Marion Post Wolcott Main Street. Sheridan, Wyoming 1941

Government blows bubble. Rinse and repeat.
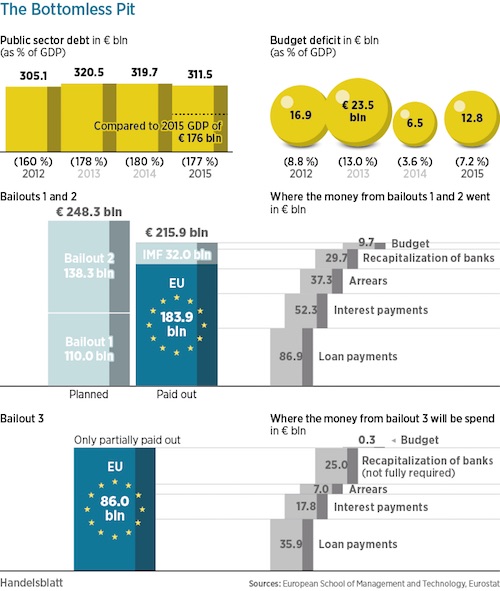
• Beijing’s Property Sales Surge 65% In 2015 (R.)
Property sales in Beijing rose 64.8% in 2015, boosted by more favorable housing policies, according to a real estate white paper released by the city’s government. Increased government stimulus sparked a sharp reversal in the market after sales volumes fell 30% in 2014, the white paper said. The benchmark interest rate for housing loans also dropped to its lower level in almost a decade, after several interest rate cuts, the paper noted. “The country’s housing credit and tax policies have been at their most favorable levels in recent years,” the paper said.
The number of newly-built commercial homes and existing stock sold in Beijing increased 26% and 90.7% respectively year-on-year in 2015, according to the paper published by Beijing Municipal Commission of Housing and Urban-Rural Development. China reported slightly stronger-than-expected economic growth in the second quarter as the housing boom and a government infrastructure building spree boosted demand for materials from cement to steel. But recent data has also indicated that property investment growth is cooling. Some of the country’s biggest cities have had to impose curbs on property purchases as sharp price rises raise fears of possible asset bubbles.

This bubble is popping, though.
• How a Chinese Highway Became a Boulevard of Broken Dreams (WSJ)
A highway project here that is four years behind schedule and hundreds of millions of dollars over budget helps explain why Beijing s effort to raise infrastructure spending is an increasingly ineffective way to boost the economy. When construction on the Chang An Expressway began in 2008 it seemed a sure bet. Its private partners stood to collect decades of lucrative toll revenue. The economy and the environment would benefit by slashing three hours off a four-hour trip. But the project, in central Hunan province, has been beset by financial problems, resident protests and a corruption probe, issues that also have hindered hundreds of other projects in China.
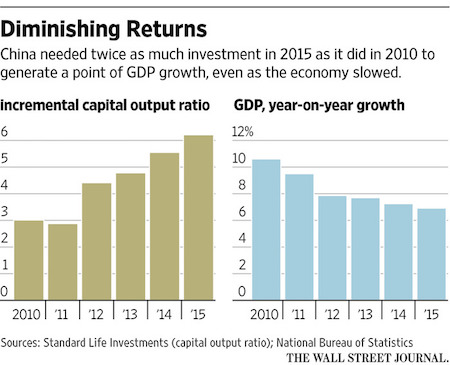
Such setbacks are hurting Beijing s efforts to halt a decline in economic growth that is rippling across the globe and threatening political stability at home. China also is drawing less benefit from the infrastructure projects it completes. After a 15-year period in which the country built thousands of roads, airports, bridges and buildings, the economic benefit of adding even more is decidedly less valuable. Local governments’ heavy debt loads from prior stimulus efforts are further obstructing China’s efforts to stimulate the economy with infrastructure spending. More of their borrowed money is going to pay back previous loans. Many of these projects lose money, adding still more debt.
The upshot: China needed twice as much investment per unit of growth in 2015 as it did in 2010, official data show. This hasn’t stopped Beijing from doubling down on infrastructure spending as exports, manufacturing and other growth engines sputter. The government plans to spend $749 billion on transport projects over the next three years, compared with $171 billion worth built last year.

Crackdown? Only in name. China is addicted to the shadows.
• China Shadow Banking Assets Grew 30% In 2015 (R.)
Shadow banking activity in China has expanded further and now accounts for nearly a third of the total banking sector assets, raising financial risks in the world’s second-largest economy, rating agency Moody’s Investor Service said on Wednesday. Shadow banking assets in China increased by 30% last year, reaching almost 54 trillion yuan (6.17 trillion pounds), according to Moody’s estimates. That is equivalent to about 78% of China’s total economic output and 27.6% of its banking assets. In 2011, shadow banking products accounted for 17.2% of total banking assets, and the share grew to 24.3% in 2014. China’s crackdown on risky practices in the thinly regulated shadow banking system has taken on fresh urgency amid a growing number of corporate defaults, and as policymakers appear worried about the risks of relying on too much debt-fuelled stimulus.
Despite this, shadow banking’s share in bank loans and total bank assets has expanded rapidly, as sectors and firms reeling from overcapacity and poor credit profiles turn to other sources of funding, and investors hunt for higher yields. “The rise in overall leverage and further expansion of shadow banking activity are pushing up financial risks,” said the Moody’s report, adding the growth highlights “spillover risks” to the financial system due to its interconnectedness. Years of breakneck growth for China’s top insurers have been partly fuelled by a splurge on shadow banking-linked products that could punch multi-billion-dollar holes in their balance sheets, a Reuters analysis showed.
Mid-tier Chinese banks are also increasingly using complex instruments to make new loans and restructure existing loans that are then shown as low-risk investments on balance sheets, masking the scale and risks of the slowing economy. The takeover tussle embroiling top Chinese developer China Vanke has also showed how local banks are increasingly exposed to highly volatile domestic stock markets through shadow lending products. “The increasing size of the shadow banking system means that during a disorderly contraction, banks could have difficulty replacing shadow banking credit, leaving borrowers who rely on such financing at risk of a credit crunch,” Moody’s said.

Shadow banking comes in many different guises.
• An Auction House Learns the Art of Shadow Banking (BBG)
A year before he got caught up in a U.S. money-laundering investigation, Malaysian financier Jho Low was looking to borrow more than $100 million without having to answer all the nosy know-your-customer questions required by U.S. banks such as JPMorgan Chase. “Prefer the boutique banks that can move fast vs the large ones like JPM,” Low wrote on March 13, 2014, to an employee of a private art dealership that had sold him a painting by Claude Monet for $35 million a few months earlier. The lender “can take all the art no problems,” he wrote the next day. “All in Geneva free port. Speed is the most important and one with a fairly quick and relaxed kyc process.”
Low got his money a month later, not from a bank but from Sotheby’s, an auction house that isn’t subject to the same money-laundering scrutiny by regulators. He pledged 17 works of art, valued between $191.6 million and $258.3 million, to secure a $107 million loan, according to a U.S. Justice Department complaint filed July 20 in an effort to seize more than $1 billion of assets allegedly siphoned from a Malaysian state fund. As prices for art skyrocketed, Sotheby’s and other firms have become shadow banks, making millions of dollars of legal loans outside the regulated financial system and raising concerns that such financing could facilitate money laundering. Sotheby’s tripled lending to $682 million over the four years ended in 2015.
Last year it almost doubled, to $1 billion, a revolving credit facility provided by banks including JPMorgan and HSBC that it can use to make loans. “One way to launder is to use art as a security for a loan,” said David Hall, who spent 10 years as a special prosecutor for the Federal Bureau of Investigation’s Art Crime Team and is now a partner at law firm Wiggin & Dana. Hall, who wouldn’t comment about Sotheby’s or the Low case, said the aim is to use ill-gotten funds to purchase assets that can be used as collateral for a loan. “The level of scrutiny you’ll receive from a bank is much higher than you will receive from an auction house.”

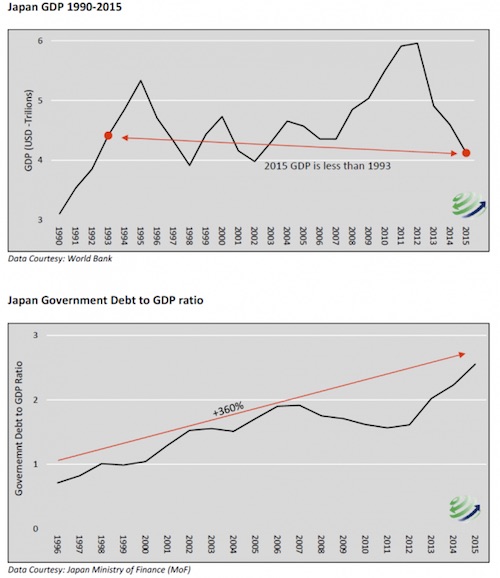
It’s everybody’s real problem, but even more so for Japan.
• Japan’s Real Problem Is Too Much Debt (720G)
The Japanese economy has been the poster child for economic malaise and bad fortune for so long that even the most radical policy responses no longer garner much attention. In fact, recent policy actions intended to weaken the Yen have resulted in significant appreciation of the yen against the currencies of Japan’s major trade partners, further crippling economic activity. The frustration of an appreciating currency coupled with deflation and zero economic growth has produced signs that what Japan has in store for the world falls squarely in to the category of “you ain’t seen nothin’ yet.” Assuming new fiscal and monetary policies will be similar to those enacted in the past is a big risk that should be contemplated by investors.
The Japanese economy has been fighting weak growth and deflationary forces for over 25 years. Japan’s equity market and real estate bubbles burst in the first week of 1990, presaging deflation and stagnant economic growth ever since. Despite countless monetary and fiscal efforts to combat these economic ailments, nothing seems to work. Any economist worth his salt has multiple reasons for the depth and breadth of these issues but very few get to the heart of the problem. The typical analysis suggests that weak growth in Japan is primarily being caused by weak demand. Over the last 25 years, insufficient demand, or a lack of consumption, has been addressed by increasingly incentivizing the population and the government to consume more by taking on additional debt.
That incentive is produced via lower interest rates. If demand really is the problem, however, then some version of these policies should have worked, but to date they have not. If the real problem, however, is too much debt, which at 255% of Japan’s GDP seems a reasonable assumption to us, then the misdiagnoses and resulting ill-designed policy response leads to even slower growth, more persistent deflationary pressures and exacerbates the original problem.

Not much choice.
• Can the World Deal With a New Bank Crisis? (Satyajit Das)
As Europe braces for the release of its bank stress tests on Friday, the world could be on the verge of another banking crisis. The signs are obvious to all. The World Bank estimates the ratio of non-performing loans to total gross loans in 2015 reached 4.3%. Before the 2009 global financial crisis, they stood at 4.2%. If anything, the problem is starker now than then: There are more than $3 trillion in stressed loan assets worldwide, compared to the roughly $1 trillion of U.S. subprime loans that triggered the 2009 crisis. European banks are saddled with $1.3 trillion in non-performing loans, nearly $400 billion of them in Italy. The IMF estimates that risky loans in China also total $1.3 trillion, although private forecasts are higher. India’s stressed loans top $150 billion.
Once again, banks in the US, Canada, UK, several European countries, Asia, Australia and New Zealand are heavily exposed to property markets, which are overvalued by historical measures. In addition, banks have significant exposure to the troubled resource sector: Lending to the energy sector alone totals around $3 trillion globally. Borrowers are struggling to service that debt in an environment of falling commodity prices, weak growth, overcapacity, rising borrowing costs and (in some cases) a weaker currency. To make matters worse, the world’s limp recovery since 2009 is intensifying loan stresses. In advanced economies, low growth and disinflation or deflation is making it harder for companies to pay off what they owe. Many European firms are suffering from a lack of global competitiveness, exacerbated by the effects of the single currency.

Greece should sue him over this.
• Wolfgang Schäuble Bails Out Spain, Portugal (Pol.)
Ahead of Wednesday’s meeting of the EU’s 27 commissioners, Spain and Portugal looked to be headed for the eurozone’s version of politically embarrassing fiscal purgatory. There was no question that the Iberian duo’s budget deficits were in blatant breach of the single currency zone’s rules. Momentum was growing for the Commission to impose, for the first time ever, a fine totaling in the millions of euros. Even Jean-Claude Juncker, the Commission chief, had seemingly changed his previously skeptical views on sanctions, pushing his colleagues in recent weeks to enforce the rules and shore up Brussels’ credibility on eurozone governance. Then salvation arrived from an unlikely source: Wolfgang Schäuble.
The German finance minister, curmudgeonly fiscal hawk and scourge of spendthrift southern Europeans, broke with public type in a concerted, last-minute campaign to stop the sanctions, according to people familiar with his actions. Over the past weeks and days, Schäuble worked the phones and used personal encounters, pressing commissioners on the fence, mostly from his own center-right political block, to cancel the threatened fine. The behind-the-scenes intervention was driven by political considerations particular to this moment that trumped Schäuble’s long-standing demands for the eurozone nations to keep their budgets in order and abide by commonly agreed rules.
[..] As the consensus grew against a fine, Juncker urged the participants to make clear to the outside world why Brussels ducked, once again, imposing sanctions on rule breakers. “We must not be more Catholic than the Pope, but please make it known that the Pope wanted a fine of zero,” Juncker said, speaking in French at the closed-door meeting, according to a source in the room.

And now Schäuble can save Italy too.
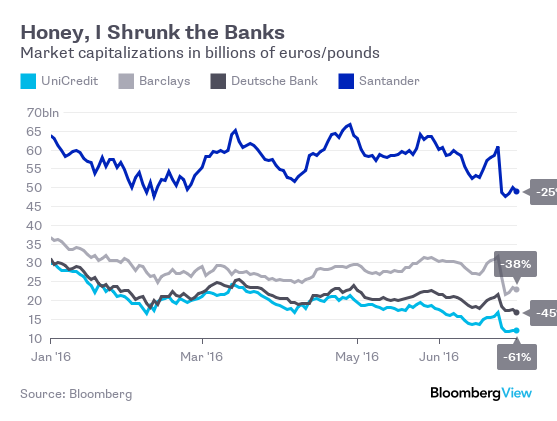
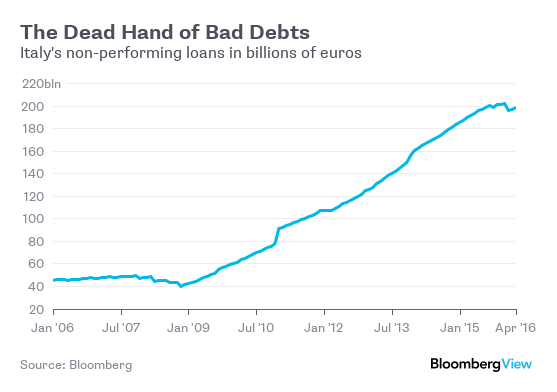
• Households on the Hook for Italy’s Next Bailout (BBG)
While the stability of Italy’s banks has been a front-burner issue for policy makers since the first tremors of the global financial crisis, the result of stress tests on Friday could usher in the final stage of solving their predicament. Retail investors own almost half of the most vulnerable securities, a legacy of banks using their customers as a piggy bank for cheap funding. UniCredit declined to comment on Imperatore’s recollection. The bank’s subordinated bonds available to retail investors trade close to par, indicating investors don’t expect to suffer losses. The bank is considering raising as much as €5 billion from shareholders and selling its entire stake in Poland’s Bank Pekao to raise capital, people familiar with the matter said on Wednesday.
At the zenith of the financial crisis, between July 2007 and June 2009, 80% of Italian banks’ bonds were sold to retail investors, according to regulator Consob. Through savers, banks funded themselves at a similar cost to the Italian government, whereas they gave professional money managers an extra%age point in debt interest, the 2010 report found. The channel of selling junior bonds to savers has virtually shut this year. So far in 2016, only one Italian bank, Mediobanca, has sold subordinated debt with an initial investment designed to attract small-scale investors – selling €200 million of junior bonds with a minimum denomination of €1,000. In the same period last year 10 banks sold €1.4 billion of notes with the same minimum subscription size.
Still, Italian savers held €31 billion of subordinated bank bonds as of October, more than double the €13 billion in the hands of foreign investors, according to the Bank of Italy. That translates to about €1,260 of the junior bank debt for every household in Italy. Banca Monte dei Paschi di Siena, which has more than €27 billion of toxic loans on its books and needs to be recapitalized, has about €5 billion of junior debt.

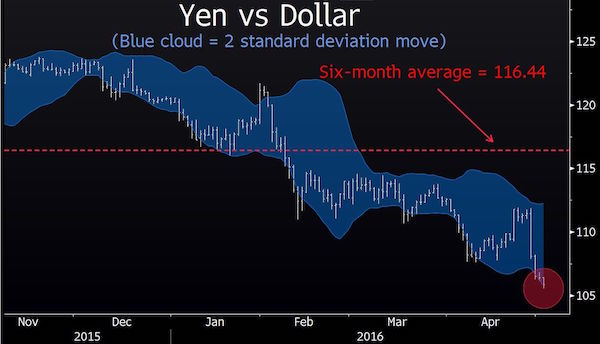
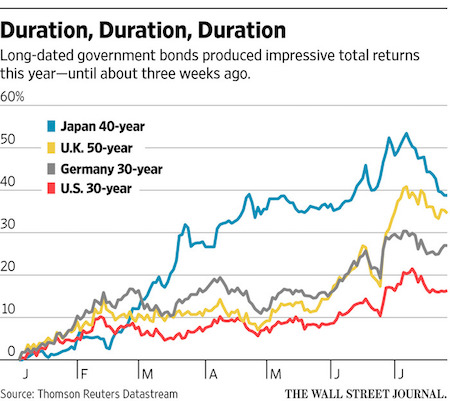
“..if yields merely rise back to where they started the year, it would be catastrophic for those who have chased longer duration. The 30-year Treasury would lose 14% of its value, while Japan’s 40-year would lose a quarter of its value..”
• Buying Longer Bonds Holds Danger (WSJ)
Investors in Japan’s 40-year bond have lost 24 years of coupon income in just three weeks as the rush into long-dated safe government paper went into sharp reverse. At one level, the 10% fall in the price of the longest-dated Japanese government bond is just a correction after this year’s extraordinary rally, which delivered returns of more than 50% before the pullback. At another, it highlights something dangerous at work in today’s markets: the scale of the risks investors are willing to take as they try to avoid anything that depends on economic growth. Japan’s bond selloff was worse than other markets’, as investors prepared for next week’s ¥28 trillion ($268 billion) spending and tax-cut package and a possible further Bank of Japan stimulus this Friday.
U.S., U.K. and German bond prices have also dropped since early July, though by less, as global demand weakened for long-duration assets. The demand for safe assets with a long duration—a proxy for how long it takes an investor to get his money back—was mirrored in stocks and corporate bonds. Rather than search out the highest-yielding assets, investors looked for those with secure yield, even if it was lower. So this year, triple-A-rated corporate bonds have outperformed double-A or single-A bonds, according to Barclays data. The same applied for junk bonds, with the higher ratings outperforming lower ones. (An exception was bonds close to or already in default, which were mainly energy companies and so were boosted by the rising oil price.)
[..] if yields merely rise back to where they started the year, it would be catastrophic for those who have chased longer duration. The 30-year Treasury would lose 14% of its value, while Japan’s 40-year would lose a quarter of its value, equal to 63 years of coupons. Has the long-run economic outlook really changed so much since January?

Excuse me? That post is already taken: “..The Clinton campaign shot back that Trump was posing a possible national security threat..”
• Trump Draws Ire After Urging Russia To Find ‘Missing’ Clinton Emails (R.)
Republican Donald Trump on Wednesday invited Russia to dig up tens of thousands of “missing” emails from Hillary Clinton’s time at the U.S. State Department, vexing intelligence experts and prompting Democrats to accuse him of urging foreigners to spy on Americans. “Russia, if you’re listening, I hope you’re able to find the 30,000 emails that are missing,” Trump, the Republican presidential nominee, told reporters. Trump made the remark at a testy news conference at his Doral golf resort in Florida that allowed him to steal some of the limelight from the Philadelphia convention where Clinton on Thursday will accept the Democratic presidential nomination for the Nov. 8 election.
The Clinton campaign shot back that Trump was posing a possible national security threat by encouraging a foreign power to conduct espionage in the United States. Some intelligence experts said the comments raised questions about Trump’s judgment. A spokesman for Trump, Jason Miller, tried to tamp down the storm of protest, saying Trump did not urge Russia to hack Clinton’s emails. Trump said on Twitter that if anyone had Clinton’s emails, “perhaps they should share them with the FBI!” The criticism of Trump’s comments reverberated at the Democratic National Convention where speakers brought up the episode to try to intensify Democratic support for Clinton, who is running neck and neck with Trump in the polls.
“Donald Trump today once again took Russia’s side. He asked the Russians to interfere in American politics,” longtime Clinton supporter and former CIA Director Leon Panetta said. “Donald Trump … is asking one of our adversaries to engage in hacking or intelligence efforts against the United States of America to affect the election.” Another speaker, retired U.S. Rear Admiral John Hutson, said of Trump: “This morning, he personally invited Russia to hack us. That’s not law and order, that’s criminal intent.”

You ain’t helping, Mikey…
• In Clash Of Billionaires, Bloomberg Calls Trump White House Race ‘A Con’ (R.)
New York media mogul Michael Bloomberg assailed fellow billionaire Donald Trump on Wednesday, calling his U.S. presidential race a “con” and ripping into his history of bankruptcies and lawsuits. “Trump says he wants to run the nation like he’s running his business? God help us,” Bloomberg told the Democratic National Convention in Philadelphia to roaring applause. “I’m a New Yorker and I know a con when I see one.” Formerly a Republican and now an independent, Bloomberg was for the most part greeted warmly by the audience in the Wells Fargo Center arena where he threw his support behind the Democrats’ presidential nominee, Hillary Clinton.
The owner of the Bloomberg media empire and a former New York City mayor, Bloomberg was an odd choice for a speaker at the Democratic conclave, where many party progressives have railed against the influence of billionaires in politics. “Let me thank all of you for welcoming an outsider here, to deliver what will be an unconventional convention speech,” he said when he took the stage, eliciting cheers. “I am not here as a member of any party. I am here for one reason: to explain why I believe it is imperative that we elect Hillary Clinton as the next president of the United States.” Bloomberg had considered running for the White House as an independent this year but dropped the idea in March, saying it could increase the chances Trump would win.
Bloomberg has known Trump casually for years and twice appeared on Trump’s reality TV show “The Apprentice.” But since Trump entered the race for president in June 2015, Bloomberg has taken issue with him, lashing out at his policies and fiery rhetoric, especially his call to ban Muslims from entering the country and his promise to wall off the Mexican border and deport millions of undocumented foreigners.

If they can get the FBI to stop, what good would the IRS be?
• IRS Launches Investigation Of Clinton Foundation (DC)
IRS Commissioner John Koskinen referred congressional charges of corrupt Clinton Foundation “pay-to-play” activities to his tax agency’s exempt operations office for investigation, The Daily Caller News Foundation has learned. The request to investigate the Bill, Hillary and Chelsea Clinton Foundation on charges of “public corruption” was made in a July 15 letter by 64 House Republicans to the IRS, FBI and Federal Trade Commission (FTC). They charged the foundation is “lawless.” The initiative is being led by Rep. Marsha Blackburn, a Tennessee Republican who serves as the vice chairwoman of the House Committee on Energy and Commerce, which oversees FTC. The FTC regulates public charities alongside the IRS.
The lawmakers charged the Clinton Foundation is a “lawless ‘pay-to-play’ enterprise that has been operating under a cloak of philanthropy for years and should be investigated.” Koskinen’s July 22 reply came only a week after the House Republicans contacted the tax agency. It arrived to their offices Monday, the first opening day of the Democratic National Convention in Philadelphia. “We have forwarded the information you have submitted to our Exempt Organizations Program in Dallas,” Koskinen told the Republicans. The Exempt Organization Program is the division of the IRS that regulates the operations of public foundations and charities.
It’s the same division that was led by former IRS official Lois Lerner when hundreds of conservative, evangelical and tea party non-profit applicants were illegally targeted and harassed by tax officials. Blackburn told TheDCNF she believes the IRS has a double standard because, “they would go after conservative groups and religious groups and organizations, but they wouldn’t be looking at the Clinton Foundation for years. It was as if they choose who they are going to audit and question. It’s not right.” Blackburn said she and her colleagues will “continue to push” for answers on the Clinton Foundation’s governing policies, including its insular board of directors. She said they also will examine conflicts of interest and “follow the money trail.”

No schools, no papers, no TV. How does that country run?
• Turkey Shuts Down 45 Newspapers, 16 TV Stations (AP)
Turkey’s state run news agency says close to 1,700 officers have been formally discharged from the military following the country’s failed coup. Anadolu Agency also says the government has decided to close down dozens of media organizations, including 45 newspapers and 16 television stations. The government says a U.S.-based Muslim cleric is behind the failed uprising by a faction within the military that led to some 290 deaths on July 15. Thousands have been detained for suspected links to the coup, including Calgary’s Davud Hanci, an imam for the Correctional Service Canada and the Alberta correctional services who went to Turkey with his family on July 7 to visit his ailing father.
Hanci was detained and accused of working for U.S.-based cleric Fethullah Gulen, who Turkey alleges orchestrated the failed July 15 military coup. Gulen has repeatedly denied the claims. Hanci’s friends and family say he is innocent and they fear for his safety. Tens of thousands in Turkey have also been purged from state institutions. Earlier, authorities issued warrants for the detention of 47 former executives or senior journalists of Turkey’s Zaman newspaper for alleged links to Gulen. Such detentions have raised concerns that people could be targeted simply for criticizing the government. The media watchdog Reporters Without Borders condemned Turkey’s purges of journalists, saying they have assumed “increasingly alarming proportions.”

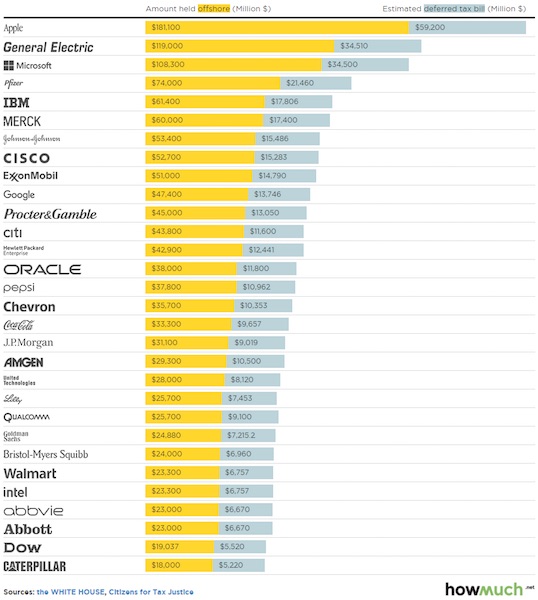
“Apple and its massive $181.1 billion overseas stash, a $70 billion increase from the prior year.”
• Taxes On Apple’s Offshore Assets Would Cover Most Of US Education Budget (MW)
The amount of money stashed overseas by U.S. multinationals has exploded in recent years, doubling between 2008 and 2014 to more than $2 trillion. For some perspective on the numbers, cost-estimating website HowMuch.net crunched the most recent data and created a telling interactive chart. Topping the list: Apple and its massive $181.1 billion overseas stash, a $70 billion increase from the prior year.
That total corresponds to $59.2 billion in deferred taxes, which is enough to cover more than two-thirds of the federal budget for education, training and employment, according to the 2014 numbers compiled by Citizens for Tax Justice last October. Elsewhere, General Electric’s taxes could take care of almost 5% of our Social Security costs, while taxes from Microsoft had it kept its money in the U.S., could have covered a fifth of all federal spending on veteran’s benefits. According to estimates, the prevalence of offshore tax havens causes the U.S. to lose out on $90 billion in federal income taxes each year. That’s no small chunk.

“The average person checks their phone 150 times a day. Why do we do this? Are we making 150 conscious choices?”
• The Slot Machine in Your Pocket (Spiegel)
When we get sucked into our smartphones or distracted, we think it’s just an accident and our responsibility. But it’s not. It’s also because smartphones and apps hijack our innate psychological biases and vulnerabilities. I learned about our minds’ vulnerabilities when I was a magician. Magicians start by looking for blind spots, vulnerabilities and biases of people’s minds, so they can influence what people do without them even realizing it. Once you know how to push people’s buttons, you can play them like a piano. And this is exactly what technology does to your mind. App designers play your psychological vulnerabilities in the race to grab your attention. I want to show you how they do it, and offer hope that we have an opportunity to demand a different future from technology companies.
If you’re an app, how do you keep people hooked? Turn yourself into a slot machine. The average person checks their phone 150 times a day. Why do we do this? Are we making 150 conscious choices? One major reason why is the number one psychological ingredient in slot machines: intermittent variable rewards. If you want to maximize addictiveness, all tech designers need to do is link a user’s action (like pulling a lever) with a variable reward. You pull a lever and immediately receive either an enticing reward (a match, a prize!) or nothing. Addictiveness is maximized when the rate of reward is most variable.
Does this effect really work on people? Yes. Slot machines make more money in the United States than baseball, movies, and theme parks combined. Relative to other kinds of gambling, people get “problematically involved” with slot machines three to four times faster according to New York University professor Natasha Dow Schüll, author of “Addiction by Design.”