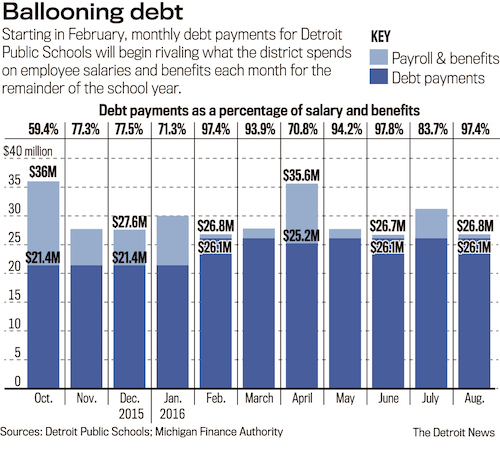
Ann Rosener Reconditioning spark plugs, Melrose Park Buick plant, Chicago 1942



Kudo’s to the WSJ for a bit of reflection. Just about all other outlets I’ve seen, parade analysts opining in hollow phrases.
• China GDP at 25-Year Low, Long Slog Increases the Pain (WSJ)
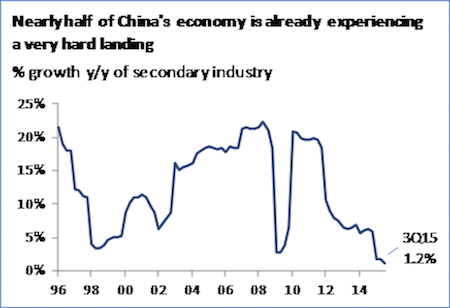
Whether or not one believes China’s GDP data, the news is depressing. There was little in the fourth quarter to indicate that gobs of monetary and fiscal easing are doing anything but cushioning the economy through an increasingly painful slog. China’s headline GDP grew 6.8% in the fourth quarter. But in nominal terms, it grew just under 6%, the slowest since last century. With debt in the economy still growing at twice that rate, this implies that a huge amount of new lending is going nowhere but to pay off old loans, not to stimulate the economy. It’s a vicious cycle that will be hard for China to escape. The reason nominal GDP was lower than headline GDP—it’s usually the other way around—was a negative price deflator, indicating overall deflation.
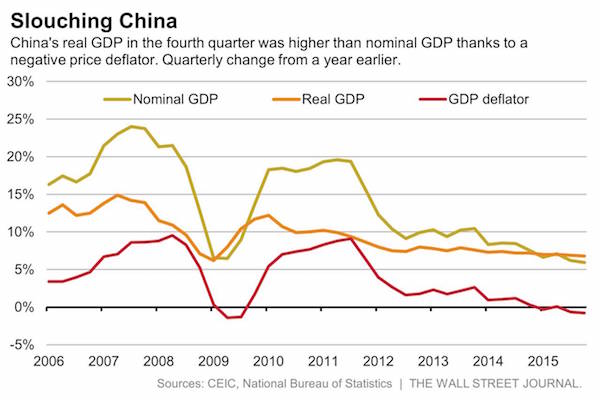
It was the third time in four quarters that China’s deflator has been negative, giving the headline number a boost. Some suspect that China is monkeying with the deflator; the larger it is, the more it improves the headline figure. Nor is the deflator the only figure that private economists suspect is distorting the GDP series. Oxford Economics points to industrial-output numbers that it calls overly optimistic. Adjusting for that, it said China’s GDP grew 6.1% in the fourth quarter. Capital Economics, using various proxy indicators, puts growth at 4.5%. Other indicators support the dour outlook. Industrial-production growth slowed to 5.9% in December from 6.2% in November. Services sustained the party, up 8.2% from a year earlier in the fourth quarter.
But even that is a slowdown from the previous two quarters, a sign of how much the stock-market crash and volatility in the financial-services industry are undermining the idea that China can seamlessly shift the economy from industrial output to services. The poor end to the year is especially depressing in light of the stimulus pumped into the economy over the past six months. How much worse would its performance have been without a sharp ramp-up in government spending, low interbank rates and multiple cuts in interest rates and reserve requirements? For investors who are spooked whenever China’s currency and stock markets plunge, the data are hardly reassuring. And the increasing outflows of yuan from the economy suggest locals are nervous, too.

When bad news gets so awful it must lead to something good. Something like that.
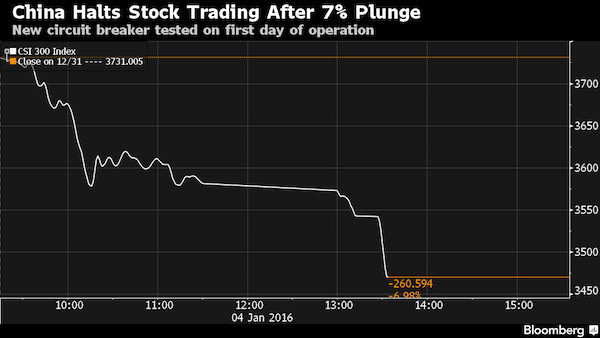
• China Stocks Surge As GDP Triggers Expectations Of Beijing Stimulus (MW)
China shares turned higher Tuesday, as investors weighed the likelihood of further stimulus from Beijing following data that the economy grew at its slowest pace in a quarter of a century. The Shanghai Composite Index traded up 2.8%, after flitting near the flat line and Australia’s S&P/ASX climbed 0.9%. Japan’s Nikkei closed up by 0.6% and South Korea’s Kospi rose 0.6%. The region’s markets were reacting to the latest batch of data from the world’s second largest economy. Growth slowed to 6.9% in 2015, compared to 7.3% in 2014. China also expanded by an annualized 6.8% during the fourth quarter alone, shy of 6.9% expected by economists surveyed by The Wall Street Journal. “It does suggest that more stimulus [from authorities] may be needed to push forth the pace of expansion,” said Niv Dagan at Peak Asset Management.
“Investors are happy to take a backward step and increase their cash weighting until things stabilize.” Investors have been reluctant to buy up the region’s shares, remaining nervous about how Chinese authorities will guide their markets and lower oil prices. Doubts linger about the ability of China’s central bank to curb yuan speculation, which was the initial trigger for selling in markets worldwide earlier this year. China’s Shanghai Composite Index, which has fallen nearly 17% this year, has dragged markets in Japan and Australia near bear market territory, defined as a 20% fall or more from a recent high. Efforts by authorities to talk up the underlying health of the Chinese economy this weekend may have helped calm some fears among investors and encouraged them to return to markets, said Angus Nicholson at IG. “Chinese markets have already suffered such a dramatic correction this year that I think some of these official assurances have helped bring a few buyers back to the table,” he said.

It has legs.
• The Case for Chaos in Trying to Pick Bottom of U.S. Equity Rout (BBG)
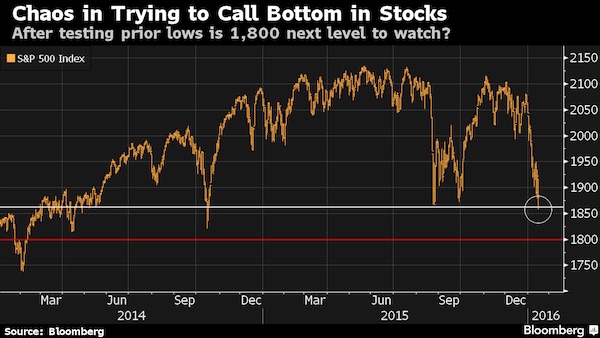
In a market bouncing up and down 2% a day, investor psychology is taking a beating in U.S. stocks. But nerves may need to fray further before the volatility abates. For all of last week’s twists, measures of investor anxiety sit well below levels from the last selloff, when shares plunged 11% in August. Twice last week the Chicago Board Options Exchange Volatility Index jumped more than 10% in a day, yet it ended 34% below its summer high. To those who monitor sentiment for clues to the market’s direction, these aren’t things that add up to capitulation, when bulls give up and prices fall to levels where calm is restored. While last week’s losses capped an 8% tumble that equaled the worst start to a year on record, they see enough optimism left to keep gyrations coming. “Wholesale panic” is what’s needed before the market turns, according to Scott Minerd at Guggenheim Partners.
“You start to see a huge surge in volatility because everybody is just trying to get through the exits, and they’re pushing prices down just to get out of the positions.” Ten days into 2016 and more than $2 trillion has been wiped from American stocks, with the Standard & Poor’s 500 Index careening to the lowest close since August. Alternating swings in the Dow Jones Industrial Average over the last three days were the wildest since S&P stripped the U.S. of its AAA credit rating in 2011. The Chicago Board Options Exchange Volatility Index, a gauge of trader trepidation tied to options on the S&P 500, ended the week at 27.02, more than 60% above its average level in 2015. At the same time, it sits 12% below its mean reading during the six-day rout that started Aug. 18 – and 34% below its highest close in that stretch.

In comes the Dallas Fed.
• Big US Banks Brace For Oil Loans To Implode (CNN)
Firms on Wall Street helped bankroll America’s energy boom, financing very expensive drilling projects that ended up flooding the world with oil. Now that the oil glut has caused prices to crash below $30 a barrel, turmoil is rippling through the energy industry and souring many of those loans. Dozens of oil companies have gone bankrupt and the ones that haven’t are feeling enough financial stress to slash spending and cut tens of thousands of jobs. Three of America’s biggest banks warned last week that oil prices will continue to create headaches on Wall Street – especially if doomsday scenarios of $20 or even $10 oil play out. For instance, Wells Fargo is sitting on more than $17 billion in loans to the oil and gas sector. The bank is setting aside $1.2 billion in reserves to cover losses because of the “continued deterioration within the energy sector.”
JPMorgan is setting aside an extra $124 million to cover potential losses in its oil and gas loans. It warned that figure could rise to $750 million if oil prices unexpectedly stay at their current $30 level for the next 18 months. “The biggest area of stress” is the oil and gas space, Marianne Lake, JPMorgan’s chief financial officer, told analysts during a call on Thursday. “As the outlook for oil has weakened, we would expect to see some additional reserve build in 2016.” Citigroup built up loan loss reserves in the energy space by $300 million. The bank said the move reflects its view that “oil prices are likely to remain low for a longer period of time.” If oil stays around $30 a barrel, Citi is bracing for about $600 million of energy credit losses in the first half of 2016. Citi said that figure could double to $1.2 billion if oil dropped to $25 a barrel and stayed there.

Interesting to see where this goes now that Kaplan has opened the door.
• The Fed Responds To Zero Hedge: Here Are Some Follow Up Questions (ZH)
Over the weekend, we gave the Dallas Fed a chance to respond to a Zero Hedge story corroborated by at least two independent sources, in which we reported that Federal Reserve members had met with bank lenders with distressed loan exposure to the US oil and gas sector and, after parsing through the complete bank books, had advised banks to i) not urge creditor counterparties into default, ii) urge asset sales instead, and iii) ultimately suspend mark to market in various instances. Moments ago the Dallas Fed, whose president since September 2015 is Robert Steven Kaplan, a former Goldman Sachs career banker who after 22 years at the bank rose to the rank of vice chairman of its investment bank group – an odd background for a regional Fed president – took the time away from its holiday schedule to respond to Zero Hedge. This is what it said.

We thank the Dallas Fad for their prompt attention to this important matter. After all, as one of our sources commented, “If revolvers are not being marked anymore, then it’s basically early days of subprime when mbs payback schedules started to fall behind.” Surely there is nothing that can grab the public’s attention more than a rerun of the mortgage crisis, especially if confirmed by the highest institution. As such we understand the Dallas Fed’s desire to avoid a public reaction and preserve semantic neutrality by refuting “such guidance.” That said, we fully stand by our story, and now that we have engaged the Dallas Fed we would like to ask several very important follow up questions, to probe deeper into a matter that is of significant public interest as well as to clear up any potential confusion as to just what “guidance” the Fed is referring to.

The world beyond spot prices. Still, a tad sensationalist.
• The North Dakota Crude Oil That’s Worth Less Than Nothing (BBG)
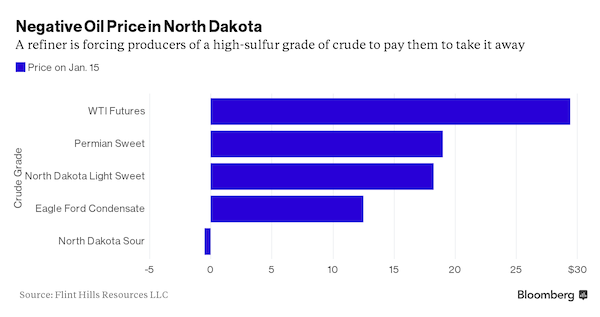
Oil is so plentiful and cheap in the U.S. that at least one buyer says it would need to be paid to take a certain type of low-quality crude. Flint Hills Resources, the refining arm of billionaire brothers Charles and David Koch’s industrial empire, said it would pay -$0.50 a barrel Friday for North Dakota Sour, a high-sulfur grade of crude, according to a list price posted on its website. That’s down from $13.50 a barrel a year ago and $47.60 in January 2014. While the negative price is due to the lack of pipeline capacity for a particular variety of ultra low quality crude, it underscores how dire things are in the U.S. oil patch. U.S. benchmark oil prices have collapsed more than 70% in the past 18 months and West Texas Intermediate for February delivery fell as low as $28.36 a barrel on the New York Mercantile Exchange on Monday, the least in intraday trade since October 2003.
“Telling producers that they have to pay you to take away their oil certainly gives the producers a whole bunch of incentive to shut in their wells,” said Andy Lipow, president of Lipow Oil in Houston. Flint Hills spokesman Jake Reint didn’t respond to a phone call and e-mail outside of work hours on Sunday to comment on the bulletin. The prices posted by Flint Hills Resources and rivals such as Plains All American Pipeline are used as benchmarks, setting reference prices for dozens of different crudes produced in the U.S. Plains All American quoted two other varieties of American low quality crude at very low prices: South Texas Sour at $13.25 a barrel and Oklahoma Sour at $13.50 a barrel. High-sulfur crude in North Dakota is a small portion of the state’s production, with less than 15,000 barrels a day coming out of the ground, said John Auers at Turner Mason in Dallas. The output has been dwarfed by low-sulfur crude from the Bakken shale formation in the western part of the state, which has grown to 1.1 million barrels a day in the past 10 years.

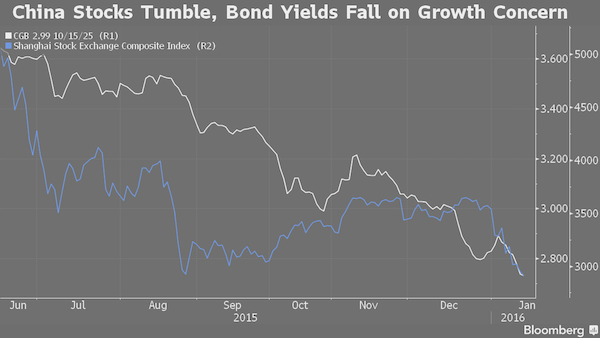
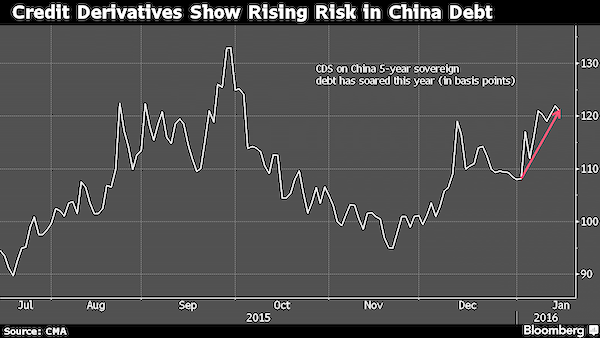
China 2016: Stock losses prompt money to flee into bonds and real estate. But for all the wrong reasons.
• China’s Hot Bond Market Seen at Risk of Default Chain Reaction (BBG)
China’s bond investors are raking it in as an equity rout scatters cash into fixed-income securities. But concerns are rising that spreading defaults and a sliding yuan will spark a selloff. Credit derivatives that are seen as a gauge of risk in the market have spiked 22 basis points since Dec. 31, the worst start to a year in data going back to 2008. The number of listed firms with debt double equity has jumped to 339 amid a weakening economy, from 185 in 2007. Traders surveyed by Bloomberg in December said note failures will spread. “2016 is a year when we will see systemic risks emerge in China’s credit market,” said Ji Weijie, credit analyst in Beijing at China Securities Co., the top arranger of bond offerings from state-owned and listed firms.
“There may be a chain reaction as more companies are likely to fail in a slowing economy and related firms could go down too.” The 18% tumble in China’s benchmark stock gauge this year has so far buoyed bonds, cutting yield premiums on local securities to record lows and on dollar debentures from the nation to the least in eight years. A reversal may be coming as the yuan’s slide spurs capital outflows that have forced the central bank to inject liquidity to hold down borrowing costs, a task it can’t manage indefinitely, according to First State Cinda. The weakest economic growth in a quarter century prompted onshore defaults to jump to at least seven in 2015 even as Premier Li Keqiang vowed to limit failures. Hua Chuang Securities said investors should avoid buying notes for now as surging supply also adds to risks that the hot onshore market will cool.
Such concerns have yet to be reflected in prices. The extra yield on top-rated local corporate debentures due in five years over similar-maturity government notes dropped 3.4 basis points since the start of the year to 57.3 basis points, near a record low. The premium on dollar securities from China is at 274 basis points, near the least since 2007, a Bank of America Merrill Lynch index shows. “The Chinese government wants to maintain a low domestic borrowing rate to support growth by injecting liquidity into the system,” said Ben Sy, the head of fixed income, currencies and commodities at the private banking arm of JPMorgan Chase & Co. in Hong Kong. “CDS, on the other hand, is a proxy for global investors’ sentiment toward China and it can be speculative in nature.”

Steel can fall by half along with shipyards.
• Chinese Shipyards See New Orders Fall by Almost Half in 2015 (BBG)
New orders received by Chinese shipbuilders fell by nearly half last year from 2014, suggesting more consolidation is in order as the country’s appetite for raw materials wanes and shipping rates languish at multiyear lows. Shipbuilders in China received new orders amounting to 31.3 million deadweight tons last year, a world-leading 34% share of the global market, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology said Monday. Backlog orders fell 12% to 123 million deadweight tons, or 36% of global market share. Chinese shipbuilders have sought government support as excess vessel capacity depresses shipping rates, leading to contracts being canceled.
South Korean and Singaporean shipyards are also feeling the pain, compounded by a bribery scandal in Brazil that has further affected orders. China Rongsheng Heavy Industries, once the country’s largest private shipyard, exited the sector last year amid heavy losses and changed its name to China Huarong Energy to reflect its new business focus. In early January, Zhoushan Wuzhou Ship Repairing & Building became China’s first state-owned shipbuilder to go bankrupt in a decade. In a sign of ongoing restructuring in the sector, the 10 leading shipbuilders on the mainland accounted for 53% of total orders completed and 71% of new orders received in 2015, the ministry said.

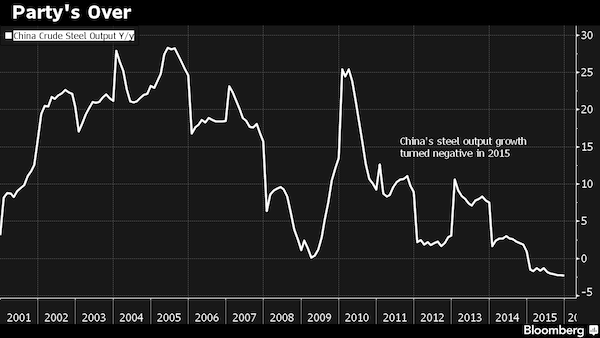
A big story for this year. The global steel glut is beyond proportions. Time for tariffs and protectionism.
• World’s Biggest Steel Industry (China) Shrinks for First Time Since 1991 (BBG)
Steel output in the world’s largest producer posted the first annual contraction in a quarter century. Mills in China, which make half of global supply, churned out less last year for the first time since at least 1991 as local demand dropped, prices sank and producers struggled with overcapacity. Crude steel production shrank 2.3% to 803.83 million metric tons, the statistics bureau said Tuesday. December output fell 5.2% to 64.37 million tons from a year earlier. Demand is weakening as policy makers seek to steer the economy away from investment toward consumption-led growth. The economy expanded 6.9% last year, the slowest full-year pace since 1990, data showed. Steel output will probably drop 2.6% this year, weakening the outlook for iron ore as global miners increase shipments, Citigroup has estimated.
“This marks the start of declining steel output in China as the economy slows,” Xu Huimin, an analyst at Huatai Great Wall Futures in Shanghai, said. “We’re likely to see more output cuts this year, though the magnitude of declines will be quite similar to 2015. Supply cuts in a glut are a long-drawn process as mills seek to maintain market share.” Crude-steel output in China surged more than 12-fold between 1990 and 2014, and the increase is emblematic of the country’s emergence as the world’s second-largest economy. Demand soared as policy makers built out infrastructure, shifted millions of people into cities and promoted consumption of autos and appliances.

“Shanghai, up a healthy 15.5%..” Pray tell what’s healthy about that.
• Strong China Property Data Masks Big Problem of Unsold Homes (Reuters)
For an economy facing its slowest economic growth in a quarter century, a 7.7% year-on-year rise in new home prices in December would seem to offer China some light at the end of the tunnel. But the headline number, published by the National Bureau of Statistics on Monday, masks China’s massive property problem – a vast amount of unsold apartments mainly in its smaller cities. Property prices were rising fast in mega cities like southern Shenzhen, where prices rocketed by nearly 47%, Shanghai, up a healthy 15.5%, and Beijing, which posted a respectable 8% gain over a year ago. But the recovery that began in October, after 13 months of straight decline, has only spread to just over half the 70 cities captured by official data, leaving others languishing far behind.
Wang Jianlin, China’s richest man and chairman of property and entertainment conglomerate Dalian Wanda Group, said on Monday that it could take four to five years for the market to digest the inventory in tier three and four cities. China has some 13 million homes vacant – enough to house the families of several small countries – and whittling down the excess is among Chinese policymakers top priorities for 2016. Dalian Wanda expects a significant decline in real estate income as it diversifies its business away from property. But, planning an initial public offering, Wang reckoned the market would manage so long as authorities took a gradual approach to the inventory issue. “Sales are highly concentrated in first- and second-tier cities, where 36 top cities account for three-quarters of the total sales value. So the portion from third- and fourth-tier cities is very low. As long as they destock slowly, there is no problem,” he told the Asia Financial Forum in Hong Kong.
Meantime, Wang said property investment in China’s first tier cities was the most risky due to high land costs, and his firm’s real estate focus is largely on the commercial sector in the lower-tier cities. Still, analysts reckon it will take a lot longer before the price recovery translates into growth in property investment that can help the overall economy regain momentum. “Property investment is expected to see a single-digit decline this year despite recovering home prices, so it will continue to weigh on GDP,” said Liao Qun, China chief economist at Citic Bank International in Hong Kong. That will hardly dull the pain for investors worried by a depreciation in the yuan currency and crumbling stock markets since the start of the year.

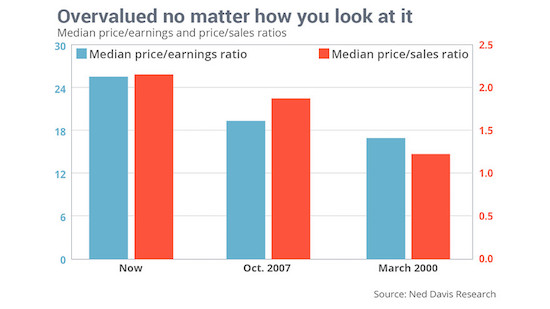
Imagine that were your pension money. Invested in a market that is grossly overvalued. Abe is a madman.
• Japan Makes Plans for Pension Fund to Invest in Stocks (WSJ)
Japan’s government is preparing legislation that would allow its $1.1 trillion public pension reserve fund to directly buy and sell stocks, a plan that is sparking divisions over the state fund’s role in private markets. The Government Pension Investment Fund currently entrusts its stock-investment money to outside managers. The welfare ministry plans to present a plan for direct investment to parliament this spring, though legislation might take until later in the year to pass, say politicians and government officials. The change would mark another step in the GPIF’s transformation from a conservative investor into one that resembles other global pension and sovereign-wealth funds. Prime Minister Shinzo Abe has encouraged the shift to reinvigorate Japan’s financial markets and improve corporate governance.
“GPIF could contribute more to Japan’s economy by constructively interacting not only with money managers, but also with corporations,” said GPIF chief investment officer Hiromichi Mizuno. “As Japan’s biggest asset owner, we can jump start a positive chain reaction of better governance between businesses and investors.” The plan has raised concerns among some business leaders and politicians who say the giant fund could distort markets with its stock picks or act as a tool for politicians to exert influence over companies. “I am most worried about political intervention,” said Keio Business School associate professor Seki Obata, who previously served on the GPIF’s investment advisory committee.
“In theory, I’m in support of in-house stock investing, but Japan is still the most immature country and society in terms of asset-management issues.” The Abe administration has already been criticized for using the GPIF to influence financial markets. In 2014, the fund said it was nearly doubling its allocation to equities, which some investors criticized as a “price-keeping operation”—an attempt to pump up the stock market. Criticism started again after the fund posted an ¥8 trillion loss in the third quarter of 2015, and further losses are likely in the current quarter if Japanese stocks continue their current slide. The Nikkei Stock Average has fallen more than 10% since the beginning of the year and fell 1.1% Monday.

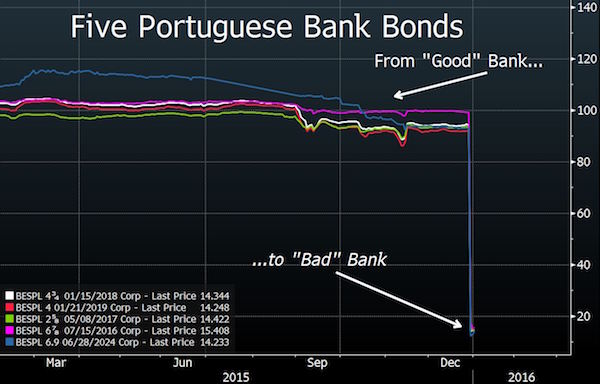
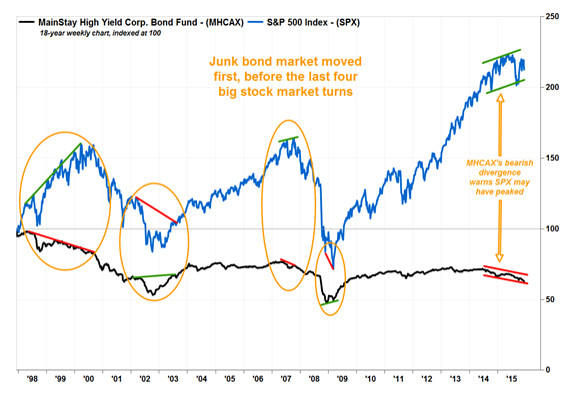
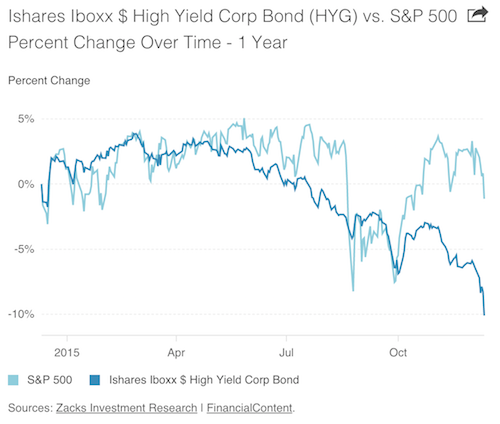
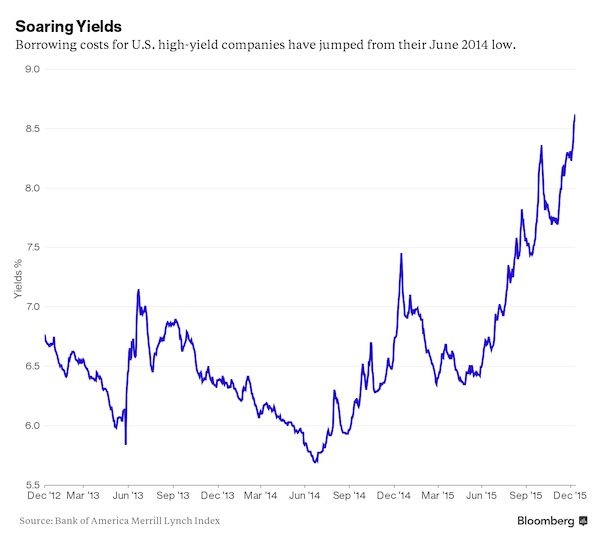
Turning to junk. Shorting Banco Dei Paschi has already been banned.
• Italy Banks Lose $82 Billion of Cheap Financing From Savers (BBG)
Italian savers ditched €75 billion of bank bonds in the year ended September, further depriving lenders of a cheap source of funding. Retail holdings of the notes tumbled 27% in the period to €200 billion, extending declines since 2012, based on Bank of Italy data released on Monday. There was a €5 billion drop in the three months ended September, marking a slowdown from previous quarters. Savers are shunning bank bonds as losses at four small lenders in November have made more people aware that the investments are risky. The cash drain has contributed to a slump in prices for junior bonds, as lenders turn to more expensive wholesale financing and contend with tighter European Union rules on state aid.
“A lot of these banks have survived better thanks to retail funding,” Alberto Gallo at RBS, said before the data was released. “If you take out the retail-funding channel some banks may find it more expensive to fund.” A new EU bail-in regime, which forces lenders to impose losses on creditors before they can accept state aid, has driven declines in Italian bank bonds this year, Gallo said. Banca Popolare di Vicenza’s €200 million of 9.5% subordinated notes due September 2025 have dropped to 74 cents on the euro from 96 cents on Dec. 31, according to data compiled by Bloomberg. Banca Monte dei Paschi di Siena SpA’s€ 379 million of 5.6% September 2020 bonds have fallen to 72 cents from 95 cents.

Numbered days.
• Italy PM Renzi Sharpens His Rhetorical Barbs At EU (FT)
When Matteo Renzi visited Berlin last July he delivered a subtle warning to the assembled crowd at Humboldt university that a new deal was needed to save European integration. “A world that is changing so quickly needs a place that it can call home in terms of values, ideals, and passion – and that place is Europe,” the Italian prime minister said, weaving in references to Sophie Scholl, a symbol of German resistance to the Nazis, and Willy Brandt, the former chancellor. “We risk wasting it if we hand it over to bureaucrats and technocrats”. But the 41-year-old former mayor of Florence has now turned to much more pointed complaints, perhaps feeling that his delicate and vague admonitions of last summer were conveniently ignored.
Mr Renzi has sharply escalated his confrontational rhetoric towards the European Commission and the German government, triggering surprise and irritation in Brussels and Berlin. Italy’s increasingly bitter recriminations span a wide range of issues — from migration to energy, banking and budget policy — Mr Renzi feels that the EU is either applying its rules too rigidly, or is adopting double standards that often benefit Germany, to the detriment of Italy. “Europe has to serve all 28 countries, not just one,” he told the FT in an interview last month. Mr Renzi’s attacks on the EU — which have also made him an unlikely David Cameron sympathiser, if not an ally, ahead of Britain’s EU referendum — are undoubtedly a reflection of shifting public opinion in Italy over the past decade.
Whereas Italians used to be among the biggest supporters of European integration, years of economic stagnation and recession have brought a wave of disillusion with its outcomes, particularly when it comes to the euro. Mr Renzi, who took office nearly two years ago, saw his poll numbers drop substantially over the course of 2015, with the populist anti-euro Five Star Movement and Northern League consolidating their positions as Italy’s second and third largest political parties respectively. And Mr Renzi faces two key electoral tests this year: municipal elections in some of the largest Italian cities, including Rome and Milan, and a referendum on constitutional reforms to strip power from the Italian Senate that the prime minister has staked his political future on, threatening to resign should he lose.

Funny thing is, he’s the first one other than Le Pen to say it out loud. Still, €2 billion won’t get him anywhere.
• Hollande Says France In State Of Economic, Social Emergency (BBC)
President Francois Hollande has set out a €2bn job creation plan in an attempt to lift France out of what he called a state of “economic emergency”. Under a two-year scheme, firms with fewer than 250 staff will get subsidies if they take on a young or unemployed person for six months or more. In addition, about 500,000 vocational training schemes will be created. France’s unemployment rate is 10.6%, against a EU average of 9.8% and 4.2% in Germany. Mr Hollande said money for the plan would come from savings in other areas of public spending. “These €2bn will be financed without any new taxes of any kind,” said President Hollande, who announced the details during an annual speech to business leaders.
“Our country has been faced with structural unemployment for two to three decades and this requires that creating jobs becomes our one and only fight.” France was facing an “uncertain economic climate and persistent unemployment” and there was an “economic and social emergency”, he said. The president said recently that the country’s social emergency, caused by unemployment, was as serious as the emergency caused by terrorism. He called on his audience to help “build the economic and social model for tomorrow”. The president also addressed the issue of labour market flexibility. “Regarding the rules for hiring and laying off, we need to guarantee stability and predictability to both employers and employees. There is room for simplification,” he said.
“The goal is also more security for the company to hire, to adapt its workforce when economic circumstances require, but also more security for the employee in the face of change and mobility”. However, the BBC’s Paris correspondent Hugh Schofield said there was widespread scepticism that the plan would have any lasting impact. “Despite regular announcements of plans, pacts and promises, the number of those out of work continues to rise in France. “With a little over a year until the presidential election in which he hopes to stand for a second term, President Hollande desperately needs good news on the jobs front. But given the huge gap so far between his words and his achievements, there is little expectation that this new plan will bear fruit in time”, our correspondent said.

Russia can’t borrow in world markets. The upside of that is it has very little debt.
• Russia Considers Suspending Loans to Other Countries (Moscow Times)
Russia could suspend loans to foreign countries as the country’s budget continues to be strained by economic recession, the Interfax news agency reported Monday, citing Deputy Finance Minister Sergei Storchak. “The budget is strained, more than strained. I think we are in a situation where we are forced to take a break from issuing new loans,” Storchak was quoted by the news agency as saying. Given the current state of the national budget, the undertaking of new obligations involves increased risk, he added, according to Interfax.
Russia’s federal budget for this year, based on oil prices of $50 per barrel, will likely face problems as the oil price continues to drop dramatically. As of Monday morning, the price of Brent crude fell to $28 dollars per barrel following the lifting of sanctions against Iran, Interfax reported. Storchak also said that negotiations on Russia’s $5 billion loan to Iran were continuing and that no final decision had been taken yet. Last year, Iran requested a $5 billion loan from Russia for the implementation of joint projects, including the construction of power plants and development of railways.

As much as I want to stay out of US politics, Jim’s observations here warrant a thorough read.
• Worse Than 1860 (Jim Kunstler)
The Republican Party may be closer to outright blowup since the rank and file will never accept Donald Trump as their legitimate candidate, and Trump has nothing but contempt for the rank and file. If Trump manages to win enough primaries and collect a big mass of delegate votes, the July convention in Cleveland will be the site of a mass political suicide. The party brass, including governors, congressmen, senators and their donor cronies will find some device to deprive Trump of his prize, and the Trump groundlings will revolt against that move, and the whole nomination process will be turned over to the courts, and the result will be a broken organization. The Federal Election Commission may then have to appeal to Capital Hill to postpone the general election. The obvious further result will be a constitutional crisis.
Political legitimacy is shattered. Enter, some Pentagon general on a white horse. Parallel events could rock the Democratic side. I expect Hillary to exit the race one way or another before April. She comes off the shelf like a defective product that never should have made it through quality control. Nobody really likes her. Nobody trusts her. Nobody besides Debbie Wasserman Schultz and Huma Abedin believe that it’s her turn to run the country. Factions at the FBI who have had a good look at her old State Department emails want to see her indicted for using the office to gin up global grift for the Clinton Foundation. These FBI personnel may be setting up another constitutional crisis by forcing Attorney General Loretta Lynch either to begin proceedings against Clinton or resign.
Rumors about her health (complications from a concussion suffered in a fall ) won’t go away. And finally, of course, Senator Bernie Sanders is embarrassing her badly at the polls. The Democrats could feasibly end up having to nominate Bernie on a TKO, but in doing so would instantly render themselves a rump party peddling the “socialist” brand — about the worst product-placement imaginable, given our history and national mythos. In theory, the country might benefit from a partial dose of socialism such as single-payer Medicare-for-all — just to bust up the odious matrix of rackets that medicine has become — but mega-bureaucracy on the grand scale is past its sell-by date for an emergent post-centralized world that needs its regions to get more local and autonomous.
The last time the major political parties disintegrated, back in the 1850s, the nation had to go through a bloody convulsion to reconstitute itself. The festering issue of slavery so dominated politics that nothing else is remembered about the dynamics of the period. Today, the festering issue is corruption and racketeering, but none of the candidates uses those precise terms to describe what has happened to us, though Sanders inveighs against the banker class to some effect. Trump gets at it only obliquely by raging against the “incompetence” of the current leadership, but he expresses himself so poorly in half-finished sentences and quasi-thoughts that he seems to embody that same mental incapacity as the people he rails against.

“You can only imagine what happens when the weather improves,” he said.”
• End Of Europe? Berlin, Brussels’ Shock Tactic On Migrants (Reuters)
Is this how “Europe” ends? The Germans, founders and funders of the postwar union, shut their borders to refugees in a bid for political survival by the chancellor who let in a million migrants. And then — why not? — they decide to revive the Deutschmark while they’re at it. That is not the fantasy of diehard Eurosceptics but a real fear articulated at the highest levels in Berlin and Brussels. Chancellor Angela Merkel, her ratings hit by crimes blamed on asylum seekers at New Year parties in Cologne, and EU chief executive Jean-Claude Juncker both said as much last week. Juncker echoed Merkel in warning that the central economic achievements of the common market and the euro are at risk from incoherent, nationalistic reactions to migration and other crises.
He renewed warnings that Europe is on its “last chance”, even if he still hoped it was not “at the beginning of the end”. Merkel, facing trouble among her conservative supporters as much as from opponents, called Europe “vulnerable” and the fate of the euro “directly linked” to resolving the migration crisis – highlighting the risk of at the very least serious economic turbulence if not a formal dismantling of EU institutions. Some see that as mere scare tactics aimed at fellow Europeans by leaders with too much to lose from an EU collapse – Greeks and Italians have been seen to be dragging their feet over controlling the bloc’s Mediterranean frontier and eastern Europeans who benefit from German subsidies and manufacturing supply chain jobs have led hostility to demands that they help take in refugees.
Germans are also getting little help from EU co-founder France, whose leaders fear a rising anti-immigrant National Front, or the bloc’s third power, Britain, consumed with its own debate on whether to just quit the European club altogether. So, empty threat or no, with efforts to engage Turkey’s help showing little sign yet of preventing migrants reaching Greek beaches, German and EU officials are warning that without a sharp drop in arrivals or a change of heart in other EU states to relieve Berlin of the lonely task of housing refugees, Germany could shut its doors, sparking wider crisis this spring. With Merkel’s conservative allies in the southern frontier state of Bavaria demanding she halt the mainly Muslim asylum seekers ahead of tricky regional elections in March, her veteran finance minister delivered one of his trademark veiled threats to EU counterparts of what that could mean for them.
“Many think this is a German problem,” Wolfgang Schaeuble said in meetings with fellow EU finance ministers in Brussels. “But if Germany does what everyone expects, then we’ll see that it’s not a German problem – but a European one.” Senior Merkel allies are working hard to stifle the kind of parliamentary party rebellion that threatened to derail bailouts which kept Greece in the euro zone last year. But pressure is mounting for national measures, such as border fences, which as a child of East Germany Merkel has said she cannot countenance. “If you build a fence, it’s the end of Europe as we know it,” one senior conservative said. “We need to be patient.”

Call the assembly together then.
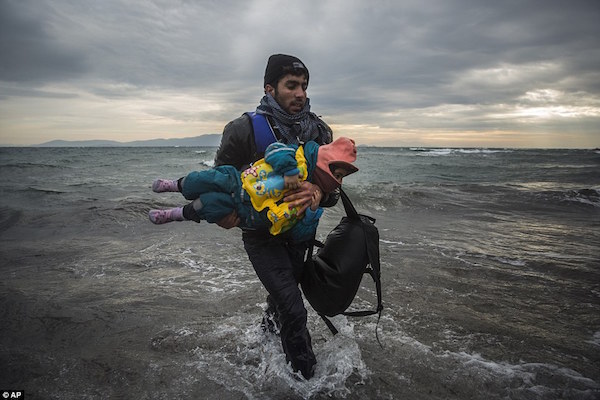
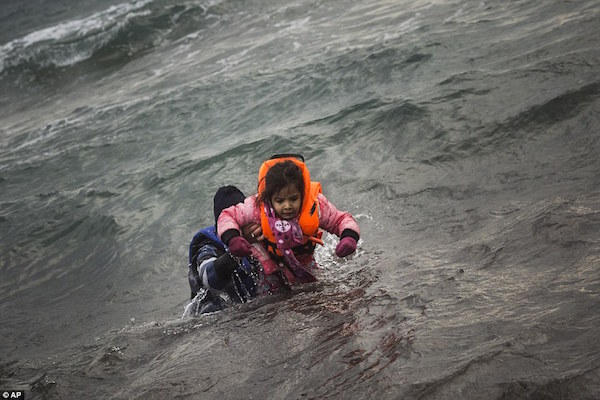
• UN Seeks Mass Resettlement Of Syrians (AP)
The new chief of the U.N. refugee agency said Monday the world should find a fairer formula for sharing the burden of Syria’s crisis, including taking in tens of thousands of refugees from overwhelmed regional host nations. Filippo Grandi, who assumed his post earlier this month, heads an agency grappling with mounting challenges as Syria’s five-year-old civil war drags on. Humanitarian aid lags more and more behind growing global needs, including those caused by the Syrian conflict. More than 4 million Syrians have fled their homeland, the bulk living in increasingly difficult conditions in neighboring countries such as Jordan and Lebanon, while hundreds of thousands have flooded into Europe. Grandi came to Jordan after a stop in Turkey. Later this week, he is due in Lebanon. He visited the Zaatari refugee camp in Jordan after meeting with King Abdullah II in the capital, Amman.
His agency, UNHCR, hopes to raise money for refugees at a London pledging conference in February, followed by an international gathering in March in Geneva where countries would commit to taking in more refugees. “I think we need to be much more ambitious” about resettling refugees, Grandi said. “We are talking about large numbers … in the tens of thousands.” “What is needed is a better sharing of responsibilities, internationally, for a crisis that cannot only concern the countries neighboring Syria,” he said. Hundreds of thousands of refugees entered Europe in 2015, often with the help of smugglers who ferried them across the Mediterranean in dangerous voyages. Grandi said it was time to create legal ways for some refugees to leave overburdened host countries.

Either stop bombing or face mass migration on a much larger scale than what we’ve already seen. At least it’s not complicated.
• Davos Boss Warns Refugee Crisis Could Become Something Much Bigger (BBG)
As the crash in commodities prices spreads economic woe across the developing world, Europe could face a wave of migration that will eclipse today’s refugee crisis, says Klaus Schwab, executive chairman of the World Economic Forum. “Look how many countries in Africa, for example, depend on the income from oil exports,” Schwab said in an interview ahead of the WEF’s 46th annual meeting, in the Swiss resort of Davos. “Now imagine 1 billion inhabitants, imagine they all move north.” Whereas much of the discussion about commodities has focused on the economic and market impact, Schwab said he’s concerned that it will also spur “a substantial social breakdown. That fits into what Schwab, the founder of the WEF, calls the time of “unexpected consequences” we now live in.
In the modern era, it’s harder for policy makers to know the impact of their actions, which has led to “erosion of trust in decision makers.” “First, we have to look at the root causes of this,” Schwab said. “The normal citizen today is overwhelmed by the complexity and rapidity of what’s happening, not only in the political world but also the technological field.” That sense of dislocation has fueled the rise of radical political leaders who tap into a rich vein of anger and xenophobia. For reason to prevail, Schwab said, “we have to re-establish a sense that we all are in the same boat.” The theme for this year’s meeting is the Fourth Industrial Revolution, which the WEF defines as a “fusion of technologies that is blurring the lines between the physical, digital, and biological spheres.”
While that presents huge opportunities, Schwab warns that technological innovation may result in the loss of 20 million jobs in the coming years. Those job cuts risk “hollowing out the middle class,” Schwab said, “a pillar of our democracies.” At the same time, Schwab argues, trends like the sharing economy and the changes wrought by technology mean economists must adapt the tools they use to assess well-being. “Many of our traditional measurements do not work anymore,” he said. After decades watching the ebbs and flows of the global economy, Schwab said the current anxiety is “not new” for him. But he said that as the world gets ever more interconnected, the consequences of such turmoil could become more grave. This week’s WEF meeting, he said, will offer policy makers “the first opportunity after the markets have come down to look at the situation and coordinate.”

It’s been so long since I wrote there should an emergency UN meeting on refugees, I don’t even remember when. Let me renew that call. The EU must be afraid it wouldn’t like the outcome.
• German Minister Urges Merkel To Prepare To Close Borders (Reuters)
Chancellor Angela Merkel’s transport minister has urged her to prepare to close Germany’s borders to stem an influx of asylum seekers, arguing that Berlin must act alone if it cannot reach a Europe-wide deal on refugees. Alexander Dobrindt said Germany could no longer show the world a “friendly face” – a phrase used by Merkel as refugees began pouring into Germany last summer – and that if the number of new arrivals did not drop soon, Germany should act alone. “I urgently advise: We must prepare ourselves for not being able to avoid border closures,” Dobrindt, a member of the Bavarian Christian Social Union (CSU), told the Muenchner Merkur newspaper.
The CSU, the Bavarian sister party to Merkel’s conservative Christian Democrats (CDU), has ramped up pressure on the chancellor over her open-door refugee policy that saw 1.1 million migrants arrive in Germany last year alone. CSU leader Horst Seehofer told Der Spiegel magazine in a weekend interview that he would send the federal government a written request within the next two weeks to restore “orderly conditions” at the nation’s borders. Bavaria is the main entry point to Germany for refugees. “I would advise us all to prepare a Plan B,” Dobrindt said in an advanced release of an interview to run in the Muenchner Merkur’s Tuesday edition. Merkel has vowed to “measurably reduce” arrivals this year, but has refused to introduce a cap, saying it would be impossible to enforce without closing German borders.
Instead, she has tried to convince other European countries to take in quotas of refugees, pushed for reception centers to be built on Europe’s external borders, and led an EU campaign to convince Turkey to keep refugees from entering the bloc. But progress has been slow. Dobrindt rejected Merkel’s argument that closing borders would jeopardize the European project. “The sentence, the closure of the border would see Europe fail, is true in reverse. Not closing the border, just going on, would bring Europe to its knees,” he said.