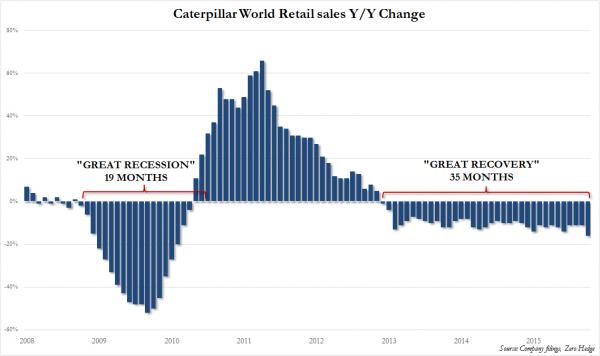
DPC Heart of Chinatown, San Francisco, after earthquake and fire 1906

And the MH17 report that lost all credibility long ago. Got to keep the customer entertained.
• Small Army Of Fed Speakers, OPEC On Tap For Wednesday (CNBC)
A flurry of Fed speakers, including the Fed chair, will keep markets busy Wednesday. There are also mortgage applications at 7 a.m. EDT, durable goods data at 8:30 a.m. EDT and oil inventory data at 10:30 a.m. EDT. OPEC, meanwhile, is meeting in Algeria and could continue to create volatility in oil prices after headlines from there triggered a near 3% plunge Tuesday. Fed Chair Janet Yellen appears before the House Financial Services Committee at 10 a.m. on supervision and regulation. The Fed chair was personally criticized in the presidential debate Monday night by GOP candidate Donald Trump, who said the Fed’s decision to keep rates low was political and that it’s creating a bubble in the stock market.
“It has to worry the markets that potentially you could have a president getting into a nasty dispute with the chairman of the Fed in early 2017. That’s something the market would not like to see. I think the Fed has not done a very good job communicating. It’s a cacophony of confusing comments. There’s reason to criticize the Fed, but the personal attack on Yellen is unprecedented,” said Greg Valliere, chief global strategist at Horizon Investments. Traders are watching to see if Yellen is in the political hot seat on banking regulation and supervision when she appears before the committee.
Read more …

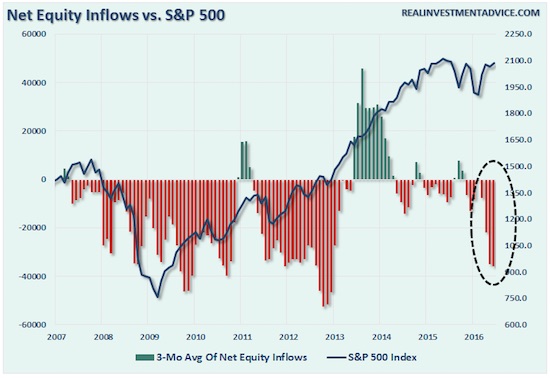
One side of US deflation is falling wages…
• “Negative Growth” of Real Wages is Normal for Much of the Workforce (WS)
The chart below shows the%age change of real wages (left, y-axis) as these men aged (horizontal, x-axis). As young adults, their wages soared by up to 10% a year. Then the rate of growth fell off sharply. When the men in this cohort turned 40 in the 1990s, wage growth disappeared. By around the year 2000, the real wage peak in the US, when the oldest men in this cohort turned 50, wages had begun to decline for most of them. By the time these men were in the mid-50s, their wages across the board were heading south – and for many of them, rapidly. Hence this colorful, drooping spaghetti:
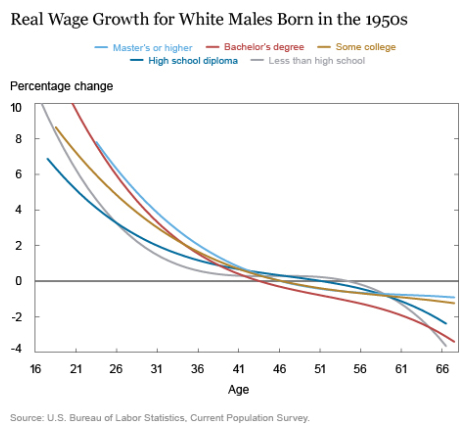
This “negative real wage growth” – devastating as it may be for those experiencing it – is nothing special, according to the New York Fed. And it crushes not just white men, but everyone: “Real wages tend to rise early in a worker’s career, flatten out mid-career, and then decline as the worker approaches retirement. This inverted U-shape pattern is a well-established feature in the labor economics literature.” The report explained it further: “Labor economists explain the rapid real wage growth early in a worker’s career as a combination of on-the-job learning and better matching of workers to jobs. A large portion is due to job matching as workers change jobs in search of a position that better utilizes their skills. As workers age, the decline in the pace of their real wage growth reflects a diminished incentive to invest in new skills (because their remaining work life is shorter) and fewer job changes (because they have found a good job match).”
The report divides life for its purposes into three phases, terms of wage growth: • Fast growth, up to age 40, • Flat growth, ages 41-54, • “Negative growth,” age 55 and older. Now there’s another problem mucking up the overall and ever-elusive real-wage growth miracle everyone has been counting on: demographics. The US population is aging. There are more people aged 40 and over in the workforce, and their incomes are now flat or declining. The portion of the population in the first phase when wages are growing fast has plunged from close to 60% in the 1980s to the mid-40% range currently. And the portion of workers with wages in the “negative growth” phase has ballooned. Given the demographics, real wage declines among workers over 50 will continue to hammer the national averages.
Read more …

…and when wages are falling, so must prices.
• Grocery Prices Are Plunging (BBG)
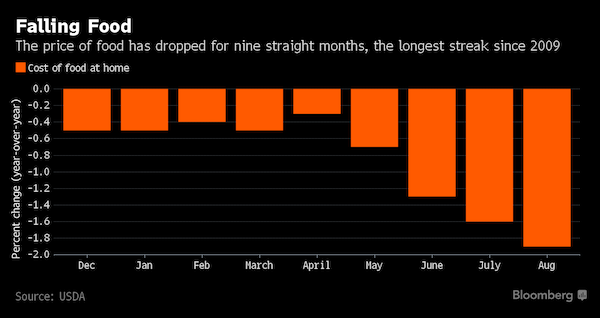
Call it the Great Grocery-Store Giveaway of 2016. In Austin, Texas, Randalls slashed prices for boneless beef ribs by 40%, to $3.99 a pound. Not to be outdone, the H-E-B grocer down the street charged $1 a pound less. Not long ago, Albertsons advertised a deal you don’t normally see on your finer cuts of meat: “buy 1 get 1 free” specials on “USDA Choice Petite Sirloin Steak.” And what does $1 buy these days? In North Bergen, New Jersey, you could pick up a dozen eggs at Wal-Mart. OK, the price was actually $1.14. A mile away, check out Aldi, the German supermarket discounter, which can actually break the buck – 12 eggs for 99 cents. A year ago, you would have paid, on average, three times that price.
In a startling development, almost unheard of outside a recession, food prices have fallen for nine straight months in the U.S. It’s the longest streak of food deflation since 1960 – with the exception of 2009, when the financial crisis was winding down. Analysts credit low oil and grain prices, as well as cutthroat competition from discounters. Consumers are winning out; grocery chains, not so much. Their margins and, in some cases, their stock prices, are taking a hit. Eggs and beef have have grown especially inexpensive, and it isn’t only an American phenomenon: In England, Aldi recently offered its prized 8-ounce wagyu steaks from New Zealand for about $6.50 – a little more than the price of a pint of beer. “The severity of what we’re seeing is completely unprecedented,” said Scott Mushkin at Wolfe Research, who has studied grocery prices around the country for more than ten years. “We’ve never seen deflation this sharp.”
Read more …

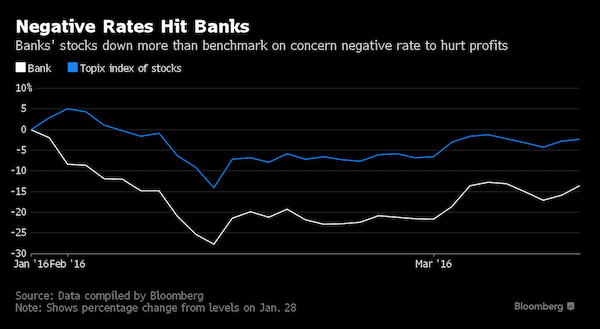
“The can has been kicked down the road for years. Now negative interest rates appear to have inadvertently crushed the can.”
• EU Banking Mayhem, One Bank at a Time, then All at Once (WS)
Here are the 29 banks in the ESTX Banks Index of Eurozone banks (so Swiss and UK banks, for example are not included). It shows the percentage drop from their 52-week high. But for some of these banks, particularly for Italian and Portuguese banks, that 52-week high was just about last year’s 52-week low, so relentless has their decline been over the years. Some of them had already been reduced to penny stocks years ago, and for them, in euro terms, the biggest losses occurred back then. So these mayhem banks, color coded by country:
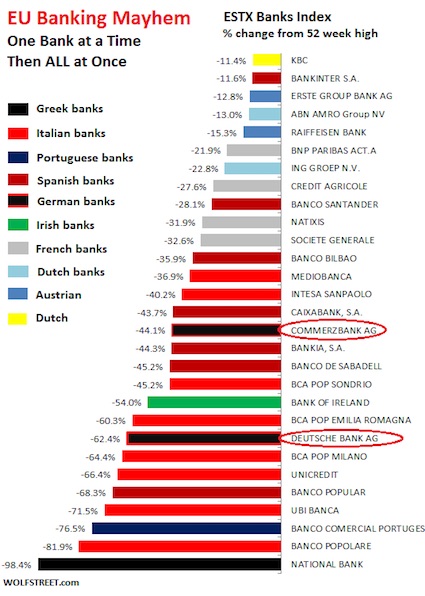
If a bank stock plunges from €0.04 to €0.01 over the 52-week period, such as Banco Comercial Português in Portugal, it has been toast for longer than 52 weeks, and the percentage plunge is essentially meaningless because shares were worthless to begin with. The shares of five of these banks trade under €1. Another 8 banks trade under €3. These 29 banks form a big part of the European financial system. It includes some of the world’s largest banks, such as Deutsche Bank, Societe Generale, and BNP Paribas. It includes a slew of other “systemically important financial institutions,” such as Unicredit, ING, and Santander. They’re troubled at the same time. The can has been kicked down the road for years. Now negative interest rates appear to have inadvertently crushed the can.
Read more …

Deutsche won’t go alone. Just like saving only Deutsche is far from enough. The dominoes suppart each other.
• Deutsche Bank Troubles Cast Long Shadow Over European Banking (BBG)
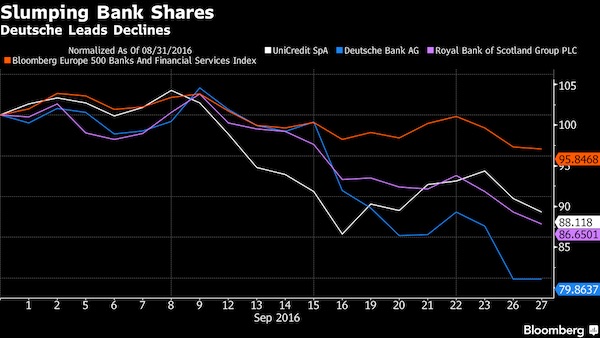
The turmoil swirling around Deutsche Bank has brought simmering concerns about the health of Europe’s banks back to a boil. Germany’s largest lender extended losses to a record low this week, dragging down European financial stocks, after the U.S. Department of Justice requested $14 billion to settle claims tied to fraudulent mortgage-backed securities. While the bank said it won’t pay anywhere close to that amount, the dust-up fueled doubts over its capital levels and refocused investors on the industry’s faults. “One word – Deutsche,” David Moss at BMO Global Asset Management in London, said when asked to sum up the recent slump in European banks. “That’s the biggest thing – it’s reignited the risk around regulation, fines and litigation.”
Dismissing concern about the bank’s finances, Chief Executive Officer John Cryan told Bild in an interview published late Tuesday that capital “is currently not an issue,” and accepting government support is “out of the question for us.” Deutsche Bank has tumbled almost 20% this month, while Royal Bank of Scotland – which also faces a looming Justice Department fine – fell 13%, and Italy’s UniCredit slumped 12%. The Bloomberg Europe 500 Banks and Financial Services Index has declined 4.2% in September, making it the worst month since June, when Britain’s vote to exit the European Union roiled markets and sent bank shares plunging.
[..] European banks are grappling with tougher regulatory requirements, sputtering economic growth and negative interest rates, which squeeze lending margins and crimp investment returns. In Italy, where banks are burdened with some €360 billion of soured loans, UniCredit is working on a plan to boost capital that may include asset sales and a stock offering, according to people familiar with the matter. In Germany, Commerzbank scaled back its full-year profit goals and may announce thousands of job cuts this week,
Read more …

They already have.
• IMF Warns Central Banks Could Lose Deflation Fight (AFP)
The IMF warned Tuesday that central banks are struggling to beat back deflationary forces and that governments need to spend to help them succeed. In a new assessment of global economic conditions, the IMF said many countries worldwide are battling disinflation – low and slowing inflation – due to weak global economic growth.If central banks around the world cannot halt this stall, and if companies and people increasingly believe they can’t halt it, their economies risk sinking into a deflationary spiral – where prices generally start to fall and companies and consumers hold back spending and investment, stalling the economy. In this case, “countries can’t afford to be complacent,” the Fund warned. The report said deflationary pressures in many countries are coming from abroad, in the form of sinking prices of both commodities and manufactured goods.
“The breadth of the decline in inflation across countries and the fact that it is stronger in the tradable goods sectors underscore the global nature of disinflationary forces,” the IMF said. Weak inflation challenges central banks’ ability to use monetary policy to stimulate demand, the IMF notes, because interest rates are likely to already be very low, giving them little room to cut further. That has been the case with top central banks including the Fed, the ECB and the BOJ, with the latter two already having taken some interest rates negative. “Eventually, ‘persistent’ disinflation can lead to costly deflationary cycles – as we have seen in Japan – where weak demand and deflation reinforce each other, and end up increasing debt burdens and hindering economic activity and job creation.”
Read more …

How to politicize the Fed?!
• A Legal Barrier to Higher US Interest Rates (WSJ)
Defending the Fed’s recent decision to put off raising interest rates again, Fed Chair Janet Yellen told reporters last week that she and other Fed governors wanted “to see some continued progress” before taking that step. Politics, she insisted, had nothing to do with it. What Ms. Yellen didn’t say is that the Fed couldn’t raise its rates without breaking the law. Since when are Fed rate increases illegal? Since the 2007-08 subprime meltdown and financial disaster, actually. Until then the Fed could set any target it liked for the federal-funds rate—the interest rate banks pay for overnight loans of cash reserves. To keep the fed-funds rate from rising above target, the Fed pumped more reserves into the banking system. To keep it from dropping below, it took reserves away.
But after Lehman Brothers failed in 2008, the Fed’s efforts to keep the fed-funds rate from dropping below its target proved futile. To set a floor on how far the rate could go, the Fed started paying interest on banks’ reserve balances with the Fed, taking advantage of the 2006 Financial Services Regulatory Relief Act giving it permission to do so. Alas, it didn’t work. Government-sponsored enterprises Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac and the Federal Home Loan Banks, which also kept deposit balances at the Fed but weren’t eligible for interest on reserves (IOR), started making overnight loans to banks at rates below the IOR rate. In effect, this turned what the Fed hoped would be a floor on the fed-funds rate into a ceiling. To raise rates now, the Fed increases the rate on reserves.
So what’s to keep the Fed from raising rates this way again? The 2006 Financial Services Regulatory Relief Act is what. For that law only allows the central bank to pay interest on reserves “at a rate or rates not to exceed the general level of short-term interest rates.” The rub is that the Fed’s IOR rate of 50 basis points (0.5%) already exceeds the closest comparable market rates: those on shorter-term Treasury bills. At the start of this month, the four-week T-bill rate was just 26 basis points; since then it has slid even lower, all the way down to 10 basis points. Judging by these numbers, the Fed is already flouting the law. Another hike would mean flouting it all the more flagrantly. Lawmakers will be duty-bound to object. The law can only be stretched so far. Unless “general short-term rates” rise markedly, Congress can be expected to question the legality of any Fed rate increase. If it comes to that, Ms. Yellen will find it very hard to dissemble her way out of it.
Read more …

2016 will be known as the good old days.
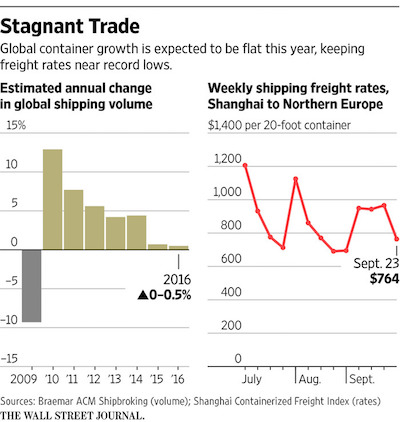
• Global Container Volume on Track for Worst Year Since 2009 (WSJ)
Global container volumes are on track for zero growth this year, which would mark the sector’s worst performance since the 2009 economic crisis and a sure catalyst for further bankruptcies and possible acquisitions in the beleaguered shipping industry, shipping executives said. Freight rates, the predominant source of income for shipping companies, fell 20% in the benchmark Asia to Europe trade route this week compared with last week to $767 per container. Rates have mostly stayed well below $1,000 since the start of the year and operators say anything below $1,400 is unsustainable. They aren’t expected to turn around soon.
China’s Golden Week holiday starts at the beginning of October, marking the slow season for operators as many Chinese factories cut production levels after an output frenzy in the summer months when western importers stack up products for the year-end holidays. “The industry faces its worst year since the Lehman Brothers collapse,” said Jonathan Roach, an analyst at London based Braemar ACM. “Demand is around zero and any moves to increase freight rates will likely fail.” Hanjin, South Korea’s biggest operator and the world’s seventh largest in terms of capacity, filed for bankruptcy protection last month and is under court order to sell its own ships and returning chartered ships to their owners. Container operators, which move everything from clothes and shoes to electronics and furniture, are burdened by 30% more capacity in the water than demand.
Read more …

And they’ll keep their jobs?
• Wells Fargo Executives Forfeit Millions, CEO To Forgo Salary (G.)
Wells Fargo executives will forfeit millions of dollars in the wake of revelations that the bank’s sales quotas led to the creation of more than 2m unauthorized accounts. The bank’s chief executive John Stumpf will forgo his salary for the coming months as independent directors launch a new investigation into Wells Fargo’s retail banking and sales practices. Last year, Stumpf made about $19.3m. Stumpf will also forfeit unvested equity awards worth about $41m. Carrie Tolstedt, who oversaw the retail banking at Wells Fargo while the unauthorized accounts were opened, was slated to receive as much as $124.6m after retiring this summer, according to Fortune. The bank said on Tuesday that she would not receive an undisclosed severance and would forfeit about $19m in unvested awards.
Less than three weeks ago, Wells Fargo announced that it had agreed to pay $185m in penalties after an audit found that its employees opened as many as 1.5m deposit accounts and 565,000 credit card accounts without customers’ consent. The accounts were opened by the bank’s staff in hopes of meeting their monthly sales quota and earning their incentive bonuses. Wells Fargo workers have tried to draw attention to the “unreasonable” quotas before – some even staged a protest in front of the bank’s headquarters last year. When Stumpf testified in front of the US Senate last week, he drew ire from US lawmakers. Many of them called for the bank to recoup pay from Stumpf and Tolstedt and hold them accountable.
Read more …

The EU has made Greek recovery impossible. Spending power has been murdered, and a whole generation of younger people is 50-60% long-term unemployed. It makes no difference what anyone forecasts.
• Worries Grow Over Greek Economic Forecast (WSJ)
Greece’s economic recovery is proving elusive, challenging the forecasts of the country’s government and foreign creditors still counting on growth reviving this year. The IMF said last week that the economy is stagnating, in the first admission from creditors that Greece’s recovery is off track again. Growth will only restart next year, the head of the IMF’s team in Greece said on a conference call with reporters, without offering details. Of particular concern is that exports, which are supposed to lead Greece out of trouble, are on a slow downward trajectory, hampered by capital controls, taxes and a lack of credit. “There is no chance we will see a rebound unless we see some bold political decisions that would introduce a more stable business environment,” said Dimitris Tsakonitis, general manager at mining company Grecian Magnesite.
The bailout agreement between Greece and its German-led creditors assumes rapid growth from late 2016 onward, including an official forecast of 2.7% growth in 2017. Private-sector economists believe next year’s growth could be closer to 0.6%. Weaker growth would undermine the budget, likely leading to fresh arguments with lenders about extra austerity measures. Greece is still grappling with the measures it has already agreed to. Late on Tuesday the country’s parliament approved pension overhauls and other policy changes that have been delayed for months, holding up bailout funding.
Read more …

Good to note. Berlin buys back its water, and forces Athens to sell it. “It’s not any more a democracy or equality in the EU. It’s a kind of business..”
No society should ever agree to sell its basic needs to foreigners. Leaders who do that anyway should be fired.
• Germany’s Hypocrisy Over Greece Water Privatisation (G.)
Greek activists are warning that the privatisation of state water companies would be a backward step for the country. Under the terms of the bailout agreement approved by the Greek parliament today, Greece has pledged to support an existing programme of privatisation, which includes large chunks of the water utilities of Greece’s two largest cities – Athens and Thessaloniki. There is ongoing debate about water privatisation and the role of business. Across Europe a wave of austerity-driven privatisation proposals has led to protests in Ireland, Italy, Greece and Spain. At the same time, some of northern Europe’s largest cities, including Paris and Berlin, are buying back utilities they sold just last decade.
President of the Thessaloniki water company trade union George Argovtopoulos said a move to a for-profit model would raise prices for consumers and degrade services. “It’s not any more a democracy or equality in the EU. It’s a kind of business,” he said, adding that austerity measures that require water privatisation smacked of a “do as I say, but not as I do” approach from Germany. “We know that in Berlin, just two years ago they remunicipalised the water there, although they paid just under €600m to Veolia [to buy back its stake]. It’s clear that the model of privatisation of water has failed all around the world,” he said. The German finance ministry refused to comment ahead of a Eurogroup meeting in Brussels on Friday where the third bailout deal looked set to be signed.
[..] Austerity-led changes to water supply have been fiercely resisted across Europe’s most indebted countries. In Dublin this year, huge protests erupted over plans to directly charge water users who previously paid for water through their taxes. This was seen as a first step towards selling off Ireland’s water supply. A water privatisation push by former Italian prime minister Silvio Berlusconi was crushed by a 95% referendum vote in 2011. A similar referendum in Thessaloniki last year delivered a 98% vote against. A 2014 report by the Transnational Institute’s Satoko Kishimoto found that across the world 180 cities had bought back (or remunicipalised) their water supply. She said this was a response to almost universally higher water prices and the loss of control over a fundamental resource.
Read more …

Another author claiming that “..the scientific consensus within and outside of China is that GMOs are safe..”
• China Wants GMOs. The Chinese People Don’t. (BBG)
The latest food safety scandal in China might be its most damaging. Earlier this week, a former doctoral student at one of the country’s national testing centers for genetically modified organisms went public with allegations of scientific fraud, including claims that records were doctored extensively, that unqualified personnel were employed under illegal contracts and – most seriously – that authorities refused to take action when his concerns were aired privately. On Wednesday, China’s Ministry of Agriculture responded to a social media storm by suspending operations at the center. That might take care of the current scandal, but the Chinese public’s hostility toward GMOs won’t go away so easily.
Those concerns have only grown over the past decade as the government has increased its support of GMOs, including approval of the state-owned ChinaChem Group’s $43 billion takeover offer for the Swiss seed giant Syngenta. These efforts have galvanized a very public opposition that transcends China’s typical political fault lines, and created one of the government’s most intractable headaches. Feeding China’s huge population has never been easy. But over the last three decades, the challenges have become considerably greater as urbanization devoured farmland, and pollution made even more of it unusable. Today, the government is faced with the task of feeding 21% of the world’s population with 9% of its arable land. Its reliance on foreign goods has made China the world leader in imports since 2011.
Officials now fear the country could become dependent on foreigners for its food supply and the government remains committed to maintaining self-sufficiency in rice, wheat, and other key grains. As a result, the political pressure to increase yields is considerable. In fact, this pressure is centuries-old. Domesticated rice first appeared in the Yangtze River Valley at least 8,000 years ago, and Chinese farmers and scientists have been innovating ever since. In 1992, China became the first country to introduce a GMO crop into commercial production, when it sowed a virus-resistant tobacco plant on 100 acres. Since then, the government has issued safety certificates for a wide range of GMO crops, ranging from chili peppers to petunias. Yet, so far at least, only cotton has gone into wide cultivation. Other GMOs – especially rice, a staple of the Chinese diet – are still awaiting approval to be domestically cultivated.
Read more …

The blessings of plastic.
• Single Clothes Wash May Release 700,000 Microplastic Fibres (G.)
Each cycle of a washing machine could release more than 700,000 microscopic plastic fibres into the environment, according to a study. A team at Plymouth University in the UK spent 12 months analysing what happened when a number of synthetic materials were washed at different temperatures in domestic washing machines, using different combinations of detergents, to quantify the microfibres shed. They found that acrylic was the worst offender, releasing nearly 730,000 tiny synthetic particles per wash, five times more than polyester-cotton blend fabric, and nearly 1.5 times as many as polyester. “Different types of fabrics can have very different levels of emissions,” said Richard Thompson, professor of marine biology at Plymouth University, who conducted the investigation with a PhD student, Imogen Napper.
“We need to understand why is it that some types of [fabric] are releasing substantially more fibres [ than others].” These microfibres track through domestic wastewater into sewage treatment plants where some of the tiny plastic fragments are captured as part of sewage sludge. The rest pass through into rivers and eventually, oceans. A paper published in 2011 found that microfibres made up 85% of human-made debris on shorelines around the world. The impact of microplastic pollution is not fully understood but studies have suggested that it has the potential to poison the food chain, build up in animals’ digestive tracts, reduce the ability of some organisms to absorb energy from foods in the normal way and even to change the behaviour of crabs.
Read more …