DPC French Market, New Orleans 1910



I don’t think I have much in common with Nigel Lawson -aka Lord Lawson of Blaby-, but it’s important that this ‘little fact’ be known and exposed. Even a superstate needs values if it is to survive. The EU ain’t got any left. Who wants to belong to that?
• The EU Exists Only To Become A Superstate (Lawson)
For Britain, the issue in the coming European referendum is not Europe, with its great history, incomparable culture, and diverse peoples, but the European Union. To confuse the two is both geographically and historically obtuse. European civilisation existed long before the coming of the EU, and will continue long after this episode in Europe’s history is, hopefully, over. On the European mainland it has always been well understood that the whole purpose of European integration was political, and that economic integration was simply a means to a political end. In Britain, and perhaps also in the US, that has been much less well understood, particularly within the business community, who sometimes find it hard to grasp that politics can trump economics. The fact that the objective has always been political does not mean that it is in any way disreputable.
Indeed, the most compelling original objective was highly commendable. It was, bluntly, to eliminate the threat to Europe and the wider world from a recrudescence of German militarism, by placing the German tiger in a European cage. Whether or not membership of the EU has had much to do with it, that objective has been achieved: there is no longer a threat from German militarism. But in the background there has always been another political objective behind European economic integration, one which is now firmly in the foreground. That is the creation of a federal European superstate, a United States of Europe. Despite the resonance of the phrase, not one of the conditions that contributed to making a success of the United States of America exists in the case of the EU. But that is what the EU is all about. That is its sole raison d’être. And, unlike the first objective, it is profoundly misguided.
For the United Kingdom to remain in the EU would be particularly perverse, since not even our political elites wish to see this country absorbed into a United States of Europe. To be part of a political project whose objective we emphatically do not share cannot possibly make sense. It is true that our present Prime Minister argues that he has secured a British “opt-out” from the political union, but this is completely meaningless. “But,” comes the inevitable question, “what is your alternative to membership of the EU?” A more absurd question it would be hard to envisage. The alternative to being in the EU is not being in the EU. And it may come as a shock to the little Europeans that most of the world is not in the EU – and that most of these countries are doing better economically than most of the EU.

Why don’t I see nobody accuse the US of currency manipulation?! That still the Shanghi Accord legacy?
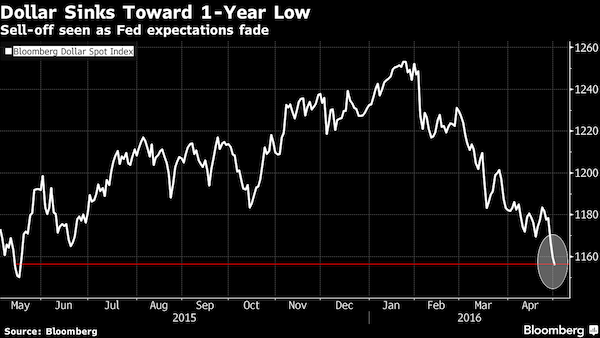
• US Dollar Falls To 1-Year Low (BBG)
The dollar fell to an 18-month low against the yen and touched its weakest since August versus the euro amid speculation that the U.S. won’t raise interest rates any time soon. The U.S. currency has lost ground versus most major peers over the past month as traders lowered expectations for a rate increase by the Federal Reserve in June to 12%. The Bloomberg Dollar Spot Index headed for the lowest close in almost a year, after a report showed manufacturing in the U.S. expanded less than forecast. Persistent weakness dragged the dollar down against the euro for a third straight month in April – its longest losing streak since 2013 – amid signs U.S. policy makers aren’t convinced the global and domestic economies can withstand higher borrowing costs.
It fell on Tuesday against Australia’s currency as Chinese equities climbed by the most in nearly three weeks. The U.S. has posted disappointing growth data as nascent signs of recovery emerge in Europe and China’s growth momentum accelerates. “The Fed is completely out of the picture now for the next few weeks – even with the June meeting, there’s got to be a lot of doubt about whether the Fed can raise rates,” said Shaun Osborne at Bank of Nova Scotia in Toronto. “The dollar has just not done particularly well over the past few weeks as the Fed has moved toward delaying rate hikes, and that’s a situation that definitely will continue, certainly for the near term.”

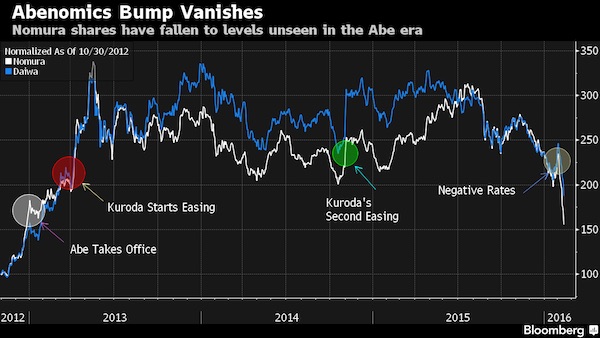
Abe must be going nuts.
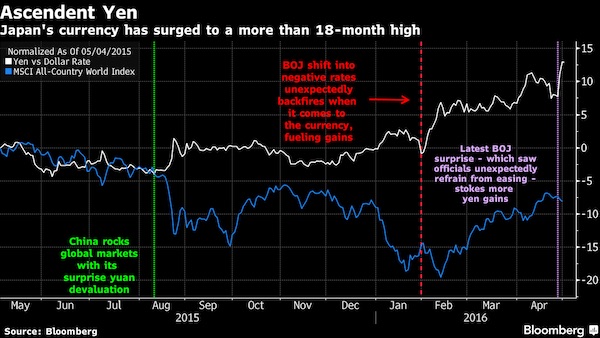
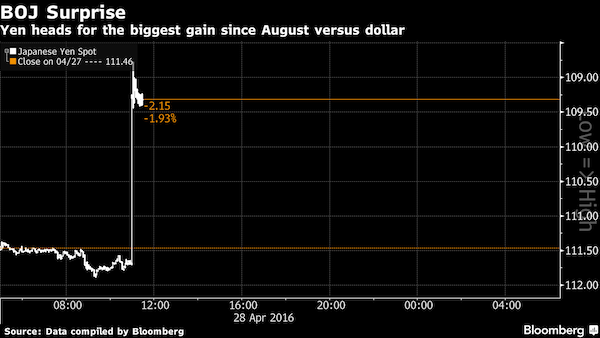
• Yen Under Pressure to Extend World-Beating Rally Against Dollar (BBG)
The yen’s world-beating rally against the dollar looks to be gathering momentum, as central bank inaction on both sides of the Pacific Ocean leaves inflation expectations to drive the exchange rate. Japan’s currency extended its climb to an 18-month high Monday after Bank of Japan Governor Haruhiko Kuroda refrained from adding to stimulus on Thursday. That took its gain this year to 13%, the most among developed-market peers. The BOJ’s decision came just hours after Federal Reserve Chair Janet Yellen frustrated dollar bulls by reiterating she’s in no rush to cool the economy by raising interest rates. JPMorgan sees further yen gains after the U.S. put Japan on a new currency watch list.
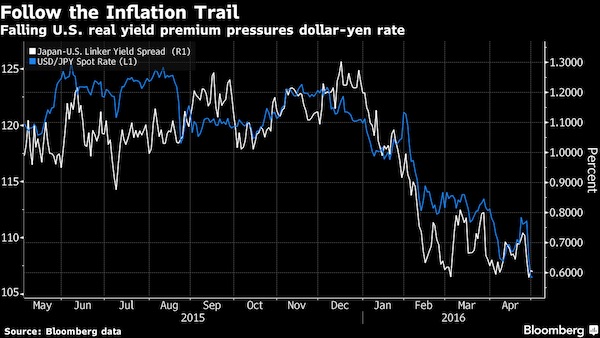
With consumer price pressures building in the U.S. and dissipating in Japan, that narrows the gap in so-called real yields – the returns an investor can expect after accounting for inflation – supporting yen strength. If both central banks stay on the sidelines, Credit Suisse projects Japan’s currency could rapidly appreciate toward 90 per dollar. “So long as the Fed signals that they are being cautious in raising rates, real yields in the U.S. will decline, leading the dollar weaker,” said Hiromichi Shirakawa, the Swiss lender’s chief Japan economist and a former BOJ official. “The currency market is in a rather dangerous zone.” The BOJ’s benchmark for measuring progress toward its 2% target showed prices retreated at an annual 0.3% pace in March, the biggest decline since April 2013, the month that Kuroda initiated his stimulus program.
It had previously hovered near zero for more than a year. By contrast, the Fed’s preferred measure of inflation, based on the prices of goods and services consumers buy, rose 0.8% in the year through March. The so-called core measure, which strips out food and energy prices, climbed 1.6%. That’s seen a Treasury market gauge of inflation expectations over the coming decade – called the break-even rate – jump to 1.7% from as low as 1.2% in February. The equivalent measure in Japan is languishing at 0.3%. Benchmark 10-year Treasury Inflation Protected Securities yield around 0.1%, compared with about minus 0.5% for equivalent Japanese notes.
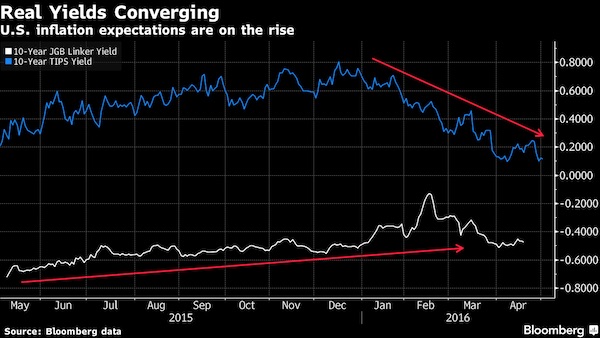
Japan met two of three criteria used to judge unfair practices in the U.S. report: a trade surplus with the U.S. above $20 billion, and a current-account surplus amounting to more than 3% of gross-domestic product. The third would be a repeated depreciation of the currency by buying foreign assets equivalent to 2% of gross domestic over a year. Meeting all three would trigger action by the U.S. president to enter discussions with the country and seek potential penalties. China, Germany, South Korea and Taiwan also made the watch list.

“..Perhaps Jack Lew’s “currency manipulation” report was enough to stall the Japanese currency war for now?..”
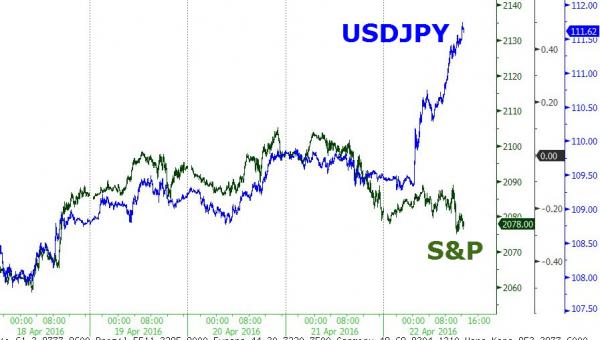
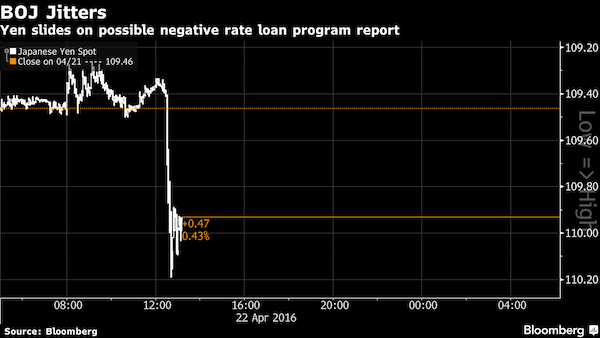
• Kuroda Kollapse Kontinues As USDJPY Nears 105 Handle (ZH)
Either The BoJ steps in soon and intervenes (even by just “checking levels”) or Kuroda-san is truly terrified of The G-20. USDJPY has now crashed 7 handles since last Thursday’s shock BoJ disappointment crashing to within 5 pips of a 105 handle tonight for the first time in 18 months…

Erasing the entire devaluation post-Fed, post QQE2…

Perhaps Jack Lew’s “currency manipulation” report was enough to stall the Japanese currency war for now? Or is China greatly rotating its Yuan devaluation pressure against another member of its basket…?

Charts: Bloomberg

1) What recovery? 2) Abe and Kuroda are powerless prisoners to America’s dollar manipulation
• BOJ Chief Kuroda Warns Current Yen Strength Risks Harming Recovery (BBG)
Bank of Japan Governor Haruhiko Kuroda warned that the yen’s biggest rally since Abenomics began risks harming the nation’s economic recovery. Speaking to reporters in Frankfurt Monday, Kuroda also reiterated that BOJ policy makers won’t hesitate to expand monetary stimulus in order to achieve their 2% inflation target. Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe said the same day in Paris that rapid movements in exchange rates are undesirable, according to national broadcaster NHK. “There is a risk that the yen’s current appreciation brings an unwelcome impact on the economy,” Kuroda said on the sidelines of an annual gathering of finance chiefs from members of the Asian Development Bank, which he used to lead.
“We will be closely monitoring the impact of financial markets on the real economy and prices.” A weaker currency has been a linchpin of Abe’s program to stoke growth and exit deflation. Japan’s economy is at risk of sliding into its second recession in two years after contracting in the final three months of 2015, while inflation remains far from the BOJ’s target. One gauge showed consumer prices retreated at an annual 0.3% pace in March, the biggest decline since April 2013, the month that Kuroda initiated his stimulus program. The yen has climbed 13% against the dollar this year, the best performance among its developed-market peers. That has chipped away at the 36% decline over the previous four years, which was triggered by Abe’s pledge of unlimited monetary easy to correct yen strength.
Kuroda and his board left policy settings unchanged at a meeting Thursday, spurring a nearly 5%, two-day surge in the yen against the dollar. It reached an 18-month high of 106.05 per greenback on Tuesday, before trading at 106.19 as of 9:54 a.m. in Singapore. Japanese markets are closed for holidays Tuesday, Wednesday and Thursday this week.

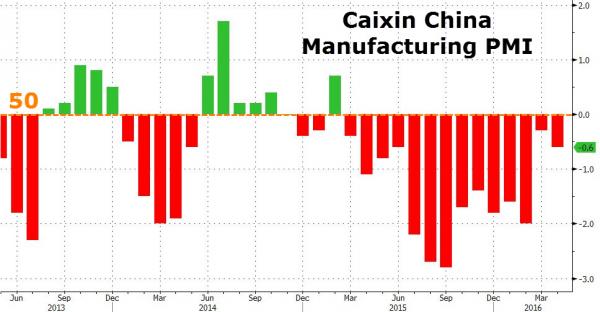
Beyond salvation.
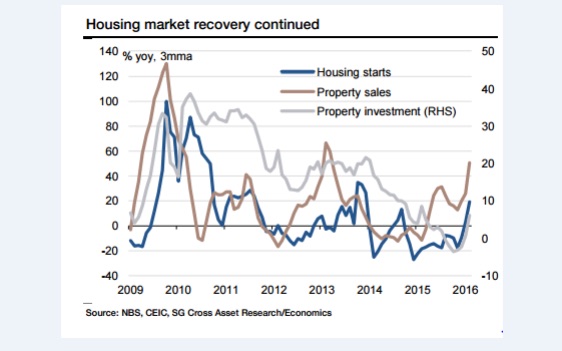
• China Factory Activity Contracts for 14th Straight Month In April (CNBC)
Activity in China’s manufacturing sector unexpectedly declined further in April, a private survey showed Tuesday, reviving doubts over the health of the world’s second-largest economy. The Caixin Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) fell to 49.4 in April from 49.7 in March, according to Markit, which compiles the index. A reading above 50 indicates expansion; one below indicates contraction. The Caixin PMI, which focuses on smaller and medium-sized enterprises, was last in expansionary territory in February 2015. The official PMI, which targets larger companies, printed at 50.2 in April, the second successive month of expansion, figures released over the weekend showed. The survey findings follow recent economic data that appeared to suggest that China’s economy was slowly regaining its poise after a torrid 12 months.
China’s exports rose at their fastest clip in a year in March, while industrial profits also picked up in the first quarter. A flurry of rate cuts and easing of reserve requirement have helped bolster sentiment, while the capital outflows that had unnerved sentiment at the start of the year have slowed. The Caixin survey, however, cast a more somber picture. Respondents reported stagnant new orders, while new export work fell for a fifth month running. Companies shed staff as client demand was muted. “The fluctuations indicate the economy lacks a solid foundation for recovery and is still in the process of bottoming out. The government needs to keep a close watch on the risk of a further economic downturn,” said He Fan at Caixin Insight Group.

What blows up must blow down.
• Fed’s Williams Sees Big Drop In Asset Prices As Systemic Risk (R.)
San Francisco Fed President John Williams reiterated Monday his view that the U.S. economy is ready for higher interest rates, but flagged the risk of broad-based declines in asset prices as a result. “It makes sense for us to be moving interest rates gradually back to more a normal level over the next couple years,” Williams said. “I actually think that’s a sign of strength for the global economy.” Speaking at a panel on systemic risk at the Milken Institute Global Conference, Williams said the biggest systemic financial risk currently is the possibility that “broad sets of assets are going to see big movements downward” as interest rates rise. “That’s an area that I think is a potential risk.” Williams did not suggest he sees another crisis brewing, adding that U.S. regulators have made “amazing” progress in shoring up banks against potential future failure.
“What I worry a lot more about is when people forget about the financial crisis, when they forget about the terrible things that happened,” he said, suggesting that may not happen for another five or ten years. The Fed raised interest rates for the first time in nearly a decade last December, but has held off raising them any further amid global stock volatility and worries over a decline in global growth. Even after the Fed resumes raising rates, Williams said, it will not be able to lift them as high as it has in the past. Most Fed officials currently think that the rate at which the economy can sustain healthy employment and steady prices has probably fallen to about 3.25% in the long run, a full %age point lower than was the case before the crisis. But there are significant downside risks to that estimate, Williams said.

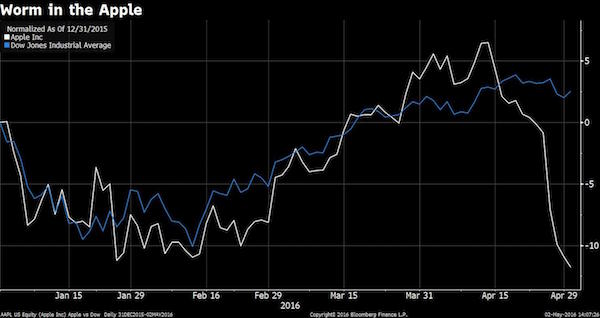
No. 1 US stock for years.
• Apple’s Losing Streak Is Nearing Historic Levels (BBG)
So far in 2016, Apple is the dog of the Dow. After an underwhelming earnings report led to the shares’ worst week since January 2013, Apple stock extended its losses to kick off May, closing down 0.18% on Monday. The benchmark index’s laggard has declined by nearly 11% so far this year heading into today’s session: Bespoke Investment Group notes that Monday’s negative close marks eight straight sessions in the red for Apple—something that last happened in July 1998, and has now happened only four times in the company’s history. More than $79 billion in Apple’s market capitalization has been erased over the past eight sessions.
The company’s heavy weighting in major sector and benchmark indexes, coupled with the stock’s terrible two-week stretch, has made $4 billion in assets of exchange-traded funds evaporate over this stretch. “Smart beta” ETFs are poised to trounce their more popular peers, Bloomberg’s Eric Balchunas observes, in the event that this span of underperformance continues. There’s a possible silver lining for Apple bulls, and investors who own those market-cap-weighted ETFs: The stock tends to bounce back in earnest following these rare stretches of rotten performance. “Two of the three eight-day streaks saw the stock fall on day nine as well, but the stock has never experienced a losing streak longer than nine trading days,” Bespoke writes. “While the next day and next week returns following eight-day losing streaks lean negative, the stock has been higher over the next month all three times for a median gain of 8.01%.”

Well, there is, but Draghi’s masters don’t want it.
• No Alternative To Low Rates For Now, Draghi Says (R.)
Low interest rates are not harmless but they are only the symptom, not the cause of an underlying problem across major economies, ECB President Mario Draghi said on Monday, arguing that there was no alternative for now. “Thus the second part of the answer to raising rates of return is clear: continued expansionary policies until excess slack in the economy has been reduced and inflation dynamics are sustainably consistent again with price stability,” Draghi told a conference. “There is simply no alternative to this today.” “The only potential margin for maneuver is in the composition of the policy mix, that is, the balance of monetary and fiscal policy,” he added.

Corruption is not a deficiency, it’s the MO.
• ECB Report Says Investors May Be Profiting From Leaked US Data (FT)
US investors may be profiting from leaked economic data releases that allow them to front-run market-moving news, according to a research paper published by the ECB. Macroeconomic news announcements can move markets, as traders watch for indications about how the economy is performing. The data are released to everyone at the same time to ensure fairness but ECB researchers said they had found evidence of “informed trading” ahead of US data releases. Of the 21 market-moving announcements analysed, seven “show evidence of substantial informed trading before the official release time”, according to the paper, including two releases from the US government. The pre-release “price drift” accounts for about half of the overall price impact from the announcement.
The researchers looked at the impact on futures tracking the S&P 500 stock index and the 10-year Treasury bond for the 30 minutes preceding the announcement. The researchers also note that the price impact has become worse since 2008, and estimate that since 2008 profits in the S&P “e-mini” futures market alone amount to about $20m per year. “These results imply that some traders have private information about macroeconomic fundamentals,” said the report. “The evidence suggests that the pre-announcement drift likely comes from a combination of information leakage and superior forecasting based on proprietary data collection and reprocessing of public information.”
The paper raises questions about the safeguards used to ensure data are protected up until scheduled release time. Important economic indicators in the US are subject to the “Principle Federal Economic Indicator” guidelines, but the report notes that many distributors of the data are not subject to the same rules. “To ensure fairness, no market participant should have access to this information until the official release time,” the report added. “Yet, in this paper we find strong evidence of informed trading before several key macroeconomic news announcements.”

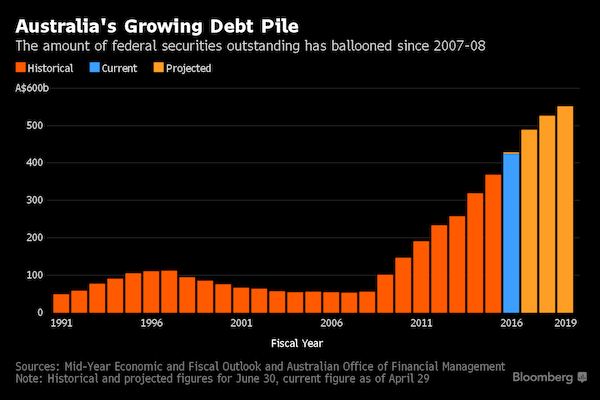
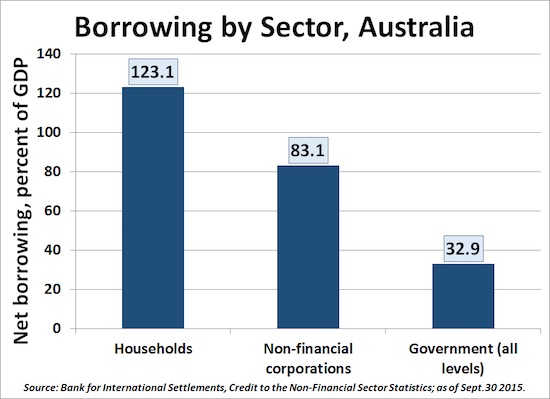
Household debt is a much bigger factor is some countries than others. In Australia, it’s far bigger than government debt. But the latter is what all political talk is about. “Pumping up fear of government debt is always an essential step in preparing the public to accept cutbacks in essential public services.”
• Six Counterpoints About Australian Public Debt (Stanford)
In the lead-up to today’s pre-election Commonwealth budget, much has been written about the need to quickly eliminate the government’s deficit, and reduce its accumulated debt. The standard shibboleths are invoked liberally: government must face hard truths and learn to live within its means; government must balance its budget (just like households do); debt-raters will punish us for our profligacy; and more. Pumping up fear of government debt is always an essential step in preparing the public to accept cutbacks in essential public services. And with Australians heading to the polls, the tough-love imagery serves another function: instilling fear that a change in government, at such a fragile time, would threaten the “stability” of Australia’s economy.
However, this well-worn line of rhetoric will fit uncomfortably for the Coalition government, given its indecisive and contradictory approach to fiscal policy while in office. The deficit has gotten bigger, not smaller, on their watch, despite the destructive and unnecessary cutbacks in public services imposed in their first budget. Their response to Australia’s fiscal and economic problems has consisted mostly of floating one half-formed trial balloon after another (from raising the GST to transferring income tax powers to the states to cutting corporate taxes), with no systematic analysis or framework. And their ideological desire to invoke a phony debt “crisis” as an excuse for ratcheting down spending will conflict with another, more immediate priority: throwing around new money (or at least announcements of new money), especially in marginal electorates, in hopes of buying their way back into office.
In short, the politics of debt and deficits will be both intense and complicated in the coming weeks. To help innoculate Australians against this hysteria, here are six important facts about public debt, what it is – and what it isn’t.
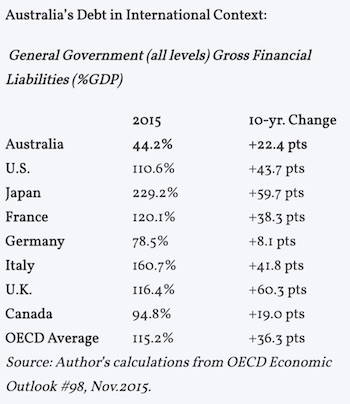
1. Australia’s public debt is relatively small
3. Other sectors of society borrow much more than government

Somone should explain to these people what’s going on. Mum and Dad will lose their shirts AND their skirts. Ironically, some insist more homes must be build. Ironoc, because that would mean even steeper losses for those buying into today’s craze.
• ‘Bank of Mum and Dad’ Behind 25% Of British Mortgages (G.)
The “Bank of Mum and Dad” will help finance 25% of UK mortgage transactions this year, according to research. Parents are set to lend their children £5bn to help them on to the property ladder. If the lending power was of all these parents was combined, it would be a top 10 mortgage provider. Nigel Wilson, chief executive of Legal & General, which carried out the research, said the data showed a number of issues, including house prices being “out of sync with wages”. The research estimated that the Bank of Mum and Dad will provide deposits for more than 300,000 mortgages. The homes purchased will be worth £77bn and the average contribution is £17,500 or 7% of the average purchase price.
But relying on parental support might soon be unsustainable as parents could be giving away more than they can afford. Wilson said that in London the funding method was reaching “tipping point” already as parental contributions made up more than 50% of the wealth (excluding property) of the average household in the capital. He said: “The Bank of Mum and Dad plays a vital role in helping young people to take their early steps on to the housing ladder.” Not all young people have parents who can afford to help them and some who do still do not have enough to buy a place of their own, he said. He added: “We need to fix the housing market by revolutionising the supply side – if we build more houses, demand can be met at a sensible level and prices will stabilise relative to wages.”

Positive feedback.
• Dominoes: Vanishing Arctic Ice Shifts Jet Stream, Which Melts Glaciers (WaPo)
Investigating the factors affecting ice melt in Greenland — one of the most rapidly changing places on Earth — is a major priority for climate scientists. And new research is revealing that there are a more complex set of variables affecting the ice sheet than experts had imagined. A recent set of scientific papers have proposed a critical connection between sharp declines in Arctic sea ice and changes in the atmosphere, which they say are not only affecting ice melt in Greenland, but also weather patterns all over the North Atlantic. The new studies center on an atmospheric phenomenon known as “blocking” — this is when high pressure systems remain stationary in one place for long periods of time (days or even weeks), causing weather conditions to stay relatively stable for as long as the block remains in place.
They can occur when there’s a change or disturbance in the jet stream, causing the flow of air in the atmosphere to form a kind of eddy, said Jennifer Francis, a research professor and climate expert at Rutgers University. Blocking events over Greenland are particularly interesting to climate scientists because of their potential to drive temperatures up and increase melting on the ice sheet. “When they do happen, and they kind of set up in just the right spot, they bring a lot of warm, moist air from the North Atlantic up over Greenland, and that helps contribute to increased cloudiness and warming of the surface,” Francis said. “When that happens, especially in the summer, we tend to see these melt events occur.” Now, two new studies have suggested that there’s been a recent increase in the frequency of melt-triggering blocking events over Greenland — and that it’s likely been fueled by climate change-driven losses of Arctic sea ice.
A paper set to be published Monday in the International Journal of Climatology reveals an uptick in the frequency of these blocking events over Greenland since the 1980s. A team of researchers led by the University of Sheffield’s Edward Hanna used a global meteorological dataset relying on historical records to measure the frequency and strength of high pressure systems over Greenland all the way back to the year 1851. Previous analyses had only extended the record back to 1948, so the new study is able to place recent blocking events in a much larger historical context. When the researchers analyzed the data, they found that the increase in blocking frequency over the past 30 years is particularly pronounced in the summer, the time of year when blocking events are likely to have the biggest impact on ice melt.

Clueless, rudderless, valueless.
• Germany Wants To Extend Border Controls For Another 6 Months (AP)
Germany and some other EU countries are planning to ask the European Commission for an extension of border controls within the Schengen passport-free travel zone for another six months because they fear a new wave of migrants. Interior Minister Thomas de Maizere’s spokesman says a letter is being sent Monday asking for an extension of the controls on the German-Austrian border, which were implemented last year when thousands of migrants crossed into Germany daily. De Maizere has expressed concern before that an increasing number of migrants will try to reach Europe this summer by crossing the Mediterranean Sea from lawless Libya to Italy, then travel north to Austria and Germany. Germany registered nearly 1.1 million new arrivals last year and is keen to bring the numbers down in 2016.
Germany’s defense minister, meanwhile, said it was up to Italy to protect its borders but other European countries must be ready to help if needed. Ursula von der Leyen’s comments Monday touched on the potential problems Italy could have with increased arrival of migrants looking for an alternative route into the EU now that the West Balkans route is closed and Turkey has committed to taking back those arriving illegally to Greece. She said a solution must be found “together with Italy.” Austria plans to impose border controls at its main border crossing with Italy to prevent potential attempts by migrants to enter, and with Austria bordering Germany, von der Leyen’s comments indicate her country’s concern that it also may have to deal with new waves of migrants seeking entry.

“..We have to protect ourselves against the Islamic State group..”
• Denmark Extends Controls On German Border (EN)
Denmark has extended temporary controls on its border with Germany, first imposed in January to help regulate an influx of migrants. The measures have been prolonged by another month until the beginning of June. The European Commission, struggling to prevent the collapse of the Schengen agreement, has confirmed it will soon authorise more such extensions. The Danish government says it has joined several countries in writing to the Commission asking for a two-year extension. “Together with the Germans, the French, the Austrians and the Swedes I have today sent a letter to the EU commission asking for the possibility to extend the border control for the next two years,” said Inger Støjberg, Danish minister of immigration and integration.
“I have done so because we need to look out for Denmark. We have to protect ourselves against the Islamic State group, who are trying to take advantage of the situation where there are holes in borders. But also as protection against the influx of refugees coming through Europe.” The Commission could give the green light as early as Wednesday to countries within the passport-free Schengen zone wishing to extend exceptional border controls. The five countries have taken the measures because of the influx of migrants and refugees heading north via the so-called Balkans route after entering Europe via the Greek shores. Although the crisis has eased, the governments say many migrants are still camped along the route and in Greece.

The cattle trade continues unabated. Europeans are as immoral as their leadership.
• EU States Face Charge For Refusing Refugees (FT)
European countries that refuse to share the burden of high immigration will face a financial charge of about €250,000 per refugee, according to Brussels’ plans to overhaul the bloc’s asylum rules. The punitive financial pay-off clause is one of the most contentious parts of the European Commission’s proposed revision of the so-called Dublin asylum regulation, due to be revealed on Wednesday. It represents the EU’s most concerted attempt to salvage an asylum system that collapsed under the weight of a million-strong migration to Europe last year, endangering the principle of passport-free travel in the Schengen area. In recent weeks migrant flows to Greece have fallen due to tighter controls through the western Balkans and a deal with Turkey to send-back asylum seekers arriving on Greek islands.
However, the EU remains as politically divided as ever over strengthening the bloc’s asylum rules. While acknowledging these political constraints, the commission’s reforms aim to gradually shift more responsibility away from the overwhelmed frontline states, such as Greece, in future crises, primarily through an automatic system to share refugees across Europe if a country faces a sudden influx. Crucially, this is backed by a clause that allows immigration-wary countries to pay a fee — set at a deliberately high level — if they want to avoid taking relocated asylum seekers for a temporary period. According to four people familiar with the proposal, this contribution was set at €250,000 per asylum seeker in Monday’s commission draft. But those involved in the talks say it may well be adjusted in deliberations over coming days.
“The size of the contribution may change but the idea is to make it appear like a sanction,” said one official who has seen the proposal. Another diplomat said in any event the price of refusing to host a refugee would be “hundreds of thousands of euros”. Eastern European states such as Poland and Hungary would welcome alternatives to mandatory asylum quotas but will balk at the high penalties suggested. At the commission’s recommended rate, Poland would need to pay around €1.5bn to avoid its existing 6,200 quota to relocate refugees from Italy and Greece. These financial contributions are in part designed to fix incentives around migrant quotas, which have badly failed and proved almost impossible to implement even once agreed in law. The commission proposal builds on the EU’s flagship emergency scheme to relocate 160,000 refugees, which has barely redistributed 1% of its target since it was agreed last year.

And how many did you say are unaccounted for, Europe?
• 90,000 Unaccompanied Minors Sought Asylum In EU In 2015 (R.)
Some 88,300 unaccompanied minors sought asylum in the EU in 2015, 13% of them children younger than 14, crossing continents without their parents to seek a place of safety, EU data showed on Monday. More than a million people fleeing war and poverty in the Middle East and Africa reached Europe last year. While that was roughly double the 2014 figure, the number of unaccompanied minors quadrupled, statistics agency Eurostat said. Minors made up about a third of the 1.26 million first-time asylum applications filed in the EU last year. EU states disagree on how to handle Europe’s worst migration crisis since World War II and anti-immigrant sentiment has grown, even in countries that traditionally have a generous approach to helping people seeking refuge.
Four in 10 unaccompanied minors applied for asylum in Sweden, where some have called for greater checks, suspicious that adults are passing themselves off as children in order to secure protection they might otherwise be denied. Eurostat’s figures refer specifically to asylum applicants “considered to be unaccompanied minors,” meaning EU states accepted the youngsters’ declared age or established it themselves through age assessment procedures. More than 90% of the minors traveling without a parent or guardian were boys and more than half of them were between 16 and 17 years old. Half were Afghans and the second largest group were Syrians, at 16% of the total. After Sweden, Germany, Hungary and Austria followed as the main destinations for unaccompanied underage asylum seekers.