DPC ‘On the beach, Palm Beach’ 1905

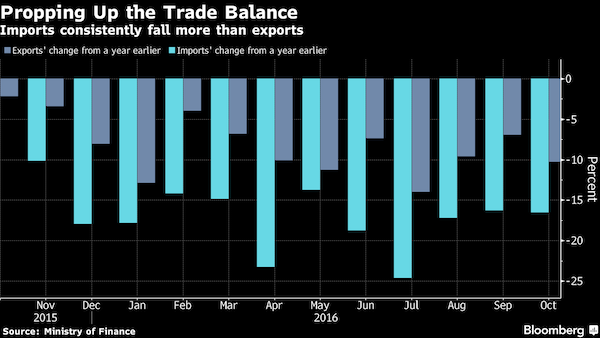
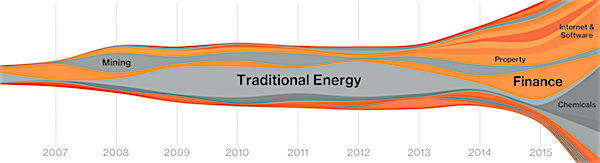
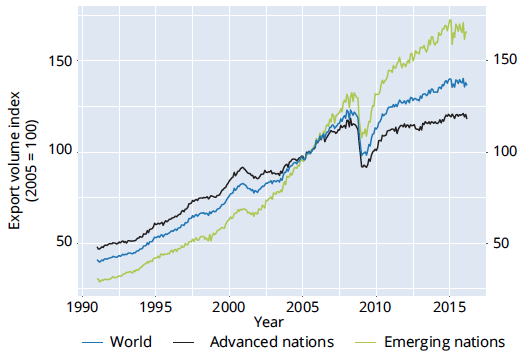
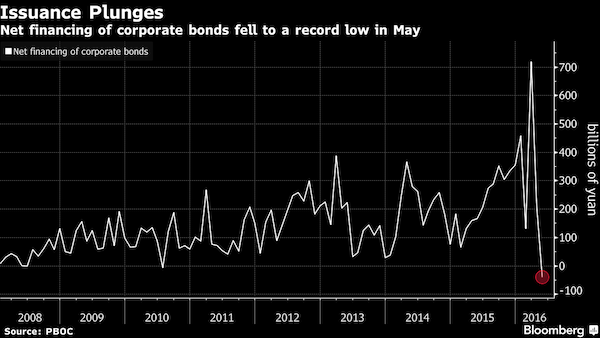
“Unsurprisingly, China was responsible for almost all of the growth in debt last year.”
• Emerging Market Debt Up 24% In 2015 To $18 Trillion (VW)
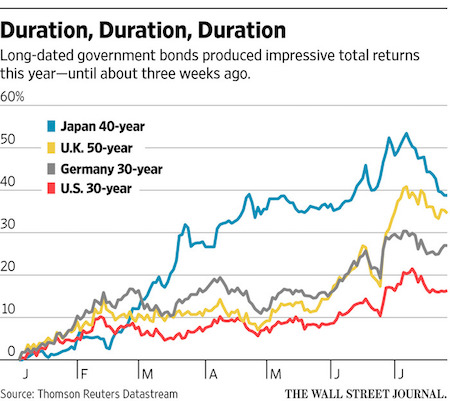
Alongside gold and developed market Sovereign bonds, developed market equities and bonds have been some of the hottest trades this year. According to Bank of America’s “Flow Show” report published at the end of last week, around $2 billion flowed into emerging market debt funds over the last week. This marks the seventh straight week of inflows into such funds. Over this period, more than $20 billion has been invested in emerging market bond funds, the largest amount on record. Meanwhile and $5 billion found its way into emerging market stock funds last week, taking the seven-week total to $14.6 billion for emerging market equity funds, a near two-year high.
Emerging market debt funds have become a hot commodity this year as the yields on developed market bonds plunge to levels that offer little in the way of return. Bond funds have attracted $138 billion so far this year. On the other hand, equity funds have seen outflows of $128 billion since the start of 2016 (all of these outflows come from mutual funds, low-cost equity ETF have attracted $52.5 billion of assets so far this year). It seems that emerging markets are only too happy to generate more debt to meet the increasing demand for investors. According to research from Bank of America’s quantitative fixed income strategist Jane Brauer, last year the total value of global emerging market outstanding debt rose to $18.2 trillion, up around $2 trillion year-on-year.
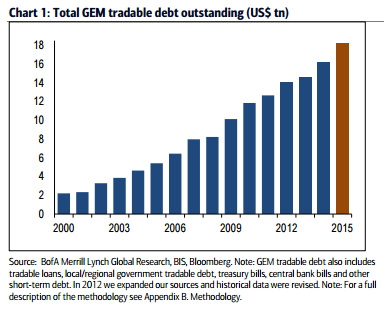
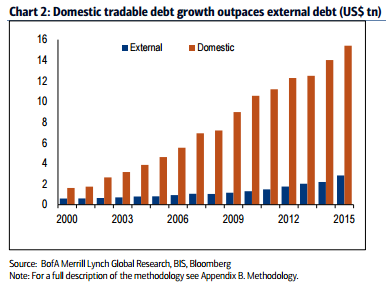
In local currency terms this gain is 24% but in US dollar terms, thanks to dollar depreciation, the rise in debt looks much more subdued at only 12%. For 2014 the total value of global emerging market outstanding debt grew by 12% year-on-year and on average the emerging market debt stock has increased by approximately 14% per annum since the year 2000. Unsurprisingly, China was responsible for almost all of the growth in debt last year. China total debt rose by $2 trillion during 2015. China domestic debt skyrocketed by 30% in 2015 in US dollar terms, with the government and financial institutions local debt components both increasing 36%.
Read more …

The more central banks print, the more trust evaporates.
• China Caught In ‘Dead Money’ Trap; PBOC Pleads For Fiscal Stimulus (AEP)
China is at mounting risk of a Japanese-style “liquidity trap” as monetary policy loses traction and the economy approaches credit exhaustion, forcing a shift towards Keynesian fiscal stimulus. Officials at the PBOC have begun to call for a fundamental change in strategy, warning that interest rate cuts have become an increasingly blunt tool. They cannot easily stop companies hoarding cash or halt the slide in private investment. Sheng Songcheng, the PBOC’s head of analysis, set off a storm last month by warning that the economy had “started to show some signs of being caught in a liquidity trap”. He has since stepped up his pleas for action by the fiscal authorities to relieve the burden on the central bank, a Chinese variant of the parallel drama that is being played out in Europe and Japan.
Mr Sheng told China Business News on Monday that the country has a very low reliance on foreign borrowing and can easily afford to shore up the economy with a Keynesian boost. “China can let its deficit-to-GDP ratio rise to over 3pc or even 5pc in the long run. It can spur growth more effectively by lowering corporate taxes than by cutting the interest rate,” he said. The powerful State Council has now joined the chorus with calls this week for a $75bn cut in business taxes to boost confidence and channel stimulus to the productive economy. Caixin magazine said Chinese companies are hoarding record sums of “dead money” rather than spending it. The growth rate of private investment has dropped to 2.1pc over the last seven months, the lowest since the global financial crisis. The central bank is effectively ‘pushing on a string’, an expression coined by John Maynard Keynes in the 1930s.
Read more …

But most of the shadow loans are not inside the banks.
• China’s Best-Performing Bank A ‘Mirage’ Of Shadow Lending (BBG)
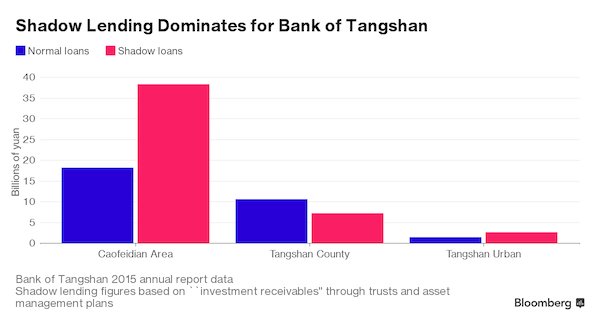
The best-performing bank in China is in a struggling city in the northeast where weeds sprout alongside the concrete skeletons of high rises in an industrial zone that mostly looks like a ghost town. Steel plants have laid off tens of thousands of workers. Cranes stand idle on construction sites. Wipe away a spiderweb on a dirty glass door at an empty complex with smashed windows and there’s a notice from the local government demanding rent unpaid since November 2014. Yet the Bank of Tangshan’s financial statements hardly reflect these realities. Instead, this small lender reports the fastest growth of 156 Chinese financial institutions and the lowest level of bad loans, a mere 0.06%. Its profit jumped 436% in two years and assets soared almost 400% since the start of 2014 to 177.9 billion yuan ($26.7 billion).
It’s largely driven by shadow lending. The bank is the most prominent example of the off-loan-book wizardry that’s turbo-charging some of China’s small and mid-sized banks, creating opaque risks that could lead to failures, bailouts or liquidity shocks that jolt the nation and global markets in the years ahead. “It’s a mirage built upon risks,” said He Xuanlai, of Commerzbank. The Singapore-based analyst cited smaller banks’ use of so-called “investment receivables” — including asset management plans and wealth management products — to boost lending without facing requirements to bolster capital and loan-loss provisions. “It’s hard to assess the banks’ true asset quality.”
This form of shadow lending is so widespread that a survey of 26 banks by Moody’s Investors Service found that they’d quadrupled use of the products since 2012, with small and mid-sized lenders contributing an outsize share. The IMF estimates that Chinese banks held $2.3 trillion of shadow credit products at the end of last year, adding to a build-up that could pose “substantial risks” to the financial system. Some little-known Chinese banks have already been quietly bailed out, UBS said.
Read more …

What caused Brexit.
• More Than 1.5 Million UK Households In Extreme Debt (G.)
About 1.6m UK households are living in extreme debt, according to a report by the TUC, which says official figures underestimate the intense burden of repayment on many families and individuals. Contrary to official data, which suggests that households have been repaying debt accumulated before the financial crisis, the Britain in the Red report says households are finding it harder than ever to cope as wages have fallen. “More than 1m families with a household income below £30,000 are in extreme debt and ongoing wage stagnation is making the problem worse,” the report says. Total unsecured debt, including car loans and credit cards, but excluding mortgages, for UK households rose by £48bn between 2012 and 2015 to £353bn.
As wages declined, the real burden of repaying debt became tougher. The TUC said 3.2m households are in problem debt, defined as spending more than 25% of total household income on unsecured debt repayments. About 1.6m households are in extreme debt, paying out 40% or more of household income to creditors. The problem is growing fastest among the working poor, people with jobs but insufficient pay to stay financially afloat. OECD figures show that UK real wages fell by 10.4% between 2007 and 2015, making the task of keeping up debt repayments harder. In 2015, 9% of low-income households with an adult in employment were in extreme problem debt, almost double the figure of 5% in 2014, the report found.
Read more …

One day you’ll find out how insane this is.
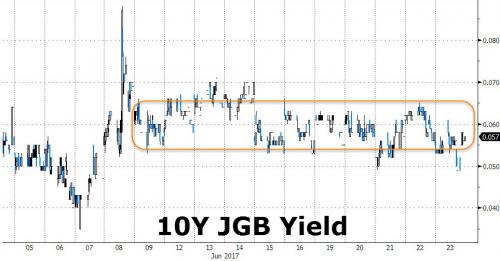
• Monetary Policy Has Nationalized The Japan Stock Market (CNBC)
Even a resurgent yen hasn’t dampened Japan’s stock rally over the past couple months, but that’s not necessarily because investors like the market. The Nikkei 225 index has surged around 10% since late June, even as the yen has climbed against the dollar, with the pair testing levels under 100. Normally this would be bad news for stocks as a stronger yen is a negative for exporters as it reduces their overseas profits when converted to local currency. So what explains the buoyant stock market? Analysts attributed the gains to the Bank of Japan (BOJ), not fundamentals.
In a report titled, “BOJ nationalizing the stock market,” Nicholas Smith, an analyst at CLSA, said that the central bank’s exchange-traded fund (ETF) buying program was distorting the market. At its late July meeting, the BOJ said it would increase its ETF purchases so that their amount outstanding will rise at an annual pace of 6 trillion yen ($56.7 billion), from 3.3 trillion yen previously. Those purchases were particularly distorting to the market because they focused largely on funds tracking the Nikkei 225 index, Smith said in a note dated Sunday, estimating that more than half of the BOJ’s ETF buying was likely in Nikkei-tied funds.
Read more …

Kuroda and Abe are destroying their own markets by destroying price discovery.
• Bank of Japan’s Rush Into Stocks Raises Fears Of Market Distortions (R.)
The Bank of Japan’s near doubling of its purchases of Tokyo shares is causing investors to worry the central bank will dominate financial markets, which could lead to price distortions as it continues to grease the economy. The BOJ’s buying spree will make it harder for investors to sift good companies from bad, and raises a host of other problems including misallocating capital, making equities trading more speculative and reducing incentives for companies to meet shareholder needs, analysts say. More than three years of massive monetary stimulus has already resulted in the central bank cornering the Japanese government bond (JGB) market and distorting interest rates. “The increased BOJ purchasing provides a very favorable demand environment for listed equities,” said Michael Kretschmer, CIO at Pelargos Capital in the Hague.
“Nevertheless, in the long run we strongly doubt these type of monetary gimmicks aimed at price setting of risk assets can have a sustained positive impact on economic growth.” The BOJ doesn’t dominate the stock market as it does JGBs, but its revved up buying of index-based shares has shifted attention to the central bank’s behavior and away from how companies perform. [..] Some liken the increased purchases by the BOJ – the only central bank in the world that buys stocks at the moment – to failed government efforts over more than two decades to prop up the market by pressing government-related financial institutions to buy after the bursting of the late-1980s asset bubble.
[..] With foreign investors largely staying away, disappointed at the lack of progress in Japan’s structural reforms, the BOJ is almost sure to be the biggest buyer on the Tokyo Stock Exchange for the foreseeable future. “The market is driven completely by the BOJ’s buying rather than views on each companies’ earnings,” said a fund manager at a Japanese asset management firm.
Read more …

“..the Fed is already factoring in a scenario in which a shock to the economy leads to additional QE of either $2 trillion, or in a worst case scenario, $4 trillion..”
• Fed Admits $4 Trillion More In QE Needed In Case Of “Economic Shock” (ZH)
In a Fed Staff working paper released over the weekend titled “Gauging the Ability of the FOMC to Respond to Future Recessions” and penned by deputy director of the division of research and statistics at the Fed, the author concludes that “simulations of the FRB/US model of a severe recession suggest that large-scale asset purchases and forward guidance about the future path of the federal funds rate should be able to provide enough additional accommodation to fully compensate for a more limited [ability] to cut short-term interest rates in most, but probably not all, circumstances.” So far so good, however, there are some notable problems with the paper’s assumptions, as Citi head of G10 FX, Steven Englander, observes.
He writes that the paper’s basic framework is to take the standard US economic model used by the Fed, give it a negative shock big enough to push the unemployment rate up by 5%age points (big but not unprecedented over the last 50 years) and deploying the Fed’s policy rate, QE and forward guidance tools to see if they are adequate to get the economy back on track. Negative rates and helicopter money are not used. The two simulations assume: 1) the economy is in equilibrium initially with inflation at 2%, r* at 1%, so equilibrium nominal fed funds is 3%; 2) the economy is in equilibrium initially with inflation at 2%, r* at zero (secular stagnation) and equilibrium nominal fed funds at 2%.
He compares three policy approaches. The first assumes a linear world where fed funds can go into negative territory but there is no breakdown in the structure of economic relationships. It is probably not a realistic view of policy ineffectiveness at negative rates, but it is mean to be a baseline. The second just takes fed funds down to zero and keeps it there long enough for unemployment to return to baseline. “The third takes fed funds down to zero and augments it with additional $ 2trn of QE and forward guidance. A variation on the third policy response function doubles the amount of QE in the second simulation.” In other words, the Fed is already factoring in a scenario in which a shock to the economy leads to additional QE of either $2 trillion, or in a worst case scenario, $4 trillion, effectively doubling the current size of the Fed’s balance sheet.
Read more …

Mirror trades designed to get capital out of Russia. Nice piece.
• Deutsche Bank’s $10-Billion Scandal (New Yorker)
Deutsche Bank is an unwieldy institution with headquarters in Frankfurt and about a hundred thousand employees in seventy countries. When it was founded, in 1870, its stated purpose was to facilitate trade between Germany and other countries. It soon established footholds in Shanghai, London, and Buenos Aires. In 1881, the bank arrived in Russia, financing railways commissioned by Alexander III. It has operated there ever since. During the Nazi era, Deutsche Bank sullied its reputation by financing Hitler’s regime and purchasing stolen Jewish gold. After the war, the bank concentrated on its domestic market, playing a significant role in Germany’s so-called economic miracle, in which the country regained its position as the most potent state in Europe.
After the deregulation of the U.S. and U.K. financial markets, in the nineteen-eighties, Deutsche Bank refreshed its overseas ambitions, acquiring prominent investment banks: the London firm Morgan Grenfell, in 1989, and the American firm Bankers Trust, in 1998. By the new millennium, Deutsche Bank had become one of the world’s ten largest banks. In October, 2001, it débuted on the New York Stock Exchange. Although the bank’s headquarters remained in Germany, power migrated from conservative Frankfurt to London, the investment-banking hub where the most lavish profits were generated. The assimilation of different banking cultures was not always successful. In the nineties, when hundreds of Americans went to work for Deutsche Bank in London, German managers had to place a sign in the entrance hall spelling out “Deutsche” phonetically, because many Americans called their employer “Douche Bank.”
In 2007, the bank’s share price hit an all-time peak: a hundred and fifty-nine dollars. But as it grew fast it also grew loose. Before the housing market collapsed in the United States, in 2008, sparking a global financial crisis, Deutsche Bank created about thirty-two billion dollars’ worth of collateralized debt obligations, which helped to inflate the housing bubble. In 2010, Deutsche Bank’s own staff accused it of having masked twelve billion dollars’ worth of losses. Eric Ben-Artzi, a former risk analyst, was one of three whistle-blowers. He told the SEC that, had the bank’s true financial health been known in 2008, it might have folded, as Lehman Brothers had. Last year, Deutsche Bank paid the SEC a $55 million fine but admitted no wrongdoing. Ben-Artzi told me that bank executives had incurred a tiny penalty for a huge crime. “There was cultural criminality,” he said. “Deutsche Bank was structurally designed by management to allow corrupt individuals to commit fraud.”
Read more …

When has that ever stopped the greater fool?
• Goldman Says It’s Too Late to Chase the Booming Real Estate Sector (BBG)
Real estate stocks were a buying opportunity a few years ago, but at this point Goldman Sachs says the area is too risky for investors. At the end of this month, Real Estate will separate from Financials to become its own sector in the S&P 500. While those stocks have outpaced the S&P 500 so far in 2016, analysts led by David Kostin at Goldman Sachs say there are a lot of challenges, and they are not recommending investors try to make up for the missed gains. “Real Estate has outpaced the S&P 500 by 156 basis points year-to-date, which has hurt large-cap mutual fund returns given their underweight allocation to the sector,” Kostin and company write.
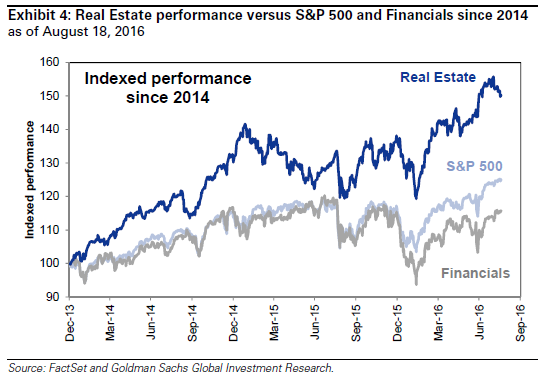
One thing that could help the new sector, however, is that even if those fund managers just move from underweight to neutral, there could be a big inflow of funds. According to Goldman, close to half of large-cap core funds managers have zero exposure to the sector. The analysts forecast as much as $19 billion in new demand, as funds that aren’t currently in real estate try to play catch up. That may be good enough not to slap a sell rating on these stocks, but it isn’t enough to give them a buy rating. “Looking forward, we recommend a Neutral weighting to the Real Estate sector given slowing top-line revenue growth, average relative valuation, and risks from a higher interest rate environment,” they conclude.
Read more …

“I taught the law of war when I was on active duty [..] You can’t kill children, newlyweds, doctors and patients – those are exempt targets under the law of war..”
• Congressman Seeks to “Stop Madness” of US Support for Saudi War in Yemen (IC)
For months, a California congressman has been trying to get Obama administration officials to reconsider U.S. backing for the Saudi-led war in Yemen. And for months, he has been given the runaround. Ted Lieu, a Democrat representing Los Angeles County, served in the Air Force and is a colonel in the Air Force Reserves. The brutal bombing of civilian areas with U.S.-supplied planes and weapons has led him to act when most of his colleagues have stayed silent. “I taught the law of war when I was on active duty,” he told The Intercept. “You can’t kill children, newlyweds, doctors and patients – those are exempt targets under the law of war, and the coalition has been repeatedly striking civilians,” he said. “So it is very disturbing to me. It is even worse that the U.S. is aiding this coalition.”
But he and a very few other lawmakers who have tried to take bipartisan action to stop U.S. support for the campaign are a lonely bunch. “Many in Congress have been hesitant to criticize the Saudis’ operational conduct in Yemen,” Lieu said. He didn’t say more about that. The matter has gotten ever more urgent since August 7, when the Saudi-led coalition relaunched an aggressive campaign of attacks after Houthi rebels in Yemen rejected a one-sided peace deal. More than 60 Yemeni civilians have been killed in at least five attacks on civilian areas since the new bombing campaign began. On August 13, the coalition bombed a school in Haydan, Yemen, killing at least 10 children and injuring 28 more.
Lieu released a statement two days later, harshly condemning the attack. “The indiscriminate civilian killings by Saudi Arabia look like war crimes to me. In this case, children as young as 8 were killed by Saudi Arabian air strikes,” he wrote. “By assisting Saudi Arabia, the United States is aiding and abetting what appears to be war crimes in Yemen,” Lieu added. “The administration must stop enabling this madness now.” Then, mere minutes after his office sent out the statement about the August 13 attack, another tragedy started making headlines: The coalition had just bombed a hospital operated by the international medical humanitarian group Doctors Without Borders (MSF), killing 19.
Read more …

Something tells me this is not a done deal.
• Hillary Emails Recovered By FBI To Be Released Just Before Election Day (G.)
Nearly 15,000 emails recovered by the FBI from the private server used by Hillary Clinton when she was secretary of state are set to be made public just before the presidential election in November, it emerged in court on Monday. The state department said it was reviewing 14,900 documents that came to light in the now-closed investigation into the handling of sensitive information that flowed through the server in question. That is a major addition to the 30,000 emails that Clinton’s lawyers considered work-related and returned to the department in December 2014. The FBI cleared Clinton of criminal conduct but found her to have have been “extremely careless”, and the saga continues to dog her.
On 5 August the FBI completed a transfer of several thousand previously undisclosed work-related emails for the state department to review and publish. Responding to the news, the Republican National Committee chairman, Reince Priebus, said Clinton “seems incapable of telling the truth”. State lawyers told federal judge James Boasberg on Monday they expected to release the emails in batches on 14, 21 and 28 October and 4 November. The election, against Republican nominee Donald Trump, takes place on 8 November. Boasberg ordered that the department should aim for a more ambitious deadline. The judge set another hearing for 22 September, so progress can be reviewed.
Tom Fitton, president of the conservative legal group Judicial Watch, which brought the case under a Freedom of Information Act (Foia) request, tweeted: “FBI found almost 15,000 new Clinton documents. When will state release them?” Another federal judge, Emmet Sullivan, last week ordered Clinton to answer written questions from Judicial Watch. Her answers are not due until after the presidential election.
Read more …

“The Oversight committee is slated to hold a hearing next month to look at the possibility of bringing perjury charges against the former secretary of state. FBI Director James Comey has been named as a possible witness.”
• Chaffetz: FBI’s Notes From Clinton Interview Keep Changing (WE)
The FBI has handed Congress two copies of notes from its interview with Hillary Clinton about her private email server, but according to the chairman of the House Oversight Committee, the two sets of notes aren’t consistent with each other. “The … thing that is stunning to me, which I found out last night, is the FBI gave us one set of documents. Then we asked them, and they … gave us a second copy in a classified setting. But they’re different,” said committee Chairman Rep. Jason Chaffetz in a Monday morning interview on MSNBC. The Utah Republican said he had no explanation, and that he would have to seek one from the FBI. “We have a second set of documents that’s now different. You turn them page by page, and they’re different. I don’t know why that happens,” Chaffetz added.
Chaffetz said there was “new information” in the second set of documents, which has left the committee confused. “So we’re going back to square one. We’ve only had them for days, but still, the second copy is different from the first copy. Why is that?” he asked. Asked whether he would pursue perjury charges against Clinton for making misleading statements to Congress, Chaffetz demurred, but did criticize the FBI. “I’m stunned the FBI director came before Congress and testified that during their year-long investigation, they never looked at the under oath testimony from Hillary Clinton.” “You’re kidding me? You’re doing an investigation about the email scandal, and you never look at what she said under oath? Politicians lie, but when you’re under oath, you can’t do that,” Chaffetz said.
The Oversight committee is slated to hold a hearing next month to look at the possibility of bringing perjury charges against the former secretary of state. FBI Director James Comey has been named as a possible witness. It would the second time in as many months that Comey has been called before Congress to explain the investigation into Clinton’s emails.
Read more …

Emails, Clinton Foundation, I still can’t see how she would be electable. Time to bring in Joe Biden?
• Foundation Ties Bedevil Hillary Clinton’s Presidential Campaign (NYT)
The kingdom of Saudi Arabia donated more than $10 million. Through a foundation, so did the son-in-law of a former Ukrainian president whose government was widely criticized for corruption and the murder of journalists. A Lebanese-Nigerian developer with vast business interests contributed as much as $5 million. For years the Bill, Hillary and Chelsea Clinton Foundation thrived largely on the generosity of foreign donors and individuals who gave hundreds of millions of dollars to the global charity. But now, as Mrs. Clinton seeks the White House, the funding of the sprawling philanthropy has become an Achilles’ heel for her campaign and, if she is victorious, potentially her administration as well.
With Mrs. Clinton facing accusations of favoritism toward Clinton Foundation donors during her time as secretary of state, former President Bill Clinton told foundation employees on Thursday that the organization would no longer accept foreign or corporate donations should Mrs. Clinton win in November. But while the move could avoid the awkwardness of Mr. Clinton jetting around the world asking for money while his wife is president, it did not resolve a more pressing question: how her administration would handle longtime donors seeking help from the United States, or whose interests might conflict with the country’s own.
The Clinton Foundation has accepted tens of millions of dollars from countries that the State Department — before, during and after Mrs. Clinton’s time as secretary — criticized for their records on sex discrimination and other human-rights issues. The countries include Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Kuwait, Oman, Brunei and Algeria. Saudi Arabia has been a particularly generous benefactor. The kingdom gave between $10 million and $25 million to the Clinton Foundation. (Donations are typically reported in broad ranges, not specific amounts.) At least $1 million more was donated by Friends of Saudi Arabia, which was co-founded by a Saudi prince.
Read more …

Germany’s call yesterday for people to hoard cash changes this game.
• US Banks Want To Cut Branches, But Customers Keep Coming (R.)
Despite banks’ nudging toward online tools, many U.S. customers are not ready to give up regular visits to their nearest branch, complicating the industry’s efforts to slim down. U.S. banks have trimmed the number of branches by 6% since it peaked in 2009, according to Federal Deposit Insurance Corp data. The 93,283 branches open at the end of last year was the lowest level in a decade. Yet analysts who have examined the data say banks should have done more to offset the pressure on revenue from low interest rates and regulatory demands. The number of FDIC-insured banks has fallen by more than 25% over that time even as industry assets have grown, indicating room for greater branch consolidation.
Bank executives argue, however, that branches remain crucial for acquiring new customers and doing more business with existing ones. Closures, they say, would hurt revenue more than help reduce costs. “Our customers still want to visit us,” Jonathan Velline, Wells Fargo’s head of ATM and store strategy, told Reuters in an interview. “They’re still coming to our stores and our ATMs at pretty consistent rates.” Bankers across the industry share that view. They say online banking complements traditional services for U.S. customers, but few have gone fully digital.
Read more …

Jim gets back to basics: oil was always a one-off, and there are no replacements.
• Dark Dynamics (Jim Kunstler)
What the world is witnessing, without actually paying much attention, is the death of our debt-based economy — that is, borrowing the means to thrive in the now from a future that can’t really furnish it anymore. The illusion that the future would always provide was a legacy of the cheap energy era. That era ended in 2005. The basic promise is broken and with it the premise for living as we had been. The energy available today, especially oil, is no longer cheap enough to run the industrial economies designed to run on it. Any way that you look at the dynamic, Modernity loses. With oil under $50 a barrel, and gasoline under $3 a gallon (back east), the public apparently thinks that the Peak Oil story is dead and gone.
But when it costs $75 a barrel to pull the stuff out of the ground, and the stuff only sells for $47 a barrel, the oil companies’ business model doesn’t really work. The shale oil companies especially have been gaming the system by issuing bonds that pay relatively high interest rates in an investment climate where almost nothing else offers enough yield to live on, especially for pension funds and insurance companies. Two little upward bumps this year in the price of oil toward the $50 range prompted a wish that the good old days of high-priced oil were coming back, that the oil business would be profitable again. The trouble is that high oil prices – say, over $100 a barrel, as it was in 2014 – crush advanced economies, so that demand for oil crashes, and with it productive activity.
Without productivity, the debts issued by companies (and even governments) don’t get repaid. There really is no “sweet spot” in this energy cost equation. A lot of wishful thinkers would like to believe that you can run contemporary life on something beside oil. But the usual “solutions,” solar and wind energy, don’t pencil out, especially when you consider that the hardware for running them – the photovoltaics, charge controllers, batteries, turbines, and blades, can’t be mass-produced and distributed without the very fossil fuels they are supposed to replace.
Read more …

James Galbraith runs with Yanis’ ideas for DiEM25.
• From The Destruction Of Greece To Democracy In Europe (Galbraith)
In Protesting the Treaty of Versailles ending World War I, John Maynard Keynes wrote: “The policy . . . of depriving the lives of millions of human beings, of depriving a whole nation of happiness should be abhorrent and detestable — abhorrent and detestable, even if it were possible, even if it enriched ourselves, even if it did not sow the decay of the whole civilized life of Europe.” Last year’s third bailout of Greece, imposed by Europe and the International Monetrary Fund, does to Greece what Versailles did to Germany: It strips assets to satisfy debts. Germany lost its merchant marine, its rolling stock, its colonies, and its coal; Greece has lost its seaports, its airports — the profitable ones — and is set to sell off its beaches, the public asset that is a uniquely Greek glory.
Private businesses are being forced into bankruptcy to make way for European chains; private citizens are being forced into foreclosure on their homes. It’s a land grab. And for what? To satisfy old public debts, incurred for tanks, submarines, the Olympics, big construction projects outsourced to German firms, and to hide deficits in health care, with creditor connivance — a quagmire of graft to support an illusion, that Greece could “compete” as part of the euro. Already in 2010 the IMF knew it was breaking its own rules by pretending that Greece could recover quickly, sustain a huge primary surplus, and repay its debts. Why? To help save French and German banks, which the IMF’s sainted managing director, Dominique Strauss-Kahn, wanted to do, because he wanted to be president of France.
Europe crushed the Greek resistance in 2015. Not because Wolfgang Schäuble, the German finance minister, thought his economic plan would work; he candidly told the Greek finance minister, Yanis Varoufakis, that “as a patriot” he would not sign it himself. But Germany wants to impose its order on Italy and on France, where civil society continues to fight back. And Chancellor Angela Merkel could not admit to her voters, or to fellow Europeans from Slovakia to Portugal, that back in 2010 she’d saved Germany’s banks by saddling them with Greek debts that could never be paid. Greece was given collective punishment as a lesson. It was done to show that “there is no alternative.” It was done to stop any other attempt to develop, articulate, and defend a more rational policy. It was done to protect the power of the ECB, the German government in Europe, and the policy-making authority, in face of a long record of failure, of the IMF.
Read more …

Routine procedure.
• Coast Guard Fired at Migrant Boats, European Border Agency Documents Show (IC)
On a smuggler’s boat from Turkey two years ago, 19-year-old Rawan watched the passengers start to panic as a Greek coast guard vessel approached them head on, circling twice. Rawan heard two gunshots ring out from the Greek patrol. Fearing arrest, the driver of Rawan’s boat, a Turkish fisherman, turned the vehicle around to flee back to Turkey. Then Rawan heard more shots. When the bullet hit her in the lower back, at first she felt nothing. Then, Rawan says, it felt like fire. Rawan’s husband had made it to Germany a year earlier; both were fleeing their home in Damascus, Syria. Rawan and 12 other Syrians were headed for the Greek island of Chios on a small fiberglass boat, much faster than the inflatable dinghies that many refugees use for the 5-mile crossing.
Before the shots, Rawan heard “stop” blare over a loudspeaker on the coast guard vessel. She and four others were in the forward compartment of the boat, and more people were sitting in the back near the outboard engine. Rawan’s father-in-law, Adnan Akil, was also shot in the lower back, and Amjad A., another Syrian refugee who asked that only his first name and last initial be used, was shot in the shoulder. Akil says he clearly remembers the chain of events leading up to the shooting. One officer had a pistol, the other had a submachine gun. Akil, Rawan, and other witnesses say they heard one officer shoot in automatic bursts. “We were shouting and screaming for the driver to stop,” remembers Braa Abosaleh, another Syrian refugee who was on the boat that day.
When the driver didn’t stop, the coast guard rammed their boat from the back right side. Akil and Rawan remember the driver stopping the boat, pretending he was going to surrender. As the officers put down their weapons and approached, the driver fired up the engine again and turned back toward Turkey. This time, the coast guard shot directly at the fleeing boat.
Read more …

I fear for Greece between now and (into) 2017.
• Greece Plans New Refugee Centers As New Arrivals Soar (Kath.)
Greek authorities hope that the construction of a new migrant reception center in Thiva, central Greece, which is set to be completed in the coming days, will ease congestion in camps on the country’s eastern Aegean islands, while plans are also under way to open a refugee facility on Crete. “The situation on the islands is only marginally under control,” a source inside the Public Order Ministry told Kathimerini on condition of anonymity on Monday. Authorities are said to be drawing up plans to create so-called “closed-structure” detention camps on the islands to separate individuals who are scheduled to be repatriated – as well as troublemakers – from those who have passed a first screening in their claim for international protection.
Meanwhile, migrants with a criminal past will be transferred from the islands to pre-departure centers on mainland Greece. About 300 individuals have already been transferred and another 100 are to follow in the coming days. Less straightforward are the government’s plans to construct migrant reception facilities on the island of Crete. Officials at the Ministry for Immigration Policy told Kathimerini that, by the end of September, local authorities are expected to propose sites where these facilities could be built. “Any plans are to take effect as of November, after the island’s tourism season has drawn to a close,” an unnamed official said.
Read more …