Jean-Michel Basquiat Aboriginal 1984

Coming to you from a Russian propaganda channel.
• Why Did US Stock Market Crash On Monday? Blame The Central Banks (Steve Keen)
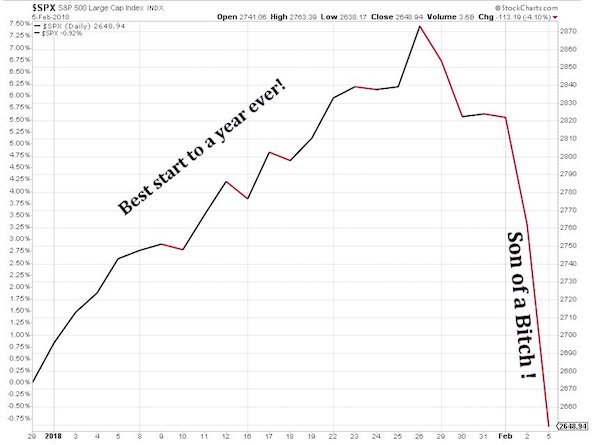
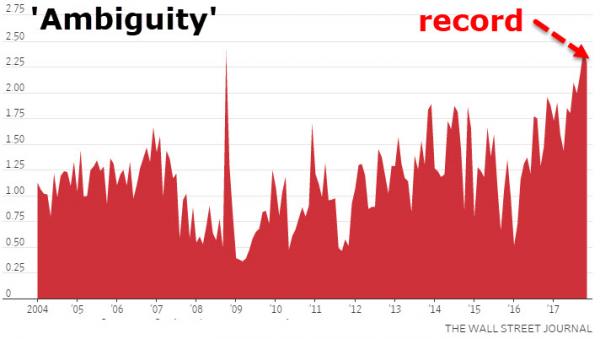
Everyone who’s asking “why did the stock market crash Monday?” is asking the wrong question. The real poser is “why did it take so long for this crash to happen?” The crash itself was significant—Donald Trump’s favorite index, the Dow Jones Industrial (DJIA) fell 4.6% in one day. This is about four times the standard range of the index—and so according to conventional economics, it should almost never happen. Of course, mainstream economists are wildly wrong about this, as they have been about almost everything else for some time now. In fact, a four% fall in the market is unusual, but far from rare: there are well over 100 days in the last century that the Dow Jones tumbled by this much. Crashes this big tend to happen when the market is massively overvalued, and on that front this crash is no different.
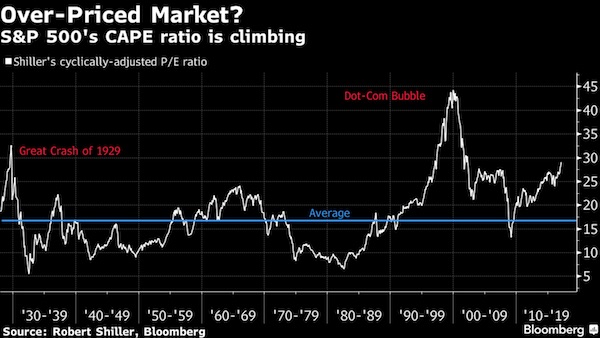
It’s like a long-overdue earthquake. Though everyone from Donald Trump down (or should that be “up”?) had regarded Monday’s level and the previous day’s tranquillity as normal, these were in fact the truly unprecedented events. In particular, the ratio of stock prices to corporate earnings is almost higher than it has ever been. There is only one time that it’s been higher: during the DotCom Bubble, when Robert Shiller’s “cyclically adjusted price to earnings” ratio hit the all-time record of 44 to one. That means that the average price of a share on the S&P500 was 44 times the average earnings per share over the previous 10 years (Shiller uses this long time-lag to minimize the effect of Ponzi Scheme firms like Enron).
The S&P500 fell more than 11% that day, so Monday’s fall is minor by comparison. And the market remains seriously overvalued: even if shares fell by 50% from today’s level, they’d still be twice as expensive as they have been, on average, for the last 140 years. After the 2000 crash, standard market dynamics led to stocks falling by 50% over the following two years, until the rise of the Subprime Bubble pushed them up about 25% (from 22 times earnings to 28 times). Then the Subprime Bubble burst in 2007, and shares fell another 50%, from 28 times earnings to 14 times. This was when central banks thought The End of the World Is Nigh, and that they’d be blamed for it. But in fact, when the market bottomed in early 2009, it was only just below the pre-1990 average of 14.5 times earnings.

Give it a few days, and complacency may well be reinstated.
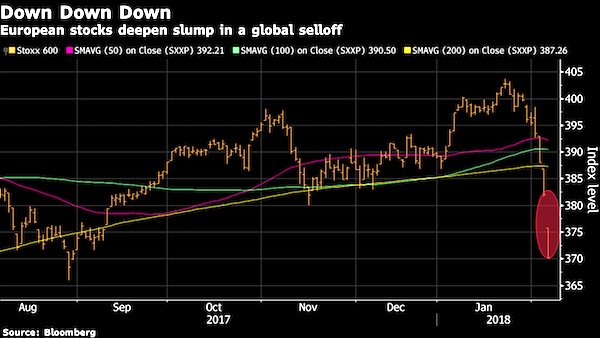
• Asian Shares On Edge As US Futures Slip (R.)
Asian shares reversed their earlier gains on Wednesday as investors dumped U.S. stock futures for safer harbors, a sign market participants remain jittery after this week’s global markets rout. While most analysts believed this week’s distressed selling looks to have run its course for the moment, allowing volatility to abate a little, the prospect of monetary tightening across the globe remains a challenge for the long term. “If we look at some of the drivers of the recent volatility – the natural correction and the bond sell-off – we don’t foresee any of these factors contributing to a lengthy period of extreme volatility,” said Tom Kenny, senior economist at ANZ. “The correction is probably a healthy development and is not reflective of a souring of the macroeconomic outlook.”
Investors took their cues from a late rebound on Wall Street overnight, though many had an anxious eye on E-Mini futures for the S&P 500 which slipped about 1% in late Asian trading. Dow Minis were down 0.9%. MSCI’s broadest index of Asia-Pacific shares outside Japan was a tad softer, having risen as much as 2% in early trade. Japan’s Nikkei eased too but was still up 0.2%. Chinese blue chips and South Korea’s KOSPI index dropped more than 2%. “The only surprise about the current volatility is that it hasn’t happened sooner. Normally, even in a bull market, investors should expect a sell-off of 10-percent-plus at some point,” said Richard Titherington, chief investment officer of EM Asia Pacific Equities. “While a major market downturn is possible, it is not our current expectation. The underlying backdrop of an improving global economy, a weakening U.S. dollar and a pickup in global earnings all remain supportive factors.”

Why have these things ever been allowed into existence? Who and what do they serve? The American people?
• Two Tiny Volatility Products Helped Fuel Sudden Stock Slump (BBG)
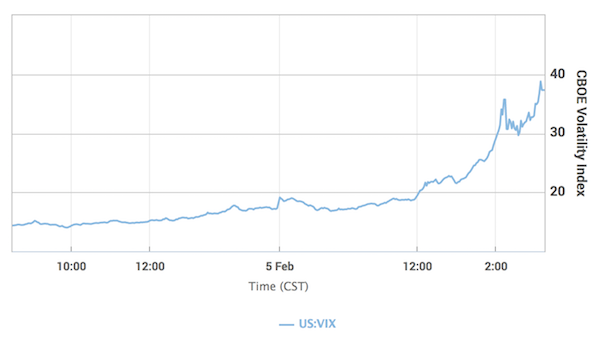
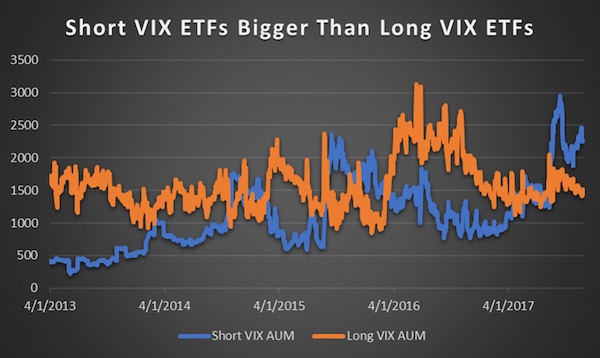
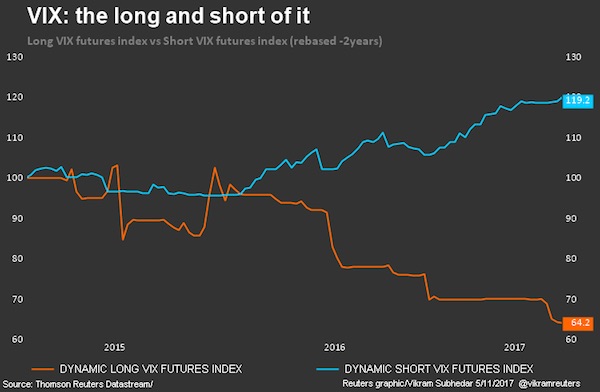
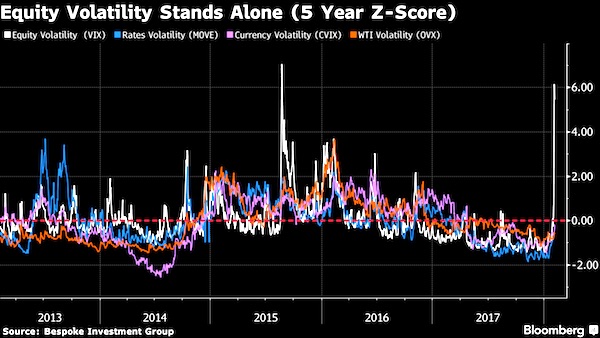
Two days after a sudden spike in volatility sparked a stock-market crash, market participants are left to ponder the wreckage of the sell-off and the mysterious dynamics that caused it. One theory that’s emerging: the curious case of the tail wagging the dog. Two exchange-traded products that democratized access to one of Wall Street’s most tried-and-true strategies – selling volatility – had just $3.6 billion in assets on Monday. That’s a tiny fraction of the roughly $2 trillion estimated to be linked to short-volatility strategies – and a speck of dust compared to the $23 trillion in market value of S&P 500 companies. Yet the popularity of these vehicles might have contributed to one of the most violent moves in U.S. equities in history: one that saw the Dow Jones Industrial Average slump more than 6% in a span of six minutes.
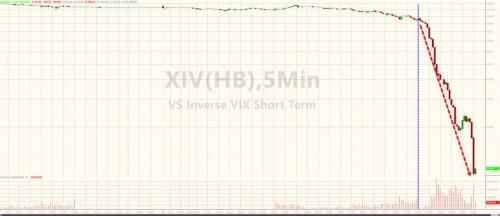
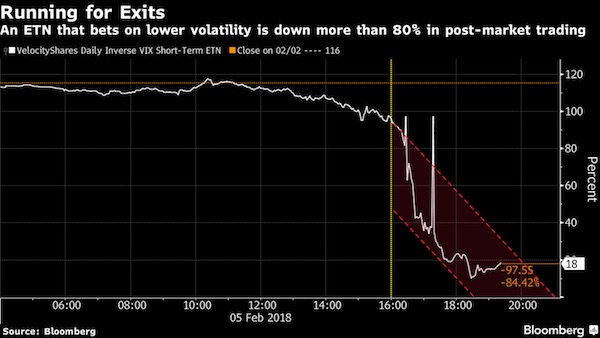
After the dust settled, the combined assets in the two exchange-traded products shrank to $135 million. One of them – the VelocityShares Daily Inverse VIX Short-Term ETN, known as XIV – will soon be extinct. No one knows for sure what played out on the afternoon of Feb. 5 on Wall Street, cautioned Societe Generale SA managing director Ramon Verastegui, but there’s reason to believe the sharpness of the retreat in equities was linked to traders’ understanding of how the exchange-traded products would behave. As funds’ assets swelled, so too had their power to move the underlying VIX futures markets, he suggests. And market participants knew it. Products such as XIV and its close relation, the ProShares Short VIX Short-Term Futures ETF (SVXY), aim to offer investors exposure to the inverse of the daily moves at the front portion of the VIX futures curve, and typically benefit from market tranquility.
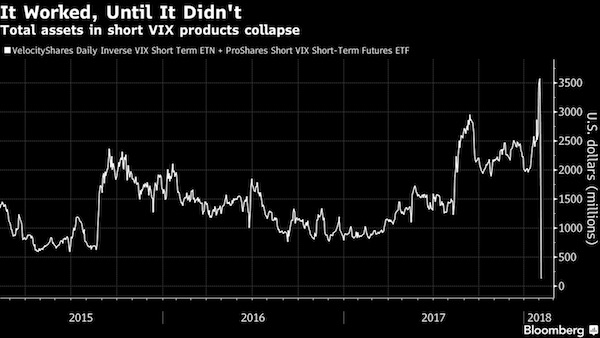
Demand from leveraged VIX exchanged-traded products was “the major driver for the move post the cash close,” Barclays analysts led by Maneesh Deshpande said. There are other clues in the case — notably that the big fall in stocks hasn’t yet significantly affected other asset classes. That the volatility spike was concentrated in equities supports the notion of a VIX product-propelled plunge, according to George Pearkes, macro strategist at Bespoke Investment Group. During other eruptions of volatility — the aftermath of China’s shock devaluation of the yuan in August 2015, for instance – volatility in stocks, bonds, currencies and even oil jumped. “This is the exact opposite of a number of different volatility spikes we’ve seen in recent years,” he said in an interview on Bloomberg TV. “Frankly, it’s a reason to think that some of the worst of the recent moves in the VIX and the delta moves in cash equities have been driven specifically by equity-vol products that have not spread out to other asset classes.”

If it were just $8 billion, we wouldn’t be having this talk.
• Inside Wall Street’s $8 Billion VIX Time Bomb
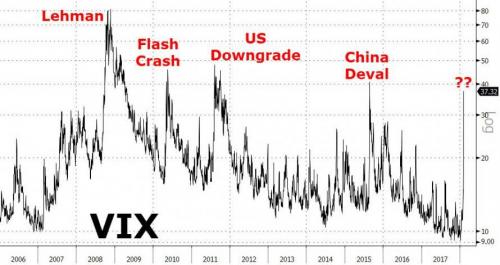
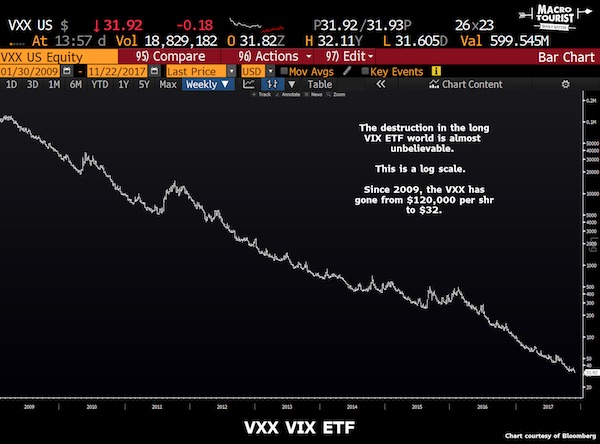
It was the hot trade on Wall Street, a seemingly sure thing that lulled everyone from hedge fund managers to small-time investors. Now newfangled investments linked to volatility in the stock market – until a few years ago, obscure niche products – have exploded in spectacular fashion. The shock waves have only just begun. How these investments proliferated is a classic story of Wall Street salesmanship and old-fashioned greed. In a few short years, financial engineering transformed expectations about the ups and downs of the stock market into an asset class that could be marketed and sold – as tradable as stocks but, it turns out, sometimes far riskier. Call it the volatility-financial complex. All told, financial players have created more than $8 billion of products tied to one index alone.
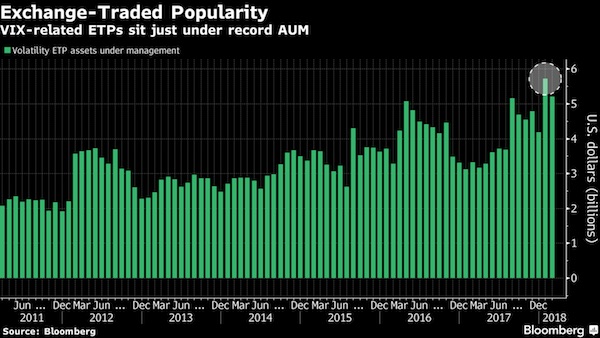
In a low-interest-rate world, investors desperate for returns snapped them up, and bankers collected fees along the way. But, as with mortgage investments a decade ago, complacency – in this case, over a history-defying period of market calm – masked potential dangers. No one is saying the wild swings of late presage a broad collapse like the one that hit in 2008. But the fallout nonetheless provides a glimpse into the myriad products, and growing complexity, driving global markets a decade after the last debacle. The risks, in hindsight, were clear enough even before the Dow Jones industrial average plummeted nearly 1,600 points on Monday, snapped back, and then took a wild bungee jump of nearly 1,200 points Tuesday. The CEO of Barclays, which pioneered notes linked to U.S. market volatility, warned only last month that investors might be losing their heads.
“If this thing turns, hold on to your hat,” Jes Staley told a panel at the World Economic Forum in Davos. Now, hats have been blown off by a whirlwind the likes of which Wall Street has never seen. To some, the volatility complex feels like a monster that’s been lurking in the shadows. Even one of the inventors of the VIX, Devesh Shah, is perplexed why these products exist in the first place. “Everybody knew that this was a huge problem,” said Shah, who was in his 20s when he helped create what’s become the market’s fear barometer. “Everybody knows that Inverse VIX is going to go to zero at some point, and all these inverse and leveraged products, not just in the VIX but elsewhere too, at the end of the day cost people a lot of money.”

VIX as CDOs with lipstick on.
• The Death Of The “Death Of Contagion” Central Bank Meme (Luongo)
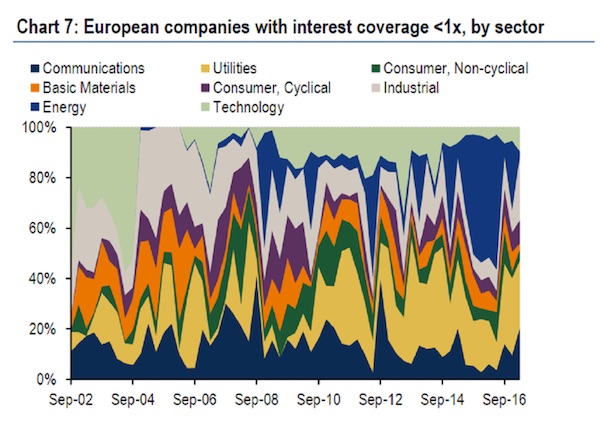
Last year now-former FOMC Chair Janet Yellen downplayed the possibility of another financial crisis. In her hubris she believes the central banks have walled off the financial system from ‘contagion risks’ brought on by over-investment in synthetic derivative market products. Like generals, however, central planners are always fighting the last war. We’re experiencing a major correction in the equity markets brought on in a mean-reversion exercise thanks to central banks trying to shore up their defenses around the last battle they lost, namely off-exchange, unregulated CDOs — synthetic debt-based investment products. Humans are clever and will always find a way around a problem. The problem is incentives. he banks created CDO’s because there was a demand for investment returns far above what the central banks were allowing the market to pay, by setting interest rates well below the real risk profile of the investment community.
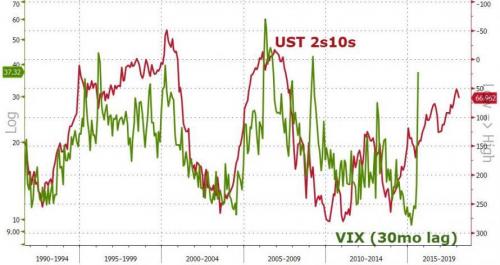
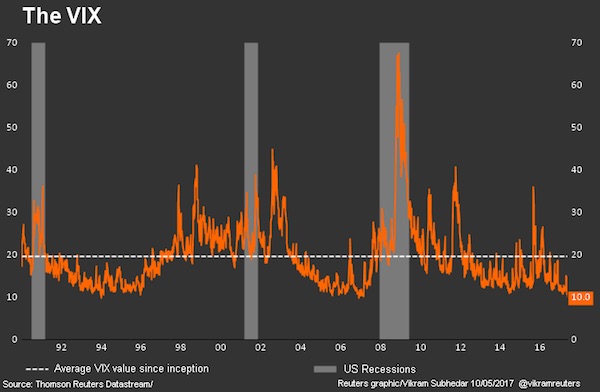
In other words, government bonds were over-priced and investors went looking for better returns. Now that Yellen et.al. have stamped out most of that market investors still need yield. And that’s where the equity markets and the VIX come in. The response to the 2008 financial crisis was zero-bound interest rates and trillions in liquidity created by the central banks sitting around looking for yield. It found its way into the equity markets which over the past six plus years been on an historic rally off the October 2011 low. During that time the VIX became more important. What was once only discussed by the real pros was now in the hands of everyone. Contagion risks jumped asset classes. For the uninitiated the VIX — or volatilty index — is a bet about the behavior of the S&P 500, itself an index of stocks. Higher VIX values equal higher implied future volatility in the S&P 500 and vice versa.
In mathematical terms the S&P 500 is the first derivative of any single stock. Stocks in the index trade in sympathy with it regardless of their current business. The VIX is then the 2nd derivative of any stock in your portfolio. During a rally the VIX falls. But, now with so many products out there, ETNs — Exchange Traded Notes — both leveraged and un-leveraged — to speculate in the VIX it became easier and more profitable to trade it than the S&P 500 or individual stocks. Trading volumes in these products have soared. The tail didn’t just wag the dog, it became the dog. Now these ETN’s are another derivative of the equity markets. And if they are leveraged, i.e. the note trades with twice or three times the volatility of the VIX itself (volatility of volatility), then options on these ETNs is the fourth derivative of the underlying stock. Volatilty of volatility of volatility.

No doubt there.
• Icahn: “One Day This Thing Is Just Going To Implode” (CNBC)
Billionaire Carl Icahn told CNBC on Tuesday there are too many exotic, leveraged products for investors to trade, and one day these securities are going to blow up the market. The market is a “casino on steroids” with all these exchange-traded funds and exchange-traded notes, he said. These funds, especially the leveraged ones, are the “fault lines” that will eventually lead to an earthquake on Wall Street, he said. “These are just the beginnings of a rumbling.” The latest example is an obscure security, designed to be a bet on a calm market, that’s being blamed for causing an influx of selling in recent days. The VelocityShares Daily Inverse VIX Short-Term exchange-traded note (XIV) blew up overnight as investors were forced to sell when the market went haywire. As a result, Credit Suisse on Tuesday said as of Feb. 20, it will end trading for its XIV, which was supposed to give the opposite return of the Cboe Volatility Index (VIX), often referred to as the market’s fear gauge.
“The market itself is way over-leveraged,” Icahn said on “Fast Money Halftime Report,” predicting that “one day this thing is just going to implode.” He described the possible implosion as “maybe eventually worse than 1929,” making reference to the stock market crash that contributed to the Great Depression. “The market has become a much more dangerous place,” he said, adding the current volatility is a precursor of potential trouble. “It’s telling you something, giving you a warning.” Investors are piling into index funds thinking they’ll never go down, Icahn said. “Passive investing is the bubble right now, and that’s a great danger.” But as much as he was sounding alarm bells, Icahn said, “I don’t think this is the explosive time.” The market will “probably bounce back,” he continued. “I don’t think this is the beginning of the end.”

I read far too much praise for Yellen. Stockman doesn’t swallow it either.
• Good Riddance, Janet, You Were A Colossal Failure, Part 1 (Stockman)
This is one for the record books. During Janet Yellen’s last week in office, the Dow dropped by 1,095 points or 4.1%. But by her lights, apparently, that wasn’t even a warning bell – just the market clearing its collective throat. So on the way out the door our Keynesian school marm could not resist delivering what will soon be seen as a grand self-indictment. There’s nothing to worry about, she averred, because Wall Street’s OK and main street is positively awesome: “I don’t want to label what we’re seeing as a bubble….(even if) asset valuations are generally elevated….(but) when I see the unemployment rate fall to 4.1%…I feel very good about the progress we’ve seen there.” No, there is a monumental bubble out there that was born, bred and nurtured at the hands of the Fed.
At the same time, Yellen and her merry band of money printers had virtually nothing to do with the 4.1% unemployment rate – even if that were a valid measure of return to full employment prosperity, which it is not. To the contrary, the mainstreet economy is sick as a dog, and it is the Fed’s giant Wall Street bubbles which made it so. That said, hereupon follows the ringing economic and financial indictment that Janet Yellen so richly deserves. In the first place, that Fed’s dangerous digression into massive QE and 100 months of near-ZIRP had virtually nothing to do with the limpid “recovery” that has transpired since the June 2009 bottom. And we do mean its contribution amounted to nothing – as in zero, zip and zilch.
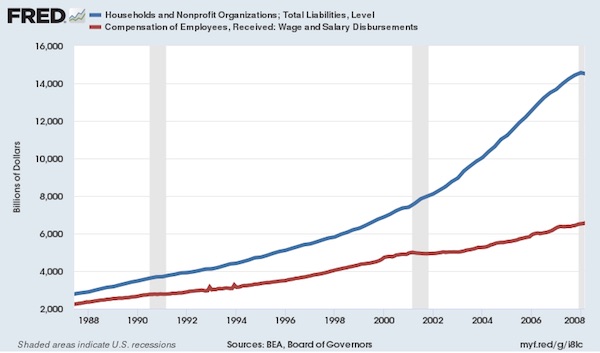
[..] In general, our thesis is that central bank stimulus of household spending is equivalent to a one trick pony. Once all the latent headroom on household balance sheets and income statements to raise leverage levels is used up, cheap debt loses its efficacy in the main street economy. In fact, that is exactly what has happened. During the first 20-years of the Greenspan-incepted era of Bubble Finance, household leverage ratios exploded. Whereas wage and salary incomes rose by $4.2 trillion or 2.9X, household liabilities soared by nearly $12 trillion or 5.2X. Over the two decades, therefore, household leverage ratios (liabilities to earned income) nearly doubled from 124% to 224%.

Yellen has been a terribly destructive force for America. It’s just that the consequences take time to seep through.
• How “Opioid Janet” Got Wall Street Hooked On Monetary Heroin, Part 2 (Stockman)
Janet Yellen deserves exactly none of the adulation being conferred upon her tenure by the mainstream financial press. In fact, her reign will be judged by history as a spectacular failure that left main street high and dry—even as it finally and completely addicted Wall Street to the toxic monetary heroin that is the specialty of Keynesian central bankers. Accordingly, it may take a dozen or more episodes like the 12% crash of the last few days to finally purge the “buy the dips” addiction that is rampant in the casinos. Pending that day of deliverance, however, the soon-to-be shaking and shivering cold turkeys of Wall Street will surely come to see that Opioid Janet was not their friend at all, but their very worst nightmare.
[..] much of the mischief, madness and reckless speculation now implanted in the global financial markets happened during the Yellen-enabled global QE phase of 2014-2018. During that period, for example, corporate debt issuance set all-time records. But as we documented in Part 1, the proceeds went into financial engineering and bidding up the price of existing shares to ludicrous heights, not new growth capital. Likewise, carry trade speculation by front-runners went to mindless extremes, such as the fact that the Italian 10-year note traded under 1.0% during points in 2016. The facts that Italy’s public debt stood at 133% of GDP, that its political system was completely broken and dysfunctional and that its economy was 10% smaller than it had been earlier in this century were irrelevant to the price of its debt.
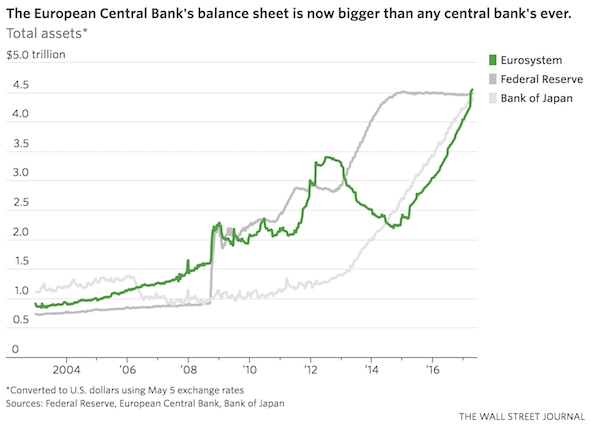
The latter was being set by front-running speculators who were buying on massive repo leverage what the idiot central banker, Mario Draghi, promised them he would be buying, too. Indeed, as Yellen dithered, deferred, ducked and delayed the urgent imperative of monetary normalization at the Fed, the other lesser central banks were given leave to expand their collective balance sheets at a stupendous $2.2 trillion annual rate during much of 2016-2017. With two massive central bank vaults swinging their doors wide open, it’s no wonder that upwards of $15 trillion of sovereign debt traded with a negative yield during the peak of the madness.
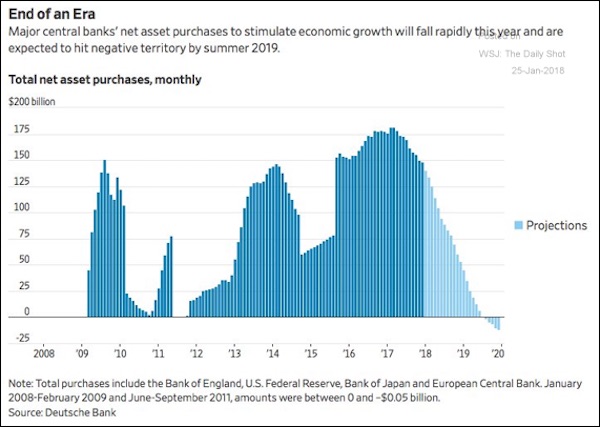
And that wasn’t the half of it. By killing the yield on sovereigns, Yellen and her convoy of Keynesian central bankers forced money managers into what will soon be evident as crazy-ass risk taking in order to scrape-up a semblance of yield. Not only did European junk bonds trade inside the UST 10-year yield at one point, but the corporate bond market was literally primed for an explosion of issuance by fund managers desperate for returns. The proceeds, of course, went almost entirely into funding giant, pointless M&A deals, stock buybacks and other forms of debt-financed recapitalization.

“Workers” and “working classes” is the language of the 1850s. It‘s not going to get you anywhere today.
• The EU Is The Enemy Of The Working Classes (Spiked)
here are two European Unions, it seems. There is the EU that stands up for the citizen, for his or her rights; the EU that can face down the behemoths of global capitalism and rein in their avarice and callousness; the EU that has legally enshrined workers’ freedoms, and which exists as a bulwark against untrammelled neoliberalism. And then there is the real EU. That heroic EU is a castle in the anti-Brexit sky, built by those who identify themselves as left-wing. It is maintained by those Labour MPs and peers who, as they did on the eve of Labour’s autumn conference, ceaselessly urge Labour leader Jeremy Corybn ‘to commit to staying in the Single Market and Customs Union… and to work with sister parties and others across Europe to improve workers’ rights’.
It is fortified by the self-appointed keepers of the left-wing flame, those among the commentariat who never tire of telling us that ‘workers’ rights… would be imperilled’ by a so-called ‘Hard Brexit’. And it is peopled by all those who cling to this image of the EU as an essentially social-democratic institution, sticking it gently to the man, defying the Daily Mail, and protecting working men and women against the inhuman workings of capital. Then there’s the other EU, the one that actually exists. This is the EU that uses the pooled-without-consent sovereignty of its member states to pursue its own institutional self-preservation, impoverishing struggling Eurozone members, from Spain to Italy, in the name of economic stability; imposing leaders-cum-administrators on recalcitrant electorates in the interests of austerity; and brazenly betraying workers’ rights at every self-interested turn.
This EU – the actual EU, the one stubbornly committed to its own, not citizens’, interests – is not on the side of the worker. And it never was. Because this EU, when the economic imperative demands, is always against the worker. But those attached to their fantasy left-wing ideal of the EU refuse to see the reality. To face up to this reality would simply be too much. It would mock their left-wing pretensions, humiliate and expose them for what they are: a craven defence of the status quo – a status quo in which they have long prospered. This is presumably why so little attention has been given to what happened in Greece last month, when the real EU was there for all to see. The EU forced the Syriza-led government of Alex Tsipras to implement new anti-union legislation, rendering strike action illegal unless over 50% of union members have formally approved it. The effect of such a measure, as the British trade-union movement discovered in the 1980s, will be to strangle workers’ freedoms in bureaucracy, and emasculate organised labour.

The country with the most political power in the EU already has the richest citizens. And they stand to get richer. Those is Spain, Italy, Greece: not so much. Two-tier Europe is here.
• German Pay Deal Heralds End Of Wage Restraint In Europe’s Largest Economy (R.)
A hard-fought deal on pay and working hours for industrial employees in southwestern Germany sets a benchmark for millions of workers across Europe’s largest economy and heralds wage growth in the coming years. The agreement between labour union IG Metall and the Suedwestmetall employers’ federation, struck overnight, foresees a 4.3% pay raise from April and other payments spread over 27 months. Tough pay negotiations are expected to end years of wage restraint in Germany, potentially aiding the ECB as it tries to get euro zone inflation back up to the bank’s target rate of just below 2%. On an annual basis, the agreement is equivalent to a 3.5% increase in wages, according to Commerzbank analyst Eckart Tuchtfeld, well below IG Metall’s initial demand for a 6% hike over 12 months, but was still seen as a good deal.
“The agreed pay rises, and accompanying measures, are at the top end of expectations and should result in annual wage increases of close to 4% over the next couple of years,” Pictet economist Frederik Ducrozet said. The “pilot” deal, struck against a backdrop of a strong economic recovery and the lowest unemployment since German unification in 1990, covers half a million employees in southwestern Germany, home to industrial powerhouses like car maker Daimler. It is expected to be applied in the rest of Germany as well and is likely to influence negotiations in other industries.
Germany’s second-biggest union, Verdi, is due to publish its wage demand for public sector workers on Thursday. Verdi and IG Metall together account for about 15% of the German workforce. IG Metall’s deal will reinforce market expectations for the ECB to dial back stimulus further this year as growth in the bloc is now self generating and wages are moving slowly upwards. It comes as world stock and bond markets are selling off on fears that a jobs bonanza in the United States may force early interest rate hikes there. But the euro zone outlook is much different with the jobless rate still at almost 9% and the broader slack, which includes part-time and temporary workers, perhaps twice as high, economists say.

Farmers say they can’t get people to harvest their crops. Question: have you tried raising their wages enough? Something tells us if you pay them well, they will be glad to come work. Something also tells us you haven’t done that. You may say: that makes my products uncompetitive, but that’s another discussion altogether.
Also: the article says “Enough broccoli to feed 15,000 people for a year was wasted..” on that farm. And: the farmer’s loss was “between £30,000 and £50,000.” Does that mean he can feed people for £2 a year? £3? It certainly reads that way.
• UK Crops Left To Rot After Drop In EU Farm Workers In Britain (Ind.)
British farmers have been forced to leave thousands of pounds worth of vegetables to rot in their fields, because of a drop in the number of farm workers from the EU. James Orr, whose farm outside St Andrews produces potatoes, carrots, parsnips, broccoli, cauliflower, said his farm suffered a 15% drop in the number of workers between August and November. “We simply could not harvest everything, and as a result we left produce in the field to rot,” he told Scotland’s Sunday Herald newspaper. Enough broccoli to feed 15,000 people for a year was wasted, he added. Mr Orr’s farm supplies more than 1,000 tones of the vegetable and he estimated he lost between £30,000 and £50,000.
The UK farming industry is heavily dependent on pickers from the EU, particularly those from eastern Europe. Britain’s low unemployment rate and the the seasonal nature of the work makes it difficult to attract domestic workers. But the fall in the value of sterling against the Euro since the Brexit vote, means the UK has become less attractive to seasonal workers from Romania and Bulgaria. Farmers also fear that a Brexit deal restricting freedom of movement could leave them with even fewer people to help harvest their crops. [..] NFU Scotland President Andrew Mr McCornick told the Herald access to workers was a key priority for the industry. “This year, there has been a shortage of between 10 and 20% of seasonal workers coming from the EU,” he said. It was essential a scheme was introduced in 2018 that would provide work permits for up to 20,000 workers from outside the EU, he added.

Mouzalas says: “Whoever says that emptying the islands will improve the situation is wrong..” That doesn’t seem an honest assessement, because it would certainly improve the situation on the islands.
• Refugee Arrivals Have Doubled Since August, Greek Migration Minister Says (K.)
Migrant and refugee arrivals onto Greek shores have doubled since August 20 to reach as many as 180 people a day in clement weather, Migration Policy Minister Yiannis Mouzalas said on Tuesday. The increase in arrivals from Turkey has resulted “in a bad situation again” on the islands of the eastern Aegean that host migrant reception and processing centers, Mouzalas admitted, saying that the ministry is trying to improve conditions at overcrowded and under-resourced facilities. Speaking on Thema radio, Mouzalas accused the European Union of contributing to the problem by failing to honor its commitments to Turkey in a deal for that country to take back asylum seekers whose applications are rejected and to crack down on migrant trafficking from its shores.
Mouzalas was also critical of what he described as contradictory reactions from local authorities and communities on the affected islands. “On the one hand, they prevent moves to improve conditions and on the other they are hysterical about dissolving the deal with Turkey at any cost so as to transfer the migrants to the mainland,” Mouzalas said, referring to reactions toward ministry plans for increasing the number of housing units at certain island camps. “Whoever says that emptying the islands will improve the situation is wrong,” Mouzalas said, reiterating concerns that moving all migrants and refugees to the mainland will simply encourage more arrivals. “In 2017, we transferred 27,000 people to the mainland and 19,000 arrived on the islands,” he added.