Dorothea Lange Play street for children. Sixth Street and Avenue C, NYC June 1936



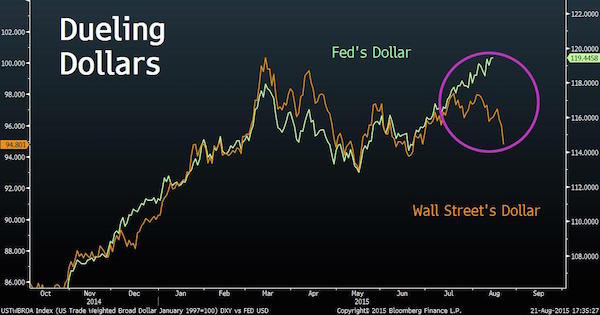
That’s a lot of POOF! by now. Makes one wonder what has EU exchanges feeling so happy today.
• China Stocks Plunge 7.63% As Selloff Picks Up Again (MarketWatch)
Chinese stocks tumbled Tuesday, bringing two-day losses to more than 15%, while other markets in Asia started to turn negative again after a bounce in earlier trading. Shares in Shanghai finished down 7.63% and fell as much as 8.2% in the afternoon. China’s main index breached the 3,000 level for the first time since December 2014. That follows a drop of 8.5% drop on Monday, the worst single-day loss in more than eight years. Shares in Hong Kong were down 0.7%, and the Nikkei closed 4% lower. Both benchmarks had risen as high as 2.9% and 1.6%, respectively, earlier in the day. The lack of support from Beijing for the market continued to spook investors.
“The market feels like it’s self-imploding because it’s used to a lot of hand holding,” said Steve Wang brokerage Reorient Group. Instead, regulators “are taking a wait and see approach… they intervened a lot in the past” and it didn’t work. In its latest effort to counter intensifying capital outflows from a weakening economy and a tumbling stock market, China’s central bank on Tuesday injected more cash into the financial system. The People’s Bank of China offered 150 billion yuan ($23.40 billion) of seven-day reverse repurchase agreements, a form of short-term loan to commercial lenders, as part of a routine money market operation. The bank injected a net 150 billion yuan into the financial system last week, marking its biggest pump priming exercise since the early February.
But the move fell short of expectations for larger measures, such as a cut to bank’s reserve requirements which could free up hundreds of billions of yuan for loans. Some analysts have said that even a cut in reserve ratio requirements of banks won’t be enough to rescue the market. “The intensity of the global stock rout demands something more substantial from both the monetary and fiscal side,” said Bernard Aw at Singapore based brokerage IG. “There are doubts whether China can cope with the persistent capital outflows, and domestic equity meltdown, given that it has already put in some heavy-hitting measures, and funded over $400 billion to a state agency to buy stocks,” said he added.

It was fun to see how Bloomberg et al were forced to change their upbeat headlines throughout the Asia trading day.
• China Stocks Extend Biggest Plunge Since 1996 on Support Doubts (Bloomberg)
Chinese shares slumped, extending the steepest four-day rout since 1996, on concern the government is paring back market support. The Shanghai Composite Index tumbled 4.3% to 3,071.06 at the midday break, taking its decline since Aug. 19 to 19%. About 14 stocks fell for each that rose on Tuesday. Stocks slumped even as equities rallied around Asia. Speculation around the government’s intentions has escalated since Aug. 14, after China’s securities regulator signaled authorities will pare back the campaign to prop up share prices as volatility falls. The China Securities Regulatory Commission made no attempt to reassure investors after Monday’s plunge, unlike a month ago when officials issued two statements shortly after an 8.5% drop.
“It’s panic selling and an issue of confidence,” said Wei Wei at Huaxi Securities in Shanghai. “The government won’t step in to rescue the market again as it’s a global sell-off and it’s spreading everywhere now. It’s not going to work this time.” The CSI 300 Index dropped 3.9%, led by technology, industrial and material companies. The Hang Seng Index advanced 1.6% after a gauge of price momentum dropped to the lowest since the October 1987 stock-market crash. The Hang Seng China Enterprises Index rose 0.5% from its lowest level since March 2014. Unprecedented government intervention has failed to stop a more than $4.5 trillion rout since June 12 amid concern the slowdown in the world’s second-largest economy is deepening. Officials have armed a state agency with more than $400 billion to purchase stocks, banned selling by major shareholders and told state-owned companies to buy equities.

“This was the fastest growth in credit in any country, EVER. It dwarfs both Japan’s Bubble Economy and the USA’s combination of the DotCom and Subprime Bubbles.”
• China Crash: You Can’t Keep Accelerating Forever (Steve Keen)
As I noted in last week’s post “Is This The Great Crash Of China?”, the previous crash of China’s stock market in 2007 lacked the two essential pre-requisites for a genuine crisis: private debt was only about 100% of GDP, and it had been relatively constant for the previous decade. This bust however is the real deal, because unlike the 2007-08 crash, the essential ingredients of excessive private debt and excessive growth in that debt are well and truly in place. China’s resilience against credit crises came to an end in 2009, when in a response to government directives, Chinese banks began lending to anyone with a pulse.
The growth in private debt rocketed from 17% per year at the beginning of 2009 (versus nominal GDP growth of 8% at the same time) to 37% per year by the beginning of 2010 (nominal GDP growth peaked six months later at 20% per year). By the beginning of this year, private debt had hit 180% of GDP and had grown by over 80% of GDP in the previous seven years. This was the fastest growth in credit in any country, EVER. It dwarfs both Japan’s Bubble Economy and the USA’s combination of the DotCom and Subprime Bubbles. China’s bubble drove private debt up by as much in 5 years as Japan managed in over 17 years, and more than the USA’s debt rose in the entire Clinton-Bush debt bubble from 1993 until 2010 (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: China’s credit bubble grew as much in 5 years as Japan’s did in 18
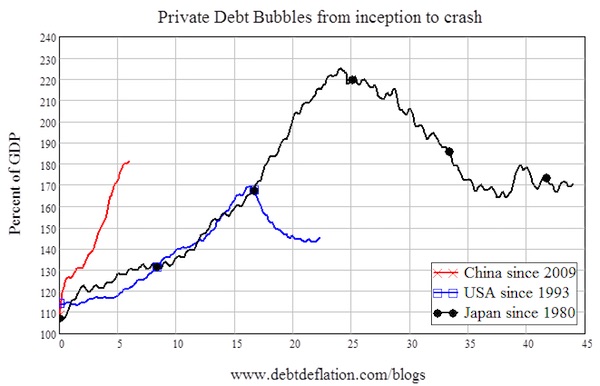
Since last week’s post, the crash in the Shanghai stock market has gone into overdrive. Shares fell 8.5% today, bringing the fall in the index to 20% in the last 5 days and 37% since the market peaked on June 12th. This is the downside of the credit bubble that China used to sidestep the Global Financial Crisis in 2008. It kept the wheels of the Chinese economy spinning when they had threatened to seize up in 2008, but it set China up for the fall it is now experiencing—and this fall is not going to be limited to the Shanghai Index.
Much of the 80%+ of GDP borrowed since 2009 went into property speculation by developers, which in turn fuelled much of the apparent growth of the Chinese economy. One key peculiarity about China’s economy—and there are many—is that much of its growth has come from the expansion of industries established by local governments (“State Owned Enterprises” or SOEs). Those factories have been funded partly by local governments selling property to developers (who then on-sold it to property speculators for a profit while house prices were rising), and partly by SOE borrowing. The income from those factories in turn underwrote the capacity of those speculators to finance their “investments”, and it contributed to China’s recent illusory 7% real growth rate.

China’s a vortex.
• The Gravity of China’s Great Fall (Economist)
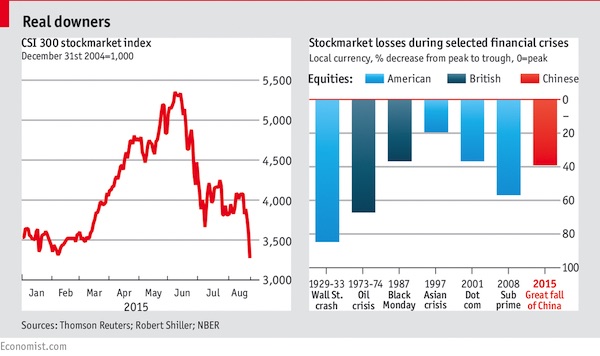
Asian markets are once again driving traders batty. A mammoth plunge in China’s stockmarkets on Monday, August 24th, touched off a wild day on global markets: in which Japanese and European stocks plummeted (as did American shares, before staging a remarkable turnaround) prompting commentators to liken the situation to previous crises from the Wall Street crash of 1929 to the Asian financial crisis of 1997. Asian share prices have had a brutal summer. China deserves much of the blame. Its own market has crashed (falling by almost 40% from its peak, and losing all the ground gained in 2015) amid worries about the pace of China’s economic slowdown. Slackening Chinese demand for goods and commodities would represent a big blow to its Asian neighbours.
The region has also been squeezed by a reversal of capital flows back toward the rich world, which has been accelerating as America’s Federal Reserve moves closer to interest rate increases. The currencies of Asia’s large economies have been falling as a result: Malaysia’s ringgit is down by 19% since May 1st, for example, while the Indonesian rupiah has dropped 8%. Despite those declines, which boost export competitiveness in those economies, export growth has slowed dramatically. There will probably be more market wobbles ahead.

Ambrose called this one spectacularly wrong mere days ago. Whole other tone now.
• China’s Market Leninism Turns Dangerous For The World (AEP)
The world financial system is at a dangerous juncture. Markets no longer believe that China’s Communist leaders are in full control of the country’s $27 trillion debt bubble, or know how to manage fast-moving events beyond their ken. This sudden loss of confidence in the anchor economy of East Asia has struck before the West is fully back on its feet after its own debacle seven years ago. Interest rates are still near zero in the US, the eurozone, Britain and Japan. Fiscal deficits are at unsafe levels. Debt is 30 percentage points of GDP higher than it was at the onset of the Lehman crisis. The safety buffers are largely exhausted. “This could be the early stage of a very serious situation,” said Larry Summers, the former US Treasury Secretary.
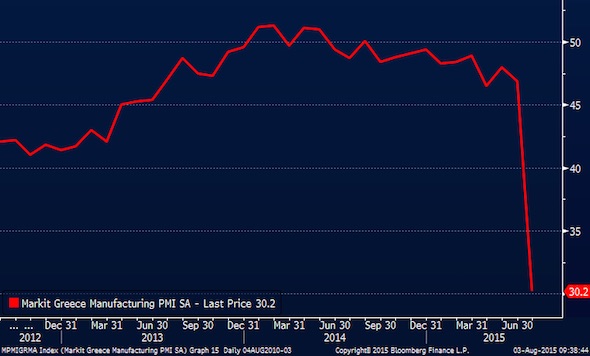
He compared it to the two spasms of the Asian crisis in the summer of 1997 and again in August 1998. Ominously, he also compared it to the “heart attack” of August 2007, when credit markets seized up on both sides of the Atlantic and three-month US Treasury yields plummeted to zero. That proved to be a false alarm, but it was an early warning of the accumulating stress that would bring down Western finance a year later. Full-blown contagion is now ripping through the international system. The main equity indexes in Europe and the US have all sliced through key levels of technical support. Once the S&P 500 index on Wall Street broke below its 200-day and 50-week moving averages last week, it was extremely vulnerable to any bad news. This came last Friday with yet more grim manufacturing data from China.
JP Morgan says the Caixin PMI indicator that so alarmed markets is skewed to the weakest segment of the Chinese economy and overstates the trouble, but such subtleties are lost in a panic. It turned into a global rout after the Shanghai composite index crashed 8.5pc on China’s “Black Monday”, pulverizing its July lows after the central bank (PBOC) – oddly passive – refused to come to the rescue as expected with a cut in the reserve requirement ratio for banks. Beijing’s botched efforts to prop up the country’s stock markets have collapsed. An estimated $300bn of state-orchestrated buying achieved nothing, overwhelmed by an avalanche of selling by investors forced to cover margin debt.
Professor Christopher Balding from Peking University wrote on FT Alphaville that China is lurching from one incoherent policy to another, shedding credibility and its aura of omnipotence at every stage. “There is a very real risk that Beijing is losing control of the story,” he said. The speed with which this episode has now engulfed US markets – trading at 50pc above their historic average on the long-term Shiller price/earnings ratio, and primed for trouble – suggests that events could all too easily metastasize into a self-perpetuating crisis of confidence. The Dow may have rebounded after a record 1,090-point drop at the opening bell, but such tremors cannot be ignored. “Circuit-breakers are needed, given how quickly markets have moved. Crises are highly non-linear events and ruling them out isn’t wise,” said Manoj Pradhan from Morgan Stanley.

Whatever they do won’t be enough.
• China Central Bank Injects $23.4 Billion as Yuan Intervention Drains Funds (BBG)
China’s central bank added the most funds to the financial system in open-market operations in six months as currency-market intervention to prop up the yuan strained the supply of cash. The People’s Bank of China auctioned 150 billion yuan ($23.4 billion) of seven-day reverse-repurchase agreements, according to a statement on its website. That compares with 120 billion yuan maturing Tuesday, leaving a net injection of 30 billion yuan. The PBOC also sold 60 billion yuan of three-month treasury deposits on behalf of the Ministry of Finance at 3%, according to a trader who bid at the auction. “Banks have become more reluctant to lend and we expect the PBOC to offer liquidity support,” said Liu Dongliang at China Merchants Bank.
“The amount was smaller than expected.” Major banks have been seen selling dollars toward the close of onshore trading in Shanghai on most days since a surprise yuan devaluation on Aug. 11. The intervention removes funds from the financial system and risks driving borrowing costs higher unless the monetary authority releases additional cash. China’s foreign-exchange reserves will drop by some $40 billion a month for the rest of this year, according to the median of 28 estimates in a Bloomberg survey. The monetary authority injected a net 150 billion yuan last week using reverse-repurchase agreements. It also added 110 billion yuan via its Medium-term Lending Facility.

No lack of people who’d deny this.
• Imploding Chinese Stock Market Does Not Bode Well For World Economy (Forbes)
The China hard landing aficionados (all five of them) may have something to celebrate with the implosion of Chinese equities, but the world economy does not. On Monday, investors woke up to yet another rout in both Chinese markets. The Deutsche X-Trackers A-Shares (ASHR) exchange traded fund was down 16% in the first half hour of trading on the NYSE and the iShares FTSE China (FXI) was down by 9%. This is capitulation at its best. Everyone is seeing who can scream “fire” the loudest. “When investors look at their trading dashboard this morning, they do not have just one factor which making them anxious about riskier assets…it is a combination of factors which reminds them that the sell-off in the markets is becoming very serious and similar to that of 2008, especially with regards to China,” says Naeem Aslam at AvaTrade International in Edinburgh.
Besides the massive stock market correction underway in China, the fundamentals of the economy are not what they used to be. While many businessmen on the ground in China say no one is in panic mode yet, momentum is clearly not in the their favor. This impacts the world, whether we like it or not. China is the world’s No. 2 economy and one of the world’s biggest consumers of raw materials, as in oil and soybeans. And when they consume less, prices decline, and when prices decline, it means less money for Iowa farmers, lower profits for big agribusiness like Bunge and — though many won’t cry over this — a weaker ruble and worsening recession in Russia.
In fact, on Monday morning the Russian ruble cracked 71 to 1, its weakest free-float level ever against the dollar. The weakening of emerging market currencies against the dollar is spreading suggesting that worries about emerging markets are deepening as investors think China demand is suddenly falling off a cliff. All BRIC currencies, including South Africa, have weakened substantially today. The trend is likely to continue, Barclays Capital analyst Guillermo Felices says.

It’s about their links to shadow banks, to a large extent.
• The Next Shoe To Drop In China? The Banks (MarketWatch)
To many investors, the problem with China is a suspicion that things could be much worse than is officially being let on. My own experience with a Bank of China ATM at the Hong Kong-Shenzhen border last Friday certainly got me thinking — just how bad is China’s liquidity crunch? The problem was the ATM menu options had been limited to funds balance, transfer and deposit but none for withdrawal. And it did not appear personal, as all three cash machines were the same, refusing locals and foreigners alike. This might be dismissed as merely anecdotal but it comes in the same week that global markets have zeroed in on Chinese capital flight risks and authorities have been scrambling to inject liquidity into the banking system.
In the past week the central bank made three interventions to boost liquidity, totaling some 350 billion yuan. Despite this interbank rates have remain elevated and reports suggest the People’s Bank of China’s next move will be to cut bank-reserve ratios to free up potentially another 678 billion yuan for lending. Turning off the cash withdrawal functions of ATMs at the border is certainly one way to stem capital leakage, albeit a rather draconian and clumsy one. While it is also unlikely, it is not unreasonable to be wary of unexpected policy moves coming out of Beijing. After all, few would have predicted measures, such as mass share suspensions and the banning of large shareholders from selling equities, that have been announced in recent weeks to support domestic stock prices.
Any signs that the fault line in China’s highly leveraged economy is spreading to its financial system, brings with it another layer of potential systematic risk. This always looked a possibility when authorities used the banking system and public funds to support equity markets. [..] Analysts warn that it is futile for the government to try to support both currency and assets markets. According to Stuart Allsopp at BMI Research, Beijing will increasingly have to choose between propping up the equity market and defending the currency from further downside pressure. As the veil of government support for both markets has been pierced and gives way to market forces, he says lower equity prices and continued weakness in the yuan look inevitable.
The PBOC now has to balance drawing down its foreign-exchange reserves to prevent aggressive weakness in the yuan, and the extent to which it can reduce liquidity from the domestic financial system. BMI expects the rate of growth of domestic money supply will have to slow sharply in order to firm up the value of the yuan, in the process weighing heavily on domestic asset prices.

Cold turkey.
• China Stock Market Panic Shows What Happens When Stimulants Wear Off (Guardian)
Financial markets have gone cold turkey. For the past seven years, they have been given regular doses of strong and dangerous narcotics. The threat that the drugs will no longer be available has resulted in severe withdrawal symptoms. Unlike in 2007, the crash could be seen coming. Wall Street and the City were taken completely by surprise by the subprime crisis, but have had plenty of warning that something nasty might be brewing in China. Anybody caught unawares really hasn’t been paying attention. But this is about more than China. Financial markets in the west have been booming for the past six years at a time when the real economy has been struggling. Recovery from the last recession has been patchy and weak by historical standards, but that has not prevented a bull market in equities.
The reason for this is simple: the markets have been pumped full of stimulants in the form of quantitative easing, the money creation programmes adopted by central banks as a response to the last crisis. On the day that QE was launched in the UK, 9 March 2009, the FTSE 100 stood at 3542 points. Its recent peak on 27 April this year was 7103 points, a gain of 100.5%. There is a similar correlation between the three rounds of QE in the US and the performance of the S&P 500, which was up more than 200% during the same period. But there were always doubts about what might happen when central banks decided it was time to remove some of the stimulus they have been providing for the past seven years. Now we know.
The Federal Reserve and the Bank of England halted their QE programmes and started to muse publicly about the timing of the first increase in interest rates. At that point, financial markets merely needed a trigger for a big selloff. China has provided that, because the world’s second biggest economy has shown distinct signs of slowing. What was inevitably dubbed “Black Monday” began in east Asia where there was disappointment that Beijing did not provide fresh support for shares in Shanghai overnight. Having been accused of acting like quacks dispensing dodgy remedies on previous stock market rescue missions, China’s leaders decided they would tough it out. Big mistake. The stimulus junkies needed a fix and when they didn’t get one they had a bad dose of the shakes.

Finding the bad guys.
• China Launches Crackdown On ‘Underground Banks’ Amid Capital Flight Fears (SCMP)
Police in China have launched a two-month crackdown against “underground banks” amid concerns about cash flowing in and out of the country illegally and fuelling speculation in the country’s volatile stock markets. The campaign will focus on illegal financing in shares markets, plus funding for terrorism and banking connected to corrupt officials, state media reported.It will last until late November. Meng Qingfeng, a vice minister of public security who oversees the country’s manhunt for economic fugitives overseas and headed last month’s crackdown on “malicious short-selling” in China’s stock markets, said underground banking had undermined the country’s economic security and the order of the financial market, the state-run news agency Xinhua reported.
The ministry will also despatch special taskforces to areas where underground banking activity is particularly severe. Meng said that since April the police, the central bank and the State Administration of Foreign Exchange have cracked down on a number of illegal fund transfers through underground banks and offshore companies. Some 66 underground banks handling assets of about 430 billion yuan (HK$520 billion) have been discovered. More than 160 suspects have been arrested. Some of the crackdowns took place in Guangdong, Liaoning and Zhejiang provinces, Xinhua said, plus in Shanghai and the Xinjiang region.

Nice contrarian view.
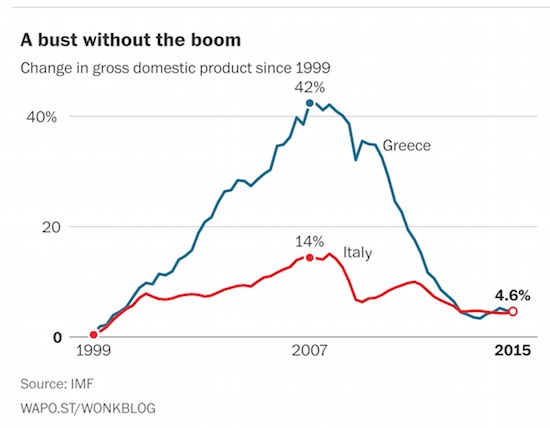
• How Greece Outflanked Germany And Won Generous Debt Relief (MarketWatch)
Alexis Tsipras, who is likely to continue as Greek prime minister after precipitating a general election for next month, arrived in power in January attempting to resolve an “impossible trinity”: relaxing the economic squeeze, rescheduling Greece’s unpayable debts, and keeping the country in the euro. Satisfactorily achieving all three aims appeared unachievable — and it was. Yet Tsipras appears to have achieved greater success than Angela Merkel, his main European sparring partner. The German chancellor, too, promised her electorate three unrealizable goals. However, frightened of being made a scapegoat worldwide for ejecting Greece from the euro, she seems to have caved in to international pressure even more than Tsipras.
The debt rescheduling under way for Greece, partly prompted by the IMF’s accurate labelling of Greek debts as unsustainable, appears reminiscent of the relief that West Germany gained from a “troika” of international lenders (France, the U.K. and the U.S.) at the 1953 London debt conference. At a time when global economic storm clouds are darkening, Greek voters may well thank Tsipras for shifting much of the country’s borrowings on to concessionary terms. The big question is whether, once the full generosity of Greek debt relief becomes widely known, other large-scale debtors around the world — ranging from indebted Chinese local authorities to borrowers from Italy, Portugal and Spain — will demand similar concessions from creditors.
The new €86 billion low-cost Greek bailout will probably not be fully redeemed until 2075 — a similar extension of loan repayments that was granted to West Germany in 1953, with some long-standing borrowings not repaid until 57 years later, in 2010. Further effective Greek debt reductions will occur in the autumn as part of a deal to keep the IMF as a direct underwriter of Greek debt. Germany’s insistence on bringing in the IMF is politically expedient yet economically contradictory. Greece’s biggest creditor believes the only way to make its lending domestically palatable is to keep on board another lender (the IMF), which will do so only if Germany asks its taxpayers to shoulder fresh burdens through stretching out loan repayments and lowering interest costs.
Merkel’s promises to German voters have had a Tsipras-like quality: maintain the unity of euro members, avoid full-scale Greek debt restructuring, and keep euro economic policies in line with German-style orthodoxy. Both Merkel and Tspiras have resolved their individual “trilemmas” by attempting to keep their respective electorates in the dark about the extent to which they have diluted their principles.

Sorry, Yanis, can’t have a political union, can’t have a banking union.
• Varoufakis: Greek Deal Was A Coup d’État (EurActiv)
Ignoring the will of the people by pursuing unpopular austerity policies plays into the hands of Europe’s extreme right, say Yanis Varoufakis and Arnaud Montebourg. “Fakis, Fakis,” the militant socialists chanted in Frangy-en-Bresse, in France, on Sunday (23 August). The annual “Fête de la Rose”, a gathering regularly attended by France’s former finance minister Arnaud Montebourg, has taken place since 1972. Once the scourge of the Eurogroup, the rock star economist Yanis Varoufakis was visibly delighted to be in the village of Frangy (dubbed Frangis in his honour), despite the rain, and to launch a fresh attack on European leaders and the current Greek government.
“What happened on 12 July was a real coup d’état and a defeat for all Europeans,” the former finance minister said, referring to Greece’s acceptance of the harsh conditions attached to the latest aid package. A package that also cost him his job as the country’s minister of finance. Similarly, Arnaud Montebourg lost his job as French Minister of the Economy exactly one year ago, after openly criticising the French government’s austerity policies at the 2014 Fête de la Rose. “I do not believe the September elections can lead to an alliance that will create the conditions for an economic policy that works for Greece,” Yanis Varoufakis warned. He said he was “torn” by the splitting of the Syriza party, although he was not officially a party member.
25 Syriza MPs announced on Friday that they would form a new party, following the resignation of the Prime Minister, Alexis Tsipras, who hopes the elections will give him a larger majority and a stronger mandate to enact his plans. The two ex-ministers strived to highlight the dangers of continued austerity in Greece. “Without political union, the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU) is a big mistake. Now that we have it, we must repair it. What we need today is a real common investment policy, and a real banking union,” the Greek economist said. Yanis Varoufakis told EurActiv that the emergence of an allied European left, in opposition to the current system, was a possibility.
“I believe that an alliance of Europeans from across the political spectrum, who share one radical idea, the idea of democracy, is possible,” he joked. “For 20 years, the principle of democracy has been trampled on in Europe. But it remains a common idea. If we want to make the transition to a democratic Europe, we need to empower the citizens, rather than the current cartel of lobbies.” This view was shared by his host. Arnaud Montebourg said, “Power is held by an oligarchy in Europe.”

And every other property market that’s bubbling.
• US Short Sellers Betting On Canadian Housing Crash (National Post)
Large Wall Street investors who made billions when the U.S. housing market collapsed in 2008 are now betting real estate values in Vancouver and other Canadian cities will crash, financial insiders say. The hedge fund investors, known as short sellers, are betting against what they believe is a housing bubble in Vancouver, Toronto, Calgary and other Canadian cities. They believe Canadians hold too much mortgage debt, and that Canadian banks, mortgage insurers and “subprime” private lenders will lose money on unpaid loans when property prices fall. “The cross currents are beyond crazy in Vancouver — it’s a mix of money laundering, speculation, low interest rates,” said Marc Cohodes, once called Wall Street’s highest-profile short-seller by The New York Times.
“A house is something you live in, but in Vancouver you guys are trading them like the penny stocks on Howe Street.” He says Vancouver real estate has reached peak insanity, and any number of factors could trigger a collapse. Local real estate professionals predicted the U.S. investors are likely to lose their shirts betting against Vancouver property, which they described as a special market thriving on international demand. But one Canadian housing analyst who advises U.S. clients, including Cohodes, said major investors are currently “building positions” against Canadian housing targets. They are forecasting a raise in historically low U.S. interest rates this fall will spill financial stress into Canada. “All of the big global macro funds that were involved in betting against the U.S. in 2007 and 2008 and 2009, they’ve all studied Canadian housing for a few years,” said the Canadian analyst.
“I know a number of them are shorting Canadian housing. It looks like an accident waiting to happen.” This is although housing markets in Vancouver and Toronto have continued to rocket higher since international short-sellers started circling in 2013. Short sellers use complex financial arrangements to make rapid profits when publicly traded stocks fall in value. In this case, they are betting against businesses connected to property and household debt. They are also betting against the Canadian dollar, because they believe it will decline significantly in a housing bust. Most of these traders are employed by secretive New York investment funds that shy away from publicity, partly because they want to disguise how they lay their bets.

We won’t stop until it’s all gone.
• Tropical Forests Totalling Size Of India At Risk Of Being Cleared (Guardian)
Tropical forests covering an area nearly the size of India are set to be destroyed in the next 35 years, a faster rate of deforestation than previously thought, a study warned on Monday. The Washington-based Center for Global Development, using satellite imagery and data from 100 countries, predicted 289m hectares (714m acres) of tropical forests would be felled by 2050, with dangerous implications for accelerating climate change, the study said. If current trends continued tropical deforestation would add 169bn tonnes of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere by 2050, the equivalent of running 44,000 coal-fired power plants for a year, the study’s lead author told the Thomson Reuters Foundation.
“Reducing tropical deforestation is a cheap way to fight climate change,” said environmental economist Jonah Busch. He recommended taxing carbon emissions to push countries to protect their forests. UN climate change experts have estimated the world can burn no more than 1tn tonnes of carbon in order to keep global temperature rises below two degrees – the maximum possible increase to avert catastrophic climate change. If trends continued the amount of carbon burned as a result of clearing tropical forests was equal to roughly one-sixth of the entire global carbon dioxide allotment, Busch said. “The biggest driver of tropical deforestation by far is industrial agriculture to produce globally traded commodities including soy and palm oil.” The study predicted the rate of deforestation would climb through 2020 and 2030 and accelerate around the year 2040 if changes were not made.