Jack Delano Residents of rooming house for rail workers, Clinton, Iowa 1943



Want to bet the ‘real’ number will be way above zero?
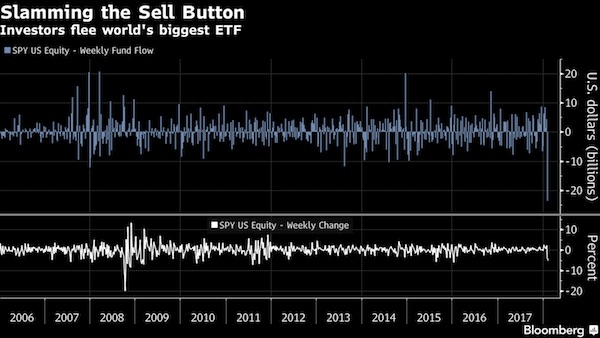
• US Economy Heads Toward Zero Growth in Q1 (WolfStreet)
The consistency with which nearly every report on the US economy has deteriorated over the last few months is astonishing. Only the jobs report has been spared that sharp downdraft. So we blame the weather, which in parts of the US was truly atrocious, while in other parts, particularly in California, it was gorgeous. Too gorgeous. This is supposed to be our rainy season, but every day the sun is out as we’re heading into our fourth year of drought. Yet the drought isn’t what keeps people from shopping or companies from ordering equipment. So out here, we’re baffled when the weather gets blamed. Today’s durable goods report for February was another shot at this wobbly edifice of the US economy.
New orders for manufactured durable goods dropped by 1.4%, the Census Bureau reported. It was the third decrease in four months. Transportation equipment fell 3.5%, also the third decrease in four months. Excluding transportation, new orders – “core” durable goods – fell 0.4%, down for the fifth month in a row. And Core Capital Goods New Orders, considered an important gauge of business spending, fell 1.4%, down for the sixth month in a row. The weather is really hard to blame for this, so folks blamed the strong dollar and slack demand in the US and globally. The data was bad enough to push the Atlanta Fed’s GDPNow model of the US economy down another step toward zero growth in the first quarter.
The Atlanta Fed started the model in 2011 to offer a more immediate picture where the economy is headed. It takes into account economic data as released and adjusts its GDP forecast for the quarter as it goes. The model is volatile. It reacts to incoming monthly data that are themselves volatile and subject to sharp revisions. So a few strong releases for March could turn this thing around on a dime. But we’re still dealing with the reality of January and February; the data has been crummy, and the Atlanta Fed’s “nowcast” is increasingly depicting an economy that is losing its struggle with growth.
Read more …

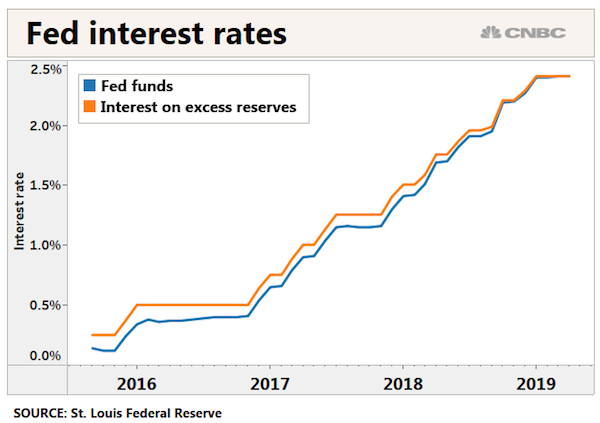
SO what exactly did the Fed purchase $1 trillion in mortgage-backed securities for? Riddle me that.
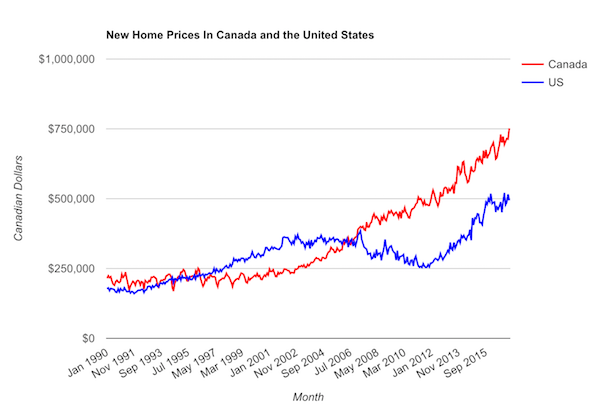
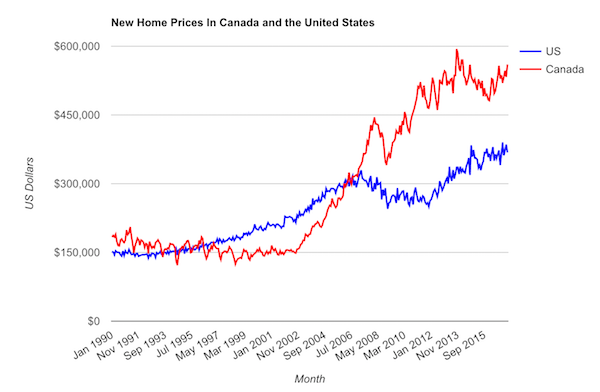
• US Home Prices Are Surging 13 Times Faster Than Wages (Bloomberg)
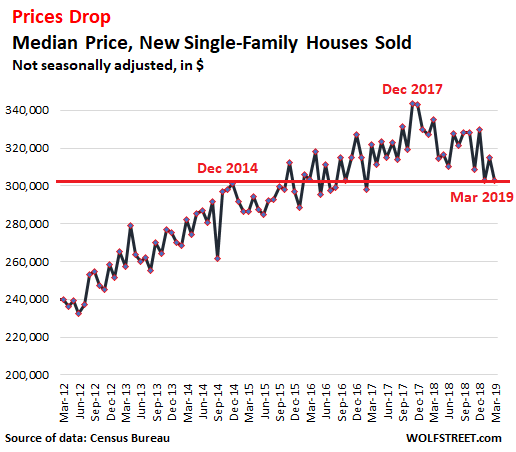
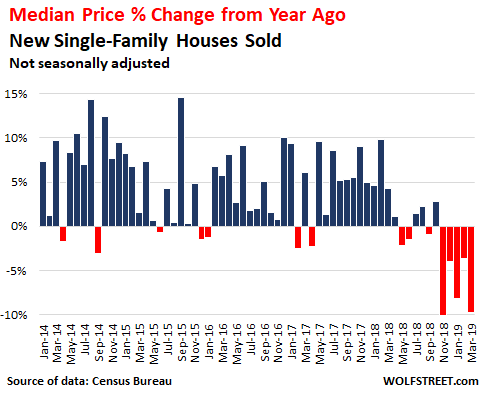
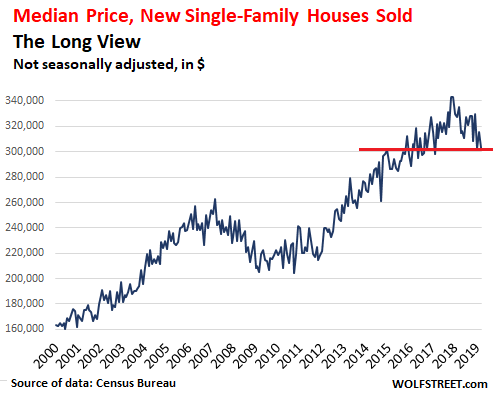
For most people, buying a home is no cheap venture. That’s especially the case when the growth in U.S. home prices is beating wage increases 13 to 1. Wages climbed by 1.3% from the second quarter of 2012 to the second quarter of 2014, compared to a 17% increase in home prices around that time, according to a new report from RealtyTrac. The real-estate data provider used the Labor Department’s weekly earnings data to measure wage growth, while home prices were derived from sales-deed data in December 2014 and compared to December 2012 on the hypothesis that a change in average wages would take at least six months to affect home prices.
Using localized earnings data, RealtyTrac also found that 76% of housing markets posted increases in home prices that exceeded the wage growth there during that time frame. How could this happen? Enter the investor. In many markets, the housing recovery has “largely been driven over the last two years by buyers who are not as constrained by incomes – namely the institutional investors coming in and buying up properties as rentals, and international buyers coming in and buying, often with cash,” Daren Blomquist, vice president at RealtyTrac and author of the report, said in an interview.
For demand from traditional buyers to improve, “either wages are going to need to go up or prices are going to need to at least flatten out and wait for wages to catch up,” he said. “You might say the third alternative is interest rates go down so you give people more buying power with their wages, but interest rates are about as low as they can go.” The trend illustrates the limited impact of the Federal Reserve’s decision to include mortgage-backed securities in its unprecedented asset-buying program. The Fed bought more than $1 trillion of those securities to prop up the housing market after it collapsed and helped trigger the worst recession in the post-World War II era.
Read more …

How Britain fell back in love with debt.
• UK Household Debt Soars By 9% To Hit A Record £239bn (Independent)
The average UK household is set to hold close to £10,000 in unsecured debt by the end of 2016, according to a leading accountancy firm. The forecast, by PricewaterhouseCoopers, was made after 2014 saw a sharp rise in unsecured debt, which bounced back to an all-time high of £239bn. The 9% rise in borrowing last year brings the average to close to £9,000, but PwC reckons that will grow. That would mean households will be closing in on the £10,000 figure if trends continue. The household debt to income ratio is projected to reach 172% by 2020, exceeding its previous peak set before the financial crisis. It includes mortgages and other debt secured on property.
Most banks all but ceased lending during the 2007/2008 shock. While mortgage lending is more strictly controlled than it was, the tap has gradually loosened when it comes to unsecured debt. PwC’s Precious Plastic: How Britons fell back in love with borrowing, published today, finds that most consumers are confident that they can manage their debt, with fewer worried about job security and pay rises as the economy improves. But the report says that despite consumers’ confidence, affordability will increasingly be called into question as the debt to income ratio steadily increases over coming years.
Read more …

To get inflation to 2%, people would need to massively raise spending. They won’t.
• ECB Bond Buying To Continue Till Inflation Reaches 2%: Draghi (WSJ)
The European Central Bank will purchase large amounts of public and private debt for at least 18 months and until it is convinced that inflation will stabilise near annual rates of 2%, the bank s president Mario Draghi has said, underscoring the ECB’s willingness to flood the eurozone with freshly minted money far into the future. In testimony to European parliament, Mr Draghi also urged Greece to commit to fully honouring its debt obligations. Its government also must be specific about areas of economic and fiscal reforms where it is in agreement with its international creditors and, where there is disagreement, how (the reforms) are going to be replaced has to be specified , he said.
Referring to the ECB s bond purchase program, now entering its third week, Mr Draghi said: We intend to carry out our purchases at least until end-September 2016, and in any case until we see a sustained adjustment in the path of inflation which is consistent with our aim of achieving inflation rates below, but close to, 2% over the medium term. Mr Draghi’s testimony comes two weeks after the ECB launched a program to purchase more than €1 trillion in bonds mostly government debt by September 2016. The purpose of the program, known as quantitative easing, or QE, is to raise inflation rates closer to the ECB’s target of near 2%.
The ECB has said it would buy bonds at a monthly clip of €60 billion and that the purchases could even extend beyond September of next year. The Governing Council will take a holistic perspective when assessing the path of inflation. It will evaluate the likelihood for inflation not only to converge to levels that are closer to 2%, but also to stabilise around those levels with sufficient confidence thereafter, Mr Draghi said. Consumer prices were down 0.3% from year-ago levels in February, the third-straight decline on an annual basis.
Read more …

Say uncle first!
• Europe Blocks Desperate Greek Attempt To Stay Afloat (Telegraph)
The Greek government will not receive €1.2bn in European rescue funds after officials ruled the Leftist government had no legal claims on the cash. Athens requested a return of the funds it said were erroneously handed to creditors from Greece’s own bank recapitalisation fund, the Hellenic Financial Stability Facility (HFSF). The transfer was originally arranged by the previous Greek administration. But eurozone officials have blocked the claim, saying it is “legally impossible” transfer the money back to the debt-stricken country. “There was agreement that, legally, there was no over payment from the HFSF to the EFSF,” said a fund spokesman. Germany’s finance ministry was also reluctant to allow the release, claiming there was “no reason” to make the transfer.
The decision is a further blow to the Greek government’s attempts to stay afloat over the next few weeks. Athens has been scrambling to make repayments to its creditors and continue to pay wages and pensions. The government now faces another €2.4bn cash squeeze in April, including a €450m loan repayment to the IMF on April 9. As part of its efforts to stay solvent, the Leftist government has also requested a €1.9bn transfer of profits held by the European Central Bank, from the holdings of Greek government bonds. So far, the ECB has rebuffed all Greek pleas to alleviate their cash squeeze. The central bank has moved to officially ban the country’s banks from increasing their holdings of short-term government debt.
Greek banks are being kept alive through the provision of an expensive form of emergency liquidity (ELA) which is rapidly being used up as capital flees the country. The ECB decided to incrementally raise the limit on ELA to €71bn – a bigger hike than in previous weeks.
Speaking in London on Wednesday, the ECB’s chief economist Peter Praet declined to comment on the Bank’s actions, saying it was important to exercise “verbal restraint” in moments of crisis. Worsening deposit flight has placed the squeeze on Greek lenders, who are only eligible for ELA as long as they are deemed to be solvent. Mr Praet said the country’s banks remained counterparties in their operations with the ECB, suggesting they remained healthy enough to continue receiving ELA.
Read more …

One plan after another.
• Eurozone Said to Give Greece Five Days to Deliver Plan (Bloomberg)
Greece has until Monday to show how it will follow through on reform commitments after the euro area ruled out speedy access to aid funds, three officials said following a conference call of finance ministry deputies. The euro zone’s other 18 members were adamant on Wednesday’s call that Greece needs to deliver specific plans to see any more bailout cash, the officials said. Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras needs to show that Greece can rebuild trust in its promises, they said. Finance deputies left the door open to €1.2 billion that has been allocated to aid the banking system, as the deputies concluded that Greece can’t tap those funds on a technicality.
As a result, Greece will have to show it will move ahead with the changes its creditors are seeking to get the bank-aid money or other bailout funds. Greece won some financial breathing room Wednesday when the European Central Bank raised the ceiling for Emergency Liquidity Assistance to Greek banks by more than €1 billion to more than €71 billion, according to two people with knowledge of the decision who asked not to be named. The ECB’s move alleviates some near-term cash needs in the banking system while keeping pressure on Tsipras to find a longer-term solution. European officials have said that Greece could default on its obligations within weeks unless there’s a breakthrough.
Greece needs to act faster so its actions can be more effective, Eurogroup Chairman Jeroen Dijsselbloem, who heads the euro-area finance ministers’ group, said in Rotterdam on Wednesday. “The main problem is the same in every country in Europe: getting things done.” Monday will be a test of whether Greece can convince its peers that it will meet their demands for an economic overhaul, the officials said. Once Greece submits its next documents, they’ll need to be reviewed by the country’s official creditors and then the finance ministry deputies in the first few days of next week, ahead of Easter holidays, one of the officials said.
Read more …

Oh, yes it is.
• Greek Central Bank Governor Stournaras Says Grexit Isn’t An Option (WSJ)
Bank of Greece Governor Yannis Stournaras said Wednesday that ditching the euro and exiting the single currency union is “not an option” for Greece. Mr. Stournaras told an audience at the London School of Economics that a Greek exit–dubbed “Grexit” in financial markets–risks triggering another severe downturn in the stricken Mediterranean economy. Greece has already improved its global competitiveness by driving down wages and prices, he said, and growth is returning. “Grexit would deliver no benefit, but a lot of pain,” Mr. Stournaras said. Quitting the eurozone would probably lead to even deeper austerity than Greece already has implemented, he said, while the adoption of an alternative currency would risk fueling runaway inflation.
His remarks come a day after the ECB instructed Greece’s biggest banks to refrain from taking on anymore short-term Greek government debt, adding to the pressure on Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras’s leftwing government in Athens to reach a deal with creditors over the terms of the nation’s €240 billion bailout package. Mr. Tsipras was elected in January on a pledge to reverse many of the budget cuts and other economic reforms demanded by Greece’s creditors in exchange for financial aid. But he has struggled to persuade lenders led by Germany and the IMF to back down, raising the specter of a disorderly Greek exit from the eurozone.
Greece now has just weeks to secure a deal to unlock billions of euros in badly needed funds to keep paying public-sector salaries and service the nation’s debts. Mr. Stournaras said Greece’s government has a unique opportunity to implement bold economic reforms and forge a durable recovery. “This is in my view a historical opportunity which should not be missed,” he said. He added that he’s more optimistic that Mr. Tsipras’s government is serious about reform than he was a month ago.
Read more …

Scenario’s.
• A Murky, Sloppy Muddle: How Greece’s Exit From Euro Could Happen (Bloomberg)
With the fight to keep Greece in the euro now in its sixth year, everyone is running out of patience. More importantly, Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras’s government in Athens is running out of money. While bond yields suggest investors expect Greece to stay in the euro, economists such as UniCredit Bank AG’s Erik Nielsen say it may be just a matter of time before he’s forced to print a new currency. Adopting the euro was always supposed to be a one-way ticket, so there is no legal precedent or political roadmap for an exit. If you’re waiting for a formal announcement of a clear resolution, you may be waiting a long time.
Next steps for Greece range from retaining the euro to catastrophic divorce; half-measures like having multiple currencies circulate, with aid recycled to repay foreign-currency debts, are also in the cards. Equally unclear is who would tell the world – and how – that Greece has entered an economic afterlife. Possible messengers include Tsipras, the ECB, EU President Donald Tusk and European Commission President Jean-Claude Juncker, among others.
Read more …

Strip mining.
• Athens Raids Public Health Coffers In Hunt For Cash (FT)
Greece’s government has raided the coffers of its public health service and the Athens metro as it widens a hunt for funds to keep itself afloat and service debts. Athens faces a €1.7bn bill for wages and pensions at the end of the month and then a €450m loan payment to the IMF on April 9. Greek government and eurozone officials believe Athens does not have funds to cover both. In another constraint on Greece’s ability to raise cash, the ECB decided to impose stricter curbs on the issuance of short-term government debt. EU officials expressed hope that a marathon Monday night meeting between Alexis Tsipras and Angela Merkel, would spark long-stalled talks over economic reforms Greece must implement to unlock €7.2bn in frozen bailout aid.
Athens has promised to deliver a list of reforms to eurozone authorities by Monday. But officials cautioned that the list would still have to be agreed with bailout inspectors before eurozone authorities could make progress on any deal to free up new funding. Though Mr Tsipras discussed his reform plans with Ms Merkel on Monday night, there were few signs that talks in Athens with bailout inspectors had become more active following the Berlin meeting. “The big ‘if’ is that they seem to move at such a glacial pace,” said an official. Greek authorities have also been seeking €1.2bn in funding that they believe was wrongly taken out of the country’s bank recapitalisation fund by eurozone authorities.
But EU officials said a quick decision on the matter was unlikely and even if Athens was awarded the cash it could only go towards bank rescues, not general government coffers. In the absence of progress, some EU officials were accelerating their preparations in case Athens runs out of cash before it agrees a reform programme. In Brussels, European Commission officials have begun looking again at EU law governing capital controls in case the growing uncertainty, or a non-payment to the IMF, spurs a renewed run on bank deposits.
Read more …

“They are scraping the bottom of the barrel for everything they can find.”
• Greek Government Takes Desperate Measures In Battle To Stay Afloat (Guardian)
The Greek government is resorting to increasingly desperate measures to keep afloat amid dire warnings the debt-stricken country could go bust within weeks. In a balancing act not seen by any European administration in recent times, the cash-strapped coalition has sequestered the reserves of public bodies, seized EU subsidies destined for farmers and postponed all payments for state supplies in the scramble to continue servicing its debt and paying salaries and pensions. Pension funds have been raided to raise money for Treasury bill auctions. “It is clear we are reaching the end and very soon won’t be able to pay,” former finance minister, Stefanos Manos, said. “They are scraping the bottom of the barrel for everything they can find.”
To cover the credit crunch, corporations in which the state has a majority stake, including the Athens Metro, have been tapped. The scheme of repo transactions – where government bonds are used for short-term borrowing requirements – is believed to have raised upwards of €600m in recent weeks. Earlier this month the leftist-led coalition suspended some €300m of EU subsidies for farmers to help pay €1.7bn in public sector wages and pensions due next week. Greek subsidiaries of multinationals have also been approached for loans.
The last-resort measures came as Deutsche Bank warned that Athens was at risk of being pushed into default on 9 April when it must meet a €450m debt repayment to the International Monetary Fund. The precarious state of Athens’ finances has been exacerbated by a precipitous decline in tax revenues – more than €1bn below target since January – said the bank’s economists. Deposit flight has also ratcheted up the pressure. More than €20bn has fled the country since the beginning of the year as savers rush to withdraw funds, worried about Greece’s ability to remain in the euro. “The risk of capital controls continues to rise,” noted the Deutsche report.
Read more …

“..the nearer Bank Rate approaches zero, the bigger the squeeze on the profits banks earn from borrowing and lending.”
• How Low Can Interest Rates Go? (BBC)
The Bank of England’s website says that the “effective lower bound” for the interest rate it sets, Bank Rate, is the current rate of 0.5%. This is the level, according to the Bank, “below which it cannot be set” – the lowest practicable official interest rate. But on this important issue the website is behind the thinking of the Bank of England’s Monetary Policy Committee, which sets Bank Rate as its main tool to keep inflation on target. Because just over a month ago, the Bank’s governor said that if low inflation were to begin to depress expectations of inflation and wage growth, the MPC could “cut Bank Rate further towards zero”.
And with inflation well below the 2% target at zero, the Bank’s chief economist, Andy Haldane, has said – as a personal rather than institutional view – that there is a meaningful chance that Bank Rate will be cut. So what has happened to demonstrate to the Bank that 0.5% is not the practicable minimum. Partly it is the example of central banks – the European Central Bank and those of Switzerland, Sweden and Denmark – whose official rates are negative: banks that place funds with them are having interest deducted from their deposits, rather than receiving interest. Their rates are less than zero. The other contributor to the fall in the effective lower bound is the recovery of Britain’s banks.
This matters because the nearer Bank Rate approaches zero, the bigger the squeeze on the profits banks earn from borrowing and lending. Think of it this way. Competition between banks should bring down the interest rate on loans when Bank Rate is cut towards zero. But savings rates would be kept by competition above zero. So the gap between the interest rate paid and received by banks would narrow: the profits on this most basic of banking activities would fall. Also the windfall received by banks from all those interest-free deposits the banks hold would be significantly cut.
Read more …

“China must recycle its trade surpluses and its $3.8 trillion reserves by one means or another. It can buy US Treasuries, Bunds, or Gilts, perpetuating a global bond bubble.”
• US Risks Epic Blunder By Treating China As An Economic Enemy (AEP)
The United States has handled its economic diplomacy with shocking myopia. The US Treasury’s attempt to cripple the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) before it gets off the ground is clearly intended to head off China’s ascendancy as a rival financial superpower, whatever the faux-pieties from Washington about standards of “governance”. Such a policy is misguided at every level, evidence of what can go wrong when a lame-duck president defers to posturing amateurs in Congress on delicate matters of global geostrategy. Washington has enraged Britain by trying to browbeat Downing Street into boycotting the project. It has forced allies and friendly countries across the Far East to make a fatal choice between the US and China that none wished to make, and has ended up losing almost everybody. Germany, France, and Italy are joining. Australia and South Korea may follow soon.
The AIIB is exactly what the world needs. China must recycle its trade surpluses and its $3.8 trillion reserves by one means or another. It can buy US Treasuries, Bunds, or Gilts, perpetuating a global bond bubble. It can make surgical investments abroad to acquire technology for its champions and pursue a narrow national interest. Or it can recycle the money in concert with other members of the AIIB – with a start-up capital of $50bn – for sewage projects, clean energy, ports, roads, and railways in Asia, helping to plug a $700bn shortfall in infrastructure investment that the World Bank is too small to cover and which is of collective benefit to the world. Britain recycled its surpluses in the 19th Century by building the world’s railways.
America did so in the 1950s through the Marshall Plan. China must do likewise, and it is hard to see why the AIIB is considered such a villainous variant. American officials castigated Britain for breaking ranks and embracing the project, as if it were kowtowing to an enemy. “We are wary about a trend of constant accommodation of China, which is not the best way to engage a rising power,” one US official told the Financial Times. One is left breathless at the historical folly of such a view in any case. As Henry Kissinger told Caixin magazine this week, the greater danger is that the US fails to accommodate the rise of China in an enlightened fashion, repeating errors made by the status quo powers faced with a prickly Germany before the First World War.
There are echoes of the Korean War in this Atlantic spat, though thankfully the stakes are less violent today. Britain tried to restrain General Douglas MacArthur and Washington’s hawks as they sent US forces charging through North Korea to the Yalu River and the Manchurian border in 1950, warning that it would force China to respond. MacArthur’s contemptuous riposte was to liken British reflexes to the betrayal of Czechoslovakia at Munich, of “desiring to appease the Chinese Communists by giving them a strip of Northern Korea.” The British experts were right. China threw four armies across the Yalu. America had arrogantly stumbled into a shooting war with the Chinese revolution, a cataclysmic mistake.
Read more …

More strip mining.
• China’s European Shopping Spree Shows No Signs Of Slowing (Ind.)
A planned takeover of the Italian tyre maker Pirelli by ChemChina is the latest in a string of Chinese acquisitions in Europe, topping up total foreign investment from China worth $18 billion in 2014, double 2013. Pirelli, the world’s fifth largest tyre maker, will be in Chinese hands after ChemChina confirmed a $7.7 billion bid on Sunday. The deal will give Pirelli a slice of the Chinese tyre market and could see its global market share rise to 10%. It’s one of the biggest European acquisitions by a Chinese company yet. But that’s unlikely to be the case for long. Chinese investors have shown increasing interest in Europe as a centre for investment in the last year, spurred on by the cheap euro and the opportunity to invest in legacy brands.
“Chinese investment in Europe has become much more diverse in recent years and is now extending into all parts of Europe.” said Thomas Gilles, Chairman of the EMEA-China Group at Baker & McKenzie. “What we’re seeing is the maturing and normalization of Chinese investment processes in line with the international economy.” The UK is top of the list. Last year, Chinese investors acquired several billion-dollar British investments. Pizza Hut went for a cool £940 million ($1.4 billion), while property bought by Chinese firms includes Chiswick Park for £875 million ($1.3 billion) and 10 Upper Bank Street for £497 million ($740 million).
Last week it emerged that a Chinese company backed by billionaire Guo Guangchang is looking acquire 18 buildings in Berlin’s Potsdamer Platz square, in what could be the biggest German property sale since 2007. Last year France sold Peugeot for £740 million ($1.1 billion).
Read more …

“.. the yuan has increased in value against the Euro almost 25% in one year..”
• US Couldn’t Corral AIIB Due To Soaring Chinese Investments In Europe (Atimes)
Stopping a stampede isn’t easy – as that old cowpoke Uncle Sam’s discovering as more European nations bolt to join China’s Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB). The weak Euro’s drawing a conga line of Chinese investments to Europe. The money’s being plunked down not only in “typical” Chinese sectors of historic interest like resources or transportation. It’s focusing geographically across the entire European opportunity and capability spectrum. The uplifting effects of this investment hasn’t been lost on the European countries who are now eager to climb aboard China’s AIIB. Ever since Europe embarked on their QE, and China has maintained stability in the yuan.
As we have noted, this is viewed as pre-condition for the non-convertible yuan to join the IMF’s SDR currency basket later this year. And the yuan has increased in value against the Euro almost 25% in one year – a trend likely to continue through the year with the long-term policies of the respective central banks likely to stay in place for the foreseeable future. According to the EU Observer: “Even before the crisis, these flows surged, tripling from less than US$1 billion per year in 2004-8 to roughly $3 billion in 2009-10. As the Eurozone crisis kicked in, Chinese investment tripled again to $10 billion in 2011. And last year, Chinese investors doubled their money in Europe to a record $18 billion.”
Chinese capital’s typically poking around for each European country’s relative market advantages. In the UK as with many foreign investors, the Chinese have focused on prime property, while in Germany they look for advanced technology. “The UK is the top destination for Chinese investment at $5.1 billion, followed by Italy at $3.5 billion,” the Observer said. As the capital needs of Southern Europe grow, Chinese capital has focused on privatisations and distressed opportunities, from the Greek ports connecting to their new Silk Road to Europe, to Portugal’s Espirito Santo Bank and Spain’s real estate foreclosures.
Read more …

They’re on to us.
• Putin Security Council Slams Obama Attempts At “New World Order” (Zero Hedge)
Moscow – which may or may not have to nuke Denmark – says the US has adopted a national security strategy that is decidedly anti-Russian. Although attempts to prove how “isolated” Putin truly is on the geopolitical stage haven’t fared very well of late (what with Russian bombers refueling at former U.S. air bases and Putin plotting Eurasian currency unions) and although Washington’s experience with China’s AIIB membership drive seems to indicate it may be the US that is in fact isolated, The Kremlin doesn’t think The White House is likely to give up on its attempts to ostracize Russia any time soon. From a Russian Security Council statement entitled “About The US National Security Strategy”:
In the long term, the United States, in cooperation with its allies will continue the policy of political and economic isolation of Russia, including limiting its ability to export energy and the displacement of all markets for military products, while making it difficult for the production of high-tech products in Russia.
Putin’s security council then proceeds to deliver a remarkably accurate description of Washington’s foreign policy aims including the desire to show off NATO military capabilities (on full display along the Russian border currently), installing puppet governments and propping them up with financial and military support (which is precisely what’s going on now in Ukraine as the US is set to provide military assistance and also financial assistance via a Ukrainian bond issue back by the full faith and credit of the US government), and preserving US hegemony by taking unilateral action across the globe at Washington’s behest (something the US does all the time):
The Strategy emphasizes the US desire to proceed with the formation of a new global economic order. A special place in this order should take a Trans-Pacific Partnership and transatlantic trade and investment partnership that will enable the US central position in the free trade zones, covering two-thirds of the world economy. The armed forces are considered as the basis of US national security and military superiority is considered a major factor in the American world leadership. While maintaining the continuity of the plans to use military force unilaterally and anywhere in the world, as well as to maintain a military presence abroad…
Significant efforts by the US and its allies will be directed to the formation of anti-Russian policy states, with which Russia has established partnership relations, as well as to reduce Russian influence in the former Soviet Union. Continue the policy of preserving the global dominance of the United States, increasing the combat capabilities of NATO, as well as to strengthen the US military presence in the Asia-Tihokeanskom region. Military force will continue to be considered as the primary means of ensuring national security and interests of the United States. Becoming more widespread to eliminate unwanted US political regimes acquire advanced technology “color revolutions” with a high probability of their application in relation to Russia.
Read more …

“Russia would no longer fight the market. Speculators needed a cold shower, she said.”
• The Central Banker Who Saved the Russian Economy From the Abyss (Bloomberg)
Panic reached the inner sanctum of the Russian central bank. It was Dec. 16 – the day Russian traders would later christen Black Tuesday – and the ruble was in a freefall.“Intervene! Intervene!” a central bank official shouted. Governor Elvira Nabiullina watched the currency on her tablet screen react to her emergency rate increase. No, she said, not this time: Russia would no longer fight the market. Speculators needed a cold shower, she said. That daring decision, related by two people with knowledge of the meeting, has begun to pay off for Nabiullina, 51, and her patron, President Vladimir Putin. Despite sanctions meant to punish Russia for its foray into Ukraine a year ago, the ruble has stabilized. Since Black Tuesday, when it plunged to a record low, the ruble has rebounded 19% against the dollar, the most among 24 emerging-market currencies.
Russia still confronts a painful recession brought on by the collapse in oil, and many of its banks are hurting. But for now, at least, the economy has stepped back from the abyss. Finance Minister Anton Siluanov last week declared the worst was over. Inside the central bank, near Red Square, the lull passes for victory. Nabiullina no longer has to squander foreign-exchange reserves in vain attempts to prop up the ruble. Now she faces the equally daunting task of binding up the wounded economy. While her central bank is nominally independent, analysts agree Putin is ultimately in charge. Yet Nabiullina has emerged as a power in her own right, with a direct line to the president.
Nabiullina isn’t afraid to speak up. When aides urged Putin to impose capital controls last year, she fought against the move and pushed for a freely floating ruble, according to people with knowledge of the matter. Putin heeded her advice — and then let Nabiullina sort out the details. “It was a historic moment because she convinced Putin to accept a market solution to a problem that threatened the whole banking system,” UBS AG Russia Chairman Rair Simonyan said. Russia might well have veered into economic isolation, he said. What Nabiullina came up with turned out to be one of the biggest financial gambles of Putin’s 15-year rule. First she raised interest rates to punishingly high levels, lifting the benchmark rate to 17% from 10.5% in one stroke. Then she stepped back from intervening on the currency market.
Read more …

“..a primary money-laundering concern..”
• Banking Enclave of Andorra Shaken by US Accusations (Bloomberg)
Juan Ovelar made a quick decision when he heard the U.S. government had accused his Andorran bank of money-laundering, and immediately withdrew most of his funds. “I’m worried that everyone will do the same as I did and there will be a knock-on effect that could affect other banks,” said Ovelar, 27, a computer expert from Argentina, in an interview outside the headquarters of Banca Privada d’Andorra in the capital Andorra La Vella. The U.S. Treasury named Banca Privada d’Andorra, the country’s fourth-largest bank, a “primary money-laundering concern” on March 10. That led to its seizure by Andorran authorities, the arrest of the chief executive officer and a run on customer funds at the lender’s Spanish unit.
The bank’s fate sent tremors through Andorra, a 181-square-mile (469 km2) Catalan-speaking microstate in the eastern Pyrenees with an economy based on skiing, tax-free shopping and banking. The scandal raises risks for its financial industry, which makes up almost a fifth of the €1.8 billion economy and is too big to be bailed out by the state, said Xavier Puig, a professor at Barcelona’s Universidad Pompeu Fabra. Customers lined up at the bank’s branches to take out their money after it limited cash withdrawals to 2,500 euros a week, starting March 16. The bank’s new management, appointed by local regulators, imposed the limit after international banks severed credit lines, a person with knowledge of the situation said.
Andorra’s government is trying to convince international banks to open credit lines so customers won’t be cut off from funds, said the person, who asked not to be identified because the talks are private. Options under consideration for the bank include the sale of assets or liquidation, the person said, adding that officials are seeking a quick solution to limit the effect on other banks. “The government is acting quickly to find a solution because the consequences can be very serious,” said Puig. “They need to amputate this part so that the gangrene doesn’t extend to the rest of the body.” Fitch Ratings put the three largest Andorran banks on watch for a possible downgrade on Monday because of “potential spill-over effects.”
Read more …

A comprehensive overview of behind the scenes US war mongering.
• Meet The Kagans: A Family Business Of Perpetual War (Robert Parry)
Neoconservative pundit Robert Kagan and his wife, Assistant Secretary of State Victoria Nuland, run a remarkable family business: she has sparked a hot war in Ukraine and helped launch Cold War II with Russia – and he steps in to demand that Congress jack up military spending so America can meet these new security threats. This extraordinary husband-and-wife duo makes quite a one-two punch for the Military-Industrial Complex, an inside-outside team that creates the need for more military spending, applies political pressure to ensure higher appropriations, and watches as thankful weapons manufacturers lavish grants on like-minded hawkish Washington think tanks.
Not only does the broader community of neoconservatives stand to benefit but so do other members of the Kagan clan, including Robert’s brother Frederick at the American Enterprise Institute and his wife Kimberly, who runs her own shop called the Institute for the Study of War. Robert Kagan, a senior fellow at the Brookings Institution (which doesn’t disclose details on its funders), used his prized perch on the Washington Post’s op-ed page on Friday to bait Republicans into abandoning the sequester caps limiting the Pentagon’s budget, which he calculated at about $523 billion (apparently not counting extra war spending). Kagan called on the GOP legislators to add at least $38 billion and preferably more like $54 billion to $117 billion.
Read more …

“..the greatest strategic disaster in US history.”
• After a Twelve Year Mistake in Iraq, We Must Just March Home (Ron Paul)
Twelve years ago last week, the US launched its invasion of Iraq, an act the late General William Odom predicted would turn out to be “the greatest strategic disaster in US history.” Before the attack I was accused of exaggerating the potential costs of the war when I warned that it could end up costing as much as $100 billion. One trillion dollars later, with not one but two “mission accomplished” moments, we are still not done intervening in Iraq. President Obama last year ordered the US military back into Iraq for the third time. It seems the Iraq “surge” and the Sunni “Awakening,” for which General David Petraeus had been given much credit, were not as successful as was claimed at the time.
From the sectarian violence unleashed by the US invasion of Iraq emerged al-Qaeda and then its more radical spin-off, ISIS. So Obama sent the US military back. We recently gained even more evidence that the initial war was sold on lies and fabrications. The CIA finally declassified much of its 2002 National Intelligence Estimate on Iraq, which was the chief document used by the Bush Administration to justify the US attack. According to the Estimate, the US Intelligence Community concluded that:
‘[W]e are unable to determine whether [biological weapons] agent research has resumed…’ And: ‘the information we have on Iraqi nuclear personnel does not appear consistent with a coherent effort to reconstitute a nuclear weapons program.’
But even as the US Intelligence Community had reached this conclusion, President Bush told the American people that Iraq, “possesses and produces chemical and biological weapons” and “the evidence indicates that Iraq is reconstituting its nuclear weapons program.” Likewise, Defense Secretary Donald Rumsfeld’s “bulletproof” evidence that Saddam Hussein had ties with al-Qaeda was contradicted by the National Intelligence Estimate, which concluded that there was no operational tie between Hussein’s government and al-Qaeda. Even National Security Advisor Condolezza Rice’s famous statement that the aluminum tubes that Iraq was purchasing “are only really suited for nuclear weapons programs, centrifuge programs,” and “we don’t want the smoking gun to be a mushroom cloud,” was based on evidence she must have known at the time was false. According to the NIE, the Energy Department had already concluded that the tubes were “consistent with applications to rocket motors” and “this is the more likely end use.”
Read more …

“..soil in allotments contains a third more organic carbon than agricultural soil and 25% more nitrogen..”
• We’re Treating Soil Like Dirt. It’s A Fatal Mistake (Monbiot)
Imagine a wonderful world, a planet on which there was no threat of climate breakdown, no loss of freshwater, no antibiotic resistance, no obesity crisis, no terrorism, no war. Surely, then, we would be out of major danger? Sorry. Even if everything else were miraculously fixed, we’re finished if we don’t address an issue considered so marginal and irrelevant that you can go for months without seeing it in a newspaper. It’s literally and – it seems – metaphorically, beneath us. To judge by its absence from the media, most journalists consider it unworthy of consideration. But all human life depends on it. We knew this long ago, but somehow it has been forgotten. As a Sanskrit text written in about 1500BC noted: “Upon this handful of soil our survival depends. Husband it and it will grow our food, our fuel and our shelter and surround us with beauty. Abuse it and the soil will collapse and die, taking humanity with it.”
The issue hasn’t changed, but we have. Landowners around the world are now engaged in an orgy of soil destruction so intense that, according to the UN’s Food and Agriculture Organisation, the world on average has just 60 more years of growing crops. Even in Britain, which is spared the tropical downpours that so quickly strip exposed soil from the land, Farmers Weekly reports, we have “only 100 harvests left”. To keep up with global food demand, the UN estimates, 6m hectares (14.8m acres) of new farmland will be needed every year. Instead, 12m hectares a year are lost through soil degradation. We wreck it, then move on, trashing rainforests and other precious habitats as we go. Soil is an almost magical substance, a living system that transforms the materials it encounters, making them available to plants.
That handful the Vedic master showed his disciples contains more micro-organisms than all the people who have ever lived on Earth. Yet we treat it like, well, dirt. The techniques that were supposed to feed the world threaten us with starvation. A paper just published in the journal Anthropocene analyses the undisturbed sediments in an 11th-century French lake. It reveals that the intensification of farming over the past century has increased the rate of soil erosion sixtyfold. Another paper, by researchers in the UK, shows that soil in allotments – the small patches in towns and cities that people cultivate by hand – contains a third more organic carbon than agricultural soil and 25% more nitrogen. This is one of the reasons why allotment holders produce between four and 11 times more food per hectare than do farmers.
Read more …

Bravo.
• No One Must Go Thirsty: Water In Public Hands Is A Right (Beppe Grillo)
“Why is the water bill so high? In the last few years, have you ever tried to understand why something that should be a right is now something that makes a big hole in your savings? Someone would like to ruin the results of the 2011 referendum, in which a massive majority of the Italian people said “no” to every law that could place the handling of public water into private hands. However, in Italy, strange things are happening: water is cut off indiscriminately and without warning on a regular basis, the price of water has gone up by 95.8% in the last few years, the profits of the municipal companies are no longer being reinvested to reduce leakage but to maximise profits. Basically, those who are now managing water resources are today thinking more about making profits, rather than about providing a service.
The money we are paying in water bills is going to enrich the shareholders with generous dividends. This is a camouflaged privatisation and it is going against what was expressed as the will of the people. The 5 Star MoVement is taking to the European Parliament one of its historical battles: that of defending one of its five stars, keeping water in public hands. The proposal is simple: NO ONE MUST GO THIRSTY The World Health Organization has done the calculations: for an individual’s minimum needs between 50 and 100 litres of water a day are required. This amount must be guaranteed for all. This is why the 5 Star MoVement is proposing a service that provides a guaranteed minimum water supply for each person. It’s not acceptable to get rich by trading in water. That’s the message from the European citizens that have signed a petition asking European institutions NOT to privatise water.
1 million 800 thousand signatures for the first example of direct democracy in Europe. The Commission’s response has been disappointing because it hasn’t put forward any new legislative proposal. The principles contained in its communication are sacred but these need to be reinforced with laws, not just words. Furthermore, as regards the dreaded liberalization of public water, the Commission has underlined that it is up to the member States to make the laws. in particular, it has emphasised that the supply of water is the responsibility of the local authorities within the member State, and it is up to them to make the decisions as to whether to manage the supply directly, indirectly or by using private suppliers.
Read more …