Arthur Rothstein Interior of migratory fruit worker’s tent, Yakima, Washington Jul 1936



“This is the least-believed economic recovery and the least-believed bull market of our careers..”
• The Least-Believed Recovery And The Least-Believed Bull Market (Bloomberg)
Investors hate stocks – again. Amid a six-year bull market that’s notable mainly for how little conviction there is in it, equity sentiment is plunging at a historic rate, falling by some measures at the fastest pace since Federal Reserve Chairman Paul Volcker had just finished pushing up interest rates in the 1980s. The cost to hedge against stock losses is soaring, valuations are contracting, and bearishness among professional stock handicappers is rising the most in three decades. Fret not. All of this is good news for bulls, if history is any guide. Since 1963, the S&P’s 500 Index has advanced an average 11% in the year after newsletter writers surveyed by Investors Intelligence were as pessimistic as they are now, data compiled by Bloomberg show. That compares with an annualized return of 8.3%.
Skepticism is one thing the rally since 2009 hasn’t lacked – and it may be the best thing stocks have going for them as corporate profits fall, concerns deepen over China’s travails, oil and commodities plunge and the Fed turns more pessimistic on global growth. Some traders even say they see bargains after S&P 500 posted its first 10% retreat in four years. “This is the least-believed economic recovery and the least-believed bull market of our careers,” said Bob Doll, chief equity strategist at Chicago-based Nuveen Asset Management, which oversees $130 billion and bought stocks during the August selloff. “The nervousness means people have stepped to the sidelines. The question is, who is left to sell? Everybody who has cash is a potential buyer.”
Investors have bailed out of stocks at every sign of trouble since 2009, from the euro crisis to ebola, with the latest catalyst coming from China’s devaluation of its currency. The distrust has been a barrier to euphoria, a quality that historically is the bigger threat to bull markets. Fear reigns, spreading faster than any time since 1984 as the S&P 500 tumbled 10% over four days in August. At the start of this month, the bull-to-bear ratio in Investors Intelligence’s survey of newsletter writers fell to a four-year low of 0.9. In April, when bulls dominated the market that was heading for an all-time high, the ratio reached 4.1.

“..they MUST raise rates or they will bankrupt countless pension funds and international where emerging markets will go into default..”
• Yellen Is Trapped in the Worst Nightmare Ever (Martin Armstrong)
Yellen has inherited a complete nightmare. Thursday’s decision to delay yet again the long-awaited liftoff from zero interest rates is illustrating that the world economy is totally screwed. There is a lot of speculation about why the Fed seems so reluctant to “normalize monetary policy”. There are of course the typical domestic issues that there is low inflation, weak wage gains in the face of strong job growth, a hike will increase the Federal deficit and then there is the argument that corporations that now have $12.5 trillion in debt. All that is nice, but with corporate debt, our clients are locking in long-term at these levels, not funding anything short-term.
Those clients who have listened are preparing for what is to come unlike government which has been forced to shorten the average duration of their debts blind to what happens when rates rise, which will be set in motion by the markets – not Yellen. Fed is really caught between a rock and a very dark place. Yes, they have the IMF and the world pleading with them not to raise rates for it will hurt other debtors who borrowed excessively using dollars to save money. The Fed is also caught between domestic policy objectives that dictate they MUST raise rates or they will bankrupt countless pension funds and international where emerging markets will go into default because commodities have collapsed and they have no way of paying off this debt that has risen to about 50% of the US national debt.
By avoiding the normalization of interest rates (hikes), the Fed has encouraged government to spend far more than they realize because money is cheap. This will eventually light the fire under the economy helping to fuel the Sovereign Debt Crisis. There appears to be no hope for the Fed and they will be forced to raise rates only when they see asset inflation in equities. Then they will have no choice. This is the worst possible mess and the longer they have waited to normalize interest rates, the worst the total crisis is becoming for they will have zero control over the economy and once that is seen, holy Hell will break lose.

“..a structural shift has beset the world economy.”
• Yellen Pause Ups Pressure on Draghi as Global Pessimism Mounts (Bloomberg)
The global economy caused Janet Yellen to pause for thought. It could spur Mario Draghi to act. After the Federal Reserve chair held off from a U.S. interest-rate increase amid concerns that world growth will weaken, her counterpart at the ECB may give clues on the need for further stimulus for the euro area. Draghi and other Governing Council members will make public appearances this week, while data releases will show whether the currency bloc is succumbing to, or shaking off, the gloom. Like the U.S., the euro area is stuck with stubbornly low inflation. Unlike Yellen, Draghi can’t yet rely on domestic demand to lift prices. Whether because the Fed’s delay leads to a stronger euro, or because of the drag of emerging markets, economists see it as increasingly likely that the ECB will be called on its pledge to boost its €1.1 trillion bond-buying program if needed.
“The worry is that, previously, central banks assumed that global growth would be materially stronger in 2016, but that doesn’t look likely now,” said Nick Kounis at ABN Amro in Amsterdam. “If the Fed had hiked rates, it would have given the ECB some breathing space. Now the pressure is on them again.” The ECB’s optimism that a home recovery coupled with stronger external demand would steer inflation back to the goal of just under 2% is now being replaced by concern that a structural shift has beset the world economy. Executive Board member Peter Praet, the institution’s chief economist, said in an interview published over the weekend that policy makers “won’t hesitate to act” if it they reach that conclusion. Draghi’s lieutenants have been reinforcing that message since the Fed’s rate decision last week.
Benoit Coeure, the ECB’s markets chief, said in a speech in Paris on Friday that prospects for growth in the euro area have “clearly weakened,” and aren’t helped by a euro that’s now strengthening against the currencies of its main trading partners. The single currency has gained 3.5% in trade-weighted terms since mid-July and more than 4% against the dollar. European bonds jumped after the Fed’s Sept. 17 decision to keep its benchmark rate at a record low. Both Praet and Coeure speak in public on Monday, followed by Draghi’s appearance at a European Parliament hearing in Brussels on Wednesday. Hours before Draghi addresses lawmakers, purchasing managers’ surveys for September may tell investors whether Europe’s manufacturing and services industries are indeed succumbing to lower external demand, or whether domestic consumers are helping to prop them up.

“..public understanding of the Fed’s behavior “an essential foundation for the monetary stability we currently enjoy.”
• Fed’s Lacker Says Economy Strong Enough For Higher Rates (Reuters)
Richmond Federal Reserve President Jeffrey Lacker on Saturday said he dissented at a Fed policy meeting because he thought the economy was now strong enough to warrant higher interest rates. Fed policymakers on Thursday voted to keep the Fed’s target interest rate at between zero and a quarter point. “Such exceptionally low real interest rates are unlikely to be appropriate for an economy with persistently strong consumption growth and tightening labor markets,” Lacker said in a statement. He was the lone dissenter among the 10 Fed officials who voted at the meeting. Lacker said the Fed’s target should rise by a quarter point. Lacker has a history of dissent in Fed policy meetings. In 2012, he voted against eight straight policy decisions by the central bank.
At the time he was urging the Fed to wind down asset purchases that were aimed at stimulating the economy. Regarding Thursday’s decision at the Fed, Lacker said a rebound in consumer spending and “tightening labor markets” meant the economy no longer needed zero interest rates. He said keeping interest rates at their current level deviated from the way the Fed has responded to the economy in the past, which was dangerous because public understanding of the Fed’s behavior was “an essential foundation for the monetary stability we currently enjoy.” “Such departures are risky and raise the likelihood of adverse outcomes,” Lacker said.

Extending the narrative.
• Fed’s Williams Still Sees 2015 Rate Hike After ‘Close Call’ (Reuters)
An interest rate hike will likely be appropriate this year given the U.S. Federal Reserve’s decision last week to stand pat was a “close call,” a top Fed policymaker said on Saturday. John Williams, a centrist and president of the San Francisco Fed, said the arguments for and against beginning to tighten U.S. monetary policy are about balanced now that the economy is on solid footing, giving him confidence in continued economic and labor market growth. Williams, the first U.S. policymaker to speak publicly since the Fed’s much-anticipated decision on Thursday, suggested he is almost ready to pull the trigger on a rate hike. He acknowledged the risks from a slowdown in China and global downward pressure on inflation, noting a rate rise in 2015 is not guaranteed.
But he said full U.S. employment should be achieved “in the near future” and inflation, while still too low for comfort, should gradually move back to a 2% goal. “Given the progress we’ve made and continue to make on our goals, I view the next appropriate step as gradually raising interest rates, most likely starting sometime later this year,” he said at a weekend conference on the China-U.S. financial system. The Fed’s decision to leave rates near zero “was a close call in my mind, in part reflecting the conflicting signals we’re getting,” he said. “The U.S. economy continues to strengthen while global developments pose downside risks to fully achieving our goals.”

Falling further as the day goes on. “The violations, which affect nearly half a million vehicles, could result in as much as $18 billion in fines.”
• Volkswagen Plunges 25% After US Emissions Cheat Scandal (Bloomberg)
Volkswagen dropped the most in almost seven years after it admitted to cheating on U.S. air pollution tests for years, risking billions in potential fines and a backlash from consumers in the world’s second-biggest car market. The shares declined as much as 17%, or €27.9, to €134.5 in Frankfurt, the most since Nov. 3, 2008. The drop extends the slump for the year to 25%, valuing the Wolfsburg, Germany-based company at €65.3 billion. Volkswagen Chief Executive Officer Martin Winterkorn said on Sunday that the company is cooperating with the probe and ordered its own external investigation into the issue. The CEO said he was “deeply sorry” for breaking the public’s trust. VW has halted sales of the car models involved, which were a cornerstone of Winterkorn’s effort to catch up in the U.S.
The violations, which affect nearly half a million vehicles, could result in as much as $18 billion in fines. Criminal prosecution is also possible. “If this ends up having been structural fraud, the top management in Wolfsburg may have to bear the consequences,” said Sascha Gommel, a Frankfurt-based analyst for Commerzbank AG, whose share rating is under review. The German carmaker admitted to fitting its U.S. diesel vehicles with software that turns on full pollution controls only when the car is undergoing official emissions testing, the Environmental Protection Agency said Friday. The violations, which affect nearly half a million vehicles, could result in as much as $18 billion in fines. Criminal prosecution is also possible.
Analysts at Kepler Cheuvreux downgraded the shares to “hold” from “buy,” cutting their target price 27% to €185. Volkswagen faces not only a short-term drop in sales and hit to its reputation but also the longer-term risk of litigation in the U.S., the analysts wrote in a note on Monday. During normal driving, the cars with the software – known as a “defeat device” – would pollute 10 times to 40 times the legal limits, the EPA estimated. The discrepancy emerged after the International Council on Clean Transportation commissioned real-world emissions tests of diesel vehicles including a Jetta and Passat, then compared them to lab results. Volkswagen had counted on clean, powerful diesel cars to help it build its sales in the U.S., where it has struggled for years. Sales of VW-brand cars in the country dropped 10% last year to 366,970.

Lame duck.
• Greece’s Year Of Tumult Enters New Chapter As Tsipras Dominates (Bloomberg)
Greek voters had the choice to reject the man who led their country closer than ever to being forced out of Europe’s single currency. Instead, they embraced him. Alexis Tsipras and his Coalition of the Radical Left, or SYRIZA, emerged from a second election in eight months with a level of support barely diminished from the emphatic victory that catapulted him both into power and a standoff with the euro region. SYRIZA, which took 35.5% of the vote compared with 28.1% for the center-right New Democracy, will enter a coalition with the same small party that helped it rule before. While the victory tightens Tsipras’s hold over Greek politics, it also exposes the paradoxes of a country whose economy is a shadow of its former self and where controls remain on bank withdrawals.
After coming to power pledging to end austerity and restore “dignity,” Tsipras now must implement the further sharp spending cuts and tax increases he ended up agreeing to in exchange for €86 billion of fresh European aid. The electorate has voted to return to power a party that “ditched its promises, switched its policies, and caused the collapse of Greek banks, bringing in an unneeded recession,” said Stathis Kalyvas, a professor of political science at Yale University. On the other hand, “this government will be called to implement a stringent set of fiscal and structural reforms that it vigorously rejected before,” he said.

What EU says is non-negotiable.
• Debt Relief Tops Tsipras Agenda, Party Official Says (Reuters)
Negotiations over Greece’s debt will top the agenda for Prime Minister-elect Alexis Tsipras from Monday as he prepares for a return to office following a surprisingly easy national election win, a senior source from his party said. Tsipras and his leftist SYRIZA party clinched a clear victory in Sunday’s poll as voters put aside his dramatic U-turn over Greece’s international bailout to offer him a second chance to steer a battered economy to recovery. SYRIZA said on Sunday it plans to govern in a coalition with the small right wing Independent Greeks party, the same partner Tsipras chose after winning the country’s previous general election in January. But to strengthen his hand in talks with EU partners over how to ease Greece’s debt burden, he will seek a broader consensus among the parties he defeated on Sunday, the party source said.
“We will continue negotiations in the coming period, with the debt issue being the first and most important battle,” the source said. “We will ask all political forces to support our efforts.” Some European governments, particularly Germany, are opposed to cutting Greece’s debt – a so-called haircut – but not averse to stretching out its repayment schedule. Eurozone officials told Reuters last week that governments are ready to cap Greece’s debt-servicing costs at 15% of GDP annually over the long term. That would mean the nominal payment would be lower if the Greek economy struggled, higher if it was more robust, they said.
Tsipras is also planning to form a national council for European policy, including representatives of parties other than the Independent Greeks and which would advise the finance minister, the SYRIZA source said. Centre-left daily newspaper Ethnos tipped Euclid Tsakalotos, the former finance minister who brokered terms of the bailout accord in August, to be re-appointed. JP Morgan analyst Malcolm Barr said he expected some sort of debt restructuring to be in place by early next year. “We continue to think that… the (bailout) programme will make enough progress to allow a restructuring of loans from euro area countries by the end of the first quarter of 2016,” he wrote in a note.

Brussels has lost all sense of the limits of interfering in sovereign nations. This is none of Schulz’s business.
• EU’s Schulz Says Cannot Understand Tsipras’ Greek Coalition Choice (Reuters)
The head of the European Parliament, Martin Schulz, lamented on Monday the decision by Greek leftist Alexis Tsipras to renew a coalition with the small right-wing Independent Greeks party. Tsipras stormed back into office with an unexpectedly decisive election victory on Sunday, claiming a clear mandate to steer Greece’s battered economy to recovery. The vote ensured Europe’s most outspoken leftist leader would remain Greece’s dominant political figure, despite having been abandoned by party radicals last month after he caved in to demands for austerity to win a bailout from the eurozone. Speaking to France Inter radio, Schulz said he could not understand Tsipras’ decision to bring the Independent Greeks, who polled less than 4% of the vote, back into government.
“I called him (Tsipras) a second time to ask him why he was continuing a coalition with this strange, far-right party,” Schulz said. “He pretty much didn’t answer. He is very clever, especially by telephone. He told me things that seemed convincing, but which ultimately in my eyes are a little bizarre.” Independent Greeks leader Panos Kammenos says the bailout by the European Union, European Central Bank and International Monetary Fund has reduced Greece to the status of a debt colony.
The party differs from Syriza on many traditionally conservative issues, pledging to crack down on illegal immigration and defend the close links between the Orthodox Church and the state. Schulz said he admired Tsipras for the way he had navigated through the last year to get himself re-elected, but said Kammenos was a loose canon who always needed to be controlled. “It’s politically and strategically something that you have to admire,” he said. “But after … this renewed mandate with this far-right, populist party, that I don’t understand.”

The US must be part of the solution too.
• A Frontline Solution to Europe’s Refugee Crisis: Remember Ellis Island (WSJ)
Tabanovce, Macedonia: This quaint Macedonian village provides a useful vantage point for anyone hoping to grasp the scale of the current European refugee crisis. Up to 7,000 refugees have been passing through here daily before crossing the border with Serbia. A generation ago this region escaped communism, then fought bitter ethnic and sectarian wars that lasted until 2001. Now its nations find themselves in the eye of a humanitarian storm. And Europe is no closer to a durable solution. Short of military intervention to stabilize some of the Middle East hotspots the refugees are fleeing, the only long-term response is to develop legal, safe conduits that bring refugees to European Union-funded and operated frontline processing centers, say, on the Greek and Italian isles and Turkey’s western coast.
Asylum-seekers would be offered fair, humane and expedient processing. Those relying on trafficker routes would be routed back to these centers. Accepted refugees would be placed depending on host-country capacity, family and communal ties, and related factors. The U.S. experience on Ellis Island at the turn of the 20th century is instructive. The island processed an astonishing 1.25 million immigrants in 1907, a banner year for U.S. immigration. In the next decade U.S. immigration authorities also mastered immigrant processing—including ultra-efficient medical checks and questioning—aboard ships. The situations aren’t precisely analogous. At Ellis Island’s height as a processing center, America maintained a more or less open-door policy.
But the main lesson for Europe today lies in the American government’s ability at that time to impose order on human chaos on a scale similar to the current refugee crisis. Central to that success was the existence of a singular executive with broad discretion to examine, process, accept and in some cases reject migrants. Compare that achievement with Europe’s mess today. As the crisis mounted, the states on the Balkan corridor—Greece, Macedonia, Serbia and Turkey—provided refugees easy passage toward Hungary. Macedonia and Serbia especially became efficient at getting refugees in and out of their territory as quickly as possible, sometimes within a day. Balkan governments knew that most refugees were headed for Germany, Sweden and the like, and after minimal processing they granted papers allowing refugees to head north.

Should have been done from the start.
• Central Europe Gives Up On Holding Refugees Back From Austria (Guardian)
The countries of central Europe suspended their resistance this weekend to Europe’s largest refugee exodus since the second world war, as Hungary, Slovenia and Croatia all shunted tens of thousands of people towards Austria, reversing most recent attempts to block their passage. At least 15,000 refugees mainly from Syria, Afghanistan and Iraq were funnelled from Croatia into Hungary and then onwards to Austria over the weekend, the Austrian news agency APA said, after Hungary temporarily gave up trying to stop refugees from crossing its border. Another 2,500 have crossed from Croatia into Slovenia, despite Slovenia initially trying to block their passage. The moves represent a volte-face from both countries – and in particular from Hungary.
The Budapest government had previously tried to stop the entry of undocumented travellers by building a fence along its southern border with Serbia, and by posting military vehicles on its western border with Croatia. But by Sunday, its resistance was mostly rhetorical. The country admitted thousands of refugees over the weekend from Croatia, whose shared border is not yet blocked by a fence, even as foreign minister Péter Szijjártó promised tougher measures in the future. Szijjártó said: “We are a state that is more than 1,000 years old that throughout its history has had to defend not only itself, but Europe as well many times. That’s the way it’s going to be now.”
Thousands more continued to enter Europe on Saturday and Sunday at the other end of the refugee route in the Greek islands, where coastguards said that 24 people were feared to have drowned on Sunday. An inflatable refugee boat, attempting to reach Lesbos from the Turkish shoreline, capsized before it reached its destination, and only 22 out of 46 passengers were rescued. The number of migrant shipwrecks in the Aegean has increased in recent days, with Sunday’s incident the sixth in a week of accidents that have left around 100 dead.
For many of the survivors, the trauma has not ended with their rescue: it emerged on Sunday that more than 200 Syrians and Iraqis saved by the Turkish coastguard following the sinking of their ship near Kos had allegedly been threatened with deportation back to the war zones they had just fled. One Syrian survivor, who asked not to be named as she is still in detention, said in a voice message: “They are threatening us that Syrians will be deported to Syria, Iraqis to Iraq. If they send us back to Syria we will die.” The Turkish government has denied any Syrians will be deported.

No kidding, the headline still said ‘emergency summit’.
• We Must Act Together, Says Merkel Ahead Of Refugee Summit (Guardian)
A divided European leadership will try to seek a credible response to the continent’s worst migration crisis since second world war at an emergency summit on Wednesday. As central European countries abandoned attempts to stop thousands of refugees from crossing their borders towards Austria on Sunday, German chancellor Angela Merkel called on her peers to accept joint responsibility. “Germany is willing to help. But it is not just a German challenge, but one for all of Europe,” Merkel told a gathering of trade unionists. “Europe must act together and take on responsibility. Germany can’t shoulder this task alone.“ Striking a more sceptical tone on migration than in previous weeks, Merkel also warned that Germany could not shelter those who were moving for economic reasons rather than to flee war or persecution.
“We are a big country. We are a strong country. But to make out as if we alone can solve all the social problems of the world would not be realistic,” she told a gathering of the Verdi trade union. The foreign ministers of the Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, Slovakia, Romania and Latvia will hold talks on Monday with their counterpart from Luxembourg, which currently holds the EU presidency, aimed at addressing divides between neighbouring states. Donald Tusk, president of the European Council, who chairs EU summits, said on Twitter on Sunday following a weekend visit to Jordan and Egypt that the EU needed to help Syrian refugees find a better life closer at home.
That will be one of the topics of discussion for Wednesday’s summit in Brussels as hundreds of thousands of refugees and migrants brave the seas and trek across the Balkan peninsula to reach the affluent countries of northern Europe. The 28-member bloc has struggled to find a unified response to the crisis, which has tested many of its newer members in the east that are unaccustomed to large-scale immigration. On Sunday Hungary erected a steel gate and fence posts at a border crossing with Croatia, the EU’s newest member state. Overwhelmed by an influx of some 25,000 migrants this week, Croatia has been sending them north by bus and train to Hungary, which has waved them on to Austria.

Europe remains in bland denial of reality. And that’s dangerous.
• Merkel Coalition at Odds Over Proposal to Cap EU Asylum Places (Bloomberg)
German Vice Chancellor Sigmar Gabriel said he doesn’t “understand” Interior Minister Thomas de Maiziere’s proposal for the European Union to set an upper limit to the number of people it accepts as asylum seekers. “It’s the opposite of what the Chancellor has rightly said, namely that those who arrive in Germany and apply for asylum need a fair procedure,” Gabriel, who’s also chairman of the Social Democratic Party, said Sunday on ARD public television. “It is not a solution to establish quotas for asylum seekers. Incidentally, it is also contrary to the German constitution.” Support for two German opposition parties not represented in parliament rose as criticism of Merkel’s handling of Europe’s refugee crisis mounted.
Backing for the Free Democrats, Merkel’s former coalition partner, and the anti-euro Alternative for Germany party each increased 1%age point to 5% in a weekly poll, Bild am Sonntag reported. “We can’t host all the people from conflict areas and all poverty refugees who want to come to Europe and to Germany,” de Maiziere told Germany’s Spiegel magazine. “The right way would be that we in the EU commit ourselves to fixed, generous quotas for the admission of refugees.” A call by one of his party deputies that de Maiziere, a member of Chancellor Angela Merkel’s Christian Democratic Union, should resign unless he succeeds at accelerating asylum procedures was “nonsense,” Gabriel said.
Labor Minister Andrea Nahles said in an interview with Deutschlandfunk public radio she expects German unemployment figures to rise next year due to “a significant increase” in the number of refugees seeking work as “not every refugee who comes now is already automatically a qualified worker.” All parties represented in the lower house of parliament shed 1%age point in the Emnid poll, with Merkel’s Christian Union bloc dropping to 40%, her Social Democrat coalition partner to 24%, the Greens to 10% and the Left party to 9%.

How about 1 million, just to begin with?
• 15,000 More Refugees To Be Resettled In US Next Year (WaPo)
The United States will increase its cap on the number of refugees it admits and resettles to 85,000 in the coming fiscal year and to 100,000 in 2017, Secretary of State John F. Kerry said Sunday. The additional refugees, up from 70,000 in the current fiscal year that ends Sept. 30, will come from countries around the world. But the increase largely reflects the 10,000 Syrian refugees that the White House earlier this month promised to admit. Kerry said the administration is exploring ways to admit even more, but Congress must approve enough money to cover the extra cost of resettlement. “This step is in keeping with America’s best tradition as a land of second chances and a beacon of hope,” Kerry said in announcing the increase during a visit to Berlin to discuss the Syrian refugee crisis with his German counterpart, Frank-Walter Steinmeier.
Even before Syrian refugees began streaming into Europe in recent weeks, the State Department had been considering a modest increase of about 5,000 refugees, including more from Congo, where human rights abuses are rampant. At the end of each fiscal year, the State Department announces the new target number for refugees. Although the administration can unilaterally set a numerical goal for the refugees it wants to accept, it is up to Congress to agree to fund the resettlement. In the current fiscal year, it cost $1.1 billion to bring 70,000 refugees to the United States, put them through an orientation program run by refugee charities and have them dispersed throughout the country. It was not immediately clear how much more it will cost to bring in more Syrians.
One of the reasons it is so expensive is that every refugee must undergo extensive background checks under security measures enacted after the terrorist attacks of Sept. 11, 2001. Those checks have been taking 18 to 24 months for Syrians, according to State Department figures. A senior State Department official said many, many more refugees could be admitted if officials can find ways to streamline the system without jeopardizing security. Refugees admitted for resettlement are selected from lists provided by the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. So far, about 1,600 of more than 18,000 Syrians referred by the U.N. refugee agency since the conflict began have arrived in the United States about 1,500 in this fiscal year alone. More than 10,000 are well along in being vetted, and they are expected to arrive in much greater numbers in the coming months.

Let’s be honest, that UN meeting willl lead to nothing at all.
• UN Meets To Fight Poverty, Europe Puts Up Razor Wire To Keep Poor Out (Guardian)
The contrast could hardly be sharper. Razor wire fences are being constructed to keep the uprooted poor out of the European Union at the very moment the United Nations meets to agree anti-poverty goals for the next 15 years. No question, the gathering in New York will be a regular jamboree. There will be mutual backslapping about the progress that has been made over the past 15 years, a good deal of it justified. Countries will solemnly pledge to meet the 17 sustainable development goals, with 169 specific targets, by 2030. They will turn a blind eye to what is happening in Serbia, Hungary, Croatia and Austria. The truth, though, is that there is a link between the UN shindig and the most severe refugee crisis in generations: inequality.
It is the obvious disparity between life in a rich country and life in a poor country that makes the long and dangerous journey to the west attractive. It is the gap between rich and poor within developed countries that has helped foster a deep suspicion, not just of unlimited migration, but of free movement of capital and goods as well. And without addressing inequality head on, ensuring that growth benefits the poor by as much as it benefits the rich, there is not the remotest chance that the ambitious goals being embraced in New York this week will be met. Here’s the picture. The SDGs replace the millennium development goals that set the framework for poverty reduction between 2000 and 2015, but are much tougher.
The MDGs sought to make progress in areas such as poverty reduction or infant mortality: the SDGs will commit the international community to more ambitious goals, which include ending poverty and hunger, and ensuring healthy lives and access to quality education for all. There are reasons to be optimistic. Much progress has been made in the past two decades, in large part due to the rapid growth in China. One billion people have been lifted out of poverty and the MDG objective of halving the number living below the global agreed minimum was achieved five years early. This will be seen by world leaders as evidence that even more can be done in the next 15 years.
But achieving the new SDGs would be a gargantuan task in the best of times. And these are not the best of times. China is growing more slowly, with concerns that doctored official figures mask a hard landing. Emerging markets in the rest of the world are being hurt both by weaker Chinese demand for their commodities and by the continued sluggishness of the big western economies. The Great Recession of 2008-09 continues to cast a long shadow.

Back to the future. “Mr. Xi is backfilling his vision and seeking a fresh source of legitimacy by reinventing the party as inheritor and savior of a 5,000-year-old civilization.”
• Why China Is Turning Back to Confucius (WSJ)
One Thursday morning in June, 200 senior officials crammed into an auditorium in the Communist Party’s top training academy to study a revolutionary idea at the heart of President Xi Jinping’s vision for China. They didn’t come to brush up on Marx, Lenin or Mao, staple fodder at the Central Party School since the 1950s. Nor were they honing their grasp of the state-guided capitalism that defined the nation for the last 35 years. They came to hear Wang Jie, a professor of ancient Chinese philosophy and a figure in the country’s next ideological wave: a renaissance of the traditional culture the Communist Party once sought to destroy.
For two hours, Prof. Wang says, he reeled off quotes from Confucius and other Chinese sages—whom the party long denounced as feudal relics—and urged his audience to incorporate traditional concepts of filial piety and moral rectitude into their personal and professional lives. “I’m getting hoarse,” Prof. Wang says over a cup of green tea after class. The previous day, he had lectured at the culture ministry and, the day before, at the commerce ministry. Monday would be the insurance regulator. “Xi Jinping’s words,” he says, “have lit a fuse.” Two years after outlining a “China Dream” to re-establish his nation as a great world power, Mr. Xi is backfilling his vision and seeking a fresh source of legitimacy by reinventing the party as inheritor and savior of a 5,000-year-old civilization.
The shift forms the backdrop for Mr. Xi’s visit to the U.S. this week and could shape China for years. Mr. Xi appears to be seeking to inoculate Chinese people against the spread of Western political ideals of individual freedom and democracy, part of what some political insiders say he views as a long-term contest of values and ideology with the U.S. The effort is gaining urgency now, as an economic slowdown and stock-market rout fray the social compact of the last three decades in which citizens traded political freedom for rapid wealth creation. With Communist dogma and Chinese-style capitalism losing appeal, the party needs fresh ideas. “It’s like the prodigal son returning,” says Guo Yingjie, a University of Sydney Chinese-studies professor who wrote a book on Chinese cultural nationalism. “China has had more than a century of anti-traditionalism. Now they’re heading in the opposite direction.”

Well, obviously: “You f***ing Americans. Who are you to tell us, the rest of the world, that we’re not going to deal with Iranians?”
• Was Standard Chartered Flouting US Iranian Sanctions? (FT)
The expletive-laden exclamation attributed to a senior Standard Chartered executive in 2006 may well come back to haunt the British bank. “You f***ing Americans. Who are you to tell us, the rest of the world, that we’re not going to deal with Iranians?” For US authorities, who included the quote in a legal filing, the statement came to define StanChart’s “obvious contempt” for American banking regulations, including sanctions designed to cut Iran off from access to the US dollar. Nine years on, after paying nearly $1bn in fines to US regulators and law enforcement agencies for sanction breaches and compliance failures, StanChart seems no closer to ending its legal problems. An FT investigation has identified transactions involving Iran that could put the bank at risk of severe penalties ranging from further fines to suspension or loss of its crucial dollar clearing licence.
Documents seen by the FT suggest that StanChart continued to seek new business from Iranian and Iran-connected companies after it had committed in 2007 to stop working with such clients. These activities include foreign exchange transactions that, people familiar with StanChart operations say, would have involved the US dollar. The documents suggest the bank — a few months after a costly settlement with US authorities in 2012 — was still internally reviewing its client list and was unable to determine in certain cases whether customers were Iranian or not. For Bill Winters, the American former JPMorgan investment banker who took over as StanChart’s chief executive in June, the stakes could hardly be higher. The London-listed lender, that specialises in Asia, the Middle East and Africa, is already grappling with slowing growth in emerging markets and a slide in commodity prices.
While it has relatively small operations in the US, the loss of its dollar clearing licence would deal a crippling blow to StanChart’s ability to finance the trade, energy and cross-border activities that have become its main focus. Suspending the dollar clearing rights for banks accused of breaching sanctions is a rare punishment. But US regulators have cracked down hard on institutions for breaching sanctions on Iran, amid concerns about money flowing to the country’s nuclear programme or to militant Islamist organisations such as Hizbollah in Lebanon or the Palestinian group, Hamas. The US has mostly relied on levying heavy fines against non-US banks for using dollars to do business with Iran — frequently causing controversy in those banks’ home countries. BNP Paribas last year paid $8.9bn in fines and had some dollar clearing rights suspended temporarily for such breaches, prompting angry accusations from French politicians of US over-reach.

I’ll believe it when I see it.
• Nine On Lagarde List Being Probed For Money Laundering (Kath.)
Greek judicial authorities are investigating the possibility that up to nine people on the Lagarde list of Greeks with deposits at the Geneva branch of HSBC were involved in a large money-laundering network, Kathimerini understands. Prosecutors from Greece recently questioned Herve Falciani, the former HSBC employee who extracted the data on the list, and he is believed to have given them information that points to the existence of a major money-laundering operation. Prior to speaking to Falciani, Greek authorities had identified three suspects. Kathimerini understands that Greek prosecutors, led by the head of the first instance prosecutor’s office, Ilias Zagoraios, have been in contact with counterparts in France, Spain and Italy regarding the matter. They are expected to make a second trip to Paris to interview Falciani in the coming weeks.

More trouble on the way.
• The Massacre Of The Kurds And The Silence Of Europe (M5S Lower House)
“In the last few days, Turkish Military units have entered northern Iraq in an operation against the guerrillas of the Kurdistan Workers’ Party (PKK). The Ankara government has defined it as land-based incursion and a “short-term” measure to finally “eliminate” the “rebels”. We are given to believe that Erdogan took the decision to intervene following the PKK attack in Igdir last Tuesday which killed 13 local police officers. But the truth is that for some months now, the Turkish army has being besieging the only entity that has demonstrated it is really able to stop the advance of ISIS. And Europe stays silent, enclosed in a shell of hypocrisy and opportunism. The “popular resistance” cells have collapsed.
They were formed last March when different member states (including Italy) gave the green light to sending in arms to the Peshmerga. Even the government stays silent. There’s not a word from Minister Gentiloni even while the Turkish air force is continuing an indiscriminate attack on rebels and civilians. This is not simply shameful. It’s showing the double standards used by the West where people are ready to tear their hair out when looking at the dead body of little Aylan, but where they are careful to stay silent when their own interests, or the interests of their allies are at stake. In fact, Turkey is the only member that NATO has in the Middle East.
It is in a strategic position (to the East it has borders with Armenia, Azerbaijan and Iran, to the South East it borders Iraq and to the South, Syria). The USA cannot do without it and the EU feels it has a duty to protect it. It doesn’t matter whether the game play involves the sacrifice of the fundamental rights of a people who for decades have been legitimately claiming their independence and autonomy. This is why the EU remains silent even in relation to Erdogan’s intentions to change the constitution to give himself more powers and even thinking of the city of Cizre that is now on its last legs – after suffering a blackout for more than a week, without new supplies of food and water. And meanwhile ISIS is moving forward, conquering, and threatening our country, but above all threatening the survival of democracy.

Reads the Automatic Earth?
• Safe Assets In A World Gone Mad (Chatham)
Gold and silver are good assets to hold to insure the preservation of EXCESS wealth but there are other assets that are even more valuable longterm. Those things that can be used to produce a product are the elements that can be used to leverage your time, resources and talents to produce wealth. The ability to produce excess is the basis of the need for wealth preservation. Physical goods in the form of equipment that can be used to create or produce goods needed by society are the basis of prosperity and wealth in the world. Gold and silver only become necessary when society begins to produce more products than the producer can use. This excess production is then traded for those things that can preserve the value of this excess production until it is needed by individuals.
Machines to build or repair such as saws and hammers, sewing machines, metal fabricating machines such as lathes and mills and machines to convert raw materials to value added products such as steel to I beams or pots and pans, wheat to flour or pasta, lumber to finished furniture and cotton to cloth are the assets that define how prosperous you are as a nation. A nation derives its wealth from having a product to sell. That will never change. It is true for nations as well as for individuals.
Individuals need to have the ability to produce something in excess of their needs to advance to the need to store that excess. This requires tools and equipment in most cases. You do not necessarily need to process your own resources to generate this excess. A miller can provide the equipment to grind grain for the community taking part of the production for his time and effort. This gives rise to the service economy where individual specialization is traded for other services and resources rendered. In most cases this service will require specialized equipment not possessed by the general population. This specialized equipment is an asset more valuable than gold and silver in many cases.

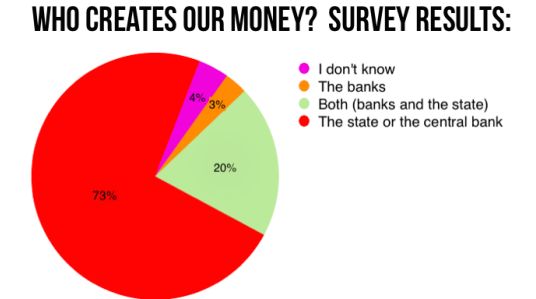
Only 4% of Swiss know.
• People Have No Idea How Money Is Created (PM.org)
Interesting news from our sister organisation MoMo in Switzerland: The survey results from a master’s thesis from the Institute of Finance and Banking at Zurich University confirm that Swiss people have no idea about how Swiss Francs are created. Here are the results and the main reactions from the press: A survey has been carried out as part of a master’s thesis at the University of Zurich about the level of knowledge in the general population about the financial system. The results are astonishing:
• Only 13% know that private commercial banks provide the majority of the money in circulation.
• However, 78% of the Swiss population would like money to be produced and distributed solely by a public organisation working for the common good, such as the National Bank.
• Only 4% preferred the system we actually have today – that money is mostly created by private, for-profit companies such as commercial banks.The survey results reinforce the Vollgeld Initiative, which currently has more than 90,000 signatures of the 100,000 required to force a binding national referendum in Switzerland. The study shows clearly that the Swiss people do not know who actually creates the Swiss Franc: Only 13% of the population are aware that, in the current system, private banks produce the majority of the money through the extension of loans. 73% mistakenly believe money is created by the state or by the Swiss National Bank.