Russell Lee Proprietor of small store in market square, Waco, Texas Nov 1939
| • Negative Interest, the War on Cash and the $10 Trillion Bail-In (Ellen Brown) |
| • Sub-Zero Debt Increases To $2 Trillion In Eurozone On Draghi (Bloomberg) |
| • Soaring Global Debt – The Reality Check in Numbers (O’Byrne) |
| • The Closing Of The Global Economy (Calhoun) |
| • Harmless Commodity Crash Accelerates As Dollar Soars (AEP) |
| • Ireland Is Backing Itself (David McWilliams) |
| • Greek Home Rental Costs 40% Less Since 2011 (Kath.) |
| • Four In 10 Greeks ‘Overburdened’ By Housing Costs (Kath.) |
| • Greek Shipping Currency Inflows Drop 53% In September (Kath.) |
| • Inadequate Dirty Money Regulation ‘Leaves UK Open To Terror Funds’ (Reuters) |
| • Cameron Has Guns, Bombs And A Plane – And Not One Good Idea (Hitchens) |
| • Scale Of Osborne’s Cuts To Police, Education, Councils ‘Unprecedented’ (Mirror) |
| • Austeria – A Nation Robs Its Poor To Pay For The Next Big Crash (Chakrabortty) |
| • Richard Russell, Publisher of Dow Theory Letters, Dies at 91 (Bloomberg) |
| • VW Admits Second Illegal Device In 85,000 Audi Engines (FT) |
| • Average House In Fort McMurray Lost $117,000, 20% Of Its Value In 1 Year (CH) |
| • This Is The Worst Time For Society To Go On Psychopathic Autopilot (F. Boyle) |
| • Varoufakis: Closing Borders To Muslim Refugees Only Fuels Terrorism (Guardian) |
| • Average Stay Is 17 Years: Refugee Camps Are The “Cities Of Tomorrow” (Dezeen) |
| • Canada To Turn Away Single Men As Part Of Syrian Refugee Resettlement Plan (AFP) |
| • Stranded Migrants Block Railway, Call Hunger Strike (Reuters) |



“..central banks have already pushed the prime rate to zero, and still their economies are languishing. To the uninitiated observer, that means the theory is wrong and needs to be scrapped.”
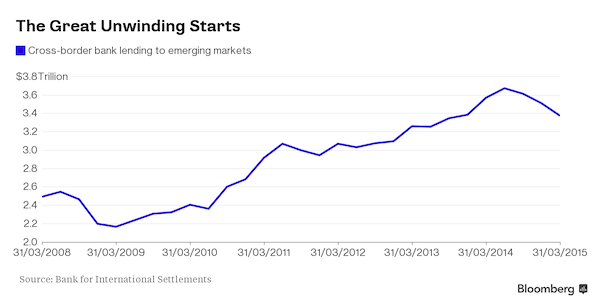
• Negative Interest, the War on Cash and the $10 Trillion Bail-In (Ellen Brown)
Remember those old ads showing a senior couple lounging on a warm beach, captioned “Let your money work for you”? Or the scene in Mary Poppins where young Michael is being advised to put his tuppence in the bank, so that it can compound into “all manner of private enterprise,” including “bonds, chattels, dividends, shares, shipyards, amalgamations . . . .”? That may still work if you’re a Wall Street banker, but if you’re an ordinary saver with your money in the bank, you may soon be paying the bank to hold your funds rather than the reverse. Four European central banks – the European Central Bank, the Swiss National Bank, Sweden’s Riksbank, and Denmark’s Nationalbank – have now imposed negative interest rates on the reserves they hold for commercial banks; and discussion has turned to whether it’s time to pass those costs on to consumers.
The Bank of Japan and the Federal Reserve are still at ZIRP (Zero Interest Rate Policy), but several Fed officials have also begun calling for NIRP (negative rates). The stated justification for this move is to stimulate “demand” by forcing consumers to withdraw their money and go shopping with it. When an economy is struggling, it is standard practice for a central bank to cut interest rates, making saving less attractive. This is supposed to boost spending and kick-start an economic recovery. That is the theory, but central banks have already pushed the prime rate to zero, and still their economies are languishing. To the uninitiated observer, that means the theory is wrong and needs to be scrapped. But not to our intrepid central bankers, who are now experimenting with pushing rates below zero.
The problem with imposing negative interest on savers, as explained in the UK Telegraph, is that “there’s a limit, what economists called the ‘zero lower bound’. Cut rates too deeply, and savers would end up facing negative returns. In that case, this could encourage people to take their savings out of the bank and hoard them in cash. This could slow, rather than boost, the economy.” Again, to the ordinary observer, this would seem to signal that negative interest rates won’t work and the approach needs to be abandoned. But not to our undaunted central bankers, who have chosen instead to plug this hole in their leaky theory by moving to eliminate cash as an option. If your only choice is to keep your money in a digital account in a bank and spend it with a bank card or credit card or checks, negative interest can be imposed with impunity. This is already happening in Sweden, and other countries are close behind.
Read more …

His understanding of what he’s doing is sub-zero too.
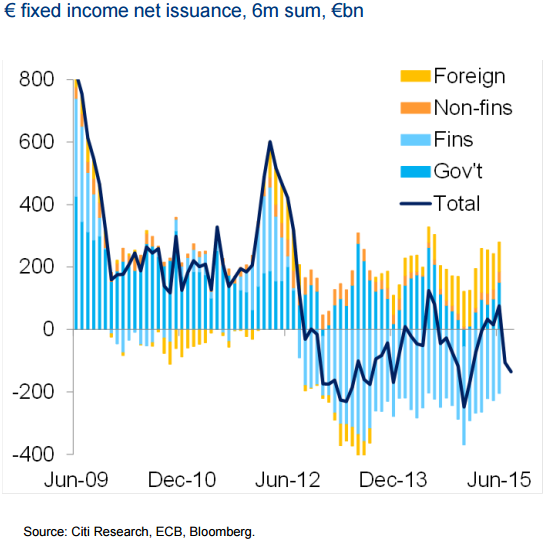
• Sub-Zero Debt Increases To $2 Trillion In Eurozone On Draghi (Bloomberg)
Investor expectations of expanded monetary easing from ECB President Mario Draghi have pushed the amount of euro-area government securities that yield below zero to more than $2 trillion. Bonds across the region climbed last week when Draghi said the institution will do what’s necessary to rapidly accelerate inflation. The statement recalled the language of his 2012 pledge to do “whatever it takes” to preserve the euro and it solidified investor bets on further stimulus at the ECB’s Dec. 3 meeting. While 10-year bonds fell Monday, the two-year note yields of Germany, Austria and the Netherlands all dropped to records. “The ECB is doing little to counter this market speculation,” said Christoph Rieger at Commerzbank in Frankfurt. “Should they not deliver now it would clearly cause a huge backlash with regards to the euro and overall valuations.”
The anticipation of greater easing has also undercut the euro. The single currency weakened to a seven-month low on Monday after futures traders added to bearish bets. A 10 basis- point cut in the deposit rate is now fully priced in, according to futures data compiled by Bloomberg, while banks from Citigroup to Goldman Sachs, are predicting an expansion or extension of the ECB’s €1.1 trillion quantitative-easing plan. Negative-yielding securities now comprise about one-third of the $6.4 trillion Bloomberg Eurozone Sovereign Bond Index. The amount compares with $1.38 trillion before Draghi’s Oct. 22 press conference, where he pledged to re-examine stimulus at the institution’s December meeting.
Read more …

“Indeed, not only does war lead to debt, but high levels of debt lead to more war.”
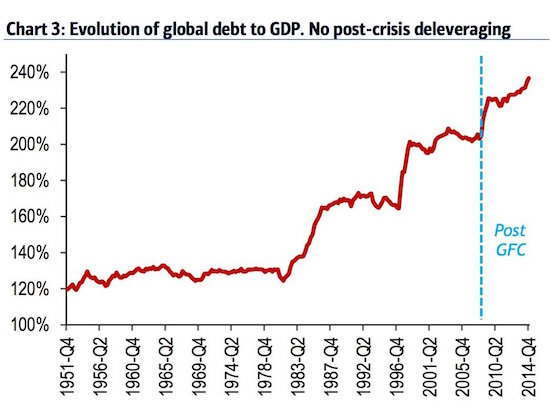
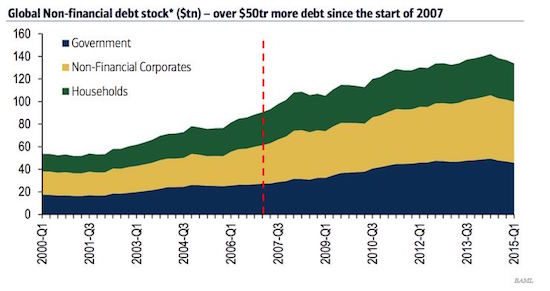
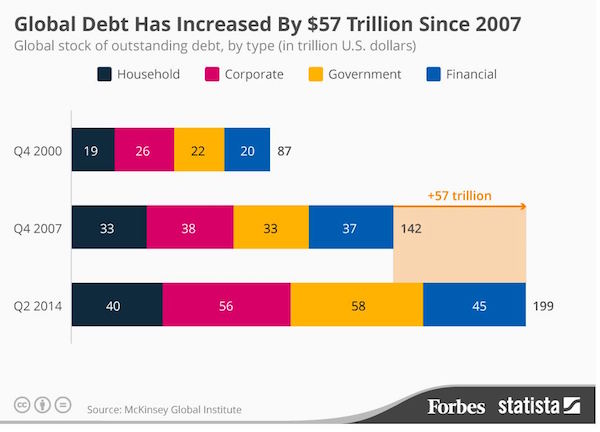
• Soaring Global Debt – The Reality Check in Numbers (O’Byrne)
The fact that global debt is growing throughout the world is widely acknowledged and well documented. However, when faced with the numbers, the magnitude of the problem is still quite shocking to read. An article last week in Washington’s blog gives us a stark and timely reminder of those facts. The volatile geo-political environment we are entering into, coupled with this growth-stifling debt, makes for a dangerous economic combination.
“The debt to GDP ratio for the entire world is 286%. In other words, global debt is almost 3 times the size of the world economy. Both public and private debt are exploding and – despite what mainstream economists think – 141 years of history shows that excessive private debt can cause depressions”.
These global debt figures cannot be ignored. Indeed, many erudite economic commentators have been highlighting the reckless monetary policies being pursued by governments around the world that is feeding our debt crisis.
“The underlying cause of this debt glut is the $12 trillion of free or cheap money created by central banks since 2009, combined with near-zero interest rates. When the real price of money is close to zero, people borrow and worry about the consequences later.” Paul Mason.
Similiarly, Jeremy Warner’s recent warnings about our imminent slide into fiscal crisis in “Europe is sliding towards the abyss, and the terrorists know it” reminds us of the vast expense of going to war. A decision that has very long-term repercussions economically and is a situation over which it would appear we have little or no control over, if the threat of terrorism is to be contained. “Indeed, not only does war lead to debt, but high levels of debt lead to more war.”
Read more …

Borders, protectionism, the fiancial crisis makes them inevitable. And now it gets help.
• The Closing Of The Global Economy (Calhoun)
I don’t often write about global geopolitics because I think, in general, investors spend too much time worrying about things they can’t control or aren’t going to happen or wouldn’t matter much if they did. The best example is the Middle East which has been a mess my entire life and long before it for that matter. Changing your investments based on the latest threat in or from the Levant is a recipe for constant chaos. The only accurate prediction about the Middle East will always be that the various factions that have been fighting for centuries will continue to fight. And that no matter who is in charge they will have to sell oil to make ends meet. And make no mistake oil is the only economic reason we care about the region.
The recent Paris attacks, though, have me thinking more about how global geopolitics is affecting the global economy. The terrorist attacks Europe has experienced in Madrid, London, Paris and other locales are raising old barriers across the continent. Borders where goods, people and capital have crossed freely for the last few decades are now manned and monitored again. Capital largely continues to flow freely but people and goods are starting to be restricted; you can’t restrict the flow of people without also obstructing the flow of goods. For now, the people and goods continue to flow, just more slowly. One can’t help but think though that if the borders become literal barriers again it won’t be long before the metaphoric ones – protectionist policies – return as well.
If one also considers the antipathy toward Germany that permeates most of Europe and the perception – and reality to some degree – that the EU and especially the EMU are much more favorable for the Teutonic members than the Latin ones, then one begins to see how the fragile union might devolve into its former squabbling, fractured self. The feared break up of Europe and the Euro has until now been based on economic considerations but physical security would seem a larger concern at this point. If the EU can’t guarantee physical security and has already failed at providing economic security, it’s raison d’etre is….what exactly? To provide employment for feckless bureaucrats?
The desire for physical security isn’t confined to Europe obviously; the Paris attacks have amped up the political debate in the US over immigration, with Syrian refugees and physical security now replacing Latin Americans and economic security as the targets. The emergence of Donald Trump as a right wing populist to challenge the near universally populist Democrats means that both parties are now pandering to the population’s baser instincts of fear and greed. That isn’t to say that their fears aren’t real or legitimate just that the solutions offered by populist politicians are simplistic and unlikely to achieve the intended results. Indeed, history says that walling ourselves off from the world is more likely to create less security, physical and economic, rather than more.
Read more …

A curious attempt at denial by Ambrose:”..the expected revival of Chinese metal demand disappoints yet again.”
• Harmless Commodity Crash Accelerates As Dollar Soars (AEP)
Copper prices have crashed to their lowest level since the Lehman Brothers crisis and industrial metals have slumped across the board as a flood of supply overwhelms the market. The violent sell-off came as the US dollar surged to a 12-year high on expectations of an interest rate rise by the US Federal Reserve next month. The closely-watched dollar index rose to within a whisker of 100, and has itself become a key force pushing down commodities on the derivatives markets. Copper prices fell below $4,500 a tonne on the London Metal Exchange for the first time since May 2009, hit by rising inventories in China and warnings from brokers in Shanghai. Prices have fallen 32pc this year, and 55pc from their peak in 2011 when China’s housing boom was on fire.
Known to traders as Dr Copper, the metal is tracked as a barometer of health for the world economy but has increasingly become a rogue indicator. China consumes 45pc of the world’s supply, distorting the picture. Beijing is deliberately winding down its “old economy” of heavy industry and break-neck construction, switching to a new growth model that is less commodity-intensive. “Dr Copper should be struck off the list,” said Julian Jessop, from Capital Economics. “He is telling us a lot about China and the massive over-supply of copper on the market, but he is not telling us anything much about the economy in the US, Europe or the rest of the world.” The CPB index in the Netherlands shows that global trade began to recover four months ago after contracting earlier in the year, and the JP Morgan global PMI index for manufacturing has risen since then to 51.3 – well above the boom-bust line.
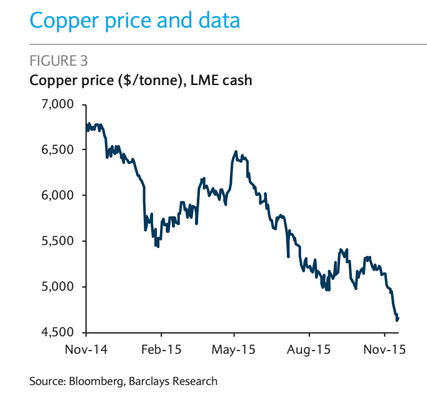
The trigger for the latest plunge in copper prices was a decision last week by the Chilean group Codelco to slash its premium for Chinese customers by 26pc, effectively launchng a price war for global market share. “We’re trying to lower costs. We’re not cutting production,” said the group’s chief executive, Nelson Pizarro. Glencore has already said it will suspend output in Zambia and the Congo for two years until new equipment is installed, and others are doing likewise. But Codelco is the key player. Kevin Norrish, at Barclays Capital, said Codelco is in effect copying Saudi Arabia’s tactics in the oil market: using its position as the copper industry’s low-cost giant with a 10pc global share to flush out the weakest rivals. The price war comes as the expected revival of Chinese metal demand disappoints yet again.
Warehouse stocks in Shanghai have risen to their highest in five years, though LME inventories have been falling since September. Views are starkly divided over the outlook for copper, as it is for the whole nexus of commodities. Goldman Sachs says the demise of China’s “old economy” will lead to a near permanent glut through to the end of the decade. Natasha Kaneva, from JP Morgan, said it would take another one to two years to touch the bottom of the mining cycle, predicting further price falls of 12pc-28pc. “We remain bearish on all the base metals,” she said. But the International Copper Study Group is sticking to its guns, insisting that there will be a global copper shortage of 130,000 tonnes next year.
Read more …

“..everyone knows that a balance sheet with too much debt, like Ireland’s, is made more robust by less debt, not more debt. The bailouts mean the opposite.”
• Ireland Is Backing Itself (David McWilliams)
On the fifth anniversary of the troika’s arrival, let’s be clear on what has actually helped us recover Six years after its inaugural outing, the atmosphere at the Global Irish Economic Forum on Friday in Dublin Castle couldn’t have been more different. Back then, there was a palpable sense of panic and many reasons to be fearful; this time, there was a sense of a steadied ship and many reasons to be optimistic. This weekend also happens to be the fifth anniversary of the bailout. That was the weekend that the IMF rocked into town and nailed their demands to the door of the Department of Finance. One of the more galling episodes in the run-up to this anniversary has been watching the IMF’s chief negotiators pointing the finger of blame at the ECB about Frankfurt forcing successive Irish governments to take on odious bank debts rather than burning bondholders.
It’s a pity they were not so vocal on the issue of odious debt at the time, and it underscores just how pointless this institution now is, in Europe at least. Let’s remember what the bailout was in reality. The bailout wasn’t so much a bailout, which at least visually conjures up the image of a friend in a canoe bailing out water to keep the canoe afloat. These European bailouts were really a response to the financial markets declining to lend to the stricken states. Once the private sector refused to lend, the public sector had to, or the economies would have imploded. This is where the IMF and the EU came in. They lent to us, and we committed to do certain things – and this public commitment, and the troika’s oversight, coaxed the markets to lend to our government again.
But everyone knows that a balance sheet with too much debt, like Ireland’s, is made more robust by less debt, not more debt. The bailouts mean the opposite. A balance sheet that was laid low by too much debt was forced to take on more debt. However, as the ECB undertook to buy all this debt if necessary, the risk premium of this debt fell – the rate of interest fell. Is a country with more debt less or more risky? Traditionally, you would say more risky, but with the ECB backstopping the government bond market, the opposite has occurred. However, in terms of what prompted the Irish recovery, while Italy, Portugal and Greece remain in the doldrums, this bailout doesn’t explain things adequately.
For example, the chief baiter of debtor countries, Finland, is now in recession, so it’s clear that the state of the public finances isn’t sufficient to explain the recovery for the man on the street. If public finances alone were sufficient, Finland would be booming. What affects the man on the street are the employment opportunities around him in the real economy. The government’s narrative is that the recovery – which is still fitful – was due to some European confidence fairy which magically spread confidence dust all over Ireland after the bailout. But the bailout only replaced private creditors with public creditors. We are still debtors, just to different creditors. I don’t buy the government’s story – not because I don’t want to, but because I can’t, as a trained economist, see how this eurozone transmission mechanism might work.
Read more …

Yes, you can rent an apartment in Athens for €200.
• Greek Home Rental Costs 40% Less Since 2011 (Kath.)
The price of rentals has declined considerably since the start of the financial crisis across all categories, with house rents costing an average of 40% less than in 2011, when the drop began. This decline has all but offset the rate growth recorded over the 11-year period from 2000 to 2011, estimated at 43% on average. The drop is even bigger in Attica, where, according to data collected by estate agents, rates have fallen by 7 to 8% in the last 12 months alone, despite an increase in demand for rented property. In Athens city center, rates for apartments have dropped by 50% or more since 2011, as this mostly concerns older flats covering a surface of 60-70 square meters.
This means that a one-bedroom flat will set a renter back by €150-200 a month, depending on the area and the condition of the property. Sector professionals stress that as long as citizens’ purchasing power declines, rental rates will continue to shrink. Most landlords, they say, would rather shave their asking price to ensure they will at least collect the rent due than insist on a higher rate they may never collect. Alpha Bank, however, reports a slowdown in the decline of rental rates in the second quarter of 2015.
Read more …

Real Greece: rental costs down 40%, but 40% of Greeks still can’t afford them.
• Four In 10 Greeks ‘Overburdened’ By Housing Costs (Kath.)
Four in 10 Greeks spend more than 40% of their disposable income on housing costs, more than double the European Union average, according to a new study by Eurostat, the European Commission’s statistics service. On average, 11.4% of households in the 28-member EU spent more than 40% of their disposable income in 2014 on housing, a rate that that the Commission considers a housing cost “overburden.” Greece ranks first, with households spending 40.7% of their disposable income on housing, followed by Germany with 15.9%, the Netherlands with 15.4% and Romania with 14.9%. At the lower end of the scale are Malta and Cyprus, with 1.6% and 4% respectively, followed by France and Finland, both with 5.1%.
The continual reduction of household income in Greece since the crisis struck in 2010 – wages have been slashed and pensions cut several times – has been accompanied by higher electricity prices, higher value-added tax on food and more property taxes. According to figures presented over the weekend by the Panhellenic Federation of Property Owners (POMIDA), Greek households will be called upon to pay eight times more in property taxes next year than they did in 2010.
Read more …

Greece can’t catch a break: it also gets hit by the global demise of shipping.
• Greek Shipping Currency Inflows Drop 53% In September (Kath.)
The drop in foreign currency inflows from shipping, which started in July following the introduction of capital controls in late June, has picked up again, with the reduction in September coming to 53%, on the back of a 46% decline in August and 60% in July, according to Bank of Greece figures. When one considers that the lion’s share of foreign currency in the sector comes from oceangoing shipping, it becomes clear that the capital controls have had a sinking effect on the foreign account balance and the cash flow of banks. In the first half of the year the inflow has posted an annual increase. The foreign currency inflow from shipping dropped to €598.2 million in September against €1.274 billion in the same month last year. In August it had amounted to €570.7 million (from €1.069 billion in August 2014) and in July it had come to €470.7 million from €1.172 billion in July 2014.
This means that the inflow declined by a total of €1.7 billion in the third quarter of the year. The decline is even greater considering that the exchange rate of the euro has fallen significantly from last year and the above amounts given in euros concern dollar payments. The decline is mainly attributed to the capital controls and the fact that a notable number of shipping firms, often under pressure from foreign shareholders, were forced to redirect their revenues from chartering and ship transactions to other countries so that they could meet their international obligations. Another factor is the fall in global dry-bulk market rates, which have reached historic lows. As most of the Greek-owned fleet comprises dry-bulk carriers – and not tankers whose rates are showing very good yields – it is estimated that the current, last quarter of the year will see a further decline in the foreign currency inflows from shipping.
Read more …

This is by design. Invariably is.
• Inadequate Dirty Money Regulation ‘Leaves UK Open To Terror Funds’ (Reuters)
Britain’s “woefully inadequate” anti-money laundering system has left the country wide open to corrupt money and terrorism funds and needs radical overhaul, a leading anti-corruption group said on Monday. Each year billions of pounds of dirty money flow through Britain, but the system for identifying it is too fragmented and unaccountable to be effective, according to a report by Transparency International UK (TI-UK). “The UK supervision system which should be protecting the country from criminal and terrorist funding is not fit for purpose,” said TI-UK’s Head of Advocacy and Research Nick Maxwell. “Those vulnerabilities can be exploited by sophisticated terrorist organizations as well as the corrupt.” Penalties for professionals such as lawyers and estate agents who fail to comply with anti-money laundering regulations are also too small to act as a deterrent, the report said.
Money laundering is the process of disguising the origins of money obtained from crime and corruption by hiding it within legitimate economic activities. The government’s 2015 money laundering and terrorist financing national risk assessment said there was “evidence of terrorist financing activity in the UK” which uses the same methods as criminal money laundering and “poses a significant threat to the UK’s national security.” Money laundering is also pushing up London property prices because money commonly ends up in high-value physical assets such as real estate and art. Britain’s National Crime Agency’s economic crime director told The Times newspaper this year that London property prices were being artificially driven up by overseas criminals wanting to hide their assets.
Read more …

“..if grand personages like him had to shuffle through the security screens, belts off, shoes off, shampoo humourlessly confiscated, like the rest of us, these daft and illogical rules would have been reviewed long ago.”
• Cameron Has Guns, Bombs And A Plane – And Not One Good Idea (Hitchens)
So far there is little sign of serious thought about the Paris atrocities. We are to have more spooks, though spooks failed to see it coming, and failed to see most of the other outrages coming, and the new ones will be no more clairvoyant than the old ones. France and Belgium are reaching for emergency laws, surveillance, pre-trial detention, more humiliation of innocent travellers and all the other rubbish that has never worked in the past and won’t work again. David Cameron (in a nifty bit of news management) takes the opportunity to announce that he will henceforth be spared from flying like a normal human being, in an ego-stroking Blaircraft paid for by you and me. Austerity must have been having a day off. Actually, if grand personages like him had to shuffle through the security screens, belts off, shoes off, shampoo humourlessly confiscated, like the rest of us, these daft and illogical rules would have been reviewed long ago.
British police officers dress up like Starship Troopers, something they’ve obviously been itching to do for ages and now have an excuse to do, the masked women involved looking oddly like Muslim women in niquabs. It’s not the police’s job to do this. If things are so bad that we need armed people on the streets, then we have an Army and should deploy it. If not, then spare us these theatricals, which must delight the leaders of ISIS, who long for us to panic and wreck our own societies in fear of them. Next comes the growing demand for us to bomb Syria. Well, if you want to. Only a couple of weeks ago all the establishment experts were saying that the Russian Airbus massacre was obviously the result of Vladimir Putin’s bombing of Syria. Now the same experts say it’s ridiculous to suggest that our planned bombing of Syria might bring murder to the streets of London or to a British aircraft.
Perhaps it’s relevant to this that Pierre Janaszak, a radio presenter who survived the Bataclan massacre in Paris, said he heard one fanatic in the theatre say to his victims, ‘It’s the fault of Hollande, it’s the fault of your President, he should not have intervened in Syria.’ There may be (I personally doubt it) a good case for what’s left of the RAF to drop what’s left of our bombs on Syria. It may be so good that it justifies risking a retaliation in our capital, and that we should brace ourselves for such a war. But I think those who support such bombing should accept that there might be such a connection, and explain to the British people why it is worth it. I am wholly confused by the Cameron government’s position on Syria.
It presents its desire to bomb that country as a rerun of the Parliamentary vote it lost in 2013. But in 2013, Mr Cameron wanted (wrongly, as it turned out) to bomb President Assad’s forces and installations, to help the Islamist sectarian fanatics who are fighting to overthrow the secular Assad state. This is more or less the exact opposite of what he seems to want now. Far from being a rerun, it is one of the most embarrassing diplomatic U-turns in modern British history.
Read more …

“People die this way and governments fall.”
• Scale Of Osborne’s Cuts To Police, Education, Councils ‘Unprecedented’ (Mirror)
Chancellor George Osborne will this week take the axe to police, councils and welfare as he unleashes the most brutal cuts in history. He will brush aside warnings from police chiefs by pressing ahead with the reductions to their budgets when he unveils his spending review on Wednesday. Funding to local government, transport and higher education will also be slashed – and experts said the scale of the cuts was unprecedented. “We have never had anything like it,” said Paul Johnson of the Institute for Fiscal Studies economic think-tank. Mr Osborne is pushing on with the measures despite being told they may put services such as social care and child protection at risk – and also undermine the fight against terrorism . The Chancellor, when challenged, did not deny that police numbers could be reduced , saying: “Every public service has to make sure it is spending its money well.”
Senior police figures, including former Scotland Yard Commissioner Ian Blair, have warned that axing community support officers (PCSOs) will be a disaster because they work with Muslim youngsters who are being radicalised. Lord Blair said: “National security depends on neighbourhood security and the link between the local and the national is about to be badly damaged.” He added: “This is the most perilous terrorist threat in our history. “With their long, successful track record in counter-terrorism, police have adapted well to the changing circumstances and, at the last moment, the very best defences they have built, the neighbourhood teams and the fast and accurate response to multi-site concurrent attacks, are being degraded. “People die this way and governments fall.”
Mr Osborne revealed all departments had now signed up to the spending review which will see them have to make cuts of around 30% on average. The Chancellor is also likely to hit further education and welfare, including housing benefit and the universal credit, in his determination to have a budget surplus by the end of the decade. Council chiefs warned they would struggle to provide services such as care for the elderly, bin collections, street lighting, social work and pothole repairs. Town hall spending on key services has already fallen by up to a quarter since David Cameron became Prime Minister in 2010, while expenditure on roads and transport services has dropped 20% in the last five years and education budgets have fallen by 24%.
Read more …

“Osborne proudly promises a “permanent change” and “a new settlement” for the UK.“
• Austeria – A Nation Robs Its Poor To Pay For The Next Big Crash (Chakrabortty)
A familiar dance begins on Wednesday, as soon as George Osborne reveals his blueprint for Britain. The analysts immediately begin poring over his plans for the next five years. They tell us how deep are the cuts in neighbourhood policing, how tight the squeeze for your local school – and the knock-on effect for the Tory leadership hopes of George and Theresa and Boris. But many will miss the backdrop forming right behind them. Britain is now halfway through a transformative decade: staggering out of a historic crash, reeling through the sharpest spending cuts since the 1920s, and being driven by David Cameron towards a smaller state than Margaret Thatcher ever managed. None of this is accidental. While much commentary still treats the Tories as merely muddling through a mess they inherited, Osborne proudly promises a “permanent change” and “a new settlement” for the UK.
The chancellor has the ambition, the power and the time – 10, perhaps 15 years in office – to do exactly that. Between 1979 and 1990 Thatcher permanently altered Britain and, going by what we already know, Osborne is on course to engineer a similar shift. I think of the country we are morphing into as Austeria. It has three defining characteristics: it is shockingly unequal, as a deliberate choice of its rulers; it looks back to the past rather than investing in its future; and it has shrunk its public services for the benefit of its distended, crisis-prone banking sector. Let’s start with the unfairness. Remember Osborne’s promise, “we’re all in it together”? He is ensuring the opposite.
Wanting to make massive cuts without rendering his party unelectable, the chancellor is deliberately targeting austerity at those sections of society where he calculates he can get away with it. That means slashing local council funding, hoping angry voters will turn on their town halls rather than Whitehall. It means running down prisons. What may be clever Tory politics is desperately unfair policy. The Centre for Welfare Reform calculates Osborne’s austerity programme has so far hit disabled Britons nine times harder than the average, while those with severe disabilities were 19 times worse off. Watch for them to be punished again on Wednesday, as the government looks to cut welfare and local government again.
Read more …

Icon.
• Richard Russell, Publisher of Dow Theory Letters, Dies at 91 (Bloomberg)
Richard Russell, who shared his technical analysis with subscribers through the influential Dow Theory Letters since 1958, has died. He was 91. He died Nov. 21 at his home in La Jolla, California, his family said in a message to subscribers on the publication’s website. He had entered a hospital a week earlier and was diagnosed with blood clots in his leg and lungs “and other untreatable ailments,” his family said. He returned home under hospice care. An adherent of the investing principles of Charles Dow, founder of the Wall Street Journal, Russell published his newsletter continuously from 1958, never missing an issue in more than half a century. In his last column, published Nov. 16, Russell wrote: “I read 10 newspapers a day, but the news is getting increasingly difficult to digest down to something understandable, and the vast array of news sources becomes more and more complex. I can only imagine what the newspapers will look like in 10 years.”
Stock analyst Robert Prechter wrote in his 1997 book: “Russell has made many exceptional market calls. He recommended gold stocks in 1960, called the top of the great bull market in stocks in 1966 and announced the end of the great bear market in December 1974.” In 1969 Russell devised the Primary Trend Index, composed of eight market indicators that he never publicly divulged – his own secret recipe. When his index outperformed an 89-day moving average, it was time to buy. When it underperformed the 89-day moving average, a bear market was at hand. “The PTI is a lot smarter than I am,” Russell said. The benchmark is unrelated to the Russell 2000 and other indexes maintained by Seattle-based Russell Investments.
Read more …

How much crazier can it get? They’re lying about something or the other new every single day.
• VW Admits Second Illegal Device In 85,000 Audi Engines (FT)
Audi has conceded that the engines in a further 85,000 cars from the Volkswagen group contained an illegal defeat device, raising questions of how systematic the cheating was at the German carmaker. The luxury car brand of the VW group said it estimated that correcting the engine management software used in Audi, VW and Porsche models would cost in the mid-double-digit millions of euros. It admitted that the software was in all three-litre V6 diesel engines manufactured by Audi and sold from 2009 until this year. The admission further undermines VW’s insistence that the cheating in the two-month-old emissions scandal was limited to a rogue group of engineers. The German carmaker has already admitted installing a defeat device in 11m diesel cars worldwide.
It is also facing a third emissions problem after disclosing that 800,000 cars, including some with petrol engines, had been sold with the stated carbon dioxide levels as too low and the fuel efficiency too high. Audi sent its chief executive and engineers to meet the US Environmental Protection Agency last week. Late on Monday night, it sent out a statement saying that it had failed to disclose three auxiliary emissions control devices (AECDs) to regulators. Without disclosure and subsequent approval from regulators, AECDs are not legal. Audi added: “One of them is regarded as a defeat device according to applicable US law. Specifically, this is the software for the temperature conditioning of the exhaust-gas cleaning system.” The admission causes significant embarrassment to VW, which appeared set for a confrontation with the EPA over the issue. When the EPA first disclosed in early November that it had found a defeat device in the three-litre engines, VW sent out a terse statement, saying that it would co-operate with the EPA.
Read more …

Will the tar sands ever be cleaned up? Who would pay for that?
• Average House In Fort McMurray Lost $117,000, 20% Of Its Value In 1 Year (CH)
The slumping oilpatch in Alberta continues to take its toll on the Fort McMurray housing market, as the average MLS sale price of a home in that northern community plunged by more than $117,000 in October. Data obtained from the Canadian Real Estate Association indicates that the average sale price for the month of $468,199 was down 20% from $585,438 in October 2014. Sales also plunged by 41% to 85 from 144 a year ago. Year-to-date, MLS sales in Fort McMurray are down by 44.8%. In October, Lloydminster saw MLS sales dip by 54.3%, falling to 43 transactions from 94 last year while the Alberta West area experienced a decline of 52.7%, dropping to 70 from 148 a year ago.
Year-to-date MLS sales in Alberta are down 21.1% from last year. Besides Fort McMurray, the CREA statistics show the hardest hit areas in the province are Lloydminster (down 34.1%); South Central Alberta (down 31.6%) and Calgary, (down 28.9%). Calgary’s resale housing market led the country in October — in a negative way. MLS sales in the Calgary region were 1,810 for the month, down 36.4% from a year ago. The rate of decline was the highest among Canada’s major housing markets, according to a report by the Canadian Real Estate Association. In Alberta, sales fell 28.9% to 4,327 transactions. Across the country, however, MLS sales were up 0.1% to 41,653. CREA said national activity stood near the peak recorded earlier this year and reached the second highest monthly level in almost six years.
Read more …

“Abdelhamid Abaaoud? ..they’d have got him even if they just went through lists of terrorists alphabetically.”
• This Is The Worst Time For Society To Go On Psychopathic Autopilot (F. Boyle)
There were a lot of tributes after the horror in Paris. It has to be said that Trafalgar Square is an odd choice of venue to show solidarity with France; presumably Waterloo was too busy. One of the most appropriate tributes was Adele dedicating Hometown Glory to Paris, just as the raids on St-Denis started. A song about south London where, 10 years ago, armed police decided to hysterically blow the face off a man just because he was a bit beige. In times of crisis, we are made to feel we should scrutinise our government’s actions less closely, when surely that’s when we should pay closest attention. There’s a feeling that after an atrocity history and context become less relevant, when surely these are actually the worst times for a society to go on psychopathic autopilot. Our attitudes are fostered by a society built on ideas of dominance, where the solution to crises are force and action, rather than reflection and compromise.
If that sounds unbearably drippy, just humour me for a second and imagine a country where the response to Paris involved an urgent debate about how to make public spaces safer and marginalised groups less vulnerable to radicalisation. Do you honestly feel safer with a debate centred around when we can turn some desert town 3,000 miles away into a sheet of glass? Of course, it’s not as if the west hasn’t learned any lessons from Iraq and Afghanistan. This time round, no one’s said out loud that we’re going to win. People seem concerned to make sure that Islam gets its full share of the blame, so we get the unedifying circus of neocons invoking God as much as the killers. “Well, Isis say they’re motivated by God.” Yes, and people who have sex with their pets say they’re motivated by love, but most of us don’t really believe them. Not that I’m any friend of religion – let’s blame religion for whatever we can.
Let’s blame anyone who invokes the name of any deity just because they want to ruin our weekend, starting with TGI Friday’s. The ringleader, Abdelhamid Abaaoud, evaded detection by security services by having a name too long to fit into one tweet. How could the most stringent surveillance in the world not have picked up Abdelhamid Abaaoud before? I mean, they’d have got him even if they just went through lists of terrorists alphabetically. We’re always dealing with terror in retrospect – like stocking up on Imodium rather than reading the cooking instructions on your mini kievs. The truth is that modern governments sit at the head of a well-funded security apparatus. They are told that foreign military adventures put domestic populations at risk and they give them the thumbs up anyway.
Read more …

“..if somebody knocks on your door at three in the morning, and they’re wet, they’re bleeding, they’ve been shot at, and they’re frightened, what do you do?”
• Varoufakis: Closing Borders To Muslim Refugees Only Fuels Terrorism (Guardian)
Europe must not close its borders to refugees in the wake of the Paris terrorist attacks, Greece’s former finance minister Yanis Varoufakis has cautioned, saying rising intolerance towards Muslim refugees would only fuel further violence. Speaking on the Q&A program on Australia’s ABC, Varoufakis said he was proud of the Greek people’s response to the refugee crisis, despite the country being gripped by economic crises. “We have two [thousand], three [thousand], 5,000, 10,000 people being washed up on our shores, on the Aegean Islands, every day. In a nation, by the way, that is buffeted by a great depression, where families, on those islands in particular, are finding it very hard to put food on the table for their children at night.
“And these people in their crushing majority, I’m proud to report, opened their doors to these wretched refugees. And the thought comes to my mind very simply: if somebody knocks on your door at three in the morning, and they’re wet, they’re bleeding, they’ve been shot at, and they’re frightened, what do you do? I think there’s only one answer: you open the door, and you give them shelter, independently of the cost-benefit analysis, independently of the chance that they may harm you.” [..] Varoufakis said while Europe was struggling to cope with both the refugee crisis and Paris attacks, it was a mistake to read one as the cause of the other. “There’s no doubt that when you have a massive exodus of refugees that there may very well be a couple of insurgents that infiltrate [that population], but it’s neither here nor there.”
“Both the terrorist attacks and the refugee influx are symptoms of the same problem. But one doesn’t cause the other.“ The vast majority of the people who exploded bombs, and blew themselves up, and took AK47s to mow people down, these were people who were born in France, in Belgium. Think of the bombings in London. Britain doesn’t have free movement [over its borders] it is not part of the Schengen treaty. So the notion that we’re going to overcome this problem by erecting fences, electrifying them, and shooting people who try to scale them … the only people who benefit from that are the traffickers, because their price goes up … and Isis. They are the only beneficiaries.”
Read more …

Good point.
• Average Stay Is 17 Years: Refugee Camps Are The “Cities Of Tomorrow” (Dezeen)
Governments should stop thinking about refugee camps as temporary places, says Kilian Kleinschmidt, one of the world’s leading authorities on humanitarian aid (+ interview). “These are the cities of tomorrow,” said Kleinschmidt of Europe’s rapidly expanding refugee camps. “The average stay today in a camp is 17 years. That’s a generation.” “In the Middle East, we were building camps: storage facilities for people. But the refugees were building a city,” he told Dezeen. Kleinschmidt said a lack of willingness to recognise that camps had become a permanent fixture around the world and a failure to provide proper infrastructure was leading to unnecessarily poor conditions and leaving residents vulnerable to “crooks”. “I think we have reached the dead end almost where the humanitarian agencies cannot cope with the crisis,” he said.
“We’re doing humanitarian aid as we did 70 years ago after the second world war. Nothing has changed.” Kleinschmidt, 53, worked for 25 years for the United Nations and the United Nations High Commission for Refugees in various camps and operations worldwide. He was most recently stationed in Zaatari in Jordan, the world’s second largest refugee camp – before leaving to start his own aid consultancy, Switxboard. He believes that migrants coming into Europe could help repopulate parts of Spain and Italy that have been abandoned as people gravitate increasingly towards major cities. “Many places in Europe are totally deserted because the people have moved to other places,” he said.
“You could put in a new population, set up opportunities to develop and trade and work. You could see them as special development zones which are actually used as a trigger for an otherwise impoverished neglected area.” Refugees could also stimulate the economy in Germany, which has 600,000 job vacancies and requires tens of thousands of new apartments to house workers, he said. “Germany is very interesting, because it is actually seeing this as the beginning of a big economic boost,” he explained. “Building 300,000 affordable apartments a year: the building industry is dreaming of this!” “It creates tons of jobs, even for those who are coming in now. Germany will come out of this crisis.”
Read more …

Bit of a weird compromise?!
• Canada To Turn Away Single Men As Part Of Syrian Refugee Resettlement Plan (AFP)
Canada will accept only whole families, lone women or children in its mass resettlement of Syrian refugees while unaccompanied men – considered a security risk – will be turned away. Since the Paris attacks launched by Syria-linked jihadis, a plan by the new prime minister, Justin Trudeau, to fast-track the intake of 25,000 refugees by year’s end has faced growing criticism in Canada. Details of the plan will be announced Tuesday but Canada’s ambassador to Jordan confirmed that refugees from camps in Jordan, Lebanon and Turkey will be flown to Canada from Jordan starting 1 December. Speaking in Jordan on Monday, ambassador Bruno Saccomani said the operation would cost an estimated C$1.2bn (US$900m), the official Petra news agency reported.
According to Canadian public broadcaster CBC, the resettlement plan will not extend to unaccompanied men. Québec premier Philippe Couillard seemed to corroborate that report ahead of a meeting with Trudeau and Canada’s provincial leaders where the refugee plan was high on the agenda. “All these refugees are vulnerable but some are more vulnerable than others, for example women, families and also members of religious minorities who are oppressed,” he said, although he rejected the notion of “exclusion” of single men. Faisal Alazem of the Syrian Canadian Council, a nonprofit group in talks with the government to sponsor refugees, told Radio-Canada of the plans: “It’s a compromise.”
Read more …

Sweet Jesus.
• Stranded Migrants Block Railway, Call Hunger Strike (Reuters)

Migrant with his mouth sewn shut at Greek/Macedonian border Nov 23, 2015 (Reuters/Ognen Teofilovski)
Moroccans, Iranians and Pakistanis on Greece’s northern border with Macedonia blocked rail traffic and demanded passage to western Europe on Monday, stranded by a policy of filtering migrants in the Balkans that has raised human rights concerns. One Iranian man, declaring a hunger strike, stripped to the waist, sewed his lips together with nylon and sat down in front of lines of Macedonian riot police. Asked by Reuters where he wanted to go, the man, a 34-year-old electrical engineer named Hamid, said: “To any free country in the world. I cannot go back. I will be hanged.” Hundreds of thousands of migrants, many of them Syrians fleeing war, have made the trek across the Balkan peninsula having arrived by boat and dinghy to Greece from Turkey, heading for the more affluent countries of northern and western Europe, mainly Germany and Sweden.
Last week, however, Slovenia, a member of Europe’s Schengen zone of passport-free travel, declared it would only grant passage to those fleeing conflict in Syria, Iraq and Afghanistan, and that all others deemed “economic migrants” would be sent back. That prompted others on the route – Croatia, Serbia and Macedonia – to do the same, leaving growing numbers stranded in tents and around camp fires on Balkan borders with winter approaching. Rights groups have questioned the policy, warning asylum should be granted on merit, not on the basis of nationality.
“To classify a whole nation as economic migrants is not a principle recognized in international law,” said Rados Djurovic, director of the Belgrade-based Asylum Protection Center. “We risk violating human rights and asylum law,” he told Serbian state television.On the Macedonian-Greek border, crowds of Moroccans, Iranians and others blocked the railway line running between the two countries, halting at least one train that tried to cross, a Reuters photographer said. A group of Bangladeshis had stripped to the waist and written slogans on their chests in red paint. “Shoot us, we never go back,” read one. “Shoot us or save us,” read another.
Read more …