so from the pro-Grexit Left Platform, have enough support and willpower to reject any deal that looks like humiliation. So Tsipras and his cabinet went to Brussels to make one more big concession, but fully prepared to endure an unwilling “rupture” with lenders, leading to the imposition of capital controls and a default, if they judge lenders are actually trying to humiliate them and force them to the exit. They understand the likely chaos would not just be economic. The second of the pro-euro demonstrations is due to be held tonight.
So far has the mood darkened between this essentially right-wing, pro-austerity movement and the mass base of Syriza that it has in the past week become routine for people to start throwing around the words “civil war”, and no longer in the jokey way they used to. People fear, sooner or later, that the left and right will stop alternating their demonstrations in Syntagma Square and start vying for control of it. As I’ve explained before, this is because the election of Syriza triggered a kind of recovered memory syndrome on both sides of politics, about the cold war and fascist collaboration and dictatorship in the 1970s.
Read more …

How to gut a society 101.
• The Euro “Young Adults Living With Their Parents” Zone (Zero Hedge)
A ‘region’ divided… because nothing says ‘recovery’ like 45-55% of young peripheral European adults (25-34 year olds!!) living with their parents.
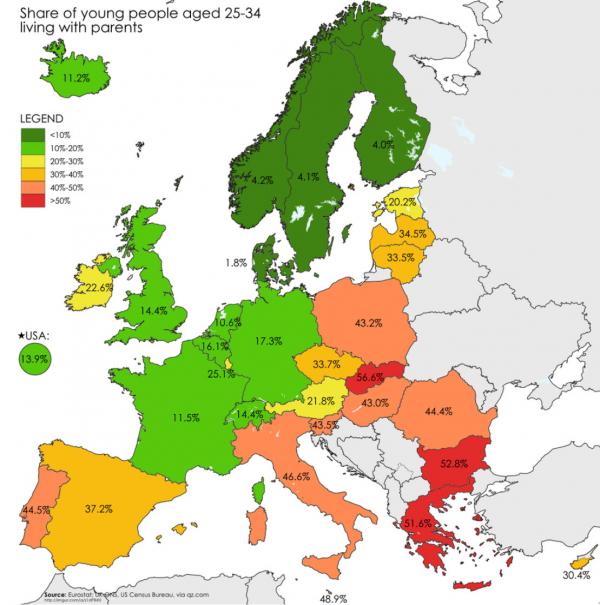
Read more …

The crash will be momentous.
• Chinese Investors Are Swimming Naked in a Bubble (Pesek)
The question is, can Beijing put a bottom under history’s biggest equity bubble? As JPMorgan strategist Adrian Mowat sees it, “policy makers will step in if the market correction gets beyond a comfortable level. I would imagine if the correction continues [this] week you will hear something reassuring.” He’s not necessarily wrong for the moment. China will indeed throw everything it has at the market: central bank rate cuts, tweaking margin-trading rules, slowing the pace of initial public offerings, talking up share prices, you name it. What is wrong, though, is the belief that China can prevent the crash of a market already defying the most wildly optimistic of economic scenarios. Beijing can’t do it anymore than Tokyo could in 1990, Seoul in 1997 or Washington in 2008.
China is reaching the limits of its ability to prolong a rally that turned 928 days old Friday. Beijing has encouraged companies to pursue splashy IPOs in order to sustain the excitement on stock markets, and lure Chinese households to open trading accounts. The thought is that if average Chinese feel wealthy, they’ll buy into Xi’s vision of a “China Dream” and the legitimacy of the Communist Party. But the market bubble has grown to unsustainable proportions. The median stock, for instance, has a price-to-earnings ratio of 98, while the Shanghai Composite, which has a heavy weighting toward low-priced bank shares, is valued at 23 times. The reason bank shares are so depressed, of course, is China’s dueling bubble in debt.
China has $28 trillion of public and private debt; then there’s the unprecedented $363 billion of margin debt that’s supporting shares. It doesn’t help that China’s economic fundamentals have turned for the worse. As Bloomberg Intelligence analyst Kenneth Hoffman detailed in a report Friday, Chinese demand for steel is collapsing. On June 18, Bloomberg’s steel profitability lost $37 per metric ton, hitting a record low. Chinese manufacturing activity, Hoffman wrote, could be in for a “major decline,” even if Beijing ramps up its stimulus programs.
Read more …

Everybody does it. Except for Russia?!
• India Infrastructure: Built On Debt (FT)
Some day, the Delhi Metro will be able to take race fans to the Buddh International Circuit, a $400m, 16-turn, state-of-the-art track on the outskirts of India’s sprawling capital. And once a gleaming new highway is completed, the track will be connected to Delhi and the tourist destination of Agra. But for now, there is little traffic on the highway leading to Buddh and even less on the pristine racetrack. It has been three years since Formula One abandoned the Buddh International Circuit, adding it to the sporting world’s crowded list of white elephants. It does not stand in total isolation, however. Block after block of concrete skeletons of towers that were meant to provide up to 200,000 apartments line the highway, casting shadows on dusty wasteland, dried riverbeds and mesquite weeds.
Welcome to what is likely India’s largest ghost city, which extends across five expansive parcels of land along the highway adjacent to the racetrack. What was meant to be the crowning achievement of Jaypee Group and Jay Prakash Gaur, its 85-year-old patriarch, has become a monument instead to unrealistic aspirations and poor execution on the one hand and a shortfall in growth, the high cost of capital and an uncertain political landscape on the other. The scale of Jaypee’s ghost city rivals that of some of China’s famous unoccupied cities. Fortunately for Jaypee, it also owns a collection of power and cement plants across India as well as three listed companies. Unfortunately, it also has about $12bn of debt, creditors and analysts say.
Jaypee is not alone in its plight. The company is ranked number six of 10 indebted Indian conglomerates that collectively owe about $125bn to their bankers, and account for 13% of all bank loans in India, according to data from Ashish Gupta, an analyst with Credit Suisse. Others on the list include Lanco, a construction and power company; GVK, an energy and transport group; and GMR, an infrastructure conglomerate. They are among the companies that should be leading India’s efforts to bolster its inadequate infrastructure, but instead are hampered by high debt levels and weak balance sheets. In many ways, the difficulties of these groups embody the problems facing modern India, where private sector investment has virtually ground to a halt. The cost of capital is high, and banks are reluctant to extend credit because they have too many bad loans.
Read more …

Nice historical metaphor.
• “What We Are Paying For Is 20 Years Of Blunder & Neglect” (Simon Black)
In May 1940, a visibly concerned Winston Churchill traveled to Paris to survey the city’s defenses. Nazi forces had already blasted past French units and were rolling easily through the Somme Valley towards Paris. There wasn’t much time. And Churchill bluntly asked the commanders in his notoriously pitiful French, “Où est la masse de manoeuvre?” “Where are your reserve forces?” He later wrote in his memoirs that their response was one of the most shocking moments of his life. “Aucune,” replied the commander. “We have none.” Hitler took Paris within a few weeks. And on June 22, 1940, seventy-five years ago to the day, French diplomats signed a peace treaty making France a vassal state of Nazi Germany.
Maxime Weygand, France’s most esteemed general, remarked of the occasion, “What we are paying for is twenty years of blunder and neglect.” Given the extraordinary risks in the system right now, these words may soon come to haunt us as well. Seven years ago a global financial crisis was spawned from too much debt, artificially low interest rates, and a complete misperception of obvious risks (like loaning money to dead people…) They ‘solved’ that problem with even more debt, lowering interest rates below zero, and continuing to ignore obvious risks (like buying stocks at all-time highs). You don’t have to be a financial genius to see the absurdity in this logic. Based on their own financial statements, most Western governments are completely insolvent, and most major central banks are close to insolvency.
They’ve already ratcheted interest rates down to zero (or below) and have racked up a mountain of debt. There are effectively no tools left for governments and central banks to deal with another major crisis. Like Paris in 1940, they have no Plan B. They’re completely defenseless to support the financial system or the currency in the event of a major shock. We should all take a moment to appreciate this level of incompetence. This doesn’t happen overnight. It takes decades of “blunder and neglect” to engineer financial vulnerability on this scale. But they’ve somehow managed to pull it off. The only question is– how long until the next financial shock? Because it’s not a question of ‘if’, but ‘when’.
Read more …

How nonsensical is this?
• Wages of Sin Still Weigh on Big Banks (WSJ)
The tide might not be turning. Hopes that regulatory and compliance costs at the biggest U.S. banks might begin to retreat after years of rising may be premature. As several recent stumbles make clear, banks still have more work to do to get right with regulators. Examples abound. The Office of the Comptroller of the Currency recently determined that six banks, including J.P. Morgan Chase and Wells Fargo, had failed to satisfy a 2011 order to fix foreclosure practices. As a consequence, the banks face restrictions on purchases of mortgage-servicing rights. Bank of America, which got a passing grade from the OCC on its foreclosure fix, was told by the Federal Reserve this year that its “stress test” performance had showed that management isn’t forward looking enough…
BofA has said it would spend $100 million to improve its stress-test abilities. The fact big banks still are running afoul of regulators raises doubts about the idea lenders can quickly cut back on the billions of dollars of additional costs they have incurred since the financial crisis. And that means bank results could disappoint compared with forecasts built on lower costs. Banks’ ability to cut costs continues to be important given revenue growth is lackluster and net-interest margins remain squeezed by superlow interest rates. Although the Federal Reserve is expected to begin raising overnight rates this year, that won’t immediately relieve the pressure. Banks have been promising to improve their efficiency ratios, which measure costs as a percentage of net revenue.
JP Morgan, for example, said in a presentation in February that it was aiming for a 55% efficiency ratio, down from 58% to 60% over the past few years. Wells Fargo says it targets 55% to 59%, compared with its current 58.8% ratio. Citigroup says it is targeting the mid-50s for its core business. The persistence of elevated regulatory and compliance costs could stymie their efforts. If costs remain high and revenue doesn’t pick up meaningfully, it will be hard to hit those targets. And while stress-test costs already are baked into bank expenses, the biggest banks are having to increase spending in hope of clearing another regulatory hurdle: living wills. Up until last year, banks didn’t pay too much attention to these. A regulatory shot across their bows, though, has forced them to devote far more time and resources to them.
Read more …

Look out below.
• $140 Billion Bond Fund Goes To Cash, “Braces For Bond-Market Collapse” (ZH)
Recently, it’s become readily apparent that some of the world’s top money managers are getting concerned about what might happen when a mass exodus from bond funds collides head on with a completely illiquid secondary market for corporate credit. Indeed, bond market illiquidity is the topic du jour and has almost become something of a cliche among pundits and mainstream financial media outlets years after we first raised the issue in these pages. But just because something has become fashionable to discuss doesn’t mean it’s not worth discussing and indeed, we’re at least pleased to see that the world is suddenly awake to the fact that a primary market supply bonanza catalyzed by rock-bottom borrowing costs and yield-starved investors could spell disaster when paired with shrinking dealer inventories.
[..] whether you’re talking about corporate credit or “risk free” government debt, liquidity simply isn’t there and as was on full display last October, wild swings in illiquid markets will be exacerbated by the presence of parasitic HFTs. Meanwhile, Treasury market participants are shifting to futures and corporate bond fund managers are using ETFs to offset “diversifiable” outflows, phenomena which prove investors are actively avoiding credit markets by resorting to derivatives, a practice which only serves to make the underlying markets still more illiquid.
Read more …

”..derivative interest rate swaps and credit default swaps that have been laid into history’s greatest financial minefield.”
• History in Free Verse (Jim Kunstler)
History might not rhyme, exactly, but it’s not bad for free verse. Greece is this century’s Serbia — a tiny, picturesque backwater nation blundering haplessly into the center stage of geopolitics. And the European Union is, whaddaya know, Germany in drag, on financial steroids. Nobody knows what will happen next in the struggle to wring some kind of debt repayment promises out of poor Greece. Without “restructuring” — a virtual national bankruptcy proceeding — there can be no plausible promises of repayment. Both sides seem to have exhausted their abilities to juke their way out. The European Union and its wing-men at the ECB and the IMF can only pretend to kick that fabled can down the road because it has turned into a cement-filled 50-gallon drum.
The Greek government can only pretend to further dismantle its civil service and pension systems lest angry citizens toss it out and replace it with a new government, perhaps an ugly and pugnacious one made up of Golden Dawn party Nazis. In the background, Spain, Portugal, Italy, Ireland, and perhaps even France wait without peeping to see if Greece is allowed to restructure, because you can be sure they will demand the same privilege to debt relief. But that’s hardly possible because the ECB has been engineering a shift of debt-holding away from the big corporate banks — which made all the stupid loans — to the taxpayers of their member states, especially Germany, which stands to be the biggest bag-holder when a contagion of serial default seeps across the continent.
This implies, of course, that along the way to that outcome something sickening happens to the price of all the bonds that the debt is embodied in. Namely, its value craters for the simple reason that the threat of non-payment makes interest rates shoot up to reflect the actualization of risk. That would certainly set off the booby-trap of derivative interest rate swaps and credit default swaps that have been laid into history’s greatest financial minefield. Thus, the big banks that were supposedly shielded by the ECB shell game of Hide the Debt Pea Somewhere Else, will blow up in a daisy-chain of unpayable obligations. The net effect of all that will be the disappearance of nominal wealth — it crosses an event horizon into a black hole never to be seen again.
The continent discovers it is a lot poorer than it thought. Fifty years of financial engineering comes to the grief it deserves for promoting the idea that it’s possible to get something for nothing. The same thing more or less awaits the USA, China, and Japan. For the USA in particular the signs of bankruptcy have been starkly visible for a long time outside the bubble regions of New York, Washington, and San Francisco. You see it in the amazing decrepitude of the built environment — the cities and towns left for dead, the struggling suburban strip malls tenanted if at all by wig shops and check-cashing operations, the rusted bridges, pot-holed highways, the Third World style train service.
Read more …

“..most houses in the US aren’t really worth the skinny little sticks that hold up their roofs..”
• Pop Goes The Bubble (Dmitry Orlov)
And so all that Americans can do with all this free money is gamble with it. There are lots of worthwhile ways to spend money—build public transportation, for instance—but the problem is that none of them make money. And that, stupid though it seems, is a requirement. But creating a huge, wasteful financial casino alongside the real economy doesn’t help the real economy—it crowds it out. And it doesn’t really make money either; it makes bubbles. This should in some measure explain the more or less continuous economic shrinkage that has been happening in the US so far this century. It is also worth noting that, dire though these negative effects already seem, Americans have by no means seen the worst of it yet.
The story one commonly hears is that the US is the richest country on earth. Well, that may be true, on average, if you include financial wealth (which tends to be rather ephemeral), overvalued real estate (which is another great big bubble), promises that won’t be kept (such as the various retirement schemes that will never pay out) and much else that isn’t quite real. But it is definitely true that the US also has the largest group of incredibly poor people—much poorer than the poorest person in the poorest country on Earth. Their wealth is measured in the hundreds of thousands of dollars—but with a negative sign in front.
They are deep in debt from investing in overvalued real estate (most houses in the US aren’t really worth the skinny little sticks that hold up their roofs), or from getting an overpriced higher education (which has qualified them to serve coffee), or from running up other kinds of debt. Some of them may still look rich and prosperous for the moment, but that’s only because… you guessed it, four whole decades of ever-lower interest rates! Once interest rates start ticking up, and their entire incomes are gobbled up by interest payments, they will start looking as destitute as they actually are.
Read more …

How long can a government act against its own laws?
• Ukraine President Poroshenko Admits Overthrow of Yanukovych Was a Coup (Zuesse)
Ukraine’s President Petro Poroshenko requests the supreme court of Ukraine to declare that his predecessor, Viktor Yanukovych, was overthrown by an illegal operation; in other words, that the post-Yanukovych government, including Poroshenko’s own Presidency, came into power from a coup, not from something democratic, not from any authentic constitutional process at all. In a remarkable document, which is not posted at the English version of the website of the Constitutional Court of Ukraine, but which is widely reported outside the United States, including Russia, Poroshenko, in Ukrainian (not in English), has petitioned the Constitutional Court of Ukraine (as it is being widely quoted in English):
“I ask the court to acknowledge that the law ‘on the removal of the presidential title from Viktor Yanukovych’ as unconstitutional.” I had previously reported, and here will excerpt, Poroshenko’s having himself admitted prior to 26 February 2014, to the EU’s investigator, and right after the February 22nd overthrow of Yanukovych, that the overthrow was a coup, and that it was even a false-flag operation, in which the snipers, who were dressed as if they were Ukrainian Security Bureau troops, were actually not, and that, as the EU’s investigator put his finding to the EU’s chief of foreign affairs Catherine Ashton [and with my explanatory annotations here]:
“the same oligarch [Poroshenko — and so when he became President he already knew this] told that well, all the evidence shows that the people who were killed by snipers, from both sides, among policemen and people from the streets, [this will shock Ashton, who had just said that Yanukovych had masterminded the killings] that they were the same snipers, killing people from both sides [so, Poroshenko himself knows that his regime is based on a false-flag U.S.-controlled coup d’etat against his predecessor]. … Behind the snipers, it was not Yanukovych, but it was somebody from the new coalition.”
This was when Ashton first learned that the myth that Yanukovych had been overthrown as a result of public outrage at his having rejected the EU’s offer of membership to Ukraine was just a hoax. (Actually, the planning for this coup was already under way in the U.S. Embassy by at least early 2013, well prior to Yanukovych’s EU decision. Furthermore, the Ukrainian public’s approval of the government peaked right after Yanukovych announced his rejection of the EU’s offer, but then the U.S.-engineered “Maidan” riots caused that approval to plunge.)
If the Court grants Poroshenko’s petition, then the appointment of Arseniy Yatsenyuk by the U.S. State Department’s Victoria Nuland on 4 February 2014, which was confirmed by the Ukrainian parliament (or Rada) at the end of the coup on February 26th, and the other appointments which were made, including that of Oleksandr Turchynov to fill in for Yanukovych as caretaker President until one of the junta’s chosen candidates would be ‘elected’ on May 25th of 2014, which ‘election’ Poroshenko won — all of this was illegal.
Read more …

Now there’s history for you.
• What Would Europe Look Like If The Soviets Hadn’t Defeated Hitler? (John Wight)
Never has a leader so catastrophically misjudged the character of an enemy as Hitler misjudged the Soviet Union and its people prior to launching his invasion of the country on June 22, 1941. Hitler and other top Nazis were convinced that the Soviet Union would crumble under the weight of the largest military operation ever mounted, codenamed Operation Barbarossa. German and Axis forces comprising 4 million men, 3,600 tanks, over 4,000 aircraft, and 46,000 artillery pieces attacked the Soviet Union along a 2,900-kilometer front from the Baltic in the north to the Black Sea in the south.
Hitler’s grand ideological project of colonizing Eastern Europe, granting the German and German-speaking peoples so-called “lebensraum” (living space), destroying in the process the “degenerate” and “inferior” Slav peoples, untermenschen, while crushing the threat of “Jewish Bolshevism” to his vision of a racially pure Aryan Europe, was now under way. From the outset it was to be a war of annihilation in which millions would be slaughtered. Many Western historians have attempted, when interpreting this aspect of the Second World War, to represent it a struggle between two equally monstrous totalitarian systems. This is of course completely false – a blatantly revisionist and ideological attempt to undermine the role of the Soviet and Russian people in crushing fascism in the interests not only of themselves, their country and culture, but also in the interests of humanity as a whole.
Read more …