Vincent van Gogh The sower 1888

Nuts all around.
• Liquidity Crisis Coming: Here, There, Everywhere (Mish)
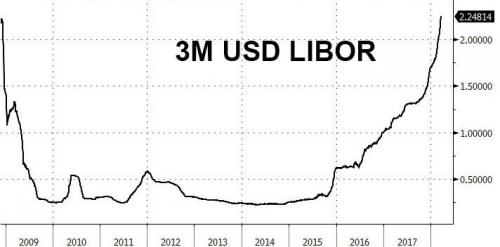
The problem is global. Central bank actions explain most of what you need to know. Italian bonds provide a good example. Despite the recent, massive selloff in Italian bonds, 10-year Italian bonds still trade at roughly the same yield as US 10-year bonds. Is there no default risk? No eurozone exit risk? Of course there is. But those bonds trade where they do because the ECB is engaged in QE to a far greater extent than the the Fed ever did. How nuts is that? 88% of the S&P is with Vanguard, BlackRock, and State Street. How nuts is that? Close to $7 trillion in bonds trade with a negative yield. The figure was close to $10 trillion at one point. How nuts is that?
According to LCD, covenant-lite loan now account for a record 75% of the roughly $970 billion in outstanding U.S leveraged loans. Covenant-lite agreements vary, but they allow things like paying interest with more debt rather than cash or skipping repayments entirely for periods of time. How nuts is that? This is totally nuts, across the board. Puplava calls it “mindless”. I suspect he would be the first to admit that he seriously understated the concern. My “totally nuts” position is also too mild, but I also struggle for the precise words. A global liquidity crisis looms. It is entirely central-bank sponsored. Just don’t expect me, Puplava, or anyone else to tell you precisely when the crisis will hit. But it will. And when it does, don’t fool yourself into believing that you can necessarily escape in time.


How to keep everything overpriced.
• The Trump Effect Is Keeping Bull Market Alive – Robert Shiller (CNBC)
Nobel Prize-winning economist Robert Shiller hasn’t been the most optimistic voice on Wall Street, but he isn’t writing off the bull market. His chief reason: President Donald Trump’s pro-business influence. “There is a sort of optimism about the markets under Trump, and that’s continuing. I don’t see a reason for it about to change,” the Yale professor said Tuesday on CNBC’s “Trading Nation.” “There’s something about how the world is reacting to the president. Something about his self-confidence which is gradually lifting our spirits.” Shiller believes the momentum is so powerful, it’s essentially propping up a bull market that is getting long in the tooth.
“We’ve seen an overpriced stock market. We’ve seen concerns about that for years now,” he said. Shiller acknowledged it’s definitely possible the U.S. stock market could generate gains this year, but he warned the Trump effect “is not a very reliable thing.” So, he said the best strategy is to diversify abroad in this environment. “If you have been overexposed to the United States in your portfolio, this is a time to reconsider that,” Shiller said. “Not to pull out, but to balance things … Europe is cheaper than the U.S..”

These clowns really believe this: “self-sustaining growth”.
• Global Growth Too Dependent On Cheap Borrowing – OECD (G.)
Unemployment will drop to its lowest level since 1980 across the world’s richest nations, but global growth remains dependent on cheap borrowing and government spending, the Organisation for Economic Cooperation & Development (OECD) has warned in its latest global economy health check. The rise of tit-for-tat protectionist trade barriers, the return of volatile financial markets, and soaring oil prices also spell trouble for the global economy as it heads towards the 10-year anniversary of the 2008 banking collapse, the OECD said.
“The economic expansion is set to continue for the coming two years, and the short-term growth outlook is more favourable than it has been for many years,” said Angel Gurría, secretary general of the OECD, the Paris based thinktank for the world’s 35 richest nations, including the US, Britain, Brazil, Mexico and Russia. “However, the current recovery is still being supported by very accommodative monetary policy, and increasingly by fiscal easing. This suggests that strong, self-sustaining growth has not yet been attained.” Central banks in Britain, the eurozone, Japan and the US have kept interest rates low and pumped funds into their economies via quantitative easing to maintain investment and promote growth. Governments have eased back on austerity measures, allowing more state funds for infrastructure projects and welfare payments, especially pensions.

In the end, people want to keep sovereignty. Which has largely been sold off by their leaders.
• The Euro Has To Be Abandoned If Europe Is To Be Saved (Syll)
The euro has taken away the possibility for national governments to manage their economies in a meaningful way – and in Italy, just as in Greece a couple of years ago, the people have had to pay the true costs of its concomitant misguided austerity policies. The unfolding of the repeated economic crises in euroland during the last decade has shown beyond any doubts that the euro is not only an economic project but just as much a political one. What the neoliberal revolution during the 1980s and 1990s didn’t manage to accomplish, the euro shall now force on us.
But do the peoples of Europe really want to deprive themselves of economic autonomy, enforce lower wages and slash social welfare at the slightest sign of economic distress? Is increasing income inequality and a federal Uberstate really the stuff that our dreams are made of? I doubt it. History ought to act as a deterrent. During the 1930s our economies didn’t come out of the depression until the folly of that time, the gold standard, was thrown on the dustbin of history. The euro will hopefully soon join it.

Countries will be forced to leave.
• Italy Crisis: Workers Are Paying For Decisions Made Nearly 30 Years Ago (Clark)
You could say that Italy’s current problems – indeed all of Europe’s economic woes – go back to the early 1990s, when wrong-headed decisions were made by the European elite and enshrined in the Maastricht Treaty – which workers have been paying for ever since. Cuts in public spending have increased unemployment, which in turn has increased the deficit, which has led to more cuts, and so on and so on. Italy‘s National Debt is now 132% of its GDP. Although growth rates are now positive, its average annual rate of growth from 1999-2016 was zero. With 31.7% youth unemployment, La Dolce Vita and Ryan Paris’s catchy song, is a long distance memory.
The tragedy is that it was all so predictable. One man who warned what Europe was letting itself in for in the rush to squeeze as many countries as possible into the Eurozone, was the late Labour politician Peter Shore, the UK’s secretary of state for economic affairs from 1967-69 and trade minister from 1974-6. In the early-to-mid 1990s I was teaching economics in Switzerland and was in correspondence with Shore. He very kindly sent me copies of parliamentary debates where he had railed against the Maastricht Treaty and its imposition of a financial strait-jacket on EEC/EU members – regardless of the state of their economies.
Shore told the House of Commons on March 24, 1993: “The most astonishing omission from the treaty is the fact that it never faces the issue of the counter-recession policy, about which it contains not a word. One lesson that we should have learned from the disasters of the inter-war years was that tendency to go too high in a boom, and too low in recession and slump. “Why is that aspect not written into the protocol? Why does it not say that we must recognise those counter-cyclical problems, and will certainly do so if unemployment grows by X per cent? Instead of having merely 3% and 60% for borrowing and debt, why not have 3, 4 or 5% of the level of unemployment or the fall in GDP?”

“Events in Italy are changing everything.”
• Italy Crisis Dents Greek Hopes Of Returning To Bond Markets (G.)
Greece is watching the unfolding crisis in Italy with growing nervousness. Events in Rome are eliciting a sense of deja vu in Athens, the capital long on the frontline of the eurozone crisis. And nerves are being rattled. “We want a stable, democratic and pro-European Italy,” the country’s foreign minister, Nikos Kotzias, told reporters. “We are worried that if there is instability and it has an impact on the financial situation, this could create problems for us.” The turmoil in Italy could not come at a worse time for Greece. After almost a decade of exclusion from international markets, the debt-stricken nation had set its sights on returning to much-needed normality this summer.
Hopes had been high that when it emerged from its third multi-billion EU-funded bailout programme, Athens would regain market access. But on Wednesday government officials, bankers and analysts were decidedly downbeat. All agreed that with political uncertainty raging across the Ionian Sea, and global investors jittery, the prospect of Greece tapping markets any time soon was beginning to resemble a pipe dream. With soaring bond yields – interest rates on government borrowing – it was out of the question the country could afford the interest rates that would allow it to assume the mantle of post-bailout normality.
“What is happening in Italy worries us immensely,” a senior Bank of Greece official said. “The bond markets have gone mad in southern Europe. With such yields it is totally prohibitive that Greece could return to them when the programme ends.” [..] Italy’s financial turmoil has put hopes of “a clean exit,” on the back burner. “The government’s narrative of clean breaks, and going it alone, is over for now,” a well-placed official conceded. “Events in Italy are changing everything.”

With Italy on the horizon? It amkes little difference, nobody wants to reduce the principal of the debt. And that is what is needed.
• Eurozone, IMF Seek Last-Minute Deal On Greek Debt Relief At G7 This Week (R.)
Euro zone policy-makers will seek last-minute backing this week from the IMF for their debt-relief offer to Greece, to ensure it is credible with markets and draws investors back to Greece after it exits its bailout. The talks are to take place on the sidelines of a meeting of in Canada of finance ministers and central bankers from the world’s top seven economies, the G7, in June, officials involved in the negotiations said. The bailout ends on Aug. 20. “This thing has to be done now,” one senior official involved in the talks said. If no deal is agreed by next Monday, the official said, the IMF would most likely not take part in the bailout at all.
After three successive bailouts since Athens lost market access in 2010, euro zone governments are now Greece’s main creditors, with total loans of €230 billion so far. The IMF took part in the first two bailouts, but has refused to join in the third, which began in 2015. It says the euro zone must agree on how to make Greek debt, now at 179% of GDP, sustainable. Euro zone finance ministers have argued they can only give such details towards the end of the three-year bailout. So the IMF has remained only an observer over the past three years. [..] The IMF and the euro zone agree there should be no “haircut” – a reduction in the principal of the debt – but only an extension of maturities and grace periods.

I smell bailouts.
• Fed Proposes Changes To Rule Limiting Risky Trading On Wall Street (AP)
The Federal Reserve is proposing to ease a rule aimed at defusing the kind of risk-taking on Wall Street that helped trigger the 2008 financial meltdown. The Fed under new leadership on Wednesday unveiled proposed changes to the Volcker Rule, which bars banks’ risky trading bets for their own profit with depositors’ money. The high-risk activity is known as proprietary trading. The proposed changes would match the strictest applications of the rule to banks that do the most trading – 18 banks with at least $10bn in trading assets and liabilities. They account for 95% of all US bank trading and include some foreign banks with US operations, Fed officials said.
Less stringent requirements would apply to banks that do less trading. The idea is to make it easier for banks to comply with the Volcker Rule without sacrificing the banks’ safety and soundness, the officials said. “The proposal will address some of the uncertainty and complexity that now make it difficult for firms to know how best to comply, and for supervisors to know that they are in compliance,” Fed chair Jerome Powell said at a meeting of the Fed governors. “Our goal is to replace overly complex and inefficient requirements with a more streamlined set of requirements.”

The EU is not about to give in.
• US To Hit EU With Steel And Aluminum Tariffs (G.)
The Trump administration is reportedly planning to impose import tariffs on European steel and aluminum after finding no satisfaction in its effort to win trading concessions on the issue. An announcement dropping the EU from an exemption to global tariffs of 25% on imported steel, and 10% on aluminum, could come on Thursday, according to the Wall Street Journal. The move is likely to bring retaliatory action from European Union trade regulators who have warned they will target American products as motorcycles, jeans and bourbon if additional US tariffs are imposed.
Signs of increasing friction between the US and Europe over trade came early Wednesday when Wilbur Ross, the US commerce secretary, drew a sharp line with the EU over Chinese trade negotiations, telling counterparts at a trade development panel in Paris that Europe is using tariffs as an “excuse” to refuse trade negotiations. “China are paying their tariffs,” Ross told the panel. “China hasn’t used that as an excuse not to negotiate … It’s only the EU that is insisting we can’t negotiate if there are tariffs,” he added. Ross’s comments were made in response to EU criticism of import tariffs the Trump administration imposed on dozens of trade partners in March. On Tuesday, the White House added $50bn in new tariffs despite telling China the trade dispute was “on hold” while negotiations continued.

Make Detroit great again.
• Abe Slams US Vehicle Tariff Hikes As ‘Unacceptable’ (JT)
Prime Minister Shinzo Abe on Wednesday condemned U.S. President Donald Trump’s reported move to impose tariffs of up to 25% on imported vehicles as unwarranted and offensive. “If the U.S. slaps Japan, its ally, with tariffs like this, that would be incomprehensible and unacceptable,” Abe told the head of the Democratic Party for the People, Yuichiro Tamaki, during a debate between party leaders in the Diet. The Trump administration recently launched a Section 232 national security probe into whether vehicle and parts imports are harming the U.S.’s domestic auto industry — a step that could provide Trump with the legal basis to institute tariffs.
The move followed yet another surprise announcement by the Trump administration in March that Japan, unlike Washington’s other key allies and partners, wouldn’t be excluded from steel and aluminium tariffs. Tamaki said the hike, if realized, would “deal a severe blow to Japan’s economy.” “Did you get an advance notice on this measure?” Tamaki asked Abe. “You yourself often claim that Japan and the U.S. are 100% together. If there had been no heads-up from the U.S. side on this matter, I’d have to suspect that we may not be seen as their ally.” Abe dodged Tamaki’s question, but stressed he had explained to Trump in their past conversations that Japanese automobile makers are “vastly contributing” to the U.S. economy by creating jobs.

Why am I not surprised?
• George Osborne’s London Evening Standard Sells Its Editorial Independence (OD)
London’s Evening Standard newspaper, edited by the former chancellor George Osborne, has agreed a £3 million deal with six leading commercial companies, including Google and Uber, promising them “money-can’t-buy” positive news and “favourable” comment coverage, openDemocracy can reveal. The project, called London 2020, is being directed by Osborne. It effectively sweeps away the conventional ethical divide between news and advertising inside the Standard – and is set to include “favourable” news coverage of the firms involved, with readers unable to differentiate between “news” that is paid-for and other commercially-branded content.
Leading companies, most operating global businesses, were given detailed sales presentations by Evening Standard executives at the newspaper’s west London offices in an effort to sign them up to the lucrative deal. Among those that have paid half a million pounds each to be involved are international taxi-app firm Uber, which is facing an imminent court appeal against the decision to cancel its licence to operate in London. The Evening Standard has previously come under fire for not declaring Osborne’s £650,000-a-year part time job with the fund managers BlackRock, who hold a £500m stake in Uber.
The global tech giant, Google, still recovering from reputational damage over its low UK tax bills and criticism over its close relationship to the Cameron-Osborne government, has also signed up. Some companies, including Starbucks, walked away from the Evening Standard’s pitch, rejecting the offer of paying to boost their reputations through tailored news and comment. London 2020 is scheduled to start on June 5. Unbranded news stories, expected to be written by staff reporters – but paid for by the new commercial “partners” as part of the 2020 deal – have already been planned for inclusion in the paper’s news pages within a week of the project’s launch.
The London Evening Standard has a circulation of close to 900,000 and distributes more copies within a two-mile radius of Westminster than the Times does across the UK nationally. Many London commuters, who pick up their free copy of the Standard at underground and rail stations, will be unaware that they will be reading paid-for news coverage that is part of a wider commercial deal. An increasing number of British newspapers often carry “native advertising”, essentially paid-for commercials designed to look like independent editorial articles.

It is a sad day.
• Bayer Wins US Nod For Monsanto Deal To Create Agrochemical Giant (R.)
Bayer won U.S. approval for its planned takeover of Monsanto after agreeing to sell about $9 billion in assets, clearing a major hurdle for the $62.5 billion deal that will create by far the largest seeds and pesticides maker. Makan Delrahim, who heads the U.S. Justice Department’s (DoJ) Antitrust Division, said the asset sales agreed to by Bayer were the “largest ever divestiture ever required by the United States.” A Bayer spokesman said the planned sale of businesses with 2.2 billion euros ($2.54 billion) in sales to BASF already agreed to address antitrust concerns, mainly in Europe, were not materially different from the DoJ’s demands. “Receipt of the DOJ’s approval brings us close to our goal of creating a leading company in agriculture,” Bayer CEO Werner Baumann said in a statement.
Bayer’s move to combine its crop chemicals business, the world’s second-largest after Syngenta, with Monsanto’s industry-leading seeds business, is the latest in a series of major agrochemicals tie-ups. U.S. chemicals giants Dow Chemical and DuPont merged in September 2017 and are now in the process of splitting into three units. In other consolidation in the sector, China’s state-owned ChemChina purchased Syngenta and two huge Canadian fertilizer producers merged to form a new company, now called Nutrien. Bayer committed to selling its entire cotton, canola, soybean and vegetable seeds businesses and digital farming business, as well its Liberty herbicide, which competes with Monsanto’s Roundup.

As the industry that produces them gets bigger.
• The British Countryside Is Being Killed By Herbicides And Insecticides (G.)
In June 2011 I took a long drive up the A1, the Great North Road. At Scotch Corner I turned for Barnard Castle. The villages were well kept, the countryside was green, the fields dotted with sheep. Everything was normal. Or so I thought. Beyond Barnard Castle I took a narrow lane into part of Upper Teesdale and suddenly colours exploded along the roadside. I stopped the car and jumped out. There was a bed of orchids, hundreds of them, and behind that, billowing banks of violet, scarlet, white, yellow and cornflower blue. I had seen alpine meadows, but this took my breath away. Further into the dale I found a footpath that led me down beside a shady brook. There were more orchids of a different species and a grass snake hunting frogs in a pool.
Out in the open again, there was the haunting cry of curlews overhead, then redshanks, plovers and snipe. I spent two days up there, talking to environmentalists and farmers involved in the upland hay meadow project for the North Pennines area of outstanding natural beauty (AONB). The landowners were being paid to restrict the use of fertiliser, not employ herbicides, and stop grazing after mid-May. Together with some seeding programmes and careful monitoring, the meadows had become magnificent. When I drove back home, I came down to a countryside where the only flowers were dandelions, watched over by crows. The monotonous green of the rye grass was unbroken. Compared to what I had just experienced, it felt like a desert. I felt cheated. My entire adult life had been spent admiring a shoddy and simplified reproduction, a poor impersonation of a much-loved friend.
[..] Seven years on, the statistics for the British countryside are heartbreaking. Over a quarter of all British birds are under threat, eight species are almost extinct. Three-quarters of all flying insects have disappeared since 1945, including a staggering 60 different moths. Orchid ranges have shrunk by half; two species are gone. The State of Nature 2016 report described Britain as being “among the most nature-depleted countries in the world”. [..] 40% of all species are in moderate or steep decline. Over a quarter of the hedgehog population has disappeared in a decade. Toads are down 68% in 30 years, water voles are no longer found in 94% of the places where they once lived. Likewise mountain hares are in steep decline, as are rabbits. Even that great survivor, the fox, has lost over 40% of its population.